Petrogenesis and tectonic setting of the Late Permian A-type granitic dyke swarm in Ulungur, East Junggar
-
摘要:
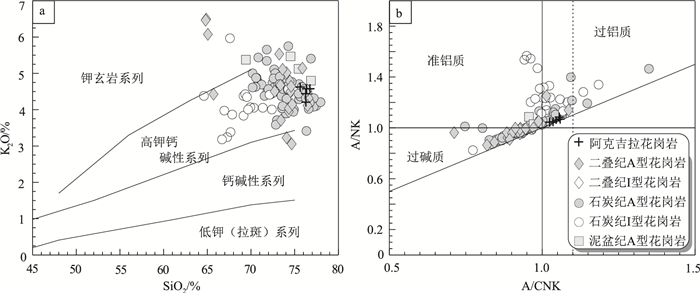
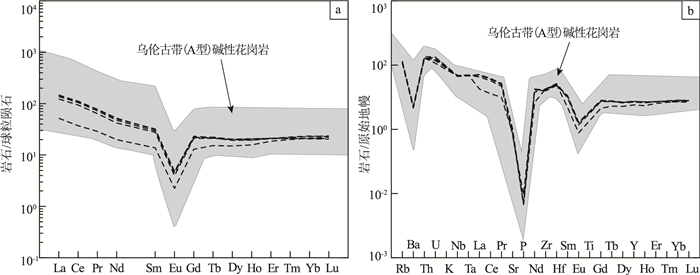
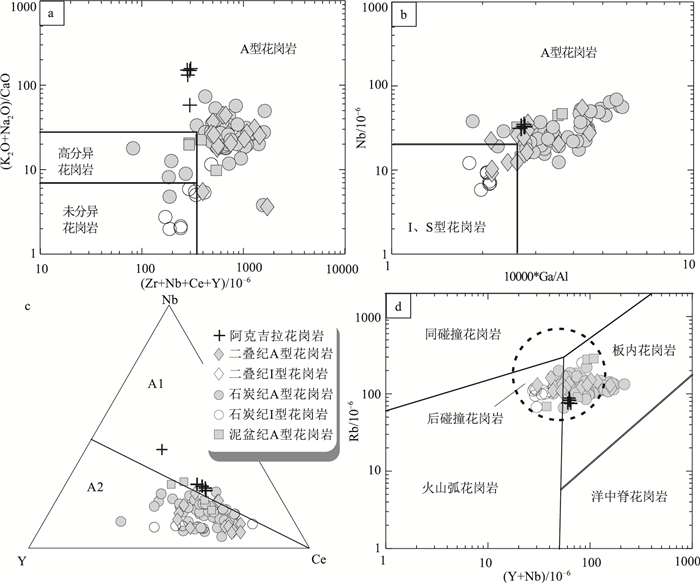
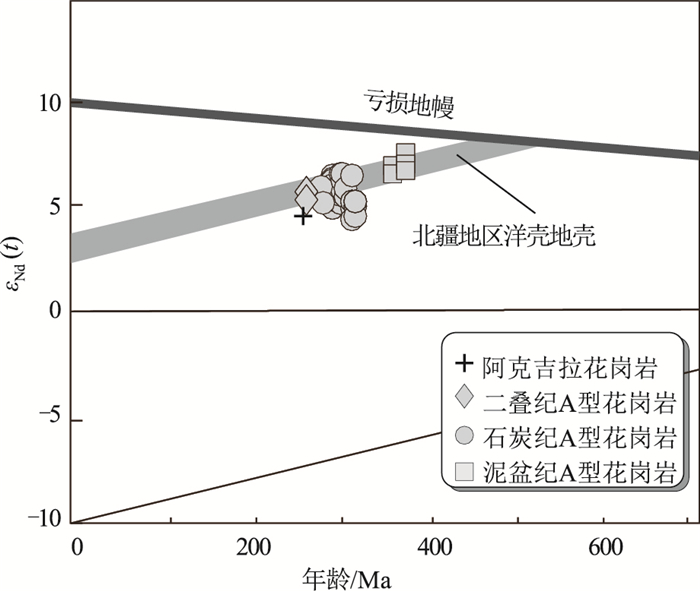
中亚造山带西南缘的东准噶尔地区出露大量晚古生代花岗岩,是揭示该造山带地壳演化的良好对象。在东准噶尔北缘乌伦古西北的阿克吉拉识别出一套走向与区域构造线总体垂直的晚古生代花岗质岩墙,其时代和成因研究对深入理解本区的构造演化具有重要意义。SHRIMP锆石U-Pb测年结果显示其侵位于晚二叠世(266±2 Ma)。岩石地球化学组成上,它们具有高硅(SiO2=75.66%~76.69%)、富碱(Na2O+K2O=8.67%~9.16%)、低钙(CaO=0.06%~0.14%)和镁(MgO=0.04%~0.06%)的特征;具有明显的负Eu异常(δEu=0.16~0.18),相对亏损Ba、Sr、P、Ti等,明显富集Nb、Zr、Th、Ta、Hf等高场强元素,具有较大的Ga/Al值(>2.6),指示该花岗岩属弱过铝质A1型花岗岩。岩石具有正的εNd(t)值(+4.7)和年轻的模式年龄(655 Ma),暗示源区物质主要为年轻幔源物质。综合分析,推测该岩墙形成于后碰撞环境,由地幔上涌引起新生下地壳部分熔融而成。
Abstract:A large number of Late Paleozoic granites occur in the East Junggar on the southwest margin of the Central Asian Orogenic belt, providing a good chance to reveal the crustal evolution of the Central Asian Orogenic Belt. In this study, a series of Late Paleozoic granitic dykes striking vertically to the suture zone were recognized in Akejila, northwest of Ulungur of East Junggar. Their timing of emplacement and petrogenesis are critical to understand the tectono-crustal evolution of the study area. SHRIMP zircon U-Pb dating yielded a Late Permian age (266±2 Ma). Geochemical analyses indicate that they are characterized by relatively high concentration of silica (SiO2=75.66%~76.69%) and alkali (Na2O+K2O=8.67%~9.16%), but low calcium (CaO =0.06%~0.14%) and magnesia (MgO =0.04%~0.06%)content. The obvious negative Eu anomaly (δEu=0.16~0.18), relative depletion of Ba, Sr, P and Ti, and significant enrichment of Nb, Zr, Th, Ta and Hf, as well as high Ga/Al value (>2.6) characterize the weakly peraluminous A1 type granites. The positive εNd(t) value (+4.7) and a young model age (655 Ma) suggest that these dykes are mainly derived from the juvenile mantle. Therefore, the comprehensive analysis indicates that the dykes were formed by the partial melting of the juvenile lower crust caused by the upwelling of the mantle in a post-collision setting.
-
Keywords:
- East Junggar /
- A-type granite /
- U-Pb age /
- Permian /
- post-collision
-
致谢: 感谢审稿专家提供的宝贵意见,感谢中国地质科学院孟贵祥研究员团队在野外给予的帮助。
-
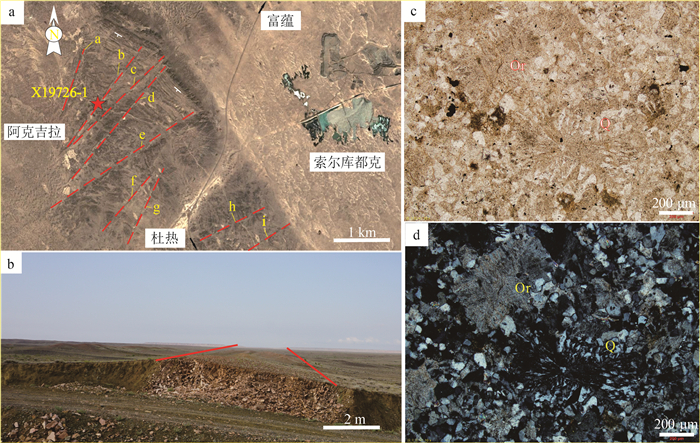
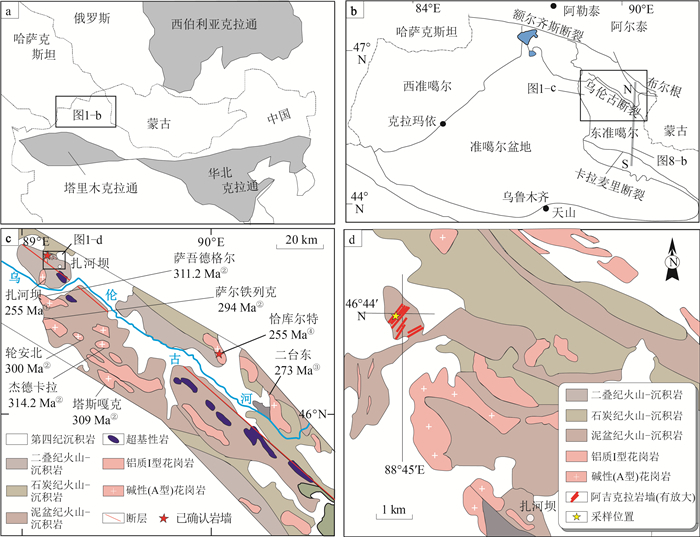
图 1 中亚造山带地质简图(a)、东准噶尔构造位置图(b)、乌伦古碱性花岗岩带区域地质图(c)[13, 28]和阿克吉拉岩墙区域地质图
(d,底图据参考文献[30])(数据据参考文献[31-35]①②③④)
Figure 1. Geological map of the Central Asian orogenic belt(a), tetonic map of East Junggar(b), regional geological map of the Ulungur alkali-rich granite belt(c), and geological map of Akejila dykes(d)
图 6 A型花岗岩(Zr+Nb+Y+Ce)-(K2O+Na2O)/CaO(a)、10000×Ga/Al -Nb(b) 判别图解[43]、Nb-Y-Ce分类图解(c)[46]及(Y+Nb)-Rb构造环境判别图解(d)[63]
(数据来源同图 4)
Figure 6. (Zr+Nb+Y+Ce)-(K2O+Na2O)/CaO(a), 10000×Ga/Al -Nb(b), Nb-Y-Ce discriminant diagrams(c)for the subdivision of the A-type granites, and (Y+Nb)-Rb tectonic discrimination diagram(d)
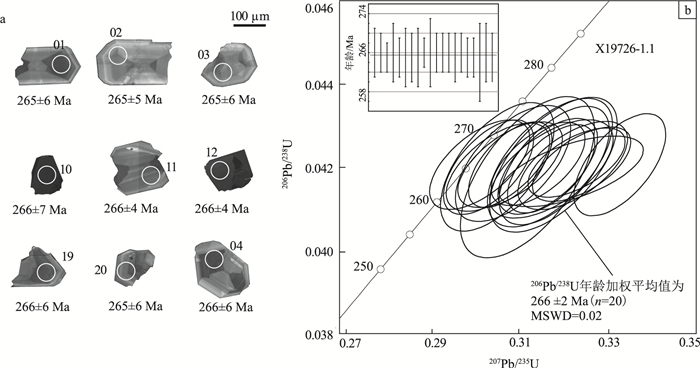
表 1 东准噶尔阿克吉拉细晶花岗岩(X19726-1.1)SHRIMP锆石U-Pb同位素分析结果
Table 1 SHRIMP zircon U-Pb analytical results of the aplite granite of the Akejila pluton from the East Junggar
测点 Pbrad/10-6 238U/10-6 232Th/10-6 Th/U 同位素比值 年龄/Ma 207Pb/206Pb 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ 207Pb/206Pb 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ 1 683.0 7297.0 31770.7 4.4 0.05756 0.00100 0.33286 0.00679 0.04206 0.00081 513 20 292 5 266 5 2 27.2 533.4 333.2 0.6 0.05554 0.00104 0.32428 0.00728 0.04207 0.00059 434 26 285 6 266 4 3 34.5 656.8 585.9 0.9 0.05536 0.00138 0.32195 0.01068 0.04190 0.00056 427 50 283 8 265 3 4 31.0 577.3 501.7 0.9 0.05264 0.00167 0.31719 0.00924 0.04211 0.00102 313 30 280 7 266 6 5 89.4 1714.9 1532.1 0.9 0.05499 0.00097 0.31745 0.00646 0.04196 0.00070 412 21 280 5 265 4 6 34.8 701.7 485.0 0.7 0.05296 0.00111 0.30538 0.00840 0.04201 0.00102 327 28 271 7 265 6 7 18.6 339.7 207.2 0.6 0.04703 0.00187 0.30342 0.00667 0.04200 0.00075 51 24 269 5 265 5 8 49.5 1008.1 870.9 0.9 0.05564 0.00119 0.31814 0.00816 0.04204 0.00094 438 26 280 6 265 6 9 27.7 504.9 343.1 0.7 0.05096 0.00164 0.32316 0.00719 0.04211 0.00055 239 28 284 6 266 3 10 506.3 6177.0 22562.9 3.7 0.05532 0.00119 0.31796 0.00945 0.04206 0.00107 425 30 280 7 266 7 11 30.8 608.5 437.3 0.7 0.05235 0.00120 0.30142 0.00740 0.04206 0.00071 301 28 268 6 266 4 12 36.6 748.1 624.2 0.8 0.05359 0.00086 0.30827 0.00617 0.04206 0.00068 354 21 273 5 266 4 13 27.0 480.5 408.2 0.8 0.04900 0.00185 0.30826 0.00773 0.04206 0.00068 148 30 273 6 266 4 14 40.1 861.6 514.2 0.6 0.05525 0.00108 0.31669 0.00736 0.04202 0.00076 422 24 279 6 265 5 15 38.8 798.7 546.9 0.7 0.05475 0.00111 0.31453 0.00695 0.04208 0.00066 402 24 278 5 266 4 16 24.9 440.2 344.3 0.8 0.06286 0.01484 0.30555 0.00766 0.04200 0.00070 703 27 271 6 265 4 17 49.3 1020.5 744.6 0.7 0.05591 0.00122 0.32230 0.00811 0.04204 0.00070 449 28 284 6 265 4 18 92.8 1847.7 1851.8 1.0 0.05492 0.00116 0.31212 0.00992 0.04176 0.00128 409 32 276 8 264 8 19 52.2 1092.0 796.4 0.7 0.05402 0.00133 0.30890 0.00853 0.04209 0.00092 372 29 273 7 266 6 20 40.1 781.0 842.4 1.1 0.05500 0.00130 0.31751 0.00913 0.04196 0.00078 412 33 280 7 265 5 表 2 阿克吉拉细晶花岗岩主量、微量和稀土元素分析结果
Table 2 Analytical results of major, trace elements and REE of the Akejila aplite granites
样品 X19726-1.1 X19726-1.2 X19726-1.3 X19726-1.4 X19726-1.5 样品 X19726-1.1 X19726-1.2 X19726-1.3 X19726-1.4 X19726-1.5 SiO2 76.41 76.25 76.26 76.69 75.66 Sc 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0 TiO2 0.11 0.11 0.11 0.11 0.11 Be 3.0 1.0 5.0 3.0 4.0 Al2O3 12.59 12.73 12.69 12.78 12.92 Cs 0.5 0.3 0.4 0.2 0.4 Fe2O3 1.10 1.21 1.26 0.97 1.17 Sn 2.0 3.0 3.0 2.0 2.0 MnO 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01 W 1.2 1.5 1.1 1.0 1.3 MgO 0.06 0.05 0.07 0.04 0.06 Mo 0.9 2.2 1.8 1.6 1.1 CaO 0.07 0.06 0.14 0.06 0.06 Cu 0.6 0.4 0.5 0.3 0.5 Na2O 4.32 4.57 4.20 4.28 4.54 Pb 0.5 1.8 1.6 1.4 1.1 K2O 4.55 4.21 4.47 4.57 4.62 Zn 5.0 9.0 10.0 4.0 8.0 P2O5 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.02 0.01 As 1.5 1.4 1.1 1.0 0.9 FeO 0.20 0.20 0.21 0.20 0.20 Au 0.5 0.5 3.6 0.5 0.5 烧失量 0.70 0.70 0.70 0.40 0.80 Tl 0.1 0.1 0.1 0.1 0.1 总计 99.23 99.21 99.22 99.53 99.16 Se 0.5 0.5 0.5 0.5 0.5 Mg# 0.35 0.31 0.37 0.26 0.35 Hf 7.7 7.5 7.1 7.4 8.2 K2O+Na2O 8.87 8.78 8.67 8.85 9.16 Ta 2.0 1.90 1.9 2.0 2.0 A/NK 1.05 1.05 1.08 1.07 1.04 Th 14.3 13.20 13.80 14.1 15.7 A/CNK 1.04 1.04 1.06 1.06 1.03 U 2.9 3.20 3.60 2.40 3.7 La 12.30 35.00 34.40 29.10 32.60 Co 0.3 0.3 0.2 0.3 0.4 Ce 22.80 64.70 68.40 57.60 64.40 Ni 20.0 20.0 20.0 20.0 20.0 Pr 2.74 7.39 7.31 6.06 6.87 Rb 78.7 72.5 80.4 80.6 84.3 Nd 9.30 24.30 23.60 19.60 22.20 Sr 16.2 18.1 19.9 14.3 22.2 Sm 2.11 4.79 4.92 4.24 4.52 Ga 18.7 18.7 18.8 18.7 18.2 Eu 0.13 0.28 0.27 0.23 0.26 V 8.0 8.0 10.0 8.0 8.0 Gd 2.66 4.54 4.76 4.33 4.47 Zr 201.4 184.1 176.7 189.4 202.3 Tb 0.57 0.80 0.82 0.79 0.83 Nb 33.9 31.6 31.9 32.5 33.7 Dy 3.81 4.90 5.09 5.06 5.17 Ba 33.0 32.0 36.0 33.0 37.0 Ho 0.89 1.10 1.10 1.17 1.17 ΣREE 91.26 187.88 192.48 170.09 184.70 Er 3.07 3.53 3.44 3.48 3.47 LREE 49.38 136.46 138.90 116.83 130.85 Tm 0.51 0.53 0.54 0.57 0.56 HREE 41.88 51.42 53.58 53.26 53.85 Yb 3.60 3.59 3.51 3.98 3.88 LR/HR 1.18 2.65 2.59 2.19 2.43 Lu 0.57 0.53 0.52 0.58 0.60 δEu 0.17 0.18 0.17 0.16 0.18 Y 26.20 31.90 33.80 33.30 33.70 注:主量元素含量单位为%,微量和稀土元素含量单位为10-6 表 3 东准噶尔乌伦古花岗岩带主要富碱花岗岩Sm-Nd同位素特征
Table 3 The Sm-Nd isotope data of the alkali-rich granites from Ulungur granite belt in the East Junggar
样品号 岩性 年龄/Ma Sm Nd 147Sm/144Nd 143Nd/144Nd 2α εNd(t) TDM/Ma T2DM/Ma 参考文献 X19726-1.1 细晶花岗岩 265 2.11 9.30 0.1372 0.512848 1 4.7 745 655 本文 08WLG-13 A型花岗岩 308 8.07 38.72 0.1260 0.512769 8 5.3 665 635 [52] 08WLG-16 A型花岗岩 308 7.36 41.60 0.1070 0.512749 7 5.7 575 606 [52] 08WLG-17 A型花岗岩 308 9.64 54.37 0.1072 0.512746 7 5.6 581 612 [52] 08WLG-07 A型花岗岩 308 12.90 62.29 0.1252 0.512809 6 6.0 590 568 [52] G40 过碱性花岗岩 325 9.6 52.00 0.1116 0.51272 14 5.18 640 670 [32] G46 过碱性花岗岩 325 10.3 40.5 0.1539 0.51282 12 5.4 840 650 [32] G72 过碱性花岗岩 322.1 8.5 50 0.1041 0.51268 11 4.57 650 710 [32] G81 过碱性花岗岩 322.1 5.6 32.4 0.1052 0.51272 10 5.43 600 650 [32] G20 二长花岗岩 322 4.2 23.3 0.1093 0.51271 14 5.1 640 680 [32] G29 二长花岗岩 322 3.45 18.9 0.1103 0.51273 12 5.42 620 650 [32] OT01 花岗闪长岩 309.6 3.49 16.4 0.1287 0.5128 13 5.95 630 600 [32] OT09 花岗闪长岩 309.6 4.04 18.6 0.1313 0.51283 12 6.4 590 560 [32] KLP04 花岗闪长岩 314.7 5.7 28.5 0.1207 0.51279 10 6.05 590 590 [32] G120 正长花岗岩 308.5 3.96 17.4 0.1381 0.51286 10 6.69 590 530 [32] JR2 过碱性花岗岩 300 13.49 70.58 0.1155 0.512792 6 6.09 557 [28] JR6 过碱性花岗岩 300 13.33 67.13 0.1201 0.512829 5 6.67 523 [28] SW1 过碱性花岗岩 300 15.09 88.33 0.1033 0.512788 7 6.47 501 [28] SW2 过碱性花岗岩 300 14.74 76.43 0.1166 0.512806 8 6.37 541 [28] SW3 过碱性花岗岩 300 9.90 42.75 0.1400 0.512811 6 5.56 702 [28] SW5 过碱性花岗岩 300 16.60 78.29 0.1282 0.512817 5 6.13 594 [28] SW6 过碱性花岗岩 300 12.33 62.52 0.1192 0.512797 6 6.04 570 [28] SW8 过碱性花岗岩 300 9.96 45.55 0.1323 0.512827 5 6.17 606 [28] SR6 过碱性花岗岩 300 5.15 19.79 0.1574 0.512848 6 5.61 819 [28] SR121 过碱性花岗岩 300 12.02 56.00 0.1297 0.512769 4 5.12 692 [28] SR127 过碱性花岗岩 300 9.59 33.68 0.1722 0.512877 6 5.56 1003 [28] STS6 过碱性花岗岩 300 9.30 46.29 0.1214 0.512751 5 5.06 660 [28] STS9 碱性脉 300 2.94 17.24 0.1031 0.512737 10 5.54 570 [28] STS86 过碱性花岗岩 300 9.08 34.09 0.1611 0.512847 4 5.44 878 [28] XCH1 铝质花岗岩 270 7.06 32.09 0.1330 0.5128 7.00 5.55 641 [28] XCH2 铝质花岗岩 270 5.52 26.19 0.1275 0.5128 9.00 5.84 591 [28] XCH4 铝质花岗岩 270 7.51 31.82 0.1427 0.5128 9.00 5.52 694 [28] XCH6 铝质花岗岩 270 7.1 31.37 0.1368 0.5128 14.00 5.85 627 [28] XCH11 铝质花岗岩 270 6.55 32.73 0.1211 0.5128 15.00 5.51 597 [28] 表 4 东准噶尔乌伦古带富碱性花岗岩带主要岩体形成时代
Table 4 The age data of alkali-rich granites from Ulungur granite belt in the East Junggar
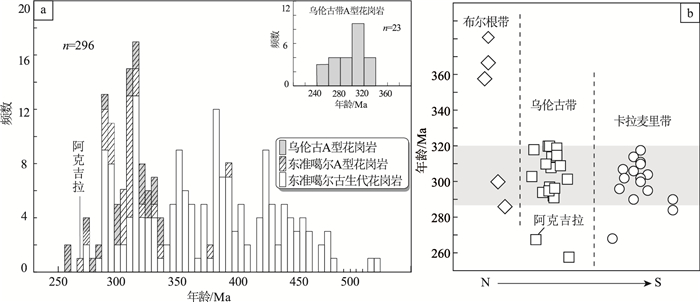
样号 岩体 年龄/Ma 误差/Ma 岩性 参考文献 X19726-1 阿克吉拉 265 1.9 A型花岗岩 本文 08WLG-07 杰德卡拉 291 A型花岗岩 [52] JR1 杰德卡拉 314.2 5.2 过碱性花岗岩 [28] LNB111 轮安北 300 过碱性花岗岩 [28] SR3 萨尔铁列克 292 碱性花岗岩 [45] 08WLG-13 萨尔铁列克 308 A型花岗岩 [52] SR121 萨尔铁列克 322.1 2.2 过碱性花岗岩 [28] SW1 萨吾德格尔 311.2 2.5 过碱性花岗岩 [28] STS5 塔斯嘎克 325 2 过碱性花岗岩 [28] G40 塔斯嘎克 301 过碱性花岗岩 [32] KLP02 库日喀孜干 314.7 2 正长花岗岩 [32] G76 萨尔铁列克 322.1 2.2 石英花岗岩 [32] G49 南-塔斯嘎克 325 2 过碱性花岗岩 [32] W-1 阿舒达斯 319.3 2.5 碱性花岗岩 [32] 02ET01 二台东 273 32 富碱闪长岩 [34] St7 萨尔铁列克 302 霓石钠铁闪石花岗岩 [29] St12-1 萨尔铁列克 294 钠铁闪石细晶花岗岩 [29] C8 塔斯嘎克 309 黑云母花岗岩 [29] SW5 萨吾德格尔 300 碱性花岗岩 [45] YP-3 蕴都卡拉 315.2 碱性花岗岩 [65] ZHB-1 扎河坝 250 碱性长石花岗岩 [66] ZHB-7 扎河坝 250 钾长花岗岩 [66] J12 恰库尔特 255 2.4 碱性花岗岩 [67] -
Şengör A M C, Natal'in B A, Burtman V S. Evolution of Altaid tectonic collage and Paleozoic crustal growth in Eurasia[J]. Nature, 1993, 364: 299-307. doi: 10.1038/364299a0
Yakubchuk A. Architecture and mineral deposit settings of the Altaid orogenic collage: a revised model[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2004, 23: 761-779. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2004.01.006
Jahn B M, Wu F Y, Chen B. Granitoids of the Central Asian Orogenic Belt and continental growth in the Phanerozoic[J]. Transactions Royal Society of Edinburgh, Earth Sciences, 2000, 91(1/2): 181-193.
Kovalenko A, Clemens J D, Savatenkov V. Petrogenetic constraints for the genesis of Archaean sanukitoid suites: geochemistry and isotopic evidence from Karelia, Baltic Shield[J]. Lithos, 2005, 79(1/2): 147-160. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0024493704002737
Windley B F, Garde A A. Arc-generated blocks with crustal sections in the North Atlantic craton of West Greenland: Crustal growth in the Archean with modern analogues[J]. Earth Science Reviews, 2009, 93(1/2): 1-30. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S001282520800130X
肖文交, 方爱民, 李继亮, 等. 西昆仑造山带复式增生楔的构造特征与演化[J]. 新疆地质, 2003, (1): 31-36. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8845.2003.01.005 Xiao W J, Kröner A, Windley B F. Geodynamic Evolution of Central Asia in the Paleozoic and Mesozoic[J]. International Journal of Earth Sciences, 2009, 98: 1185-1188. doi: 10.1007/s00531-009-0418-4
Xiao W J, Windley B F, Yuan C, et al. Paleozoic multiple subduction-accretion processes of the southern Altaids[J]. American Journal of Science, 2009, 309: 221-270. doi: 10.2475/03.2009.02
Xiao W J, Huang B, Han C M, et al. A review of the western part of the Altaids: a key to understanding the architecture of accretionary orogens[J]. Gondwana Research, 2010, 18(2): 253-273. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1342937X10000262
肖文交, 舒良树, 高俊, 等. 中亚造山带大陆动力学过程与成矿作用[J]. 新疆地质, 2008, (1): 4-8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8845.2008.01.002 Wang T, Tong Y, Zhang L, et al. Phanerozoicgranitoids in the central and eastern parts of Central Asia and their tectonic significance[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2017, 145: 368-392. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2017.06.029
董连慧, 屈迅, 朱志新, 等. 新疆大地构造演化与成矿[J]. 新疆地质, 2010, 28(4): 351-357. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8845.2010.04.002 韩宝福, 季建清, 宋彪, 等. 新疆准噶尔晚古生代陆壳垂向生长(Ⅰ)——后碰撞深成岩浆活动的时限[J]. 岩石学报, 2006, (5): 1077-1086. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200605003.htm 李锦轶. 新疆东部新元古代晚期和古生代构造格局及其演变[J]. 地质论评, 2004, 50(3): 304-322. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.2004.03.015 李锦轶, 肖序常. 对新疆地壳结构与构造演化几个问题的简要评述[J]. 地质科学, 1999, (4): 3-5. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKX199904001.htm 王涛, 王晓霞, 郭磊, 等. 花岗岩与大地构造[J]. 岩石学报, 2017, 33(5): 1459-1478. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201705006.htm 童英, 王涛, 洪大卫, 等. 北疆及邻区石炭-二叠纪花岗岩时空分布特征及其构造意义[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2010, 29(6): 619-641. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2010.06.003 胡霭琴, 韦刚健, 邓文峰, 等. 阿尔泰地区青河县西南片麻岩中锆石SHRIMP U-Pb定年及其地质意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2006, (1): 1-10. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200601001.htm 张峰, 陈建平, 徐涛, 等. 东准噶尔晚古生代依旧存在俯冲消减作用——来自石炭纪火山岩岩石学、地球化学及年代学证据[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2014, 38(1): 140-156. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK201401013.htm 潘桂棠, 陆松年, 肖庆辉, 等. 中国大地构造阶段划分和演化[J]. 地学前缘, 2016, 23(6): 1-23. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201606006.htm 刘家远, 喻亨祥, 吴郭泉. 新疆东准噶尔两类碱性花岗岩及其地质意义[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 1999, (2): 3-5. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYDH902.003.htm 忻建刚, 袁奎荣, 刘家远. 新疆东准噶尔北部碱性花岗岩的特征、成因及构造意义[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 1995, (3): 214-226. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK503.003.htm Su Y, Zheng J, Griffin W L, et al. Geochemistry and geochronology of Carboniferous volcanic rocks in the easternJunggar terrane, NW China: Implication for a tectonic transition[J]. Gondwana Research. 2012, 22(3/4): 1009-1029. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1342937X12000330
郭芳放, 姜常义, 卢荣辉, 等. 新疆北部卡拉麦里地区黄羊山碱性花岗岩的岩石成因[J]. 岩石学报, 2010, 26(8): 2357-2373. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201008012.htm 刘家远, 喻亨祥, 吴郭泉. 新疆北部卡拉麦里富碱花岗岩带的碱性花岗岩与锡矿[J]. 有色金属矿产与勘查, 1997, (3): 2-8. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSJS703.000.htm 白建科, 陈隽璐, 彭素霞. 新疆奇台县黄羊山岩浆热液型石墨矿床含矿岩体年代学与地球化学特征[J]. 岩石学报, 2018, 34(8): 2327-2340. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201808009.htm Tong Y, Wang T, Jahn B M, et al. Post-accretionary Permian granitoids in the Chinese Altai orogen: geochronology, petrogenesis and tectonic implications[J]. American Journal of Science, 2014, 314(1): 80-109. doi: 10.2475/01.2014.03
Han B F, Wang S G, Jahn B M, et al. Depleted-mantle source for the Ulungur River A-type granites from North Xinjiang, China: geochemistry and Nd-Sr isotopic evidence, and implications for Phanerozoic crustal growth[J]. Chemical Geology, 1997, 138(3/4): 135-159. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S000925419700003X
刘家远, 袁奎荣. 新疆乌伦古富碱花岗岩带碱性花岗岩成因及其形成构造环境[J]. 高校地质学报, 1996, (3): 18-22. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXDX603.001.htm 薛春纪, 赵战锋, 吴淦国, 等. 中亚构造域多期叠加斑岩铜矿化: 以阿尔泰东南缘哈腊苏铜矿床地质、地球化学和成岩成矿时代研究为例[J]. 地学前缘, 2010, 17(2): 53-82. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201002012.htm Chen Y, Wang Y, Wang J, et al. Zircon U-Pb Age, Geochemistry and geological implication of the 255 Ma Alkali-rich dykes from Ulungur Area, North Xinjiang[J]. Journal of Earth Science, 2013, 24(4): 519-528. doi: 10.1007/s12583-013-0346-x
Liu W, Liu X, Liu L. Underplating generated A- and I-type granitoids of the East Junggar from the lower and the upper oceanic crust with mixing of mafic magma: Insights from integrated zircon U-Pb ages, petrography, geochemistry and Nd-Sr-Hf isotopes[J]. Lithos, 2013, 179: 293-319. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2013.08.009
王式洸, 韩宝福, 洪大卫, 等. 新疆乌伦古河碱性花岗岩的地球化学及其构造意义[J]. 地质科学, 1994, (4): 373-383. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKX404.006.htm 赵振华, 王中刚, 邹天人, 等. 新疆乌伦古富碱侵入岩成因探讨[J]. 地球化学, 1996, (3): 205-220. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.1996.03.001 赵阳. 东准噶尔恰库尔图地区石炭纪碱性花岗岩地球化学特征及构造环境[D]. 中国地质大学(北京)硕士学位论文, 2020. 宋彪, 张玉海, 万渝生, 等. 锆石SHRIMP样品靶制作、年龄测定及有关现象讨论[J]. 地质论评, 2002, 48(S1): 26-30. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP2002S1006.htm Bunkley-Williams L, Williams E H. Ability of Pederson Cleaner Shrimp To Remove Juveniles of the Parasitic Cymothoid Isopod, Anilocra Haemuli, From the Host[J]. Crustaceana, 1998, 7(18): 862-869. http://www.ingentaconnect.com/content/brill/cr/1998/00000071/00000008/art00004
Black L P, Kamo S L, Allen C M, et al. TEMORA 1: a new zircon standard for Phanerozoic U-Pb geochronology[J]. Chemical Geology, 2003, 200(1): 155-170. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0009254103001657
Ludwig K R. Eliminating mass-fractionation effects on U-Pb isochron ages without double spiking[J]. Geochimica Et Cosmochimica Acta, 2001, 65(18): 3139-3145. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(01)00637-8
张建军, 童英, 王涛, 等. 新疆东准噶尔琼河坝地区绿石沟早石炭世岩体中基性岩墙群成因及其构造动力学背景[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2019, 38(5): 606-630. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2019.05.002 Vianna S Q, Lafon J M, Milhomem N J O M, et al. U-Pb geochronology, Nd-Hf isotopes, and geochemistry of Rhyacian granitoids from the Paleoproterozoic Louren? o domain(Brazil), southeastern Guiana Shield[J]. Journal of South American Earth Sciences, 2020, 104. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/345185038_The_Origin_of_Tertiary_High-Alumina_Basalts_in_Central_Urumieh-Dokhtar_Magmatic_Arc_Iran_Constraints_from_Geochemistry_U-Pb_Geochronology_and_Nd-Hf_Isotopes
Jahn B M, Condie K C. Evolution of the Kaapvaal Craton as viewed from geochemical and Sm+Nd isotopic analyses of intracratonic pelites[J]. Geochimica Et Cosmochimica Acta, 1995, 59(11): 2239-2258. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(95)00103-7
Whalen J B, Currie K L, Chappell B W. A-type granites: Geochemicalcharacteristics[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1987, 95: 420-436. doi: 10.1007/BF00402203
Sun S S, Mcdonough W F. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: implications for mantle composition and processes[J]. Geological Society London Special Publications, 1989, 42(1): 313-345. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.1989.042.01.19
Wang S, Han B, Hong D, et al. Geochemistry and tectonic significance of alkali granites along theUlungur River, Xinjiang[J]. Chinese journal of geochemistry, 1995, 14(4): 323-335. doi: 10.1007/BF02872631
Eby G N. Chemical subdivision of the A-type granitoids: Petrogenetic and tectonic implications[J]. Geology, 1992, 20(7): 641-644. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1992)020<0641:CSOTAT>2.3.CO;2
Shellnutt J G, Jahn B M, Dostal J. Elemental and Sr-Nd isotope geochemistry of microgranular enclaves from peralkaline A-type granitic plutons of the Emeishan large igneous province, SW China[J]. Lithos, 2010, 119(1/2): 34-46. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0024493710001878
Turner S P, Foden J D, Morrison R S. Derivation of some A-type magmas by fractionation of basaltic magma: An example from the Padthaway Ridge, South Australia[J]. Lithos, 1992, 28(2): 151-179. doi: 10.1016/0024-4937(92)90029-X
韩宝福, 王式洸, 孙元林, 等. 新疆乌伦古河碱性花岗岩Nd同位素特征及其对显生宙地壳生长的意义[J]. 科学通报, 1997, (17): 1829-1832. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.1997.17.011 许保良. A型花岗岩的岩石学亚类及其物质来源[J]. 地学前缘, 1998, (3): 113-124. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.1998.03.011 Collins W J, Beams S D, White A J R, et al. Nature and origin of A-type granites with particular reference to southeastern Australia[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1982, 80(2): 189-200. doi: 10.1007/BF00374895
Shen X, Zhang H, Wang Q, et al. Late Devonian-Early Permian A-type granites in the southern Altay Range, Northwest China: Petrogenesis and implications for tectonic setting of "A2-type" granites[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2011, 42(5): 986-1007. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2010.10.004
Creaser R A, Fanning C M. A U-Pb zircon study of the Mesoproterozoic Charleston Granite, Gawler Craton, South Australia[J]. Australian Journal of Earth Sciences, 1993, 40(6): 519-526. doi: 10.1080/08120099308728101
Harris N B W, Marzouki F M H, Ali S. The Jabel Sayid complex, Arabian Shield: geochemical constraints on the origin of peralkaline and related granites[J]. Journal of the Geological Society, 1986, 143(2): 287-295. doi: 10.1144/gsjgs.143.2.0287
Wu F Y, Sun D Y, Li H M, et al. A-type granites in northeastern China: age and geochemical constraints on their Petrogenesis[J]. Chemical Geology, 2002, 187(1/2): 143-173. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0009254102000189
Frindt S, Trumbull R B, Romer R L. Petrogenesis of the Gross Spitzkoppe topaz granite, central western Namibia: a geochemical and Nd-Sr-Pb isotope study[J]. Chemical Geology, 2004, 206(1/2): 43-71. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0009254104000403
Harris L B, Li Z. Palaeomagnetic dating and tectonic significance of dolerite intrusions in the Albany Mobile Belt, Western Australia[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1995, 131(3): 143-164. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0012821X95000133
Montero P, Bea F, Corretgé L G, et al. U-Pb ion microprobe dating and Sr and Nd isotope geology of the Galieiro Igneous Complex: A model for the peraluminous/peralkaline duality of the Cambro-Ordovician magmatism of Iberia[J]. Lithos, 2009, 107(3/4): 227-238. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0024493708002338
Moreno J A, Molina J F, Bea F, et al. Th-REE- and Nb-Ta-accessory minerals in post-collisional Ediacaran felsic rocks from the Katerina Ring Complex(S. Sinai, Egypt): An assessment for the fractionation of Y/Nb, Th/Nb, La/Nb and Ce/Pb in highly evolved A-type granites[J]. Lithos, 2016, 258/259: 173-196. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2016.04.020
Green T H. Significance of Nb/Ta as an indicator of geochemical processes in the crust-mantle system[J]. Chemical Geology, 1995, 120(3/4): 347-359. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/000925419400145X
王强, 赵振华, 许继峰, 等. 天山北部石炭纪埃达克岩-高镁安山岩-富Nb岛弧玄武质岩: 对中亚造山带显生宙地壳增生与铜金成矿的意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2006, (1): 11-30. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200601002.htm Eby G N. The A-type granitoids: A review of their occurrence and chemical characteristics and speculations on their petrogenesis[J]. Lithos, 1990, 26(1): 115-134. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/002449379090043Z
Pearce J A, Harris N B W, Tindle A G. Trace Element Discrimination Diagrams for the Tectonic Interpretation of Granitic Rocks[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1984, 25: 956-983. doi: 10.1093/petrology/25.4.956
阿里木江·艾合买提, 宫相宽, 李咸阳, 等. 东准噶尔东北缘阿舒达斯晚石炭世碱性花岗岩SHRIMP锆石U-Pb定年、岩石地球化学特征及构造意义[J]. 新疆地质, 2020, 38(2): 184-191. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJDI202002009.htm 王式洸, 韩宝福, 洪大卫, 等. 新疆乌伦古河碱性花岗岩的地球化学及其构造意义[J]. 地质科学, 1994, (4): 373-383. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKX404.006.htm 张海军, 朱伯鹏, 吴晓贵. 新疆蕴都卡拉A型碱性花岗岩岩石地球化学特征及其构造意义[J]. 中山大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 58(1): 39-49. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZSDZ201901005.htm 张东阳, 高阳, 苏慧敏, 等. 新疆东准噶尔北部扎河坝富碱花岗质岩石矿物学特征及物理化学条件[J]. 矿物岩石, 2007, (4): 30-38. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWYS200704005.htm Liu W. Fluid-rock interaction during subsolidus microtextural development of alkali granite as exemplified by the Saertielieke pluton, Ulungur of the northern Xinjiang, China[J]. Chemical Geology, 2002, 182(2): 473-482. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0009254101003333
Wang S, Han B, Hong D, et al. Geochemistry and tectonic significance of alkali granites along theUlungur River, Xinjiang[J]. Chinese Journal of Geochemistry, 1995, 14: 323-335. doi: 10.1007/BF02872631
Chen Y F, Wang Y W, Wang J B, et al. Zircon U-Pb Age, Geochemistry and Geological Implication of the 255 Ma Alkali-Rich Dykes from Ulungur Area, North Xinjiang[J]. Journal of Earth Science, 2013, 24(4): 519-528. doi: 10.1007/s12583-013-0346-x
邓江红, 王道永. 新疆富蕴扎河坝地区蛇绿岩带基本特征及大地构造意义[J]. 成都理工学院学报, 1995, (4): 8-14. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CDLG504.001.htm 甘林, 唐红峰, 韩宇捷. 新疆东准噶尔野马泉花岗岩体的年龄和地球化学特征[J]. 岩石学报, 2010, 26(8): 2374-2388. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201008013.htm 李秉政. 东准噶尔卡拉麦里增生楔蛇绿混杂岩物质组成及就位机制[D]. 新疆大学硕士学位论文, 2019. 刘阁, 杨硕, 靳刘圆, 等. 东准噶尔乌尊塔格辉长岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄、地质地球化学特征及构造意义[J]. 新疆地质, 2019, 37(2): 139-145. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJDI201902002.htm 熊双才, 杨俊弢, 张征峰, 等. 东准噶尔老爷庙地区早石炭世黑山头组火山岩地质、地球化学特征及构造环境分析[J]. 新疆地质, 2019, 37(2): 194-200. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJDI201902011.htm 杨高学, 李永军, 司国辉, 等. 东准库布苏南岩体LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb测年[J]. 中国地质, 2008, (5): 849-858. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI200805007.htm 杨高学, 李永军, 吴宏恩, 等. 东准噶尔卡拉麦里地区黄羊山花岗岩和包体LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb测年及地质意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2009, 25(12): 3197-3207. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200912010.htm 杨高学, 李永军, 司国辉, 等. 东准噶尔贝勒库都克铝质A型花岗岩微量元素地球化学特征及地质意义[J]. 地球科学与环境学报, 2010, 32(1): 34-39. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XAGX201001008.htm 郑海峰, 刘阁, 靳刘园, 等. 东准噶尔卡拉麦里地区六棵树组火山岩年代学、地球化学及构造意义[J]. 新疆地质, 2019, 37(4): 457-463. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJDI201904006.htm 朱笑青, 王中刚, 王元龙, 等. 新疆后造山碱性花岗岩的地质特征[J]. 岩石学报, 2006, (12): 2945-2956. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200612011.htm Jiang X Y, Ling M X, Kai W, et al. Insights into the origin of coexisting A1 and A2 type granites: Implications from zircon Hf-O isotopes of the Huayuangong intrusion in the Lower Yangtze River Belt, eastern China[J]. Lithos, 2018, 318/319: S480186278.



 下载:
下载: