The tectonic setting of the Early-Middle Triassic volcanic-sedimentary succession in Funing-Napo area, the south margin of Nanpanjiang Basin, South China
-
摘要:
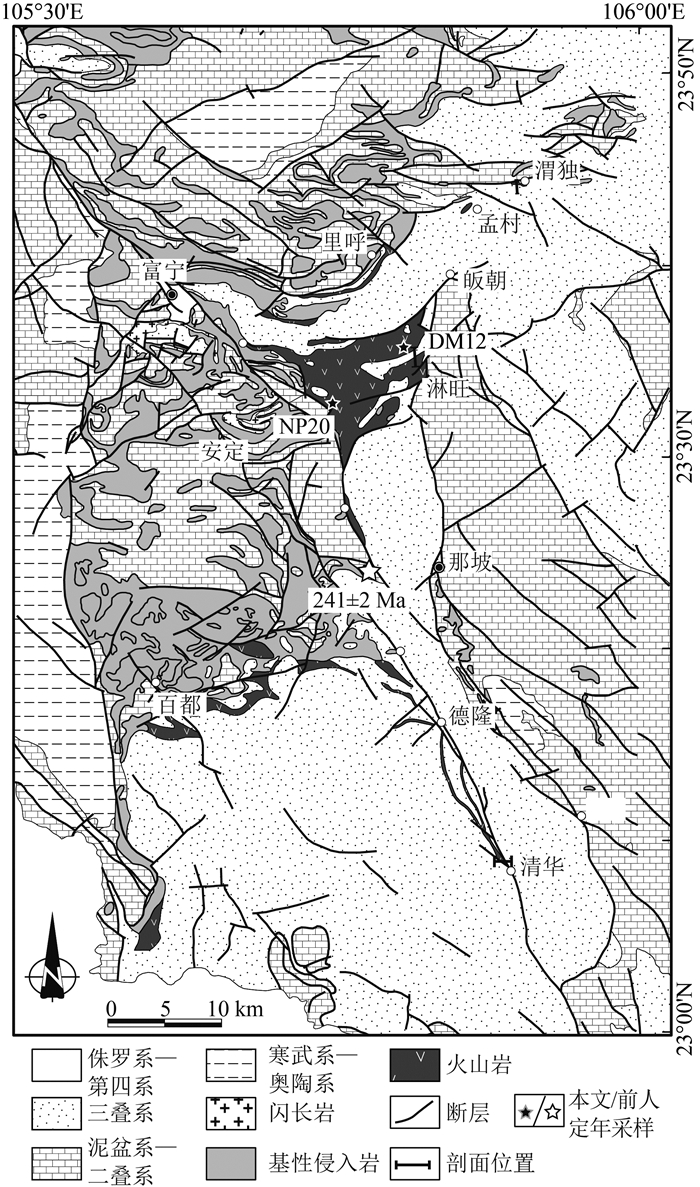
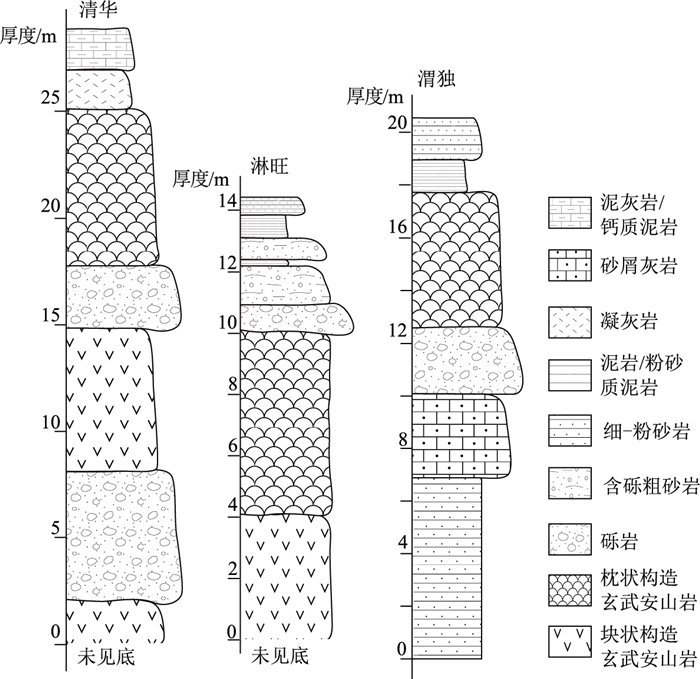
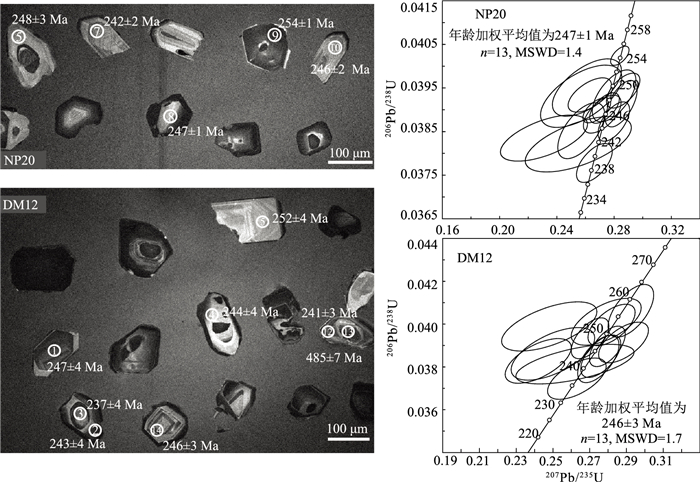
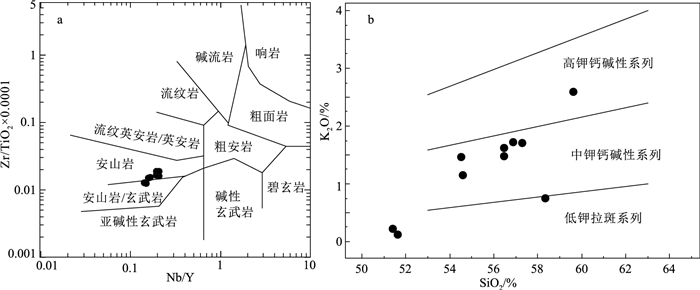
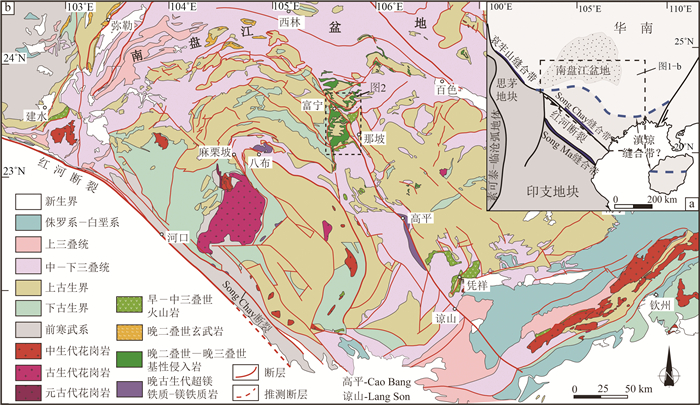
南盘江盆地南缘发育大量早—中三叠世岩浆岩和巨厚三叠系,为研究沿中越边界一带是否发生洋盆俯冲消亡过程提供了重要的岩浆-沉积证据。选取中越边界地区出露面积最大的富宁—那坡地区早—中三叠世火山岩及相关沉积作为研究对象,通过系统的地质填图和剖面测量,查明这套火山-沉积组合具有下部玄武安山岩,上覆碳酸盐岩质砾岩、含砾粗砂岩和钙质砂岩的沉积序列,与岛弧环境火山-沉积序列相似。玄武安山岩SHRIMP锆石U-Pb定年结果为247±1 Ma和246±3 Ma,与野外产于中三叠统碎屑岩之下的地质事实相符。结合前人研究成果,确定这套火山岩形成于早—中三叠世(247~242 Ma)。全岩地球化学分析结果显示,玄武安山岩富集大离子亲石元素(LILEs,Rb、Th和U)和轻稀土元素(LREE),其具有明显的Nb、Ta和Ti负异常。火山-沉积序列和火山岩地球化学特征表明,富宁—那坡地区早—中三叠世火山-沉积组合形成于与俯冲相关的弧环境。中越边界地区早—中三叠世弧火山岩与蛇绿混杂岩带的时空展布特征表明,该地区晚古生代洋盆发生了向北的俯冲消减。
Abstract:The Late Paleozoic to Early Mesozoic tectonic evolution process along the Sino-Vietnam border, particularly the subduction polarity of the Late Paleozoic ocean basin, is still controversial.Massive Early—Middle Triassic magmatic rocks and thick Triassic siliciclastic system occurred in the south margin of Nanpanjiang Basin provide important magmatic and sedimentary evidences for settling dispute.The Funing-Napo Triassic volcanic rocks, as the largest magmatic outcrop, are the ideal object for studying the tectonic evolution along the Sino-Vietnam border.The systematic profile survey and geological mapping indicates that the volcanic-sedimentary succession that consists of lower basaltic andesites overlain by carbonate conglomerates, pebbly sandstones and calcareous sandstones, which is similar to the volcanic-sedimentary sequence in island arc setting.Zircon SHRIMP U-Pb dating results of basaltic andesites are 247±1 Ma and 246±3 Ma, which are consist with field occurrence that basaltic andesite is overlain by Middle Triassic clastic rocsk.Combined with previous results, it is determined that the volcanic rocks were formed at 247~242 Ma.The geochemical analysis shows that basaltic andesites are enriched in LILEs (Rb, Th and U) and LREE, with a remarkable negative Nb-Ta and Ti anomalies.Both the geochemical characteristics of basaltic andesites and the volcanic-sedimentary sequence suggest that the Early—Middle Triassic volcanic-sedimentary succession was formed in a subduction-related arc setting.The spatial and temporal distribution characteristics of Early-Middle Triassic volcanic arc and ophiolitic mélange, implies that a north-dipping subduction occurred along Sino-Vietnam border.
-
Keywords:
- basaltic andesite /
- Island arc /
- Triassic /
- Nanpanjiang Basin /
- South China
-
区域地质调查和填图是地质工作的基础,也是衡量一个国家基础地质调查和研究程度及水平的重要指标,具有重要的战略意义。中国地质调查局高度重视基础地质调查与填图方式、方法的改革,树立“地质填图的过程就是科学研究的过程”的理念,确定“需求决定工作部署”、“问题决定调查方式”的工作思路,提升解决制约重大资源环境的基础地质问题和地球系统科学问题的能力。在中国地质调查局总工室和基础部的协调、领导下,由中国地质科学院地质研究所、地质力学所联合地调局六大区域地质调查中心开展了国际分幅和非国际分幅的中大比例尺专题试点填图,取得了重要进展。这是中国第一次较系统地构建填图方法体系。2019年11月6—7日,中国地质调查局召开了第三次全国区域地质调查工作会议。同时,成立了全国区域地质调查专家委员会,并组织了全国区调填图方法研讨会,来自全国地质行业近100人参加了培训和研讨,有30人在会议上交流发言,展现了区调改革在技术方法上的创新及取得的一批新进展、新发现,收效良好。
本专辑是本次会议成果的一次体现。本专辑共收录15篇论文,内容涉及短周期密集台阵方法在专题填图中的运用、遥感技术的使用等,以及地层、岩浆岩(侵入岩和火山岩)、变质岩、蛇绿混杂岩、构造、古生物、矿床等基础学科填图成果;还有论文,包括岩溶地区填图方法和地貌演变、造山带构造变形、侵入岩、蛇绿混杂岩、年轻变质事件及热泉的填图成果介绍,将在下一辑发表。这些论文集中展示了填图的成果。
(1)地球物理方法在填图中的运用。新填图方法和理念的运用是现代填图的重要内容,卢占武等介绍了利用短周期密集台阵进行近地表结构调查的应用实例,提出了该技术在专题地质填图中的应用前景,丰富和完善了专题填图的技术方法体系。李娜等介绍了高光谱遥感技术在中国西部基岩区填图中的应用,高光谱遥感数据对不同岩性段和岩相带、细小构造等区分能力突出,提高了地质调查填图的效率和质量。
(2)蛇绿混杂岩填图。蛇绿混杂岩的填图历经数十年的探索,也是造山带研究的基础数据来源,王国强等系统介绍了近十余年来北山造山带关键地段1:5万区域地质调查和综合研究成果,突出了造山带蛇绿混杂岩带填图方法在北山地区的实践和应用。付长垒等在大比例尺填图的基础上,在拉脊山识别出连续的洋岛海山火山-沉积组合序列,为造山带古洋盆构造演化研究提供了新思路。
(3)侵入岩区填图。侵入岩是造山带的重要组成部分,对它们的刻画和研究一直是造山带研究的基础性工作。苑新晨等对滇西澜沧江地区南段复式岩基进行研究,确定其是古特提斯封闭及保山-思茅地块碰撞的响应。卢鹏等在前期开展同位素填图的基础上,在东准噶尔乌伦古河地区识别出一套晚古生代富碱细晶花岗质岩墙,这期岩墙在整个中亚造山带中普遍发育,具有重要的构造环境指示意义。车亚文等在1:5万填图的基础上,对大兴安岭南段林西地区辉长闪长岩开展系统工作,确定其与蒙古-鄂霍茨克洋闭合引起的碰撞后伸展背景有关。王帅等报道了1:5万填图发现的迪彦庙SSZ型蛇绿岩北部晚石炭世马尼塔埃达克岩,确定其为洋内俯冲岩石组合的重要组成部分,表明古亚洲洋东段在晚石炭世处于洋内俯冲消减过程中。
(4)沉积岩区填图。沉积岩区填图是建立地层系统与格架、恢复区域和生命演化的重要手段。向忠金等通过对中越边界富宁—那坡地区的1:5万填图,查明早—中三叠世火山岩及其相关沉积序列,确定了扬子南缘地区印支期岛弧火山-沉积环境。石秋圆等报道了新建立的中—上三叠统卡尼阶岩石地层单位——嘎热扎地组,该工作填补了措勤中—上三叠统卡尼阶岩石地层单位的空白。安显银等报道了在西藏察雅地区侏罗纪红层中发现的恐龙化石,丰富了侏罗系恐龙的地理分布,有助于了解亚洲地区蜥脚类和兽脚类恐龙的早期演化和分异。
(5)变质岩区填图。变质岩填图是填图的难点,也是获得突破和新发现的主要基础。李猛等对东昆仑西段金水口岩群白沙河岩组的碎屑锆石进行研究,指出东昆仑早古生代可能存在一条近千千米的高压变质岩带。张连祥等通过莱阳地区1:5万变质基底填图,限定了胶北荆山群禄格庄组的原岩为古元古代,推测粉子山群小宋组与祝家夼组沉积时可能靠近被动大陆边缘的一侧,而禄格庄组更靠近岩浆岛弧的一侧,二者可能属于同时异相沉积的产物。
(6)复杂构造区填图。构造地质是中国填图中最薄弱的环节,复杂现象和关系的识别及构造过程的建立得益于详细地地质填图。张北航等在1:5万填图的基础上,厘定出狼山地区自晚侏罗世以来发育6期陆内变形,并认为先存构造和欧亚板块边缘自晚侏罗世以来不同方向的增生是控制狼山地区陆内变形的主要因素。柯昌辉等通过对白云鄂博矿田内褶皱及断层构造特征的剖析,确定了中元古代—晚古生代4期构造活动,对矿区深部及外围找矿工作具有重要的指导意义。
本专辑的文章是填图试点的部分成果及方法探索,希望能够为今后进一步开展中大比例尺(1:5万和1:2.5万)区域地质填图和专题填图起到推广和借鉴作用,成功的经验和失败的教训都是未来继续工作不可多得的财富。希望专辑中介绍的新方法、新理念能够逐步为广大一线工作认可,并运用到新时期地质调查工作中。
张 进 王 涛
中国地质科学院地质研究所
2020年12月20日
致谢: 中国科学院大学江文、周斌和邓莉,广西区域地质调查研究院彭展和覃斌贤工程师,成都理工大学李伟歌、羊洪志等参加了野外地质填图和剖面测量工作;SHRIMP锆石U-Pb定年分析工作得到了北京离子探针中心董春燕和杨淳老师的帮助;中国地质科学院地质研究所张进研究员和审稿专家对本文提出了宝贵意见,在此一并表示衷心的感谢。 -
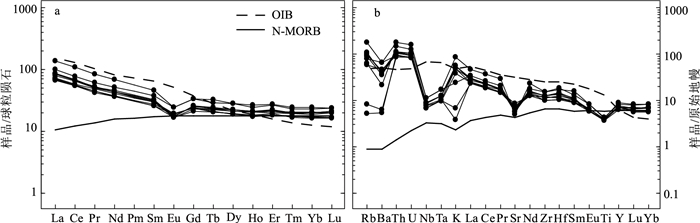
图 7 富宁—那坡地区早—中三叠世火山岩稀土元素球粒陨石标准化配分图(a)和微量元素原始地幔标准化蛛网图(b)
(球粒陨石、原始地幔、洋岛玄武岩(OIB)和正常洋中脊玄武岩(N-MORB)值据参考文献[36])
Figure 7. Chondrite-normalized REE patterns (a) and primitive mantle-normalized spider diagram (b) for the Early-Middle volcanic rocks in the Funing-Napo area
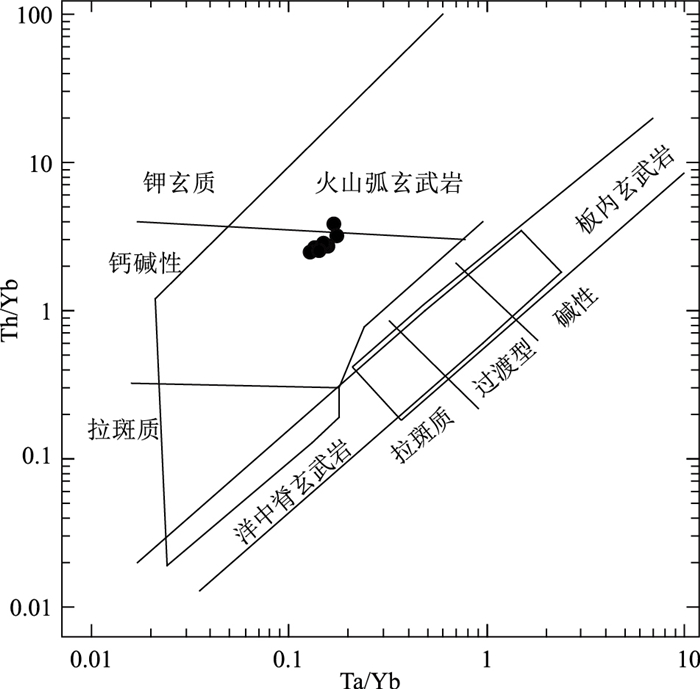
图 9 富宁—那坡地区早—中三叠世火山岩Ta/Yb-Th/Yb图解[48]
Figure 9. Diagram of Ta/Yb-Th/Yb for the Early-Middle Triassic volcanic rocks in the Funing-Napo area
表 1 富宁—那坡地区火山岩SHRIMP锆石U-Pb分析结果
Table 1 SHRIMP zircon U-Pb data for the volcanic rocks in the Funing-Napo area
测点 Pb/10-6 U/10-6 Th/10-6 Th/U 207Pb/235U % 206Pb/238U % 误差相关系数 206Pb/238U年龄/Ma σ 207Pb/206Pb年龄/Ma σ 不谐和度 NP20-1 — 473 152 0.33 0.2610 6.1 0.03951 1.1 0.173 250 3 95 140 -163 NP20-2 — 1329 1040 0.81 0.2679 2.4 0.03899 0.5 0.204 247 1 187 54 -32 NP20-3 — 652 134 0.21 0.2863 2.7 0.03944 0.7 0.252 249 2 313 58 20 NP20-4 0.16 287 150 0.54 0.2800 3.6 0.03932 1.0 0.277 249 2 267 80 7 NP20-5 — 212 105 0.51 0.2570 7.3 0.03931 1.2 0.161 249 3 68 170 -265 NP20-6 — 887 689 0.80 0.2798 2.6 0.03873 0.8 0.301 245 2 302 56 19 NP20-7 — 441 81 0.19 0.2310 8.7 0.03835 0.9 0.105 243 2 -131 210 285 NP20-8 — 1020 630 0.64 0.2733 2.5 0.03904 0.6 0.239 247 1 231 56 -7 NP20-9 — 2912 2736 0.97 0.2840 1.5 0.04024 0.4 0.242 254 1 249 33 -2 NP20-10 — 521 102 0.20 0.2717 3.2 0.03890 0.7 0.231 246 2 225 72 -9 NP20-11 — 471 291 0.64 0.2662 3.1 0.03778 0.8 0.252 239 2 246 69 3 NP20-12 — 749 424 0.58 0.2849 2.6 0.03914 0.9 0.341 248 2 320 56 23 NP20-13 — 654 120 0.19 0.2630 3.8 0.03934 0.7 0.174 249 2 123 88 -102 NP20-14 — 294 179 0.63 0.2550 9.6 0.03821 1.1 0.113 242 3 118 230 -105 NP20-15 — 212 137 0.67 0.2570 4.2 0.03852 1.1 0.260 244 3 122 96 -99 DM12-1 0.16 459 325 0.73 0.2884 3.1 0.03914 1.6 0.529 248 4 348 60 29 DM12-2 — 1251 739 0.61 0.2760 2.6 0.03850 1.7 0.649 244 4 285 45 15 DM12-3 — 264 177 0.69 0.2630 4 0.03745 1.7 0.431 237 4 239 83 1 DM12-4 — 263 120 0.47 0.2500 6 0.03861 2.1 0.342 244 5 45 140 -438 DM12-5 — 172 74 0.45 0.2480 6.9 0.03989 1.9 0.276 252 5 -50 160 603 DM12-6 — 1559 703 0.47 0.2702 2.5 0.03934 1.6 0.617 249 4 186 46 -34 DM12-7 — 518 323 0.64 0.2747 2.7 0.03837 1.9 0.688 243 4 282 45 14 DM12-8 — 214 103 0.50 0.2420 4.9 0.03828 1.8 0.368 242 4 -11 110 2262 DM12-9 — 843 583 0.71 0.2924 2.8 0.04062 2.0 0.723 257 5 295 44 13 DM12-10 — 1118 605 0.56 0.2819 3 0.03996 1.6 0.532 253 4 248 58 -2 DM12-11 — 222 103 0.48 0.2790 4.5 0.04011 1.8 0.401 254 5 215 95 -18 DM12-12 — 820 135 0.17 0.2620 8.1 0.03813 1.6 0.203 241 4 190 180 -27 DM12-13 0.06 936 147 0.16 0.6700 1.9 0.07820 1.6 0.823 485 7 679 23 28 DM12-14 0.08 748 493 0.68 0.2796 2.3 0.03896 1.6 0.689 246 4 288 38 14 表 2 富宁—那坡地区火山岩全岩主量、微量和稀土元素分析结果
Table 2 Major, trace element and REE contents of the volcanic rocks in the Funning-Napo area
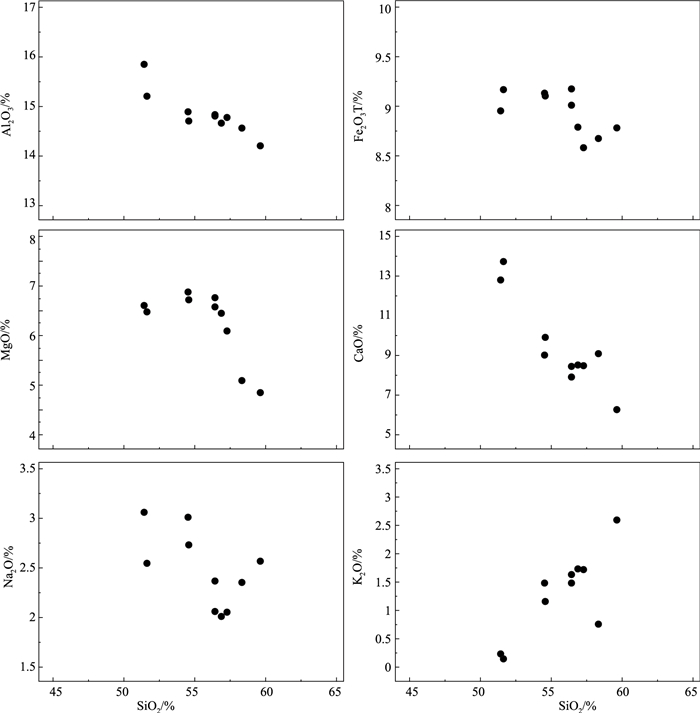
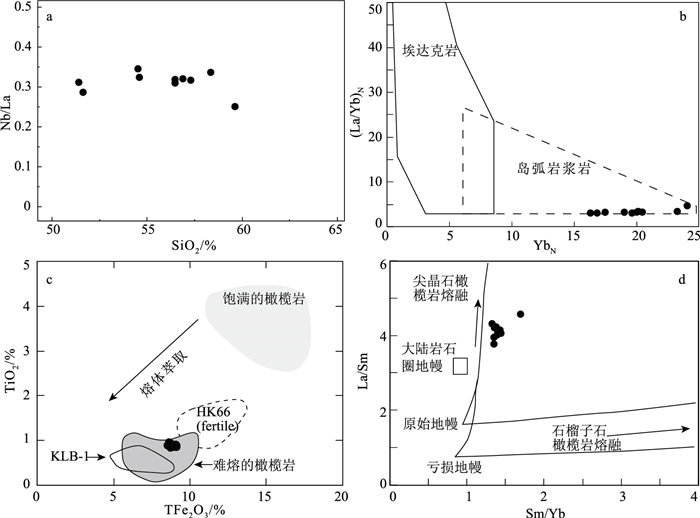
元素 11NP21-2 11NP21-3 11NP21-4 11NP21-5 GCH-2 GCH-4 13DM-2 13DM-3 13DB-7 14WD-4 元素 11NP21-2 11NP21-3 11NP21-4 11NP21-5 GCH-2 GCH-4 13DM-2 13DM-3 13DB-7 14WD-4 SiO2 56.50 57.32 56.91 56.49 54.64 54.57 51.68 51.46 59.66 58.37 Hf 4.39 4.2 3.96 4.46 3.55 3.42 3.23 3.21 5.27 5.74 TiO2 0.84 0.86 0.81 0.84 0.87 0.88 0.87 0.89 0.93 0.93 Ta 0.52 0.51 0.51 0.52 0.4 0.42 0.43 0.41 0.7 0.7 Al2O3 14.79 14.76 14.65 14.83 14.69 14.88 15.20 15.83 14.19 14.55 Co 33 31.2 30 34 37.9 39 38.1 39.7 26.6 26.9 TFe2O3 9.01 8.58 8.78 9.17 9.10 9.12 9.16 8.95 8.78 8.67 U 2.16 2.15 1.98 2.05 1.74 1.78 1.71 1.8 3.35 2.65 MnO 0.13 0.12 0.12 0.13 0.14 0.15 0.16 0.16 0.13 0.12 La 20.8 20.1 18.9 19.8 16.6 16.5 17.3 15.9 32.1 23.6 MgO 6.56 6.07 6.43 6.75 6.71 6.87 6.47 6.59 4.83 5.08 Ce 41.8 40.5 39.2 40.5 34.4 33.6 35.6 33.2 66.0 47.2 CaO 8.41 8.44 8.49 7.86 9.89 8.98 13.71 12.77 6.23 9.06 Pr 4.97 4.96 4.73 5.00 4.20 4.21 4.64 4.03 8.09 5.75 Na2O 2.05 2.05 2.00 2.36 2.72 3.00 2.54 3.05 2.56 2.35 Nd 21.2 20.5 20.1 20.5 17.4 17.1 19.0 17.0 31.8 24.2 K2O 1.60 1.70 1.70 1.46 1.13 1.45 0.11 0.21 2.57 0.73 Sm 4.95 4.64 4.56 4.84 4.14 3.91 4.56 4.00 7.00 5.81 P2O5 0.10 0.10 0.10 0.10 0.09 0.09 0.09 0.09 0.12 0.12 Eu 0.99 1.02 0.97 0.99 1.11 1.10 1.11 0.98 1.41 1.40 烧失量 1.91 1.75 2.24 1.81 2.78 2.86 3.00 3.27 2.11 3.19 Gd 5.37 5.20 4.79 5.31 4.84 4.95 4.86 4.31 6.98 6.87 Mg# 59 59 59 60 60 60 59 60 52 54 Tb 0.92 0.88 0.83 0.87 0.77 0.78 0.86 0.77 1.20 1.10 Ba 302 270 273 248 330 467 37.4 44.3 451 151 Dy 5.74 5.63 5.39 5.71 4.88 4.76 5.34 4.91 7.19 7.17 Rb 61.8 68.4 64.3 57.3 37.6 50.8 3.29 5.25 115 39.9 Ho 1.21 1.16 1.15 1.20 1.04 1.04 1.16 0.98 1.50 1.37 Sr 144 154 136 120 145 179 137 148 106 123 Er 3.70 3.49 3.34 3.64 3.05 3.25 3.51 3.07 4.53 4.42 Y 32 32.3 29 32.3 33.5 34.1 34.3 32.6 41.3 37.6 Tm 0.51 0.52 0.50 0.51 0.44 0.43 0.49 0.45 0.63 0.59 Zr 140 141 128 139 129 134 110 110 171 173 Yb 3.40 3.46 3.23 3.41 2.97 2.79 3.35 2.87 4.09 3.95 Nb 6.41 6.35 6.03 6.29 5.35 5.68 4.94 4.92 7.99 7.9 Lu 0.53 0.51 0.51 0.53 0.43 0.42 0.50 0.43 0.60 0.60 Th 9.47 9.24 8.75 9.26 7.82 7.83 8.27 7.22 15.4 12.6 ΣREE 116.09 112.57 108.20 112.81 96.27 94.84 102.28 92.90 173.12 134.03 Pb 9.66 9.98 11.5 12.5 7.8 9.16 9.66 11.2 11.9 13.2 δEu 0.59 0.64 0.63 0.60 0.76 0.77 0.72 0.72 0.61 0.68 Ni 63.6 58.9 54.3 63 60.6 50.5 59.1 65.2 40.2 47.2 (La/Yb)N 3.7 3.5 3.6 3.5 3.4 3.6 3.1 3.4 4.8 3.6 V 177 169 160 174 215 223 198 210 141 162 Cr 297 260 260 284 227 243 206 222 173 206 注:主量元素含量单位为%,微量和稀土元素含量单位为10-6 -
Sone M, Metcalfe I. Parallel Tethyan sutures in mainland Southeast Asia: New insights for Palaeo-Tethys closure and implications for the Indosinian orogeny[J]. Comptes Rendus Geoscience, 2008, 340(2): 166-179.
Metcalfe I. Gondwana dispersion and Asian accretion: Tectonic and palaeogeographic evolution of eastern Tethys[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2013, 66: 1-33. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2012.12.020
Cai J, Zhang K. A new model for the Indochina and South China collision during the Late Permian to the Middle Triassic[J]. Tectonophysics, 2009, 467(1): 35-43. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0040195108006100
Faure M, Lepvrier C, Nguyen V V, et al. The South China block-Indochina collision: Where, when, and how?[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2014, 79: 260-274. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2013.09.022
Jian P, Liu D, Kröner A, et al. Devonian to Permian plate tectonic cycle of the Paleo-Tethys Orogen in southwest China(Ⅰ): Geochemistry of ophiolites, arc/back-arc assemblages and within-plate igneous rocks[J]. Lithos, 2009, 113(3/4): 748-766.
Jian P, Liu D, Kröner A, et al. Devonian to Permian plate tectonic cycle of the Paleo-Tethys Orogen in southwest China(Ⅱ): Insights from zircon ages of ophiolites, arc/back-arc assemblages and within-plate igneous rocks and generation of the Emeishan CFB province[J]. Lithos, 2009, 113(3/4): 767-784. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0024493709001480
Lai C, Meffre S, Crawford A J, et al. The Central Ailaoshan ophiolite and modern analogs[J]. Gondwana research, 2014, 26(1): 75-88. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2013.03.004
Findlay R H, Trinh P T. The Structural Setting of the Song Ma Region, Vietnam and the Indochina-South China Plate Boundary Problem[J]. Gondwana Research, 1997, 1(1): 11-33. doi: 10.1016/S1342-937X(05)70003-4
Liu J, Tran M, Tang Y, et al. Permo-Triassic granitoids in the northern part of the Truong Son belt, NW Vietnam: Geochronology, geochemistry and tectonic implications[J]. Gondwana Research, 2012, 22(2): 628-644. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2011.10.011
Zhang R Y, Lo C H, Chung S L, et al. Origin and tectonic implication of Ophiolite and Eclogite in the Song Ma Suture Zone between the South China and Indochina Blocks[J]. Journal of Metamorphic Geology, 2013, 31: 49-62. doi: 10.1111/jmg.12012
锺大赉, 吴根耀, 季建清, 等. 滇东南发现蛇绿岩[J]. 科学通报, 1998, (13): 1365-1370. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB199813003.htm Genyao W, Dalai Z, Qi Z, et al. Babu-Phu Ngu Ophiolites: A Geological Record of Paleotethyan Ocean Bordering China and Vietnam[J]. Gondwana Research, 1999, 2(4): 554-557. doi: 10.1016/S1342-937X(05)70193-3
王忠诚, 吴浩若, 邝国敦. 桂西晚古生代海相玄武岩的特征及其形成环境[J]. 岩石学报, 1997, (2): 135-140. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB702.014.htm Guo F, Fan W, Wang Y, et al. Upper Paleozoic Basalts in the Southern Yangtze Block: Geochemical and Sr-Nd Isotopic Evidence for Asthenosphere-Lithosphere Interaction and Opening of the Paleo-Tethyan Ocean[J]. International Geology Review, 2004, 46(4): 332-346. doi: 10.2747/0020-6814.46.4.332
董云鹏, 朱炳泉. 滇东南建水岛弧型枕状熔岩及其对华南古特提斯的制约[J]. 科学通报, 1999, (21): 2323-2328. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.1999.21.018 吴根耀, 吴浩若, 钟大赉, 等. 滇桂交界处古特提斯的洋岛和岛弧火山岩[J]. 现代地质, 2000, (4): 393-400. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2000.04.002 吴根耀, 季建清, 何顺东, 等. 广西凭祥地区早二叠世的岩浆弧及其构造意义[J]. 矿物岩石, 2002, (3): 61-65. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6872.2002.03.014 吴浩若. 晚古生代-三叠纪南盘江海的构造古地理问题[J]. 古地理学报, 2003, 5(1): 63-76. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1505.2003.01.006 Lepvrier C, Faure M, Van V N, et al. North-directed Triassic nappes in Northeastern Vietnam(East Bac Bo)[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2011, 41(1): 56-68. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2011.01.002
张斌辉, 丁俊, 张林奎, 等. 滇东南八布蛇绿岩的SHRIMP锆石U-Pb年代学研究[J]. 地质学报, 2013, 87(10): 1498-1509. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201310002.htm Liu H C, Peng T, Guo X. Geochronological and geochemical constraints on the coexistent N-MORB and SSZ-type ophiolites in Babu area(SW China)and tectonic implications[J]. Journal of the Geological Society, 2018, 175: 667-678. doi: 10.1144/jgs2017-121
黄虎, 杜远生, 黄志强, 等. 桂西晚古生代硅质岩地球化学特征及其对右江盆地构造演化的启示[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2013, 43(02): 304-316. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK201302015.htm Halpin A J, Thanh T H, Chun-Kit L, et al. U-Pb zircon geochronology and geochemistry from NE Vietnam: A tectonically disputed territory between the Indochina and South China blocks[J]. Gondwana Research, 2016, 34: 254-273. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2015.04.005
Zhou M F, Zhao J H, Qi L, et al. Zircon U-Pb geochronology and elemental and Sr-Nd isotope geochemistry of Permian mafic rocks in the Funing area, SW China[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 2006, 151(1): 1-19. doi: 10.1007/s00410-005-0030-y
Huang H, Du Y, Yang J, et al. Origin of Permian basalts and clastic rocks in Napo, Southwest China: Implications for the erosion and eruption of the Emeishan large igneous province[J]. Lithos, 2014, 208/209: 324-338. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2014.09.022
陈雪峰, 刘希军, 许继峰, 等. 桂西那坡基性岩地球化学: 峨眉山地幔柱与古特提斯俯冲相互作用的证据[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2016, 40(3): 531-548. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK201603010.htm 胡丽沙, 杜远生, 杨江海, 等. 广西那龙地区中三叠世火山岩地球化学特征及构造意义[J]. 地质论评, 2012, 58(3): 481-494. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0371-5736.2012.03.009 江文, 向忠金, 夏文静, 等. 滇东南富宁地区基性侵入岩与峨眉山地幔柱存在成因关系吗?——来自1:5万洞波幅和皈朝幅地质填图的证据[J]. 岩石学报, 2017, 33(10): 3109-3122. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201710009.htm 皮桥辉, 胡瑞忠, 彭科强, 等. 云南富宁者桑金矿床与基性岩年代测定——兼论滇黔桂地区卡林型金矿成矿构造背景[J]. 岩石学报, 2016, 32(11): 3331-3342. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201611008.htm 夏磊, 闫全人, 向忠金, 等. 广西那坡盆地火山岩-碳酸盐岩混杂型滑塌堆积: 特殊的弧前域构造指相标志及其大地构造意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2018, 34(3): 685-700. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201803010.htm Compston W, Williams I S, Kirschvink J L, et al. Zircon U-Pb ages for the Early Cambrian time-scale[J]. Journal of the Geological Society, 1992, 149(2): 171-184. doi: 10.1144/gsjgs.149.2.0171
Black L P, Kamo S L, Allen C M, et al. Improved 206Pb/238U microprobe geochronology by the monitoring of a trace-element-related matrix effect: SHRIMP, ID-TIMS, ELA-ICP-MS and oxygen isotope documentation for a series of zircon standards[J]. Chemical Geology, 2004, 205(1/2): 115-140. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0009254104000361
Williams I S, Buick I S, Cartwright I. An extended episode of early Mesoproterozoic metamorphic fluid flow in the Reynolds Range, central Australia[J]. Journal of Metamorphic Geology, 1996, 14(1): 29-47.
Winchester J A, Floyd P A. Geochemical discrimination of different magma series and their differentiation products using immobile elements[J]. Chemical Geology, 1977, 20: 325-343. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0009254177900572
Le Maitre R W, Bateman P, Dudek A, et al. A Classification and Glossary of Terms[M]. Blackwell, Oxford, 1989: 1-193.
Sun S S, Mcdonough M F. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: implications for mantle composition and processes[J]. Geological Society Special Publication, 1989, 42: 313-345.
Hofmann A W, Jochum K P, Seufert M, et al. Nb and Pb in oceanic basalts: new constraints on mantle evolution[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1986, 79(1): 33-45.
Rudnick R L, Gao S. Composition of the Continental Crust[J]. Treatise on Geochemistry, 2003, 3: 1-64.
Martin H. Adakitic magmas: modern analogues of Archaean granitoids[J]. Lithos, 1999, 46(3): 411-429.
Falloon T J, Green D H, Hatton C J, et al. Anhydrous partial melting of a fertile and depleted peridotite from 2 to 30 kbar and application to basalt petrogenesis[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1988, 29(6): 1257-1282. doi: 10.1093/petrology/29.6.1257
Hirose K, Kushiro I. Partial melting of dry peridotites at high pressures: Determination of compositions of melts segregated from peridotite using aggregates of diamond[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1993, 114(4): 477-489. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0012821X9390077M
Xiao L, Xu Y G, Mei H J, et al. Distinct mantle sources of low-Ti and high-Ti basalts from the western Emeishan large igneous province, SW China: implications for plume-lithosphere interaction[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2004, 228(3/4): 525-546.
Hirose K. Melting experiments on Iherzolite KLB-1 under hydrous conditions and generation of high-magnesian andesitic melts[J]. Geology, 1997, 25(1): 42-44. http://petrology.oxfordjournals.org/cgi/ijlink?linkType=ABST&journalCode=geology&resid=25/1/42
Wu F, Walker R J, Yang Y, et al. The chemical-temporal evolution of lithospheric mantle underlying the North China Craton[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2006, 70(19): 5013-5034.
Kepezhinskas P, Mcdermott F, Defant M J, et al. Trace element and Sr+Nd+Pb isotopic constraints on a three-component model of Kamchatka Arc petrogenesis[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica acta, 1997, 61(3): 577-600. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0016703796003493
Woodhead J D, Hergt J M, Davidson J P, et al. Hafnium isotope evidence for 'conservative' element mobility during subduction zone processes[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2001, 192(3): 331-346. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0012821X01004538
Hanyu T, Tatsumi Y, Nakai S, et al. Contribution of slab melting and slab dehydration to magmatism in the NE Japan arc for the last 25 Myr: Constraints from geochemistry[J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2006, 7(8): 1-29. doi: 10.1029/2005GC001220
Pearce J A. Trace element characteristics of lavas from destructive plate boundaries[C]//Thorpe R S. Andesites.London: John Wiley & Sons, 1982: 525-548.
Xia L. The geochemical criteria to distinguish continental basalts from arc related ones[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2014, 139: 195-212. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0012825214001743
Watkins R. Volcaniclastic and carbonate sedimentation in late Paleozoic island-arc deposits, Eastern Klamath Mountains, California[J]. Geology, 1985, 13: 709-713.
Soja C. Island-arc carbonates: characterization and recognition in the ancient geologic record[J]. Earth-science reviews, 1996, 41(1/2): 31-65. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0012825296000293
Dorobek S. Carbonate-platform facies in volcanic-arc settings: Characteristics and controls on deposition and stratigraphic development[J]. The Geological Socienty of America Special Paper, 2007, 436: 1-36. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/284141450_Carbonate-platform_facies_in_volcanic-arc_settings_Characteristics_and_controls_on_deposition_and_stratigraphic_development
Hoa T T, Izokh A E, Polyakov G V, et al. Permo-Triassic magmatism and metallogeny of Northern Vietnam in relation to the Emeishan plume[J]. Russian Geology and Geophysics, 2008, 49(7): 480-491. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1068797108001107
Qin X F, Wang Z Q, Zhang Y L, et al. Geochemistry of Permian mafic igneous rocks from the Napo-Qinzhou Tectonic Belt in Southwest Guangxi, Southwest China: Implications for Arc-back arc basin magmatic evolution[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2012, 86(5): 1182-1199. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/86253X/201205/43766269.html
吴根耀, 马力, 钟大赉, 等. 滇桂交界区印支期增生弧型造山带: 兼论与造山作用耦合的盆地演化[J]. 石油实验地质, 2001(1): 8-18. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYSD200101001.htm 陈泽超, 林伟, Michel F, 等. 越南东北部早中生代构造事件的年代学约束[J]. 岩石学报, 2013, 29(5): 1825-1840. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201305027.htm 杜远生, 黄虎, 杨江海, 等. 晚古生代-中三叠世右江盆地的格局和转换[J]. 地质论评, 2013, 59(1): 1-11. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP201301002.htm 覃小锋, 王宗起, 张英利, 等. 桂西南早中生代酸性火山岩年代学和地球化学: 对钦-杭结合带西南段构造演化的约束[J]. 岩石学报, 2011, 27(3): 794-808. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201103019.htm Condie K C. Plate tectonics and crustal evolution[M]. Pregrmon Press, Oxford, 1997.
云南省地质矿产局. 云南省区域地质志[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1990. 杨江海, 杜远生, 于鑫, 等. 滇东南八布早二叠世含火山岩屑砂岩指示古特提斯洋俯冲[J]. 地球科学, 2017, 42(1): 24-34. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201701002.htm Geology and Earth Resource of Viet Nam. Geological map of VietNam (1:3500000). Publishing House for Science and Tectnology, HaNoi, 2011.
中国地质调查局武汉地质调查中心. 1:1000000中南地质图. 2012. 云南省地质局. 1:20万富宁幅地质图及区域地质调查报告. 1978. 广西壮族自治区地质局. 1:20万百色幅, 德隆幅地质图及区域地质调查报告. 1976.



 下载:
下载: