Regional geochemistry, metallogenetic model and ore prospects of the western Xiaoqinling Au-Mo polymetallic ore-concentrated area, China
-
摘要:
小秦岭金钼多金属矿集区地质构造复杂,构造岩浆活动强烈,金、钼、银等化探异常连片成带分布,综合异常众多,成矿条件良好。小秦岭矿集区西部岩石地球化学分析表明,区内小岩体酸度较高、中等富碱,主要为高钾钙碱性系列,存在一定程度的壳幔物质混合。大花岗岩基主要沿EW向与NE向2组构造交汇部位上侵,小斑岩体主要受次级构造的控制,常在花岗岩基外带一定范围内或小岩体内及其周围成矿,地层、构造和岩浆活动三者是关键性的控矿因素。结合金、钼矿床地质特征、成矿规律、成矿机制分析等,提出了该区金矿床的构造岩浆活化成矿模式,总结了钼矿床成矿模式;依据区域矿化富集规律和找矿实践,建立了系统的区域找矿模型,并在此基础上,指出下一步找矿靶区和找矿方向。
Abstract:The Xiaoqinling Au-Mo polymetallic ore-concentrated area with complex structure and active magmatism is characterized by continuous zones of Au-Mo-Ag geochemical anomalies and ideal metallogenic conditions.The small plutons in the area belongs to the high potassium calc-alkaline series, with relatively high acidity and moderately rich alkali, and there is a certain degree of crust-mantle mixing material involved in them.The large granite plutons are mainly emplaced on the intersection of EW-trending and NE-trending structures.While, subject to the strata-structure-magmatism united control, the small mineralized porphyries controlled by secondary structures are distributed around the large granite plutons or within small intrusives.The metallogenic model of tectono-magmatic activation is drawn from combination of geology, metallogenic regularity and mechanism etc.of Au-Mo deposits.Based on the regional mineralization regularity and prospecting practice, the systematic regional prospecting model is established, and ore prospects are outlined.
-
白云鄂博稀土-铌-铁矿床是世界级的综合性矿床,蕴含着稀土、铌、铁、钪、萤石等多达26种矿产资源,极具经济和科学研究价值。自1927年发现以来,已经形成了主矿、东矿、西矿、东介勒格勒、菠萝头5个主要矿段,其中铁矿石总储量约14.68×108 t[1]。经过60多年的开采,最早开发的主矿、东矿露天开采服务年限到目前仅有4~5年。东介勒格勒和菠萝头矿段的保有资源量少,品位低,矿体小而散。因此,铁矿保障资源严重不足,寻找接替资源迫在眉睫。
自20世纪80年代以来,国内外众多学者在赋矿岩石的成因[2-11]、成岩成矿时代[10-24]、稀土矿物学[25-30]等方面取得一系列重要进展,为碳酸岩型矿床成矿理论发展做出了突出贡献。尽管对白云鄂博赋矿岩石的成因目前仍存在不同认识,但越来越多的地质学、地球化学证据支持中元古代岩浆碳酸岩的成因观点[31-32],即白云鄂博赋矿岩石为白云石碳酸岩。然而,白云石碳酸岩的形成受什么构造控制?铁矿体在白云石碳酸岩中的空间分布规律受什么控制等科学问题仍亟待解决。
白云鄂博矿区地处华北克拉通北缘渣尔泰-白云鄂博-化德中元古代裂谷带中(图 1)。华北克拉通是世界上最古老的克拉通之一,经历了自元古宙以来复杂的构造演化[33-36],包括古元古代末期—新元古代的多期裂谷事件[37]、古生代与俯冲有关的多期岩浆[13, 38]、变质和变形作用[19, 39]等。长时间的构造演化使得矿床构造地质情况十分复杂[40-41]。长期以来对白云鄂博的构造研究主要聚焦在其大地构造属性及矿区外围的构造变形上,对白云鄂博主要控矿构造形迹及其对矿床控制作用的研究仍较薄弱。一直以来,白云鄂博找矿模型是以向斜控矿作为指导,这在早期控制白云鄂博矿床浅部资源起到了非常好的效果。然而,随着矿区的进一步开采揭露和深部钻孔的进一步施工,矿区的构造样式和成矿地质模型也需要进一步研究[32]。
![]() 图 1 中国大地构造纲要图(a)、华北克拉通中元古代裂谷带简图(b)和白云鄂博地区大地构造分区图(c)[33]Figure 1. Tectonic sketch map of China (a) and sketch map showing Mesoproterozoic rift zones in the North China Craton (b) and the geotectonic divisions map of Bayan Obo area (c)
图 1 中国大地构造纲要图(a)、华北克拉通中元古代裂谷带简图(b)和白云鄂博地区大地构造分区图(c)[33]Figure 1. Tectonic sketch map of China (a) and sketch map showing Mesoproterozoic rift zones in the North China Craton (b) and the geotectonic divisions map of Bayan Obo area (c)本文围绕白云鄂博主要控矿构造形迹及其对矿床的控制作用,通过对主矿区、东矿区精细的矿田构造填图,查明矿区构造变形性质、变形序次及其对矿体的形成控制及破坏作用,结合铁矿体空间分布规律,探讨各构造形迹与成矿的关系,对矿区深部和外围找矿部署工作具有重要的指导意义。
1. 区域地质构造特征
白云鄂博矿床位于乌兰宝力格深断裂和白银角拉克大断裂2条断裂带的交汇处(图 1-c),这2条断裂带基本控制了区内的构造格局、成矿作用及岩浆活动[8]。乌兰宝力格断裂位于矿区北侧10 km,是赤峰-白云鄂博断裂的一部分,常被作为华北克拉通与北侧古亚洲洋俯冲增生杂岩的界线,沿断裂带发育多期海西期岩浆侵位和火山事件。白银角拉克-宽沟大断裂的展布方向大致为近东西向,西至白银角拉克地区,东至宽沟地区,全长约40 km。西侧白银角拉克地区显示倾向北的逆断层性质,断裂标志发育明显,在东侧宽沟地区的断裂特征不显著,脉岩常沿断裂出现,向东与乌兰宝力格深大断裂带汇合。
除区域性深大断裂外,1:5万专题地质填图显示矿区及外围的构造情况十分复杂。断裂构造以近东西向产出的由北向南的逆冲推覆为突出特征,大小断裂密布,多呈叠瓦式产出。褶皱构造存在多期次不同方向和不同性质的叠加褶皱变形构造,大中型褶皱构造的枢纽倾伏较缓,轴向近东西,而小型褶皱大多零星分布于其内部。研究区最主要的褶皱构造为宽沟背斜。宽沟背斜的轴向近东西向,且枢纽向西倾伏,核部为古元古界花岗片麻岩及宝音图群变质杂岩,两翼为白云鄂博群。该背斜东端南翼被海西期花岗岩侵入,西部南翼以往被认为发育次级向斜(即白云向斜),白云鄂博矿床处于宽沟背斜的南翼。
矿区断裂构造特别发育(图 2),包括近东西向、北西西向、北西向、北东向和近南北向,导致矿区岩石地层单元走向上不连续[19]。矿区主要断裂构造以近东西向为主,包括北侧的赛乌素韧性剪切带、宽沟断裂、白云鄂博矿区南侧的逆冲断层和韧性剪切带等[19]。从矿区碳酸岩和其他岩石单元的变形特征看,无论是赋矿白云石碳酸岩还是长城系都拉哈拉组、尖山组、蓟县系比鲁特组,均显示韧性剪切变形的特征,矿区整体应处于一个巨形韧性剪切带中,矿区北侧的赛乌素韧性剪切带和南侧的韧性剪切带[19]可能都是该巨型韧性剪切带的一部分,但具体发育特征仍需进一步的工作证实。
![]() 图 2 白云鄂博主、东矿区地质及构造分布图1—第四系;2—白垩系固阳组;3—长城系尖山组;4—长城系都拉哈拉组;5—新太古界乌拉山群;6—二叠纪二长花岗岩;7—黑云母花岗闪长岩;8—中元古代白云石碳酸岩;9—花岗岩脉;10—石英斑岩脉;11—闪长岩/闪长玢岩脉;12—碳酸岩脉;13—碱性岩脉;14—钠角闪石岩脉;15—钠辉石钠角闪石碱性岩脉;16—铁矿化体;17—低品位铁矿化带;18—实测或推测正断层;19—实测或推测逆断层;20—实测或推测性质不明断层;21—韧性剪切带;22—断层序号Figure 2. Geological and structural map of the main mine and east mine in the Bayan Obo ore deposit
图 2 白云鄂博主、东矿区地质及构造分布图1—第四系;2—白垩系固阳组;3—长城系尖山组;4—长城系都拉哈拉组;5—新太古界乌拉山群;6—二叠纪二长花岗岩;7—黑云母花岗闪长岩;8—中元古代白云石碳酸岩;9—花岗岩脉;10—石英斑岩脉;11—闪长岩/闪长玢岩脉;12—碳酸岩脉;13—碱性岩脉;14—钠角闪石岩脉;15—钠辉石钠角闪石碱性岩脉;16—铁矿化体;17—低品位铁矿化带;18—实测或推测正断层;19—实测或推测逆断层;20—实测或推测性质不明断层;21—韧性剪切带;22—断层序号Figure 2. Geological and structural map of the main mine and east mine in the Bayan Obo ore deposit矿区一带主要出露中元古界白云鄂博群,主要包括长城系都拉哈拉组、尖山组,蓟县系哈拉霍格特组和比鲁特组,其南西两侧出露花岗岩岩基,北侧花岗岩则呈岩株产出。区内地质构造方向与东西褶皱带的方向一致,中元古界白云鄂博群的走向、重要断层的走向、花岗岩岩基长轴方向及岩脉侵入方向,均为东西向;节理亦以东西向的纵节理最发育;矿化地区亦呈东西带状,说明成矿作用受东西向构造的控制。
2. 白云鄂博矿区控矿构造特征
2.1 褶皱构造特征
白云鄂博附近地区地质构造为一大复背斜形式,轴向为东西或近东西向。错综的逆断层和南北向断层使构造更加复杂化,因此大复背斜中的小背斜和小向斜,亦呈多种形式出现。因地区不同,倾斜方向及倾斜角度不同。其主要褶皱分述如下。
(1) 宽沟背斜构造:为复背斜的中央背斜部分。其位置在哈拉达岭以南主矿、东矿以北的宽沟。构成核部的岩石为震旦系底部的岩层。背斜构造向西倾没,因此长城系都拉哈拉组一段和二段仅出现于背斜的东段,即查汗鄂博—尖山一带,向西则仅有长城系尖山组一段岩层出露。
背斜东段两翼的岩层,分别向两翼倾斜,倾角大于45°,最大至60°~70°。西段岩层倾角亦陡。再向西至阿布达,此背斜构造为一横断层所切。
宽沟背斜东段核部长城系都拉哈拉组一段和二段,受显著的混合岩化作用,一部分成为混合岩。向西至尖山一带,背斜核部有小的闪长岩侵入体出露,并有石英脉断续出现。阿布达背斜核部的都拉哈拉组一段岩层,亦受混合岩化作用形成混合岩。
(2) 北部向斜构造:宽沟背斜的北翼,向东至查汗鄂博,因断层关系造成岩层缺失现象,再向北在蓟县系比鲁特组一段之上,哈拉霍圪特组又重新出露,并向北倾斜,造成以蓟县系比鲁特组一段为褶轴的倒转向斜构造。向斜构造的东段构造较复杂。向北哈拉霍圪特组岩层重复出露多次,并均向北倾斜,造成多次倒转褶皱。向斜的西段向北,蓟县系比鲁特组岩层亦自成向南倒转的褶皱多次,直至白云布拉格以东地区。
(3) 南部“向斜”构造:宽沟背斜南部,从东介勒格勒南部和主矿、东矿北部的都拉哈拉组产状看,向形是存在的。基本上是以比鲁特组一段硅质板岩为核部的向形构造,轴向为东西向。但本次专题填图的结果显示,主要的赋矿岩石应为沿断裂产出的白云石碳酸岩,如果将白云石碳酸岩剔除,向形两侧的岩层岩性及厚度都不具有对比性,故南部“向斜”构造究竟是否存在还是被侵入岩改造,仍需进一步研究。
2.2 断层构造特征
矿区受多期叠加褶皱变形的影响,韧性剪切、脆性断层非常发育[42]。构造填图结果显示,矿区从中元古代—海西期至少发育4期构造活动,包括近东西向控岩断层(F1)、近东西向逆-平移断层(F2)、近东西向褶皱和韧性剪切构造、北东向左行走滑正断层(F3)(图 2),它们不仅控制矿床的形成,在很大程度上也影响矿床的破坏与保存,同时也控制着矿体的形态、产状。
2.2.1 近东西向控岩断层特征(F1)
该断层主要沿白云石碳酸岩与顶板长城系尖山组界线分布(图 2),贯穿整个主矿、东矿区,其控制了白云石碳酸岩的产出和矿体的形成。断层倾角一般大于60°,断层面平直,整体走向近东西向,断层面局部呈舒缓波状。在露头上,表现为白云石碳酸岩和顶板板岩呈断层接触,断层带内从白云石碳酸岩→比鲁特组硅质板岩依次出现断层泥、构造角砾岩和碎裂岩。根据剪节理、构造透镜体等运动学标志(图版Ⅰ),判定该断层为正断层,与前人划分的高位断层和东介勒格勒断层性质一致。从图版Ⅰ可以看出,断层面产状呈现2组:一组为154°∠84°、134°∠75°;另一组为230°∠65°、210°∠63°,推断其可能为共轭张性断层系,形成这2组断层的应力场应为近南北向拉伸、东西向挤压。此外,沿构造带上含矿碳酸岩中常见小型包卷层理,同生褶皱构造,滑动搓碎的角砾等,其中较清晰和具指向意义的是同生褶皱构造,可能属于早期裂谷作用形成的伸展断层。
伸展断层是本区的控岩主断层,控制了含矿白云石碳酸岩侵位,高位同生断层及白云石碳酸岩是这个阶段的产物。这与中元古代白云鄂博裂谷拉张环境匹配。虽然本区遭受过多期构造的强烈改造,裂谷早期的构造在局部地区已发生解体或被掩盖,但从剖面上,裂谷早期同生构造依然控制断陷盆地的发展及演化。后期联合地体的拼贴碰撞导致的挤压褶皱可能主要表现在地壳表层。深部构造样式还保留了早期构造的特点。
该断层为白云石碳酸岩侵位同期或更早发育的一组陡倾的正断层,主要证据有断层角砾岩中往往见萤石化、磁铁矿化等矿化,为主要的控岩控矿断层。
2.2.2 近东西向逆-平移断层特征(F2)
该组断层在主矿、东矿南部非常发育,其产于白云石碳酸岩顶部的板岩中,紧邻控岩断层,断层延伸稳定,在东矿东部、东矿西部、主矿东部、主矿中西部具有露头显示(图版Ⅱ)。断层带宽度一般为5~20 m,局部见构造破碎带,宽达25 m(东矿西端)。走向近东西向,倾向在160°~180°之间,倾角在75°~85°之间,擦痕产状为250°~255°∠10°~30°。根据擦痕、阶步、次级的剪节理判断,该组断层应为左行逆-平移断层,且以走滑为主。
构造填图结果显示,断层构造位于矿体南侧,产状也较矿体陡,很明显,断层切割深部矿体,对矿体造成破坏。
白云鄂博东矿15、16、17勘探线剖面显示(图 3),白云石碳酸岩与上部板岩界线延伸稳定,但在深部两者界线发生突变,且在突变的白云石碳酸岩中,在预计的断层带,均发现了基性岩脉的存在(WK15-0、WK16-04、WK17-04),这也验证了预期断层构造的存在。两者界线测量显示,深部矿体向上推移大于300 m,因断层以走滑为主,横向位移可能远大于300 m,故断层对矿体破坏性较大,很可能导致了主矿、东矿深部矿体向东推移。
2.2.3 近东西向韧性剪切构造
该组韧性剪切构造主要发生在主矿、东矿南侧,是一期非贯穿性构造,在矿区形成东西向的韧性剪切带。在矿区范围内,该带西起西矿南侧,向东经主矿、东矿南侧向东延伸,规模超过10 km。
该组韧性剪切构造在不同性质的岩石中有不同的表现:在细粒白云石碳酸岩中,变形不明显(图版Ⅲ-a);在矿体顶板富钾板岩中,由于岩石能干性较强,岩石受剪切发生脆性碎裂(图版Ⅲ-b);在细粒白云石碳酸岩与接触云母岩接触带,可以明显看到差异性韧性变形(图版Ⅲ-c);在钠长石发育的地段,可以明显看到早期钠长石脉透镜体化(图版Ⅲ-d);在萤石化发育的地段,眼球状构造异常发育(图版Ⅲ-e);糜棱岩中发育各种指向性清楚的显微构造,包括白云石碎斑、长石碎斑、石英波状消光等。白云石碎斑系列沿剪切破裂面发生滑移,拖尾构造显示运动方向为左旋剪切(图版Ⅲ-f)。此外,在矿区南部中元古界白云鄂博群尖山组糜棱岩化长石石英岩中还发育大量的矿物线理,一组与糜棱面理倾向垂直的钠铁闪石代表物质运移方向。
野外露头显示,受此韧性剪切带影响,主矿、东矿之间矿体上盘板岩陡倾的劈理十分发育(图版Ⅳ-a),侵入板岩中的碱性脉小型紧闭褶皱也非常发育(图版Ⅳ-b、c、d),在局部地段也可以看到近东西向、北西向的小型逆冲断层(图版Ⅳ-e、f),断层的规模和标志层位移显示,本期断层规模较小,对矿体的破坏有限。
2.2.4 北东向左行走滑正断层特征(F3)
该组断层构造主要见于主矿东部坑底和东矿北侧1480 m平台(图 4)。由于断层发育在白云石碳酸岩内部,岩石能干性较低,故在露头上延续性较好,但断层宽度较窄,断层泥和构造角砾岩不发育。断层走向为北东向,倾向南东(110°~120°),倾角陡立(68°~78°)。断层面上的擦痕显示,该断层具有左行走滑性质,属于正断层,导致了主矿、东矿位置的错动。主矿、东矿矿体中段平面图显示,该断层位移较小,对矿体的破坏有限。
根据其对白云石碳酸岩的切割关系,该构造形成于白云石碳酸岩侵位之后,同属于白云石碳酸岩侵位晚期的伸展环境的构造。
3. 构造控矿模式
3.1 矿区构造时序
根据不同构造相互间的切割关系及其与控岩控矿的关系,矿区内褶皱、断层和韧性剪切带时序应为:近东西向控岩断层(F1)→近东西向逆-平移断层(F2)→近东西向褶皱构造和韧性剪切构造→北东向左行走滑正断层(F3)。主要有以下证据。
近东西向控岩断层为矿区控岩主断层构造,其控制了含矿白云石碳酸岩侵位,断层角砾岩证据表明,该断层为白云石碳酸岩侵位同期或更早发育的一组陡倾的正断层;勘探线剖面图显示,近东西向逆-平移断层(F2)切割了铁矿体和白云石碳酸岩体,故F2晚于F1;精细的构造填图显示,北东向左行走滑正断层(F3)明显切割了早期形成的F1和F2断层,故F3断层形成最晚。近东西向褶皱构造和韧性剪切构造与F1、F2、F3的时序关系没有明显的地质证据,仅根据矿区应力场的转变推测,尚需要开展进一步的研究。
3.2 构造活动与区域地质演化的耦合
(1) 结晶基底形成期:大量的同位素年龄统计[43]显示,白云鄂博地区结晶基底的形成跨越了2个时期:新太古代(约2550 Ma)和古元古代(2040~1900 Ma)。其中,约2550 Ma的年龄记录,与华北克拉通早期的TTG岩类及早期花岗岩的集中侵位时代一致,为华北克拉通最重要的陆壳(活动陆缘、岛弧)增生、克拉通化峰期[44-50]。2040~1900 Ma年龄记录是一期碰撞造山事件的体现[51-52]。
(2) 裂谷形成期:中元古代,白云鄂博及其外围发育大量火成碳酸岩墙群和基性岩墙群,其形成时间与Columbia超大陆裂解事件(1.4~1.2 Ga)吻合,是超大陆最终裂解的产物[10, 33-34, 53]。矿区发育该裂谷系的北支,是由白云鄂博群组成的白云鄂博裂谷带。以裂谷沉积为主的白云鄂博群主要由一套碎屑岩、泥页岩、碳酸盐岩组成,并有碱性火山建造,与下伏结晶基底色尔腾山群呈角度不整合。其中,碎屑岩和碳酸盐岩沉积总厚度达万米,与白云鄂博群总厚度的比值可达0.9,说明白云鄂博群是在强烈拗陷中快速堆积,并伴随切割很深的同沉积断裂[54],矿区控制白云石碳酸岩产出的近东西向正断层正是裂谷形成阶段的构造响应。
(3) 俯冲碰撞造山期:早古生代志留纪晚期,华北板块与西伯利亚板块发生俯冲碰撞造山[41, 55]。受其影响,白云鄂博矿区地层强烈褶皱变质,断层构造非常发育,其中包括形成近东西向展布的乌兰宝力格深断裂和白云鄂博-白银角拉克大断裂[56]。此外,在近南北向水平压力作用下,低序次的北东向走滑断裂在该区,尤其在乌兰宝力格深断裂带北侧较发育,也成为在区域上较突出的构造形变。晚古生代—早中生代,由于西伯利亚板块的不断向南俯冲,引起内蒙古边缘陆壳褶皱隆起的不断加剧,当宽沟背斜的岩石塑性变形达到顶点时,超过了岩石的塑性极限,发生破裂,进而发育一系列近东西向的断层。当两大陆块碰撞时,在南北区域压应力作用下,宽沟大断层演化成逆断层,且在矿区范围内相继出现逆-平移断层和北东向、北西向共轭走滑断裂。
西伯利亚板块向南俯冲阶段,受南北方向压应力构造作用,矿区发育一系列轴向近东西向的褶皱和韧性剪切构造,并伴随近东西向陡倾劈理带。在两大陆块碰撞晚期,在南北区域压应力持续作用下,近东西向的张应力导致了矿区北东向正断层构造的形成。
3.3 构造控矿模式与找矿潜力
(1) 中元古代中期,随着白云鄂博裂谷系的形成,白云鄂博群在强烈拗陷中快速堆积,并伴随切割很深的同沉积断裂,沿断裂上升的白云石碳酸岩岩浆作用形成了主要的稀土-铌-铁矿床。反射地震剖面显示(图 5),东介勒格勒断裂和高位同生断裂均倾向南,可能暗示东介勒格勒矿段的白云石碳酸岩体倾向与主矿、东矿基本一致,均向南倾斜。基于稀土-铌-铁矿床与白云石碳酸岩具有密切的成因关系,这一发现可以为东介勒格勒矿段的下一步勘探工作部署提供依据。
(2) 古生代以来,华北板块与西伯利亚板块发生俯冲碰撞造山作用在矿区形成了一系列近东西向逆-平移断层、近东西向的褶皱构造,并伴随近东西向的韧性剪切构造,它们对先期形成的矿体进一步改造和破坏。
早阶段形成的近东西向褶皱构造,包括宽沟背斜和白云“向斜”。由于碳酸岩岩浆沿陡倾的正断层上升形成白云石碳酸岩并形成稀土-铌-铁矿体,近南北向的挤压褶皱对矿体的改造和破坏并不显著。
随着南北向挤压应力的进一步挤压,岩石塑性变形达到顶点时形成的近东西向逆-平移断层可能产生了一定规模的横向位移,对先期形成的矿体进一步破坏(图 6-a)。由于断层倾角大于矿体倾角,断层必然对深部矿体进行切割并破坏。
大量实地调查和勘探资料显示,东矿段15、16、17勘探线剖面(图版Ⅲ)上,白云岩与上盘板岩的接触界线发生突变可以作为断层上盘向上推移的标志,可用于推算该组断层的纵向断距。通过计算,15、16、17号勘探线白云石碳酸岩垂直推覆位移大于300 m,野外实测擦痕线理产状倾角取23°,根据近东西向断层位移推算示意图(图 6-b、c),近东西向逆-平移断层水平位移大于700 m。
(3) 古生代末期,受近东西向剪切分量应力作用,主矿、东矿南侧发育一期非贯穿性韧性剪切构造。受其影响,矿体在横向和纵向上均发生透镜体化,且在矿体和矿石尺度上都有清晰地显示(图 6-b、c,图版Ⅲ)。由于韧性剪切活动可以改变岩石组构特征,促使矿物、岩石细粒化和矿物晶格变形,增加元素的活性、扩散系数和扩散速度[57],可能与成矿有一定的成因关系。所以,该期构造变形对成矿的影响仍有待进一步研究,本文不做深入展开。
(4) 晚古生代末期—早中生代,随着南北区域挤压应力持续作用,近东西向的张应力导致矿区发育北东向正断层构造。这一组断层构造在地表露头上不明显,但在白云鄂博主矿、东矿区布格重力异常等值线图上有清晰地显示(图略),可能与碳酸岩岩石的性质有关。根据白云鄂博主矿、东矿体水平断面图上的矿体标志(图 6-d)和重力异常等值线图中的矿体异常标志推测,北东向构造对矿体的破坏性较小,可能导致东矿矿体向北东方向推移了约100 m,并相对主矿体向下滑移了一定的距离。
4. 结论
(1) 内蒙古白云鄂博矿区内构造活动演化具有多期性,中元古代—海西期至少发育4期构造活动,包括近东西向控岩断层(F1)、近东西向逆-平移断层(F2)、近东西向褶皱和韧性剪切带构造和北东向左行走滑正断层(F3)。
(2) 沿白云石碳酸岩与顶底板围岩界线分布的近东西向断层控制了白云石碳酸岩的产出和矿体的形成;白云石碳酸岩侵位后,近东西向逆-平移断层对矿体进行了第一次破坏,导致主矿、东矿南侧的深部矿体向东平移,钻孔WK14-01的深部矿体应为主矿深部的矿体平移所致;成矿期后发育一期近南北向的挤压变形事件对矿体进行了第二次破坏,导致矿区白云鄂博群紧闭褶皱的形成和矿体发生透镜体化;主矿、东矿之间的北东向左行走滑正断层对矿体进行了第三次破坏,导致主矿、东矿位置的错动。这些认识将对矿区深部及外围找矿工作具有重要的指导意义。
致谢: 对审稿专家提出的宝贵意见表示衷心感谢。感谢参与研究工作的团队成员。 -
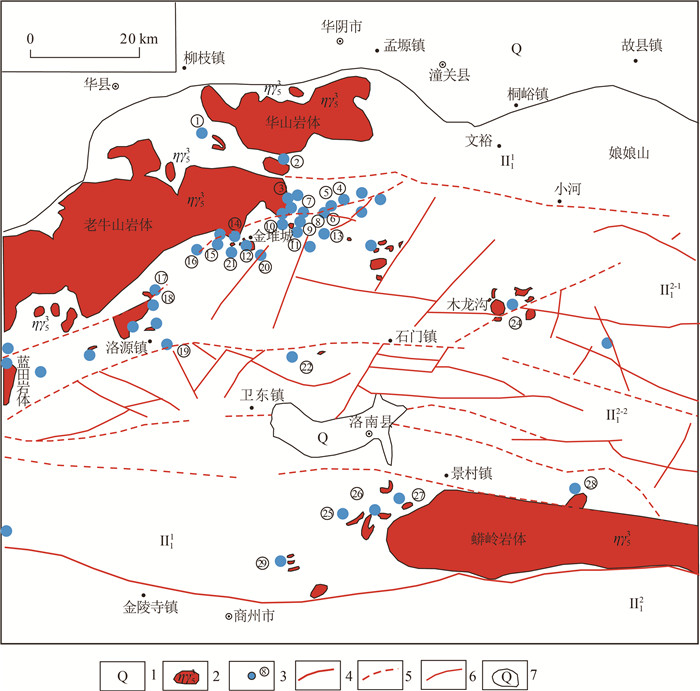
图 2 小秦岭矿集区西部钼矿床(点)分布图
1—第四系坡积物;2—燕山期岩体;3—矿床(点)位置及编号(①—麦糠窑矿床;②—西沟矿床;③—文公岭矿点;④—碌碡沟矿点;⑤—水草坪矿点;⑥—太子坪矿点;⑦—大石沟矿床;⑧—宋家沟矿床;⑨—石家湾矿床;⑩—桃园矿床;⑪—双庙矿床;⑫—金堆城矿床;⑬—二道河矿床;⑭—张家院矿点;⑮—东坪东沟脑矿点;⑯—八里坡矿床;⑰—短沟岔矿点;⑱—角落岔矿床;⑲—洛源周家沟矿床;⑳—西马路沟矿床;㉑—木子沟脑矿床;㉒—李家洼矿床;㉓—黑山周家沟矿点;㉔—木龙沟矿点;㉕—桃家坪矿床;㉖—火链沟矿床;㉗—寺沟矿床;㉘—南长沟矿点;㉙ —南台沟矿点);4—深大断裂带;5—推测断裂带;6—一般断层;7—地质界线;Ⅰ11—太华隆起;Ⅰ12—金堆城凹陷;Ⅰ12-1—金堆城凹陷北部区;Ⅰ12-2—金堆城凹陷南部区;Ⅱ11—纸房-永丰褶皱束;Ⅱ12—太白-商县褶皱束
Figure 2. Distribution of molybdunium deposits in the western Xiaoqinling ore-concentrated area
图 3 小秦岭矿集区西部化探综合异常示意图
Q—第四系;
Figure 3. Schematic map of geochemical anomalies in the western Xiaoqinling ore-concentrated area
图 5 小秦岭矿集区西部小岩体球粒陨石标准化稀土元素配分图(a)和原始地幔标准化微量元素蛛网图(b)
(标准化数据据参考文献[50])
Figure 5. Chondrite-normalized REE patterns(a)and primitive mantle- normalized trace element patterns(b)of small intrusives in the western Xiaoqinling ore-concentrated area
表 1 小秦岭矿集区西部小岩体元素地球化学特征
Table 1 Elements geochemical characteristics of small intrusives in the western Xiaoqinling ore-concentrated area
岩体 金堆城岩体 八里坡岩体 石家湾岩体 岩性 花岗斑岩[66] 钾长花岗斑岩[65] 细粒钾长花岗斑岩[65] 含脉钾长花岗斑岩[65] 粗粒钾长花岗岩[65] 花岗斑岩[66] 似斑状二长花岗岩[67] 钾长花岗岩[68] SiO2 72.89 74.06 73.71 73.1 73.16 74 73.2 74.41 78.14 74.22 72.87 69.98 70.72 69.92 73.76 73.11 73.64 71.62 70.80 71.11 69.87 71.02 71.95 73.04 70.52 TiO2 0.14 0.14 0.14 0.08 0.16 0.2 0.15 0.04 0.04 0.11 0.13 0.22 0.21 0.21 0.11 0.1 0.11 0.14 0.16 0.16 0.21 0.15 0.12 0.19 0.22 Al2O3 13.12 12.5 12.94 12.26 12.79 13 12.6 13.04 11.18 12.71 14.01 15.02 14.93 15.46 13.74 14.24 14.15 14.81 15.53 15.22 15.74 15.13 14.54 13.95 14.71 TFeO - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 2.1 1.99 1.62 1.97 2.3 2.33 2.65 2.36 1.86 - - Fe2O3 1.89 1.2 0.98 1.31 1 1 1.21 0.8 0.53 1.34 1.65 2.18 2.05 1.93 - - - - - - - - - 0.85 1.15 FeO - - - - - 0.8 0.79 - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 0.57 1.02 MnO 0.02 0.01 0.04 0.02 0.01 0.1 0.09 0.04 0.02 0.04 0.06 0.1 0.09 0.07 0.1 0.11 0.07 0.09 0.13 0.12 0.16 0.14 0.1 0.02 0.03 MgO 0.13 0.07 0.3 0.06 0.28 0.3 0.37 0.13 0.1 0.21 0.24 0.38 0.33 0.28 0.33 0.25 0.23 0.3 0.34 0.36 0.46 0.34 0.25 0.34 0.54 CaO 0.73 0.66 0.9 0.56 0.7 1 1.08 0.51 0.52 0.98 1.21 2.38 2.43 2.15 1.7 1.76 1.73 2.11 2.37 2.18 2.74 2.2 1.77 0.71 1.81 Na2O 1.49 1.36 1.53 0.54 1.18 2.2 1.63 0.78 1.19 1.23 3.75 4.16 4.26 4.41 3.36 3.43 3.44 3.67 3.97 3.7 3.72 3.97 3.58 3.15 3.42 K2O 6.97 7.93 7.18 9.87 8.46 6 6.61 8.77 7.7 7.58 5.09 3.94 3.76 4.15 4.31 4.41 4.43 4.1 3.98 4.24 3.85 4 4.51 5.36 5 P2O5 0.03 0.03 0.04 0.04 0.06 0 0.04 0.02 0.01 0.04 0.05 0.09 0.07 0.04 0.05 0.05 0.05 0.06 0.07 0.08 0.09 0.08 0.05 0.07 0.11 烧失量 1.85 1.29 1.71 1.28 1.2 1.5 2.08 1.11 0.68 - - 0.8 0.61 0.69 0.82 0.48 0.83 0.66 0.61 0.88 0.86 0.85 0.86 0.88 0.93 总计 99.26 99.25 99.47 99.12 99 100.1 99.85 99.65 100.11 98.46 99.06 99.25 99.46 99.31 99.76 100.06 99.85 101.27 102.97 102.93 104.04 102.98 101.72 99.13 99.46 K2O+ Na2O 8.46 9.29 8.71 10.41 9.64 8.2 8.24 9.55 8.89 8.81 8.84 8.1 8.02 8.56 7.67 7.84 7.87 7.77 7.95 7.94 7.57 7.97 8.09 8.51 8.42 Na2O /K2O 0.21 0.17 0.21 0.05 0.14 0.37 0.25 0.09 0.15 0.16 0.74 1.06 1.13 1.06 0.78 0.78 0.78 0.90 1.00 0.87 0.97 0.99 0.79 0.59 0.68 A/CNK 1.16 1.04 1.09 0.97 1.03 1.09 1.07 1.11 1 1.06 1.01 0.97 0.96 0.99 1.03 1.05 1.04 1.03 1.03 1.04 1.03 1.02 1.04 1.14 1.03 A/NK 1.31 1.16 1.26 1.06 1.15 1.29 1.28 1.21 1.09 1.24 1.2 1.35 1.35 1.32 1.35 1.37 1.35 1.41 1.43 1.43 1.53 1.39 1.35 1.27 1.33 La 21.50 12.00 18.20 10.30 16.40 27.00 25.90 9.08 12.21 29.69 27.46 31.10 30.00 35.20 8.25 10.82 8.20 16.04 20.25 17.57 26.47 18.41 12.49 38.30 39.30 Ce 36.20 19.30 27.10 14.90 27.70 53.00 55.60 19.20 25.78 55.08 52.54 58.00 56.28 62.60 14.90 16.46 13.73 27.76 35.52 31.56 50.86 32.56 21.76 56.00 61.80 Pr 4.47 2.66 3.59 2.15 3.38 5.30 5.30 2.39 2.95 5.69 5.30 6.32 6.15 7.05 1.93 2.33 1.87 3.43 4.31 3.87 5.62 3.94 2.75 6.71 7.20 Nd 16.40 10.00 13.20 8.52 13.10 19.00 18.40 10.90 10.86 20.18 18.89 21.52 21.02 23.46 8.73 10.07 8.26 14.94 18.46 16.92 24.33 16.93 11.97 22.20 24.30 Sm 3.34 2.10 2.39 1.57 2.39 4.00 3.98 3.98 2.44 4.14 3.71 3.39 3.32 3.52 1.57 1.72 1.56 2.49 2.98 2.89 4.03 2.87 2.11 3.50 3.87 Eu 0.47 0.33 0.54 0.39 0.58 2.50 2.38 0.47 0.46 0.66 0.66 1.00 1.05 1.08 0.42 0.44 0.41 0.68 0.80 0.77 0.99 0.78 0.58 0.66 0.78 Gd 3.18 1.81 2.45 1.52 2.06 5.10 5.05 3.74 2.37 2.99 3.10 2.65 2.67 2.69 1.89 1.91 1.73 2.75 3.30 3.14 4.46 3.18 2.36 2.55 2.60 Tb 0.50 0.30 0.38 0.25 0.33 0.50 0.71 0.64 0.40 0.48 0.52 0.33 0.34 0.32 0.19 0.19 0.19 0.26 0.30 0.29 0.44 0.29 0.22 0.45 0.45 Dy 2.90 1.71 2.36 1.46 1.71 4.50 4.52 3.54 2.49 2.43 2.74 1.74 1.77 1.64 1.21 1.21 1.22 1.59 1.78 1.75 2.79 1.77 1.36 2.08 2.30 Ho 0.58 0.36 0.46 0.28 0.34 0.80 0.78 0.74 0.52 0.48 0.60 0.33 0.33 0.30 0.21 0.21 0.22 0.27 0.30 0.29 0.48 0.30 0.24 0.38 0.41 Er 1.86 1.15 1.46 0.85 1.04 1.90 1.89 2.31 1.64 1.59 1.75 0.96 0.98 0.80 0.80 0.79 0.79 0.94 1.04 1.03 1.71 1.07 0.85 1.10 1.25 Tm 0.28 0.18 0.23 0.12 0.17 0.40 0.41 0.34 0.26 0.22 0.25 0.14 0.14 0.12 0.11 0.11 0.11 0.12 0.13 0.13 0.22 0.14 0.11 0.17 0.20 Yb 1.96 1.20 1.75 0.85 1.06 1.60 1.66 2.57 2.08 1.53 1.89 1.06 1.02 0.74 1.01 1.00 0.98 1.03 1.19 1.12 1.86 1.24 1.01 1.12 1.31 Lu 0.30 0.19 0.28 0.13 0.19 0.20 0.25 0.38 0.33 0.22 0.28 0.17 0.16 0.11 0.15 0.15 0.15 0.15 0.17 0.16 0.26 0.18 0.15 0.16 0.20 Y 17.90 10.70 12.80 7.74 9.36 13.00 13.80 - - - - 11.30 11.14 8.85 6.67 6.63 6.75 7.63 8.70 8.50 13.72 8.71 6.99 9.89 11.00 ΣREE 93.94 53.29 74.39 43.29 70.45 125.80 126.83 60.28 64.79 125.38 119.69 128.71 125.23 139.63 41.37 47.41 39.42 72.45 90.53 81.49 124.52 83.66 57.96 135.38 145.97 LREE /HREE 7.13 6.72 6.94 6.93 9.21 7.39 7.31 3.23 5.42 11.61 9.75 16.44 15.90 19.78 6.43 7.51 6.31 9.19 10.03 9.30 9.19 9.24 8.20 15.90 15.74 LaN/YbN 7.87 7.17 7.46 8.69 11.10 12.10 11.19 2.53 4.21 13.92 10.42 21.05 21.10 34.12 5.86 7.76 6.00 11.17 12.21 11.25 10.21 10.65 8.87 24.53 21.52 δEu 0.43 0.51 0.68 0.76 0.78 1.69 1.62 0.37 0.58 0.55 0.58 0.98 1.04 1.03 0.75 0.75 0.77 0.80 0.78 0.78 0.71 0.79 0.79 0.65 0.71 δCe 0.86 0.80 0.77 0.74 0.86 1.02 1.10 0.99 1.02 0.97 1.00 0.96 0.96 0.92 0.88 0.77 0.83 0.87 0.89 0.90 0.97 0.89 0.87 0.79 0.84 Li - - - - - 10 11.1 - - - - - - - 6.75 10.39 13.16 13.92 16.91 13.16 23.94 18.04 8.83 - - Be - - - - - 3.9 3.62 - - - - - - - 3.02 3.05 3.4 4.12 3.38 3.57 3.8 4.52 4.04 - - Sc - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 0.73 0.99 0.86 0.89 0.94 1.04 1.35 1.11 0.80 2.05 3.41 V - - - - - 9.8 13.2 - - - - - - - 10.71 9.62 6.69 12.46 12.41 13.51 14.99 13.13 10.7 19.9 27.5 Cr - - - - - 22 14 - - - - - - - 2.24 7.02 3.64 2.58 2.77 6.52 7.04 6.26 3.59 2.55 0.58 Co - - - - - 2.4 2.63 91.8 116 58.9 71.3 2.16 3.11 1.91 1.68 1.98 2.02 2.1 1.91 1.13 1.25 2.24 Ni - - - - - 8.4 6.82 - - - - - - - 0.72 1.58 0.37 0.36 0.12 0.24 0.12 0.1 0.09 - - Cu 23.9 17.4 16.8 21.9 25.6 21 19.2 26.5 14 25 12.9 21.85 13.62 11.91 21.54 11.08 13.61 4.12 4.44 5.65 8.04 6.31 4.80 4.72 4.61 Zn - - - - - 29 24.7 86.8 11 188 31.2 - - - 40.23 39.24 29.2 45.91 54.26 44.27 63.77 56.19 44.54 29.9 28.7 Mo 127 283 74.1 868 565 - - - - - - 111.28 110.42 210.43 - - - - - - - - - - - Ga - - - - - 20 19.9 22.3 17 20 21.7 - - - 66.52 80.22 62.64 120.8 125.1 129.7 133.3 120.6 105 - - Rb 308 358 333 466 385 278 304 - - - - 174.98 167.52 124.1 99.34 124.3 125.5 129.4 114.8 118.6 115.9 127.5 170.3 149 144 Sr 96.9 55.7 79.3 110 212 190 159 71.8 108.17 161.55 284.33 679.8 724.8 741.8 278.6 291.1 256.8 520.3 602.2 564.8 637.6 561.2 414.5 294 638 Zr 112 100 109 56.1 123 113 110 36.4 59.92 104.07 122.82 168.52 160.48 164.98 96.14 116.2 111.9 147.9 177.9 201.8 252.5 188.9 150.5 151 196 Nb 63.6 60 46.4 30 47.3 50 48.3 70.4 53.97 49.61 44.53 19.86 19.33 17.77 20.72 19.78 21.71 19.95 22.04 18.39 25.14 22.46 21.39 31.1 31.6 Cs - - - - - 2.4 2.46 2.46 15 2.94 2.46 - - - 1.58 1.45 2.36 4.04 2.56 3.42 4.14 3.44 2.25 2.66 2.12 Ba 686 411 603 926 1418 858 824 338 499.9 1309 1240 1422.6 1432.4 2166 991.5 1184 935.6 1798 1876 1957 2007 1749 1500 1540 2131 Hf 3.94 402 4.42 2.33 4.05 3.6 3.63 2.62 3.92 3.849 4.563 3.88 3.63 3.94 3.48 3.81 3.9 4.06 4.41 4.91 6.01 4.81 4.71 5.01 6.26 Ta 3.51 3.67 3.59 1.62 2.93 3.4 3.05 7.18 4.732 3.024 3.604 0.83 0.81 0.68 0.98 0.99 1.24 0.91 0.98 0.89 1.13 1.05 1.09 1.1 1.05 Pb - - - - - 41 40.6 78.4 39 49.7 41.6 - - - 108.5 50.81 39.78 40 43.9 46.65 44.95 46.09 54.05 29.7 32.8 Th 22 15.1 17.7 9.45 12.4 23 21.7 19.3 17.545 21.161 21.925 6.55 5.66 6.09 3.59 4.06 5.16 4.37 5.33 4.69 6.31 5.06 4.14 13.7 15.5 U 13.5 10.9 15.2 9.43 5.72 14 15.3 25.1 25.57 18.93 14.45 7.1 3.85 4.72 6.16 5.52 17.13 3.3 3.36 3.27 4.82 5.55 7.77 6.51 6.45 注:参考文献[67]为与本文联合工作数据。主量元素含量单位为%,微量和稀土元素含量单位为10-6 表 2 小秦岭矿集区西部钼金多金属矿床综合找矿模型
Table 2 Comprehensive exploration model for Mo-Au deposits in western Xiaoqinling ore-concentrated area

斑岩型钼矿 构造蚀变岩型金矿 地质模型 构造位置 近NNE向和NWW向断裂的交会部位 NE向次级断裂与EW向构造交会部位 成矿时代 燕山期(140~135 Ma) 印支期—燕山期(220~130 Ma) 容矿岩石 花岗斑岩、花岗闪长斑岩、石英二长斑岩、安山(玢)岩 黑云斜长片麻岩 赋矿位置 斑岩体内、外接触带或围岩中 含金构造破碎蚀变带及混合岩化发育区 容矿构造 侵入斑岩体和接触带 NE向构造破碎带 矿物特征 矿石矿物主要为黄铁矿、辉钼矿、白钨矿、磁铁矿、磁黄铁矿、黄铜矿和闪锌矿,脉石矿物主要为石英、钾长石、斜长石、钙铁榴石、富铁透闪石、白云石、角闪石、金云母、萤石等 矿石矿物以黄铁矿为主,脉石矿物主要有钾长石、石英、斜长石、绿泥石、绢云母等 矿石结构与构造 片状、放射状、自形-半自形粒状、镶嵌状等结构;浸染状、网脉状、细脉浸染状、块状、条带状构造 他形-半自形/自形晶粒状结构、压碎结构;浸染状、角砾状构造 蚀变及矿化类型 钾化、硅化、碳酸盐-沸石化、金云母-阳起石化、透闪石化、青磐岩化等,具一定的分带性;钾化带多发育于斑岩体、角岩中,伴随有辉钼矿化及黄铁矿化;硅化带分布范围广,在岩体顶部和边缘最强烈,常形成硅化外壳,与钼矿化关系密切 钾化、硅化、黄铁矿化、褐铁矿化、绢云母化为主,绿泥石化、碳酸盐化次之。金矿与前者关系密切 物探模型 重、磁异常 重力低或呈相对重力低;弱磁异常,岩体内异常低缓,接触带附近磁异常较强、梯度陡。NE向、NW向交汇排列的航磁异常反映岩体的空间展布形态 重力高与重力低过渡的梯度带或梯度带两侧的等值线转弯处;正负磁异常梯度带旁侧的低正磁异常,航磁化极后的南北梯度带附近 激电异常 低电阻率、高充电率(10%~18%)异常 低电阻率、高充电率异常 化探模型 1:5万分散流异常 Au、Ag、Mo、Pb、Bi、Zn多元素组合异常辉钼矿、白钨矿等自然重砂异常 面积>1 km2的Au、Ag、Pb、Hg(Cu)多元素组合异常 1:1万次生晕异常 以Mo、Pb为主,或伴有Au、Ag组合异常 以Au、Ag、Pb、Hg为主,或伴有Cu、Mo的组合异常,Au>5×10-9 原生晕异常 Mo≥100×10-6~200×10-6,指示钼矿化体;Mo≥300×10-6,指示钼矿体 Au < 10×10-9,指示金矿化异常体,Au>10×10-9,指示金矿化体 -
王相, 唐荣扬, 李实, 等. 秦岭造山与金属成矿[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 1996: 123-146. 黎世美, 瞿伦全, 苏振邦, 等. 小秦岭金矿地质和成矿预测[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1996: 1-244. 王瑞廷, 袁海潮, 孟德明, 等. 小秦岭地区金钼多金属矿成矿特征与找矿预测[J]. 地球科学与环境学报, 2014, 36(1): 19-31. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XAGX201401004.htm Mao J W, Goldfarb R J, Zhang Z, et al. Gold deposits in the Xiaoqinling-Xiong'ershan Region, Qinling Mountains, Central China[J]. Minerialium Deposita, 2002, 37(3): 306-325. http://www.springerlink.com/content/8lpceuu5kefg9ae5/
毛景文, 李晓峰, 张荣华, 等. 深部流体成矿系统[M]. 北京: 中国大地出版社, 2005: 121-175. 毛景文, 谢桂青, 张作衡, 等. 中国北方中生代大规模成矿作用的期次及其地球动力学背景[J]. 岩石学报, 2005, 21(1): 169-188. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200501018.htm 毛景文, 叶会寿, 王瑞廷, 等. 东秦岭中生代钼铅锌银多金属矿床模型及其找矿评价[J]. 地质通报, 2009, 28(1): 72-79. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2009.01.009 Mao J W, Xie G Q, Pirajno F, et al. Late Jurassic-Early Cretaceous Granitoid Magmatism in Eastern Qinling, Central-Eastern China: SHRIMP Zircon U-Pb Ages and Tectonic Implications[J]. Australian Journal of Earth Sciences, 2010, 57: 51-78. doi: 10.1080/08120090903416203
毛景文, 周振华, 丰成友, 等. 初论中国三叠纪大规模成矿作用及其动力学背景[J]. 中国地质, 2012, 39(6): 1437-1471. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2012.06.001 毛景文, 张作衡, 裴荣富, 等. 中国矿床模型概论[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2012: 1-560. 薛良伟, 石铨曾, 尉向东, 等. 小秦岭石英脉型金矿的反转成矿机制[J]. 科学通报, 1998, 49(2): 203-206. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.1998.02.022 尚瑞均, 严阵. 秦巴花岗岩[M]. 武汉: 中国地质大学出版社, 1988: 35-116. 吴根耀. 燕山运动和中国大陆晚中生代的活化[J]. 地质科学, 2002, 37(4): 453-461. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0563-5020.2002.04.009 白万成, 卿敏. 小秦岭金矿田构造演化与金矿成矿作用[J]. 黄金地质, 2000, 6(2): 1-8. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJDZ200002000.htm 冯建之, 岳铮生, 肖荣阁, 等. 小秦岭深部金矿成矿规律与成矿预测[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2009: 1-266. 姚书振, 丁振举, 周宗桂, 等. 秦岭造山带金属成矿系统[J]. 地球科学, 2002, 27(5): 599-604. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-2383.2002.05.020 张正伟, 朱炳泉, 常向阳, 等. 东秦岭钼矿带成岩成矿背景及时空统一性[J]. 高校地质学报, 2001, 7(3): 307-315. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2001.03.007 谢才富, 熊成云, 胡宁, 等. 东秦岭造山带"两阶段双带"区域成矿模式[J]. 地质科技情报, 2004, 23(2): 77-81. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7849.2004.02.012 张本仁, 骆庭川, 高山, 等. 秦巴岩石圈构造及成矿规律地球化学研究[M]. 武汉: 中国地质大学出版社, 1994: 257-311. 栾世伟, 陈尚迪. 小秦岭金矿主要控矿因素及成矿模式[J]. 地质找矿论丛, 1990, 5(4): 1-14. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZZK199004000.htm 王靖华, 张复新, 于在平, 等. 秦岭金属矿床成矿系列与大陆造山带构造动力学背景[J]. 中国地质, 2002, 29(2): 192-196. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2002.02.016 陈衍景, 富士谷. 豫西金矿成矿规律[M]. 北京: 地震出版社, 1992: 1-209. 张进江, 郑亚东, 刘树文. 小秦岭金矿田中生代构造演化与矿床形成[J]. 地质科学, 2003, 38(1): 74-84. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKX200301009.htm 张正伟, 张中山, 董有, 等. 东秦岭钼矿床及其深部构造约束[J]. 矿物学报, 2007, 27(3/4): 372-378. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-KWXB2007Z1019.htm 朱赖民, 张国伟, 李犇, 等. 与秦岭造山有关的几个关键成矿事件及其矿床实例[J]. 西北大学学报(自然科学版), 2009, 39(3): 381-391. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBDZ200903007.htm 胡受奚, 林潜龙. 华北与华南古板块拼合带地质与成矿[M]. 南京: 南京大学出版社, 1988: 236-442. 胡正国, 钱壮志. 小秦岭地质构造新认识[J]. 地质论评, 1994, 40(4): 289-295. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.1994.04.001 陈毓川, 朱裕生, 孙文珂, 等. 中国矿床成矿模式[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1993: 1-102. 黄凡, 陈毓川, 王登红, 等. 中国钼矿主要矿集区及其资源潜力探讨[J]. 中国地质, 2011, 38(5): 1111-1134. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2011.05.001 王成辉, 王登红, 黄凡, 等. 中国金矿集区及其资源潜力探讨[J]. 中国地质, 2012, 39(5): 1125-1142. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2012.05.002 燕建设, 牛树银, 冯建之, 等. 小秦岭地区构造控矿作用分析[J]. 中国地质, 2013, 40(2): 538-548. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2013.02.018 胡海珠, 李诺, 邓小华, 等. 秦岭地区印支期钼矿化特征及找矿前景[J]. 中国地质, 2013, 40(2): 549-565. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2013.02.019 袁海潮, 焦建刚, 李小东. 东秦岭八里坡钼矿床地球化学特征与深部成矿预测[J]. 地质与勘探, 2009, 45(4): 35-41. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT200904005.htm 冯延清, 钱壮志, 张江江, 等. 东秦岭燕山期中酸性小岩体成矿规律[J]. 地球科学与环境学报, 2014, 36(1): 128-140. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XAGX201401013.htm 张宗清, 张国伟, 刘敦一, 等. 秦岭造山带蛇绿岩、花岗岩和碎屑沉积岩同位素年代学和地球化学[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2006: 227-232. 张复新, 杜孝华, 王伟涛, 等. 秦岭造山带及邻区中生代地质演化与成矿作用响应[J]. 地质科学, 2004, 39(4): 486-495. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0563-5020.2004.04.004 陈衍景, 陈华勇, 刘玉林, 等. 碰撞造山过程内生矿床成矿作用的研究历史和进展[J]. 科学通报, 1999, 44(16): 1681-1689. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.1999.16.001 卢欣祥, 于在平, 冯有利, 等. 东秦岭深源浅成型花岗岩的成矿作用及地质构造背景[J]. 矿床地质, 2002, 21(2): 168-178. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2002.02.009 石铨曾, 秦国群, 周旭, 等. 豫西后造山阶段的剥离伸展构造与金矿化[J]. 河南地质, 1993, 11(1): 27-36. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HNDD199301006.htm 王义天, 毛景文. 碰撞造山作用期后伸展体制下的成矿作用——以小秦岭金矿集中区为例[J]. 地质通报, 2002, 21(8/9): 562-566. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=200208128&flag=1 范宏瑞, 谢奕汉, 赵瑞, 等. 豫陕小秦岭脉状金矿床三期流体复式运移成矿作用[J]. 岩石学报, 2003, 19(2): 260-266. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200302006.htm 黄典豪, 吴澄宇, 杜安道, 等. 东秦岭地区钼矿床的铼-锇年龄及其地质意义[J]. 矿床地质, 1994, 13(3): 221-230. http://www.cqvip.com/Main/Detail.aspx?id=1418820 Stein H J, Markey R J, Morgan J W, et al. Highly precise andAccurate Re-Os Ages for Molybdenite from the East Qinling Molybdenum Belt, Shannxi Province China[J]. Economic Geology, 1997, 92: 827-835. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.92.7-8.827
王义天, 毛景文, 卢欣祥, 等. 河南小秦岭金矿区Q875脉中深部矿化蚀变岩的40Ar-39Ar年龄及其意义[J]. 科学通报, 2002, 47(18): 1427-1431. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2002.18.015 齐秋菊, 王晓霞, 柯昌辉, 等. 华北地块南缘老牛山杂岩体时代、成因及地质意义——锆石年龄、Hf同位素和地球化学新证据[J]. 岩石学报, 2012, 28(1): 279-301. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201201023.htm 王义天, 叶会寿, 叶安旺, 等. 小秦岭文峪和娘娘山花岗岩体锆石SHRIMP U-Pb年龄及其意义[J]. 地质科学, 2010, 45(1): 167-180. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0563-5020.2010.01.015 卢欣祥, 尉向东, 董有, 等. 小秦岭-熊耳山地区金矿时代[J]. 黄金地质, 1999, 5(1): 12-17. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJDZ901.002.htm 焦建刚, 袁海潮, 何克, 等. 陕西华县八里坡钼矿床锆U-Pb和辉钼矿Re-Os年龄及其地质意义[J]. 地质学报, 2009, 83(8): 1159-1166. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2009.08.014 朱赖民, 张国伟, 郭波, 等. 东秦岭金堆城大型斑岩钼矿床LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年及成矿动力学背景[J]. 地质学报, 2008, 82(2): 203-220. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE200802006.htm Sun S S, McDonough W F. Chemical and Isotopic Systematics of Oceanic Basalts: Implications for Mantle Composition and Processes[C]//Saunders A D. Magmatism in the Oceanic Basins. Special Publication of Geological Society of London, 1989, 42: 313-346.
栾世伟, 曹殿春, 方耀奎, 等. 小秦岭金矿床地球化学[J]. 矿物岩石, 1985, 5(2): 2-7. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWYS198502000.htm 陈衍景, 富士谷, 陈泽铭, 等. 论豫西金矿成矿模式和找矿方向[J]. 地质科技情报, 1991, 10(4): 63-67. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ199104020.htm 王志光, 崔亳, 徐孟罗, 等. 华北地块南缘地质构造演化与成矿[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 1997: 1-255. 陈衍景, 郭光军, 李欣. 华北克拉通花岗绿岩地体中中生代金矿床的成矿地球动力学背景[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 1998, 28(1): 35-40. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK199801006.htm 张国伟, 张本仁, 袁学诚, 等. 秦岭造山带与大陆动力学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2001: 117-159. 范宏瑞, 谢奕汉, 赵瑞, 等. 小秦岭含金石英脉复式成因的流体包裹体证据[J]. 科学通报, 2000, 45(5): 537-541. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2000.05.018 卢欣祥, 尉向东, 于在平, 等. 小秦岭-熊耳山地区金矿的成矿流体特征[J]. 矿床地质, 2003, 22(4): 377-385. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2003.04.006 王义天, 毛景文, 叶安旺, 等. 小秦岭地区中深部含金石英脉的同位素地球化学特征及其意义[J]. 矿床地质, 2005, 24(3): 270-279. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2005.03.006 李厚民, 叶会寿, 毛景文, 等. 小秦岭金(钼)矿床辉钼矿铼-锇定年及其地质意义[J]. 矿床地质, 2007, 26(4): 417-424. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2007.04.005 李诺, 孙亚莉, 李晶, 等. 小秦岭大湖金钼矿床辉钼矿铼锇同位素年龄及印支期成矿事件[J]. 岩石学报, 2008, 24(4): 810-816. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200804021.htm 卢欣祥, 罗照华, 黄凡, 等. 秦岭-大别山地区钼矿类型与矿化组合特征[J]. 中国地质, 2011, 38(6): 1518-1535. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2011.06.012 高昕宇, 赵太平, 高剑峰, 等. 华北陆块南缘小秦岭地区早白垩世埃达克质花岗岩的LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄、Hf同位素和元素地球化学特征[J]. 地球化学, 2012, 41(4): 303-325. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0379-1726.2012.04.004 袁海潮, 王瑞廷, 焦建刚, 等. 东秦岭华县西沟钼矿床Re-Os同位素年龄及其地质意义[J]. 地球科学与环境学报, 2014, 36(1): 120-127. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XAGX201401012.htm 王京彬, 邹滔, 王玉往, 等. 中国钼多金属矿床的组合类型、成矿作用和成矿谱系[J]. 矿床地质, 2014, 33(3): 447-470. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2014.03.001 焦建刚, 钱壮志, 王勇茗, 等. 华县西沟地区花岗岩体地球化学及成矿潜力[J]. 地质找矿论丛, 2007, 22(4): 270-276. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1412.2007.04.006 李洪英, 毛景文, 王晓霞, 等. 陕西金堆城钼矿区花岗岩Sr、Nd、Pb同位素特征及其地质意义[J]. 中国地质, 2011, 38(6): 1536-1550. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2011.06.013 焦建刚, 袁海潮, 刘瑞平, 等. 陕西华县八里坡钼矿床岩石地球化学特征及找矿意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2010, 26(12): 3538-3548. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201012008.htm 赵海杰, 毛景文, 叶会寿, 等. 陕西洛南县石家湾钼矿相关花岗斑岩的年代学及岩石成因: 锆石U-Pb年龄及Hf同位素制约[J]. 矿床地质, 2010, 29(1): 143-157. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2010.01.013 范永香, 阳正熙. 成矿规律与成矿预测[M]. 徐州: 中国矿业大学出版社, 2003: 108-186. 施俊法, 唐金荣, 周平, 等. 世界找矿模型与矿产勘查[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2010: 1-72. 裴荣富. 中国矿床模式[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1995: 242-279. 阳正熙. 矿产资源勘查学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2006: 1-178. 方维萱, 李亚林, 黄转莹. 小秦岭地区金矿床成矿构造地球化学动力学研究[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2000, 24(2): 155-162. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1552.2000.02.008 方维萱. 小秦岭含金石英脉矿物地球化学研究[J]. 地质与勘探, 1996, 32(3): 40-45. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT603.007.htm 方维萱. 陕西小秦岭地区断裂构造地球化学特征[J]. 地质与勘探, 1990, 26(12): 40-43. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT199012009.htm 西北有色地质勘查局712总队. 陕西省洛南县葫芦沟金矿地质详查报告. 1992: 1-89. 西北有色地质勘查局712总队. 陕西省华县西沟钼矿地质普查报告. 2003: 1-97.




 下载:
下载: