An analysis of metallogenic physical conditions of the Yuqia eclogite-type rutile deposit in the North Qaidam
-
摘要:
鱼卡榴辉岩型金红石矿床位于柴北缘超高压变质带西侧,是青藏高原发现的第一个超大型金红石矿床。为研究该矿床的控矿因素和成矿机制,在详细的野外地质调查和岩相学研究的基础上,利用电子探针对该矿床榴辉岩中的各特征矿物进行分析。研究表明,粗粒块状高钛榴辉岩的石榴子石保存了较完整的成分环带,从核部到边部,石榴子石的化学成分、矿物包裹体的种类和粒度都具有明显的分带性;细粒片麻状低钛榴辉岩的矿物颗粒较小,石榴子石的成分环带较差。鱼卡榴辉岩的p-T演化特征反映,它们经历了深俯冲阶段的升温升压到早期折返阶段的升温降压,再到之后的降温降压的顺时针演化轨迹。榴辉岩中进变质矿物组合和生长环带的保存说明,榴辉岩的形成经历了相对快速俯冲和折返的动力学过程,钛成矿作用时金红石很少发生转变。超高压变质前后为金红石最主要的成矿期。
Abstract:The Yuqia eclogite-type rutile deposit is located on the west side of the northern margin of the Qaidam Basin UHP metamorphic belt. And it is the first ultra-large rutile deposit found on the Tibetan Plateau. In order to study the ore-controlling factors and metallogenic mechanism of this deposit, the authors conducted detailed field geological survey and petrographic study. The characteristic minerals in the eclogite of the deposit were analyzed by electron microprobe analysis. It is shown that the garnets of coarse-grained high-Ti eclogite have preserved relatively complete compositional zoning; from the core to the edge, the garnet has a distinct zonality in chemical composition, type and granularity of mineral inclusions. However, the mineral particles in the fine and gneiss low-Ti eclogite are smaller, and the composition of the garnet is poor. Characteristics of p-T evolution of Yuqia eclogite show that it experienced a clockwise evolutionary trajectory from the temperature and pressure rise of the deep subduction stage to the temperature rise and pressure decrease of the early exhumation stage and then to the decrease of both temperature and pressure. The eclogite belongs to the metamorphic mineral assemblage with the preservation of the growth zone, which suggests that the formation of eclogites went through a dynamic process of relatively rapid subduction and reentry exhumation.
-
Keywords:
- metallogenic conditions /
- rutile deposit /
- eclogite /
- Yuqia /
- North Qaidam
-
非洲大陆经历了多期多阶段复杂的构造、岩浆、变质和沉积作用过程,其形成和演化可追溯至太古宙。哥伦比亚超大陆、罗迪尼亚超大陆、冈瓦纳大陆和泛古陆的拼合与裂解,以及巨神海(Iapetus Ocean)、大西洋、印度洋、特提斯洋等大型洋盆的开启和关闭等一系列构造运动,奠定了非洲大陆的构造面貌。非洲大陆在漫长的地质演化进程中,形成了丰富的金、铬、铂族、铜、钴、锰、铁、铝土矿、铀、镍、钛、钒、金刚石、石墨、煤、磷、萤石、石油、天然气等金属、非金属矿产资源[1],也是中资企业境外矿业投资的重点地区之一。由于特殊的历史原因,非洲大陆的大地构造研究存在研究程度低、资料参差不齐、语言多样(英、法、德等)等问题,导致前人工作多聚焦于局部重点矿山和重要成矿区带。Petters[2]详细介绍了非洲大陆构造演化,Bouabdellah等[3]对北部非洲构造单元及特征进行了描述,但并未对非洲大陆的大地构造单元划分进行深入分析,对于非洲大陆的大地构造单元划分缺乏成熟的方案。
2005年以来,中国地质调查局武汉地质调查中心和中国地质调查局天津地质调查中心分别在北部非洲和南部非洲开展了十几年的地质-地球化学调查、地质图修编、区域成矿规律研究等工作,在阿特拉斯造山带、西非克拉通、东非造山带、刚果克拉通等地区的区域地质背景、构造演化历史、成矿作用特征等方面取得了一定认识。在此基础上,本文结合非洲其他重点地区的已有研究成果,以板块构造与地球动力学理论为指导,划分出非洲大陆特定构造阶段和大地构造环境中形成的、各个不同尺度、不同岩石-构造组合的构造单元,并简要总结主要构造单元的地质背景与特征,以期深化对非洲大陆的区域地质认识,服务于非洲大陆区域地质研究和成矿预测评价,并对今后中国-非洲国际合作地质调查的工作部署提供一定指导,对中资企业矿业投资提供有益借鉴。
1. 地质背景
非洲大陆是非常古老的大陆,其地球演化历史至少可追溯至3660 Ma[4]。非洲除西北部以外,大部分地区自前寒武纪起就是一个较稳定的隆起陆块,下伏太古宙—元古宙结晶基底[5-13]。非洲南部出露3000 Ma前尚未变质的基底,是世界上早前寒武纪地质记录保存最好的地区。非洲的石炭系—侏罗系与南美洲、印度、澳大利亚和南极洲的地层类似,故被认为与前述几个洲或国家曾同属于冈瓦纳古陆。
非洲大陆可分为特提斯构造域和冈瓦纳大陆,特提斯域仅分布在非洲西北部摩洛哥—突尼斯一带,属于阿尔卑斯褶皱带的一部分;除非洲西北部以外的大部分地区则属于冈瓦纳大陆[14]。一般认为,非洲冈瓦纳大陆地质演化经历了4个阶段[15]:①古老克拉通陆核的形成阶段(大于3500 Ma),古老陆核最早出现于古太古代后期的非洲中南部,以南非卡普瓦尔(Kaapvaal)克拉通的形成[4]为代表;②克拉通化阶段(3500~1650 Ma),非洲大陆总体经2500 Ma的沙姆瓦(Shamvaian)运动和1650 Ma的马永贝(Mayombe)运动完成克拉通化;③构造运动和陆内裂解阶段(1650~600 Ma),以650~620 Ma的泛非运动为代表,非洲大陆发生大范围的构造运动[13, 16];④盖层和大断裂发育阶段(600 Ma以来),泛非运动之后非洲大陆很少再受构造运动的影响,变形作用通常以宽阔的盆地形式出现,晚古生代以来的构造运动仅影响大陆的西北缘和东、西沿海地带[17-18]。白垩纪以来,非洲大陆内部出现大规模断裂,先后形成中西非裂谷和东非裂谷,是2条世界上最大的裂谷带[19-22]。
前寒武系在非洲分布最广泛,由变质程度不同的岩层组成,并受到不同程度的混合岩化作用和花岗岩化作用,其中以南非发育最全。南非的斯威士兰超群和津巴布韦的塞巴奎超群是非洲出露最老的岩层。
古生界大部分出露在非洲北部,海进范围最大可到达几内亚湾。寒武系以南非纳马群最具代表,此外少量分布于摩洛哥和亚喀巴湾[23-24]。奥陶系限于西北非和撒哈拉地区,大多为浅水砂岩沉积。海相志留系主要为笔石页岩,出露在西非和撒哈拉地区。泥盆系与志留系为海相连续沉积,分布广泛,层序完整,化石丰富。从石炭系上威斯特伐利亚阶开始转为陆相含煤沉积。
中生界以海相沉积为主,三叠系碳酸盐岩中夹有盐岩和石膏层。侏罗纪除发育高原玄武岩外,整个大陆几乎都处在剥蚀阶段,晚侏罗世海水沿索马里进入坦噶尼喀地区。白垩纪海侵范围扩大,沿东、西海岸一直伸向南非开普山,动物群属印度—太平洋和地中海型。在大陆内部撒哈拉、提贝斯提、苏丹等地为陆相和潟湖相沉积。白垩纪后期,海域范围缩小,在北非隆起上保存了一系列始新世—上新世湖相沉积,海相沉积仅出现于北非和大陆东、西海岸一带,为货币虫灰岩及有孔虫页岩、泥灰岩。第四纪有冲积物、海成阶地、沙漠沙、火山熔岩、凝灰岩等。
非洲大陆的岩浆活动强烈,尤以前寒武纪和新生代最强烈。太古宙岩浆活动表现为镁铁质岩和超镁铁质岩、花岗岩和过碱性岩类;中生代有高原玄武岩喷溢和金伯利岩侵位;新生代的火山作用分布在大陆内部和海域的一些岛屿上,尤其在东非和中非较集中[25]。
2. 构造单元划分
本次研究基于非洲大陆特有的地质背景和构造演化过程,在板块构造-地球动力学理论指导下,以地层划分和对比、沉积岩建造、火山岩建造、侵入岩浆活动、变质变形等地质记录,以及成矿规律和矿产资源预测需求为基础,以不同规模相对稳定的古老大陆区块和不同时期的造山系大陆构造相分析为主线,以特定区域构造时间形成的优势大地构造相的时空结构和存在状态为划分构造单元的基本原则。
基于以上原则,以法国地质调查局(Bureau de Recherches GGerches GR et MiniMini,简称BRGM) 发布的1 2000万非洲地质图为基础,综合前人研究成果,以区域地质图修编为抓手,根据关键地质事件的性质、特点、序列、时代和空间分布特征,聚焦各构造区带时间-空间-事件的差异,依据区域地球物理特征对已进行构造分区的单元及其边界进行再厘定。最终,本文将非洲大陆划分为2个一级构造单元、10个二级构造单元和55个三级构造单元(图 1;表 1)。
![]() 图 1 非洲构造单元划分图(各级构造单元序号注释同表 1)Figure 1. Tectonic units of African表 1 非洲构造单元划分Table 1. Tectonic units of African
图 1 非洲构造单元划分图(各级构造单元序号注释同表 1)Figure 1. Tectonic units of African表 1 非洲构造单元划分Table 1. Tectonic units of African一级构造单元 二级构造单元 三级构造单元 Ⅰ特提斯构造域 Ⅰ-1阿特拉斯褶皱造山带 Ⅱ冈瓦纳构造域 Ⅱ-1东非造山带 Ⅱ-1-1努比亚造山带 Ⅱ-1-2莫桑比克地盾 Ⅱ-1-3东非裂谷(东支) Ⅱ-1-4欧加登-索马里中新生代凹陷 Ⅱ-2撒哈拉克拉通 Ⅱ-2-1利比亚-埃及中新生代凹陷 Ⅱ-2-2乍得新生代凹陷 Ⅱ-2-3尼罗河新生代凹陷 Ⅱ-2-4达尔富尔-努巴山隆起 Ⅱ-3西非克拉通 Ⅱ-3-1雷圭巴特地盾 Ⅱ-3-2莱奥地盾 Ⅱ-3-3马恩地盾 Ⅱ-3-4陶德尼盆地 Ⅱ-3-5沃尔特盆地 Ⅱ-4环西非克拉通泛非活动带 Ⅱ-4-1图阿雷格地盾 Ⅱ-4-2贝宁—尼日利亚地盾 Ⅱ-4-3小阿特拉斯带 Ⅱ-4-4廷杜夫-拉甘盆地 Ⅱ-4-5罗克列德—毛里塔尼亚构造带 Ⅱ-4-6阿尔及利亚中南盆地 Ⅱ-4-7尼日尔盆地 Ⅱ-5大西洋沿岸断陷盆地带 Ⅱ-5-1非洲西北沿海盆地 Ⅱ-5-2赤道大西洋盆地 Ⅱ-5-3阿普第阶含盐盆地 Ⅱ-6乌班吉迪斯造山带 Ⅱ-7刚果克拉通 Ⅱ-7-1加蓬变质带 Ⅱ-7-2加蓬地块 Ⅱ-7-3西刚果造山带 Ⅱ-7-4安哥拉地块 Ⅱ-7-5卡奥科活动带 Ⅱ-7-6卡赛地块 Ⅱ-7-7卢弗里安构造带 Ⅱ-7-8伊鲁米德构造带 Ⅱ-7-9班韦乌卢地块 Ⅱ-7-10基巴拉构造带 Ⅱ-7-11东北刚果地块 Ⅱ-7-12乌干达地块 Ⅱ-7-13Rusizian构造带 Ⅱ-7-14北东基巴拉造山带 Ⅱ-7-15坦桑尼亚克拉通 Ⅱ-7-16乌本迪-乌萨迦兰构造带 Ⅱ-7-17安东吉-塔纳纳利佛地块 Ⅱ-7-18齐沃利造山带 Ⅱ-7-19贝马里武构造带 Ⅱ-8中南非泛非活动带 Ⅱ-8-1卢里奥盆地 Ⅱ-8-2南伊鲁米德构造带 Ⅱ-8-3赞比西活动带 Ⅱ-8-4达马拉活动带 Ⅱ-8-5那马奎活动带 Ⅱ-8-6开普造山带 Ⅱ-8-7纳塔尔活动带 Ⅱ-9卡拉哈里克拉通 Ⅱ-9-1卡普瓦尔克拉通 Ⅱ-9-2海斯活动带 Ⅱ-9-3林波波构造带 Ⅱ-9-4津巴布韦克拉通 Ⅱ-9-5马刚迪构造带 Ⅱ-9-6乔马-卡罗莫地块 一级构造单元划分:根据全球尺度板块构造研究[26],非洲大陆跨2个一级构造单元,分别是特提斯构造域和冈瓦纳构造域。将大陆西北缘摩洛哥到突尼斯的阿特拉斯造山带划为特提斯构造域,其余部分划为冈瓦纳构造域。
二级构造单元划分:根据非洲陆壳形成及演化历史,非洲陆块经新元古代泛非运动固化形成稳定陆壳,其后板块内部裂解形成断陷盆地,接受古生代—新生代沉积。因此,笔者将新元古代泛非运动作为标志性构造运动,以独立运动的板块及板块之间的构造带作为二级构造单元的划分依据,参照国内外区域研究成果[3, 27-33],共划分出10个二级构造单元。包括4个前新元古代克拉通(大于1000 Ma):撒哈拉克拉通、西非克拉通、刚果克拉通和卡拉哈里克拉通;4条新元古代(1000~520 Ma)活动带:东非造山带、乌班吉迪斯造山带、环西非克拉通泛非活动带和中南非泛非活动带;1条中新生代造山带,即阿特拉斯褶皱造山带;1个中新生代沉积盆地带,即环大西洋断陷盆地带。
三级构造单元划分:在造山带/活动带二级构造单元内部,根据区域地质发展过程的总体特征和优势大地构造相的时空结构,以结合带、弧盆系和夹持于其间的地块作为三级构造单元,构成造山带/活动带构造单元划分的基本骨架;在克拉通二级构造单元内部,则依据不同演化阶段不同基底和盖层的岩石建造组合,以及表壳岩的火山-沉积记录、岩石组合、地球化学、热事件等特征,将克拉通内部进一步划分为地盾、造山带、凹陷等55个三级构造单元[34-42]。
3. 主要构造单元特征
3.1 Ⅰ-1阿特拉斯褶皱造山
带阿特拉斯褶皱造山带位于非洲大陆西北缘,地处摩洛哥、阿尔及利亚、突尼斯的北部,属于特提斯构造域的一部分。该造山带为一套新生代陆内褶皱逆冲带,地层单元主要为中生代地层,其中三叠纪地层最大厚度达5 km,主要由一套红层碎屑岩(砾岩、砂岩、粉砂岩、泥岩)系列和碳酸盐层组成[43]。
造山带的形成主要分为2个阶段:①三叠纪—晚白垩世大陆张裂形成了阿特拉斯裂谷,以及中生代盆地沉积作用;②晚白垩世—全新世盆地反转,阿特拉斯裂谷开始上升,边界断层沿中生代薄岩层插入相邻地区形成逆冲断层[44]。
3.2 Ⅱ-1东非造山带
3.2.1 Ⅱ-1-1努比亚造山带
努比亚造山带位于东非造山带北部,是晚前寒武纪—早古生代的东非造山带北缘部分,分布在红海西岸埃及至索马里一带。地质年代和同位素研究[45]表明,努比亚造山带主要是由一系列新元古代绿岩地体叠加推覆形成的增生型造山带;主要岩性为镁铁质—长英质岛弧熔岩、火山碎屑岩和相关沉积岩的变质(绿片岩相)火山沉积型层序,由解体的蛇绿质杂岩分隔开[46-47]。构造期早、中、晚期,不同侵入体切割了这些层序。尽管已经发现了可以追溯至1025 Ma的更老原岩,但火山沉积型层序基本属于新元古代(800~700 Ma)。620~530 Ma,区内大规模长英质岩浆活动,形成大量造山后稀有金属花岗岩和花岗伟晶岩[48-50]。
努比亚造山带的构造特征主要表现为一系列弧-弧缝合带、弧-陆缝合带和区域变形带(如褶皱-冲断带、冲断层带和走滑断层系)[51-55]。弧-弧缝合带主要为反映洋盆发育的蛇绿岩带,具体包括Allaqi-Heiani-Onib-Sol Hamed-Yanbu(YOSHGAH)缝合带、Nakasib-Bir Umq缝合带、Baraka-Tulu Dimtu缝合带、Adola-Moyale缝合带等[45, 56]。弧-陆缝合带主要表现为莫桑比克洋盆消失后,岩浆弧与大陆板块的拼接。努比亚造山带的区域变形带大多为北向或北西向的剪切带。
大量蛇绿岩指示努比亚造山带经历了长期的造山演化历史[57]:从大陆裂解形成洋盆(870~800 Ma)到洋壳俯冲形成岛弧(800~670 Ma),再到后造山阶段(650~600 Ma)努比亚造山带与前新元古代东西部的大陆板块相撞[58-60],使阿拉伯-努比亚造山带发生变形,产生了沿正北走向的缩短区域和多数北西向左旋走滑断层及少量北东向右旋走滑断层[61],最后在后造山阶段(600~550 Ma)经历新生地壳的逃逸构造、走滑剪切、张性断裂等一系列的构造演化过程[45, 62]。
3.2.2 Ⅱ-1-2莫桑比克地盾
莫桑比克地盾呈南北向展布,从南端的莫桑比克北部和马拉维穿过坦桑尼亚和肯尼亚境内延伸到苏丹、埃塞俄比亚及红海海岸的索马里北部。莫桑比克地盾处于一个巨大的板块碰撞造山带的低地壳水平面上,其地盾的泛非地层或已经历高级变质作用,或已在严重受侵蚀的碰撞带中被侵蚀掉。莫桑比克地盾的地层年龄,并不仅限于泛非时期;岩石的发育时间仍处于推测阶段,它们可能处于太古宙或基巴拉时期。
3.2.3 Ⅱ-1-3东非裂谷(东支)
东非裂谷(东支)位于东非造山带中东部,主要分为阿法尔(Afar)坳陷和埃塞俄比亚主裂谷(MER)2个分区。2个分区受地质构造影响,其演化及产物明显不同。阿法尔坳陷及周缘为始新世—中新世火山岩、中新世火成岩、上新世火山岩及第四纪火山岩和沉积岩。坳陷北部为北北西向的达纳基尔洼地(Danakil),洼地内主要为一套海相蒸发岩,由最近30 Ma以来海水重复入侵形成,近年发现多处钾盐矿床,具有重要的经济意义[63]。MER可分为3部分,北MER从阿法尔拗陷边界往南到Koka湖地区,南MER北边界为北纬7°的Awasa地区,中MER介于两者之间。裂谷地区由上隆的基底及上覆沉积岩组和始新世—近代火山岩组成。
3.2.4 Ⅱ-1-4欧加登-索马里中新生代凹陷
欧加登-索马里中新生代凹陷位于东非造山带东部,为跨埃塞俄比亚东部与索马里的中新生代盆地,面积大于35×104 km2,其形成与伸展构造有关,自晚古生代以来间歇性地演化至新近纪[64]。欧加登盆地北部、西北部为埃塞俄比亚主裂谷所限,西部、西南部为前寒武纪结晶基底,南部、东部、北东部与在统一区域背景上发展起来的索马里盆地相接[64]。盆地最深处沉积厚度达10 km,时代从晚古生代—古近纪,为深海—浅海相和陆相沉积物。已有资料显示,该凹陷盆地为油气资源的远景区[65]。
3.3 Ⅱ-2撒哈拉变克拉通
撒哈拉变克拉通[66],表示后期造山活动改造活化的克拉通,但局部的流变学、年代学和同位素特征依然识别出克拉通特征。受后期活化改造影响,撒哈拉变克拉通可进一步划分出Ⅱ-2-1利比亚-埃及中新生代凹陷、Ⅱ-2-2乍得新生代凹陷、Ⅱ-2-3尼罗河新生代凹陷和Ⅱ-2-4达尔富尔-努巴山隆起4个三级构造单元。
3.3.1 Ⅱ-2-1利比亚-埃及中新生代凹陷
利比亚-埃及中新生代凹陷位于撒哈拉克拉通东北部,跨越利比亚北部和东部及埃及尼罗河以西的大部分地区,同时包含苏丹西北部地区。该凹陷被Al Kufrah盆地大面积覆盖,东南侧出露Uweiant-Kamil构造窗。
AlKufrah盆地是变撒哈拉克拉通东北部一个北东—南西向延伸的坳陷,面积约40×104 km2,横跨利比亚东南部、苏丹西北部和乍得东北部。该盆地是北部非洲地区大型古生代沉积盆地,也是重要的油气资源盆地。该盆地从前寒武纪一直活动到近代,中部被古生代和中生代碎屑沉积地层覆盖,利比亚境外最大沉积厚度为4500 m[67]。其中寒武系、奥陶系和泥盆系是重要的含油气地层。晚奥陶世(Hirnantian)冰川沉积是区域上的关键油气藏,但其具有非常复杂的结构。此外,下伏的中奥陶统砂岩也是重要的储集层,其中晚奥陶世冰川不整合面与上覆的下志留统页岩盖层相互作用形成所谓的“潜山”地层圈闭。下志留统页岩是“冰期储集层”重要的烃源岩和盖层[68-70]。
Uweiant-Kamil构造窗位于利比亚、埃及和苏丹三国接壤处。未变形的古生代—中生代地层和火山岩-侵入岩不整合覆盖于下伏前寒武纪结晶基底之上。基底中主要为3160~590 Ma的前寒武纪岩石,包括TTG片麻岩和少量辉长质-辉绿质片麻岩组成的变质侵入杂岩、强烈混合岩化的变质沉积岩和正片麻岩及大量埃迪卡拉纪花岗岩类,可能代表了3.3~3.1 Ga的弧岩浆活动[71-72]。直到新元古代泛非期,花岗岩活动重新活化,形成大量750~600 Ma的新生地壳物质[71-72]。混合岩化片麻岩被少量同构造期的S型花岗岩、晚构造期闪长岩、花岗闪长岩和黑云母花岗岩侵入,各个时代的岩脉和次火山岩均较常见。前寒武纪—泛非期,受多期(至少3期)不同强度的变形作用影响,形成大量剪切带、褶皱和逆冲推覆断层。
3.3.2 Ⅱ-2-2乍得新生代凹陷
乍得新生代凹陷位于撒哈拉克拉通西南部,主体位于非洲中部的乍得共和国,少部分跨入尼日尔、尼日利亚和中非共和国。乍得新生代凹陷的构造属性为一个活动的陆内盆地,根据沉积旋回和不整合界面,将盆地内白垩系沉积序列分为:①Albian Asu河群;②Cenomanian晚期—Santonian早期的Cross River群,由海相Nkalagu组和边缘海相砂岩组成;③Sanantonian晚期煤系层序[73]。新近纪—第四纪,在直径约500 km的范围内沉积了厚约500 m的新生代沉积物。乍得新生代凹陷的形成与25 Ma前的周缘抬升有关,一个约500 km宽的环形山麓将盆地与11个离散的隆起(ASL最高达3 km)分开[74]。地震反射资料显示出明显的断层褶皱特征,其主要构造方向为北东—南西向,与贝努伊海槽表层构造模式平行。盆地内的断裂包括基底卷入断裂和拆离断裂。褶皱为简单对称构造,局限于盆地深部。同时伴随少量挤压构造。侵入体的存在使构造模式更复杂。明显的构造和地震成因地层表明该盆地为裂谷成因。此外,沉积学、地震构造等特征表明,乍得新生代凹陷迈杜古里地区具有良好的白垩系油气远景,具有较高的构造和地层圈闭潜力[75]。
3.3.3 Ⅱ-2-3尼罗河新生代凹陷
尼罗河新生代凹陷位于撒哈拉克拉通东南部,与东非造山带相邻,主要分布于非洲中部苏丹和南苏丹两国,整体呈北西—南东向,北西端分别向北西和北分为两支,南东端呈楔形。穆格莱德(Muglad)盆地是尼罗河新生代凹陷三级构造单元的主体。穆格莱德盆地出露面积超过12×104 km2,最大沉积厚度超过15 km,是在前寒武系结晶基底之上发育的中—新生代大型陆内被动裂谷盆地,主体由一系列凸起和凹陷组成,主构造线方向为北西—南东[76-77]。受冈瓦纳大陆裂解、非洲大陆周缘大西洋、印度洋、红海张裂等构造事件影响,该盆地经历了早白垩世Abu Gabra组沉积期、晚白垩世达尔富尔群沉积期及新生代Nayil-Tendi组沉积期三大同裂谷作用阶段。早白垩世盆地原型为多个地堑及半地堑分隔式分布,是与大西洋张开有关的伸展应力场作用的产物;晚白垩世Darfur群沉积时期盆地原型为地堑及半地堑继承发育,但沉积中心东移,是与印度洋张开有关的伸展应力场作用的产物;新生代Nayil-Tendi组沉积时期原型盆地主要为发育在Kaikang坳陷的地堑、半地堑,是与红海张开有关的伸展应力场作用所致[78-79]。依据3期裂谷作用在各凹陷的发育程度差异及构造沉降和沉积充填过程的不同,将各凹陷裂谷叠合方式划分为早断型、继承型与活动型3种类型。3期裂谷作用在各凹陷的时空叠合差异控制了各凹陷油气成藏条件及富集规律的不同,早断型凹陷成藏组合以下部成藏组合为主,继承型以中部成藏组合为主,而活动型凹陷以上部成藏组合为主。
3.3.4 Ⅱ-2-4达尔富尔-努巴山隆起
达尔富尔-努巴山隆起位于撒哈拉克拉通中部,为一呈北西—南东向横跨撒哈变拉克拉通的三级构造单元,跨越利比亚、尼日尔、乍得、苏丹、南苏丹等国家。自北西向南东依次可识别出迈尔祖格克拉通(Murzuq Craton)、提贝斯提地块(Tibesti Massif)、达尔富尔地块(Darfour Massif)、努巴山(Nuba mountains)等地质构造单元。迈尔祖格克拉通与西侧的图阿雷格地盾(Tuareg Shield)相邻,是一个剥蚀残余的古生代和中生代沉积盆地[80]。提贝斯提地块横跨利比亚南部和乍得北部,主要为上Tibesti岩群和下Tibesti岩群(约900 Ma)2套绿片岩相—角闪岩相变质表壳岩系。这2套岩群的岩石组合主要为变沉积岩和变火山岩,上部不整合覆盖砂岩、页岩和碳酸盐岩[81]。达尔富尔地块位于乍得盆地以东、乌班吉迪斯造山带以北,与乍得盆地之间有一条明显的重力异常带。达尔富尔地块主要出露前寒武纪变克拉通岩石,局部可见新生代火山岩露头[82]。努巴山位于白尼罗河以西,主要表现为高出海平面约600 m的广阔准平原,岩性主要为绢云母-绿泥岩片岩、石墨片岩、石英岩、燧石、大理岩等,局部可见变辉长岩和蛇纹岩。区内褶皱变形常见,同时发育大量断裂构造,形成地堑-地垒相间的格局[83]。
3.4 Ⅱ-3西非克拉通
3.4.1 Ⅱ-3-1雷圭巴特地盾
雷圭巴特地盾位于西非克拉通北部,其南部为陶德尼盆地,东北部为廷杜夫盆地,西部为毛里塔尼亚构造带。雷圭巴特地盾分为东、西2套地质单元,二者被一个剪切带分隔[84-85]。地盾西部主要由中太古代—古元古代岩石组成,主要为一套混合片麻岩和绿岩组合;地盾东部由古元古代—新元古代岩石组成,主要为绿岩和新元古代火山沉积岩。
3.4.2 Ⅱ-3-2莱奥地盾
莱奥地盾位于西非克拉通南部,其北部为陶德尼盆地,东部为沃尔特盆地,西部为马恩地盾。地层单元主要为古元古界比里姆(Birimian)岩系及其上覆的古元古界塔库瓦(Tarkwaian)岩系[86-87]。比里姆岩系分为以变质火山岩为主的上比里姆群和以变质沉积岩为主的下比里姆群,两者为整合接触。下比里姆群底部以千枚岩和杂砂岩为主,向上变为千枚岩、浅变质凝灰岩、杂砂岩和长石砂岩;上比里姆群由变质的玄武岩、安山质熔岩组成。塔库瓦岩系为河流相的沉积环境,主要由砾岩、角砾岩、粗砂岩、石英岩和千枚岩组成[88]。
3.4.3 Ⅱ-3-3马恩地盾
马恩地盾位于西非克拉通西南部,其东部为莱奥地盾,西部为罗克列德构造带。地盾主要由利昂期(Leonian)(3400~2900 Ma)和利比里亚期(Liberean)(2900~2600 Ma)岩石组成,可细分为基底杂岩和表壳岩带[27]。基底杂岩由花岗岩、片麻岩和混合岩组成。太古宙基底主要为凯内马(Kenema)岩群,为英云闪长岩-奥长花岗岩片麻岩-混合岩组合,获得3100 Ma和3400 Ma的Rb-Sr测年结果,代表本区最古老的岩石。表壳岩带则由绿岩和变质沉积岩组成。比里姆绿岩带形成于2200~2000 Ma,代表了幼年期增生地体系列。其三分之二为花岗岩和片麻岩,其余为变质沉积岩和变质火山岩,包含枕状玄武岩熔岩、安山质-英安质火山碎屑岩和熔岩、火山碎屑浊积岩、含锰硅质岩和复理石型浊积岩。晚期花岗岩岩浆作用与高绿片岩相的区域变质作用伴生[88]。
3.4.4 Ⅱ-3-4陶德尼盆地
陶德尼盆地位于西非克拉通中部,将西非克拉通大面积结晶基底覆盖,盆地北部为雷圭巴特地盾,南部为莱奥地盾,东部为图阿雷格地盾,西部为毛里塔尼亚构造带。该盆地记录了中元古代—石炭纪的不连续沉积历史,其沉积地层总厚度为2000~4000 m,平均厚度为1250 m[89-90]。最新的Re-Os年龄(1107±12 Ma、1109±22 Ma和1105±37 Ma)表明,陶德尼盆地基底岩石的时代为中元古代[90]。盆地的地层总体为一套海相碎屑沉积岩,含少量白云质石灰岩及厚层叠层石灰岩[91]。
3.4.5 Ⅱ-3-5沃尔特盆地
沃尔特盆地位于西非克拉通东南部,其东部为贝宁-尼日利亚地盾,西部为莱奥地盾。该盆地为缓倾的向斜盆地,其中最古老的沉积物出露在边缘,年轻的沉积物主要位于盆地中央。盆地沉积地层主要为Voltain超群,分为底部的长石层序,即Dapango-Bombouaka群;中部的复理石序列,即Pendjari群;上部的磨拉石序列,即Obosum群。
3.5 Ⅱ-4环西非克拉通泛非活动带
3.5.1 Ⅱ-4-1图阿雷格地盾
图阿雷格地盾位于西非克拉通与撒哈拉克拉通之间,其北部为阿尔及利亚中南盆地,南部为尼日尔盆地。图阿雷格地盾主要由太古宙—古元古代或新元古代的地体组成,是西非克拉通东部泛非带地表出露的主要部分之一,由3个地块组成:①阿尔及利亚南部的阿哈加尔地块(Hoggar massif);②马里北部的伊福加斯山地块(Adrar Iforas massif);③尼日尔北部的艾尔地块(Air massif)。这3个地块在新元古代末期的泛非造山运动期间,由图阿雷格地盾和西非克拉通碰撞拼合而成[92]。
3.5.2 Ⅱ-4-2贝宁—尼日利亚地盾
贝宁-尼日利亚地盾位于西非克拉通东南部,其北部为尼日尔盆地,南部为赤道大西洋盆地。该地盾可分为3部分:Voltain前陆盆地、贝宁褶皱带和尼日利亚高级片麻岩基底[92]。地盾基底岩石组成主要为太古宙花岗闪长质多旋回灰色片麻岩及英云闪长质杂岩,上覆元古宙盖层残片主要为混合变质沉积岩。太古宙基底再活化岩石为混合片麻岩杂岩,约占尼日利亚国土面积的一半,主要为石英长石质黑云角闪片麻岩、片岩和混合岩。
3.5.3 Ⅱ-4-3小阿特拉斯造山带
小阿特拉斯造山带位于阿特拉斯褶皱造山带以南,其北部为阿特拉斯褶皱造山带,西南部为雷圭巴特地盾,东南部为廷杜夫-拉甘盆地。小阿特拉斯带处于西非克拉通西北张裂边缘,是北非泛非期(500 Ma)最重要的造山带之一。在构造上,小阿特拉斯带可分为西、中和东3个部分,其西部主要为古元古代岩石,属于西非克拉通的西北边界[93],中部是缝合带[94-95],东部属于泛非活动带。
3.5.4 Ⅱ-4-4廷杜夫-拉甘盆地
廷杜夫-拉甘盆地位于西非克拉通以北,其南部为雷圭巴特地盾和陶德尼盆地,北部为小阿特拉斯带。该盆地属于冈瓦纳大陆北缘发育的大撒哈拉陆缘盆地[63],主要地层为强烈褶皱和变质(绿片岩相)的寒武纪—奥陶纪—石炭纪海相地层,上覆陆相白垩纪—上新世沉积盖层。
3.5.5 Ⅱ-4-5罗克列德-毛里塔尼亚构造带
罗克列德-毛里塔尼亚构造带位于西非克拉通以西,沿克拉通西部边缘呈狭长带状分布,属于泛非期—华力西期的多期次活动带[96-97]。该构造带由自西向东逆冲到西非克拉通上的几个外来地体组成[98]。K-Ar和Ar-Ar白云母测年结果显示,最终逆冲发生在315~305 Ma之间,并且伴随陶德尼盆地内的泥盆纪磨砾层褶皱[99-101]。
3.6 Ⅱ-5大西洋沿岸断陷盆地带
3.6.1 Ⅱ-5-1非洲西北沿海盆地
非洲西北沿海盆地位于罗克列德-毛里塔尼亚构造带以西,主要由索维拉-哈纳盆地、塔尔法亚-阿尤恩盆地、达克拉-阿尤恩-塔尔法亚盆地和毛里塔尼亚盆地组成[102]。总体而言,这些盆地沉积物由三叠纪红层裂谷层序、早侏罗世膏盐沉积、侏罗纪—早白垩世碳酸盐岩序列,以及白垩纪—新生代海相碎屑序列组成[102]。
3.6.2 Ⅱ-5-2赤道大西洋盆地
赤道大西洋盆地位于莱奥地盾、贝宁-尼日利亚地盾以南,主要由利比里亚盆地、象牙海岸盆地、达荷美盆地和尼日尔三角洲盆地组成。盆地沉积物主要为侏罗纪—白垩纪陆相沉积岩及新生代大陆砂岩。
3.6.3 Ⅱ-5-3阿普第阶含盐盆地
阿普第阶含盐盆地位于刚果克拉通以西,包括杜阿拉盆地、加蓬盆地、刚果盆地、宽扎盆地和木萨米迪什盆地。阿普第阶盆地具有非常明显的地层统一性,侏罗纪—早白垩世主要为河流与湖泊沉积物,中生代晚期—新生代主要由3套单元组成,分别为陆相沉积物、蒸发岩和海相沉积物。
3.7 Ⅱ-6乌班吉迪斯造山带
乌班吉迪斯造山带(Oubanguides orogenic belt)横跨非洲中部,从喀麦隆向东延伸至苏丹,宽200 km,长约4000 km,主体位于喀麦隆、中非共和国与刚果(金)之间,在刚果(金)东北部呈北北西—南南东走向,在喀麦隆和中非共和国呈东西走向[103],是撒哈拉变克拉通与刚果克拉通的边界[104],与巴西东北部的博尔博雷马构造省(Borborema Province)在岩石组成和构造属性上皆可对比。乌班吉迪斯造山带记录了约2100 Ma的Eburnian构造-热事件和约600 Ma的泛非构造-热事件[105],其南侧为大型基底逆冲断层,北侧为大型右旋走滑断层[103],并被网状右旋走滑断层切割成众多断块,从西北到东南依次为新元古代西喀麦隆(West Cameroon)构造域、古元古代—新元古代阿达马瓦-亚德(Adamawa- Yade)构造域和占主导地位的新元古代雅温得(Yaounde)构造域。在泛非期晚期,这些断块和断层经历了区域性的右旋走滑和褶皱作用。区域上大量南北向的拉伸线理,可能指示了泛非期晚期的构造运动由北西—南东缩短方向引起,并在约550 Ma形成同构造花岗岩。地球物理资料解译显示,在阿达马瓦-亚德构造带南部存在密度较大的下地壳物质,可能是刚果克拉通的下逆冲部分,指示新元古代刚果克拉通与阿达马瓦-亚德构造域发生过变克拉通作用[106-107]。乌班吉迪斯造山带是非洲大陆重要的金资源富集地。
3.8 Ⅱ-7刚果克拉通
3.8.1 Ⅱ-7-2加蓬地块
加蓬地块位于刚果克拉通西北部,其北部为乌班吉迪斯造山带,南部为西刚果造山带。该地块主要包括3.19~3.12 Ga变形的花岗岩-绿岩、约3.15 Ga的强变质岩、2.95~2.85 Ga侵入的钙碱性英云闪长岩和花岗岩及低变质的中酸性火山岩(2.97~2.94 Ga)。后期的超基性岩侵入时间为2.78 Ga,在地块稳定之前即造山作用晚期存在2.8~2.5 Ga侵入的花岗岩[108]。
3.8.2 Ⅱ-7-3西刚果造山带
西刚果造山带平行于大西洋沿岸,北始加蓬,向南通过刚果(布)、刚果(金)Bas-Congo省、卡宾达,最终至安哥拉北部。西刚果成矿带延长约1400 km,宽150~300 km,是一条北西—南东向新元古代造山带,造山事件介于500~800 Ma之间[109]。西刚果造山带中段位于刚果(金)Bas-Congo省和北安哥拉,具明显弯曲,呈北西—南东走向。在西刚果造山带中段北东向地区逐渐变为前陆盆地。
与泛非期造山有关的区域变质主要为低压—高温变质作用,西刚果造山带西部为角闪岩相—麻粒岩相变质作用,中间带为绿片岩相变质作用,东部为未变质的沉积岩。西刚果造山带缺乏蛇绿岩残留体,也缺乏泛非期同造山或造山后花岗岩基。
3.8.3 Ⅱ-7-4安哥拉地块
安哥拉地块位于刚果克拉通西南部,其北部为西刚果造山带,南部为卡奥科活动带。该地块主要岩性为片麻岩和片岩组成的变质杂岩,经历了2.8~2.7 Ga的麻粒岩相变质作用,并被2.83~2.60 Ga的花岗岩侵入,上部被火山沉积岩覆盖(北部为Jamba组,南部为Utende-Chela超群)。安哥拉地块在后期的Eburnian事件(2.2~1.8 Ga构造事件,使上地壳和同期花岗岩发生褶皱和变质作用)中被重新改造[110]。
3.8.4 Ⅱ-7-6卡赛地块
卡赛地块位于刚果克拉通中部,其东北部为东北刚果地块和基巴拉造山带,东南部为卢弗里安构造带。该地块主要由英云闪长质片麻岩和花岗闪长岩组成,全岩Rb-Sr等时线年龄为3.49~3.33 Ga[111],2.9~2.8 Ga和2.83 Ga期间分别被紫苏花岗岩和花岗岩体侵入,区域变质作用使原岩发生麻粒岩相的变质,另外2.7~2.6 Ga广泛发育钙碱性花岗岩侵入体,与早期的变质岩发生混合岩化作用[110]。
3.8.5 Ⅱ-7-7卢弗里安构造带
卢弗里安构造带也称加丹加带或中非铜钴成矿带或卢弗里安铜钴成矿带,位于刚果克拉通东南部,其西北部为卡赛地块,北部为基巴拉造山带,东部为班韦乌卢地块和伊鲁米德构造带。该构造带形成于泛非构造运动时期,区域内的岩石单元主要包括前寒武纪的基底、加丹加超群及卡拉哈里(Kalahari)组[112]。构造带主要包括2个活动阶段:第一个阶段是765~735 Ma的构造带内沉积岩的形成时期,第二个阶段是510~500 Ma的多阶段构造叠加时期,即泛非运动时期[16]。
3.8.6 Ⅱ-7-8伊鲁米德构造带
伊鲁米德构造带位于刚果克拉通东南部,其西部为卢弗里安构造带,北部为班韦乌卢地块和乌本迪-乌萨迦兰活动带,南部为南伊鲁米德构造带。伊鲁米德构造带包括变形的基底单元和变质沉积层序2个部分,强烈变质作用可使岩石变质至角闪岩相,但是也较好地保存了古元古代的火山岩层序。其中,浅海相石英砂岩和泥质岩变形地层在西南部被命名为卡诺纳(Kanona)群,在东北部被命名为Manshya河群[113]。
3.8.7 Ⅱ-7-9班韦乌卢地块
班韦乌卢地块位于刚果克拉通东部,其西部为卢弗里安构造带,东部为伊鲁米德构造带,北部为乌本迪-乌萨迦兰活动带。该地块包括1个结晶基底和1个弱变形沉积盖层,基底火成岩为卢阿普拉(Luapula)-坦噶尼喀(Tanganyika)斑岩,下部盖层为高原系(Plateau Series),上部盖层为卢阿普拉地层(Luapula Beds)。
3.8.8 Ⅱ-7-10基巴拉造山带
基巴拉造山带位于刚果克拉通中东部,其东部为Rusizian构造带,西部为乌干达地块、东北刚果地块和卡赛地块,南部为卢弗里安构造带。基巴拉造山带不仅包含一次碰撞造山事件,也包括北部盆地的形成,其主要发生在1.4~1.0 Ga,其中在1375 Ma发生了非造山双峰构造岩浆伸展运动,裂谷作用破坏了统一的陆块,进而形成大量的基性—超基性层状侵入体(如Kapalagulu杂岩体)及源于地幔的岩浆岩,加热上地壳,使其发生部分熔融,形成大量的S型花岗岩[114-115]。
3.8.9 Ⅱ-7-11东北刚果地块
东北刚果地块位于刚果克拉通中部,其东部为基巴拉造山带,北部为乌干达地块,南部为卡塞地块。该地块的西部主要为Bomu杂岩(闪岩-片麻岩)和Ganguan绿岩带;北部主要为西尼罗杂岩;南部主要为上刚果花岗岩(upper Congo granite)和基巴拉绿岩带。基巴拉组绿岩带分布于古老片麻岩之上,主要由基性火山岩组成[116];西尼罗杂岩由高级变质片麻岩和残余的基性绿岩组成;Ganguan绿岩带分布于Bomu杂岩上部,主要由弱变质的石英岩、板岩、碧玉铁质岩、滑石片岩和辉绿岩组成[117-118]。
3.8.10 Ⅱ-7-13 Rusizian构造带
Rusizian构造带主要位于刚果(金)的中东部,出露于基伍省(Kivu)、马涅马省(Maniema)和北加丹加地区,出露岩性主要为Rusizian群。该带被后期中元古代基巴拉活动带改造/叠加,其北东侧为KAB带,南西侧为KIB带。关于此构造单元的形成,目前存在2种观点:一种观点认为,太古宙陆缘活动带可能为刚果克拉通与坦桑尼亚克拉通拼合过程中形成;另一种观点认为,其是古元古代乌本迪活动带北东向的延伸。
3.8.11 Ⅱ-7-14北东基巴拉造山带
北东基巴拉造山带位于非洲中部中元古代基巴拉构造带的北部,被Kabanga—Musongati(KM)基性—超基性线性杂岩体分为东部区域(ED)和西部区域(WD),其内分别沉积Kagera超群和Akanyaru超群。所有地层开始沉积于乌本迪造山作用之后,且碎屑物主要来源于坦桑尼亚克拉通及周边古元古代活动带。
3.8.12 Ⅱ-7-15坦桑尼亚克拉通
坦桑尼亚克拉通位于刚果克拉通东部,其东部为莫桑比克地盾,南部为乌本迪-乌萨迦兰活动带,西部为北东基巴拉造山带。克拉通在形成过程中发生了多期构造变质变形事件,伴有大量的火山、岩浆活动,主要由多多马超群、尼安兹超群和卡维隆多超群3个岩石地层单元组成。多多马超群构成克拉通的基底,岩性主要包括高级变质的TTG片麻岩、混合岩、花岗岩、花岗闪长岩等,也有少量低级变质的绿泥石绢云母片岩等[119];尼安兹超群主体为火山岩相,底部原岩为镁铁质火山岩系,中部为含炭质或铁质的沉积岩、凝灰岩、条带状铁建造(BIF)和燧石岩,最上部为长英质火山岩[120];卡维隆多超群不整合覆盖于尼安兹超群之上,主要为砾岩、砂岩和粉砂岩,少量凝灰岩,属于较典型的磨拉石建造[121]。
3.8.13 Ⅱ-7-16乌本迪-乌萨迦兰活动带
乌本迪-乌萨迦兰活动带的主要岩层单位为乌本迪活动带的乌本迪超群及乌萨伽兰活动带的伊斯马尼序列和康斯群,主体为一套片麻岩及变质的火山岩-沉积岩系,岩系中普遍发育角闪石-黑云母-石榴子石-蓝晶石片麻岩,也见榴辉岩。这些古元古代活动带内有许多后造山期的辉长岩类及花岗岩类侵入体,赋存贱金属,剪切带赋存金、各种宝石和工业矿物。该带东部受新元古代泛非造山运动作用改造,形成莫桑比克带,其岩性、构造、成矿特性均与乌本迪带相似。
3.8.14 Ⅱ-7-17安东吉-塔纳纳利佛地块
安东吉块体岩石单元分为2个部分:东部—北部由变形较弱的二长花岗岩和混合岩(新太古代马索拉岩套)及镁铁质片岩(太古宙马纳纳拉群)组成;西部—南部为大面积的变质沉积岩(片岩、石英岩、磁铁石英岩、斜长角闪岩和超镁铁质岩组成的太古宙安巴迪里塔纳(Ambodiritana)组和TTG岩系的诺斯博拉哈岩套(中太古代)),总体变质程度较弱,为绿片岩相—角闪岩相[122-123]。塔纳纳利佛块体由新太古代变质基底和古元古代变质沉积地层组成。其中,新太古代变质基底呈三角状,占前寒武系面积的一半;岩石单元包括由花岗岩、混合岩组成的元古宙比奇博卡岩套,由副片麻岩变质岩组成的元古宙索菲亚群和元古宙翁德鲁祖群[123-125]。
3.8.15 Ⅱ-7-18齐沃利造山带
齐沃利造山带主要分布于北西向元古宙拉诺查拉剪切带以南,自西向东由弗和波利群和阿罗炎、阿诺炎块体组成。南部元古宙块体指分布于北西向拉诺查拉剪切带南部的元古宙块体地质单元,Besairie[126]、Windly等[127]和Gaf-Bgr[128]均有划分方案。根据Gaf-Bgr的三分方案[128],马达加斯加南部元古宙块体自西向东由弗和波利群、阿罗炎块体和阿诺炎块体组成。
弗和波利群位于最西侧,处于麻粒岩西南端,该单元岩石以富含基性—超基性岩和高压环境为特征。主要岩性为由矽线石-石榴子石片麻岩、厚层大理岩、斜长角闪岩、花岗质片麻岩、角闪石岩-辉石岩和少量豆荚状、透镜状蛇纹石岩组成的副片麻岩,原岩物质可能来源于约850 Ma的块体,而镁铁质变质岩原岩被认为是850~700 Ma的岛弧玄武岩和安山岩[125]。Collins[129]认为, 其代表新元古代早期的火山裂谷地层。阿罗炎及阿诺炎单元与马达加斯加南部巨大的麻粒岩的主体对应,该单元的岩石(片麻岩、变粒岩、大理岩及较少见的角闪岩)反映了以沉积物质为主的来源,并伴有许多酸性火山岩夹层[123, 125, 129]。
3.8.16 Ⅱ-7-19贝马里武构造带
贝马里武构造带位于马达加斯加的最北部,是由2块新元古代—早寒武世地体组成的三角形构造带,其南部不整合叠加于太古宙安东吉块体和元古宙塔纳纳利佛块体之上[123]。其中南部的萨哈塔哈群由石英岩、云母片岩、长英质片麻岩、大理岩等副变质岩和角闪石片麻岩、斜长角闪岩及混合岩组成,变质程度达高角闪岩相—麻粒岩相,其中碎屑锆石年龄为2.2~1.8 Ga。北安其拉贝岩套由一系列片理化钙碱性岩浆岩组成,形成时代为746~758 Ma,岩石地球化学特征显示岩体形成于俯冲带活动大陆边缘[130-131]。北部达赖纳超群主要由低变质火山-沉积岩组成,自西向东火山成分逐渐增加,根据成分划分为维系卡、米拉努阿、达赖纳3个群,其中维系卡群含大量变质碎屑沉积岩,其石英岩获得2.5~3.38 Ga碎屑锆石;米拉努阿群含少量石英岩、大理岩,新元古代火山岩为主要物源区,其最大沉积年龄不超过723±12 Ma;达赖纳群出露于块体东部,主要由绿片岩相变火山岩和火山碎屑岩组成,其中变流纹岩获得713~739 Ma的锆石U-Pb年龄。马纳巴塔岩套形成于705~718 Ma,其地球化学特征与北安其拉贝岩套相似,由一系列钙碱性侵入体组成[123, 130-131]。
3.9 Ⅱ-8中南非泛非活动带
3.9.1 Ⅱ-8-1卢里奥盆地
卢里奥盆地经历了新元古代莫桑比克地盾改造叠加,岩石褶皱作用明显。该区出露的新元古代岩石地层单元包括MIrui岩套、Sierra Nacaga岩套等,主要岩性为片麻岩、片麻状花岗岩、花岗岩、紫苏花岗岩、麻粒岩、辉长岩、云英岩、石英闪长岩等。
3.9.2 Ⅱ-8-2南伊鲁米德构造带
南伊鲁米德构造带位于赞比亚东部,是赞比亚东部一系列构造地质体的堆积,包括塞伦杰原生地质体(Parautochthonous Serenje)、卢安瓜地体(Luangwa terranes)和Nyimba地体(Nyimba terranes),它们都属于伊鲁米德造山带的一部分,且这些岩层内的构造运动趋势主要为北西向。
3.9.3 Ⅱ-8-3赞比西活动带
赞比西活动带处于中元古代南伊鲁米德构造带的西南端,西部为卡拉哈里沙漠覆盖,呈东西向的楔形带状展布于赞比亚中南部。该带为韧性变形强烈的剪切带,岩石主要包括花岗片麻岩、变质碳酸盐岩、滑石硅质岩等,其变质程度可达到角闪岩相—榴辉岩相。赞比西活动带记录了多期变形变质和花岗质岩浆活动历史,与赞比亚的卢费里安构造带和纳米比亚的达马拉(Damaran)造山带同为大陆范围的泛非造山运动,开始于850 Ma,结束于500~450 Ma。赞比西活动带第一次主要造山事件发生于820 Ma。赞比亚其他地区构造晚期和后期的花岗岩有Mtuga花岗岩和Mkushi地区含铜花岗细晶岩(607±39 Ma/570~569 Ma),同构造花岗岩和约530 Ma的Hook花岗杂岩体,后造山的花岗岩和靠近赞比亚东部Petauke 490 Ma的Sinda岩基。总的来说,沿赞比西—卢费里安—达马拉走向的泛非造山运动跨越了多个时代,并且记录了赞比西活动带和卢费里安构造带的演化过程。
3.9.4 Ⅱ-8-4达马拉活动带
达马拉活动带位于中南非泛非活动带西部,其南部为那马奎活动带,北部为刚果克拉通,西部海岸带处与泛非期卡奥科活动带相连。该活动带由刚果克拉通和卡拉哈里克拉通碰撞形成,在新元古代—早古生代经历多期次的变形变质作用。达马拉活动带可分为4个北东向的构造单元[132],从北西到南东可分为:①北部台地,由厚的奥塔维组碳酸盐岩序列组成;②北部带,由褶皱的、向北逆冲的断陷火山岩、沉积岩和相关的侵入体组成[133];③中部带,以发育中高级变质岩及大量的侵入岩为特征,被奥马鲁鲁线性构造带分为南、北两部分;④奥卡汉贾线理带,将穹窿-盆地模式主导的中部带和南部带及南部边缘带的线性构造分离;⑤南部带,主要由俯冲增生杂岩组成[134]。
3.9.5 Ⅱ-8-5那马奎活动带
那马奎活动带位于中南非泛非活动带西部,其形成于格林维尔期(1000~1300 Ma)罗迪尼亚超大陆聚合过程中的那马奎造山运动时期[135]。那马奎活动带北部为达马拉活动带,东北毗邻太古宙卡普瓦尔克拉通,南部以Beattie地球物理异常带及相关的南开普造山带(Southern Cape Belt)为界[136]。
3.9.6 Ⅱ-8-3开普造山带
开普造山带地处非洲最南端,是形成于冈瓦纳大陆聚合过程中的造山带,可延伸至南美洲阿根廷、福克兰群岛及南极大陆。该褶皱带分为3部分:构造线方向近南北向展布的西分支、构造线方向近东西向展布的南分支和介于二者之间过渡的衔接带[137-138]。开普造山运动导致开普超群及上覆卡鲁超群底部Dwyka群岩石发生明显变形。西分支内部变形较弱,主要形成平缓、开阔的褶皱与单斜构造;而南分支内部变形强烈,以发育一系列北倾的叠瓦状逆冲断层、双冲构造与倒转褶皱为显著特征[139]。
3.10 Ⅱ-9卡拉哈里克拉通
3.10.1 Ⅱ-9-1卡普瓦尔克拉通
卡普瓦尔克拉通位于卡拉哈里克拉通南部,其北部为林波波构造带,西部为海斯活动带。卡普瓦尔克拉通由一系列中—低级变质的太古宙地块拼贴而成,其形成及演化过程包括早期陆核形成阶段(3100~3700 Ma)和晚期克拉通化阶段(2600~3100 Ma)[140-141]。该克拉通内部以科尔斯伯格磁性线性构造(Colesberg manetic Lineament)、塔巴津比-默奇森线性构造(Thabazimbi-Murchison Lineament)和Inyoka断裂为界,进一步划分出4个次一级地块:斯威士兰(Swaziland)地块、兰德(Witwatersrand)地块、彼得斯堡(Pietersburg)地块和金伯利(Kimberly)地块[142]。
3.10.2 Ⅱ-9-2海斯活动带
海斯活动带位于卡拉哈里克拉通西南部,其东部为卡普瓦尔克拉通,西部为那马奎活动带。该构造带是一条狭长的古元古代褶皱逆冲带,总体上为变质火山-沉积地层,其东北边界及东南边界分别被Blackridge逆冲断层和Doringberg断裂限定,而西部边界以Trooilapspan剪切带及Brackbosch断层为界[143]。Moen[143]将该变形-变质带从东到西划分为4段:Olifantshoek超群、Brulpan群、Vaalkoppies群和Wilgenhoutsdrif群。最老的变质沉积岩来自东部,其年龄为1930~1890 Ma。此外,Cornell等[144]也认为,Olifantshoek超群中存在约1750 Ma的基性岩。
3.10.3 Ⅱ-9-3林波波构造带
林波波构造带位于卡拉哈里克拉通中部,卡普瓦尔克拉通与津巴布韦克拉通之间。该构造带呈北东东向,是由太古宙的津巴布韦克拉通与卡普瓦尔克拉通发生碰撞、拼贴而形成的古元古代造山带[145]。变质带北以林波波逆冲带为界与津巴布韦克拉通相接,南以赫特(Hout)河剪切带为界与卡普瓦尔克拉通相邻。林波波构造带内部又以Magagohate-Triangle剪切带和Palala-Tshipise剪切带为界,进一步划分出3个次级地块:北部边缘带、中央带和南部边缘带。
3.10.4 Ⅱ-9-4津巴布韦克拉通
津巴布韦克拉通又称罗得西亚克拉通,位于卡拉哈里克拉通北部,为卵形花岗-绿岩区。津巴布韦克拉通北、东、南三面为相互独立的造山带:西北部边界为马刚迪(Magondi)活动带(构造变形年龄2.0~1.8 Ga),东北部为赞比西活动带(构造变形年龄1.0~0.5 Ga),南部为林波波构造带(构造变形年龄2.6~2.0 Ga)。津巴布韦克拉通以产出大量的绿岩带而闻名,面积约占整个克拉通面积的11%,克拉通内约83%的岩石为片麻岩和花岗质岩石,绿岩带呈残留体保留其中。绿岩带包括2个时代,即早于3350 Ma的塞巴奎群和3000~2600 Ma的布拉瓦约群。
3.10.5 Ⅱ-9-5马刚迪构造带
古元古代马刚迪构造带出露马刚迪超群,为一套变质沉积岩和变质火山岩组合,进一步被划分为Deweras群、Lomagundi群和Piriwiri群。
3.10.6 Ⅱ-9-6乔马-卡罗莫地块
乔马-卡罗莫地块位于赞比亚东南,北部为新元古代赞比西活动带,东南和西南缘为晚石炭世—早侏罗世卡鲁系超群。乔马-卡罗莫地块基底为花岗片麻岩,主要为下部的Chezya黑云母副片麻岩,上覆Ndonde石英-白云母片岩和Siamambo石英-白云母副片麻岩。在片麻岩和片岩的紧闭褶皱中发育中元古代辉长岩侵入体,并在变质沉积岩地层中发育Chinkozia苏长岩。中元古代末期发育石英-白云母-电气石伟晶岩和锡-(钽-铌-钨-锂-铍)伟晶岩。前人研究认为, 乔马-卡罗莫地块可能为再活化的津巴布韦克拉通的一部分[146]。
4. 结论
(1) 非洲大陆跨特提斯和冈瓦纳两大构造域,大部分属于冈瓦纳构造域,主要由太古宙—古元古代结晶基底、上覆盖层和泛非构造带组成。非洲冈瓦纳大陆地质演化主要经历4个阶段:古老克拉通陆核的形成阶段(大于3500 Ma)、克拉通化阶段(3500~1650 Ma)、构造运动和陆内裂解阶段(1650~ 600 Ma)、盖层和大断裂发育阶段(600 Ma以来)。
(2) 初步提出将非洲大陆分为2个一级构造单元,10个二级构造单元和55个三级构造单元,为该区成矿区带划分和成矿规律研究提供了重要基础。
致谢: 在野外地质调查和样品采集过程中得到中国地质大学青海大柴旦项目组各位师兄弟的帮助,样品测试过程中得到武汉理工大学杨梅君老师的帮助,在此一并表示感谢。 -
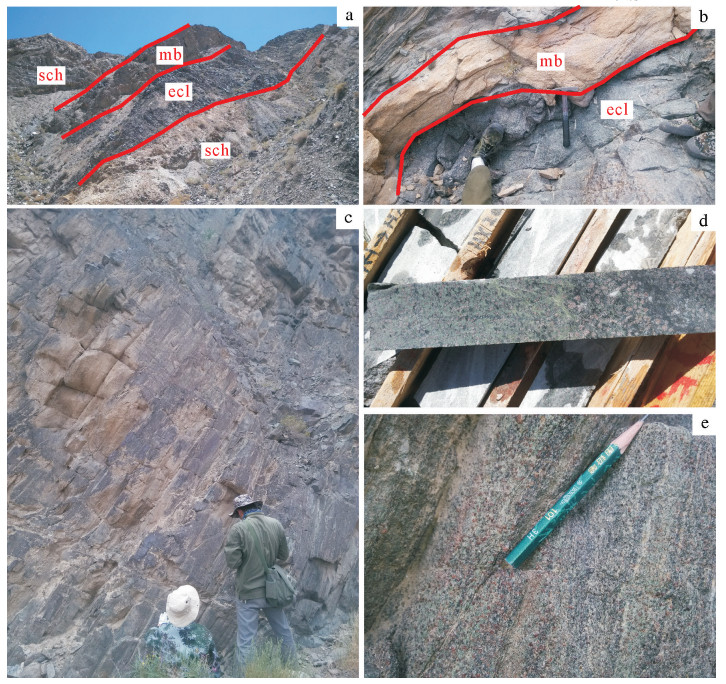
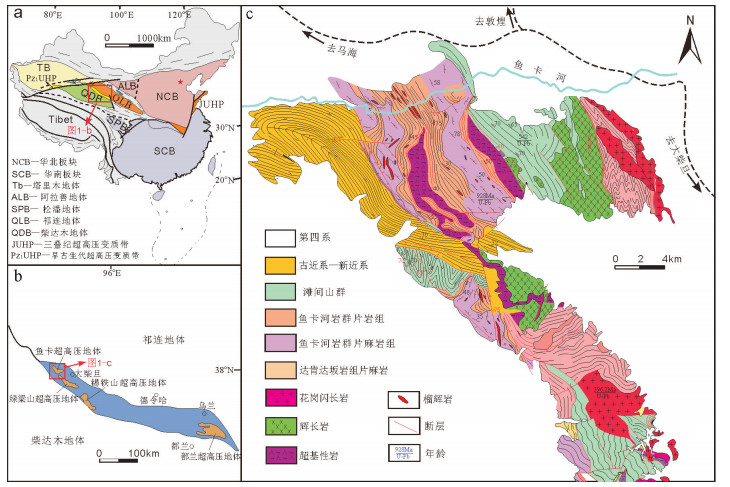
图 1 研究区位置图及地质简图(据参考文献[18]修改)
a—柴北缘超高压变质带在中国的位置;b—柴北缘区域地质简图;c—鱼卡矿区及周边地质简图
Figure 1. Geographic location and geological sketch map of the study area
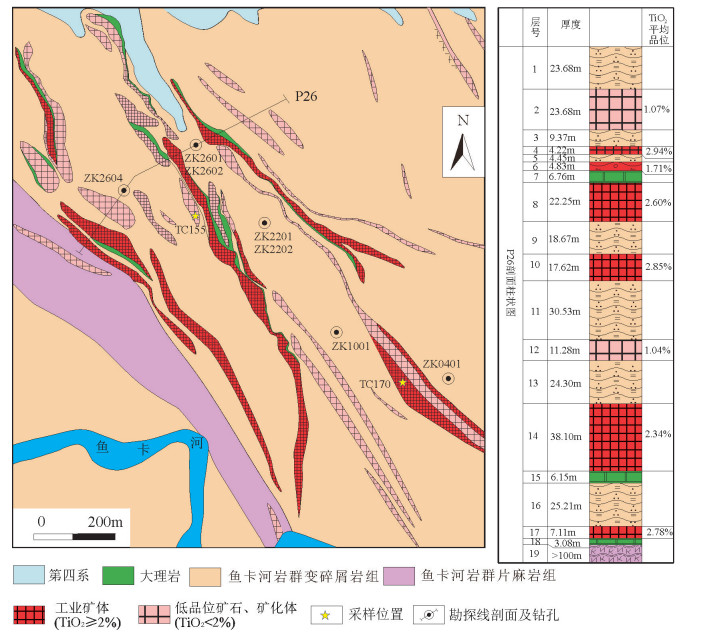
图 2 鱼卡金红石矿区地质简图及P26剖面柱状图(据参考文献[18]修改)
Figure 2. Geological sketch map of Yuka rutile deposit and the columnar section of P26
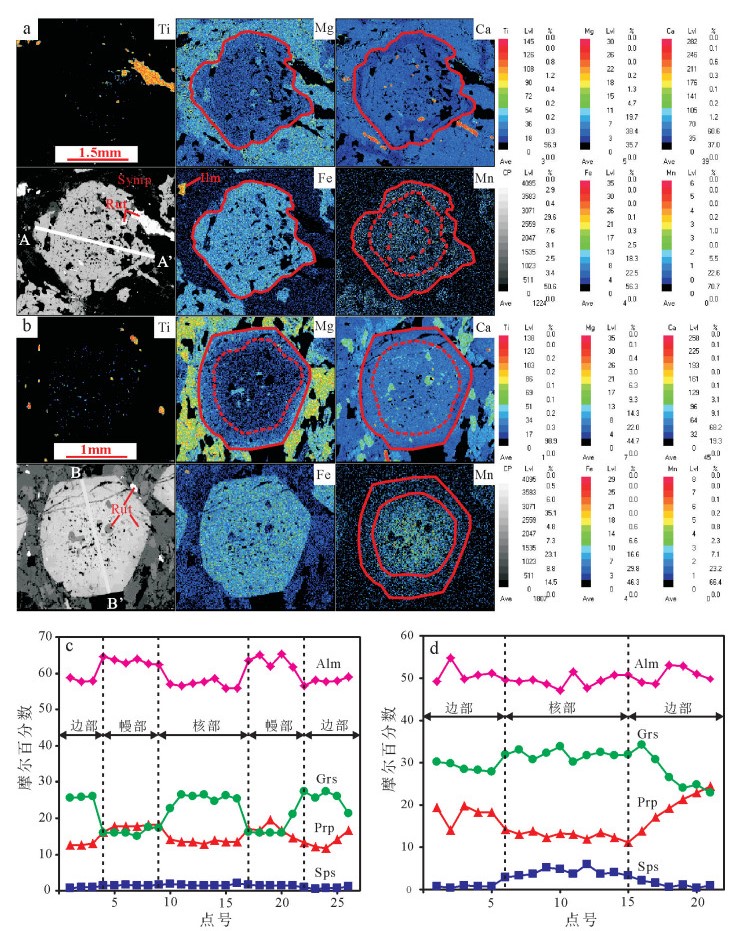
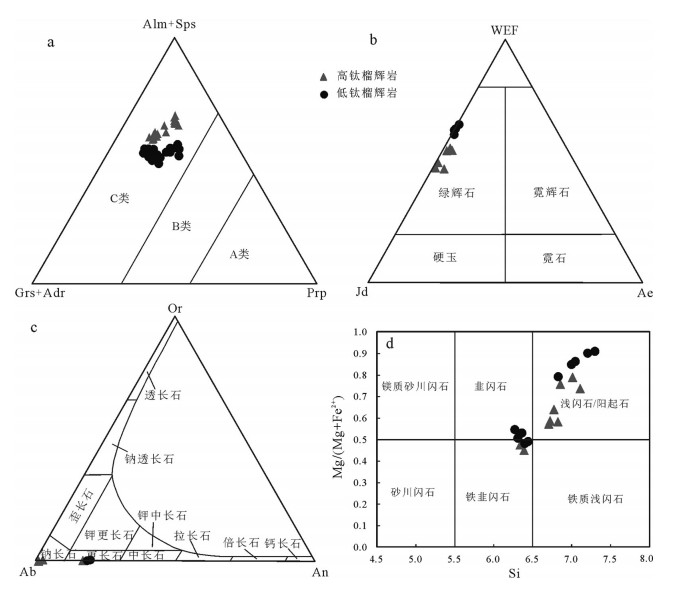
图 3 鱼卡榴辉岩石榴子石成分扫面和成分剖面(a、c为样品TC170HX2;b、d为样品TC155HX12;从黑色到红色,表示元素含量逐渐增加;矿物代号注释同表 1)
Figure 3. Scan surface and compositional profile mapping of the garnet from the Yuqia eclogite
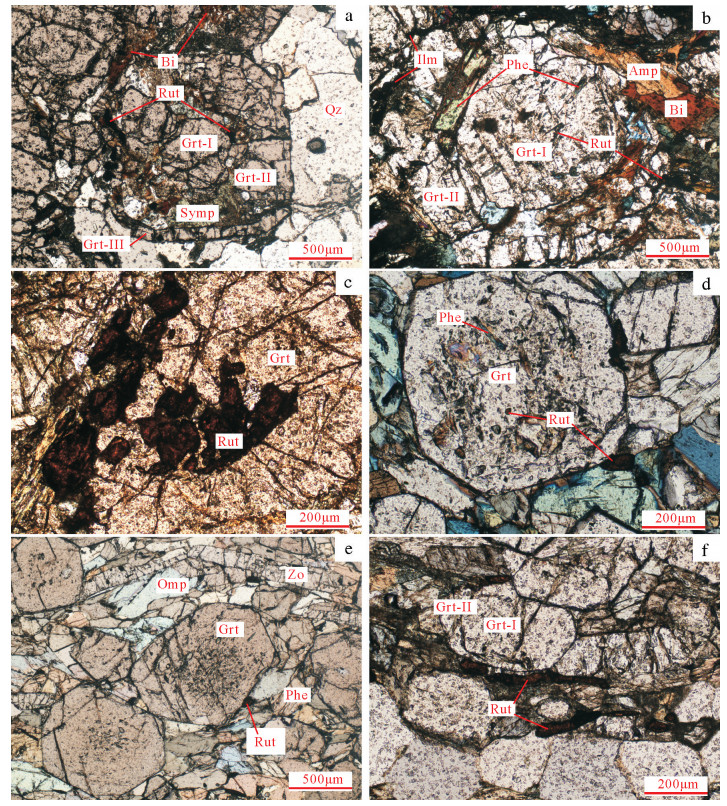
图版Ⅲ
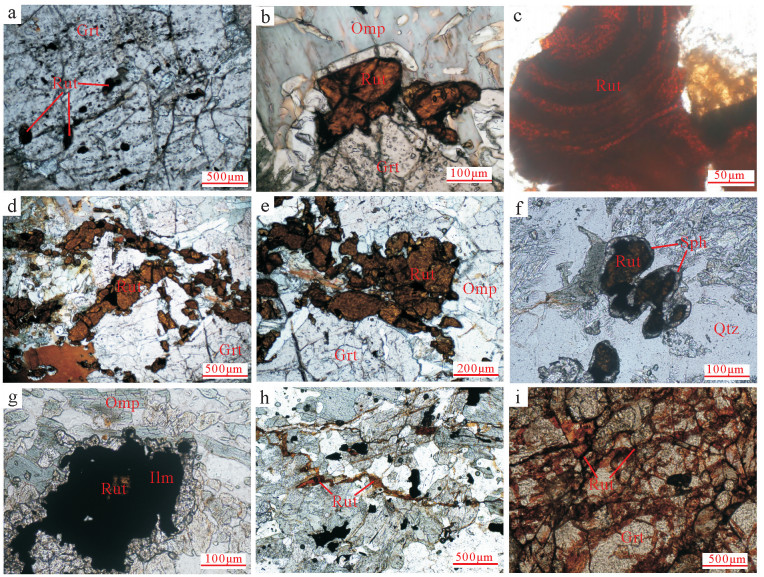
a.石榴子石中包裹的金红石(单偏光);b.绿辉石和石榴子石间的金红石(单偏光);b.金红石有明显的生长环带(单偏光);~e.矿物颗粒间形成的串珠状金红石(单偏光);f.金红石及其退变的榍石边(单偏光);g.金红石边缘退变的钛铁矿(单偏光);h.颗粒间丝缕状金红石;i.石榴子石裂纹中丝缕状金红石(据参考文献[18]修改)。Grt—石榴子石;Ilm—钛铁矿;Omp—绿辉石;Qtz—石英;Rut—金红石;Sph—榍石
图版Ⅲ.
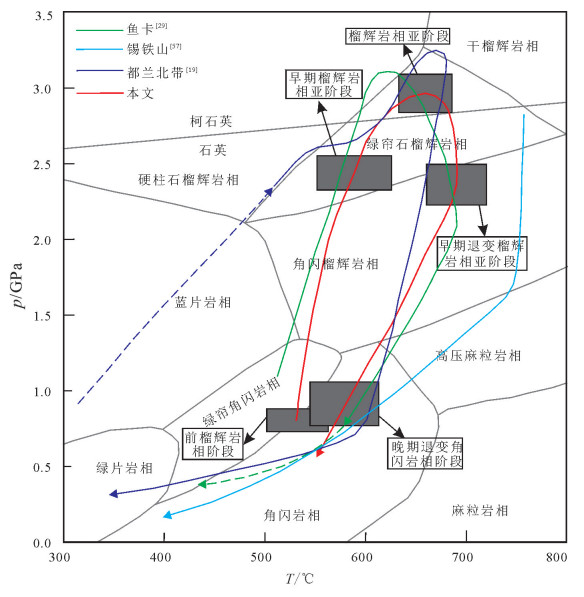
图 5 鱼卡榴辉岩的P-T演化轨迹(底图据参考文献[46])
Figure 5. P-T evolutionary trajectory of Yuqia eclogite
表 1 鱼卡榴辉岩中石榴子石电子探针分析结果
Table 1 Electron microprobe analyses of garnets from Yuqia eclogites

表 2 鱼卡榴辉岩中绿辉石电子探针分析结果
Table 2 Electron microprobe analyses of omphacites from Yuqia eclogites
% 点号 SiO2 TiO2 AI2O3 FeO MnO MgO CaO Na2O 总计 Si Ti Cr Al Fe3+ Fe2+ Mg Ca Na Sum WEF Jd Ae TC170HX2-33 56.77 0.03 10.79 6.38 0.02 6.69 12.01 7.44 100.13 2.03 0.00 0.00 0.45 0.01 0.18 0.36 0.46 0.51 4.00 49.22 49.95 0.83 TC170HX2-34 55.89 0.10 11.17 6.67 0.01 6.43 11.25 7.68 99.27 2.02 0.00 0.00 0.47 0.04 0.16 0.35 0.43 0.54 4.01 46.66 48.99 4.35 TC170HX2-35 56.36 0.06 11.28 6.25 0.05 6.47 11.13 7.69 99.31 2.02 0.00 0.00 0.48 0.01 0.18 0.35 0.43 0.54 4.00 47.13 51.94 0.92 TC170HX2-36 55.99 0.08 9.84 5.52 0.06 8.23 13.66 6.47 100.15 2.00 0.00 0.01 0.41 0.02 0.14 0.44 0.52 0.45 4.01 55.25 42.51 2.25 TC170HX2-37 56.67 0.07 9.76 5.47 0.02 8.19 13.40 6.71 100.55 2.02 0.00 0.01 0.41 0.02 0.15 0.43 0.51 0.46 4.01 54.18 44.25 1.57 TC170HX2-38 56.04 0.07 9.49 5.68 0.03 8.13 13.56 6.62 99.62 2.02 0.00 0.00 0.40 0.04 0.14 0.44 0.52 0.46 4.01 54.29 42.22 3.49 TC155HX12-27 55.66 0.07 8.54 4.50 0.00 10.00 15.74 5.00 99.60 2.00 0.00 0.00 0.36 0.00 0.14 0.54 0.61 0.35 3.99 64.85 35.15 0.00 TC155HX12-28 55.73 0.07 8.94 4.25 0.04 9.70 15.70 5.22 99.73 2.00 0.00 0.00 0.38 0.00 0.13 0.52 0.60 0.36 3.99 63.39 36.61 0.00 TC155HX12-29 56.15 0.07 9.19 4.25 0.04 9.47 15.06 5.55 99.90 2.01 0.00 0.00 0.39 0.00 0.13 0.50 0.58 0.38 3.99 61.12 38.88 0.00 TC155HX12-30 56.24 0.11 8.87 4.20 0.05 9.68 15.58 5.33 100.08 2.01 0.00 0.00 0.37 0.00 0.13 0.51 0.60 0.37 3.99 62.68 37.32 0.00 TC155HX12-31 55.10 0.08 8.27 4.52 0.00 10.06 15.94 4.96 99.12 1.99 0.00 0.00 0.35 0.00 0.14 0.54 0.62 0.35 4.00 65.08 34.80 0.12 注:Sum为基于6个氧原子数计算的阳离子总数;Ae—霓石;Jd—硬玉;WEF—硅灰石+顽火辉石+铁顽火辉 表 3 鱼卡榴辉岩中斜长石电子探针分析结果
Table 3 Electron microprobe analyses of plagioclases from Yuqia eclogites
% 点号 SiO2 TiO2 Al2O3 FeO MnO MgO CaO Na2O 总计 Si Ti Al Fe3+ Fe2+ Mn Mg Ca Na Sum Ab An Or TC170HX2-39 70.04 0.00 19.37 0.33 0.00 0.00 0.24 11.60 101.64 3.02 0.00 0.98 0.00 0.01 0.00 0.00 0.01 0.97 5.00 98.83 1.11 0.06 TC170HX2-40 69.00 0.00 15.16 2.14 0.01 3.00 3.59 8.24 101.16 3.05 0.00 0.79 0.00 0.08 0.00 0.20 0.17 0.71 5.00 80.51 19.37 0.12 TC170HX2-41 70.98 0.00 19.08 0.23 0.02 0.03 0.21 11.34 101.97 3.06 0.00 0.97 0.00 0.01 0.00 0.00 0.01 0.95 5.00 98.85 0.99 0.17 TC155HX12-32 65.52 0.05 22.40 0.39 0.03 0.00 3.84 9.34 101.65 2.86 0.00 1.15 0.00 0.01 0.00 0.00 0.18 0.79 5.00 81.33 18.49 0.18 TC155HX12-33 64.43 0.00 22.74 0.42 0.01 0.00 4.01 9.42 101.05 2.82 0.00 1.17 0.00 0.02 0.00 0.00 0.19 0.80 5.00 80.82 19.02 0.16 注:Sum为基于6个氧原子数计算的阳离子总数;Ab—钠长石;An—钙长石;Or—正长石 表 4 鱼卡榴辉岩中角闪石电子探针分析结果
Table 4 Electron microprobe analyses of amphiboles from Yuqia eclogites
% 点号 SiO2 TiO2 AI2O3 FeO MnO MgO CaO Na2O K2O Cr2O3 总计 Si Ti Al Fe Mn Mg Ca Na K Cr 总计 TC170HX12-42 47.65 0.74 8.79 10.90 0.10 14.01 11.16 2.24 0.19 0.05 95.82 7.01 0.08 1.52 1.34 0.01 3.07 1.76 0.64 0.04 0.01 15.48 TC170HX12-43 45.82 1.11 10.30 11.20 0.06 12.96 10.01 2.66 0.28 0.60 95.00 6.82 0.12 1.81 1.39 0.01 2.88 1.60 0.77 0.05 0.07 15.52 TC170HX12-44 48.09 0.27 9.00 12.87 0.03 12.50 10.70 2.18 0.07 0.01 95.72 7.11 0.03 1.57 1.59 0.00 2.76 1.70 0.62 0.01 0.00 15.39 TC155HX12-34 41.77 0.91 16.46 14.95 0.15 8.62 9.43 3.53 0.35 0.10 96.26 6.27 0.10 2.91 1.88 0.02 1.93 1.52 1.03 0.07 0.01 15.72 TC155HX12-35 41.81 0.91 15.79 16.36 0.13 8.16 9.35 3.18 0.72 0.04 96.44 6.31 0.10 2.81 2.06 0.02 1.84 1.51 0.93 0.14 0.00 15.72 TC155HX12-36 42.23 0.91 15.73 15.40 0.16 8.13 9.68 3.25 0.60 0.06 96.16 6.36 0.10 2.79 1.94 0.02 1.82 1.56 0.95 0.12 0.01 15.67 TC155HX12-37 41.78 0.83 13.95 17.45 0.17 8.03 10.14 2.93 0.50 0.54 96.29 6.37 0.09 2.51 2.23 0.02 1.83 1.66 0.87 0.10 0.06 15.73 TC155HX12-38 41.06 0.94 13.48 17.03 0.17 7.94 9.24 2.87 0.50 2.42 95.66 6.32 0.11 2.45 2.19 0.02 1.82 1.52 0.86 0.10 0.29 15.68 TC155HX12-39 50.37 0.25 9.74 8.33 0.02 14.76 9.94 2.65 0.36 0.07 96.47 7.20 0.03 1.64 1.00 0.00 3.15 1.52 0.73 0.07 0.01 15.35 TC155HX12-40 48.65 0.33 11.11 8.97 0.06 14.22 9.99 2.82 0.45 0.16 96.77 6.99 0.04 1.88 1.08 0.01 3.05 1.54 0.79 0.08 0.02 15.46 TC155HX12-41 49.19 0.34 10.93 8.75 0.04 14.30 9.88 2.88 0.43 0.10 96.84 7.04 0.04 1.84 1.05 0.01 3.05 1.52 0.80 0.08 0.01 15.43 TC155HX12-42 51.10 0.28 8.64 8.30 0.04 15.13 10.20 2.57 0.28 0.04 96.58 7.30 0.03 1.45 0.99 0.00 3.22 1.56 0.71 0.05 0.00 15.32 TC155HX12-43 46.78 0.42 12.72 9.91 0.08 12.55 9.89 2.98 0.53 0.08 95.94 6.82 0.05 2.19 1.21 0.01 2.73 1.55 0.84 0.10 0.01 15.50 注:Sum为基于6个氧原子数计算的阳离子总数 表 5 鱼卡榴辉岩中多硅白云母电子探针分析结果
Table 5 Electron microprobe analyses of phengites from Yuqia eclogites
% 点号 SiO2 TiO2 Al2O3 FeO MnO MgO CaO Na2O K2O Cr2O3 总计 Si Ti Cr Al Fe2+ Mn Mg Ca Na K Sum TC170HX2-45 53.33 0.63 26.24 2.77 0.00 3.42 0.05 0.52 9.29 0.02 96.28 3.49 0.03 0.00 2.03 0.15 0.00 0.33 0.00 0.07 0.78 6.88 TC170HX2-46 54.90 0.56 26.19 2.91 0.02 3.62 0.02 0.44 8.41 0.02 97.07 3.54 0.03 0.00 1.99 0.16 0.00 0.35 0.00 0.06 0.69 6.81 TC170HX2-47 53.56 0.55 26.25 3.07 0.01 3.55 0.02 0.46 9.08 0.02 96.57 3.50 0.03 0.00 2.02 0.17 0.00 0.35 0.00 0.06 0.76 6.87 TC170HX2-48 54.04 0.48 25.74 2.59 0.01 3.61 0.06 0.44 8.96 0.14 96.08 3.53 0.02 0.01 1.98 0.14 0.00 0.35 0.00 0.06 0.75 6.85 TC170HX2-49 52.73 0.55 26.27 3.08 0.02 3.23 0.03 0.52 8.79 0.26 95.47 3.48 0.03 0.01 2.04 0.17 0.00 0.32 0.00 0.07 0.74 6.86 TC170HX2-50 54.87 0.42 25.71 2.91 0.00 3.81 0.04 0.42 8.55 0.01 96.73 3.55 0.02 0.00 1.96 0.16 0.00 0.37 0.00 0.05 0.71 6.82 TC155HX12-44 53.03 0.59 29.01 1.73 0.01 3.36 0.00 0.62 8.50 0.11 96.96 3.41 0.03 0.01 2.20 0.09 0.00 0.32 0.00 0.08 0.70 6.84 TC155HX12-45 53.11 0.56 28.33 1.80 0.00 3.48 0.02 0.66 8.37 0.11 96.44 3.44 0.03 0.01 2.16 0.10 0.00 0.34 0.00 0.08 0.69 6.84 TC155HX12-46 52.87 0.61 28.56 1.86 0.00 3.39 0.02 0.71 8.25 0.07 96.34 3.42 0.03 0.00 2.18 0.10 0.00 0.33 0.00 0.09 0.68 6.84 TC155HX12-47 52.20 0.55 28.11 1.83 0.01 3.28 0.00 0.52 8.12 0.07 94.68 3.44 0.03 0.00 2.18 0.10 0.00 0.32 0.00 0.07 0.68 6.82 注:Sum为基于6个氧原子数计算的阳离子总数 表 6 鱼卡高钛榴辉岩和低钛榴辉岩中石榴子石环带对比
Table 6 The comparison of the garnet zoning between the high Ti and low Ti eclogites at Yuqia
样品 高钛榴辉岩 低钛榴辉岩 特征 分布较稀疏,但颗粒粗大,可占(25%~40%),呈他形,受退变影响较大,矿物包体较多 颗粒较细,数量可占一半以上,分布密集,较自形,与其他矿物界线清晰 阶段 前榴辉岩相、榴辉岩相和后榴辉岩相 前榴辉岩相和榴辉岩相 包裹体 包裹体较多,种类复杂,
粒径大;核部:角闪石、白云母、长石、金红石、石英
边部:很少金红石包裹体较少,颗粒细小;
核部:角闪石、石英、帘石类
边部:很少主量元素 组分:
Alm55.97~64.62Sps0.74~1.79Prp12.15~17.78Grs15.04~27.38;
分带:核部高Ca、Mn,低Mg;幔部高Fe、Mg,低Ca;
边部高Ca组分:
Alm48.70~54.58Sps0.35~5.95Prp11.27~24.37Grs22.88~34.38;
分带:核部和幔部高Ca、Mn,低Mg;边部高Mg,低Ca、Mn,Fe含量相对均一微量元素[6] MREE~HREE陡峭分布
HREE核边变化不明显,或略微降低,
边部HREE~10MREE~HREE平坦分布
从核到边,HREE逐步升高
核部HREE~10
边部HREE~100注:Prp—铝镁榴石;Sps—锰铝榴石;Grs—钙铝榴石;Alm—铁铝榴石 表 7 鱼卡榴辉岩中各阶段矿物
Table 7 The table of mineral formation stages of Yuqia eclogite

-
Meinhold G. Rutile and its applications in earth sciences[J]. EarthScience Reviews, 2010, 102(1/2):1-28. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqkxjz201208002
刘润泽, 李中, 陈正云, 等.新型工程金属钛的应用[J].钛工业进展, 1998, 1:3-7. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199800578453 贾明, 李胜荣, 岳来群, 等.山西代县碾子沟金红石矿床地质特征及经济意义研究[J].地质与勘探, 2006, 42(6):42-46. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0495-5331.2006.06.009 Force E R. Geology of titanium-mineral deposits[J]. Immunology, 1991, 130(2):243-253.
王永开, 徐永利, 郑有业, 等.柴达木盆地北缘鱼卡-铁石观一带金红石矿床的发现及其地质意义[J].地质通报, 2014, 33(6):900-911. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2014.06.013 陈鑫, 郑有业, 许荣科, 等.柴北缘超高压变质带折返过程对金红石成矿的制约:来自鱼卡和铁石观西地区石榴子石成分环带的证据[J].地球科学与环境学报, 2016, 38(2):143-159. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6561.2016.02.003 Chen D L, Liu L, Sun Y, et al. Geochemistry and zircon U Pb dating and its implications of the Yukahe HP/UHP terrane, the North Qaidam, NW China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2009, 35(3/4):259-272. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=a8cb0bf62f2995543e6aa2ac41cde9fc&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Song S G, Su L, Li X H, et al. Tracing the 850Ma continental flood basalts from a piece of subducted continental crust in the North Qaidam UHPM belt, NW China[J]. Precambrian Research, 2010, 183(4):805-816. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2010.09.008
Zhang G B, Ellis D J, Christy A G, et al. UHP metamorphic evolution of coesite-bearing eclogite from the Yuka terrane, North Qaidam UHPM belt, NW China[J]. European Journal of Mineralogy, 2009, 21(6):1287-1300. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=add2a64f44e315b009861000d6183996
Ren Y F, Chen D L, Kelsey D E, et al. Petrology and Geochemistry of the lawsonite (pseudomorph)-bearing eclogite in Yuka terrane, North Qaidam UHPM belt:An eclogite facies metamorphosed oceanic slice[J]. Gondwana Research, 2016, 42:220-242.
Zhang L, Chen R X, Zheng Y F, et al. Whole-rock and zircon geochemical distinction between oceanic-and continental-type eclogites in the North Qaidam orogen, northern Tibet[J]. Gondwana Research, 2016, 44:67-88.
杨经绥, 张建新, 孟繁聪, 等.中国西部柴北缘-阿尔金的超高压变质榴辉岩及其原岩性质探讨[J].地学前缘, 2003, 10(3):291-314. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2003.03.026 王惠初, 袁桂邦, 辛后田, 等.柴达木盆地北缘鱼卡河岩群的地质特征和时代[J].地质通报, 2004, 23(4):314-321. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2004.04.003 张建新, 孟繁聪, 杨经绥.柴北缘西段榴辉岩相的变质泥质岩:榴辉岩与围岩"原地"关系的证据[J].中国科学:地球科学, 2004, 34(9):825-834. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgkx-cd200409005 张建新, 孟繁聪, 杨经绥.柴北缘鱼卡榴辉岩的p-T演化历史[J].岩石矿物学杂志, 2005, 24(4):245-254. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2005.04.001 陈丹玲, 孙勇, 刘良, 等.柴北缘鱼卡河榴辉岩的超高压变质年龄:锆石LA-ICP-MS微区定年[J].中国科学:地球科学, 2007, 37(S1):279-287. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK2007S1029.htm 陈丹玲, 孙勇, 刘良.柴北缘鱼卡河榴辉岩围岩的变质时代及其地质意义[J].地学前缘, 2007, 14(1):108-116. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2007.01.010 陈鑫, 郑有业, 许荣科, 等.柴北缘鱼卡榴辉岩型金红石矿床金红石矿物学、元素地球化学及成因[J].岩石学报, 2018, 34(6):1685-1703. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201806009 Song S G, Niu Y L, Su L, et al. Continental orogenesis from ocean subduction, continent collision/subduction, to orogen collapse, and orogen recycling:The example of the North Qaidam UHPM belt, NW China[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2014, 129(1):59-84. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=8276405c6eafee1767bae93afee3e25c&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
张贵宾, 张立飞, 宋述光.柴北缘超高压变质带:从大洋到大陆的深俯冲过程[J].高校地质学报, 2012, 18(1):28-40. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2012.01.003 张贵宾, 张立飞, 宁远煜, 等.柴北缘超高压变质带的冷却历史:来自副片麻岩中锆石、金红石的U-Pb年代学和温度信息[J].岩石学报, 2014, 30(10):2835-2842. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201410004 宋述光, 牛耀龄, 张立飞, 等.大陆造山运动:从大洋俯冲到大陆俯冲、碰撞、折返的时限——以北祁连山、柴北缘为例[J].岩石学报, 2009, 25(9):39-49. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200909003 宋述光, 张贵宾, 张聪, 等.大洋俯冲和大陆碰撞的动力学过程:北祁连-柴北缘高压-超高压变质带的岩石学制约[J].科学通报, 2013, 58(23):2240-2245. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-KXTB201323001.htm 宋述光, 王梦珏, 王潮, 等.大陆造山带碰撞-俯冲-折返-垮塌过程的岩浆作用及大陆地壳净生长[J].中国科学:地球科学, 2015, 5(7):916-940. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgkx-cd201507003 张立飞, 吕增, 张贵宾, 等.大洋型超高压变质带的地质特征及其研究意义:以西南天山、柴北缘超高压变质带为例[J].科学通报, 2008, 53(18):2166-2175. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2008.18.003 杨经绥, 宋述光, 许志琴, 等.柴达木盆地北缘早古生代高压-超高压变质带中发现典型超高压矿物——柯石英[J].地质学报, 2001, 75(2):175-179. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dizhixb200102005 Song S G, Yang J S, Xu Z Q, et al. Metamorphic evolution of the coesite-bearing ultrahigh-pressure terrane in the North Qaidam, Northern Tibet, NW China[J]. Journal of Metamorphic Geology, 2003, 21(6):631-644. doi: 10.1046/j.1525-1314.2003.00469.x
Song S G, Zhang L F, Niu Y L, et al. Geochronology of diamondbearing zircons from garnet peridotite in the North Qaidam UHPM belt, Northern Tibetan Plateau:A record of complex histories from oceanic lithosphere subduction to continental collision[J]. Earth & Planetary Science Letters, 2005, 234(1/2):99-118.
Zhang J X, Meng F C. Coesite in eclogite from the North Qaidam Mountains and its implications[J]. Science Bulletin, 2009, 54(6):1105-1110. doi: 10.1007/s11434-009-0074-x
Zhang J X, Mattinson C G, Yu S Y. U-Pb zircon geochronology of coesite-bearing eclogites from the southern Dulan area of the North Qaidam UHP terrane, northwestern China:spatially and temporally extensive UHP metamorphism during continental subduction[J]. Journal of Metamorphic Geology, 2010, 28(9):955-978. doi: 10.1111/jmg.2010.28.issue-9
林成贵, 许荣科, 郑有业, 等.柴北缘鱼卡榴辉岩型金红石矿地质特征及其原岩性质探讨[J].西北地质, 2017, 50(2):142-155. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6248.2017.02.016 Coleman R G, Lee D E, Beatty L B, et al. Eclogites and Eclogites:Their Differences and Similarities[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 1965, 76(5):483-508. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1965)76[483:EAETDA]2.0.CO;2
Morimoto N. Nomenclature of Pyroxenes[J]. Mineralogy & Petrology, 1988, 39(1):55-76.
Morimoto N. Nomenclature of Pyroxenes[J]. Mineralogy & Petrology, 1988, 39(1):55-76.
Leake B E, Woolley A R, Arps C E S, et al. Nomenclature of amphiboles; Report of the Subcommittee on Amphiboles of the International Mineralogical Association, Commission on New Minerals and Mineral Names[J]. The Canadian Mineralogist, 1997, 35:219-247. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=10.1180/minmag.1997.061.405.13
魏春景, 朱文萍.多硅白云母地质压力计的研究进展[J].地质通报, 2007, 26(9):1123-1130. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2007.09.014 朱文萍, 魏春景.多硅白云母地质压力计的热力学模拟[J].中国科学:地球科学, 2007, 37(8):1014-1019. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgkx-cd200708003 陈丹玲, 孙勇, 刘良, 等.柴北缘鱼卡河榴辉岩的变质演化——石榴石成分环带及矿物反应结构的证据[J].岩石学报, 2005, 21(4):1039-1048. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200504002 张建新, 于胜尧, 孟繁聪.柴达木北缘鱼卡-落凤坡榴辉岩-片麻岩单元的变质变形演化[J].地质通报, 2008, 27(9):1468-1474. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2008.09.009 黄俊玮, 王守敬, 李洪潮, 等.某榴辉岩型金红石矿粗选试验研究[J].非金属矿, 2017, (1):46-49. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8098.2017.01.015 孙晓华, 霸慧文, 赵玉卿, 等.榴辉岩型金红石矿综合利用途径研究[J].化工矿物与加工, 2016, (8):37-39. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hgkwyjg201608010 Zhang L, Chen R X, Zheng Y F, et al. The tectonic transition from oceanic subduction to continental subduction:Zirconological constraints from two types of eclogites in the North Qaidam orogen, northern Tibet[J]. Lithos, 2016, 244:122-139. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2015.12.003
Lombardo B, Rolfo F, Compagnoni R. Glaucophane and barroisite eclogites from the Upper Kaghan nappe:implications for the metamorphic history of the NW Himalaya[J]. Geological Society London Special Publications, 2000, 170(1):411-430. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.2000.170.01.22
刘景波, 国连杰, 吴颍.豫南-鄂北大别山北部高压角闪石榴辉岩的研究[J].地质科学, 1997, 32(4):409-422. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199700065843 陈意, 叶凯, 吴春明.榴辉岩常用温压计在应用中应注意的问题[J].岩石学报, 2005, 21(4):1067-1080. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200504005 Green T H, Hellman P L. Fe Mg partitioning between coexisting garnet and phengite at high pressure, and comments on a garnetphengite geothermometer[J]. Lithos, 1982, 15(4):253-266. doi: 10.1016/0024-4937(82)90017-2
Powell R. Regression diagnostics and robust regression in geothermometer/geobarometer calibration:the garnetclinopyroxene geothermometer revisited[J]. Journal of Metamorphic Geology, 1985, 3(3):231-243. doi: 10.1111/jmg.1985.3.issue-3
Ravna E K. The garnet-clinopyroxene Fe2+-Mg geothermometer:An updated calibration[J]. Journal of Metamorphic Geology, 2000, 18(2):211-219. doi: 10.1046/j.1525-1314.2000.00247.x
Chen D L, Liu L, Sun Y, et al. Felsic veins within UHP eclogite at xitieshan in North Qaidam, NW China:Partial melting during exhumation[J]. Lithos, 2012, 136(4):187-200. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=f89c7aab6693dfbb5c89eb44f020f361&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Nakamura D, Banno S. Thermodynamic modelling of sodic pyroxene solid-solution and its application in a garnet-omphacitekyanite-coesite geothermobarometer for UHP metamorphic rocks[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1997, 130(1):93-102. doi: 10.1007/s004100050352
Ravna E J K, Terry M P. Geothermobarometry of UHP and HP eclogites and schists-an evaluation of equilibria among garnetclinopyroxene-kyanite-phengite-coesite/quartz[J]. Journal of Metamorphic Geology, 2004, 22(6):579-592. doi: 10.1111/jmg.2004.22.issue-6
Graham C M, Powell R. A garnet hornblende geothermometer:calibration, testing, and application to the Pelona Schist, Southern California[J]. Journal of Metamorphic Geology, 2010, 2(1):13-31. doi: 10.1111-j.1525-1314.1984.tb00282.x/
Carswell D A, O'Brien P J, Wilson R N, et al. Thermobarometry of phengite-bearing eclogites in the Dabie Mountains of central China[J]. Journal of Metamorphic Geology, 1997, 15(2):239-252. doi: 10.1111/j.1525-1314.1997.00014.x
Holland T, Blundy J. Non-ideal interactions in calcic amphiboles and their bearing on amphibole-plagioclase thermometry[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1994, 116(4):433-447. doi: 10.1007/BF00310910
Massonne H J, Schreyer W. Phengite geobarometry based on the limiting assemblage with K-feldspar, phlogopite, and quartz[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1987, 96(2):212-224. doi: 10.1007/BF00375235
Kohn M J. Two new geobarometers for garnet amphibolites, with applications to southeastern Vermont[J]. American Mineralogist, 1990, 75(1):89-96. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=7196c7af1855d25f9b457559cbe9377e&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Zhang C, Zhang L F, Roermund H V, et al. Petrology and SHRIMP U-Pb dating of Xitieshan eclogite, North Qaidam UHP metamorphic belt, NW China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2011, 42(4):752-767. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2011.04.002
Liou J G, Tsujimori T, Zhang R Y, et al. Global UHP Metamorphism and Continental Subduction/Collision:The Himalayan Model[J]. International Geology Review, 2004, 46(1):1-27. doi: 10.2747/0020-6814.46.1.1
Zhang J X, Yang J S, Mattinson C G, et al. Two contrasting eclogite cooling histories, North Qaidam HP/UHP terrane, western China:Petrological and isotopic constraints[J]. Lithos, 2005, 84(1/2):51-76. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=28a4efcea25300af9a595cfea5b7eb14&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Zhang C, Zhang L F, Bader T, et al. Geochemistry and trace element behaviors of eclogite during its exhumation in the Xitieshan terrane, North Qaidam UHP belt, NW China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2013, 63(sup1):81-97. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=4d19757be9b40ddccca310f98f8d2bd7&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
张聪, 田作林, 张立飞, 等.柴北缘锡铁山两类榴辉岩的退变质过程及其对俯冲带折返机制的制约[J].地质通报, 2013, 32(12):2044-2054. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20131221&flag=1 陈鑫, 许荣科, 郑有业, 等.青海柴北缘UHP变质带铁石观西榴辉岩峰期温度的确定及其地质意义[J].地质通报, 2015, 34(12):2292-2301. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2015.12.015 宋述光, 张立飞.榴辉岩的两种变质演化轨迹和俯冲大陆地壳的差异折返——以柴北缘都兰超高压地体为例[J].高校地质学报, 2007, 13(3):515-525. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2007.03.020 -
期刊类型引用(11)
1. 李春稼,张洪瑞,罗迪柯,靳立杰,高继雷,王子圣,梁云汉,贾鹏飞,刘伟,张攀. 安哥拉东北部地区Inkisi组碎屑锆石U-Pb年龄、地球化学特征及其地质意义. 地质论评. 2024(03): 1031-1046 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 靳立杰,张洪瑞,罗迪柯,贾鹏飞,高继雷,李春稼,王子圣,刘伟,周永刚. 刚果盆地西南缘Inkisi组碎屑锆石U-Pb年代学:对地层时代及物源的约束. 地质与勘探. 2024(03): 515-529 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 刘伟,张洪瑞,罗迪柯,贾鹏飞,靳立杰,周永刚,梁云汉,王子圣,李春稼. 安哥拉地块北部Dondo地区古元古代花岗岩岩石成因:Columbia超大陆聚合的响应. 地学前缘. 2024(04): 237-257 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 郑丽超,张洪瑞,韩伟鹏,宋超,罗迪柯,蔡磊光,张超,刘长友,柳军,赵博. 土壤地球化学测量在安哥拉东部沉积物覆盖区的应用. 矿产与地质. 2024(06): 1001-1014 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 任军平,张航,古阿雷,孙凯,李建武,胡鹏,孙宏伟,卢宜冠,吴兴源,周佐民,王杰,左立波,董津蒙,张津瑞. 非洲稀土资源研究进展. 地质通报. 2023(08): 1241-1257 .  本站查看
本站查看
6. 姜军胜,胡鹏,张海坤,程湘,王建雄,向文帅. 西非铁矿资源特征及成矿规律. 地质通报. 2023(08): 1276-1290 .  本站查看
本站查看
7. 何胜飞,张航,左立波,孙凯,卢宜冠,许康康,王杰. 赞比亚西北省典型铜-钴矿床地质特征与找矿方向. 地质通报. 2023(08): 1365-1376 .  本站查看
本站查看
8. 彭俊,白德胜,祁东,梁永安,楚明春. 坦桑尼亚维多利亚湖金矿田典型金矿床成矿特征与矿床成因. 地质通报. 2023(08): 1377-1389 .  本站查看
本站查看
9. 古阿雷,任军平,袁杨森,彭俊,陈靖,白令安,左立波,孙宏伟,刘晓阳,孙凯,龚鹏辉. 坦桑尼亚矿产资源及矿业投资环境. 地质通报. 2023(08): 1291-1301 .  本站查看
本站查看
10. 张鑫刚,曾国平,贾儒雅. 北非重要矿产资源时空分布与典型矿床地质特征. 地质科学. 2023(04): 1554-1570 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 刘行,王佳营,曾威,杨君,陈军强. 博茨瓦纳矿产资源开发及投资环境研究. 华北地质. 2023(04): 28-34 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)




 下载:
下载: