A geophysical technology for thematic geological mapping: Short period dense array
-
摘要:
以问题和需求为驱动的专题地质填图强调,针对某个主要地质体、沉积盆地、重要成矿带、地震带断裂系统等,采用现代化的技术手段开展针对性的专题调查和填图,以解决目标地质体结构、沉积盆地基底起伏、成矿地质体规模、断裂系统分布等重大问题。地球物理是专题填图不可缺少的手段之一,近10年发展起来的短周期密集台阵技术,因其布设灵活、应用广泛、精度高、成本低等特点备受关注。通过介绍短周期密集台阵发展现状,以及在城市、矿山、地震灾害区、沉积盆地等不同地质地貌条件下,利用短周期密集台阵进行近地表结构调查的应用实例,提出了该技术在专题地质填图中的应用前景和技术方案建议,力图通过短周期密集台阵的调查构建结构成像方法,丰富和完善专题填图的技术方法体系。
Abstract:Thematic geological mapping driven by the demands and problems emphasizes that for different geological environments such as a major geological body, sedimentary basin, important metallogenic belt and fault system, modern technical means can be adopted to carry out thematic geological investigation and mapping, so as to solve some major problems of above-mentioned geological environments.Geophysics, as one indispensable means in thematic mapping, its short-period dense array technology developed in recent 10 years has attracted much attention due to flexible layout, wide application, high precision and low cost.This paper mainly introduces the current situation of short period dense array, and its application to near surface structure investigation under different geological and geomorphic conditions such as cities, mines, earthquake and sedimentary basins, etc.The application prospect and technical scheme suggestions of its technology in thematic geological mapping is put forward to improve and perfect the method system of thematic geological mapping technology by means of constructing structure imaging method through the investigation of short period dense array.
-
区域地质调查和填图是地质工作的基础,也是衡量一个国家基础地质调查和研究程度及水平的重要指标,具有重要的战略意义。中国地质调查局高度重视基础地质调查与填图方式、方法的改革,树立“地质填图的过程就是科学研究的过程”的理念,确定“需求决定工作部署”、“问题决定调查方式”的工作思路,提升解决制约重大资源环境的基础地质问题和地球系统科学问题的能力。在中国地质调查局总工室和基础部的协调、领导下,由中国地质科学院地质研究所、地质力学所联合地调局六大区域地质调查中心开展了国际分幅和非国际分幅的中大比例尺专题试点填图,取得了重要进展。这是中国第一次较系统地构建填图方法体系。2019年11月6—7日,中国地质调查局召开了第三次全国区域地质调查工作会议。同时,成立了全国区域地质调查专家委员会,并组织了全国区调填图方法研讨会,来自全国地质行业近100人参加了培训和研讨,有30人在会议上交流发言,展现了区调改革在技术方法上的创新及取得的一批新进展、新发现,收效良好。
本专辑是本次会议成果的一次体现。本专辑共收录15篇论文,内容涉及短周期密集台阵方法在专题填图中的运用、遥感技术的使用等,以及地层、岩浆岩(侵入岩和火山岩)、变质岩、蛇绿混杂岩、构造、古生物、矿床等基础学科填图成果;还有论文,包括岩溶地区填图方法和地貌演变、造山带构造变形、侵入岩、蛇绿混杂岩、年轻变质事件及热泉的填图成果介绍,将在下一辑发表。这些论文集中展示了填图的成果。
(1)地球物理方法在填图中的运用。新填图方法和理念的运用是现代填图的重要内容,卢占武等介绍了利用短周期密集台阵进行近地表结构调查的应用实例,提出了该技术在专题地质填图中的应用前景,丰富和完善了专题填图的技术方法体系。李娜等介绍了高光谱遥感技术在中国西部基岩区填图中的应用,高光谱遥感数据对不同岩性段和岩相带、细小构造等区分能力突出,提高了地质调查填图的效率和质量。
(2)蛇绿混杂岩填图。蛇绿混杂岩的填图历经数十年的探索,也是造山带研究的基础数据来源,王国强等系统介绍了近十余年来北山造山带关键地段1:5万区域地质调查和综合研究成果,突出了造山带蛇绿混杂岩带填图方法在北山地区的实践和应用。付长垒等在大比例尺填图的基础上,在拉脊山识别出连续的洋岛海山火山-沉积组合序列,为造山带古洋盆构造演化研究提供了新思路。
(3)侵入岩区填图。侵入岩是造山带的重要组成部分,对它们的刻画和研究一直是造山带研究的基础性工作。苑新晨等对滇西澜沧江地区南段复式岩基进行研究,确定其是古特提斯封闭及保山-思茅地块碰撞的响应。卢鹏等在前期开展同位素填图的基础上,在东准噶尔乌伦古河地区识别出一套晚古生代富碱细晶花岗质岩墙,这期岩墙在整个中亚造山带中普遍发育,具有重要的构造环境指示意义。车亚文等在1:5万填图的基础上,对大兴安岭南段林西地区辉长闪长岩开展系统工作,确定其与蒙古-鄂霍茨克洋闭合引起的碰撞后伸展背景有关。王帅等报道了1:5万填图发现的迪彦庙SSZ型蛇绿岩北部晚石炭世马尼塔埃达克岩,确定其为洋内俯冲岩石组合的重要组成部分,表明古亚洲洋东段在晚石炭世处于洋内俯冲消减过程中。
(4)沉积岩区填图。沉积岩区填图是建立地层系统与格架、恢复区域和生命演化的重要手段。向忠金等通过对中越边界富宁—那坡地区的1:5万填图,查明早—中三叠世火山岩及其相关沉积序列,确定了扬子南缘地区印支期岛弧火山-沉积环境。石秋圆等报道了新建立的中—上三叠统卡尼阶岩石地层单位——嘎热扎地组,该工作填补了措勤中—上三叠统卡尼阶岩石地层单位的空白。安显银等报道了在西藏察雅地区侏罗纪红层中发现的恐龙化石,丰富了侏罗系恐龙的地理分布,有助于了解亚洲地区蜥脚类和兽脚类恐龙的早期演化和分异。
(5)变质岩区填图。变质岩填图是填图的难点,也是获得突破和新发现的主要基础。李猛等对东昆仑西段金水口岩群白沙河岩组的碎屑锆石进行研究,指出东昆仑早古生代可能存在一条近千千米的高压变质岩带。张连祥等通过莱阳地区1:5万变质基底填图,限定了胶北荆山群禄格庄组的原岩为古元古代,推测粉子山群小宋组与祝家夼组沉积时可能靠近被动大陆边缘的一侧,而禄格庄组更靠近岩浆岛弧的一侧,二者可能属于同时异相沉积的产物。
(6)复杂构造区填图。构造地质是中国填图中最薄弱的环节,复杂现象和关系的识别及构造过程的建立得益于详细地地质填图。张北航等在1:5万填图的基础上,厘定出狼山地区自晚侏罗世以来发育6期陆内变形,并认为先存构造和欧亚板块边缘自晚侏罗世以来不同方向的增生是控制狼山地区陆内变形的主要因素。柯昌辉等通过对白云鄂博矿田内褶皱及断层构造特征的剖析,确定了中元古代—晚古生代4期构造活动,对矿区深部及外围找矿工作具有重要的指导意义。
本专辑的文章是填图试点的部分成果及方法探索,希望能够为今后进一步开展中大比例尺(1:5万和1:2.5万)区域地质填图和专题填图起到推广和借鉴作用,成功的经验和失败的教训都是未来继续工作不可多得的财富。希望专辑中介绍的新方法、新理念能够逐步为广大一线工作认可,并运用到新时期地质调查工作中。
张 进 王 涛
中国地质科学院地质研究所
2020年12月20日
致谢: 本文在前期工作积累和撰写期间,与北京卫星环境工程研究所李志伟研究员、南方科技大学郭震老师、中国地质科学院梁峰博士进行了有益讨论,在此表示衷心感谢。 -
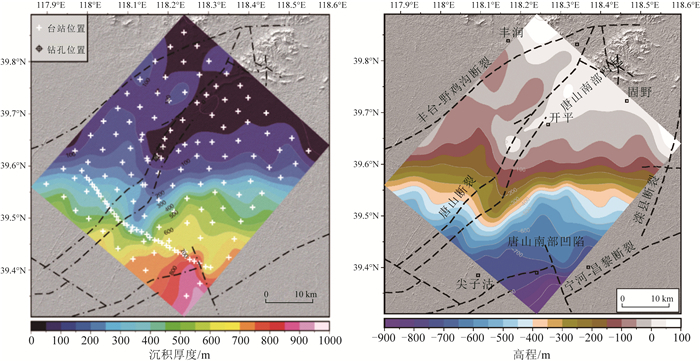
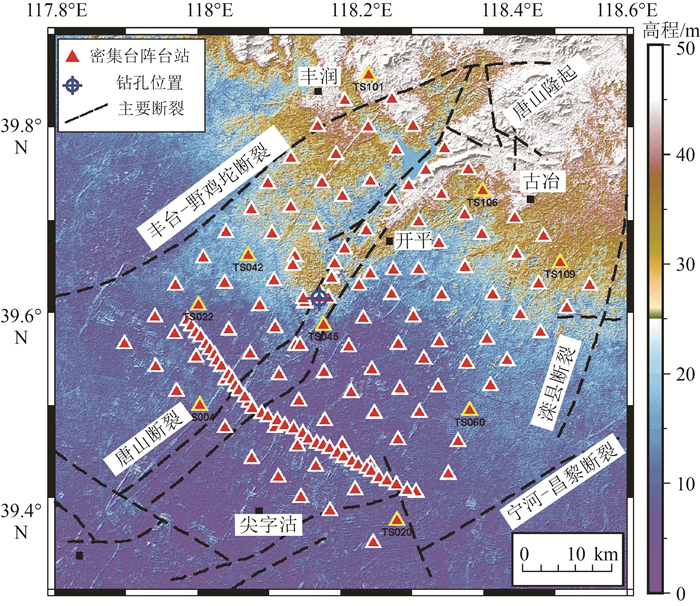
图 1 唐山断裂及邻区短周期密集台阵部署位置图[8]
Figure 1. Location of the short period dense array in Tangshan fault area
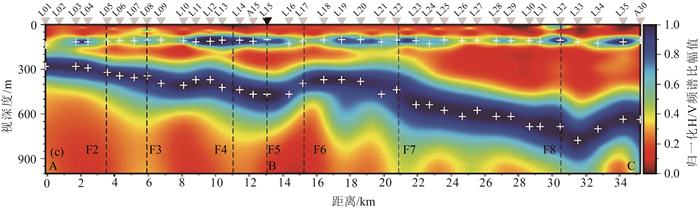
图 2 唐山断裂及邻区短周期密集台阵观测的浅层结构[19]
Figure 2. The shallow structure observed with short period dense array in Tangshan fault and adjacent area
图 3 唐山震区第四纪沉积厚度和基底埋深图[8]
Figure 3. Quaternary sedimentary thickness and basement of Tangshan earthquake area
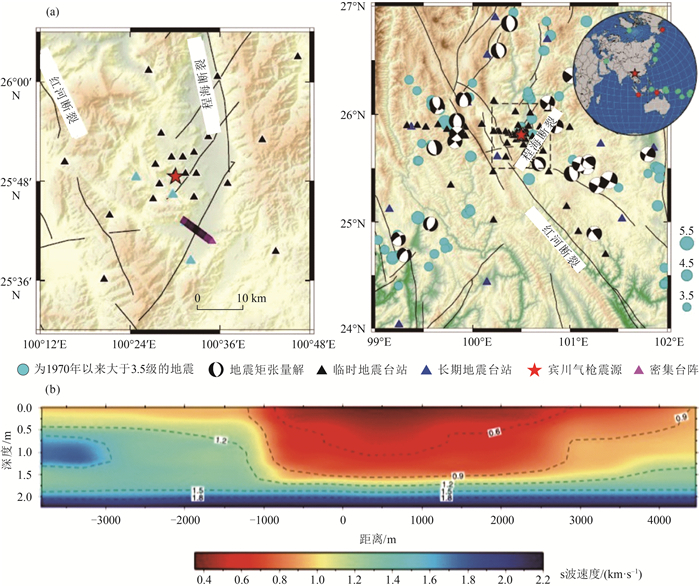
图 4 程海断裂短周期密集台阵位置及S波速度模型[22]
a—程海断裂位置与地震台站分布;b—程海断裂S波速度模型
Figure 4. Location of the short period dense array in Chenghai Fault area and shear wave velocity model
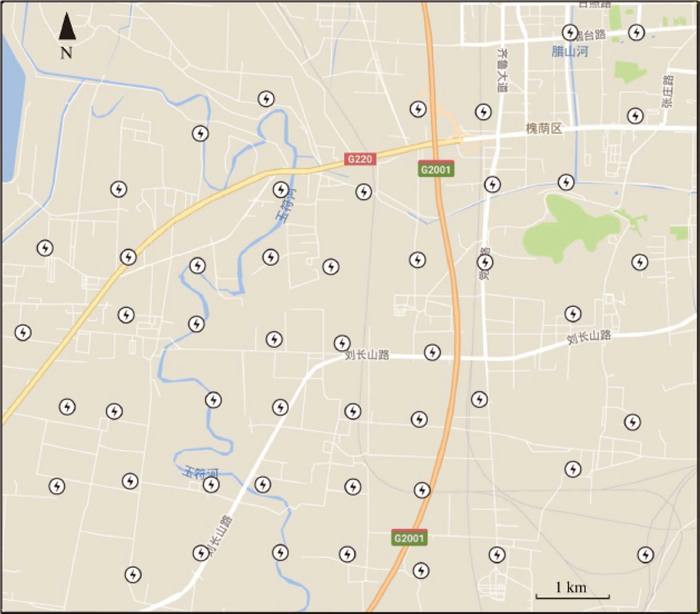
图 5 济南城区短周期密集台阵部署位置[9]
Figure 5. Location of the short period dense array in Jinan City
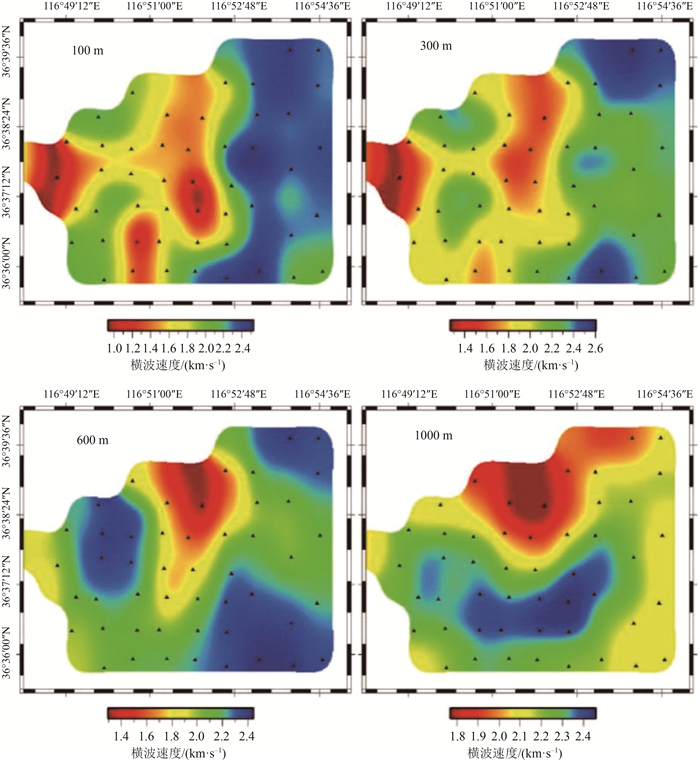
图 6 济南城区不同深度(100 m、300 m、600 m、1000 m)横波速度切片图[9]
Figure 6. Section of shear wave velocity model at different depths(100 m, 300 m, 600 m and 1000 m)in Jinan urban area
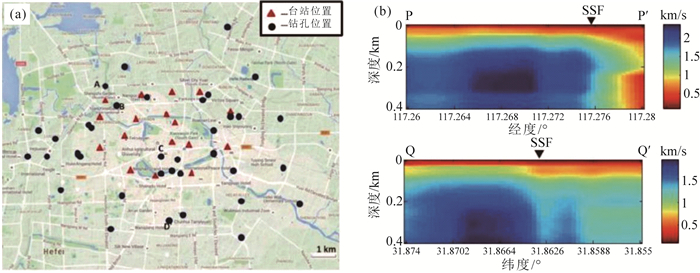
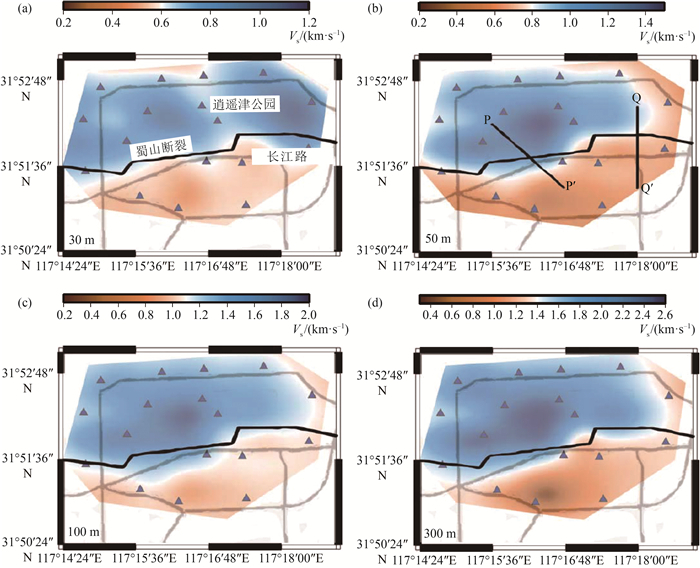
图 8 合肥市不同深度S波速度结构[24](a~d分别为30 m、50 m、100 m、300 m深度的结构)
Figure 8. The Vs structure of Hefei City at depths of 30 m, 50 m, 100 m and 300 m
图 9 新丰江水库库区地震台阵位置及浅层速度结构[25]
a—新丰江库区地理位置与地震台阵部署位置图;b—100 m、300m、450 m、650 m深度剪切波速度图像;c—剪切波垂直剖面图
Figure 9. The location of the dense seismic array and shear wave structure in Xinfengjiang Reservoir
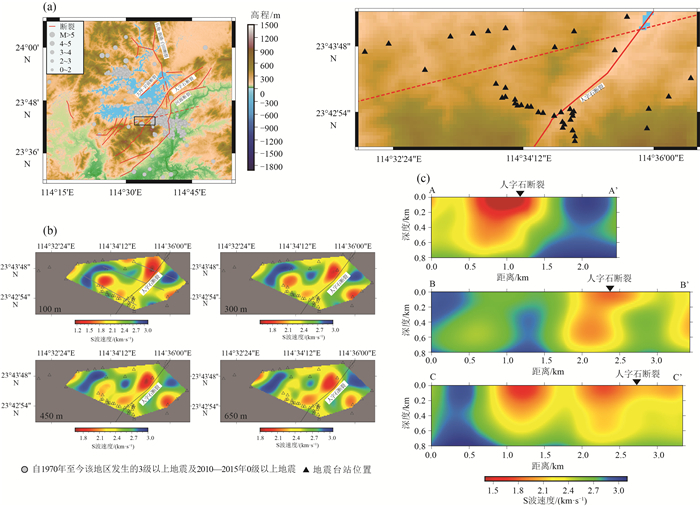
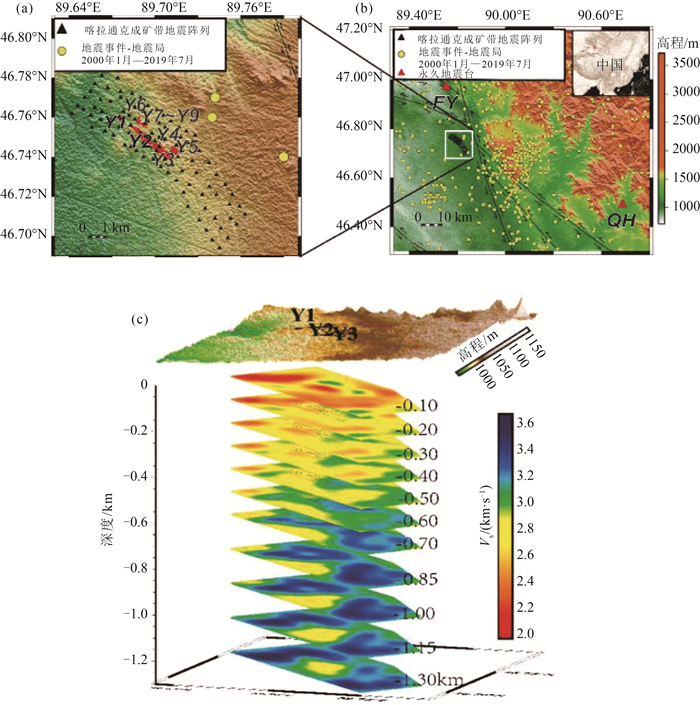
图 10 喀拉通克矿集区地震台阵部署位置及剪切波速度结构[26]
a—台阵分布;b—矿区地理位置和周围地震活动性分布;c—三维剪切波速度结构
Figure 10. Location of the seismic array and shear wave velocity structure in Karatungk mine area
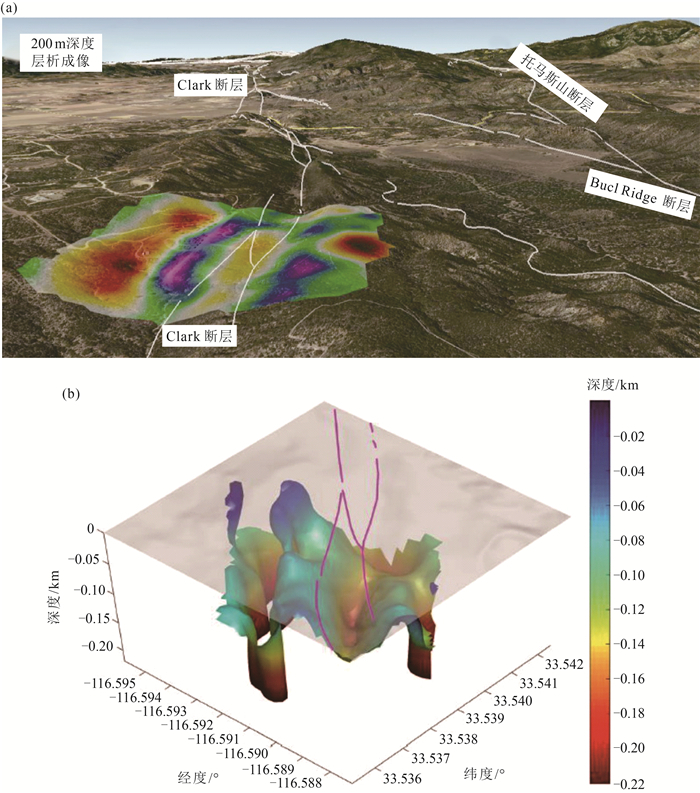
图 11 美国西海岸San Jacinto断层的浅层速度结构与地形数据、断裂信息融合实例[36]
Figure 11. Joint result of the shallow velocity, topographic data and fault information of the San Jacinto fault area in west coast of the United States
-
王涛, 计文化, 胡建民, 等. 专题地质填图及有关问题讨论[J]. 地质通报, 2016, 35(5): 633-641. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2016.05.001 孟贵祥, 吕庆田, 严加永, 等. "穿透性"探测技术在覆盖区地质矿产调查中的应用研究[J]. 地球学报, 2019, 40(5): 637-650. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB201905001.htm Lin F C, Li D Z, Clayton R W, et al. High-resolution 3D shallow crustal structure in Long Beach, California: Application of ambient noise tomography on a dense seismic array[J]. Geophysics, 2013, 78(4): 45-56. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/274518231_High-resolution_3D_shallow_crustal_structure_in_Long_Beach_California_Application_of_ambient_noise_tomography_on_a_dense_seismic_array?ev=auth_pub
Yao H J, Wang B S, Tian X B, et al. Preface to the special issue of dense array seismology[J]. Earthquake Science, 2018, 31: 225-226. doi: 10.29382/eqs-2018-0225-1
Inbal A, Clayton R W, Ampuero J P. Imaging widespread seismicity at midlower crustal depths beneath Long Beach, CA, with a dense seismic array: Evidence for a depth-dependent earthquake size distribution[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2015, 42(15): 6314-6323. doi: 10.1002/2015GL064942
Inbal A, Ampuero J P, Clayton R W. Localized seismic deformation in the upper mantle revealed by dense seismic arrays[J]. Science, 2016, 354(6308): 88-92. doi: 10.1126/science.aaf1370
Liu Z, Tian X B, Gao R, et al. New images of the crustal structure beneath eastern Tibet from a high-density seismic array[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2017, (480): 33-41. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0012821X17305587
Bao F, Li Z W, Tian B F, et al. Sediment thickness variations of the Tangshan fault zone in North China from a dense seismic array and microtremor survey[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2019, (185): 104045. https: //doi. org/10.1016/j. jseaes. 2019.104045 http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1367912019303979
梁锋, 高磊, 王志辉, 等. 利用背景噪声层析成像研究济南浅层横波速度结构[J]. 地学前缘, 2019, 26(3): 129-139. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201903020.htm Li Z W, Ni S D, Zhang B L, et al. Shallow magma chamber under the Wudalianchi Volcanic Field unveiled by seismic imaging with dense array[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2016, 43: 4951-496. doi: 10.1002/2016gl068895
张明辉, 武振波, 马立雪, 等. 短周期密集台阵被动源地震探测技术研究进展[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2020, 35(2): 495-511. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWJ202002014.htm Liu Z, Tian X B, Gao R, et al. New images of the crustal structure beneath eastern Tibet from a high-density seismic array[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2017, 480: 33-41. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2017.09.048
张路, 白志明, 徐涛, 等. 哀牢山地区新生代岩浆活动与掀斜式抬升: 来自短周期密集台阵观测的证据[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2020, 50(8): 1069-1082. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK202008003.htm Aki K. Space and time spectra of stationary stochastic waves, with special reference to microtremors[J]. Bull. Earthq. Res. Inst. , 1957, 35: 415-456. http://www.ams.org/mathscinet-getitem?mr=90217
Nakamura Y. A method for dynamic characteristics estimation of subsurface using microtremor on the ground surface[J]. Quarterly Reports, Railway Technical Research Institute, 1989, 30(1): 25-33. http://ci.nii.ac.jp/naid/10007555176
Brenguier F, Duputel Z, Shapiro N M. Towards forecasting volcanic eruptions using seismic noise[J]. Nature Geoscience, 2008, 1(2): 126-130. doi: 10.1038/ngeo104
Xu Z J, Song X D. Temporal changes of surface wave velocity associated with major Sumatra earthquakes from ambient noise correlation[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2009, 106(34): 14207-14212. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0901164106
Bensen G D, Ritzwoller M, Barmin M, et al. Processing seismic ambient noise data to obtain reliable broad-band surface wave dispersion measurements[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 2007, 169: 1239-1260. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.2007.03374.x
Bao F, Li Z W, Yuen D, et al. Shallow structure of the Tangshan fault zone unveiled by dense seismic array and horizontal-to-vertical spectral ratio method[J]. Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors, 2018, 281: 46-54. doi: 10.1016/j.pepi.2018.05.004
刘保金, 曲国胜, 孙铭心, 等. 唐山地震区地壳结构和构造: 深地震反射剖面结果[J]. 地震地质, 2011, 33(4): 901-912. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2011.04.014 郭慧, 江娃利, 谢新生. 对1976年河北唐山MS7.8地震地表破裂带展布及位移特征的新认识[J]. 地震地质, 2011, 33(3): 506-524. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2011.03.002 Yang H F, Duan Y H, Song J H, et al. Fine structure of the Chenghai fault zone, Yunnan, China, constrained from teleseismic travel time and ambient noise tomography[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 2020, 125: 1-14. doi: 10.1029/2020JB019565
林良俊, 李亚民, 葛伟亚, 等. 中国城市地质调查总体构想与关键理论技术[J]. 中国地质, 2017, 44(6): 1086-1101. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201706006.htm Li C, Yao H J, Fang H J, et al. 3D Near-surface shear-wave velocity structure from ambient-noise tomography and borehole data in the Hefei urban area, China[J]. Seismological Research Letters, 2016, 87(4): 882-892. doi: 10.1785/0220150257
王爽, 孙新蕾, 秦加岭, 等. 利用密集地震台网高频环境噪声研究广东新丰江库区浅层地下结构[J]. 地球物理学报, 2018, 61(2): 593-603. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX201802018.htm Du P X, Wu J, Wang J, et al. Imaging Karatungk Cu-Ni mine in Xinjiang, western China with a passive seismic array[J]. Minerals, 2020, 10(7): 601. doi: 10.3390/min10070601
田忠华, 刘福来, 许王, 等. 构造变形在变质岩专题填图中的作用及其意义——以辽南辽河群试点填图区为例[J]. 地质通报, 2017, 36(11): 1942-1952. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2017.11.005 童英, 郭磊, 王涛, 等. 同源花岗岩谱系填图——内蒙古二连宝德尔石林花岗岩填图试点[J]. 地质通报, 2017, 36(11): 1963-1970. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2017.11.007 薛怀民, 曹光跃, 刘哲. 陆相火山岩区岩性组合-岩相填图试验——以内蒙古西太仆寺破火山为例[J]. 地质通报, 2017, 36(11): 2030-2035. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2017.11.012 许欢, 柳永清, 旷红伟, 等. 燕山西部尚义盆地沉积岩区专题地质填图方法与成果[J]. 地质通报, 2017, 36(11): 1893-1918. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2017.11.002 闫臻, 王宗起, 付长垒, 等. 混杂岩基本特征与专题地质填图[J]. 地质通报, 2018, 37(2/3): 167-191. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=2018020301&flag=1 张进, 曲军峰, 张庆龙, 等. 基岩区构造地质填图方法思考、实践、探索[J]. 地质通报, 2018, 37(2/3): 192-221. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=2018020302&flag=1 Yao H J, Hilst R D V D, Hoop M V D. Surface-wave array tomography in SE Tibet from ambient seismic noise and two-station analysis-I. Phase velocity maps[J]. Geophysical Journal of the Royal Astronomical Society, 2006, 166(2): 732-744. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.2006.03028.x
Yao H J, Pierre G, Collins J A, et al. Structure of young East Pacific Rise lithosphere from ambient noise correlation analysis of fundamental- and higher-mode Scholte-Rayleigh waves[J]. Comptes Rendus Geoence, 2011, 343(8): 571-583. http://www.em-consulte.com/en/article/664890
Bowden D C, Tsai V C, Lin F C. Site amplification, attenuation, and scattering from noise correlation amplitudes across a dense array in Long Beach, CA[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2015, 42(5): 1360-1367. doi: 10.1002/2014GL062662
Mordret A, Roux P, Boué P, et al. Shallow three-dimensional structure of the San Jacinto fault zone revealed from ambient noise imaging with a dense seismic array[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 2019, 216: 896-905. doi: 10.1093/gji/ggy464



 下载:
下载: