Application of geometric precision correction based on high-resolution Remote Sensing Image in 1:50000 geological mapping
-
摘要:
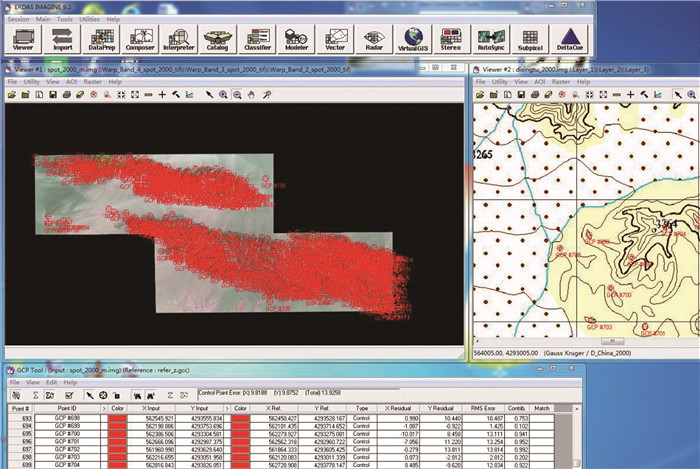
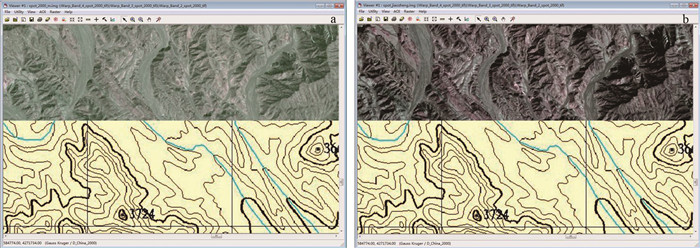
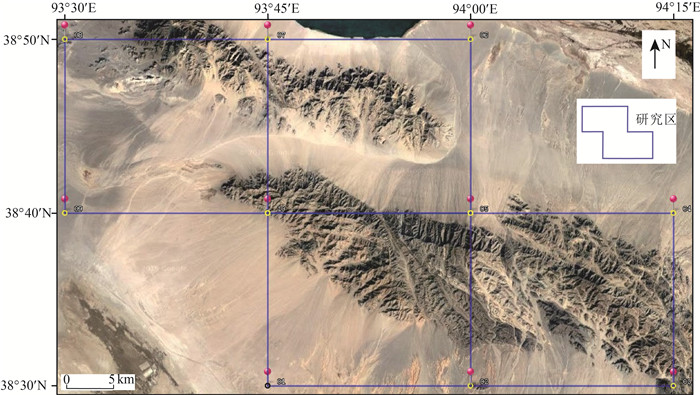
高山峡谷区海拔高、切割深,穿越条件极差,借助高分辨率遥感图像开展1:5万区域地质填图工作具有非常重要的意义。然而市场购置的遥感图像产品与实地位置信息和地形图等工作底图不匹配,其几何精度严重制约地质填图野外调查工作。为解决这一现实问题,采用高分辨率遥感图像SPOT7,以青藏高原柴达木盆地北缘赛什腾山为例开展研究,提出一套高分辨率遥感图像几何精校正技术方法。该方法在高分辨率遥感图像融合配准的基础上,创新半自动化人机交互式地面控制点选取方法,以及典型特征控制点海量选取、空间均匀分布等技术,通过对校正后遥感图像几何精度的反复检查提升,实现了高分辨率遥感图像的几何精校正。该方法校正后的遥感图像充分发挥了遥感技术的先导作用,极大地提高了野外地质填图的工作效率,可为地形复杂地区高分辨率遥感图像几何精校正提供技术参考。
Abstract:The high resolution remote sensing images can play an important role in the 1:50000 geological mapping in the alpine-gorge area with high altitude, deep cutting and poor crossing conditions.However, the remote sensing image products provided by the current market cannot match the working base maps such as field position information and topographic maps, and their geometric accuracy seriously restricts the field investigation of geological mapping.In order to solve this practical problem, a set of geometric precision correction techniques for high resolution remote sensing images is proposed by using high resolution remote sensing image SPOT7 and exemplifying Saishiteng Mountain in the northern margin of Qaidam Basin in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau as an example.Based on the fusion registration of high-resolution remote sensing images, this method innovates the semi-automatic man-machine interactive ground control point selection method, as well as the techniques of mass selection and spatial uniform distribution of typical feature control points.Through repeatedly checking and improving the geometric accuracy of corrected remote sensing images, the geometric precision correction of high-resolution remote sensing images is realized.The corrected remote sensing images give full play to the leading role of remote sensing technology, greatly improve the efficiency of field geological mapping, and can provide technical reference for geometric precision correction of high resolution remote sensing images in complex terrain areas.
-
-
表 1 研究区野外典型露头点坐标
Table 1 Coordinates of the typical outcrops in the study area
点号 X Y 典型露头 SH01 E93°48′33.8652" N38°36′34.488" 灰绿色中细粒辉长-闪长岩脉宏观特征 SH02 E93°53′16.0152" N38°39′11.898" 灰色中粗粒片麻状石英闪长岩及其中发育的浅肉红色中细粒正长花岗岩脉 SH03 E93°55′22.6344" N38°36′15.6888" 中粗粒钾化花岗岩脉,晚期的细粒辉长岩侵入其中 SH04 E93°55′44.436" N38°34′57.36" 灰白色花岗细晶岩脉宏观特征 SH05 E93°57′22.1436" N38°36′54.7056" 灰白色细晶花岗岩脉特征 SH06 E93°57′40.8024" N38°35′5.928" 灰黑色石英片岩与大理岩接触部位 SH07 E93°58′30.2484" N38°35′21.1884" 黄色云母片岩夹灰绿色绿泥石英片岩 SH08 E93°59′43.8432" N38°38′34.5444" 灰黑色中粒辉长岩及其中发育的大理岩透镜体 SH09 E93°59′40.1172" N38°32′21.3036" 灰褐色黑云斜长片麻岩中的浅色脉体,发育揉流褶皱 SH10 E93°59′53.4876" N38°35′55.5252" 灰绿色中细粒闪长岩宏观(硅化、褐铁矿化强烈) -
张进, 曲军峰, 张庆龙, 等. 基岩区构造地质填图方法思考、实践、探索[J]. 地质通报, 2018, 37(2/3): 192-221. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=2018020302&flag=1 黄理善, 李学彪, 荆林海, 等. 基于遥感技术的高寒山区矿产资源远景区快速圈定与综合评价技术集成[J]. 中国地质, 2020-02-10, 网络首发论文. https:kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.1167.P.20200210.1631.002.html. 李娜, 董新丰, 甘甫平, 等. 高光谱遥感技术在基岩区区域地质调查填图中的应用[J]. 地质通报, 2021, 40(1): 13-21. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20210102&flag=1 李永胜, 张生辉, 张彤, 等. 1: 50000矿产地质图编制与数据库建设要求[J]. 中国地质, 2020, 47(S2): 1-15. doi: 10.12029/gc2020Z201 陈圆圆, 候德华, 潘志龙, 等. 典型地区基础地质图智能编图实践——以北山地区1: 25万甜水井幅为例[J]. 地质通报, 2021-01-21, 网络首发论文. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.4648.P.20210121.1054.004.html. 黄辉, 路彥明, 李仰春, 等. 基于多元知识和编图模型的智能地质编图技术及其应用[J]. 地质通报, 2021-01-20, 网络首发论文. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.4648.P.20210120.1056.004.html. 辜平阳, 陈瑞明, 查显峰, 等. 高山峡谷区1: 50000地质填图技术方法探索与实践——以新疆乌什北山为例[J]. 地质力学学报, 2016, 22(4): 837-855. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2016.04.004 张婷, 刘军, 骆慧琴. 1: 1万DEM的生成及SPOT-5卫星数据正射校正[J]. 遥感技术与应用, 2004, 19(5): 420-423. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-0323.2004.05.025 陈静, 袁超, 陈雪洋, 等. DEM对山区高分辨率影像正射校正精度的影响[J]. 地理空间信息, 2014, 12(1): 128-131. doi: 10.11709/j.issn.1672-4623.2014.01.044 屈为刚. ENVI软件制作SPOT5遥感正射影像图方法初探[J]. 山西建筑, 2014, 40(21): 223-225. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JZSX201421120.htm 蓝晓丹, 李春干, 杜海波. 不同地面控制点采集方法对SPOT5图像几何精校正精度的影响[J]. 中南林业调查规划, 2009, 28(3): 31-35. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZLDF200903010.htm 高万里, 王宗秀, 李磊磊, 等. 柴达木盆地北缘小赛什腾山二叠纪花岗岩的发现及其构造意义[J]. 地质力学学报, 2019, 93(4): 816-829. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201904005.htm 和政军, 许志琴, 杨经绥, 等. 柴达木盆地北缘小赛什腾山晚古生代放射虫的发现及其意义[J]. 地质通报, 2002, 21(3): 156-157. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20020349&flag=1 杨亚莉, 赵宁, 成晓倩. 基于FLAASH模型的SPOT6卫星影像大气校正及评价[J]. 现代测绘, 2015, 38(2): 3-9. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSCH201502001.htm 田淑芳, 詹骞. 遥感地质学[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2013. 高晖. 不同精度控制点对遥感图像几何校正的影响[D]. 中国地质大学硕士学位论文, 2008. 钟婷, 杨敏华. 高山区遥感影象与地形数据几何配准试验研究[J]. 内蒙古林学院学报(自然科学版), 1999, 21(1): 76-81. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NMGL901.016.htm 杨国东, 赵强, 张旭晴, 等. 基于SPOT6卫星遥感数据无控制点正射校正[J]. 测绘与空间地理信息, 2018, 41(7): 1-3. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DBCH201807001.htm



 下载:
下载: