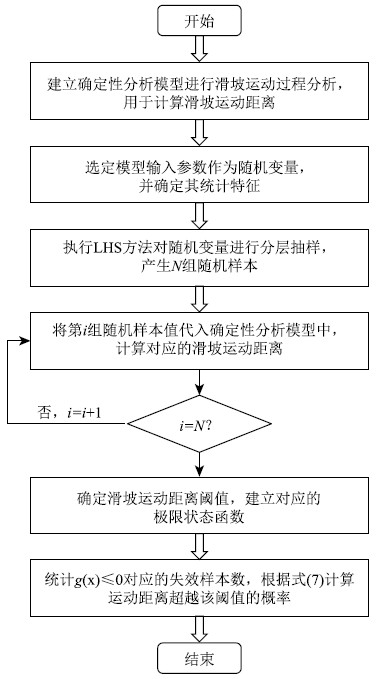
Assessment of exceedance probability of landslide run-out distance and hazard zoning
-
摘要:
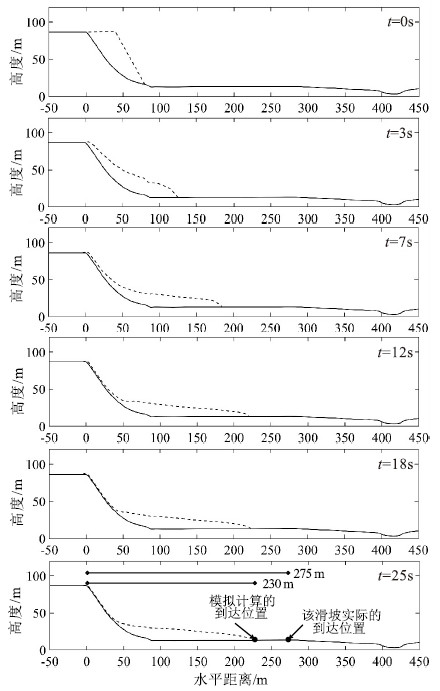
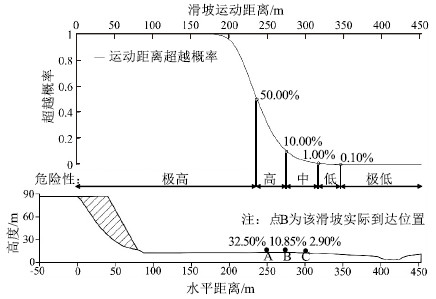
针对岩土体物理力学参数不确定性强、动态数值模拟方法对滑坡运动距离预测精度有限的问题,提出一种基于拉丁超立方采样法(LHS)的滑坡运动距离超越概率定量评价方法,以提高滑坡滑程预测结果的可靠性。该方法将滑坡计算参数考虑为服从某种概率分布的随机变量,使用LHS对随机变量进行分层抽样,并基于动态数值模型计算每组随机样本对应的滑坡运动距离,最后,通过构建不同运动距离阈值下的极限状态函数计算运动距离超越某一给定位置的概率。应用该方法对大堡子滑坡运动距离进行评价,得到该滑坡运动距离在95%置信水平下的置信区间为[196 m,302 m];并根据运动距离-超越概率图,提出以50%、10%、1%和0.1%作为分界概率值将该滑坡潜在威胁范围分为极高、高、中、低、极低5个危险性等级。计算结果显示,滑坡实际运动距离在95%置信区间内,实际的威胁范围也在划分的高-极高危险区内,说明评价结果合理,证明了基于运动距离超越概率的滑坡运动危险性评价的有效性。研究成果为滑坡运动距离评价及危险性区划提供了新的思路,具有重要的理论意义和工程实用价值。
Abstract:In view of the large uncertainties embedded in the physical and mechanical parameters of the dynamic numerical model, a quantitative method to assess exceedance probability of landslide run-out distance based on Latin Hypercube Sampling(LHS) is proposed to improve the reliability of landslide slide prediction results.In the proposed method, the input parameters are considered as random variables with probability distribution functions; the LHS is used to generate stratified samplings for the random variables, and the dynamic numerical model is used to compute the landslide run-out distance corresponding to each random sample; and finally, the exceedance probability of landslide run-out distance is calculated by constructing limit state functions for different run-out distance threshold values.The proposed method is applied to conduct a probabilistic assessment of the run-out distance for Dabaozi landslide, and the 95% confidence interval of the run-out distance is computed as[196 m, 302 m].According to the run-out distance-exceedance probability curve, the potential affected area of the landslide is classified into five categories(i.e., extremely high, high, medium, low and extremely low) based on different threshold values of exceedance probability(i.e., 50%, 10%, 1% and 0.1%).The calculation results show that the actual run-out distance of landslide is within the 95% confidence interval, and the actual threat range is also within the classified high-extremely high danger zone.The results show that the evaluation results are reasonable and the landslide movement risk evaluation based on the distance exceeding probability is also proved effective.The proposed method may provide new ideas for landslide run-out distance assessment and for hazard zoning, which has important theoretical significance and practical engineering value.
-
Keywords:
- landslide run-out distance /
- dynamic numerical model /
- LHS /
- exceedance probability /
- hazard zoning
-
华南克拉通以江南造山带为界划分为西北部的扬子板块和东南部的华夏板块[1-12]。迄今,已发现的早前寒武纪基底岩系主要出露于扬子板块,华夏板块区域则出露有限。尽管华夏板块区域沉积岩碎屑锆石年龄谱系研究揭示存在太古宙—古元古代的年龄峰值,甚至发现有4.1Ga的碎屑锆石[9, 13-15],但至今仅在武夷山区域发现出露面积有限的古元古代变质岩系,以八都岩群的花岗片麻岩和少量的角闪岩为主[16],其锆石U-Pb年龄在1910~1780Ma之间[17-18]。
扬子板块太古宙和古元古代岩石单元主要出露在北部和西南部。太古宙结晶基底主要发育在扬子板块北部,以崆岭群、黄土岭花岗岩和鱼洞子群为代表(图 1)。崆岭群片麻岩的原岩年龄为3.3~ 2.7Ga,变质时代约为2.73Ga和2.0Ga,并被1.85Ga的A型花岗岩侵入[21-24];黄土岭花岗岩的锆石U-Pb年龄为2.78~2.74Ga,锆石边部的变质年龄为2.0Ga[25];鱼洞子群角闪岩和正片麻岩锆石的上交点年龄约为2.7Ga[26]。在扬子板块的西南部,太古宙甚至古元古代早期岩石单元一直未被发现,最老的地层单元为弱变质的火山岩和沉积岩,包括大红山群、东川群和河口群,其时代为1740~1503Ma[27-28]。近期,Kou等[29]在大红山群钠长岩和变质火山岩中获得了2.0Ga的精确锆石U-Pb年龄,指示扬子板块西南部可能存在更老的基底。近期,笔者研究确认,滇中南部地区出露典型的古元古代结晶基底岩系[30],为进一步研究与刻画华南地区早前寒武纪地质过程打开了新“窗口”。在此基础上,笔者对滇中石屏地区昆阳群下伏花岗岩系开展系统的同位素年代学、岩石大地构造学研究,以更精确地标定这套古老结晶基底和后期变质事件的地质时代,探讨扬子板块早期的地质事件及其对Nuna超大陆的响应。
1. 区域地质特征
扬子板块是东亚地区重要的古老克拉通。在北部,通过秦岭-大别-苏鲁造山带与华北克拉通相隔;在南部,通过江南造山带与华夏陆块相隔;在西部,通过龙门山断裂带与松潘-甘孜陆块相隔。扬子板块西部地处欧亚、印度和太平洋三大板块交汇部位,位置重要,构造复杂,同时也是中国南方前震旦纪地层出露的重要地区之一。沿康定—西昌—攀枝花—元谋—易门—峨山一线的南北方向,发育古、中元古代深变质岩系的河口群、大红山群,浅变质火山-沉积岩系的东川群-通安组,以及晚中元古代昆阳群—会理群(图 1)。这些地层单元被认为构成了扬子板块西部的前寒武纪基底[31-42]。古、中元古代大红山群、东川群和河口群与1000Ma左右的昆阳群、会理群通常为断层接触[43-47]。这些中元古代地层被几条NNE向大断裂控制(图 1)。
大红山群主要出露于云南绿汁江断裂以西的新平县戛洒—老厂—大红山一带,以及腰街、漠沙、撮科等地,自下而上分为老厂河组、曼岗河组、红山组、肥味河组和坡头组,主要为一套石英片岩、石英岩、大理岩、变质砾岩、中基性火山岩等岩石组合,变质程度以高绿片岩相为主[34]。大红山群早先被认为是扬子板块西南部出露的最老的地层单元,但研究发现,其时代不早于1711Ma[19, 48-50](图 2);河口群主要出露于川西南会理黎溪一带,自上而下分为大营山组、落凼组和长冲组,主要为由细碧角斑岩系、片岩、大理岩等组成的一套元古宙浅变质火山-沉积岩系[51],其时代在1722~1657Ma之间[44, 52-54](图 2);东川群主要分布在云南东川、武定、禄丰一带,包括原昆阳群下亚群,自下而上分为因民组、落雪组、鹅头厂组和绿汁江组,主要由硅质碎屑岩、碳酸盐岩和少量火山岩组成,时代在1742~1503Ma之间[28, 47, 55-60](图 2);通安组主要分布在四川会理县通安—会东县南部地区,以白云岩、白云质灰岩、砂岩为主,大量辉绿岩侵入其中。其原被作为会理群的一个组,但是近年来的锆石U-Pb测年结果揭示其地层时代远早于会理群,为1.75~1.5Ga[19, 61-64](图 2);昆阳群原划分为3个亚群,下亚群包括因民组、落雪组、鹅头厂组和绿汁江组,中亚群包括大营盘组、黑山头组、大龙口组和美党组,上亚群包括柳坝塘组和华家菁组。下亚群现被归为东川群,上亚群则为新元古代地层单元[41-42],因此现昆阳群即为原昆阳群中亚群,其下部和上部主要为板岩、砂岩组合,中部为大龙口组白云岩和灰岩组合。近年,众多学者在黑山头组富良棚段凝灰岩中获得了精确的锆石U- Pb年龄:1032 ± 9Ma[40]、1047 ± 15Ma[65]、1043 ± 7Ma[66],指示富良棚段凝灰岩形成于中元古代晚期(图 2);会理群主要出露于川西南的会理、会东地区,自下而上包括力马河组、凤山营组和天宝山组。其中力马河组主要为一套板岩和石英砂岩组合,凤山营组主要为灰岩、白云岩组合,天宝山组中下部为千枚岩、板岩、砂岩组合,上部以酸性火山岩为主。这套火山岩的时代为1019~1036Ma[19, 66-68](图 2)。
![]() 图 2 扬子板块西南部古、中元古代年代地层格架及对比简图1—砂质板岩;2—板岩;3—钙质板岩;4—角砾岩;5—凝灰质砾岩;6—变英安岩;7—流纹斑岩;8—千枚岩;9—熔结凝灰岩;10—火山熔岩;11—玄武岩;12—粉砂质泥岩;13—含砾砂岩;14—粉砂岩;15—灰岩/白云岩;16—凝灰岩;17—变石英砂岩;18—片岩;19—石英岩;20—砂岩;21—大理岩;22—酸性火山岩;23—基性火山岩Figure 2. Geochronology and correlation of different stratigraphic systems used for the Paleo—Mesoproterozoic sedimentary successions in southwestern Yangtze Block
图 2 扬子板块西南部古、中元古代年代地层格架及对比简图1—砂质板岩;2—板岩;3—钙质板岩;4—角砾岩;5—凝灰质砾岩;6—变英安岩;7—流纹斑岩;8—千枚岩;9—熔结凝灰岩;10—火山熔岩;11—玄武岩;12—粉砂质泥岩;13—含砾砂岩;14—粉砂岩;15—灰岩/白云岩;16—凝灰岩;17—变石英砂岩;18—片岩;19—石英岩;20—砂岩;21—大理岩;22—酸性火山岩;23—基性火山岩Figure 2. Geochronology and correlation of different stratigraphic systems used for the Paleo—Mesoproterozoic sedimentary successions in southwestern Yangtze Block笔者在对石屏撮科地区碎屑岩进行调查研究的过程中,在高家坡—回水头—撮科一带碎屑岩下部发现下伏火成岩,以弱糜棱岩化花岗岩和花岗片麻岩为主,局部穿插辉绿岩体,与上覆碎屑岩呈断层接触。本次采集了3件样品进行年龄测定,分别为弱糜棱岩化斜长花岗岩SP19-1、糜棱岩化花岗闪长岩SP19-4和弱糜棱岩化花岗闪长岩SP19-5(图版Ⅰ)。
2. 分析方法
锆石单矿物分选在河北廊坊区域地质调查所实验室进行。在无污染的条件下,将原岩样品粉碎成全部通过60目的一次性筛网,淘洗岩石粉末,得到含锆石的重砂。再经重液和电磁分选后得到锆石样品,在双目镜下挑选出锆石颗粒。将待测锆石颗粒依照从大到小的顺序排列,与锆石标样(TEM)粘贴在已粘贴了双面胶的玻璃板上,灌注环氧树脂后制成样品靶。待树脂固结变硬后,打磨和抛光至锆石中心部位暴露。然后拍摄锆石的透射光、反射光显微图像和阴极发光(CL)图像。测定时选取无裂隙及包裹体且CL图像灰度单一的位置测定。SHRIMP锆石U-Pb同位素测定在中国地质科学院地质研究所北京离子探针中心SHRIMP Ⅱ上完成。详细的分析原理及流程参见相关文献[69-70]。一次离子流O2强度为2.5nA,束斑大小为25~30μm。标准锆石M257(U含量840×10-6)和TEM(206Pb/238U年龄为416.8Ma[71])的测值分别用于校正待测样品的U含量和206Pb/238U年龄。根据实测204Pb扣除普通Pb。每个数据点由5次扫描构成,误差为1σ,年龄加权平均值误差为2σ。数据处理使用1.02版SQUID和2.49版ISOPLOT程序[72-73]。单个数据点误差为1σ,年龄加权平均值误差为95%置信度。因样品年龄较老,采用207Pb/206Pb年龄。
3. 分析结果
(1)弱糜棱岩化斜长花岗岩SP19-1
新鲜面呈浅灰色、片状构造、粒状变晶结构。主要由斜长石、石英、黑云母组成。受糜棱岩化影响,斜长石具不均匀粘土化、绢云母化等,大多数聚片双晶不发育。黑云母也多被绿泥石、白云母等不均匀交代(图版Ⅰ-b)。CL图像显示,锆石具有典型的岩浆生长振荡环带和条纹环带,部分发育较窄的变质边。锆石形态多为长柱状,长轴为80~200μm,晶体长宽比多为2~3(图 3)。
共测试了18个数据点,测点均位于环带区域。U含量变化范围为350×10-6~2063×10-6,Th含量变化范围为98×10-6~652×10-6,Th/U值变化范围为0.17~0.92(表 1)。其中测点12.1年龄较大,207Pb/206Pb年龄为2716.1±8.5Ma。从U-Pb谐和图可以看出,除12.1外的所有测点均位于U-Pb谐和线或其附近。其中11颗锆石的207Pb/206Pb年龄为2347.3 ± 4.9Ma(MSWD=0.75,除去1.1,2.1,3.1,9.1,11.1,12.1,13.1)(图 4)。
表 1 糜棱岩化花岗岩SHRIMP锆石U-Th-Pb同位素测定结果Table 1. SHRIMP U-Th-Pb isotopic compositions for zircons from granite测点 206Pbc/% U/10-6 Th/10-6 232Th/238U 200Pb/10-6 206Pb/238U年龄/Ma 207Pb/206Pb年龄/Ma 不谐和度/% 207Pb*/206Pb* ±% 207Pb*/235U ±% 206Pb*/238U ±% 误差相关系数 SP19-1 1.1 0.01 604 98 0.17 225 2323+29 2319.0+8.3 0 0.14766 0.49 8.83 1.6 0.4338 1.5 0.951 2.1 0.01 860 195 0.23 331 2386+29 2348.6+7.2 -2 0.15023 0.42 9.28 1.5 0.4479 1.5 0.962 3.1 0.00 1085 230 0.22 411 2352+29 2313.6+6.6 2 0.14719 0.39 8.93 1.5 0.4402 1.5 0.967 4.1 0.05 299 99 0.34 114 2367+31 2345+11 -1 0.14990 0.64 9.17 1.7 0.4436 1.5 0.923 5.1 0.18 432 154 0.37 153 2217+28 2287+11 3 0.14492 0.62 8.20 1.6 0.4104 1.5 0.925 6.1 - 595 124 0.21 228 2374+32 2359.6+8.1 1 0.15120 0.48 9.28 1.7 0.4453 1.6 0.958 7.1 -- 508 278 0.56 195 2379+30 2357.2+8.8 -1 0.15099 0.52 9.29 1.6 0.4463 1.5 0.946 8.1 0.01 840 141 0.17 316 2341士29 2335.517.6 0 0.14909 0.44 9.00 1.5 0.4379 1.5 0.957 9.1 0.03 662 170 0.27 245 2306+29 2319.2+8.2 1 0.14768 0.48 8.76 1.6 0.4302 1.5 0.952 10.1 -- 427 120 0.29 161 2351+35 2346+13 0 0.1500 0.78 9.10 1.9 0.4400 1.8 0.916 11.1 0.03 2063 652 0.33 663 2048士26 2367.2+6.0 13 0.15188 0.35 7.83 1.5 0.3741 1.5 0.973 12.1 0.02 350 310 0.92 157 2702+34 2716.1+8.5 1 0.18701 0.52 13.43 1.6 0.5208 1.5 0.947 13.1 0.02 938 219 0.24 337 2253+28 2297.417.3 2 0.14582 0.42 8.41 1.6 0.4185 1.5 0.962 14.1 0.01 1013 624 0.64 390 2386+29 2342.7+6.7 -2 0.14972 0.39 9.24 1.5 0.4478 1.5 0.966 15.1 0.00 962 154 0.17 368 2373+29 2349.8+6.7 -1 0.15034 0.39 9.23 1.5 0.4451 1.5 0.966 16.1 0.03 602 258 0.44 231 2382+30 2343.848.0 -2 0.14982 0.47 9.23 1.6 0.4470 1.5 0.954 17.1 0.06 464 257 0.57 175 2348+30 2352.8+9.2 0 0.15060 0.54 9.12 1.6 0.4394 1.5 0.942 18.1 0.01 635 353 0.57 240 2351+29 2342.6+8.0 0 0.14971 0.47 9.08 1.6 04401 1.5 0.955 SP19-4 1.1 0.19 1321 329 0.26 361 1776+26 1842.0+8.5 4 0.11261 0.47 4.924 1.7 0.3171 1.7 0.963 2.1 0.01 1997 385 0.20 584 1889+27 1915.8+6.2 1 0.11732 0.35 5.508 1.7 0.3405 1.7 0.979 3.11 0.00 1781 330 0.19 503 1834+27 1964.616.4 7 0.12057 0.36 5.470 1.7 0.3291 1.7 0.977 4.1 0.03 668 155 0.24 209 2004+29 2024.5+8.7 1l 0.12469 0.49 6.27 1.7 0.3646 1.7 0.959 5.1 0.07 468 150 0.33 141 1942+29 1912+11 -2 0.11710 0.62 5.68 1.8 0.3516 1.7 0.940 6.1 0.03 2212 833 0.39 644 1882+27 1902..3+6.2 1 0.11644 0.34 5.442 1.7 0.3390 1.7 0.979 7.1 0.05 1844 307 0.17 599 2066+29 2262.4+5.8 9 0.14288 0.34 7.44 1..7 0.3779 1.7 0.980 8.1 0.02 1662 613 0.38 502 1943+28 1911.5+6.6 -2 0.11704 0.37 5.676 1.7 0.3517 1.7 0.977 9.1 0.03 946 188 0.21 342 2266+32 2316.86.9 2 0.14747 0.40 8.56 1.7 0.4212 1.7 0.972 10.1 0.05 810 123 0.16 306 2346+34 2331.7+8.6 -1 0.14876 0.50 9.00 1.8 0.4389 1.8 0.961 11.1 0.47 4821 1610 0.34 779 1106+17 1497+12 26 0.09343 0.66 2.412 1.8 0.1872 1.7 0.930 12.1 0.01 3726 1734 0.48 1030 1801+26 1843.7+5.5 2 0.11272 0.30 5.011 1.7 0.3224 1.7 0.984 13.1 0.07 2449 909 0.38 640 1710+25 1843.0+6.7 7 0.11267 0.37 4.719 1.7 0.3038 1.7 0.976 14.1 0.02 1828 513 0.29 520 1844+27 1904.3+6.5 3 0.11657 0.36 5.324 1.7 0.3312 1.7 0.977 15.1 0.68 4483 2579 0.59 778 1178+18 1586410 26 0.09798 0.56 2.710 1.8 0.2006 1.7 0.948 16.1 0.02 3803 1774 0.48 958 1 658+24 1784.0+5.9 7 0.10908 0.32 4.410 1.7 0.2932 1.7 0.982 17.1 0.04 825 189 0.24 310 2338+33 2327.2+7.1 0 0.14837 0.41 8.94 1.7 0.4373 1.7 0.971 18.1 0.03 942 191 0.21 275 1884+28 1916.848.2 2 0.11739 0.46 5.494 1.7 0.3395 1.7 0.965 SP19-5 1.1 0.04 1539 373 0.25 521 2141+31 2302.916.1 7 0.14628 0.35 7.94 1.7 0.3938 1.7 0.978 2.1 0.14 316 89 0.29 110 2187+32 2296+12 5 0.14569 0.68 8.11 1.9 0.4039 1.7 0.931 3.1 0.18 1100 248 0.23 346 2010+29 2289.2+7.6 12 0.14512 0.44 7.32 1.7 0.3659 1.7 0.967 4.1 0.06 565 189 0.34 212 2334+33 2334.0+8.2 0 0.14895 0.48 8.96 1.8 0.4363 1.7 0.963 5.1 0.04 490 219 0.46 182 2312+33 2328.5+9.0 1 0.14848 0.52 8.83 1.8 0.4313 1.7 0.956 6.1 0.03 384 131 0.35 141 2291+33 2324.319.4 1 0.14812 0.55 8.71 1.8 0.4266 1.7 0.953 7.1 0.17 626 186 0.31 217 2182+32 2308.918.7 5 0.14679 0.51 8.15 1.8 0.4029 1.7 0.958 8.1 0.07 1729 392 0.23 462 1743+26 2230.016.6 22 0.14023. 0.38 6.00 1.7 0.3106 1.7 0.976 9.1 0.02 616 85 0.14 221 2249132 2326.3+8.1 3 0.14829 0.47 8.53 1.8 0.4174 1.7 0.964 10.1 0.02 1190 236 0.20 435 2283+32 2326.0+6.3 2 0.14826 0.37 8.69 1.7 0.4251 1.7 0.977 11.1 0.05 1998 140 0.07 667 2115131 2280.8+5.9 7 0.14441 0.34 7.73 1.7 0.3884 1.7 0.980 12.1 0.07 720 191 0.27 233 2056+29 2248.4+7.8 9 0.14173 0.45 7.34 1.7 0.3756 1.7 0.965 13.1 0.03 856 155 0.19 293 2160+31 2302.9+7.2 6 0.14628 0.42 8.03 1.7 0.3980 1.7 0.971 14.1 0.05 500 151 0.31 186 2315+33 2329.8+8.6 1 0.14859 0.50 8.85 1.8 0.4320 1.7 0.959 15.1 0.05 2001 805 0.42 412 1383+21 2068.7+7.2 33 0.12786 0.41 4.220 1.7 0.2394 1.7 0.972 16.1 0.02 1606 320 0.21 541 2133+30 2302.8+6.0 7 0.14627 0.35 7.91 1.7 0.3922 1.7 0.979 17.1 0.07 340 143 0.43 124 2283+33 2329+11 2 0.14853 0.63 8.70 1.8 0.4249 1.7 0.940 18.1 0.04 580 202 0.36 211 2274133 2338.1+8.1 3 0.14932 0.48 8.71 1.8 0.4231 1.7 0.963 ![]() 图 6 扬子板块北部和西南部碎屑锆石U-Pb年龄(≥1700Ma)汇总图(据参考文献[44]修改)Figure 6. Histogram of compiled concordant detrital zircon U-Pb ages (≥1700Ma) in northern and southwestern Yangtze Block
图 6 扬子板块北部和西南部碎屑锆石U-Pb年龄(≥1700Ma)汇总图(据参考文献[44]修改)Figure 6. Histogram of compiled concordant detrital zircon U-Pb ages (≥1700Ma) in northern and southwestern Yangtze Block(2)糜棱岩化花岗闪长岩SP19-4
新鲜面呈浅灰色,似条带状构造。主要由斜长石、钾长石、石英、黑云母组成。斜长石具有粘土化、绢云母化等,表面显脏,部分粒内见微裂纹,少数见晶体弯曲现象,由于蚀变、变形等因素,聚片双晶不发育(图版Ⅰ-d)。CL图像显示,锆石颜色较深,显示高U特征,多数具有典型的岩浆生长振荡环带和韵律结构。部分可能受后期热液影响,锆石的内部环带较模糊。全部锆石颗粒基本不发育变质边。锆石形态多为长柱状,长轴为120~350μm,晶体长宽比多为1.5~2.5(图 3)。
共测试了18个数据点,测点均位于锆石环带区域。U含量变化范围为468×10-6~4821×10-6,Th含量变化范围为150×10-6~2579×10-6,Th/U值变化范围为0.16~0.59(表 1)。207Pb/206Pb年龄可划分为3组,即207Pb/206Pb年龄(均为测点的加权平均值)分别为2324.3 ± 8.6Ma(MSWD=1.04,9.1,10.1,17.1)、1909.8±5.7Ma(MSWD=0.79,2.1,5.1,6.1,8.1,14.1,18.1)和1843.1 ± 7.6Ma(MSWD=0.015,1.1,12.1,13.1)(图 4)。
(3)弱糜棱岩化花岗闪长岩SP19-5
新鲜面呈灰白色,似条带状构造。主要组成成分和比例与样品SP19-4相近(图版Ⅰ-e)。CL图像特征与样品SP19-4类似,但锆石颗粒稍小,颜色较浅,锆石内部显示出更多的岩浆生长振荡环带和韵律结构(图 3)。
共测试了18个数据点,测点均位于锆石环带区域。U含量变化范围为340×10-6~2001×10-6,Th含量变化范围为85×10-6~805×10-6,Th/U值变化范围为0.07~0.46(表 1)。从锆石U-Pb谐和图可以看出,所有测点均位于U-Pb谐和线上或其附近,其中谐和度大于等于97%的8个测点给出的207Pb/206Pb年龄加权平均值为2329.4 ± 5.9Ma(MSWD=0.32,4.1,5.1,6.1,9.1,10.1,14.1,17.1,18.1)(图 4)。
4. 讨论
4.1 滇中地区古元古代结晶基底和变质事件
弱糜棱岩化斜长花岗岩样品SP19-1的207Pb/206Pb年龄为2347.3±4.9Ma,可以代表样品的成岩年龄。其中12.1测点的年龄为2716.1±8.5Ma,与崆岭群片麻岩中的一期变质年龄(约2.73Ga)和黄土陵花岗岩锆石年龄(2.78~2.74Ga)同期[21-25],代表更老的地壳增生事件;弱糜棱岩化花岗闪长岩样品SP19-4的3组年龄分别为2324.3±8.6Ma、1909.8± 5.7Ma和1843.1±7.6Ma,其中2324.3±8.6Ma代表花岗闪长岩的成岩年龄,1843.1 ± 7.6Ma和1909.8 ± 5.7Ma为后期构造或变质事件的时代。从锆石207Pb/206Pb年龄和U含量分布图可以看出,锆石U含量越高锆石年龄越小(图 5),指示锆石受后期热事件的影响发生Pb丢失、U升高的现象。从锆石CL图像可见,年龄越小的锆石颜色越深,环带越模糊(图 3)。在样品SP19-4周边清晰可见侵入花岗闪长岩的岩脉(图版Ⅰ-c),因而可以更充分地解释这2期变质事件的合理性;2329.4±5.9Ma代表了弱糜棱岩化花岗闪长岩样品SP19-5的成岩年龄。因此,扬子板块西南部中国境内存在2.35~2.32Ga的岩浆事件和1.90Ga、1.84Ga造山或构造热事件。
近年来,众多学者对扬子板块西南部中元古代会理群、昆阳群、东川群等地层单元的碎屑锆石进行了大量的年代学分析,发现存在大量2.4~2.2Ga及少量2.0~1.8Ga的年龄值,并以此与扬子板块北部相区别(图 6),但其出露的地质体一直未被发现。Lan、Nam等在扬子板块西南部越南北部的正片麻岩中获得了3组SHRIMP锆石U-Pb年龄:2.91~2.84Ga,2.36Ga和1.96Ga,首次发现了扬子板块西南部太古宙结晶基底和后期岩浆及变质事件[74-75]。Wang等[20]进一步在越南北部此地区花岗片麻岩中获得了3组SHRIMP锆石U-Pb年龄: 2.28~2.19Ga,1.97~1.95Ga和1.83Ga。2.28~2.19Ga代表了岩浆事件的时代,而1.97~1.95Ga和1.83Ga代表了后期构造热事件的时代[20]。在中国境内,Kou等[29]在大红山群钠长岩和变质火山岩中获得了2.00Ga的锆石U-Pb年龄,指示扬子板块西南部中国境内可能存在更老的基底。本次研究继在扬子板块西南部中国境内石屏撮科地区首次发现2.35Ga花岗片麻岩结晶基底之后[30],后续在撮科—高家坡一带的弱糜棱岩化斜长花岗岩和花岗闪长岩中获得多组精确SHRIMP锆石U-Pb年龄,确认扬子板块西南部中国境内存在2.32~2.35Ga的火山岩浆事件,并发现了1.90Ga、1.84Ga的造山或变质事件。同时,建议将这一套古元古代花岗岩、花岗片麻岩和侵入其中的基性岩等命名为“石屏岩群”。
4.2 扬子板块与Nuna超大陆的重建
Nuna超大陆及扬子板块在其中的位置一直是前寒武纪研究的重要课题之一[20, 25, 76-78]。结合Lan、Nam等的数据和研究成果[74-75],Wang等将扬子板块西南部越南北部古元古代花岗片麻岩及其变质事件与北美地区Rae、Slave等古老克拉通的火山岩浆及变质事件进行对比,提出扬子板块与Laurentia克拉通、Siberia克拉通相关联,越南北部2.36Ga火山岩浆事件是北美Arrowsmith造山事件(2.50~2.45Ga和2.35~2.28Ga)在扬子板块的响应[20, 79]。而中国境内石屏地区2.35~2.32Ga的火山岩浆事件进一步为此设想补充了证据,并可作为北美Arrowsmith造山事件在扬子板块的又一反映。
2.03~1.97Ga和1.85Ga火山岩浆或变质事件在扬子板块的北部广泛发育[76-77, 80-81, 85-86],但是,在扬子板块的西南部同期的地质体和变质事件一直未被发现。Kou等[29]在扬子板块西南部大红山群钠长岩和变质火山岩中获得了2.00Ga的锆石U-Pb年龄,Wang等[20]在越南北部花岗片麻岩中获得了2.28~ 2.19Ga,1.97~1.95Ga和1.83Ga三期年龄,扬子板块西南部进而与Nuna超大陆汇聚事件相关联。本次研究进一步确认了中国石屏存在1.84Ga、1.90Ga造山或构造热事件,也是首次在扬子板块西南部发现1.90Ga的造山或构造热事件。而在1.91~1.90Ga,Rae克拉通周缘的North Atlantic克拉通和Superior克拉通(Laurentia克拉通)火山活动尤为发育[85-86]。因此,滇中地区1.90Ga的造山或构造热事件为扬子板块在Nuna超大陆重建中的位置提供了更多证据。结合前人研究成果,扬子板块西南部存在2.91~ 2.84Ga,2.36~2.32Ga,2.28~2.19Ga,1.97~1.95Ga、1.90Ga,1.84~1.83Ga的岩浆或变质事件。这些事件在Nuna大陆主体区域——北美和格陵兰地区均有体现[20, 79, 82-84]。
5. 结论
(1)滇中石屏撮科村昆阳群下伏花岗岩3个样品的锆石年龄分别为2347.3 ± 4.9Ma(MSWD= 0.75)、2324.3 ± 8.6Ma(MSWD=1.04)和2329.4 ± 5.9Ma(MSWD=0.32),代表了花岗岩的成岩年龄,进一步确认在扬子板块西南部中国境内存在2.32~ 2.35Ga的岩浆事件。建议将这一岩石体系命名为“石屏岩群”。
(2)另在糜棱岩化花岗闪长岩样品中获得了1909.8 ± 5.7Ma(MSWD=0.79)和1843.1 ± 7.6Ma(MSWD=0.015)两组SHRIMP锆石U-Pb年龄,代表了后期构造或变质事件的时代,在扬子板块西南部中国境内首次发现1.90Ga和1.84Ga的构造或变质事件。
(3)扬子板块西南部存在2.91~2.84Ga,2.36~ 2.32Ga,2.28~2.19Ga,1.97~1.95Ga,1.90Ga,1.84~ 1.83Ga的岩浆或变质事件,为扬子板块在Nuna超大陆重建中的位置和演化过程提供了更多证据。
-
图 1 拉丁超立方采样(2个随机变量,5次模拟)[25]
Figure 1. Latin Hypercube sampling(with two variables and five realizations)
图 5 大堡子滑坡全貌图(a)与剖面(b)[27]
Figure 5. Overall views(a)and a typical section(b)of Dabaozi landslide
表 1 土体参数的变异性级别[29]
Table 1 ariability classification of soil parameters
变异系数 δ≤0.1 0.1δ≤0.2 0.2δ≤0.3 0.3δ≤0.4 δ>0.4 变异性 很低 低 中等 高 很高 表 2 随机变量的统计特征
Table 2 Statistical characteristics of random variables
随机变量 ρ
/(kg·m-3)c′
/kPaφ′
/°ru 均值 1800 39 25 0.65 变异系数 0.05 0.3 0.15 - 参数范围 [0, +∞) [0, +∞) [0, +∞) [0.5, 0.8] 分布类型 对数正态 对数正态 对数正态 均匀 表 3 事件可能性分类[33]
Table 3 Event likelihood classification
不确定性 描述 概率值/% 几乎
确定由已知物理条件或过程,事件几乎确定发生 99.9 非常
可能事件极有可能发生,但也可能不会发生,如果没有发生,人们会感到惊讶 99 可能 事情是可能发生的,但不一定发生 90 完全不确定 没有理由相信一种结果比另一种结果更可能或更不可能发生 50 不可能 事件不太可能发生,但它有可能发生 10 非常不可能 不能根据已知的物理条件或其他原因完全排除事件发生的可能性 1 几乎不可能 由已知的物理条件或过程,事件几乎不可能发生 0.1 -
Dai F C, Lee C F, Ngai Y Y. Landslide risk assessment and management: an overview[J]. Engineering Geology, 2002, 64(1): 65-87. doi: 10.1016/S0013-7952(01)00093-X
吴越, 刘东升, 周忠浩. 考虑滑动过程内部崩解耗散的滑坡体运动模型[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2015, 37(1): 35-46. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTGC201501004.htm Corominas J, van Westen C, Frattini P, et al. Recommendations for the quantitative analysis of landslide risk[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment, 2014, 73(2): 209-263. http://core.ac.uk/download/pdf/38629048.pdf
詹威威, 黄润秋, 裴向军, 等. 沟道型滑坡-碎屑流运动距离经验预测模型研究[J]. 工程地质学报, 2017, 25(1): 154-163. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ201701021.htm 邵葆蓉, 孙即超, 朱月琴, 等. 基于多元回归的黄土滑坡滑动距离预测模型探讨——以甘肃天水地区为例[J]. 地质通报, 2020, 39(12): 1993-2003. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20201213&flag=1 Zhan W, Fan X, Huang R, et al. Empirical prediction for travel distance of channelized rock avalanches in the Wenchuan earthquake area[J]. Natural Hazards & Earth System Sciences, 2017, 17(6): 833-844. http://www.ingentaconnect.com/content/doaj/15618633/2017/00000017/00000001/art00012
Hungr O, McDougall S. Two numerical models for landslide dynamic analysis[J]. Computers & Geosciences, 2009, 35(5): 978-992. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science?_ob=ShoppingCartURL&_method=add&_eid=1-s2.0-S0098300408000289&originContentFamily=serial&_origin=article&_ts=1490054550&md5=89f93acdf526fbdab24cf890094345a2
Beguería S, Van Asch T W J, Malet J P, et al. A GIS-based numerical model for simulating the kinematics of mud and debris flows over complex terrain[J]. Natural Hazards and Earth System Sciences, 2009, 9(6): 1897-1909. doi: 10.5194/nhess-9-1897-2009
Christen M, Kowalski J, Bartelt P. RAMMS: Numerical simulation of dense snow avalanches in three-dimensional terrain[J]. Cold Regions Science and Technology, 2010, 63(1/2): 1-14. http://www.onacademic.com/detail/journal_1000035369102510_59d8.html
Van Westen C J, Van Asch T W J, Soeters R. Landslide hazard and risk zonation-why is it still so difficult?[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment, 2006, 65(2): 167-184. doi: 10.1007/s10064-005-0023-0
Quan L. Dynamic numerical run-out modeling for quantitative landslide risk assessment[D]. Doctoral Thesis of University of Twente, ITC, 2012, 206: 1-237.
Luna B Q, Cepeda J, Stumpf A, et al. Application of a Monte Carlo method for modeling debris flow run-out[C]//EGU General Assembly Conference. EGU General Assembly Conference Abstracts, 2012.
祝玉学. 边坡可靠性分析[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版, 1993. Zahra T. Quantifying uncertainties in Landslide Runout Modelling[M]. University of Twente Faculty of Geo-Information and Earth Observation(ITC), 2010.
Zaalishvili V B, Rogozhin E A. Assessment of seismic hazard of territory on basis of modern methods of detailed zoning and seismic microzonation[J]. Open Construction and Building Technology Journal, 2011, 5: 30-40.
唐荣昌, 张耀国, 黄祖智, 等. 四川石棉-西昌地区地震区划研究[J]. 地震研究, 1993, 16(3): 306-315. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZYJ199303011.htm 唐川, 周钜乾, 朱静, 等. 泥石流堆积扇危险度分区评价的数值模拟研究[J]. 灾害学, 1994, 9(4): 7-13. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHXU404.001.htm Wei F, Hu K, Lopez J L, et al. Method and its application of the momentum model for debris flow risk zoning[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2003, 48(6): 594. doi: 10.1360/03tb9126
Ouyang C, He S, Xu Q, et al. A MacCormack-TVD finite difference method to simulate the mass flow in mountainous terrain with variable computational domain[J]. Computers & Geosciences, 2013, 52: 1-10. http://or.nsfc.gov.cn/bitstream/00001903-5/57006/1/1000007119136.pdf
Ouyang C, He S, Tang C. Numerical analysis of dynamics of debris flow over erodible beds in Wenchuan earthquake-induced area[J]. Engineering Geology, 2015, 194: 62-72. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2014.07.012
Ouyang C, He S, Xu Q. MacCormack-TVD finite difference solution for dam break hydraulics over erodible sediment beds[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2014, 141(5): 06014026.
Ouyang C, Zhao W, He S, et al. Numerical modeling and dynamic analysis of the 2017 Xinmo landslide in Maoxian County, China[J]. Journal of Mountain Science, 2017, 14(9): 1701-1711. doi: 10.1007/s11629-017-4613-7
Xing A G, Wang G, Yin Y P, et al. Dynamic analysis and field investigation of a fluidized landslide in Guanling, Guizhou, China[J]. Engineering Geology, 2014, 181: 1-14. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2014.07.022
McKay M D, Beckman R J, Conover W J. Comparison of three methods for selecting values of input variables in the analysis of output from a computer code[J]. Technometrics, 1979, 21(2): 239-245. http://r-forge.r-project.org/scm/viewvc.php/*checkout*/doc/McKay1979.pdf?root=lhs
Olsson A, Sandberg G, Dahlblom O. On Latin hypercube sampling for structural reliability analysis[J]. Structural Safety, 2003, 25(1): 47-68. doi: 10.1016/S0167-4730(02)00039-5
吴振君. 土体参数空间变异性模拟和土坡可靠度分析方法应用研究[D]. 中国科学院研究生院(武汉岩土力学研究所)博士学位论文, 2009. 沈伟, 翟张辉, 李同录, 等. 陕西泾河南岸大堡子高速远程黄土滑坡运动过程模拟[J]. 工程地质学报, 2016, 24(6): 1309-1317. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ201606034.htm 郭剑. 一种双层结构的高速远程滑坡运动学模型及应用[D]. 长安大学硕士学位论文, 2018. 重庆市质量技术监督局. DB50/T 143-2018地质灾害防治工程勘查规范[S]. 2018. 袁晓蕾. 黄土滑坡的滑带土强度试验参数统计及可靠性研究[D]. 长安大学硕士学位论文, 2007. 倪万魁, 韩启龙. 黄土土性参数的统计分析[J]. 工程地质学报, 2001, 9(1): 62-67. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2001.01.011 Gao Y, Yin Y, Li B, et al. Investigation and dynamicanalysis of the long runout catastrophic landslide at the Shenzhen landfill on December 20, 2015, in Guangdong, China[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2017, 76(1): 13. doi: 10.1007/s12665-016-6332-8
Lacasse S, Nadim F. Learning to live with geohazards: from research to practice[M]. Geo-Risk 2011: Risk Assessment and Management, 2011: 64-116.
-
期刊类型引用(15)
1. 张英利,贾晓彤. 扬子陆块西缘寒武系砂岩的物源分析:对古地理位置重建和构造背景的指示. 地质学报. 2024(02): 363-380 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 赵德顺,赵伟策,王书来,祝新友,蒋斌斌. 云南毛坪铅锌矿床横向断裂构造控矿特征及其找矿意义. 地质与勘探. 2023(01): 1-11 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 杨兴华. 云南新平大红山铁铜矿床地层控矿规律分析. 现代矿业. 2023(04): 17-20+25 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 乔宇,王学求,韩志轩,刘福田,严桃桃,王强,吴慧. 中国西南滇黔桂关键资源远景新区锂地球化学时空分布特征及找矿预测. 地质学报. 2023(06): 1828-1847 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 李勇,李昌存,庞仕辉,杜永刚,乔小兵,陶志刚. 露天铜矿边坡工程地质分区及稳定性评价研究. 河南理工大学学报(自然科学版). 2022(01): 59-66 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 古阿雷,任军平,王杰,左立波,孙宏伟,许康康,陈靖,EZEKIAHChikambwe,EVARISTOKasumba. 赞比亚东北部陇都地区首次发现中元古代辉长岩:哥伦比亚超大陆裂解在班韦乌卢地块的响应. 地质通报. 2022(01): 34-47 .  本站查看
本站查看
7. 张良,张恒,龚成强,丁孝忠,张传恒,刘勇,高林志,刘燕学. 滇中南中元古代撮科蛇绿混杂岩地质特征及构造背景. 地学前缘. 2022(02): 180-197 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 李廷栋,刘勇,丁孝忠,庞健峰. 中国区域地质研究的十大进展. 地质学报. 2022(05): 1544-1581 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 李廷栋. 中国地质矿产调查事业发展历程. 地质力学学报. 2022(05): 653-682 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 宋志豪,刘桂萍,郭瑞清,玛依拉·艾山,崔涛. 库鲁克塔格兴地塔格群变质石英岩复杂锆石特征及指示意义. 新疆地质. 2021(01): 55-66 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 刘军平,宛胜,李静,邓仁宏,赵江泰,陈棵,吴嘉林. 滇中易门地区古元古界易门群罗洼垤组火山岩锆石U-Pb年龄及其构造热事件. 地质通报. 2021(07): 1024-1032 .  本站查看
本站查看
12. DING Xiaozhong,ZHANG Kexin,GAO Linzhi,LU Songnian,PAN Guitang,XIAO Qinghui,LIU Yong,PANG Jianfeng. Research Progress and the Main Achievements of The Regional Geology of China Preface. Acta Geologica Sinica(English Edition). 2020(04): 865-876 .  必应学术
必应学术
13. HAN Kunying,ZHANG Heng,DING Xiaozhong,REN Liudong,SHI Chenglong,PANG Jianfeng. Zircon U–Pb Ages and Lu–Hf Isotope of the Dongchuan Group in Central Yunnan, China, and their Geological Significance. Acta Geologica Sinica(English Edition). 2020(04): 1093-1116 .  必应学术
必应学术
14. 缪宇,韦少港,吕晓春,宋文婷,万理文. 滇东北中元古界下昆阳群鹅头厂组变质岩地球化学特征及其形成环境. 地质通报. 2020(10): 1538-1548 .  本站查看
本站查看
15. WANG Kai,DONG Shuwen,YAO Weihua,ZHAO Tianyu. Nature and Evolution of Pre-Neoproterozoic Continental Crust in South China: A Review and Tectonic Implications. Acta Geologica Sinica(English Edition). 2020(06): 1731-1756 .  必应学术
必应学术
其他类型引用(5)




 下载:
下载: