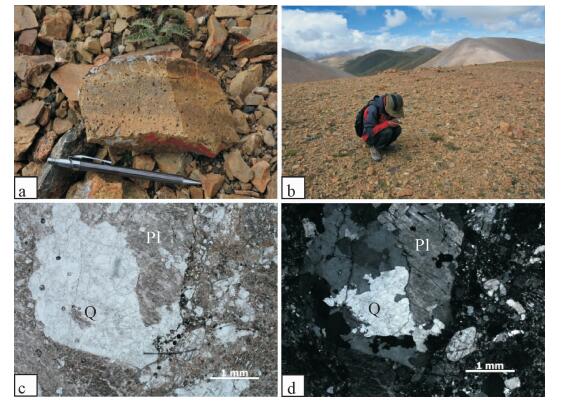
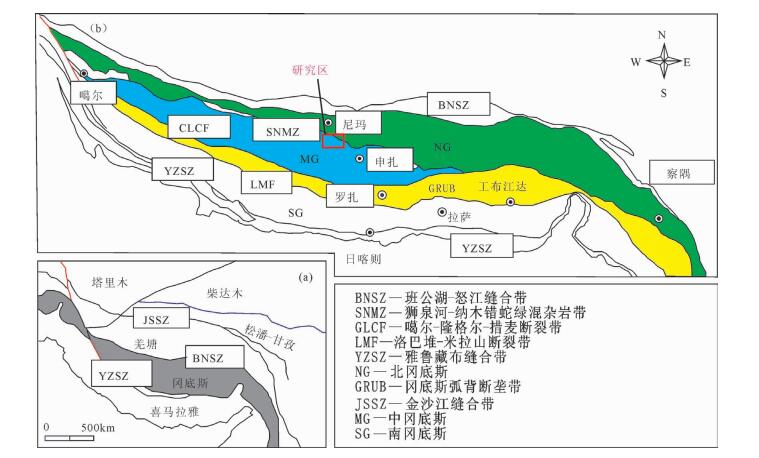
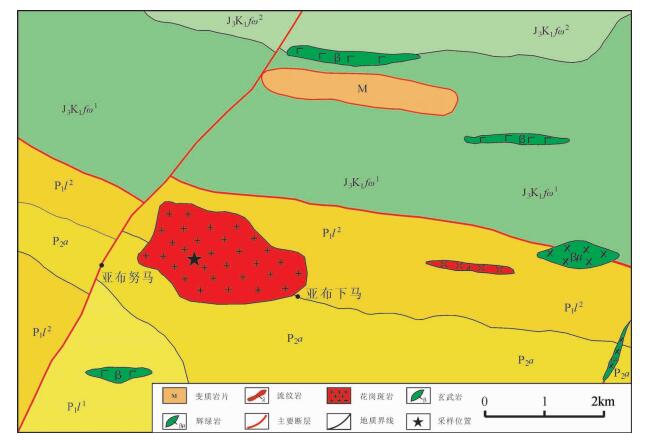
Geochemistry and zircon U-Pb age of granite porphyry in the Yabunuma region close to the southern margin of the Asuo structural melange belt, Gangdise, Tibet
-
摘要:
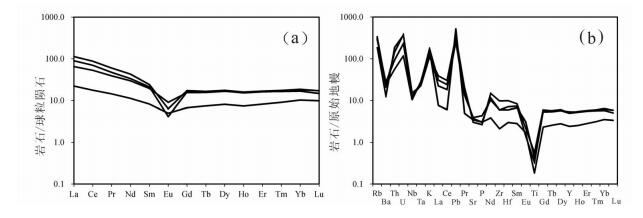
西藏中冈底斯北部尼玛县阿索乡亚布努马地区东侧出露一处花岗斑岩岩脉,LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb测年结果显示,该花岗斑岩的形成时代为晚侏罗世(161.2±5.9Ma)。全岩地球化学数据显示其高硅、富碱、富铝的特征,属于碱性准铝质花岗斑岩; 富集轻稀土元素,轻、重稀土元素分异明显,具有明显的负Eu异常,富集Rb、Pb等大离子亲石元素,亏损Ba、Sr元素及Nb、Ta、Ti、U等高场强元素,形成于岛弧环境。其源区可能为来自俯冲带增厚下地壳的深熔作用,结合区域上同时代的岩浆事件,亚布努马花岗斑岩应该形成于以班公湖-怒江洋南向俯冲为动力背景的陆缘弧环境。
Abstract:The granite porphyry vein in the Yabunuma area is located in Asuo and Nyima area of northern Central Gangdise. LAICP-MS zircon U-Pb age of 161.2±5.9Ma indicates emplacement during the Late Jurassic. The bulk rock geochemical analyses indicate the characteristics of high silica, rich alkali and Al, suggesting alkali metaluminous granite porphyry. The granite porphyry samples are rich in LREE, the fractionation between LREE and HREE is strong and shows obvious negative Eu anomalies, with the characteristics of enrichment of Rb and Pb, depletion of Ba, Sr, Nb, Ta, Ti and U, suggesting an island-arc setting. The granite porphyry is likely to root in anatexis of thickened lower crust. Considering coeval magma event in the vicinity, the authors hold that granite porphyry from Yabunuma region should have formed in an active epicontinental environment on the background of the southern subduction of Bangong Co-Nujiang Tethyan Ocean crust.
-
辽东半岛是中国重要的菱镁矿、滑石、硼、铅锌、金、银和铜成矿区。20世纪90年代以来,辽东半岛相继发现了猫岭、五龙、小佟家堡子、白云、王家崴子、四道沟等多处大、中型金矿床,该区已成为中国重要的金矿集中区。中国学者曾认为,辽东地区金矿床是产于古元古代辽东裂谷内部,受裂谷特定岩系控制的一系列金矿床[1-2]。然而,随着近年辽东地区金矿床勘查和研究的深入,发现众多金矿床受断裂构造及岩浆热液活动的复合控制[3-6]。前人在辽东地区铅锌、菱镁矿及硼矿的矿床地质及成矿理论研究方面积累了丰富的资料,而众多金矿床由于发现时间较晚,研究程度相对较低,主要存在两方面问题:①成矿时代不清,争论焦点是元古宙、中生代或多期成矿;②成矿流体和物质源区研究薄弱。由于这些关键地质问题长时间得不到有效解决,出现层控型[1]、变质热液型[3]、大气降水热液型[3]、韧性剪切带型[4]、岩浆热液型[3, 6]矿床等多种观点,极大地限制了辽东地区金矿床的理论研究水平及找矿勘查工作部署。
猫岭矿床是辽东半岛重要的大型金矿床之一,是产出在中国北方前寒武纪变质岩区为数不多的含砷浸染型金矿之一,也是著名的低品位、难选冶的金矿床[7]。笔者选择猫岭矿床开展典型矿床解剖,以期为辽东地区金矿床成矿机制及找矿方向研究提供新素材。目前,猫岭矿床的成矿时代和成矿机理研究还存在争议[7-10]。一些学者认为,金成矿作用与古元古代变质、剪切作用关系密切[7, 11-12];另一些学者认为,金成矿作用受中生代岩浆热液活动控制[13-14]。造成分歧的主要原因是缺少对猫岭矿床成矿时代的精确限定和物质源区的系统研究。本文选取猫岭矿床内卧龙泉岩体和猫岭岩体开展LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年,对载金矿物(毒砂+磁黄铁矿)开展Rb-Sr同位素测年,对成矿阶段脉石英进行H-O同位素测试,对矿石中金属硫化物开展S同位素分析,目的是确定猫岭矿床的成矿时代,查明成矿流体和成矿物质来源,探讨成矿动力学背景。
1. 区域地质背景
辽东半岛位于华北克拉通东部、郯庐断裂以东(图 1)。该区基底岩石主要由太古宙TTG岩系和古元古代浅变质沉积岩、火山岩组成,之上出露新元古代—震旦纪沉积岩[16]。太古宙岩石主要分布于金州亮甲店一带,由强变形的英云闪长岩和花岗闪长岩组成,其LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄介于2547~2518Ma之间[17]。古元古代辽河群覆盖于太古宙变质岩之上并与太古宙TTG岩系共同组成辽东半岛的基底岩石。辽河群主要由中-低级变质岩组成,包括各类片岩、片麻岩、大理岩和斜长角闪岩。中元古代后,辽东半岛经历了稳定的新元古代—古生代沉积作用,形成了一套巨厚的沉积地层[18]。
![]() 图 1 辽东半岛区域地质和主要金矿床分布简图(据参考文献[15]修改)1—中生代花岗岩;2—面理化的侏罗纪花岗岩;3—元古宙花岗岩;4—镁铁质-超镁铁质岩石;5—白垩纪陆相沉积岩;6—侏罗纪火山岩;7—石炭系-二叠系;8—寒武系-奥陶系;9—新元古代碳酸盐岩、砂岩、石英岩和板岩;10—古元古代板岩、大理岩和变泥质岩(辽河群);11—古元古代镁铁质岩浆弧带:超镁铁质岩、镁铁质岩、片麻岩、硅质岩和变泥质岩;12—片麻状混合岩和基底片麻岩;13—断裂;14—地质界线;15—金矿床:①—分水金矿;②—白云金矿;③—小佟家堡子金矿;④—石庙子金矿;⑤—王家崴子金矿;⑥—猫岭金矿;⑦—塔岭金矿;⑧—五龙金矿;⑨—四道沟金矿Figure 1. Sketch geological map of the Liaodong peninsula, showing distribution of major gold deposits in the Liaodong peninsula
图 1 辽东半岛区域地质和主要金矿床分布简图(据参考文献[15]修改)1—中生代花岗岩;2—面理化的侏罗纪花岗岩;3—元古宙花岗岩;4—镁铁质-超镁铁质岩石;5—白垩纪陆相沉积岩;6—侏罗纪火山岩;7—石炭系-二叠系;8—寒武系-奥陶系;9—新元古代碳酸盐岩、砂岩、石英岩和板岩;10—古元古代板岩、大理岩和变泥质岩(辽河群);11—古元古代镁铁质岩浆弧带:超镁铁质岩、镁铁质岩、片麻岩、硅质岩和变泥质岩;12—片麻状混合岩和基底片麻岩;13—断裂;14—地质界线;15—金矿床:①—分水金矿;②—白云金矿;③—小佟家堡子金矿;④—石庙子金矿;⑤—王家崴子金矿;⑥—猫岭金矿;⑦—塔岭金矿;⑧—五龙金矿;⑨—四道沟金矿Figure 1. Sketch geological map of the Liaodong peninsula, showing distribution of major gold deposits in the Liaodong peninsula中生代期间,辽东半岛发育大面积的花岗岩和火山岩(约20000km2),尤其是花岗岩广泛出露在辽东半岛[16, 19-20]。吴福元等[21]将辽东半岛中生代岩浆活动划分为3期,即三叠纪(212~233Ma)、侏罗纪(156~180Ma)和白垩纪(117~131Ma)。辽东半岛中生代盆地发育较局限,主要形成于晚侏罗世—早白垩世。其中,早—中侏罗世沉积盆地的分布十分有限,仅分布在瓦房店东部、本溪县东部、东南部等地区。晚侏罗世—早白垩世沉积盆地常与变质核杂岩及同构造花岗岩成对发育,表明这一时期广泛发育伸展构造[18, 22-24]。
2. 矿床地质
猫岭矿床位于辽宁省盖州市太平庄乡,大地构造位置处于华北克拉通北缘胶-辽-吉活动带。金储量约45t,平均品位3.2g/t[12]。矿区出露地层为辽河群盖县组和榆树砬子群(图 2)。辽河群盖县组分布面积最大,其变质程度较低,为绿片岩相,岩石类型为绢云千枚岩,夹薄层变质长石石英砂岩。榆树砬子群呈近EW向展布,角度不整合覆盖于辽河群盖县组之上,岩石类型为石英岩,夹绢云千枚岩、含赤铁矿石英岩及薄层变质石英砂岩。区内断裂构造较发育,主要为NE向和NNE向,次为NW向和SN向[7]。区内岩浆岩有卧龙泉岩体和猫岭岩体。卧龙泉岩体分布于矿床西北部卧龙泉一带,侵入到盖县组中,岩石类型为二长花岗岩。猫岭岩体位于矿区南部,出露面积约0.4km2,侵入到盖县组和榆树砬子群中,岩石类型为二长花岗岩。矿区内发育少量脉岩,主要为闪长玢岩、闪长岩脉,呈NW及NNE向产出。
![]() 图 2 猫岭矿床地质简图(据参考文献[12]修改)Figure 2. Geological map of the Maoling deposit
图 2 猫岭矿床地质简图(据参考文献[12]修改)Figure 2. Geological map of the Maoling deposit猫岭矿床主要有Ⅰ、Ⅱ、Ⅲ、Ⅳ号矿化蚀变带,矿化蚀变带与围岩呈渐变关系,其中Ⅰ、Ⅱ号矿化蚀变带赋存工业矿体,Ⅲ、Ⅳ号矿化蚀变带仅见金矿化现象(图 2)。Ⅰ号矿化蚀变带是主矿化带,工业矿体数众多、分布集中。矿化蚀变带长约1500m,宽80~470m,延伸300~500m,倾向288°~315°,倾角50°~70°。金矿体均赋存于矿化蚀变带中,与蚀变岩带呈渐变过渡关系,矿体规模、形态及产状均由金品位圈定。矿体产状亦受NE向、NW向韧性剪切带及次级断裂控制。矿体主要呈脉状、似层状、透镜状。矿石类型有石英脉型和蚀变岩型。矿石组构包括浸染状构造、细脉浸染状构造、脉状构造、压碎结构、自形-半自形粒状结构、交代溶蚀结构、交代残余结构、充填结构、包含结构等。矿石矿物主要为毒砂和磁黄铁矿,其次为黄铁矿、方铅矿、闪锌矿和黄铜矿(图版Ⅰ)。毒砂是主要载金矿物,占金属矿物总量的50%以上。脉石矿物主要为绢云母和石英,其次为黑云母、绿泥石、长石和方解石。自然金、银金矿和金银矿主要呈粒状、不规则状存在于毒砂、磁黄铁矿、石英等矿物晶粒或裂隙之间,少量包裹在石英和毒砂中[11]。根据岩石蚀变作用强度和矿物组合特征,围岩蚀变分为中心带和边缘带,中心带为强硅化带,富集金矿体;边缘带发育绢云母化和绿泥石化,金矿体稀少且分布不均。成矿作用划分为4个阶段:石英-毒砂±磁黄铁矿阶段(Ⅰ)、石英-磁黄铁矿±毒砂阶段(Ⅱ)、石英-多金属硫化物阶段(Ⅲ)及石英-碳酸盐阶段(Ⅳ) [7, 11-12]。
3. 样品特征及分析方法
3.1 锆石U-Pb定年
猫岭矿区卧龙泉岩体和猫岭岩体的采样位置见图 2。卧龙泉二长花岗岩(样品LM-122)呈似斑状结构,主要矿物为斜长石(35%)、钾长石(25%)、石英(25%)及黑云母(15%)。斜长石呈半自形-自形板状,聚片双晶,大小2~5mm,见轻微高岭石化。钾长石呈半自形板状或他形粒状,大小1~4mm,见条纹结构和格子状结构,部分晶体表面高岭石化。石英呈半自形或他形粒状,大小0.5~2mm。黑云母呈片状,大小0.3~1mm。副矿物见锆石、磷灰石和磁铁矿;猫岭二长花岗岩(样品LM-119)呈似斑状结构,主要矿物为斜长石(35%)、钾长石(30%)、石英(25%)及黑云母(10%)。斜长石呈半自形-自形板状,聚片双晶,大小0.5~1.5mm,见绢云母化和高岭石化。钾长石呈半自形板状或他形粒状,大小0.5~ 1mm,发育高岭石化。石英呈半自形或他形粒状,大小0.1~0.2mm。黑云母呈片状,大小0.1~ 0.3mm。副矿物见锆石、磷灰石和磁铁矿。
将采集的新鲜岩石样品破碎,按重力和磁选方法分选,最后在双目镜下根据锆石颜色、自形程度、形态等特征分类,挑选出代表性锆石。将分选好的锆石用环氧树脂制靶、打磨和抛光。锆石的阴极发光(CL)图像在北京锆年领航科技有限公司完成,仪器为日本JEOL公司生产的JSM 6510型扫描电子显微镜。LA-MC-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年测试工作在国土资源部成矿作用与资源评价重点实验室完成,锆石定年分析仪器为Finnigan Neptune型MCICP-MS及与之配套的Newwave UP 213激光剥蚀系统。激光剥蚀所用束斑直径为25μm,频率为10Hz,能量密度约为2.5J/cm2,以氦为载气。信号较小的207Pb、206Pb、204Pb(+ 204Hg)、202Hg用离子计数器(multi-ion-counters)接收,208Pb、232Th、238U信号用法拉第杯接收,实现了所有目标同位素信号的同时接收,并且不同质量数的峰基本上都是平坦的,进而可以获得高精度的数据,均匀锆石颗粒207Pb/206Pb、206Pb/238U、207Pb/235U的测试误差均为2%左右,对锆石标准的定年误差在1%左右。测试过程中每测定5~7个样品前后重复测定2个锆石标准GJ1对样品进行校正,并测量1个锆石标准Plesovice,观察仪器的状态以保证测试的精确度。详细实验测试过程见参考文献[25]。
3.2 硫化物Rb-Sr定年
用于Rb-Sr测年的10件金属硫化物样品采自猫岭矿床Ⅰ号矿化蚀变带的露天采坑内。10件样品沿Ⅰ号矿化带走向以0.5m的间距依次采集,均为石英-毒砂±磁黄铁矿脉。将矿石样品粉碎到40~ 80目,在双目镜下挑选出毒砂和磁黄铁矿单矿物,纯度达99%以上。将选出的毒砂和磁黄铁矿用蒸馏水清洗,低温蒸干,然后将纯净的单矿物样品在玛瑙研钵内研磨至200目左右待测。因为金属矿物的Rb、Sr含量较低,甚至低于0.01×10-6,为了确保RbSr同位素定年的可行性,首先在中国科学院土壤研究所技术服务中心对毒砂和磁黄铁矿样品进行了微量元素Rb、Sr含量的草测,在此基础上,挑选适合定年的样品在中国科学院土壤研究所技术服务中心进行Rb、Sr含量和同位素组成测定。具体分析方法如下:原粉末样品用混合酸溶解,取清液上离子交换柱分离,采用高压密闭熔样和阳离子交换技术分离和提纯,然后用英国产的VG354热电离同位素质谱仪测定,测定方法详见参考文献[26-27]。用于测定的美国NBS987同位素标样为:87Sr/86Sr= (0.710236±7),Sr的全流程空白为(5~7) ×10-9 g,87Sr/86Sr同位素比值用86Sr/88Sr=0.1194进行标准化。87Sr/86Sr的分析误差约为1%,λRb=1.42 × 10-11a-1。等时线年龄用Isoplot程序计算[28]。
3.3 稳定同位素分析
样品采自猫岭金矿Ⅰ号矿化蚀变带的露天采坑内,为石英-毒砂±磁黄铁矿脉和石英-磁黄铁矿±毒砂脉。H-O同位素分析在核工业北京地质研究院分析测试研究中心完成,所用仪器为MAT 253型质谱仪。矿物的氧同位素分析采用BrF5法[29];包裹体水的氢同位素分析采用爆裂法取水、锌法制氢,爆裂温度为550℃。氢、氧同位素分析误差分别为±2‰和±0.2‰,分析结果均以SMOW为标准。石英水中氧同位素根据测试的石英中氧同位素采用分馏方程1000lnαQ-W=δ18OQ-δ18OW=3.38×106/T2-3.4[30]及同一阶段内流体包裹体完全均一温度平均值计算获得。
金属硫化物样品的硫同位素分析在核工业北京地质研究院分析测试研究中心完成。金属硫化物单矿物和氧化亚铜按一定比例研磨至200目左右,并混合均匀,在真空达2.0×10-2 Pa状态下加热,进行氧化反应,反应温度为980℃,生成二氧化硫气体。在真空条件下,用冷冻法收集二氧化硫气体,并用MAT 253气体同位素质谱分析硫同位素组成。测量结果以CDT为标准,记为δ34S。分析误差优于0.2‰。硫化物参考标准为GBW-04414、GBW-04415硫化银标准,其δ34S分别是-0.07‰± 0.13‰和22.15‰±0.14‰。
4. 测试结果
4.1 锆石U-Pb年龄
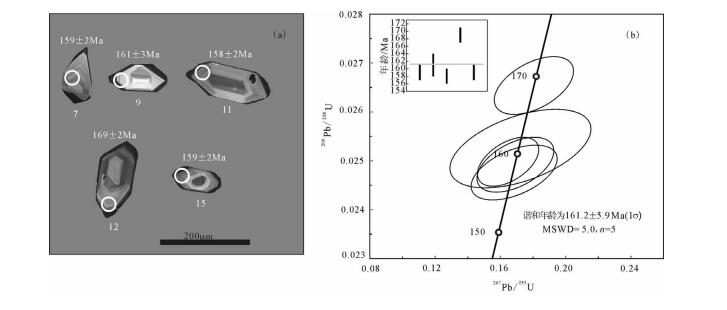
卧龙泉岩体(样品LM-122)锆石大多呈长柱状,少量为短柱状,粒径集中在50~200μm,无色透明。阴极发光图像显示,锆石大多具有清楚的生长韵律环带(图 3-a)。16颗锆石的Th/U值为0.1~ 0.8,平均值为0.2,大于0.1;Th含量为158×10-6~ 1271×10-6,平均值为581×10–6;U含量为1121×10-6~ 6450×10-6,平均值为3042×10-6(表 1)。据此认为,锆石为岩浆成因。在207Pb/235U-206Pb/238U谐和图(图 4-a)上,16个分析点落在谐和线上及其附近,其206Pb/238U年龄加权平均值为183.0 ± 1.8Ma (MSWD=0.1)。
表 1 猫岭矿床卧龙泉岩体和猫岭岩体LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Th-Pb分析结果Table 1. LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Th-Pb data of the Wolongquan and Maoling intrusions from the Maoling deposit样品号 含量/10–6 同位素比值 Th/U 年龄/Ma Pb Th U 207Pb/206Pb 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ 卧龙泉岩体 LM-122.01 168 713 5090 0.0504 0.00103 0.1983 0.0038 0.02851 0.0003 0.1 181.2 1.9 LM-122.02 143 709 4462 0.05112 0.00064 0.202 0.0027 0.0286 0.00031 0.2 181.8 1.9 LM-122.03 70 488 2205 0.04992 0.00079 0.197 0.0029 0.02864 0.0003 0.2 182 1.9 LM-122.04 51 231 1609 0.05283 0.00096 0.2091 0.0039 0.02864 0.00026 0.1 182 1.6 LM-122.05 116 776 3585 0.05073 0.0008 0.2002 0.004 0.02864 0.0005 0.2 182.1 3.1 LM-122.06 119 1077 3483 0.05096 0.00115 0.2015 0.0048 0.02865 0.00032 0.3 182.1 2.0 LM-122.07 65 373 2072 0.04976 0.0007 0.1971 0.0027 0.02871 0.00026 0.2 182.4 1.6 LM-122.08 40 158 1121 0.05488 0.00177 0.2192 0.0073 0.02878 0.00036 0.1 182.9 2.3 LM-122.09 119 557 3478 0.0565 0.00128 0.2241 0.0051 0.02883 0.0003 0.2 183.2 1.9 LM-122.10 48 955 1218 0.05624 0.0018 0.2251 0.0072 0.02887 0.00033 0.8 183.5 2.1 LM-122.11 160 1271 4533 0.0533 0.00112 0.2125 0.0037 0.02888 0.00029 0.3 183.5 1.8 LM-122.12 85 460 2843 0.05639 0.00148 0.2236 0.0075 0.02891 0.00096 0.2 183.7 6.0 LM-122.13 109 373 3168 0.05823 0.0014 0.2325 0.0046 0.02893 0.00035 0.1 183.8 2.2 LM-122.14 43 182 1378 0.05502 0.00127 0.2193 0.0048 0.02899 0.00041 0.1 184.2 2.6 LM-122.15 212 733 6450 0.05835 0.00087 0.2346 0.0042 0.02906 0.00029 0.1 184.6 1.8 LM-122.16 65 236 1972 0.05665 0.00122 0.2282 0.0051 0.02915 0.00028 0.1 185.2 1.7 猫岭岩体 LM-119.01 10 377 382 0.05065 0.00261 0.1383 0.0069 0.0199 0.00044 1.0 127.0 2.8 LM-119.02 5 153 199 0.04875 0.004 0.1337 0.0099 0.01993 0.00082 0.8 127.2 5.2 LM-119.03 7 181 255 0.04903 0.00199 0.1346 0.0055 0.01993 0.00032 0.7 127.2 2.0 LM-119.04 6 185 223 0.05034 0.003 0.1388 0.0086 0.02 0.0005 0.8 127.7 3.2 LM-119.05 11 342 444 0.0482 0.0019 0.1326 0.0048 0.02013 0.0004 0.8 128.5 2.5 LM-119.06 8 270 301 0.04901 0.00165 0.1357 0.0047 0.02023 0.00029 0.9 129.1 1.8 LM-119.07 9 242 291 0.04939 0.00353 0.1383 0.0096 0.0204 0.00054 0.8 130.2 3.4 LM-119.08 7 185 235 0.04931 0.00183 0.1378 0.0051 0.02046 0.00034 0.8 130.6 2.2 LM-119.09 9 279 331 0.04962 0.00186 0.1385 0.005 0.02047 0.00041 0.8 130.7 2.6 LM-119.10 27 420 546 0.05216 0.00234 0.2732 0.011 0.03824 0.00143 0.8 241.9 8.9 LM-119.11 8 117 141 0.04956 0.00364 0.2689 0.0213 0.03941 0.00134 0.8 249.2 8.3 LM-119.12 689 1069 1678 0.1205 0.0012 5.0004 0.0898 0.30131 0.0053 0.6 1697.8 26.2 LM-119.13 571 744 1434 0.1173 0.0018 4.9207 0.0989 0.30301 0.00477 0.5 1706.2 23.6 猫岭岩体(样品LM-119)锆石大多呈短柱状,少量为长柱状,粒径集中在50~100μm,无色透明。阴极发光图像显示,锆石多数具清楚的生长韵律环带(图 3-b)。13颗锆石的Th/U值介于0.5~ 1.0之间,平均值为0.8,大于0.1;Th含量介于117× 10-6~1069×10-6之间,平均值为351×10-6;U含量介于141×10-6~1678×10-6之间,平均值为497×10-6(表 1)。属于典型的岩浆成因锆石。在207Pb/235U-206Pb/238U谐和图上(图 4-b),9个点落在谐和线上及其附近,其206Pb/238U年龄加权平均值为128.8 ± 1.6Ma (MSWD=0.3)。另有4颗锆石的206Pb/238U年龄分别为241.9±8.9Ma、249.2±8.3Ma、1697.8±26.2Ma、1706.2±23.6Ma(点LM-119.10、LM-119.11、LM-119.12和LM-119.13),应为捕获的早期岩浆锆石。
4.2 硫化物Rb-Sr年龄
10件样品(毒砂和磁黄铁矿)的Rb、Sr含量和同位素组成测试结果见表 2。10件金属硫化物样品的Rb-Sr等时线年龄为2287±95Ma,初始锶同位素比值ISr=0.7117,MSWD=1.9 (图 5)。
表 2 猫岭矿床金属硫化物Rb-Sr同位素分析结果Table 2. Rb-Sr isotopic analyses of metallic sulfides from the Maoling deposit序号 样号 样品描述 分析矿物 Rb/10–6 Sr/10–6 87Rb/86Sr 87Sr/86Sr(2σ) 1 LM-11 石英-毒砂±磁黄铁矿脉 毒砂 0.3243 2.117 0.4508 0.725791±0.000009 2 LM-12 石英-毒砂±磁黄铁矿脉 毒砂 0.2506 1.439 0.5136 0.734573±0.000012 3 LM-12 石英-毒砂±磁黄铁矿脉 磁黄铁矿 0.6938 0.3416 5.981 0.909864±0.000010 4 LM-13 石英-毒砂±磁黄铁矿脉 毒砂 0.1235 7.408 0.0492 0.711808±0.000008 5 LM-14 石英-毒砂±磁黄铁矿脉 毒砂 0.0839 1.973 0.1247 0.714946±0.000009 6 LM-18 石英-毒砂±磁黄铁矿脉 毒砂 0.1407 0.4209 0.9834 0.742992±0.000007 7 LM-19 石英-毒砂±磁黄铁矿脉 毒砂 0.1531 0.4108 1.105 0.752298±0.000013 8 LM-20 石英-毒砂±磁黄铁矿脉 磁黄铁矿 0.7345 0.5931 3.654 0.832743±0.000009 9 LM-21 石英-毒砂±磁黄铁矿脉 毒砂 0.3821 0.5696 1.982 0.775928±0.000008 10 LM-22 石英-毒砂±磁黄铁矿脉 毒砂 0.3509 0.6188 1.675 0.761271±0.000016 4.3 稳定同位素分析结果
8件石英样品氧同位素及其中流体包裹体氢同位素测试结果见表 3。石英的δ18O值介于14.0 ‰ ~16.3 ‰之间,样品的δDW值介于-97.2‰ ~-82.6‰之间,计算出的δ18OW值介于6.3‰~9.7‰之间。
表 3 猫岭矿床氢、氧同位素分析结果Table 3. Hydrogen and oxygen isotope compositions of the Maoling deposit样号 成矿阶段 样品描述 测试矿物 δD/‰ δ18Oquartz/‰ δ18Owater/‰ T/℃ LM-2 Ⅰ 石英-毒砂±磁黄铁矿脉 石英 -87.7 15.2 8.6 308 LM-3 Ⅰ 石英-毒砂±磁黄铁矿脉 石英 -89.2 16.1 9.5 308 LM-4 Ⅰ 石英-毒砂±磁黄铁矿脉 石英 -82.6 16.3 9.7 308 LM-1 Ⅱ 石英-磁黄铁矿±毒砂脉 石英 -86.0 14.9 7.2 279 LM-5 Ⅱ 石英-磁黄铁矿±毒砂脉 石英 -89.5 14.7 7.0 279 LM-6 Ⅱ 石英-磁黄铁矿±毒砂脉 石英 -83.6 15.2 7.5 279 LM-7 Ⅱ 石英-磁黄铁矿±毒砂脉 石英 -97.2 14.0 6.3 279 LM-10 Ⅱ 石英-磁黄铁矿±毒砂脉 石英 -82.7 15.0 7.3 279 注:流体包裹体完全均一温度(T)数据据参考文献[11] 16件金属硫化物的硫同位素组成见表 4。11件磁黄铁矿的δ34S值介于+5.0‰~+7.6‰之间;5件毒砂的δ34S值为+8.5‰~+10.1‰。
表 4 猫岭矿床金属硫化物硫同位素分析结果Table 4. Sulfur isotopic compositions of metallic sulfides from the Maoling deposit序号 样号 成矿阶段 测试矿物 δ34S/‰ 数据来源 序号 样号 成矿阶段 测试矿物 δ34S/‰ 数据来源 1 LM-11 Ⅱ 磁黄铁矿 5.5 本文 22 L9* Ⅰ 毒砂 4.3 [11] 2 LM-13 Ⅱ 磁黄铁矿 5.0 本文 23 L8-1* Ⅰ 毒砂 6.8 [11] 3 LM-18 Ⅱ 磁黄铁矿 6.5 本文 24 L8* Ⅰ 毒砂 8.1 [11] 4 LM-20 Ⅰ 毒砂 8.5 本文 25 L8-2* Ⅰ 毒砂 9.1 [11] 5 LM-21 Ⅱ 磁黄铁矿 6.1 本文 26 L9-1* Ⅱ 毒砂 9.2 [11] 6 LM-22 Ⅱ 磁黄铁矿 6.1 本文 27 L14-2* Ⅰ 毒砂 9.0 [11] 7 LM-101 Ⅰ 毒砂 9.7 本文 28 L5* Ⅱ 方铅矿 6.4 [11] 8 LM-103 Ⅰ 毒砂 9.3 本文 29 L5-1* Ⅱ 黄铁矿 10.0 [11] 9 LM-104 Ⅰ 磁黄铁矿 6.8 本文 30 3LH3208* Ⅰ 毒砂 8.9 [11] 10 LM-107 Ⅰ 毒砂 9.2 本文 31 MSP94* Ⅰ 毒砂 9.9 [11] 11 LM-110 Ⅰ 毒砂 10.1 本文 32 3LH3216* Ⅰ 毒砂 9.1 [11] 12 LM-112 Ⅰ 磁黄铁矿 7.6 本文 33 3LH3227* Ⅰ 毒砂 9.7 [11] 13 LM-113 Ⅰ 磁黄铁矿 7.5 本文 34 MSP48* Ⅰ 磁黄铁矿 7.4 [11] 14 LM-114 Ⅱ 磁黄铁矿 7.3 本文 35 MSP68* Ⅰ 磁黄铁矿 7.2 [11] 15 LM-115 Ⅱ 磁黄铁矿 7.2 本文 36 MSZHC* Ⅱ 毒砂 7.4 [11] 16 LM-116 Ⅱ 磁黄铁矿 6.8 本文 37 MSZHD* Ⅱ 毒砂 9.0 [11] 17 L30 Ⅰ 毒砂 5.2 [11] 38 MND* Ⅰ 毒砂 10.2 [11] 18 L31 Ⅰ 毒砂 7.4 [11] 39 MNQD* Ⅰ 毒砂 9.8 [11] 19 L32* Ⅱ 毒砂 4.6 [11] 40 MNZHC* Ⅰ 磁黄铁矿 7.3 [11] 20 L33* Ⅰ 毒砂 10.5 [11] 41 MSCH* Ⅱ 磁黄铁矿 7.5 [11] 21 L14-1* Ⅰ 毒砂 8.7 [11] 42 MNZHD* Ⅱ 磁黄铁矿 8.3 [11] 5. 讨论
5.1 成矿流体及物质来源
刘辉等[11]对猫岭矿床开展了流体包裹体研究,发现成矿流体温度从早阶段的391~270℃逐渐降低到晚阶段的212~153℃,盐度也从早阶段的10.1%~ 9.0%NaCl降低到晚阶段的7.3%~6.3%NaCl,且各阶段成矿流体的成分组合和含量均无明显变化,表明成矿流体未发生过流体沸腾或不混溶作用。在δ18OW-δD图(图 6)中,猫岭金矿不同成矿阶段流体的氢-氧同位素组成存在一定差异,氢-氧同位素投影点靠近岩浆水区域,指示成矿流体以岩浆水为主,从成矿阶段Ⅰ到Ⅱ,成矿流体的δ18OW值向大气降水线接近,表明流体演化晚期有少量大气降水混入,这与上述成矿流体温度和盐度逐渐降低的规律吻合。
![]() 图 6 猫岭矿床δ18OW-δD体系图(据参考文献[31]修改)Figure 6. δD versus δ18OW diagram of the Maoling deposit
图 6 猫岭矿床δ18OW-δD体系图(据参考文献[31]修改)Figure 6. δD versus δ18OW diagram of the Maoling depositOhmoto[32]指出,热液矿床中硫化物的硫同位素组成是成矿溶液中总硫同位素组成、氧逸度、pH、离子强度和温度的函数。因此,热液硫化物的硫同位素组成,不仅取决于其源区物质的δ34S值,而且与成矿流体演化的物理化学条件有关,当fO2较低时,流体中硫主要以HS-、S2-形式存在,所沉淀的硫化物δ34S与整个流体δ34S近似;当fO2较高时,SO42-大量存在并沉淀富集δ34S的硫酸盐,导致成矿流体δ34S亏损,所沉淀的黄铁矿等硫化物的δ34S值较低(常为负值),低于整个体系的δ34S值。硅化和绢云母化是猫岭矿床主要的蚀变类型,硫化物主要为毒砂和磁黄铁矿,未见硫酸盐矿物。因此,猫岭矿床中金属硫化物的硫同位素组成可以近似地代表成矿溶液总硫同位素组成。目前,硫同位素主要有3个存储库,①地幔硫或岩浆硫,其δ34S值介于-3‰~+3‰之间;②海水硫,现代海水的δ34S值近似于20‰;③沉积物中的还原硫,其δ34S值以极差大并具有较大的负值为特征[33-34]。猫岭矿床的δ 34S值介于+4.3‰ ~+10.5‰之间,平均值为+7.9‰ (表 4),区别于岩浆硫同位素特征,而与赋矿地层辽河群盖县组的硫同位素组成相似(图 7)。二者的硫同位素组成在直方图上以塔式分布为特征,且峰值特征非常一致,表明猫岭矿床的硫物质源区主要为辽河群盖县组。
![]() 图 7 猫岭矿床及相关地质体硫同位素组成(硫同位素数据据本文和参考文献[11])Figure 7. Sulfur isotopic composition histograms of sulfide minerals from the Maoling deposit and regional rocks
图 7 猫岭矿床及相关地质体硫同位素组成(硫同位素数据据本文和参考文献[11])Figure 7. Sulfur isotopic composition histograms of sulfide minerals from the Maoling deposit and regional rocks5.2 成矿时代及构造背景
近年来,随着测试技术的进步和测试仪器的改良,已经可以利用金属矿物直接对矿床进行Rb-Sr同位素精确测年[35-36]。例如,石文杰等[37]获得山东龙泉站金矿床黄铁矿Rb- Sr等时线年龄为96.0 ± 2.0Ma;赵晓燕等[38]获得西藏邦铺钼多金属矿床的共生矿物(闪锌矿+黄铁矿)Rb- Sr等时线年龄为13.93±0.87Ma;杨晨英等[39]获得豫西骆驼山多金属硫铁矿的共生矿物(闪锌矿+磁黄铁矿+方铅矿) Rb-Sr等时线年龄为137.3±2.6Ma。刘建明等[40-41]指出不同矿物相的化学势具有一定差异,而化学性质不同的矿物中Rb和Sr会产生化学分异,从而使同一成矿流体中沉淀出的共生矿物具有不同的Rb、Sr比值,进而利用热液矿物组合的等时线分析成矿年龄比较可靠。本文选择猫岭矿床中共生矿物组合(毒砂+磁黄铁矿)开展Rb-Sr同位素测年研究,获得Rb-Sr等时线年龄为2287±95Ma,与喻钢等[12]获得的猫岭金矿中毒砂的Re- Os等时线年龄(2316±140Ma)在误差范围内一致。邱小平[7]认为,猫岭矿床与古元古代辽河群早期面理为同一构造期的产物,金矿化期发育的强硅化蚀变圈具有不透水性和强硬的岩石力学性质,形成了封闭-半封闭的屏蔽环境,使猫岭矿床的古元古代成矿特征(矿石矿物组成、结构构造、同位素组成、辽河群古元古代早期面理)得以完好保存,免遭后期构造-岩浆热事件的改造破坏。李文博等[42]进一步指出,利用87Rb/86Sr-1/Rb图解和87Sr/86Sr-1/Sr图解可以分析硫化物生长期间87Sr/86Sr初始值的变化情况,进而判断Rb-Sr同位素数据的合理性。在87Rb/86Sr-1/Rb图解和87Sr/86Sr-1/Sr图解(图 8)中,猫岭矿床共生矿物组合(磁黄铁矿+毒砂)的Rb、Sr含量不同,1/Sr与87Sr/ 86Sr、1/Rb与87Rb/86Sr之间不存在线性关系,且相对稳定,表明共生矿物生长期间87Sr/86Sr初始值保持不变,证明本次获得的等时线年龄具有地质意义。
猫岭矿区内卧龙泉岩体和猫岭岩体的锆石UPb年龄分别为183.0±1.8Ma、128.8±1.6Ma,岩体侵位年龄明显晚于猫岭金矿化时间,表明卧龙泉岩体及猫岭岩体与猫岭金矿化作用无成因联系。辽河群的年龄组成异常复杂,其沉积时限的精确测定一直存在较大争议[17]。近年来,地质工作者对辽河群开展了较多的精细测年工作[43],例如刘福来等[44]发现,辽河群中变质锆石的最老变质年龄约为1.95Ga,继承性碎屑锆石最小年龄为2.05Ga,认为辽河群形成时间为1.95~2.05Ga;路孝平等[17]通过辽东半岛前寒武纪花岗岩的研究,认为辽河群形成于1.85~2.16Ga;陈井胜等[43]通过辽河群火山岩成因的研究,结合前人资料,认为辽河群形成时间至少开始于2.19Ga,直到1.96Ga沉积作用结束。另有学者认为,辽河群的形成时代更早,辽东明安硼镁矿混合花岗岩的2229±3Ma年龄代表了辽河群中酸性火山岩的喷发时代[45],辽河群强烈的δCcarb13正漂移现象表明辽河群形成于2.06~2.33Ga之间[46]。猫岭矿床赋存于古元古代辽河群中,其成矿年龄为2287± 95Ma,表明辽河群的形成时代应早于2287Ma。
孟恩等[47]在辽河群中发现大量2.3Ga左右的继承岩浆锆石,指出这些锆石来源于胶-辽-吉活动带内同时期的花岗质岩石或火山岩。李三忠等[48]发现,辽吉花岗岩的年龄几乎都介于2.2~1.2Ga之间,这些花岗岩并不是辽河群沉积的基底,而是与辽河群为同一构造运动的产物[43, 49-51]。王祥俭等[52]报道了辽东宽甸地区辽河群中花岗质片麻岩体的LAICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄为2332±100Ma,认为其来源于伸展构造背景下大陆物质的部分熔融。陈井胜等[43]总结了辽河群中侵入岩及火山岩的年龄资料,发现辽河群在沉积过程中至少存在3期岩浆活动,2190~2180Ma、2110~2100Ma、1970~1960Ma,其中辽河群中最早一期的酸性火山岩的活动时间为2192±17Ma。目前,猫岭金矿区内尚未发现古元古代岩体,但其成矿年龄与辽河群中最早一期的岩浆-热液活动时间在误差范围内一致。本文的氢氧同位素资料亦表明,猫岭矿床成矿流体主要来源于岩浆热液。因此,笔者认为,猫岭矿床可能与辽河群早期的同构造岩浆-热液活动关系密切,而同期形成的强硅化蚀变圈保护金矿体免受后期地质作用的破坏。
胶-辽-吉古元古代活动带形成的构造背景及演化模式至今仍存在争论[44],一些学者认为是陆内裂谷开启-闭合模式[53-59];另有学者认为是弧-陆碰撞模式[60-62]或陆-陆碰撞模式[63-64];Zhao等[64]进一步提出,为古元古代先裂谷-后碰撞的造山演化模式。虽然胶-辽-吉古元古代活动带的地质演化过程仍有争议,但是上述几种构造模式均支持胶-辽-吉地区在古元古代早期处于伸展构造背景这一论断。因此,猫岭矿床形成于古元古代早期的伸展构造背景,成矿流体主要来源于辽河群早期的同构造岩浆热液活动,成矿物质主要来自于辽河群,同时也有少量岩浆流体的贡献。
6. 结论
(1) 猫岭矿区内卧龙泉岩体和猫岭岩体的LAICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄分别为183.0±1.8Ma和128.8±1.6Ma。金属硫化物Rb-Sr等时线年龄为2287±95Ma。猫岭矿床形成于古元古代早期的伸展构造背景。
(2) 猫岭矿床成矿流体以岩浆热液为主,混入少量大气降水。成矿物质主要来源于古元古代辽河群盖县组。金成矿作用与辽河群早期的同构造岩浆-热液活动有关,同期形成的强硅化蚀变圈保护金矿体免受后期地质作用的破坏。
致谢: 野外工作时吉林大学西藏科研队的老师、同学们及后勤师傅们给予诸多帮助,文章撰写期间,吉林大学王伟硕士提供了宝贵的意见,地球化学测试及碎屑锆石测试分析由中国地质大学(北京)科学研究院实验中心苏犁老师等帮助完成,在此一并致谢。 -
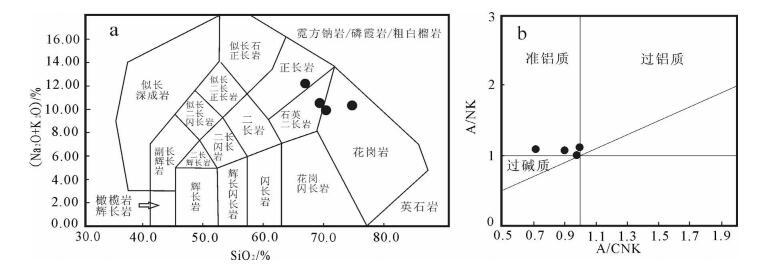
图 4 亚布努马花岗斑岩SiO2-K2O图解[9]
Figure 4. SiO2-K2O diagram of granite porphyry from the Yabunuma region
图 8 亚布努马花岗斑岩成因类型判别图解(底图据参考文献[18])
a—花岗斑岩1000Ga/Al-Nb图解; b—花岗斑岩10000Ga/Al-Ce图解; c—花岗斑岩10000Ga/Al-Zr图解
Figure 8. Various chemical discrimination diagrams for the granite porphyry from Yabunuma region
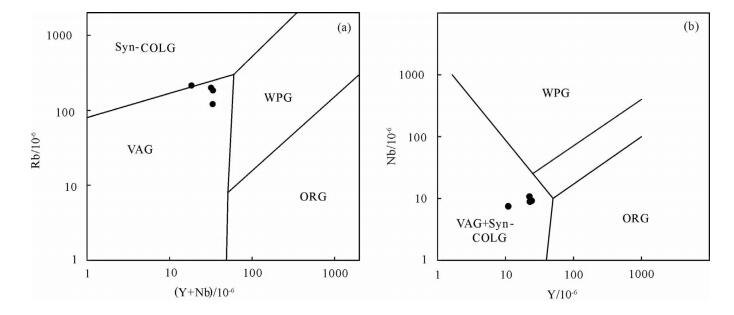
图 9 亚布努马花岗斑岩构造判别图解[29]
a—花岗斑岩(Y+Nb)-Rb图解; b—花岗斑岩Y-Nb图解; Syn-COLG—同碰撞花岗岩; VAG—火山弧花岗岩; WPG—板内花岗岩; ORG—洋中脊花岗岩
Figure 9. Discrimination diagrams for the structural environment of the granite porphyry from Yabunuma region
表 1 亚布努马地区花岗斑岩样品主量、微量和稀土元素分析结果
Table 1 Major, trace elements and REE data of the granite porphyry in the Yabunuma region
样品号 SiO2 TiO2 Al2O3 TFe2O3 MnO MgO CaO Na2O K2O P2O5 烧失量 总计 N16T18H1 68.45 0.10 13.96 0.80 0.01 0.47 3.68 4.12 5.53 0.09 2.77 99.98 N16T18H2 74.05 0.04 13.47 0.72 0.02 0.20 0.23 4.02 6.23 0.06 0.46 99.51 N16T18H4 65.96 0.08 17.39 0.81 0.01 0.45 1.72 5.64 6.37 0.06 1.50 99.98 N16T18H5 68.42 0.14 16.31 1.38 0.01 0.91 0.99 5.90 4.48 0.06 1.08 99.68 样品号 Li P K Sc Ti V Cr Mn Co Ni Cu N16T18H1 3.02 412.8 37820 3.072 547.8 4.646 0.09072 129.48 1.0356 1.835 1.8172 N16T18H2 0.18036 288.8 39540 3.184 238.6 4.276 0.4062 163 0.729 2.174 3.996 N16T18H4 1.6922 289.4 43420 4.56 428 5.06 0.4146 118.94 0.9524 1.4962 1.9416 N16T18H5 7.132 254 27620 3.206 732.6 6.724 13.75 108.3 1.0418 8.836 1.958 样品号 Zn Ga Rb Sr Y Zr Nb Cs Ba La Ce N16T18H1 12.262 11.478 183.64 82.8 24.36 67.16 9.164 2.524 188.78 15.31 32.3 N16T18H2 15.036 11.824 213.4 72.92 10.99 23.66 7.44 5.442 168.32 5.23 10.74 N16T18H4 12.702 14.226 198.8 78.36 22.96 66.72 8.88 1.9046 150.66 21.1 42.6 N16T18H5 17.604 14.31 120.78 63.82 22.58 108.94 10.718 1.3062 89.2 26.68 53.36 样品号 Pr Nd Sm Eu Gd Tb Dy Ho Er Tm Yb N16T18H1 3.686 13.824 2.97 0.5246 3.172 0.5824 4.204 0.8722 2.69 0.4194 2.844 N16T18H2 1.3616 5.226 1.2528 0.288 1.3784 0.2774 2.052 0.4176 1.3512 0.2304 1.7374 N16T18H4 4.456 15.55 3.242 0.2394 3.27 0.618 4.444 0.8974 2.764 0.4424 3.148 N16T18H5 5.674 19.98 3.69 0.3664 3.542 0.6174 4.248 0.8616 2.662 0.4218 3.052 样品号 Lu Hf Ta Pb Th U LREE HREE ∑REE LREE/HREE Eu/Eu* N16T18H1 0.374 1.85136 0.9378 17.992 7.988 4.834 68.6146 15.158 83.7726 4.526626 0.52 N16T18H2 0.2498 0.92466 1.1622 36.78 4.788 2.454 24.0984 7.6942 31.7926 3.132021 0.67 N16T18H4 0.4342 2.1964 1.086 22.68 12.252 7.938 87.1874 16.018 103.2054 5.443089 0.22 N16T18H5 0.436 3.0514 0.921 24.04 15.926 7.736 109.7504 15.8408 125.5912 6.928336 0.31 注:主量元素含量单位为%,微量和稀土元素含量为10-6 表 2 亚布努马花岗斑岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Th-Pb同位素测定结果
Table 2 U-Th-Pb composition of the zircons from the granite porphyry in the Yabunuma region as measured by LA-ICP-MS
测点 Pbrad 232Th 238U Th/U 207Pb/206Pb 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ 年龄/Ma /10-6 207Pb/206Pb 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ NT18-07 4.7 83 168 0.49 0.04922 0.00455 0.16917 0.01554 0.02492 0.00037 158 179 159 13 159 2 NT18-09 2.8 54 96 0.57 0.04947 0.00824 0.17227 0.02852 0.02525 0.00053 170 295 161 25 161 3 NT18-11 4.8 98 171 0.57 0.04932 0.00512 0.16841 0.01741 0.02476 0.00037 163 205 158 15 158 2 NT18-12 4.7 82 158 0.52 0.04931 0.00441 0.1805 0.01603 0.02654 0.00039 163 172 168 14 169 2 NT18-15 9.7 152 278 0.55 0.04781 0.00365 0.16469 0.01239 0.02498 0.00033 90 171 155 11 159 2 注:中国地质大学(北京)地学实验中心测试 -
朱弟成, 莫宣学, 王立全, 等.西藏冈底斯东部察隅高分异I型花岗岩的成因:锆石U-Pb年代学、地球化学和Sr-Nd-Hf同位素约束[J].中国科学:地球科学, 2009, 39(7):833-848. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=JDXK200907001&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ 朱弟成, 潘桂棠, 莫宣学, 等.冈底斯中北部晚侏罗世-早白垩世地球动力学环境:火山岩约束[J].岩石学报, 2006, 22(3):534-546. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200603002 朱弟成, 潘桂棠, 王立全, 等.西藏冈底斯带中生代岩浆岩的时空分布和相关问题的讨论[J].地质通报, 2008, 27(9):1535-1536. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2008.09.013 莫宣学, 董国臣, 赵志丹, 等.西藏冈底斯带花岗岩的时空分布特征及地壳生长演化信息[J].高校地质学报, 2005, 11(3):281-290. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2005.03.001 Zhu D C, Pan G T, Chung S L, et al. SHRIMP zircon age and geochemical constraints on the origin of Lower Jurassic volcanic rocks from the Yeba Formation, southern Gangdese, South Tibet[J]. International Geology Review, 2008, 50(5):442-471. doi: 10.2747/0020-6814.50.5.442
Govindaraju K.Compilation of working values and sample description for 383 geostandards[J].Geostandards and Geoanalytical Research, 1994, 18:1-158. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2494.1998.53202081.x-i1
于红.陕西商南松树沟橄榄岩矿物地球化学特征及成因机理示踪[D].中国地质大学(北京)硕士学位论文, 2011. Wiedenbeck M, Alle P, Corfu F, et al. Three natural zircon standards for U-Th-Pb, Lu-Hf, trace element and REE analyses[J]. Geostandards and Geoanalytical Research, 1995, 19(1):1-23. doi: 10.1111/ggr.1995.19.issue-1
Peccerillo A, Taylor S R. Geochemistry of eocene calc-alkaline volcanic rocks from the Kastamonu area, Northern Turkey[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy & Petrology, 1976, 58(1):63-81. doi: 10.1007-BF00384745/
Middlemost E A K. Naming materials in the magma/igneous rock system[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 1994, 37(3/4):215-224. https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/0012825294900299
Maniar P D. Tectonic discrimination of granitoids[J]. Geol.soc.am. bull., 1989, 101(5):635-643. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1989)101<0635:TDOG>2.3.CO;2
Sun S S, McDonough W F. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts:implications for mantle composition and processes[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 1989, 42(1):313-345. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.1989.042.01.19
Chappell B W. Aluminium saturation in I-and S-type granites and the characterization of fractionated haplogranites[J]. Lithos, 1999, 46(3):535-551. doi: 10.1016/S0024-4937(98)00086-3
King P L, White A J R, Chappell B W, et al. Characterization and origin of aluminous A-type granites from the Lachlan Fold belt, southeastern Australia[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1997, 38(3):371-391. doi: 10.1093/petroj/38.3.371
王强, 赵振华, 熊小林.桐柏-大别造山带燕山晚期A型花岗岩的厘定[J].岩石矿物学杂志, 2000, 19(4):297-306. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2000.04.002 Watson E B, Harrison T M. Zircon saturation revisited:temperature and composition effects in a variety of crustal magma types[J]. Earth & Planetary Science Letters, 1983, 64(2):295-304. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0012821X8390211X
刘昌实, 陈小明, 陈培荣, 等. A型岩套的分类、判别标志和成因[J].高校地质学报, 2003, 9(4):573-591. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2003.04.011 Whalen J B, Currie K L, Chappell B W. A-type granites:geochemical characteristics, discrimination and petrogenesis[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy & Petrology, 1987, 95(4):407-419. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hndzykc201103007
Richards J P. Magmatic to hydrothermal metal fluxes in convergent and collided margins[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2011, 40(1):1-26. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2011.05.006
Wang X S, Bi X W, Leng C B, et al. Geochronology and geochemistry of Late Cretaceous igneous intrusions and Mo-Cu-(W) mineralization in the southern Yidun Arc, SW China:Implications for metallogenesis and geodynamic setting[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2014, 61(8):73-95. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/258658301_Zoning_of_mineralization_in_hypogene_porphyry_copper_deposits_Insight_from_comb_microfractures_within_quartz-chalcopyrite_veins_in_the_Hongshan_porphyry_Cu_deposit_western_Yunnan_SW_China
Wu F Y, Jahn B M, Wilde S A, et al. Highly fractionated I-type granites in NE China (Ⅱ):isotopic geochemistry and implications for crustal growth in the Phanerozoic[J]. Lithos, 2003, 67(3):191-204. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0024493702002220
邱检生, 肖娥, 胡建, 等.福建北东沿海高分异Ⅰ型花岗岩的成因:锆石U-Pb年代学、地球化学和Nd-Hf同位素制约[J].岩石学报, 2008, 24(11):2468-2484. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200811002 Joplin G A. Some chemical data on members of the shoshonite association[J]. Mineralogical Magazine, 1972, (300):936-945.
Meen J K. Formation of shoshonites from calcalkaline basalt magmas:geochemical and experimental constraints from the type locality[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy & Petrology, 1987, 97(3):333-351. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/226601709_Formation_of_shoshonites_from_calcalkaline_basalt_magmas_geochemical_and_experimental_constraints_from_the_type_locality
Meen J K. Elevation of potassium content of basaltic magma by fractional crystallization:the effect of pressure[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy & Petrology, 1990, 104(3):309-331. doi: 10.1007%2FBF00321487
Marchev P, Georgiev S, Zajacz Z, et al. High-K ankaramitic melt inclusions and lavas in the Upper Cretaceous Eastern Srednogorie continental arc, Bulgaria:Implications for the genesis of arc shoshonites[J]. Lithos, 2009, 113(1/2):228-245. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S002449370900084X
Roberts M P. Origin of high-potassium, calc-alkaline, I-type granitoids[J]. Geology, 1993, 21(9):825. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1993)021<0825:OOHPTA>2.3.CO;2
闫晶晶.西藏中拉萨地块许如错岩体年代学和地球化学[D].中国地质大学(北京)硕士学位论文, 2016. Pearce J A, Harris N B W, Tindle A G. Trace element discrimination diagrams for the tectonic interpretation of granitic rocks[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1984, 25(4):956-983. doi: 10.1093/petrology/25.4.956
-
期刊类型引用(7)
1. 刘永彪,李省晔,杨镇熙,赵吉昌,胡小春,王喆. 甘肃北山破城山东一带铜金矿地球化学勘查及找矿方向. 黄金科学技术. 2024(06): 990-1001 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 孙凯,刘晓阳,何胜飞,龚鹏辉,许康康,任军平,张航,卢宜冠,邱磊. 坦桑尼亚水系沉积物地球化学特征及金资源前景. 地质通报. 2023(08): 1258-1275 .  本站查看
本站查看
3. 李欢,黄勇,张沁瑞,贾三满,徐国志,冶北北,韩冰. 北京平原区土壤地球化学特征及影响因素分析. 物探与化探. 2021(02): 502-516 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 袁和,许云鹏. 综合找矿方法在辽宁阜蒙县东五家子金矿勘查中的应用. 地质与勘探. 2021(02): 339-350 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 齐文博,师兵,王嘉炜,杨碧莹,柳坤峰. 青海省都兰县查哈西里地区地球化学异常特征及成矿远景评述. 地质与资源. 2021(04): 431-442 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 写熹,魏国辉,郭泳杰,王克友,杜玉雕. 化探综合异常的圈定——以安徽绩溪青罗山地区1∶1万土壤地球化学测量为例. 矿产与地质. 2021(04): 763-769 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 周俊朋,吴鹏,韩润生,郭忠林,王雷,龚红胜. 云南会泽铅锌矿床外围高家阱勘查区构造样式与构造地球化学找矿. 地质通报. 2019(11): 1899-1911 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(2)




 下载:
下载: