A study of tectonic style of the polymetallic ore concentration area in Southern Lhasa terrane——Evidence from deep seismic reflection profile
-
摘要:
位于冈底斯成矿带中段的雄村、娘热地区,因近年来不断发现铁、铜等金属矿床,而逐渐被关注。但是由于缺少地球物理资料,该地区地壳精细结构未能取得清楚的认识。针对横过雄村-娘热矿集区130km深地震反射剖面及25km矿集区内部加密反射剖面的数据,进行了层析静校正、能量补偿、去噪、速度分析等数据处理,获得了雄村-娘热矿集区地壳结构的反射图像。结合本区地质资料,对矿集区深部结构进行了解释和推断,揭示了上地壳多条断裂及各类地质现象,认定断裂与岩浆流动上升方向有关,研究结果对矿集区成矿背景的研究具有一定价值。
Abstract:The Niangre and Xiongcun areas in the middle section of the Gangdise metallogenic belt have gradually attracted attention due to the continuous discovery of metal deposits such as iron and copper deposits in recent years. However, due to the lack of sufficient geophysical data, the fine structure of the crust in this area has not been clearly understood, which restricts the study of the ore-forming background of this area. Employing the data of 130km deep seismic reflection profile of the Xiongcun-Niangre ore concentration area and encrypted reflection profile inside 25km of the ore concentration area, the authors carried out data processing of tomographic static correction, denoising, energy compensation and velocity analysis, and obtained the reflection image crustal structure of the Xiongcun-Niangre ore concentration area. Based on the geological data of this area, the authors explained and inferred the deep structure of the ore concentration area, revealed multiple faults in the upper crust and various geological phenomena. It is determined that the fault is related to the direction of the magma flow. The results have certain value for the study of the oreforming background of the ore concentration area.
-
岩石圈是人类目前赖以生存的唯一区域,是人类生存的必要资源来源地,也是众多地质灾害发生的区域。了解地下地层年代及性质、活动断裂的大小分布及走向,可以更好地认识岩石圈的形成与演化,有利于对资源探测、火山地震等自然灾害的预知与预防,因此对岩石圈精细结构的探索必不可少[1]。截至目前,对于岩石圈的探测已有多种地球物理方法,其中地震探测最有效,已成为探测地球结构最重要的方法之一[2]。在地震探测领域中,作为人工地震方法之一的深地震反射剖面方法以探测深度大、分辨率高、探测精准可靠等优点,被认为是探测岩石圈精细结构行之有效的技术之一[3-6],在浅层和深层地质目标探测中均有许多应用[7-8]。
采用深地震反射技术对大型矿集区开展结构探测,可以很好地解决与地下复杂地质情况相关联的成矿背景等问题,如矿集区内部及邻区是否存在断裂、出露矿床是否由断裂控制、深部是否有岩浆上涌通道等。通过探测获得矿集区的地壳精细深部结构,揭示成矿成藏过程,对大陆演化及成矿过程十分重要[9-10]。
冈底斯成矿带位于青藏高原南部,是中国重要的多金属聚集区。位于冈底斯成矿带中段的雄村、娘热地区,因近年来不断发现铁、铜等金属矿床而逐渐被关注。但是由于缺少大量的地球物理资料,对该地区地壳精细结构未能取得清楚的认识,制约了该区成矿背景的研究和进一步的找矿突破。为深入了解矿集区及邻区地下精细结构与矿产分布关系,探查矿集区地下结构特点,本文通过对西藏雄村-娘热矿集区130km长的深地震反射剖面的数据处理,获得了精细的成果剖面,以揭示雄村-娘热矿集区地壳结构,并进一步探讨深部成矿背景。
1. 区域地质概况
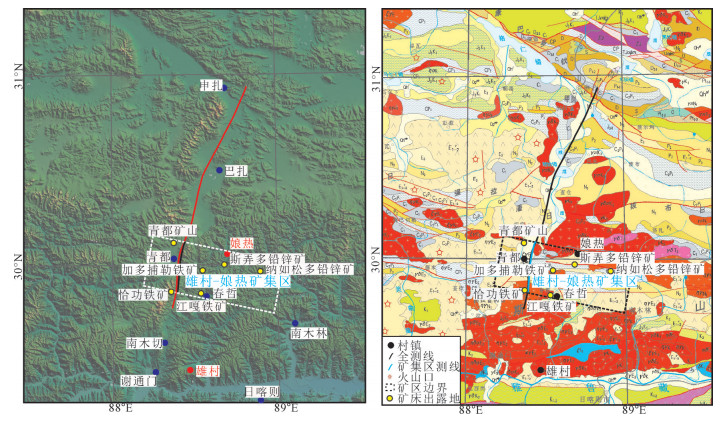
青藏高原是全球最年轻的碰撞造山地区,历经洋壳俯冲、陆陆碰撞、陆内俯冲等过程[11],不同期次、不同区域拼合,导致高原抬升不均匀,不同地体间地壳厚度发生变化[12]。冈底斯成矿带火山活动始于石炭纪,并在中生代发育,经历了多期次构造演化,矿产丰富,成矿集中,是目前青藏高原最大的巨型成矿带,有巨大的资源矿产潜力[13]。研究区处于拉萨地体内部,位于冈底斯成矿带中段,南北以雅鲁藏布江缝合带和班公湖-怒江缝合带为界[14-15],地形起伏剧烈,长约130km,横穿宽约25km的雄村-娘热矿集区(图 1)。
![]() 图 1 深地震反射剖面位置示意图[16]Figure 1. Regional location of the deep seismic reflection profile
图 1 深地震反射剖面位置示意图[16]Figure 1. Regional location of the deep seismic reflection profile区内汇集了加多捕勒铁矿床、恰功铁矿床、斯弄多铅锌矿床、纳如松多铅锌矿床等多金属矿床,平均海拔在4800m以上。工作区山体连绵起伏,高差变化大,存在多种基岩类型。
2. 数据采集及处理
数据采集是深反射剖面技术的保障,在这个环节如果取得高质量的数据才可以进行后续操作,否则会给之后的步骤带来很大困难。前人在采集中对各个参数的选取做过许多试验[17],正确选择参数方法是必要的。本次野外重点研究雄村-娘热矿集区附近地壳结构,针对目的层进行采集参数选择(表 1)。在通过雄村-娘热矿集区的25km区段,为增加浅层的数据覆盖,采用加密炮点、检波点的方式进行(表 2),在排列参数中按原测线50m道距布设基础上增加25m道距的加密炮,使剖面效果更精细。本次采样间隔为2ms,记录长度10s,小炮50kg药量,井深30m,中炮192kg药量,井深50m,部分难成井地区采用组合井。矿集区内浅层加密单炮为16kg药量,井深20m。
表 1 深地震反射剖面(130km)采集参数Table 1. Deep seismic reflection profile(130km)acquisition parameters类型 道数 放炮方式 排列参数 叠次/次 道距/m 炮距/m 偏移距/m 药量/kg 小炮 720 中间放炮 17975-25-50-25-17975 ≥60 50 250 25 50 中炮 900 17975-25-50-25-17975 1000 192 22475-25-50-25-22475 表 2 雄村-娘热矿集区加密段(25km)采集参数Table 2. Dense section(25km) acquisition parameters of Xiongcun-Niangre ore concentration area类型 方式 排列参数 叠次/次 道距/m 炮距/m 偏移距/m 药量/kg 浅层单炮 中间放炮 17975-12.5-25(50)-12.5-17975 ≥60 25 100 12.5 16 小炮 17975-12.5-50(25)-12.5-17975 50 250 50 中炮 17975-12.5-50(25)-12.5-17975 (25) 1000 192 22475-12.5-50(25)-12.5-22475 为使矿集区内部结构更清晰,本次共处理2条剖面,分别为全测线0~10s剖面和矿集区内0~10s剖面,以获得矿集区及其邻区的精细结构,查明断裂分布和岩浆活动痕迹及其自地表向深部的延伸情况。处理步骤包含建立观测系统、数据输入、静校正、能量补偿、去噪、反褶积、速度分析、动校正、叠加、偏移等,每一环节的质量都直接影响下一步骤,每一步都十分重要。
本文主要给出观测系统定义、静校正、地表一致性、叠前去噪、速度分析、叠加等的处理步骤。
2.1 观测系统定义
数据误差降到最低,按照测线偏向角大于8°时采用弯线要求,本次观测系统采用2D弯线进行定义,使用石油勘探软件ProMAX进行处理。将相关sps文件导入软件,按检波器信息文件、炮点信息文件及关系文件分别导入并计算,考虑面元覆盖次数、炮检距均匀分布、剖面叠加效果等因素,还应将激发点、接收点、CMP面元距离、条带数和纵横向尺寸等进行定义(图 2),最终进行观测系统的计算,输入到软件数据库中。
2.2 静校正
为消除地表起伏或地表层厚度与速度横向变化导致的误差,应用静校正使地表介质的影响降低。静校正基于方法原理大致分为高程静校正、折射静校正、层析静校正等[18],根据实际处理地区和具体问题选择合适方法。研究区地形复杂,折射界面不能连续识别,因此选择利用地震记录的初至时间求取速度模型,计算修正量的层析静校正方法。通过应用修正量消除地形起伏误差,为之后数据叠加和同相轴校平奠定基础(图 3)。
2.3 地表一致性
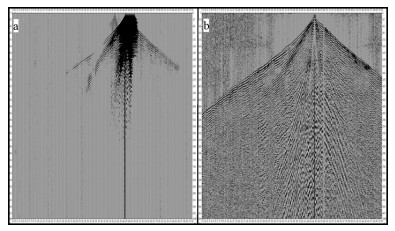
为消除地震波在传播过程中波前扩散和吸收因素的影响,以及地表条件变化引起的振幅变化,使地震波振幅更好地反映地下岩性的变化特点,处理过程中采用球面扩散补偿和地表一致性振幅补偿结合的方法,使横向和浅中深层能量变化合理,真实反映地下结构特点(图 4)。地表一致性振幅补偿采用能量分解模型,对所有的单炮进行统计,对每道计算其自相关函数,分别计算各炮点、检波点、共偏移距、CDP域的平均能量。再用这些参数计算补偿因子并作用于该道,这种方式可以消除震源能量差异、检波器耦合差异及能量衰减对反射波振幅的影响,有利于提高振幅保真度,使叠加剖面能量分布均匀。
2.4 叠前去噪
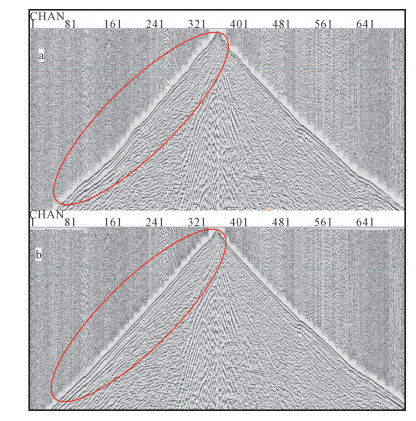
噪声压制十分复杂,不同地区、不同激发接收条件或不同岩性,随机干扰皆不相同,需浏览每一炮资料查看噪声的性质,对有针对性而不失有效信号的进行处理。对资料进行浏览分析,可以得出噪声主要为异常高振幅能量、声波、面波、线性干扰、直流电干扰、低频干扰等,不同噪声的性质不同,需要通过与有效信号某方面特性差异来区别并去除。在不影响有效信息的前提下,尽量去除干扰十分必要。图 5为去除声波的前后对比,对于一些明显掉道或干扰严重的个别道,可以通过剔道将其删除;图 6为去除低频噪声的前后对比。
2.5 速度分析
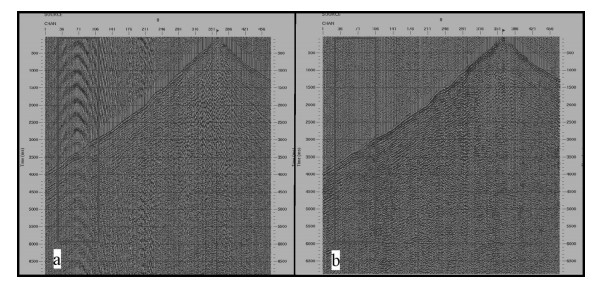
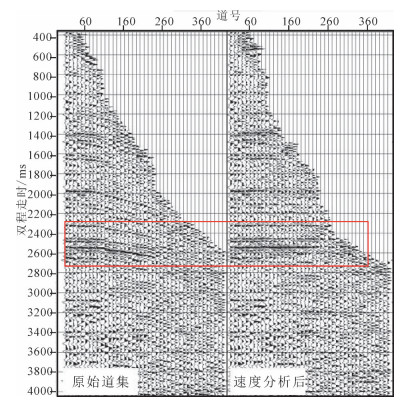
速度分析根据波到达时间与传播速度之间的关系进行尽量精确的速度参数提取,它关系到地震资料处理诸多环节的质量,提供了地下结构与岩性的信息,是十分重要的一步。速度分析是正常时差公式衍生出的:t2(x)=t2(0)+x2/V2,以t(0)为已知变量,通过点速度谱进行不断的尝试与观察,根据t(x)与V的双曲线变化,观察剖面地层是否被校平(图 7)。点速度时应根据能量团聚焦与层位对照来点,利用各波形条带观察同相轴和能量强的层位进行拾取,尽量将地层点速度后的地层实际同相轴校平,并不时调整,这样选取的速度是真实可靠的。
2.6 叠加
采用共中心点反射(CMP)叠加,在处理过程中尽可能将倾斜界面校平,使共中心点与共深度点反射(CDP)近似相等,一般按照CDP number对剖面进行排序建立水平模型。叠加不是一次性的,是一次次叠前修正、叠后处理等步骤后反复优化,最终叠加成图。
3. 主要反射特征与初步解释
3.1 全测线130km剖面反射特征与解释
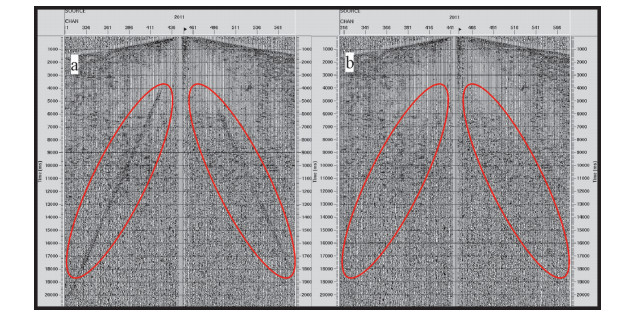
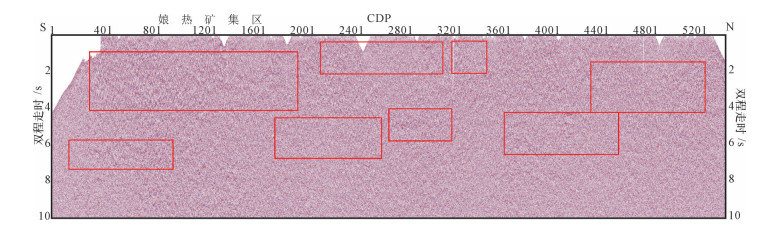
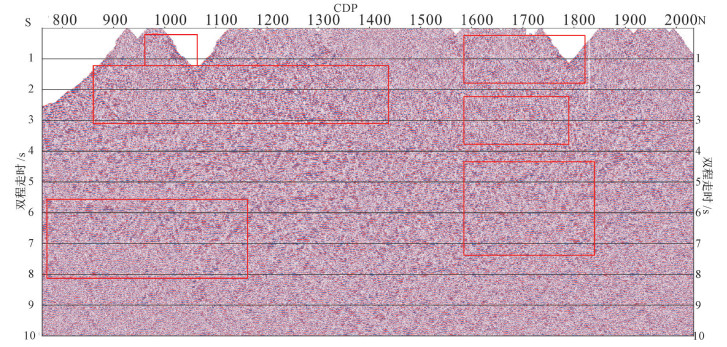
图 8为全测线130km剖面图,按CDP号从南到北1~5500排序,纵坐标为双程走时0~10s。
全测线剖面背景信息较强,有效信息不明显,但较强信号及反射同相轴依然可见。在CDP300~ 2000之间存在地下4s以上分布多个不连续且较短的同相轴,既有南倾轴也有北倾轴,包含断裂与岩层信息。个别轴一直延伸至地表,多个水平强能量轴附着于地下2s以上,地下6s左右位置具有长反射轴,并由南至北先南倾后北倾,可能为先走滑断裂后向北俯冲痕迹;矿集区位于CDP800~2000位置处,地下矿藏波阻抗与普通沉积岩及变质岩有差异,符合实际情况;在CDP2200~3200处,地下2s附近依然有较多复杂的强反射,有多个南倾且延伸至地表的同相轴,也有北倾向北俯冲的强反射,可见断裂F6,地表被新生代地层覆盖;在CDP3000附近6s处,可见极强水平连续能量轴,为地下花岗岩与其他岩石的边界,也推测为深部物质上涌到达的顶界面;在CDP3700~4600处,地下6s出现大量北倾反射轴,疑似出现大规模向北俯冲,在CDP4100附近地下6s有强反射能量且较集中,这与中国青藏高原羌塘地体和阿里地区发现的“深反射亮点”的现象与深度一致,亮点出现原因可能与岩浆的产出有关,这与矿集区附近的地质情况吻合[19];在CDP4400~ 5400之间,地下6s以上可见北倾短轴,向北俯冲痕迹明显。
结合上述反射特征、研究区地表岩性及可见断裂[20],进行解译成图,结果如图 9所示。
3.2 雄村-娘热矿集区25km剖面特征与解释
通过加密道与加密炮的实施,并通过数据处理,获得了雄村-娘热矿集区内部25km的深地震反射剖面(图 10),CDP为800~2000。
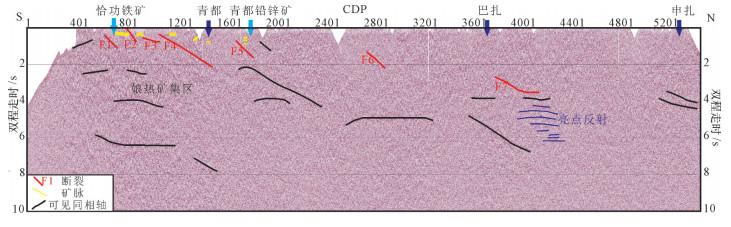
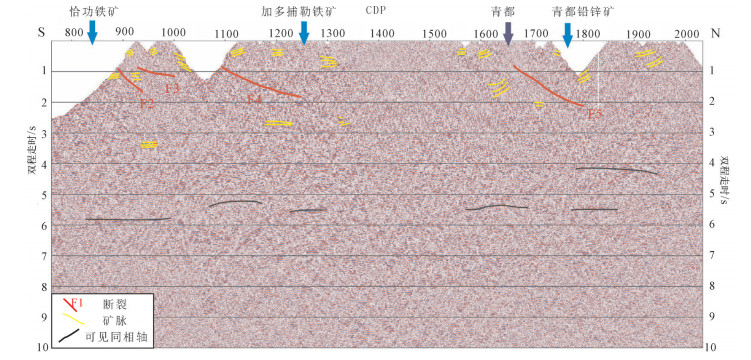
矿集区内部剖面可观察到上地壳至近地表的能量情况,在地下2s处可见多个倾向不同的同相轴,且大多为短轴叠置形态,矿集区存在4条明显的断裂。CDP1000~2000近地表存在近水平短强能量轴,CDP为1000和1200处表现为倾角较大的北倾能量轴,与地表可见的断裂位置相符;CDP为1700附近,地下2s可见较连续同相轴,同时在地下5~7s有可连续追踪的弧状同相轴。在地下6~8s处可见CDP为800~ 1000与1600~2000之间的同相轴不连续,表现为花状构造,有下方两侧向上部中间汇聚的趋势。图 11为雄村-娘热矿集区解释剖面。
从图 11可见,矿集区内矿床同相轴较明显,呈现短且清晰的叠置同相轴,且分布在断裂周围,深度较浅,以水平形态居多。矿床出露位置下方多存在断裂,与岩浆通过断裂进行上涌分布理论相符。地下6~8s处可见不连续同相轴,中间弱反射位置为岩浆流体上涌通道,表现为花状构造,有下方物质两侧通过弱反射位置向中间汇聚趋势。下部成矿物质进入上地壳后,与地壳熔融产物混合,为多金属矿产资源的形成提供了大量的物源支持。
可以推测,岩浆流体在上涌途中不断萃取围岩中各种金属物质,由于上覆岩层的隔挡,局部压力逐渐聚集增大,岩浆顶部压力过大时,含矿热液沿断裂通道向上运移到近地表,在与围岩接触部位形成矿体,经后期多次构造活动进一步迁移、富集成矿。成矿后,一些新生构造运动及新生断裂影响矿床的分布并逐渐出露地表,最终形成现今的地质环境。
4. 结语
本文利用层析静校正、地表一致性能量均衡、去噪、精细速度分析等方法,获得较清晰的全测线和矿集区内部的2个深地震反射剖面。由原始剖面可见,雄村-娘热矿集区及邻区地质构造复杂,通过对剖面进行解译讨论,清晰地揭示了上地壳多条断裂及各类地质现象;剖面上识别出多条断裂及矿床,初步认定这些浅部断裂控制了雄村-娘热矿集区的浅层矿床分布,认为断裂与岩浆流动上升方向有关;2条剖面揭示了冈底斯成矿带中段的部分上地壳结构,为矿脉分布背景的研究提供证据和资料。
致谢: 感谢中石化中南分公司第五物探大队对本次工作的数据采集。 -
图 1 深地震反射剖面位置示意图[16]
Figure 1. Regional location of the deep seismic reflection profile
表 1 深地震反射剖面(130km)采集参数
Table 1 Deep seismic reflection profile(130km)acquisition parameters
类型 道数 放炮方式 排列参数 叠次/次 道距/m 炮距/m 偏移距/m 药量/kg 小炮 720 中间放炮 17975-25-50-25-17975 ≥60 50 250 25 50 中炮 900 17975-25-50-25-17975 1000 192 22475-25-50-25-22475 表 2 雄村-娘热矿集区加密段(25km)采集参数
Table 2 Dense section(25km) acquisition parameters of Xiongcun-Niangre ore concentration area
类型 方式 排列参数 叠次/次 道距/m 炮距/m 偏移距/m 药量/kg 浅层单炮 中间放炮 17975-12.5-25(50)-12.5-17975 ≥60 25 100 12.5 16 小炮 17975-12.5-50(25)-12.5-17975 50 250 50 中炮 17975-12.5-50(25)-12.5-17975 (25) 1000 192 22475-12.5-50(25)-12.5-22475 -
Fowler C M R. The solid earth:an introduction to global geophysics[M]. Cambridge University Press, 1990.
Hubbert M K. Introduction to Geophysical Prospecting[M]. McGraw-Hill, 1960.
Brown L D. A New Map of Crustal 'Terranes' in the United States from COCORP Deep Seismic Reflection Profiling[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 1991, 105(1):3-13. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.1991.tb03439.x
Cook F A. Geometry of the Kapuskasing Structure from a Lithoprobe Pilot Reflection Survey[J]. Geology, 1985, 13(5):368-371. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1985)13<368:GOTKSF>2.0.CO;2
Nelson K D, Zhang J. A COCORP Deep Reflection Profile Across the Buried Reelfoot Rift, South-Central United States[J]. Tectonophysics, 1991, 197(24):271-293. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=10c3b1b6a97f26e02d026d40fcfe31be&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
高锐, 王海燕, 马永生, 等.松潘地块若尔盖盆地与西秦岭造山带岩石圈尺度的构造关系——深地震反射剖面探测成果[J].地球学报, 2006, 27(5):411-418. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-3021.2006.05.004 Pretorius C C, Trewick W F, Fourie A, et al. Application of 3-D Seismic to Mine Planning at Vaal Reefs Gold Mine, Number 10 Shaft, Republic of South Africa[J]. Geophysics, 2000, 65(6):1862-1870. doi: 10.1190/1.1444870
卢占武, 高锐, 李洪强, 等.深反射地震数据揭示的拉萨地体北部到羌塘地体南部地壳厚度的变化[J].中国地质, 2016, 43(5):1679-1687. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgdizhi201605016 高锐, 卢占武, 刘金凯, 等.庐-枞金属矿集区深地震反射剖面解释结果——揭露地壳精细结构, 追踪成矿深部过程[J].岩石学报, 2010, 26(9):2543-2552. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98201009003 王海燕, 高锐, 卢占武, 等.深地震反射剖面揭露大陆岩石圈精细结构[J].地质学报, 2010, 84(6):818-839. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2010.06.002 吴功建, 高锐, 余钦范, 等.青藏高原"亚东-格尔木地学断面"综合地球物理调查与研究[J].地球物理学报, 1991, 34(5):552-562. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5733.1991.05.003 李秋生, 彭苏萍, 高锐.青藏高原莫霍面的研究进展[J].地质论评, 2004, 50(6):598-612. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.2004.06.011 李廷栋.青藏高原地质科学研究的新进展[J].地质通报, 2002, 21(7):370-376. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2002.07.002 Chang C F, Zeng S L. Tectonic Features of the Mount Jolmo Lungma Region in Southern Tibet, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 1973, 1:1-12. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=d2282f34b61b96386f5b3fa3665683da&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
尹安.喜马拉雅-青藏高原造山带地质演化:显生宙亚洲大陆生长[J].地球学报, 2001, 22(3):193-230. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-3021.2001.03.001 潘桂棠等.青藏高原及邻区地质图[M].成都:成都地图出版社, 2004. 贾海青, 姜弢, 徐学纯, 等.辽西深反射地震勘探采集试验[J].吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2014, 44(4):1357-1368. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/cckjdxxb201404031 熊翥.复杂地区地震数据处理思路[M].北京:石油工业出版社, 2002. 卢占武, 高锐, 王海燕, 等.深地震反射剖面上的"亮点"构造[J].地球物理学进展, 2014, (6):2518-2525. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DQWJ201406006.htm 中国地质科学院地质研究所. 1:100万《中国地质图》[M].北京:地质出版社, 2016.



 下载:
下载: