Discovery of Late Carboniferous adakite in Manita, Inner Mongolia, and its constrains on intra-oceanic subduction in eastern Paleo-Asian Ocean
-
摘要:
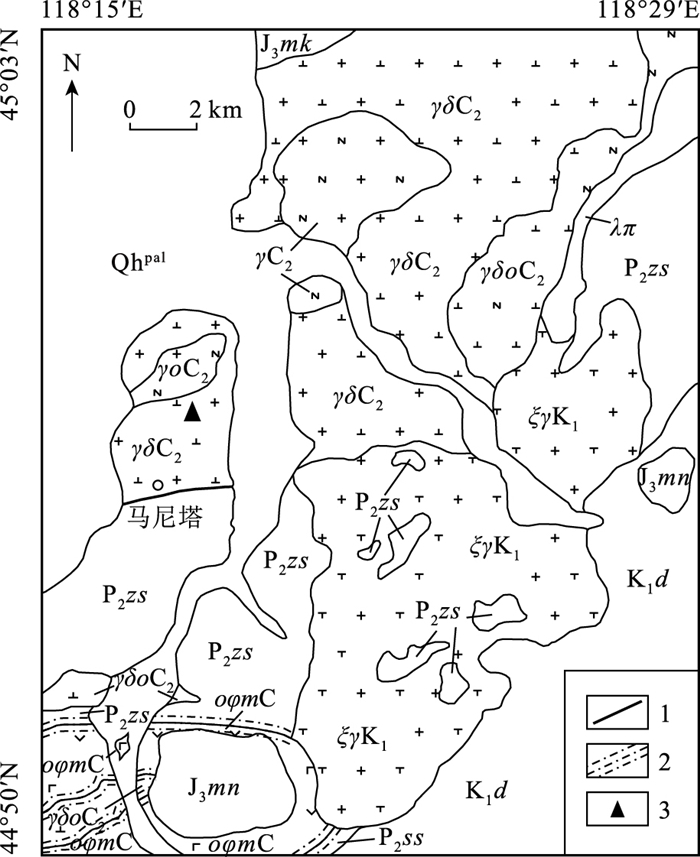
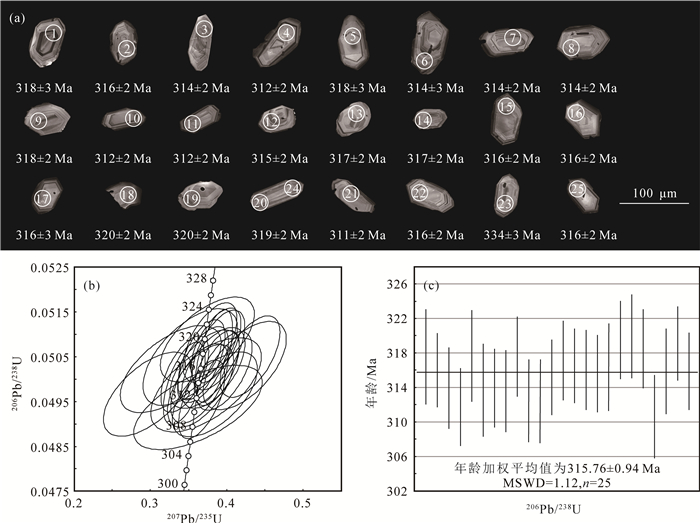
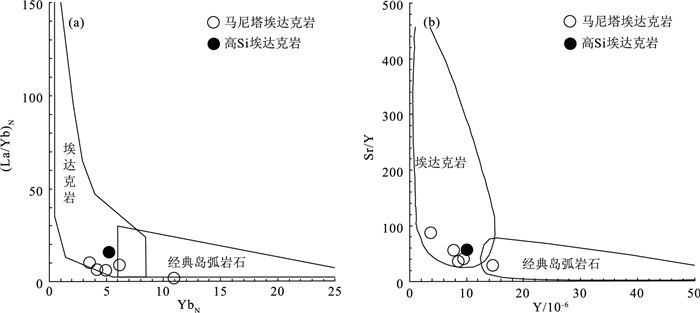
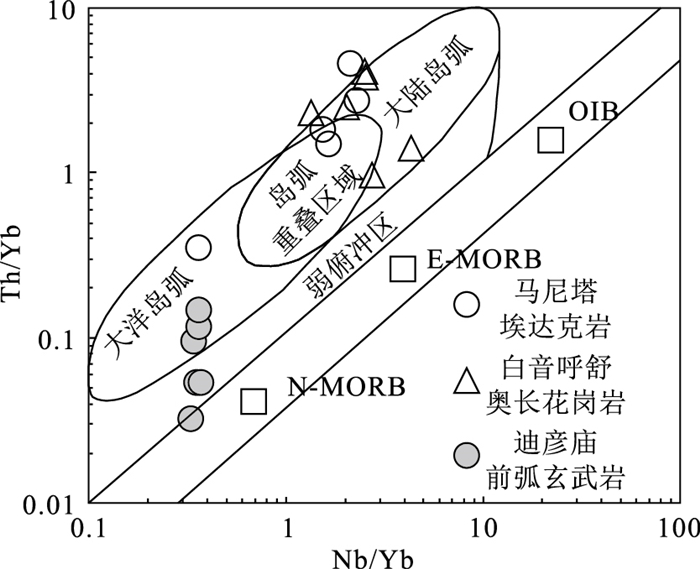
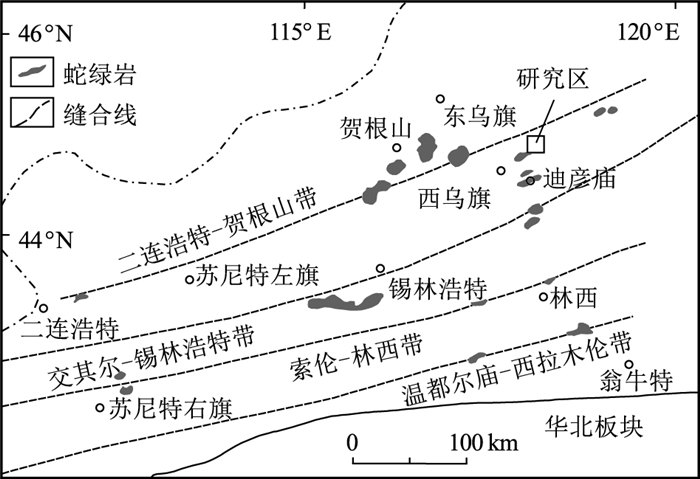
在内蒙古西乌旗迪彦庙SSZ型蛇绿岩北部新发现一套晚石炭世马尼塔埃达克岩。该埃达克岩位于兴蒙造山带东段贺根山缝合带内,岩性为花岗闪长岩和斜长花岗岩。马尼塔埃达克岩SiO2含量为61.91%~75.16%,A12O3含量为13.54%~17.42%,MgO含量为0.33%~2.49%,富钠贫钾(Na2O=4.58%~5.48%,K2O=0.40%~2.08%,Na2O/K2O=2.35~12.96),属于低钾拉斑系列和钙碱性系列岩石;富Sr贫Y(Sr=309.55×10-6~433.99×10-6,Y=3.74×10-6~14.66×10-6),相对富集大离子亲石元素(LILE)K、Rb、Sr等,亏损高场强元素(HFSE)Nb、Ta、Zr、Ti、P等;稀土元素总量偏低(35.79×10-6~70.10×10-6),轻、重稀土元素分馏明显,(La/Yb)N值为1.59~10.11,无明显Eu异常(δEu=0.91~1.51),Yb含量为0.60×10-6~1.86×10-6,符合典型埃达克岩的地球化学特征。新获得的LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄为315.76±0.94 Ma,表明马尼塔埃达克岩的形成时代为晚石炭世。马尼塔埃达克岩与迪彦庙SSZ型蛇绿岩、前弧玄武岩、白音呼舒奥长花岗岩等组成洋内俯冲岩石组合,表明古亚洲洋东段在晚石炭世并未关闭,处于洋内俯冲消减过程。
-
关键词:
- 埃达克岩 /
- SSZ型蛇绿岩 /
- LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄 /
- 洋内俯冲作用 /
- 内蒙古马尼塔
Abstract:The Late Carboniferous Manita adakite distributed along the Hegenshan suture zone in the eastern part of the Xingmeng Orogenic Belt was discovered to be outcropped in the northern section of Diyanmiao SSZ ophiolite in Xiwuqi, Inner Mongolia.It consists mainly of granodiorite and plagiogranite, which belongs to low-K tholeiitic and Calc alkaline series, chemically characterized by 61.91%~75.16% of SiO2, 13.54%~17.42% of A12O3, and 0.33%~2.49% of MgO, with intensively rich in Na2O (4.58%~5.48%), poor in K2O (0.40%~2.08%) and high ratio of Na2O/K2O (2.35~12.96).The Manita adakite also manifests high Sr (309.55×10-6~433.99×10-6) and poor Y (3.74×10-6~14.66×10-6), with relatively enriched large ion lithophile elements (LILE) K, Rb, Sr, and depleted high field strength elements (HFSE) Nb, Ta, Zr, Ti and P, etc.In addition, it features low ∑REE (35.79×10-6~70.10×10-6) and clear REE fractionation((La/Yb)N=1.59~10.11), without obvious Eu anomaly (δEu=0.91~1.51), and contains Yb (0.60×10-6~1.86×10-6).All of the geochemical characteristics indicate that the Manita pluton belongs to typical adakite.The U-Pb age of LA-ICP-MS zircon is 315.76±0.94 Ma, indicating that the formation age of Manita adakite is Late Carboniferous.The Manita adakite, Diyanmiao SSZ ophiolite, fore arc basalt and Baiyinhushu trondhjemite constitute the intra-oceanic subduction rock assemblage, which indicates that the eastern part of the Paleo-Asian Ocean was not closed in the Late Carboniferous and was in the process of subduction and extinction.
-
区域地质调查和填图是地质工作的基础,也是衡量一个国家基础地质调查和研究程度及水平的重要指标,具有重要的战略意义。中国地质调查局高度重视基础地质调查与填图方式、方法的改革,树立“地质填图的过程就是科学研究的过程”的理念,确定“需求决定工作部署”、“问题决定调查方式”的工作思路,提升解决制约重大资源环境的基础地质问题和地球系统科学问题的能力。在中国地质调查局总工室和基础部的协调、领导下,由中国地质科学院地质研究所、地质力学所联合地调局六大区域地质调查中心开展了国际分幅和非国际分幅的中大比例尺专题试点填图,取得了重要进展。这是中国第一次较系统地构建填图方法体系。2019年11月6—7日,中国地质调查局召开了第三次全国区域地质调查工作会议。同时,成立了全国区域地质调查专家委员会,并组织了全国区调填图方法研讨会,来自全国地质行业近100人参加了培训和研讨,有30人在会议上交流发言,展现了区调改革在技术方法上的创新及取得的一批新进展、新发现,收效良好。
本专辑是本次会议成果的一次体现。本专辑共收录15篇论文,内容涉及短周期密集台阵方法在专题填图中的运用、遥感技术的使用等,以及地层、岩浆岩(侵入岩和火山岩)、变质岩、蛇绿混杂岩、构造、古生物、矿床等基础学科填图成果;还有论文,包括岩溶地区填图方法和地貌演变、造山带构造变形、侵入岩、蛇绿混杂岩、年轻变质事件及热泉的填图成果介绍,将在下一辑发表。这些论文集中展示了填图的成果。
(1)地球物理方法在填图中的运用。新填图方法和理念的运用是现代填图的重要内容,卢占武等介绍了利用短周期密集台阵进行近地表结构调查的应用实例,提出了该技术在专题地质填图中的应用前景,丰富和完善了专题填图的技术方法体系。李娜等介绍了高光谱遥感技术在中国西部基岩区填图中的应用,高光谱遥感数据对不同岩性段和岩相带、细小构造等区分能力突出,提高了地质调查填图的效率和质量。
(2)蛇绿混杂岩填图。蛇绿混杂岩的填图历经数十年的探索,也是造山带研究的基础数据来源,王国强等系统介绍了近十余年来北山造山带关键地段1:5万区域地质调查和综合研究成果,突出了造山带蛇绿混杂岩带填图方法在北山地区的实践和应用。付长垒等在大比例尺填图的基础上,在拉脊山识别出连续的洋岛海山火山-沉积组合序列,为造山带古洋盆构造演化研究提供了新思路。
(3)侵入岩区填图。侵入岩是造山带的重要组成部分,对它们的刻画和研究一直是造山带研究的基础性工作。苑新晨等对滇西澜沧江地区南段复式岩基进行研究,确定其是古特提斯封闭及保山-思茅地块碰撞的响应。卢鹏等在前期开展同位素填图的基础上,在东准噶尔乌伦古河地区识别出一套晚古生代富碱细晶花岗质岩墙,这期岩墙在整个中亚造山带中普遍发育,具有重要的构造环境指示意义。车亚文等在1:5万填图的基础上,对大兴安岭南段林西地区辉长闪长岩开展系统工作,确定其与蒙古-鄂霍茨克洋闭合引起的碰撞后伸展背景有关。王帅等报道了1:5万填图发现的迪彦庙SSZ型蛇绿岩北部晚石炭世马尼塔埃达克岩,确定其为洋内俯冲岩石组合的重要组成部分,表明古亚洲洋东段在晚石炭世处于洋内俯冲消减过程中。
(4)沉积岩区填图。沉积岩区填图是建立地层系统与格架、恢复区域和生命演化的重要手段。向忠金等通过对中越边界富宁—那坡地区的1:5万填图,查明早—中三叠世火山岩及其相关沉积序列,确定了扬子南缘地区印支期岛弧火山-沉积环境。石秋圆等报道了新建立的中—上三叠统卡尼阶岩石地层单位——嘎热扎地组,该工作填补了措勤中—上三叠统卡尼阶岩石地层单位的空白。安显银等报道了在西藏察雅地区侏罗纪红层中发现的恐龙化石,丰富了侏罗系恐龙的地理分布,有助于了解亚洲地区蜥脚类和兽脚类恐龙的早期演化和分异。
(5)变质岩区填图。变质岩填图是填图的难点,也是获得突破和新发现的主要基础。李猛等对东昆仑西段金水口岩群白沙河岩组的碎屑锆石进行研究,指出东昆仑早古生代可能存在一条近千千米的高压变质岩带。张连祥等通过莱阳地区1:5万变质基底填图,限定了胶北荆山群禄格庄组的原岩为古元古代,推测粉子山群小宋组与祝家夼组沉积时可能靠近被动大陆边缘的一侧,而禄格庄组更靠近岩浆岛弧的一侧,二者可能属于同时异相沉积的产物。
(6)复杂构造区填图。构造地质是中国填图中最薄弱的环节,复杂现象和关系的识别及构造过程的建立得益于详细地地质填图。张北航等在1:5万填图的基础上,厘定出狼山地区自晚侏罗世以来发育6期陆内变形,并认为先存构造和欧亚板块边缘自晚侏罗世以来不同方向的增生是控制狼山地区陆内变形的主要因素。柯昌辉等通过对白云鄂博矿田内褶皱及断层构造特征的剖析,确定了中元古代—晚古生代4期构造活动,对矿区深部及外围找矿工作具有重要的指导意义。
本专辑的文章是填图试点的部分成果及方法探索,希望能够为今后进一步开展中大比例尺(1:5万和1:2.5万)区域地质填图和专题填图起到推广和借鉴作用,成功的经验和失败的教训都是未来继续工作不可多得的财富。希望专辑中介绍的新方法、新理念能够逐步为广大一线工作认可,并运用到新时期地质调查工作中。
张 进 王 涛
中国地质科学院地质研究所
2020年12月20日
致谢: 在野外调查和写作过程中得到中国地质大学(北京)张招崇、王根厚教授,中国地质调查局天津地质调查中心辛后田、周红英研究员等的指导和帮助,审稿专家提出了宝贵的修改意见,在此一并表示衷心的感谢。 -
图 4 马尼塔埃达克岩TAS(a)分类图解[48, 50]和SiO2-K2O(b)分类图解[49-50]
1—橄榄辉长岩;2a—碱性辉长岩;2b—亚碱性辉长岩;3—辉长闪长岩;4—闪长岩;5—花岗闪长岩;6—花岗岩;7—硅英岩;8—二长辉长岩;9—二长闪长岩;10—二长岩;11—石英二长岩;12—正长岩;13—副长石辉长岩;14—副长石二长闪长岩;15—副长石二长正长岩;16—副长正长岩;17—副长深成岩;18—霓方钠岩/磷霞岩/粗白榴岩;Ir—Irvine分界线,上方为碱性,下方为亚碱性
Figure 4. TAS classification diagram (a) and SiO2-K2O diagram (b) of the Manita adakite
图 10 马尼塔埃达克岩Nb/Yb-Th/Yb构造判别图解[64]
N-MORB—正常型洋中脊玄武岩;E-MORB—富集型洋中脊玄武岩;OIB—洋岛玄武岩
Figure 10. Nb/Yb-Th/Yb tectonic discriminant diagram of the Manita adakite
表 1 马尼塔埃达克岩主量、微量和稀土元素分析结果
Table 1 Major, trace elements and REE analyses of the Manita adakite
元素 花岗闪长岩 花岗闪长岩 花岗闪长岩 斜长花岗岩 花岗闪长岩 高Si埃达克岩 元素 花岗闪长岩 花岗闪长岩 花岗闪长岩 斜长花岗岩 花岗闪长岩 高Si埃达克岩 XT02 XT03 XT06 XT08 XT10 XT02 XT03 XT06 XT08 XT10 SiO2 66.93 65.56 64.53 75.16 61.91 64.80 V 53.69 78.88 53.14 31.62 92.15 95.00 TiO2 0.39 0.60 0.47 0.12 0.56 0.56 Cr 31.46 9.14 14.12 4.69 11.83 41.00 Al2O3 16.87 16.24 17.42 13.54 16.63 16.64 Hf 2.79 8.50 3.06 5.27 1.50 Fe2O3 0.98 2.16 1.24 1.00 2.62 4.75 Sc 7.83 6.87 7.08 2.74 20.62 FeO 1.27 1.86 1.85 0.46 3.22 Ta 0.19 0.17 1.42 0.14 0.13 MnO 0.039 0.074 0.054 0.027 0.168 0.081 Co 8.33 9.55 10.96 2.13 11.17 MgO 1.86 1.70 2.49 0.33 2.14 2.18 U 0.37 0.79 0.43 0.41 0.25 CaO 4.83 3.62 2.75 1.32 3.97 4.63 La 6.44 13.13 6.81 8.45 4.14 19.20 Na2O 5.12 4.65 5.48 4.89 4.58 4.19 Ce 14.06 27.86 15.90 15.59 9.03 37.30 K2O 0.40 1.60 1.23 2.08 1.12 1.97 Pr 1.95 3.64 2.08 1.70 1.53 P2O5 0.106 0.158 0.103 0.112 0.128 0.200 Nd 8.44 14.36 8.86 6.37 7.59 18.20 烧失量 0.97 1.63 2.08 0.84 2.48 Sm 1.88 2.73 1.91 1.15 2.11 3.40 总计 99.90 99.85 99.91 99.88 99.88 Eu 0.57 0.93 0.53 0.42 1.06 0.90 Mg# 61 42 60 30 41 48 Gd 1.53 2.35 1.59 0.95 2.14 2.80 Na2O/K2O 12.96 2.91 4.48 2.35 4.11 Tb 0.272 0.344 0.285 0.129 0.453 A/CNK 0.96 1.02 1.13 1.06 1.04 Dy 1.44 2.00 1.59 0.73 2.91 1.90 Ba 35.4 389.1 60.7 503.0 202.4 721.0 Ho 0.257 0.364 0.297 0.143 0.600 Rb 9.39 24.77 27.16 33.34 19.13 52.00 Er 0.78 1.02 0.84 0.42 1.80 0.96 Sr 433.99 431.60 309.55 324.50 433.65 565.00 Tm 0.111 0.169 0.131 0.069 0.279 Y 7.67 9.44 8.49 3.74 14.66 10.00 Yb 0.70 1.05 0.83 0.60 1.86 0.88 Zr 105.71 104.64 114.68 81.51 43.72 108.00 Lu 0.11 0.16 0.13 0.07 0.29 0.17 Nb 1.15 2.40 1.28 1.27 0.68 6.00 ∑REE 38.54 70.10 41.79 36.78 35.79 Th 1.04 2.86 1.50 2.78 0.68 LREE/HREE 6.41 8.40 6.33 10.82 2.47 Pb 2.85 6.94 2.57 7.70 3.25 (La/Yb)N 9.13 8.95 8.16 10.11 1.59 Ga 15.69 18.80 13.92 15.97 16.06 δEu 1.00 1.10 0.91 1.18 1.51 Ni 17.57 5.71 22.76 2.27 6.28 20.00 注:主量元素含量单位为%,稀土、微量元素含量单位为10-6;高Si埃达克岩为267个样品的平均值[50] 表 2 马尼塔埃达克岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Th-Pb同位素分析结果
Table 2 LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Th-Pb isotopic analyses of the Manita adakite
点号 含量/10-6 Th/U 同位素比值 年龄/Ma Pb U Th 206Pb/238U 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 207Pb/206Pb 1σ 208Pb/232Th 1σ 232Th/238U 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 207Pb/206Pb 1σ 1 9 166 84 0.51 0.0505 0.0004 0.3514 0.0253 0.0505 0.0037 0.0131 0.0004 0.5055 0.0019 318 3 306 22 217 168 2 11 214 122 0.57 0.0502 0.0003 0.3862 0.0121 0.0557 0.0017 0.0113 0.0003 0.5690 0.0101 316 2 332 10 442 68 3 14 258 216 0.84 0.0499 0.0004 0.3436 0.0112 0.0499 0.0015 0.0112 0.0003 0.8370 0.0022 314 2 300 10 192 71 4 10 207 118 0.57 0.0496 0.0004 0.3666 0.0124 0.0537 0.0018 0.0110 0.0003 0.5683 0.0011 312 2 317 11 356 74 5 18 350 165 0.47 0.0505 0.0004 0.3825 0.0100 0.0549 0.0013 0.0104 0.0003 0.4711 0.0010 318 3 329 9 408 55 6 4 81 53 0.66 0.0499 0.0004 0.3722 0.0296 0.0541 0.0043 0.0106 0.0003 0.6553 0.0033 314 3 321 26 376 179 7 9 167 137 0.82 0.0499 0.0004 0.3636 0.0154 0.0528 0.0022 0.0116 0.0003 0.8178 0.0015 314 2 315 13 322 94 8 7 147 96 0.66 0.0499 0.0004 0.3650 0.0177 0.0531 0.0025 0.0090 0.0003 0.6561 0.0042 314 2 316 15 333 108 9 10 180 121 0.67 0.0505 0.0004 0.4299 0.0160 0.0617 0.0022 0.0117 0.0003 0.6745 0.0029 318 2 363 14 665 78 10 6 122 60 0.49 0.0497 0.0004 0.2958 0.0238 0.0432 0.0034 0.0112 0.0004 0.4905 0.0019 312 2 263 21 157 198 11 5 104 69 0.67 0.0497 0.0004 0.3836 0.0228 0.0560 0.0033 0.0114 0.0003 0.6666 0.0016 312 2 330 20 453 132 12 12 216 197 0.91 0.0501 0.0003 0.3443 0.0128 0.0498 0.0018 0.0111 0.0002 0.9131 0.0025 315 2 300 11 187 84 13 11 213 156 0.73 0.0504 0.0004 0.3662 0.0126 0.0527 0.0018 0.0112 0.0003 0.7304 0.0041 317 2 317 11 314 76 14 9 180 88 0.49 0.0503 0.0003 0.3681 0.0137 0.0531 0.0019 0.0120 0.0003 0.4904 0.0012 317 2 318 12 331 83 15 9 170 91 0.53 0.0503 0.0004 0.3817 0.0170 0.0551 0.0024 0.0115 0.0003 0.5332 0.0031 316 2 328 15 416 99 16 8 159 92 0.58 0.0502 0.0004 0.3963 0.0148 0.0573 0.0021 0.0137 0.0004 0.5802 0.0031 316 2 339 13 502 82 17 7 143 64 0.45 0.0503 0.0004 0.4229 0.0223 0.0610 0.0032 0.0142 0.0005 0.4460 0.0016 316 3 358 19 638 114 18 12 223 132 0.59 0.0508 0.0004 0.3774 0.0144 0.0539 0.0020 0.0134 0.0003 0.5905 0.0017 320 2 325 12 365 84 19 6 127 8 0.06 0.0509 0.0004 0.3739 0.0252 0.0533 0.0036 0.0148 0.0004 0.0628 0.0002 320 2 323 22 342 153 20 14 277 110 0.40 0.0506 0.0004 0.3885 0.0140 0.0556 0.0020 0.0148 0.0003 0.3975 0.0015 319 2 333 12 438 79 21 8 149 66 0.44 0.0494 0.0004 0.3616 0.0344 0.0531 0.0050 0.0143 0.0005 0.4426 0.0021 311 2 313 30 334 214 22 7 128 53 0.41 0.0502 0.0004 0.3258 0.0270 0.0470 0.0039 0.0147 0.0004 0.4148 0.0021 316 2 286 24 51 197 23 6 118 37 0.31 0.0532 0.0005 0.4302 0.0302 0.0587 0.0041 0.0125 0.0006 0.3099 0.0018 334 3 363 25 554 152 24 11 221 93 0.42 0.0507 0.0003 0.3850 0.0134 0.0550 0.0019 0.0143 0.0004 0.4216 0.0008 319 2 331 11 413 78 25 7 136 55 0.40 0.0502 0.0004 0.3702 0.0185 0.0535 0.0027 0.0139 0.0004 0.4044 0.0031 316 2 320 16 349 113 注:测试单位为中国地质调查局天津地质调查中心;σ为测年误差绝对值 -
Martin H. Adakitic magmas: modern analogues of Archaean granitoids[J]. Lithos, 1999, 46(3): 411-429. doi: 10.1016/S0024-4937(98)00076-0
王焰, 张旗, 钱青. 埃达克(adakite)的地球化学特征及其构造意义[J]. 地质科学, 2000, 35(2): 251-256. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0563-5020.2000.02.016 王强, 许继锋, 王建新, 等. 北大别山adakite型灰色片麻岩的确定及其与超高压变质作用的关系[J]. 科学通报, 2000, 45(10): 1017-1024. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2000.10.002 王强, 许继锋, 赵振华. 一种新的火成岩——埃达克岩的研究综述[J]. 地球科学进展, 2001, 16(2): 20l-208. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXJZ200102009.htm 许继峰, 梅厚钧, 于学元, 等. 准噶尔北缘晚古生代岛弧中与俯冲作用有关的adakite火山岩: 消减板片部分熔融的产物[J]. 科学通报, 2001, 46(8): 684-688. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2001.08.016 Marc J D, Xu J F, Pavel K, et al. Adakites: Some variation on a theme[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2002, 18(2): 129-140.
Drummond M S, Defant M J. A model for Trondhjemite-Tonalite-Dacite Genesis and crustal growth via slab melting: Archean to modern comparisons[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1990, 95(B13): 21503-21521. doi: 10.1029/JB095iB13p21503
Stern C R, Kilian R. Role of the subducted slab, mantle wedge and continental crust in the generation of adakites from the Andean Austral Volcanic Zone[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1996, 123(3): 263-281. doi: 10.1007/s004100050155
Samaniego P, Martin H. Transition from calc-alkalic to adakitic magmatism at Cayambe volcano, Ecuador: Insights into slahmelts and mantle wedge interactions[J]. Geology, 2002, 30(11): 967-970. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(2002)030<0967:TFCATA>2.0.CO;2
刘敦一, 简平, 张旗, 等. 内蒙古图林凯蛇绿岩中埃达克岩SHRIMP测年: 早古生代洋壳消减的证据[J]. 地质学报, 2003, 77(3): 317-330. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2003.03.004 Kay R W, Kay S M. Andean adakites: three ways to make them[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2002, 18(3): 303-311. http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200203003.htm
Xu J F, Shinjo R, Defant M J, et al. Origin of Mesozoic adakitic intrusive rocks in the Ningzhen area of east China: Partial melting of delaminated lower continental crust[J]. Geology, 2002, 30(12): 1111-1114. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(2002)030<1111:OOMAIR>2.0.CO;2
Hou Z Q, Gao Y F, Qu X M, et al. Origin of adakitic intrusives generated during mid-Miocene east-west extension in southern Tibet[J]. Earth and Planetary ence Letters, 2004, 220(1/2): 139-155. http://www.onacademic.com/detail/journal_1000035461839310_7611.html
Wang Q, McDermott F, Xu J F, et al. Cenozoic K-rich adakitic volcanic rocks in the Hohxil area, northern Tibet: Lower-crustal melting in an intracontinental setting[J]. Geology, 2005, 33(6): 465-468. doi: 10.1130/G21522.1
Xu W L, Hergt J M, Gao S, et al. Interaction of adakitic melt-peridotite: Implications for the high-Mg# signature of Mesozoic adakitic rocks in the eastern North China Craton[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2008, 265(1/2): 123-137. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0012821X07006127
唐克东. 中朝陆台北侧褶皱带构造发展的几个问题[J]. 现代地质, 1989, 3(2): 195-204. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ198902005.htm 邵济安. 中朝板块北缘中段地壳演化[M]. 北京: 北京大学出版社, 1991: 1-136. 徐备, 陈斌. 内蒙古北部华北板块与西伯利亚板块之间中古生代造山带的结构及演化[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 1997, 27(3): 227-232. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK199703005.htm Badarch G, Cunningham W D, Windley B F. A new terrane subdivision for Mongolia: implications for the Phanerozoic crustal growth of Central Asia[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2002, 21(1): 87-110. doi: 10.1016/S1367-9120(02)00017-2
Nozaka T, Liu Y. Petrology of the Hegenshan ophiolite and its implication for the tectonic evolution of northern China[J]. Earth & Planetary Science Letters, 2002, 202(1): 89-104. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0012821X02007744
Xiao W J, Windley B F, Hao J, et al. Accretion leading to collision and the Permian Solonker suture, Inner Mongolia, China: Termination of the central Asian orogenic belt[J]. Tectonics, 2003, 22(6): 1-21. http://petrology.oxfordjournals.org/external-ref?access_num=10.1029/2002TC001484&link_type=DOI
Windley B F, Alexeiev D, Xiao W J, et al. Tectonic models for accretion of the Central Asian Orogenic Belt[J]. Journal of the Geological Society, 2007, 164: 31-47. doi: 10.1144/0016-76492006-022
Miao L C, Fan W M, Liu D Y, et al. Geochronology and geochemistry of the Hegenshan ophiolitic complex: Implications for late-stage tectonic evolution of the Inner Mongolia-Daxinganling Orogenic Belt, China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2008, 32(5): 348-370.
李英杰, 王金芳, 李红阳, 等. 内蒙古西乌旗梅劳特乌拉蛇绿岩的识别[J]. 岩石学报, 2015, 31(5): 1461-1470. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201505020.htm 李英杰, 王金芳, 王根厚, 等. 内蒙古迪彦庙蛇绿岩带达哈特前弧玄武岩的发现及其地质意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2018, 34(2): 469-482. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201802019.htm 徐备, 赵盼, 鲍庆中, 等. 兴蒙造山带前中生代构造单元划分初探[J]. 岩石学报, 2014, 30(7): 1841-1857. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201407001.htm 唐克东, 张允平. 内蒙古缝合带的构造演化[C]//肖序常, 汤耀庆. 古中亚复合巨型缝合带南缘构造演化. 北京: 北京科学技术出版社, 1991: 30-54. Xiao W J, Windley B F, Huang B C. End-Permian to mid-Triassic termination of the accretionary processes of the southern Altaids: implications for the geodynamic evolution Phanerozoic continental growth, and metallogeny of Central Asia[J]. International Journal of Earth Sciences, 2009, 98(6): 1189-1217. doi: 10.1007/s00531-008-0407-z
Jian P, Liu D Y, Kröner A, et al. Evolution of a Permian intraoceanic arc-trench system in the Solonker suture zone, Central Asian orogenic Belt, China and Mongolia[J]. Lithos, 2010, 118(1/2): 169-190. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0024493710001349
刘建峰, 李锦轶, 迟效国, 等. 内蒙古东南部早三叠世花岗岩带岩石地球化学特征及其构造环境[J]. 地质学报, 2014, 88(9): 1677-1690. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201409005.htm 石玉若, 刘翠, 邓晋福, 等. 内蒙古中部花岗质岩类年代学格架及该区构造岩浆演化探讨[J]. 岩石学报, 2014, 30(11): 3155-3171. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201411005.htm 刘建峰, 迟效国, 张兴洲, 等. 内蒙古西乌旗南部石炭纪石英闪长岩地球化学特征及其构造意义[J]. 地质学报, 2009, 83(3): 365-376. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE200903006.htm 陈斌, 赵国春. 内蒙古苏尼特左旗南两类花岗岩同位素年代学及其构造意义[J]. 地质论评, 2001, 47(4): 361-367. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.2001.04.005 孙德有, 吴福元, 张艳斌, 等. 西拉木伦河-长春-延吉板块缝合带的最后闭合时间——来自吉林大玉山花岗岩体的证据[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2004(2): 174-181. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ200402003.htm 刘建峰, 李锦轶, 孙立新, 等. 内蒙古巴林左旗九井子蛇绿岩锆石U-Pb定年: 对西拉木伦河缝合带形成演化的约束[J]. 中国地质, 2016, 43(6): 1947-1962. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201606008.htm 李英杰, 王金芳, 李红阳, 等. 内蒙古西乌旗迪彦庙蛇绿岩的识别[J]. 岩石学报, 2012, 28(4): 1282-1290. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201204025.htm 李英杰, 王金芳, 李红阳, 等. 内蒙西乌旗白音布拉格蛇绿岩地球化学特征[J]. 岩石学报, 2013, 29(8): 2719-2730. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201308009.htm 王金芳, 李英杰, 李红阳, 等. 内蒙古乌兰沟埃达克岩锆石U-Pb年龄及构造环境[J]. 地质通报, 2018, 37(10): 1933-1943. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20181017&flag=1 王金芳, 李英杰, 李红阳, 等. 贺根山缝合带白音呼舒奥长花岗岩锆石U-Pb年龄地球化学特征及构造意义[J]. 地质评论, 2019, 65(4): 857-872. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP201904007.htm 王金芳, 李英杰, 李红阳, 等. 内蒙古梅劳特乌拉蛇绿岩中埃达克岩的发现及其演化模式[J]. 地质学报, 2017, 91(8): 1776-1795. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2017.08.009 Li Y J, Wang G H, Santosh M, et al. Supra-subduction zone ophiolites from Inner Mongolia, North China: Implications for the tectonic history of the southeastern Central Asian Orogenic Belt[J]. Gondwana Research, 2018, 59: 126-143. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2018.02.018
Li Y J, Wang G H, Santosh M, et al. Subduction initiation of the SE Paleo-Asian Ocean: Evidence from a well preserved intra-oceanic forearc ophiolite fragment in central Inner Mongolia[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2020, 535: 116087. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2020.116087
Li Y J, Wang J F, Xin H T, et al. Subduction initiation in the southeastern Palaeo-Asian Ocean: Constraints from early Permian adakites in suprasubduction zone ophiolites, central Inner Mongolia, North China[J]. Geological Journal, 2020, 55(3): 2044-2061. doi: 10.1002/gj.3696
Liu Y S, Hu Z C, Gao S, et al. In situ analysis of major and trace elements of anhydrous minerals by LA-ICP-MS without applying an internal standard[J]. Chemical Geology, 2008, 257(1): 34-43. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/s0009254108003501
Anderson T. Correction of commen lead U-Pb analyses that do not report 204Pb[J]. Chemical Geology, 2002, 192(1/2): 59-79. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/222924679_correction_of_common_lead_in_u-pb_analyses_that_do_not_report_204pb
Yuan H L, Gao S, Liu X M. Accurate U-Pb age and trace element determinations of zircon by laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry[J]. Geostandards and Geoanalytical Research, 2004, 28(3): 353-370. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-908X.2004.tb00755.x
李怀坤, 耿建珍, 郝爽, 等. 用激光烧蚀多接收器等离子体质谱仪(LA-MC-ICPMS)测定锆石U-Pb同位素年龄的研究[J]. 矿物学报, 2009, 29(S1): 600-601. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWXB2009S1311.htm Le Maitre R W. Igneous Rocks: A Classification and Glossary of Terms 2nd Edition[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2002: 33-39.
Peccerillo A, Taylor S R. Geochemistry of eocene calc-alkaline volcanic rocks from the Kastamonu Area, Northern Turkeyu[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1976, 58(1): 63-81. doi: 10.1007/BF00384745
Martin H, Smithies R H, Rapp R, et al. An overview of adakite tonalite-trondhjemite-granodiorite(TTG), and sanukitoid: Relationships and some implications for crustal evolution[J]. Lithos, 2005, 79(1/2): 1-24. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S002449370400266X
Boynton W V. Geochemistry of the rare earth elements: meteorite studies[C]//Henderson P. Rare Earth Element Geochemistry. Elsevier, 1984: 63-114.
Sun S S, McDonough W F. Chemical and isotope systematics of oceanic basalts: implications for mantle composition and processes[C]//Sauders A D, Norry M J. Geological Society of London. Special Publication, 1989: 313-345.
Defant M J, Drummond M S. Derivation of some modern arc magmas by of young subducted lithosphere[J]. Nature, 1990, 347(6294): 662-665. doi: 10.1038/347662a0
Kelemen P B, Hangh K, Greene A R. One view of the geochemistry of subduction-related magmatic arcs, with an emphasis on primitive andesite and lower crust[J]. Treatise on Geochemistry, 2007, 3: 1-70. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780080959757003235
Claesson S, Vetrin V, Bayanova T, et al. U-Pb zircon age from a Devonian carbonatite dyke, Kola peninsula, Russia: A record of geological evolution from the Archaean to the Palaeozoic[J]. Lithos, 2000, 51(1): 95-108. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science?_ob=ArticleURL&md5=6cdb70f9b4446472f6199bd71ad85567&_udi=B6V6J-3YSY1JK-6&_user=6894003&_coverDate=03%2F01%2F2000&_rdoc=6&_fmt=high&_orig=browse&_origin=browse&_zone=rslt_list_item&_srch=doc-info(%23toc%235816%232000%23
吴元保, 郑永飞. 锆石成因矿物学研究及其对U-Pb年龄解释的制约[J]. 科学通报, 2004, 49(16): 1589-1604. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2004.16.002 Koschek G. Origin and significance of the SEM cathodoluminescence from zircon[J]. Journal of Microscopy, 1993, 171(3): 223-232. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2818.1993.tb03379.x
Pidgeon R T, Nemchin A A, Hitches G J. Internal structures of zircons from Archaean granites from the Darling Range batholith: Implications for zircon stability and the interpretation of zircon U-Pb ages[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1998, 132(3): 288-299. doi: 10.1007/s004100050422
Michael P A, Nick P. Generation of sodium-rich magmas from newly underplated basaltic crust[J]. Nature, 1993, 362(6414): 144-146.
张旗, 王二七, 王焰, 等. 燕山中晚期的中国东部高原: 埃达克岩的启示[J]. 地质科学, 2001, 36(2): 248-255. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0563-5020.2001.02.014 Atherton M P, Petford N. Generation of sodium-rich magmas from newly underplated basaltic crust[J]. Nature, 1993, 362(6416): 144-146. doi: 10.1038/362144a0
Rapp R P, Watson E B. Dehydration Melting of Metabasalt at 8-32 kbar: Implications for Continental Growth and Crust-Mantle Recycling[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1995, 36(4): 891-931. doi: 10.1093/petrology/36.4.891
Pearce J A, Lippard S J, Roberts S. Characteristics and tectonic significance of supra-subduction zone ophiolites[C]//Kokelaar B P, Howells M F. Marginal basin geology. Geological Society of London Special Publication, 1984: 77-94.
Pearce J A. Geochemical fingerprinting of oceanic basalts with applications to ophiolite classification and the search for Archean oceanic crust[J]. Lithos, 2008, 100(1/4): 14-48. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0024493707001375
薛怀民, 郭利军, 侯增谦, 等. 大兴安岭西南坡成矿带晚古生代中期未变质岩浆岩的SHRIMP锆石U-Pb年代学[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2010, 29(6): 811-823. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2010.06.016 鲍庆中, 张长捷, 吴之理, 等. 内蒙古白音高勒地区石炭纪石英闪长岩SHRIMP锆石U-Pb年代学及其意义[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2007, 37(1): 15-23. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ200701002.htm 杨俊泉, 张素荣, 刘永顺, 等. 内蒙古东乌旗莫合尔图石炭纪闪长岩的发现: 来自锆石U-Pb年代学的证据[J]. 现代地质, 2014, 28(3): 472-477. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2014.03.003 朱俊宾, 孙立新, 任纪舜, 等. 内蒙古东乌旗地区格根敖包组火山岩锆石LA-MC-ICP-MS U-Pb年龄及其地质意义[J]. 地球学报, 2015, 36(4): 466-472. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB201504012.htm 程新彬, 何付兵, 王玮, 等. 内蒙古东乌珠穆沁旗查干敖包花岗岩体时代、成因及地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2017, 31(3): 508-520. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2017.03.008 王树庆, 胡晓佳, 赵华雷, 等. 内蒙古京格斯台晚石炭世碱性花岗岩年代学及地球化学特征——岩石成因及对构造演化的约束[J]. 地质学报, 2017, 91(7): 1467-1482. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2017.07.005 Sengor A M C, Natal'in B A, Burtman V S. Evolution of the Altaid tectonic collage and Palaeozoic crustal growth in Eurasia[J]. Nature, 1993, 364: 299-307. doi: 10.1038/364299a0
刘建峰, 迟效国, 张兴洲, 等. 内蒙古西乌旗南部石炭纪石英闪长岩地球化学特征及其构造意义[J]. 地质学报, 2009, 83(3): 365-376. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE200903006.htm 公繁浩, 黄欣, 郑月娟, 等. 内蒙古西乌旗下二叠统寿山沟组海底扇的发现及意义[J]. 地质与资源, 2013, 22(6): 478-483. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1947.2013.06.007 Shang Q H. The discovery and significance of Permian radiolarians in the northern and middle Inner Mongolia, Northern Orogenic belt[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2004, 49(24): 2574-2579. doi: 10.1360/csb2004-49-24-2574
曾俊杰, 郑有业, 齐建宏, 等. 内蒙古固阳地区埃达克质花岗岩的发现及其地质意义[J]. 地球科学, 2008, 33(6): 755-763. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-2383.2008.06.003 张玉清. 内蒙古苏尼特左旗巴音乌拉二叠纪埃达克质花岗闪长岩类地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2009, 28(4): 33-42. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSKW200904005.htm 郝百武. 内蒙古那仁乌拉埃达克质花岗岩的发现、成因、锆石U-Pb年龄及其构造意义[J]. 矿物岩石, 2012, 32(1): 28-39. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6872.2012.01.005 刘军, 武广, 李铁刚, 等. 内蒙古镶黄旗哈达庙地区晚古生代中酸性侵入岩的年代学、地球化学、Sr-Nd同位素组成及其地质意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2014, 30(1): 95-108. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201401007.htm 邓晋福, 冯艳芳, 狄永军, 等. 岩浆弧火成岩构造组合与洋陆转换[J]. 地质论评, 2015, 61(3): 473-484. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP201503001.htm Safonova I, Kotlyarov A, Krivonogov S, et al. Intra-oceanic arcs of the Paleo-Asian Ocean[J]. Gondwana Research, 2017, 50: 167-194. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2017.04.005
薛建平, 苏尚国, 李成元, 等. 内蒙古索伦山地区蛇绿岩岩石单元地质特征、就位机制及时限[J]. 现代地质, 2017, 31(3): 498-507. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2017.03.007



 下载:
下载: