Lithosphere structure of Duobaoshan ore concentration area, Heilongjiang: Results of deep seismic reflection and magnetotelluric detection in Sunwu-Jinsong corridor belt
-
摘要:
探测造山带岩石圈精细结构,是探讨造山与成矿作用最有效的手段。2019年,在黑龙江省西北部孙吴−劲松廊带域,中国地质科学院完成了一条横跨黑河−贺根山缝合带北段和多宝山矿集区北西—南东向185 km长的深地震反射剖面,以及5条总计174点的大地电磁测深(宽频、音频)剖面。结果显示,多宝山矿集区的莫霍面深度在33 km(TWT 11 s)左右,呈现断续可追踪形态,其东侧中、下地壳识别出一套向西倾斜并延伸至上地幔的反射体,其倾角约为25°,推断为嫩江洋俯冲遗迹。在多宝山矿集区的西侧识别出整体向东倾斜的壳幔反射特征,表明蒙古−鄂霍茨克构造域影响范围已至黑河−贺根山缝合带。多宝山矿集区上地壳围限于卧都河—罕达汽之间的“V”形构造带中,中下地壳垂向上发育一系列长10 km左右的强反射层,解释为残留的岩浆通道。多宝山矿集区下地壳的高导体可延伸至地幔,与其上高导异常C4呈蘑菇云状展布,并与矿床的位置在空间上存在一致性,指示了幔源物质的侵入。近地表速度结构整体速度变化在1900~6100 m/s之间,高速体界面起伏较大且埋深较浅,是寻找隐伏金矿的有利区域,铜山铜矿和多宝山铜矿的斑岩岩体虽被隐伏断裂阻隔,但在深部相连,地下2000 m以内仍有很好的资源潜力。本项调查研究将浅层矿床分布与岩石圈结构联系起来,为深入研究与古老地壳缝合带与复合造山作用相联系的多宝山矿集区的地质背景提供了新视野。
Abstract:Detecting the fine structure of lithosphere in orogenic belt is the most effective means to explore orogeny and mineralisation. In 2019, the Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences completed a 185−km−long deep seismic reflection profile from northwest to southeast, and five magnetotelluric sounding (broadband and audio) profiles with a total of 174 points in the Sungwu−Jinsong corridor belt in northwestern Heilongjiang Province. The results show that the depth of the Moho in the Duobaoshan ore concentration area is about 33 km (Two way traveltime 11s), showing an intermittent and traceable pattern. A set of subduction relict are identified in the middle and lower crust on the east side of the area, which shows that it is a reflection body that inclinates to the west and extends to the upper mantle, with a dip angle of 25 degrees, and is inferred to be the subduction relict of the Nenjiang Ocean. The characteristics of crust−mantle reflection are identified in the west side of the Duobaoshan ore concentration area, which is generally inclined to the east. It is indicated that the influence of the Mongolia−Okhotsk structure has reached the Heihe−Hegenshan suture. The upper crust of the Duobaoshan ore concentration area is confined to the "V" tectonic belt between Woduhe−Handaqi, and a series of strong reflection layers around 10 km in length are developed vertically in the middle and lower crust, which is interpreted as a residual magma channel. The high conductor in the lower crust of the Duobaoshan ore concentration area can extend to the mantle, and its high−conductivity anomaly C4 on it is distributed in the form of a mushroom cloud, and is spatially consistent with the location of the ore deposits, which indicates the intrusion of mantle−sourced materials. The overall velocity of the near−surface velocity structure of the Duobaoshan ore concentration area varies from 1900 m/s to 6100 m/s, and the high velocity body interface has a large undulation and a shallow depth, which is a favourable area for searching for concealed gold mines. Although the porphyry bodies of the Tongshan copper mine and the Duobaoshan copper mine are blocked by hidden faults, they are connected at deep depth, and there is still good resource potential within 2000 m underground. This study links the distribution of shallow deposits with the lithospheric structure, and provides a new vision for further study of the geological background of the Duobaoshan ore concentration area connected with the ancient crustal suture and the composite orogenic belt.
-
油页岩属于非常规油气资源,利用蒸馏等技术处理后能够获得页岩气及页岩油,是一种前景非常好的油气资源,被列为21世纪非常重要的接替能源(侯祥麟,1994;赵政璋等,2005;刘招君等,2006;王红岩等,2009)。中国油页岩资源丰富,资源潜力大,其中松辽盆地是油页岩资源极丰富的地区,占东北地区油页岩资源总量的96%(刘招君等,2009)。松辽盆地是一个大型陆相薄互层沉积盆地,岩石物性横向变化大,地层平缓且构造幅度小,油页岩单层厚度薄,这种复杂的沉积结构增加了地震勘探的难度(李桂林,2009)。大地电磁法由于天然场源的随机性及信号微弱精度和效率较低,电阻率法则存在探测深度浅、高阻层屏蔽等缺点。测井技术在识别和评价油页岩方面较成熟(丰莉等,2016;刘同庆,2020),已被广泛应用于油页岩矿区,但是由于其空间探测范围的局限性,存在横向范围内描述储层物性变化能力很弱的缺陷。
测井具有较高的纵向地层分辨率,将测井数据作为先验信息进行电磁法约束反演,可以提高反演结果的纵向分辨率。朱宇启等(2021)在南黄海中部隆起区对海洋CSEM实测数据进行测井约束反演,突出了垂向发生明显变化的层位。Brown et al.(2012)发现,利用测井数据进行正则化约束反演比常规反演结果更紧凑地估计了储层结构。余年等(2012)利用测井数据作为先验信息开展大地电磁约束反演,与常规反演结果相比,约束反演结果对岩溶、断层、褶皱等地质构造的反映与实际吻合更好。自20世纪80年代以来,可控源音频大地电磁法和仪器都得到了很大发展,具有设备轻便、勘探深度相对较大、不受高阻层屏蔽、横向分辨率高等特点(何梅兴,2006;余年等,2012),在勘探石油、天然气、金属矿床、地热等领域得到广泛应用(秦伟,2013;李致君等,2018;李英宾等,2019)。地球物理方法和测井技术在联合研究油页岩储层特征方面几乎还是空白,本文通过松辽盆地采集的可控源音频大地电磁数据,利用测井资料作为先验信息,开展可控源音频大地电磁法和测井联合约束反演技术应用研究,将油页岩与泥页岩互层整体作为相对高阻层,进行划分识别,取得较好的效果,初步查明研究区油页岩的展布特征,为进一步勘探工作指明了有利方向。
1. 地质地球物理背景
1.1 地质条件
研究区位于松辽盆地东南隆起区(图1)。松辽盆地形成于印支运动末期—燕山运动早期,经历了多期构造运动,盆地内部划分出西部斜坡区、北部倾没区、东北隆起区、中央坳陷区、东南隆起区和西南隆起区6个一级构造单元(张利,2020)。
东南隆起区位于盆地边部,自西向东分为次一级背斜、向斜构造,主要有登娄库背斜、哈拉海向斜、农安背斜、德惠向斜、青山口背斜、杨大城子背斜;主要发育中、新生代地层,自下而上依次为白垩系火石岭组、沙河子组、营城组、登娄库组、泉头组、青山口组、姚家组、嫩江组,新近系大安组及第四系(高立新,2008;李宝毅等,2012;李翔等,2014),油页岩主要存在于白垩系青山口组一段和嫩江组一段、二段,油页岩矿层单层厚度较薄,与沉积岩地层呈互层关系。
1.2 地层电性特征
根据研究区及周缘物性资料分析,第四系为表层高阻层,古近系—新近系大安组−青山口组为低阻层,泉头组−登楼库组为中阻层,营城组−火石岭层为次高阻层,局部发育火山岩为高阻,石炭系—二叠系为基底高阻层(表1)。地层电性特征分析表明,白垩系嫩江组、青山口组电阻率整体呈现低阻特征。
表 1 研究区及周缘地区岩层电性特征Table 1. The electrical characteristics of rock strata in the study area and surrounding areas系 统 组 符号 岩性特征 ρ/(Ω·m) 电性 第四系 Q 粘土、亚粘土、砂砾石 37.9 表层高阻 古近系—新近系 大安组 Nd 泥岩、粉砂质泥岩、泥质粉砂岩 3.2 低阻层 白垩系 上统 嫩江组 K2n 砂砾岩、粉砂岩、细砂岩、泥质粉砂岩、粉砂质泥岩、泥岩、油页岩 3.9 姚家组 K2y 泥岩、粉砂质泥岩、泥质粉砂岩、粉砂岩 6.8 青山口组 K2qs 质粉砂岩、粉砂岩、粉砂质泥岩、油页岩 22.8 下统 泉头组 K1q 粉砂质泥岩、泥岩、粉砂岩、泥质粉砂岩、细砂岩、砂岩 28.2 中阻层 登楼库组 K1d 砂砾岩夹泥岩 71.5 营城组 K1yc 泥岩与火山岩间互夹煤层 211.7 次高阻层 沙河子组 K1sh 火山岩、砂泥岩夹煤线 220.0 火石岭组 K1h 火山碎屑岩、火山喷发岩 240.0 石炭系—二叠系 293.0 基底高阻 1.3 油页岩物性特征
油页岩含丰富的有机质,有机质具有低密度、高电阻率特征,在含油页岩的沉积地层中,油页岩层与围岩存在电阻率、密度等物性差异(Constable et al.,1987;贺君玲等,2006;王永明等,2007)。
综合分析研究区不同测井曲线发现,油页岩呈现中高电阻率、高自然伽马、高声波时差和低密度特征;泥岩呈现低电阻率、高自然伽马、高声波时差和高密度特征;粉砂岩具有中高电阻率、低自然伽马、低声波时差、低密度特征;粉砂质泥岩相对于泥岩电阻率偏高、自然伽马偏低、声波时差偏低、密度偏低;泥质粉砂岩相对于粉砂岩电阻率偏低、自然伽马偏高、声波时差偏高、密度高。油页岩与粉砂岩、粉砂质泥岩及泥质粉砂岩在电阻率和密度方面均呈现高电阻率、低密度特征,但与围岩泥岩存在明显的电阻率和密度差异(表2;图2),油页岩有机质含量越高,这种特征越明显。因此,根据不同测井曲线形态和曲线值可以判断出不同岩性,划分识别油页岩。
表 2 研究区白垩系不同岩性测井曲线响应分布范围Table 2. Logging response distribution range table of Cretaceous different lithology in the study area测井识别岩性 电阻率平均值/(Ω·m) 声波时差平均值/(μs·m−1) 补偿密度平均值/(g·cm−3) 自然伽马平均值/API 粉砂岩 10 ~ 13 250 ~ 430 2.15 ~ 2.62 50 ~ 115 泥质粉砂岩 6.5 ~ 17.5 240 ~ 450 2.20 ~ 2.50 75 ~ 140 粉砂质泥岩 5.5 ~ 12 275 ~ 500 2.25 ~ 2.55 90 ~ 135 泥岩 5 ~ 9 330 ~ 450 2.25 ~ 2.50 110 ~ 150 油页岩 7.5 ~ 15 ≥375 ≤2.35 ≥130 2. 勘探方法
2.1 方法原理
CSAMT法全称是可控源音频大地电磁测深法,属于人工源频率域电磁测深法,以有限长接地电偶极子为场源,其核心是采用大小随着频率改变的音频电流来建立人工电磁场,激发地下空间产生电磁感应,当电磁场变为谐变场时通过改变电磁场的频率来达到测深目的,采集电磁场参数,求取视电阻率、阻抗相位等电磁响应数据,具有工作效率高、勘探深度范围大、水平方向分辨能力高、地形影响小、高阻层的屏蔽作用小等特点。
2.2 数据采集与处理
研究区CSAMT测线均过钻井(图1),测线总长80 km,点距100 m,采用美国Zonge公司生产的GDP-3224多功能电法仪,发电输出功率30 kW。数据采用赤道偶极装置进行标量测量,发射偶极AB与测线平行布设,长度为1 ~ 2 km,接收偶极100 m,发射源接地电阻要求20 ~ 40 Ω,接收端接地电阻不大于2000 Ω;同时观测与场源平行的电场水平分量Ex和与场源正交的磁场水平分量Hy,采集频率范围为 0.125 ~ 8192 Hz。
数据处理采用人机交互的方式进行,包括去噪、静态校正、近场校正、视电阻率、相位拟断面分析等。近场校正采用过渡三角形法,消除卡尼亚电阻率在近区由于非平面波效应产生的畸变,采用空间滤波、中值滤波、曲线平移等方法进行静态位移综合校正。图3为SL-01线视电阻率和阻抗相位断面图,视电阻率、阻抗相位等值线连续光滑,噪声、近场效应及静位移影响得到较好的压制,断面图上电性层由高频到低频呈现高、低、次低、高的变化特征。
2.3 约束反演技术
常规二维正则化OCCAM反演方法是一种由电磁测深数据产生光滑模型的实用算法,体现了正则化反演优点,在保证电性分布连续或光滑的条件下,寻求有极小可能构造意义下拟合数据的模型(Constable et al.,1987),该方法收敛稳定,对初始模型依赖度低,成像效果好,被广泛应用于电磁数据处理中。研究区存在人文干扰,受干扰的数据不能真实反映地下电性结构,对地质解释的可靠性存在影响,同时可控源音频大地电磁反演存在多解性、非唯一性的问题,为此在二维正则化OCCAM反演的基础上,将研究区测井信息融入到可控源音频大地电磁资料的反演处理中,减少反演结果的非唯一性,提高成果解释的精度和合理性(孟翠贤,2003;张凯飞,2016)。二维OCCAM地电约束反演主要包括地电模型建立、反演算法与正则化因子、模型粗糙度及迭代误差分析。
(1)地电模型建立
对研究区可控源音频大地电磁测线周边测井资料进行处理分析,根据不同物性特征对钻孔处地层进行划分,重点对嫩江组和青山口组油页岩及附近地层进行划分,建立可控源音频大地电磁资料处理所需要的电阻率分布先验地电模型,数据反演过程中加入先验地电信息开展约束反演。表3、表4为SL-03线先验约束信息。
表 3 吉扶地3井油页岩及附近地层约束信息Table 3. Constraint information of oil shale and nearby strata in Well Jifudi 3序号 顶部深度/m 底部深度/m 厚度/m 电阻率/(Ω·m) 岩性 序号 顶部深度/m 底部深度/m 厚度/m 电阻率/(Ω·m) 岩性 1 258.2 268.6 10.4 9.19 泥岩 15 469.8 476.9 7.1 6.23 泥岩 2 268.6 281.4 12.8 10.70 粉砂质泥岩 16 476.9 478.0 1.1 6.99 油页岩 3 281.4 289.0 7.6 9.55 泥岩 17 478.0 483.2 5.2 5.70 泥岩 4 289.0 294.1 5.1 12.90 粉砂质泥岩 18 483.2 484.1 0.9 6.27 油页岩 5 294.1 298.3 4.2 9.44 泥岩 19 484.1 487.3 3.2 6.22 泥岩 6 298.3 306.6 8.3 11.61 粉砂质泥岩 20 487.3 489.5 2.2 8.38 粉砂质泥岩 7 306.6 312.4 5.8 9.55 泥岩 21 489.5 494.2 4.7 6.06 油页岩 8 312.4 341.0 28.6 10.92 粉砂质泥岩 22 494.2 503.2 9.0 5.25 泥岩 9 341.0 382.3 41.3 6.49 泥岩 23 503.2 507.1 3.9 12.73 油页岩 10 382.3 383.2 0.9 6.45 油页岩 24 507.1 514.0 6.9 7.19 泥岩 11 383.2 462.2 79.0 5.95 泥岩 25 514.0 519.3 5.3 11.22 油页岩 12 462.2 463.4 1.2 7.19 油页岩 26 519.3 523.1 3.8 5.91 泥岩 13 463.4 468.0 4.6 6.10 泥岩 27 523.1 524.0 0.9 10.72 油页岩 14 468.0 469.8 1.8 7.65 油页岩 28 524.0 528.7 4.7 8.34 粉砂质泥岩 表 4 吉扶地8井油页岩及附近地层约束信息Table 4. Constraint information of oil shale and nearby strata in Well Jifudi 8序号 顶部深度/m 底部深度/m 厚度/m 电阻率/(Ω·m) 岩性 序号 顶部深度/m 底部深度/m 厚度/m 电阻率/(Ω·m) 岩性 1 258.2 268.6 10.4 9.19 泥岩 15 469.8 476.9 7.1 6.23 泥岩 2 268.6 281.4 12.8 10.70 粉砂质泥岩 16 476.9 478.0 1.1 6.99 油页岩 3 281.4 289.0 7.6 9.55 泥岩 17 478.0 483.2 5.2 5.70 泥岩 4 289.0 294.1 5.1 12.90 粉砂质泥岩 18 483.2 484.1 0.9 6.27 油页岩 5 294.1 298.3 4.2 9.44 泥岩 19 484.1 487.3 3.2 6.22 泥岩 6 298.3 306.6 8.3 11.61 粉砂质泥岩 20 487.3 489.5 2.2 8.38 粉砂质泥岩 7 306.6 312.4 5.8 9.55 泥岩 21 489.5 494.2 4.7 6.06 油页岩 8 312.4 341.0 28.6 10.92 粉砂质泥岩 22 494.2 503.2 9.0 5.25 泥岩 9 341.0 382.3 41.3 6.49 泥岩 23 503.2 507.1 3.9 12.73 油页岩 10 382.3 383.2 0.9 6.45 油页岩 24 507.1 514.0 6.9 7.19 泥岩 11 383.2 462.2 79.0 5.95 泥岩 25 514.0 519.3 5.3 11.22 油页岩 12 462.2 463.4 1.2 7.19 油页岩 26 519.3 523.1 3.8 5.91 泥岩 13 463.4 468.0 4.6 6.10 泥岩 27 523.1 524.0 0.9 10.72 油页岩 14 468.0 469.8 1.8 7.65 油页岩 28 524.0 528.7 4.7 8.34 粉砂质泥岩 (2)反演算法
二维Occam地电约束反演重点是对目标函数中的模型粗糙度进行修改,推导出修改后目标函数的迭代格式,形成以地电参数作为先验信息的约束反演算法。反演过程中在目标函数中加入利用测井等资料建立的先验地电模型,在已知电性分布区域修正模型,不断地向先验地电模型靠拢,提高反演结果与实测数据的拟合度。具体流程如下:
① 建立可控源音频大地电磁反演目标函数,在目标函数模型粗糙度中加入模型约束项。
U=‖ (1) 式中, {\left\|{\partial }_{y}m\right\|}^{2}+{\left\|{\partial }_{z}m\right\|}^{2} 为模型粗糙度,μ为拉格朗日乘子,即正则化因子, W 为归一化计算后 M\times M 的对角加权矩阵, F(m) 模型为 m 在一定的激发作用下正演后取得的响应,X*2为反演拟合差。
② 根据已知钻孔及测井数据建立初始模型,构造二维粗糙度矩阵:
{R}_{1}=\alpha {\left\|C(m-{m}_{0})\right\|}^{2}+{\left\|{\partial }_{y}m\right\|}^{2}+{\left\|{\partial }_{z}m\right\|}^{2} (2) 式中, \alpha {\left\|C(m-{m}_{0})\right\|}^{2} 为先验模型的约束项, \alpha 为权重系数, {m}_{0} 为先验模型, m 为迭代过程中当前模型, C 为约束矩阵。
③ 根据约束后的目标函数,计算推导迭代格式,开展反演迭代计算。
\begin{split} &{m}_{k+1}\left(\mu \right)={\left[\alpha \mu {C}^{T}+\mu \left({\partial }_{x}^{T}{\partial }_{x}+{\partial }_{z}^{T}{\partial }_{z}\right)+ {\left(W{J}_{k}\right)}^{T}W{J}_{k}\right]}^{-1}.\\ &\qquad \left[{\left(W{J}_{k}\right)}^{T}W{d}_{k}+\alpha \mu {C}^{T}C{m}_{0}\right]\\[-1pt]\end{split} (3) 式中 ,{J}_{k} 为雅可比矩阵, {d}_{k}=d-F\left[{m}_{k}\right]+{J}_{k}{m}_{k} ,拉格朗日乘子μ为待求值。
④ 求取模型 {m}_{k+1}\left(\mu \right) 的一系列μ值,根据 \mu 值计算模型 {m}_{k+1}\left(\mu \right) 拟合差,选取数据残差平方最小的 \mu 值。
(3)正则化因子、模型粗糙度及迭代误差分析
本次约束反演正则化因子初始值为1000,模型粗糙度随正则化因子增大呈现波动变化,当正则化因子增大到一定值时,逐步变小,最后趋于稳定(图4)。经过15次迭代计算,二维地电约束反演结果趋近稳定,图5为SL-01线约束前后迭代反演曲线误差对比图,拟合差分别为0.77和0.78,拟合初期约束反演拟合误差比常规反演拟合误差大,拟合后期常规反演提前趋于稳定。
3. 效果分析
(1)常规二维OCCAM反演能够反映出规模较大的异常体,但是对于规模较小的异常体分辨能力不足,由SL-01线二维OCCAM反演与二维OCCAM约束反演剖面对比图(图6)可以看出,二维OCCAM地电约束反演剖面纵向上地层电性变化特征清楚,横向分辨率也有很大的提高,能够明显提高对异常体的分辨率,地电信息更丰富,较好地反映了研究区地层平缓、构造幅度小、岩石物性横向变化大的地质特征,油页岩与泥岩作为整体得到较好反映。
(2)以二维OCCAM地电约束反演剖面为主,结合测井、以往物探地质资料进行综合解释,可以对油页岩与泥页整体进行有效识别。图7为SL-01线二维地电约束反演及地质解释剖面,二维地电约束反演剖面纵向上呈现高—低—中—次高—高变化特征,电性结构变化与电测井曲线吻合较好。表层高阻层反映了第四系沉积地层分布与厚度变化特征,电阻率值为15 ~ 55 Ω·m,厚度10 ~ 50 m;中浅部低阻层主要反映了白垩系嫩江组、姚家组及青山口组的分布,电阻率值为3 ~ 12 Ω·m,厚度180 ~ 750 m,局部存在相对高阻异常,与电测井曲线上粉砂质泥岩、泥质粉砂岩、粉砂岩、油页岩和泥岩互层基本对应;下部中阻层代表白垩系泉头组,电阻率值为6 ~ 17 Ω·m,厚度50 ~ 100 m;下部次高阻层代表白垩系火石岭组—登楼库组,电阻率值为7 ~ 22 Ω·m,厚度400 ~ 1000 m;底部分布的高阻层代表了变质岩或侵入体基底,顶面最大埋深范围大于1000 m。利用电测井曲线及分层数据,结合约束反演剖面电阻率变化特征,将中浅部低阻层进一步划分为嫩江组、姚家组和青山口组,在嫩江组、青山口组划分的基础上,油页岩与泥岩整体作为相对高阻层可划分识别。
(3)通过研究区采集的可控源音频电磁测线地电约束反演及综合解释,对研究区地层、构造及油页岩矿层展布特征获得了整体认识:① 研究区横跨登楼库背斜和哈拉海向斜2个构造,背斜核部地层以白垩系泉头组、青山口组为主,翼部为姚家组、嫩江组,向斜核部地层以白垩系嫩江组为主,翼部为姚家组、青山口组。以登楼库背斜轴为界,两翼地层倾角均为1° ~ 6°,核部近水平,呈宽缓的背斜构造,整体控制白垩系的分布,影响油页岩矿层的空间展布。②登楼库背斜地层较哈拉海向斜整体抬升,导致研究区背斜所在区域的嫩江组基本缺失,嫩江组油页岩主要分布在哈拉海向斜,仅在背斜西部局部沉积,油页岩与泥岩互层厚度为25 ~ 100 m,埋深50 ~ 250 m。青山口组油页岩分布范围广,登楼库背斜、哈拉海向斜均有分布,油页岩与泥岩互层厚度为30 ~ 200 m,埋深400 ~ 800 m,整体呈沿登楼库背斜轴高、沿背斜轴两翼逐渐减薄的特征。
4. 结 论
(1)可控源音频大地电磁和测井联合约束反演技术能够提高对异常体的分辨率,油页岩与泥岩互层作为整体只要具有一定的规模,利用可控源音频大地电磁和测井联合约束反演技术就可以划分识别。
(2)油页岩单层厚度薄,单一地球物理方法划分识别油页岩存在很大的局限性,基于测井综合曲线分析技术的地球物理方法是油页岩勘探方法发展的方向。
(3)油页岩与砂岩、粉砂岩和粉砂质泥岩均呈现相对高电阻率特征,区分困难,可以开展可控源音频电磁法、时频电磁法等多种方法试验,利用电阻率、极化率等多参数综合分析研究。
-
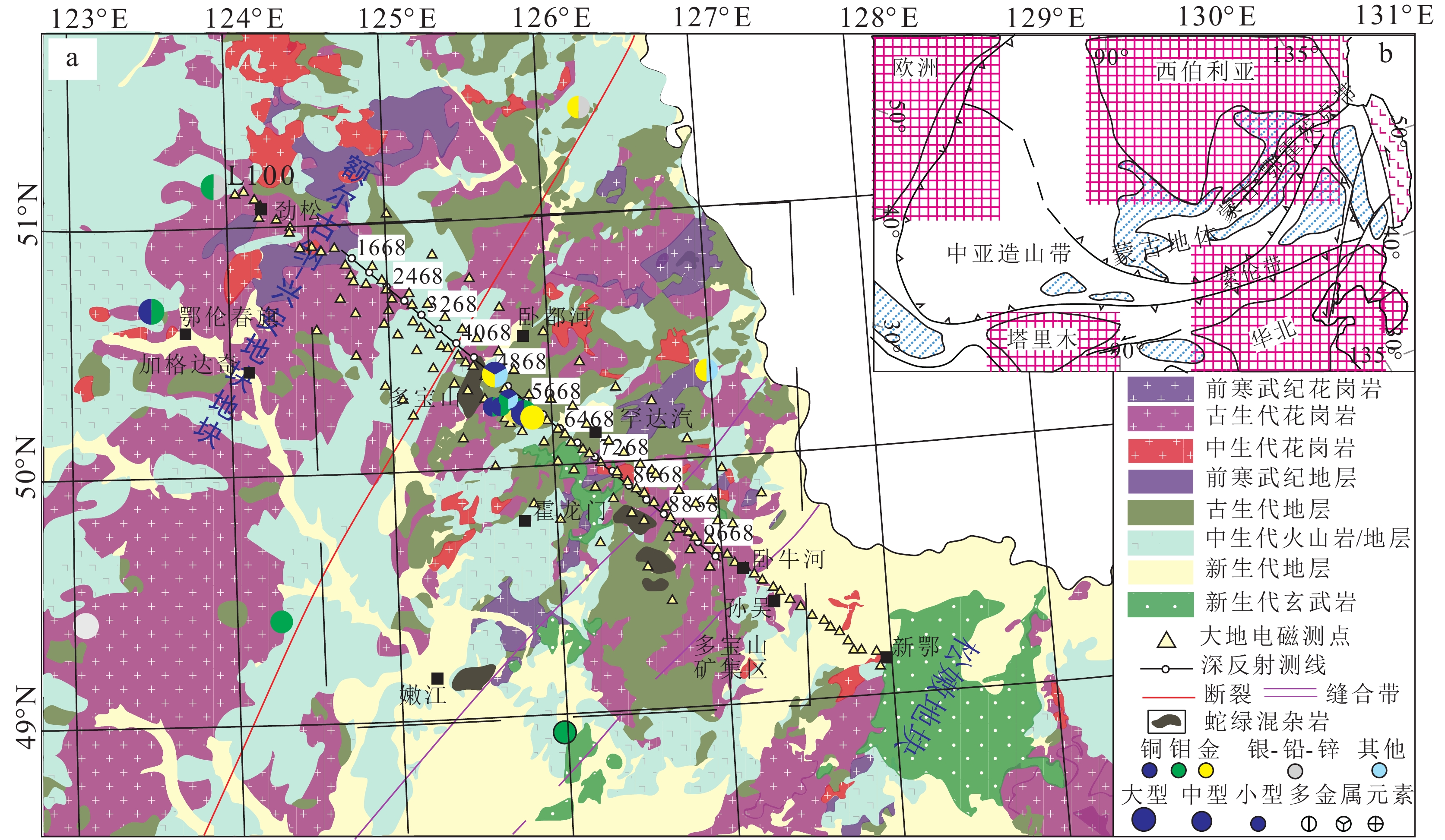
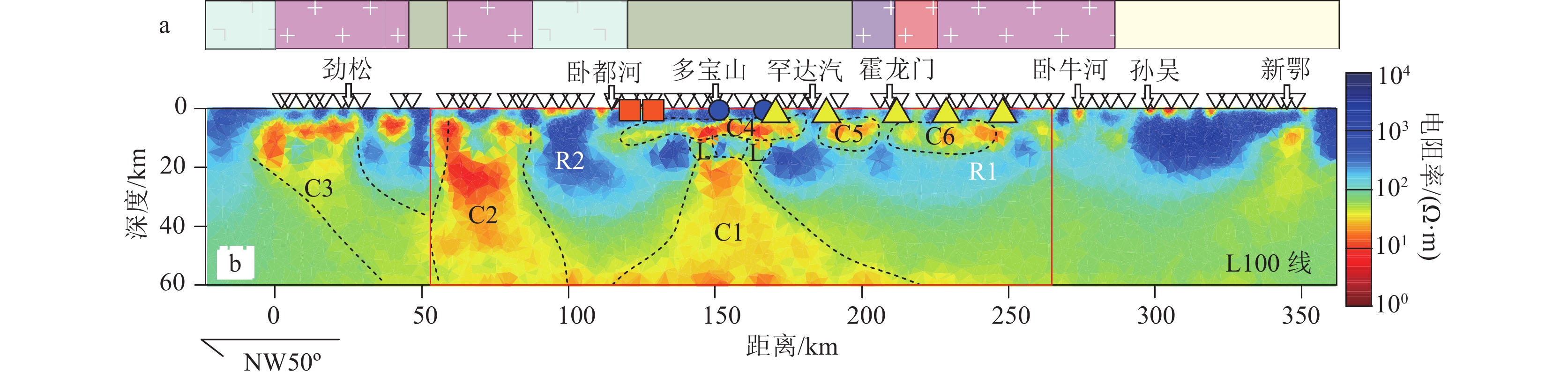
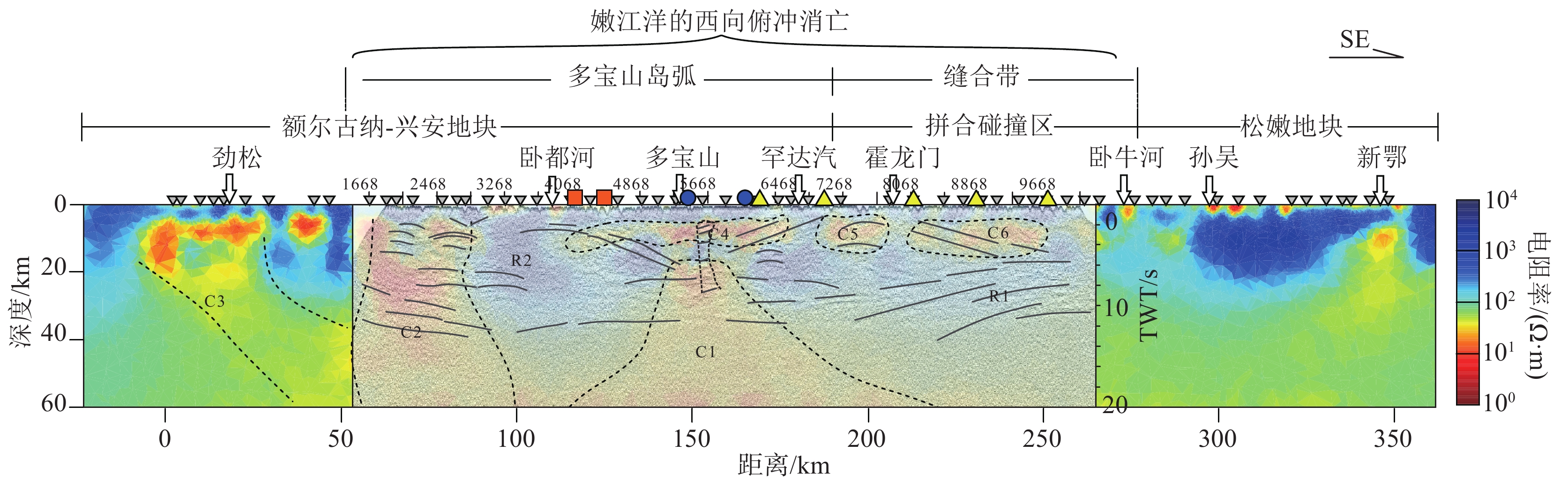
图 1 研究区位置图
a—亚洲构造框图(据Zhou et al., 2014修改);b—孙吴-劲松廊带域深部探测剖面位置图(深反射测线上标注的数字为CMP号)
Figure 1. Location map of the survey area
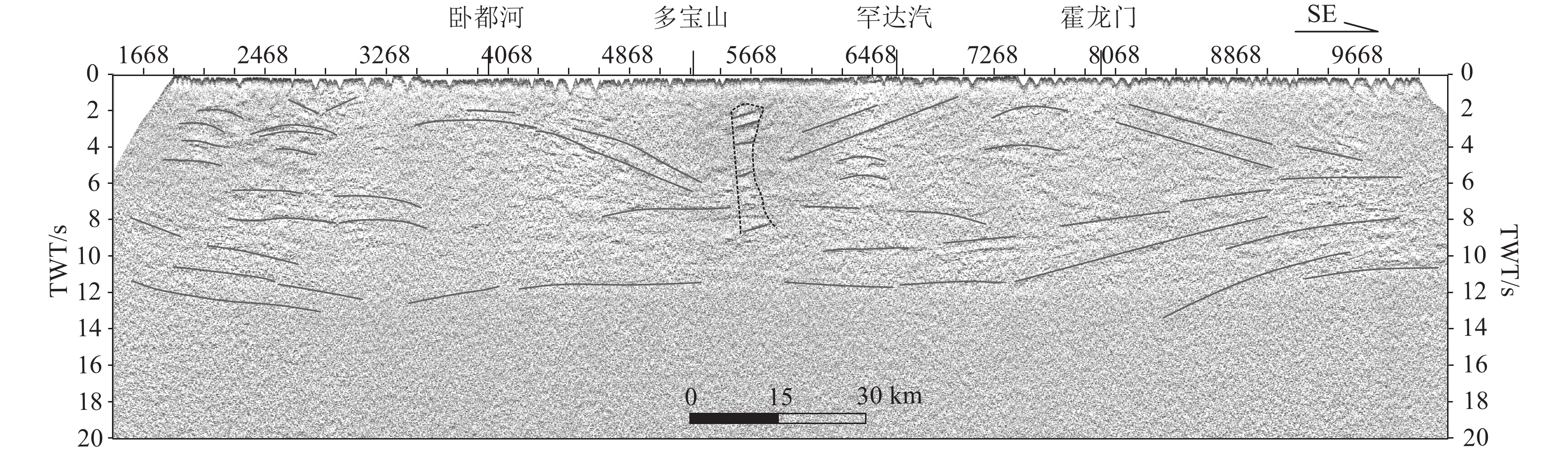
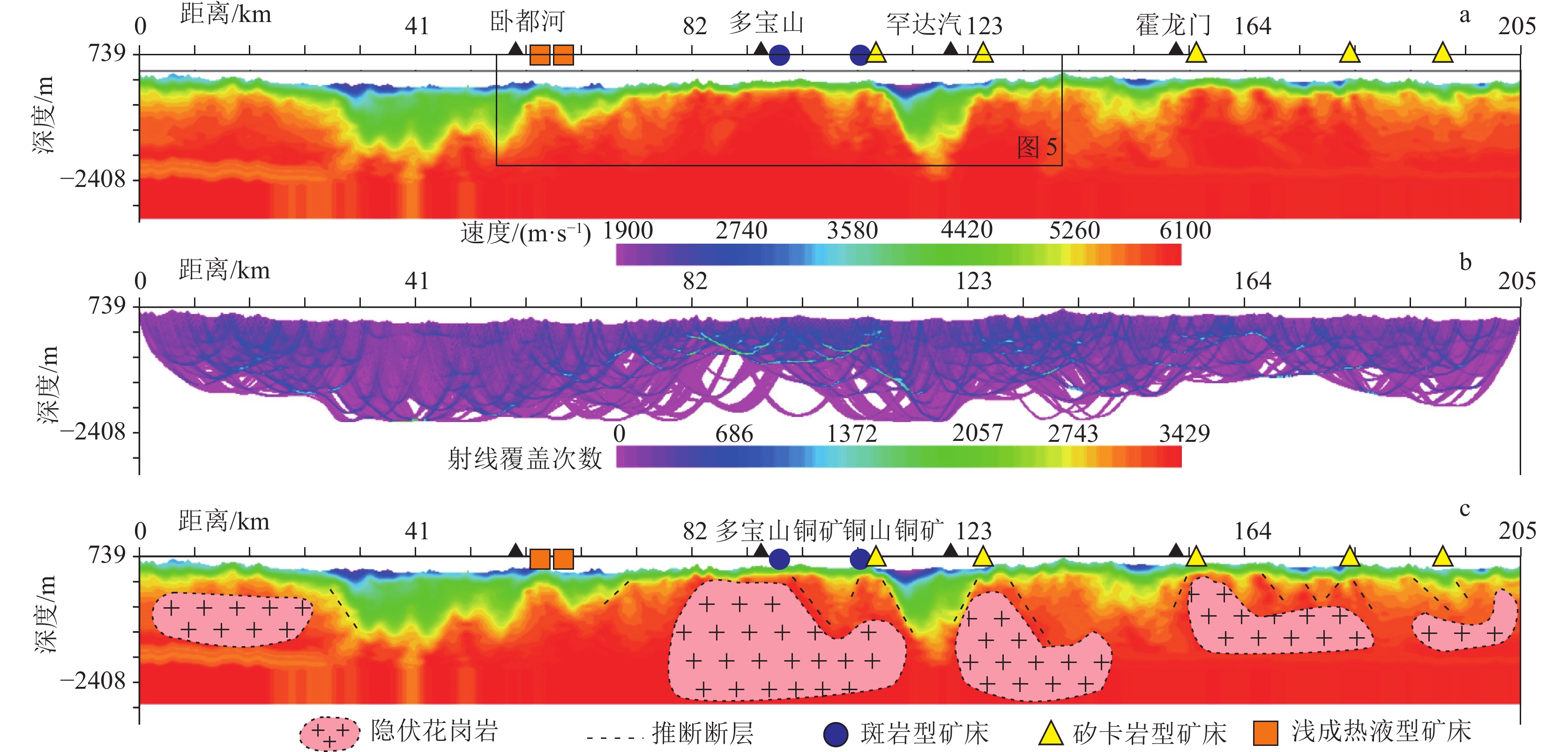
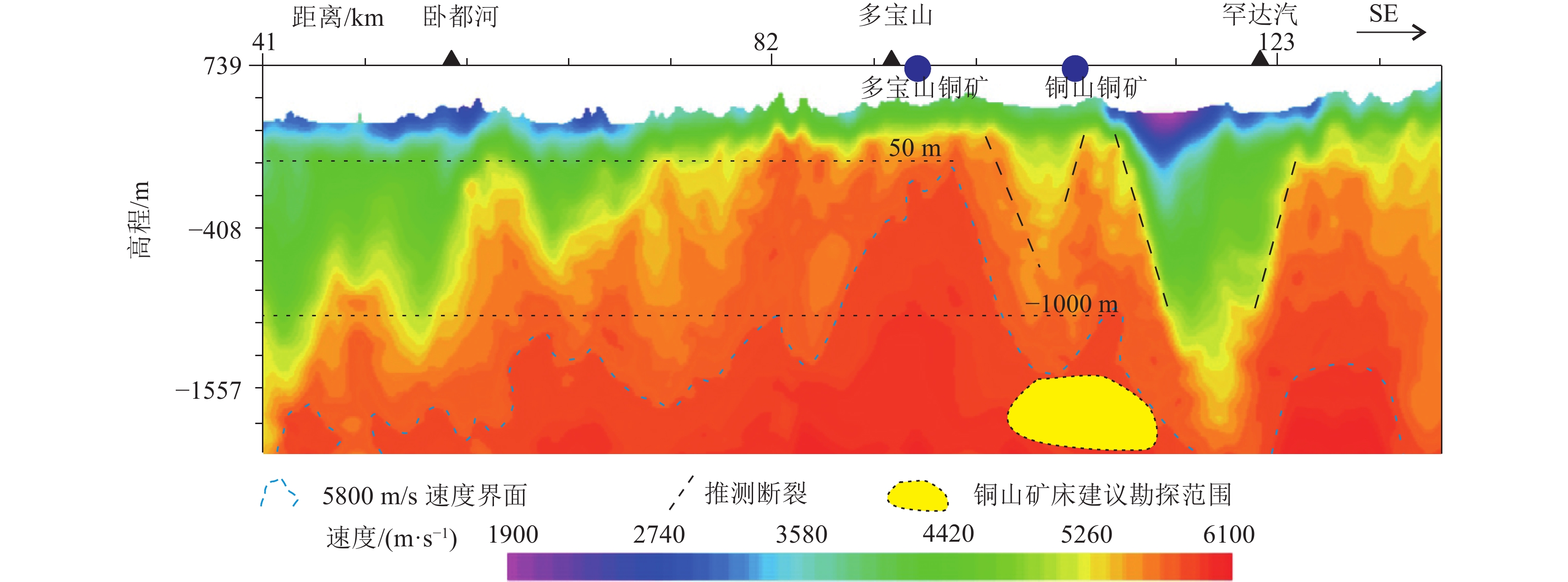
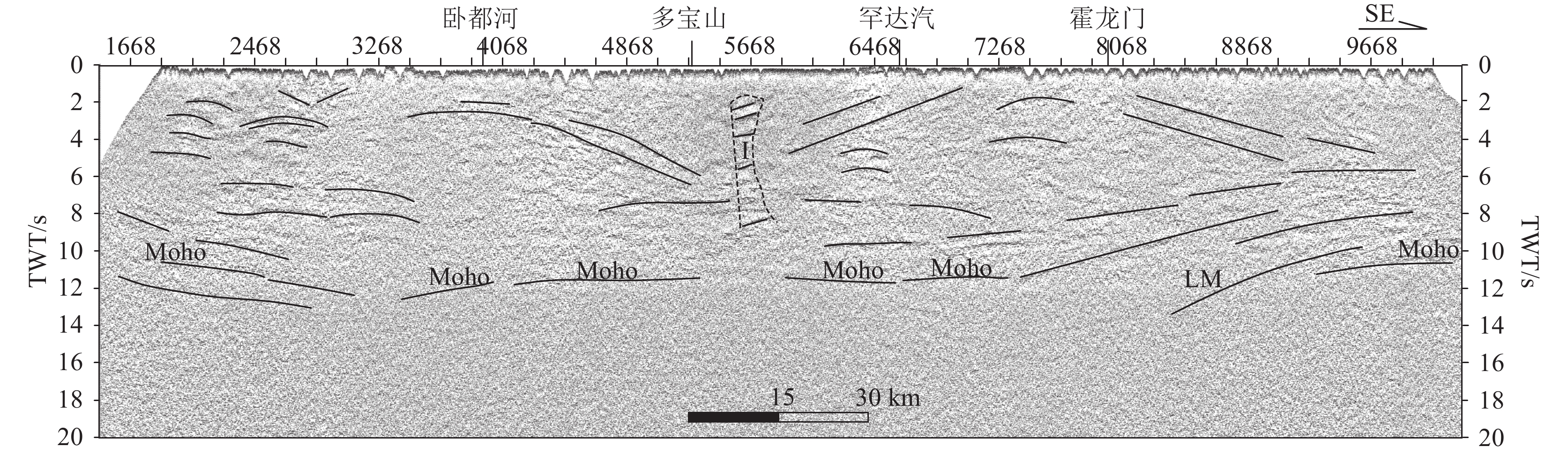
图 2 孙吴-劲松深地震反射剖面处理结果(横轴坐标的CMP点位参照图1)
Figure 2. Processing results of Sunwu-Jinsong deep seismic reflection profile
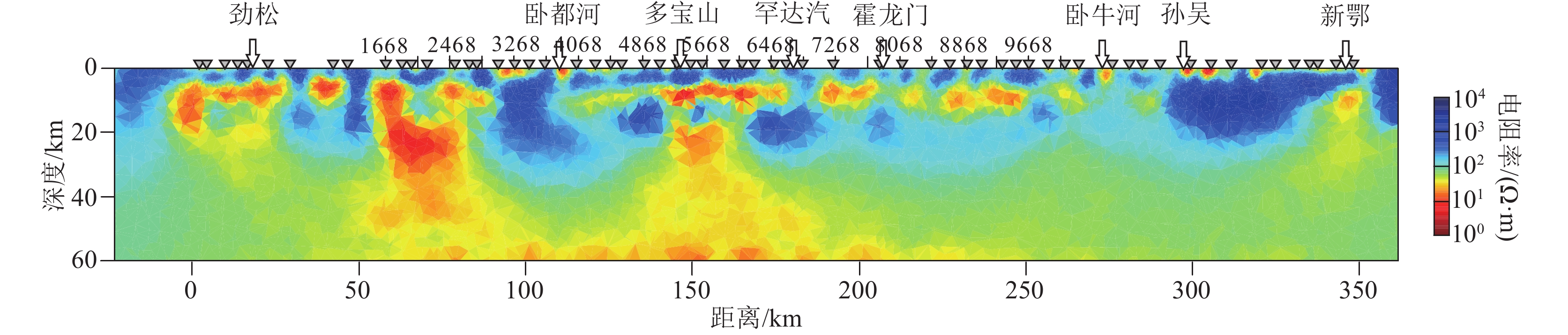
图 3 孙吴-劲松大地电磁测深剖面L100线电性结构(上方横轴标注的CMP点位参照图1)
Figure 3. Electrical structure of L100 in Sunwu-Jinsong magnetotelluric sounding profile
图 6 孙吴-劲松深地震反射剖面构造解释图(横轴标注的CMP点位参照图1)
I—岩浆通道;Moho—莫霍面;LM—倾斜地幔反射
Figure 6. Structural interpretation map of Sunwu-Jinsong deep seismic reflection profile
表 1 深地震反射数据处理技术流程及参数
Table 1 Technical flow and parameters of deep seismic reflection data processing
输入SEG-D数据并输出SEG-Y数据 定义二维观测系统,CMP间距为25 m 道编辑 ,剔除异常道 处理长度,20 s
带通滤波,6~10~44~50 Hz(浅层)、2~4~24~30 Hz(深层)单炮数据全偏移距初至波拾取 层析静校正,替换速度为4500 m/s,基准面高程为750 m 球面扩散补偿、几何扩散补偿和地表一致性振幅校正 叠前多域(f-x域和f-k)噪音衰减 地表一致性预测反褶积,算子长度200 ms 速度分析,间隔40 CMP 剩余静校正,大校正量剩余静校正、自动剩余静校正,5次 高阶动校正,手工切除 叠前时间偏移,克希霍夫偏移,偏移孔径10000 m、偏移角度45° 叠后显示,自动增益 -
Adetunji A Q, Launay G, Ferguson I J, et al. 2023. Crustal conductivity footprint of the orogenic gold district in the Red Lake greenstone belt, Western Superior craton, Canada[J]. Geology, 51(4): 377−382. doi: 10.1130/G50660.1
Brown L D, Zhao W. 1996. Bright spots, structure, and magmatism in southern Tibet from INDEPTH seismic reflection profling[J]. Science, 274(5293): 1688−1690. doi: 10.1126/science.274.5293.1688
Cai W Y, Wang K Y, Li J, et al. 2021. Geology, geochronology and geochemistry of large Duobaoshan Cu−Mo−Au orefield in NE China: Magma genesis and regional tectonic implications[J]. Geoscience Frontiers, 12(1): 265−292. doi: 10.1016/j.gsf.2020.04.013
Cai X L, Zhu J S, Cao J M, et al. 2007. 3D structure and dynamic types of the lithospheric crust in continental China and its adjacent regions[J]. Geology in China, 34(4): 543−557(in Chinese with English abstract).
Calvert A J, Sawyer E W, Davis W J, et al. 1995. Archaean subduction inferred form seismic images of a mantle suture in the Superior Province[J]. Nature, 375(6533): 670−674. doi: 10.1038/375670a0
Clutier A, Gautier S, Tiberi C. 2021. Hybrid local and teleseismic P−wave tomography in North Tanzania: Role of inherited structures and magmatism on continental rifting[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 224(3): 1588−1606.
Cook F A, Philippe Erdmer. 2005. An 1800 km cross section of the lithosphere through the northwestern North American plate: Lessons from 4.0 billion years of Earth's history[J]. Canadian Journal of Earth Sciences, 42(6): 1295−1311. doi: 10.1139/e04-106
Cook F A. 1999. Frozen subduction in Canada's Northwest territories: Lithoprobe deep lithospheric reflection profiling of the western Canadian Shield[J]. Tectonics, 18(1): 1−24.
Dong S W, Li T D, Gao R, et al. 2013. Progress of SinoProbe – Deep Exploration in China 2008—2012[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, (1): 7−23(in Chinese with English abstract).
Du Q, Ma X Y, Han C M, et al. 2008. Discussion on the genesis of porphyry copper deposit[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House: 1-91(in Chinese).
Du Y J. 2012. The metallogenic characteristics and prospecting direction of Duobaoshan Cu−Au metallogenic belt, Heilongjiang Province[D]. Master's thesis of Jilin University(in Chinese with English abstract).
Egbert G D, Booker J R. 1986. Robust estimation of geomagnetic transfer functions[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 87(1): 173−194. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.1986.tb04552.x
Feng Z Q, Liu Y J, Jin W, et al. 2019. Spatiotemporal distribution of ophiolites in the northern Great Xing'an Range and its relationship with the geotectonic evolution of NE China[J]. Geoscience Frontiers, 26(2): 120−136(in Chinese with English abstract).
Pang X J, Fu J Y, Qian C, et al. 2024. The discovery of Carboniferous high−Mg diorites and adakites in the Jalaid Banner area, the central Great Xing'an Range and their implications for the subduction of the Nenjiang ocean[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 43(8): 1430−1445(in Chinese with English abstract).
Gao J, Klemd R, Zhu M, et al. 2017. Large−scale porphyry−type mineralization in the Central Asian metallogenic domain: A review[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 165: 7−36.
Gao J, Zhu M T, Wang X S, et al. 2019. Large−scale porphyry−type mineralization in the Central Asian metallogenic domain: Tectonic background, fluid feature and metallogenic deep dynamic mechanism[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 93(1): 24−71(in Chinese with English abstract).
Gao R, Lu Z W, Liu J K, et al. 2010. A result of interpreting from deep seismic reflection profile: Revealing fine structure of the crust and tracing deep process of the mineralization in Luzong deposit area[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 26(9): 2543−2552(in Chinese with English abstract).
Gao R, Wang H Y, Zhang Z J, et al. 2011. “Cutting” the crust and the upper mantle and revealing the deep structure of the continent with the resource effect: An introduction to the project SinoProbe−02 of experimentation, deep probing techniques and integration and a discussion on key science problems[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 32(C1): 34−48(in Chinese with English abstract).
Ge W C, Wu F Y, Zhou C Y, et al. 2007. Porphyry Cu−Mo deposits in the eastern Xing’an−Mongolian Orogenic Belt: Mineralization ages and their geodynamic implications[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, (24): 3416−3427.
Guo F, Fan W M , Li C W, et al. 2009. Early Paleozoic subduction of the Paleo−Asian Ocean: Geochronological and geochemical evidence from the Dashizhai basalts, Inner Mongolia[J]. Science in China(Series D: Earth Sciences), 52(7): 940−951.
Hao Y J. 2015. Mineralization and Metallogenic Regularity of Duobaoshan Ore Concentration Area in Heilongjiang Province, Northeast China[D]. Ph. D. Doctoral dissertation, Jilin University(in Chinese with English abstract).
Hao Y J, Ren Y S, Duan M X, et al. 2015. Metallogenic events and tectonic setting of the Duobaoshan ore field in Heilongjiang Province, NE China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 97: 442−458. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2014.08.007
Hao Y J, Ren Y S, Duan M X, et al. 2016. Mineralization time and tectonic setting of the Zhengguang Au deposit in the Duobaoshan ore field, Heilongjiang Province, NE China[J]. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 9(15): 655. doi: 10.1007/s12517-016-2666-5
Hou H S, Gao R, Lu Z W, et al. 2010. Reflection seismic first−arrival wave tomography of Longqiao iron deposit and concealed deposit forecast in Luzong iron−polymetallic ore concentrated area.[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 26(9): 2623−2629(in Chinese with English abstract).
Hou H S, Wang H Y, Gao R, et al. 2015. Fine crustal structure and deformation beneath the Great Xing'an Ranges, CAOB: Revealed by deep seismic reflection profile[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 113: 491−500. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2015.01.030
Huang J Q, Zeng M X, Gong S Y. 1954. On major tectonic forms of China[M]. Beijing: Beijing Geological Publishing House(in Chinese with English abstract).
Jiang Y, Jiang S, Li S, et al. 2020. Paleozoic to Mesozoic micro−block tectonics in the eastern Central Asian Orogenic Belt: Insights from magnetic and gravity anomalies[J]. Gondwana Research, 102: 229−251.
Koptev A, Burov E, Calais E, et al. 2016. Contrasted continental rifting via plume−craton interaction: Applications to Central East African Rift[J]. Geoscience Frontiers, 7(2): 221−236. doi: 10.1016/j.gsf.2015.11.002
Li C L. 2018. Gold metallogeny and prospecting in the Nenjiang−Heihe tectonic mélange zone, Heilongjiang Province[D]. Doctoral Dissertation of China University of Geosciences (Beijing)(in Chinese with English abstract).
Li D R, Lv F L, Liu S Y, et al. 2011. Geological features and prospecting orientation of the Sankuanggou Cu−Mo−Au deposit in Nenjiang County, Heilongjiang Province[J]. Geology in China, 38(2): 415−426(in Chinese with English abstract).
Li J Y. 1998. Some new ideas on Tectonics of NE China and its neighboring areas[J]. Geological Review, 44(4): 339−347(in Chinese with English abstract).
Li J Y. 2006. Permian geodynamic setting of Northeast China and adjacent regions: closure of the Paleo−Asian Ocean and subduction of the Paleo−Pacific Plate[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 26: 207−224. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2005.09.001
Li J Y, Qu J F, Zhang J, et al. 2013. New Developments on the Reconstruction of Phanerozoic Geological History and Research of Metallogenic Geological Settings of the Northern China Orogenic Region[J]. Geologcal Bulletin of China, 32(2): 207−219(in Chinese with English abstract).
Li J Y, Liu J F, Qu J F, et al. 2019. Paleozoic Tectonic Units of Northeast China: Continental Blocks or Orogenic Belts?[J]. Earth Science, 44: 3157−3177(in Chinese with English abstract).
Li T D, Liu Y, Ding X Z, et al. 2022. Ten advances in regional geological research of China in recent years[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 96(5): 1544−1581(in Chinese with English abstract).
Li Y, Xu W L, Tang J, et al. 2018. Geochronology and geochemistry of Mesozoic intrusive rocks in the Xing’an Massif of NE China: Implications for the evolution and spatial extent of the Mongol−Okhotsk tectonic regime[J]. Lithos, 304: 57−73.
Li Y, Xu W L, Wang F, et al. 2018. Early–Middle Ordovician volcanism along the eastern margin of the Xing’an Massif, Northeast China: constraints on the suture location between the Xing’an and Songnen–Zhangguangcai Range massifs[J]. International Geology Review, 60(16): 2046−2062. doi: 10.1080/00206814.2017.1402378
Liang H D, Gao R, Hou H S, et al. 2015. Lithospheric electrical structure of the Great Xing’an Range[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 113: 501−507(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2015.01.026
Liang H D, Jin S, Wei W B, et al. 2017. Deep electrical structures of the esatern margin of the Songnen massif and the western margin of the Jiamusi massif[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 60(4): 1511−1520(in Chinese with English abstract).
Liu C, Yang B J, Wang Z G, et al. 2011. The deep structure of the western boundary belt of the Songliao basin: the geoelectric evidence[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 54(2): 401−406(in Chinese with English abstract).
Liu D Y, Jian P, Zhang Q, et al. 2003. SHRIMP dating of adakites in the Tulingkai ophiolite, Inner Mongolia: Evidence for the Early Paleozoic Subdtiction[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, (3): 317−327, 435−437(in Chinese with English abstract).
Liu G X, Zhang X Z, Yang B J, et al. 2006. Electrical structures of the lithosphere along the Jiamusi massif and its eastern edge[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, (2): 598−603(in Chinese with English abstract).
Liu Y, Zhang J, Yin C, et al. 2019. GEM3D: A 3D inversion code for geophysical electromagnetic data based on unstructured tetrahedron grid[C]//International Workshop on Gravity, Electrical & Magnetic Methods and Their Applications. 416−419.
Liu Y J, Zhang X Z, Jin W, et al. 2010. Late Paleozoic tectonic evolution in Northeast China[J]. Geology in China, 37(4): 943−951(in Chinese with English abstract).
Liu Y J, Li W M, Feng Z Q, et al. 2017. A review of the Paleozoic tectonics in the eastern part of central Asian orogenic belt[J]. Gondwana Research, 43: 123−148. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2016.03.013
Liu Y J, Feng Z Q, Jiang L W, et al. 2019. Ophiolite in the eastern Central Asian Orogenic Belt, NE China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 35(10): 3017−3047(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2019.10.05
Liu Y J, Li W M, Ma Y, et al. 2021. An orocline in the eastern Central Asian Orogenic Belt[J]. Earth−Science Reviews, 221(1): 103808.
Lu Z X, Jiang D L, Bai Y, et al. 2005. Exploration and research on the structure of the crust and upper mantlein Northeast China[J]. Journal of Disaster Prevention and Reduction, (1): 1−8(in Chinese with English abstract).
Luan J P, Yu J J, Yu J L, et al. 2019. Early Neoproterozoic magmatism and the associated metamorphism in the Songnen Massif, NE China: Petrogenesis and tectonic implications[J]. Precambrian Research, 328: 250−268. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2019.04.004
Ma Y F, Liu Y J, Qin T, et al. 2020. Late Devonian to early Carboniferous magmatism in the western Songliao–Xilinhot block, Northeast China: Implications for eastward subduction of the Nenjiang oceanic lithosphere[J]. Geological Journal, 55(3): 2208−2231. doi: 10.1002/gj.3739
Meng F W, Liu Y H, Han J T, et al. 2022. Paleozoic suture and Mesozoic tectonic evolution of the lithosphere between the northern section of the Xing'an Block and the Songnen Block: Evidence from three−dimensional magnetotelluric detection[J]. Tectonophysics, 823: 229210. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2022.229210
Na F C, Fu J Y, Wang Y, et al. 2014. LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb age of the chlorite-muscovite tectonic schist in Hadayang, Morin Dawa Banner, Inner Mongolia, and its tectonic significance[J]. Geol. Bullet. China., 33: 1326−1332 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Na F C, Song W M, Liu Y C, et al. 2018. Chronological study and tectonic significance of Precambrian metamorphic rocks in Zhalantun area of Da Hinggan Mountains[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 37(9): 1607−1619(in Chinese with English abstract).
Pan J T, Wu Q J, Li Y H, et al. 2014. Ambient noise tomography in northeast China[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 57(3): 812−821(in Chinese with English abstract).
Pan Z D, Hou H S, Zhou J B, et al. 2021. Crustal structure and paleozoic metallogenic tectonic setting of the Duobaoshan ore district, NE China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 137: 104290. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2021.104290
Pirajno F. 2016. A classification of mineral systems, overviews of plate tectonic margins and examples of ore deposits associated with convergent margins(Review)[J]. Gondwana Research, 33: 44−62. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2015.08.013
Qian C, Lu L, Qin T, et al. 2018. The early Late−Paleozoic granitic magmatism in the Zalantun region, northern Great Xing'an Range, NE China: Constraints on the timing of amalgamation of Erguna−Xing'an and Songnen blocks[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 92(11): 2190−2214(in Chinese with English abstract).
Qiang Z Y, Wu Q J. 2015. Upper mantle anisotropy beneath the north of the northeast China and its dynamic significance[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 58(10): 3540−3552(in Chinese with English abstract).
Qin K Z, Zhai M G, Li G M, et al. 2017. Links of collage orogenesis of multiblocks and crust evolution to characteristic metallogeneses in China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 33(2): 305−325(in Chinese with English abstract).
Qin K Z, Zhao J X, Fan H R, et al. 2021. On the ore−forming depth and possible maximum vertical extension of the major type ore deposits[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 28(3): 271−294(in Chinese with English abstract).
Quan J Y. 2013. Tectonic properties of Eastern Songnen Masiff from Late Neoproterozoic to Early Paleozoic[D]. Master's thesis, Jilin University(in Chinese with English abstract).
Ren J S, Niu B G, Liu Z G. 1999. Soft collision, superposition orogeny and polycyclic suturing[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, (3): 85−93(in Chinese with English abstract).
Sato H, Hirata N, Koketsu K, et al. 2006. Seismic reflection profiling in the Kanto and Kinki metropolitan areas, Japan[J]. Bulletin of Earthquake Research Institute, 81: 233−238.
Shi L, Zheng C, Yao W, et al. 2015. Geochronological framework and tectonic setting of the granitic magmatism in the Chaihe–Moguqi region, central Great Xing’an Range, China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 113: 443−453.
Simancas J F, Carbonell R, González Lodeiro F, et al. 2003. Crustal structure of the transpressional Variscan orogen of SW Iberia: SW Iberia deep seismic reflection profile (IBERSEIS)[J]. Tectonics, 22(6): 1062.
Snyder D B, Goleby B R. 2016. Seismic reflection patterns associated with continental convergent margins through time[J]. Tectonophysics, 692: 3−13. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2016.04.027
Sun D Y, Wu F Y, Lin L Q. 2001. Emplacement age of the post−orogenic A−type granites in Northwestern Lesser Xing'an Ranges, and its relationship to the eastward extension of Suo−lushan−Hegenshan−Zhalaite collisional suture zone[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, (5): 427−432.
Sun D Y, Wu F Y, Zhang Y B, et al. 2004. The final closing time of the west Lamulun River−Changchun−Yanji plate suture zone Evidence from the Dayushan granitic pluton, Jilin Province[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Earth Science Edition), (2): 174−181(in Chinese with English abstract).
Tan C Y, Wang G H, Li Y S. 2010. New progress and significance on the mineral exploration in Duobaoshan mineralization area, Heilongjiang, China[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 29(2/3): 436−445(in Chinese with English abstract).
Tang K D, Wang Y, He G Q, et al. 1995. Continental−margin structure of Northeast China and its adjacent areas[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 69(1): 16−30(in Chinese with English abstract).
Tang K D, Su Y Z. 1966. New data about the Paleozoic Formations and their significance in the Northeastern Minor Khingan[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, (1): 14−28(in Chinese with English abstract).
Velden A J, Van Staal C R, Cook F A. 2004. Crustal structure, fossil subduction, and the tectonic evolution of the Newfoundland Appalachians: Evidence from a reprocessed seismic reflection survey[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 116(11/12): 1485−1498. doi: 10.1130/B25518.1
Wang F, Xu W L, Gao F H, et al. 2014. Precambrian terrane within the Songnen−Zhangguangcai Range Massif, NE China: evidence from U–Pb ages of detrital zircons from the Dongfengshan and Tadong group[J]. Gondwana Research, 26(1): 402−413. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2013.06.017
Wang T, Zheng Y D. 2002. Mesozoic progressive transition from overthrusting to extension in the Sino−Mongolian border region and crustal−scale tangential shear[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, (Z1): 232−237(in Chinese with English abstract).
Wang T, Zhang L, Guo L, et al. 2014. The progress of the preliminary compilation of map of Mesozoic Granitoid of Asia and the research on related key issues[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 35(6): 655−672(in Chinese with English abstract).
Wang X, Wang L, Liu J, et al. 2007. Metallogeny and reformation of the Duobaoshansuperlarge porphyry copper deposit in Heilongjiang[J]. Scientia Geologica Sinica, 42(1): 124−133.
Wang Y, Fu J Y, Yang F, et al. 2015. Contraction and Extension in Nenjiang−Heihe Tectonic Belt: Evidence from the Late Paleozoic Granitoid Geochemistry[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Earth Science Edition), 45(2): 374−388(in Chinese with English abstract).
Wang Y, Qian C, Zhong H, et al. 2024. Tectonic framework, evolution and potential petroleum resources of the structural belt in the western margin of Songliao basin[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 43(7): 1073−1089(in Chinese with English abstract).
Warner M, Morgan J, Barton P, et al. 1996. Seismic reflections from the mantle represent relict subduction zones within the continental lithosphere[J]. Geology, 24(1): 39−42. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1996)024<0039:SRFTMR>2.3.CO;2
White D J, Musacchio G, Helmstaedt H H, et al. 2003. Images of a lower−crustal oceanic slab: Direct evidence for tectonic accretion in the Archean western Superior province[J]. Geology, 31(11): 997−1000. doi: 10.1130/G20014.1
Windley B F, Alexeiev D, Xiao W, et al. 2007. Tectonic models for accretion of the Central Asian Orogenic Belt[J]. Journal of the Geological Society, 164(1): 31−47. doi: 10.1144/0016-76492006-022
Wu F Y, Sun D Y, Ge W C, et al. 2011. Geochronology of the Phanerozoic granitoids in northeastern China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 41(1): 1−30. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2010.11.014
Wu G, Chen Y C, Sun F Y, et al. 2015. Geochronology, geochemistry, and Sr–Nd–Hf isotopes of the early Paleozoic igneous rocks in the Duobaoshan area, NE China, and their geological significance[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 97: 229−250. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2014.07.031
Wu X W, Zhang C, Zhang Y J, et al. 2018. 2.7 Ga monzogranite on the Songnen Massif and its geological implications[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 92: 1265−1266. doi: 10.1111/1755-6724.13609
Xiao W, Windley B F, Hao J, et al. 2003. Accretion leading to collision and the Permian Solonker suture, Inner Mongolia, China: Termination of the central Asian orogenic belt[J]. Tectonics, 22(6): 8.
Xu B, Jacques Charvet, Zhang F Q. 2001. Primary study on petrology and geochrononology of Blueschists inSunitezuoqi, Northern Inner Mongolia[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology(Scientia Geologica Sinica), (4): 424−434(in Chinese with English abstract).
Xu B, Zhao P, Bao Q Z, et al. 2014. Preliminary study on the pre−Mesozoic tectonic unit division of the Xing−Meng Orogenic Belt (XMOB)[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 30(7): 1841−1857(in Chinese with English abstract).
Xu B, Zhao P, Wang Y, et al. 2015. The pre−Devonian tectonic framework of Xing’an–Mongolia orogenic belt (XMOB) in north China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 97: 183−196. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2014.07.020
Xu W L, Sun C Y, Tang J, et al. 2019. Basement nature and tectonic evolution of the Xing'an−Mongolian Orogenic Belt[J]. Earth Science, 44(5): 1620−1646(in Chinese with English abstract).
Yang B J, Mu S M, Jin X, et al. 1996. Synthesized study on the geophysics of Manzhouli−Suifenhe Geoscience transect, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, (6): 772−782(in Chinese with English abstract).
Yang F S, Li C L, Li W L, et al. 2020. Discovery and Geotectonic Significance of Basement Debris in Duobaoshan Ore−Gathering Area, Heilongjiang Province[J]. Advances in Geosciences, 10(12): 1212−1225(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.12677/AG.2020.1012118
Yang X P, Zhong H, Yang Y J, et al. 2022. Research progress on the subduction−accretion complex: Reconstruction of the tectonic framework of the Great Xing'an Range[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 29(2): 94−114(in Chinese with English abstract).
Ye M, Zhang S H, Wu F Y, et al. 1994. The classification of the Paleozoic tectonic units in the area crossed by M−S GGT[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Earth Science Edition), (3): 241−245(in Chinese with English abstract).
Yu Q S, Zhang F X, Zeng Z F, et al. 2015. Research on geophysical field in northern part of Da Hinggan mountains[J]. World Geology, 34(1): 187−193(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zeng Q D, Liu J M, Chu S X, et al. 2014. Re–Os and U–Pb geochronology of the Duobaoshan porphyry Cu–Mo–(Au) deposit, northeast China, and its geological significance[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 79: 895−909. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2013.02.007
Zhang F Q, Chen H L, Dong C W, et al. 2008. Evidence for the existence of Precambrian Basement under the northern Songliao basin[J]. Geology in China, (3): 421−428(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang F X, Wu Q J, Li Y H, et al. 2014. The P wave velocity structure of the upper mantle beneath the Central and Southern Mongolia area[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 57(9): 2790−2801(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang M S, Peng X D, Sun X M. 1998. The Paleozoic tectonic geographical pattern of Northeast China[J]. Land & Resources, (2): 12−17(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang X Z, Yang B J, Wu F Y, et al. 2006. The lithosphere structure in the Hingmong−Jihei(Hinggan−Mongolia−Jilin−Heilongjiang) region, northeastern China[J]. Geology in China, (4): 816−823(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang X Z, Zhou J B, Chi X G, et al. 2008. Late Paleozoic tectonic−sedimentation and petroleum resources in northeastern China[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Earth Science Edition), (5): 719−725(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang X Z, Zeng Z, Gao R, et al. 2015. The evidence from the deep seismic reflection profile on the subduction and collision of the Jiamusi and Songnen massifs in the northeastern China[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 58(12): 4415−4424(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhao L F, Li X Y, Li C L, et al. 2022. Recognition of concealed porphyry body and deep prospecting practice in Duobaoshan ore concentration area based on gravity, magnetic and electromagnetic surveys[J]. Mineral Deposits, 41(6): 1217−1231(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhao Y Y, Wang J P, Zhao G J, et al. 2011. Metallogenic regularity and prospecting direction of Duobaoshan ore field, Heilongjiang Province, China[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Earth Science Edition), 41(6): 1676−1688(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhao Z, Chi X G, Liu J F, et al. 2010. Late Palozoic arc−related magnatisn in Yakeshi regin, Inner Mongolia Chronological and geochemical evidence[J]. Aca Petrobgica Sinica, 26(11): 3245−3258(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhao Z H, Zheng W Z, Qu H, et al. 2012. Cu−Au mineralization and metallogenic regularity of Duobaoshan area, Heilongjiang Province[J]. Mineral Deposits, 31(3): 601−614(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zheng J, Ge W C, M Santosh, et al. 2023. Lithospheric dripping in a soft collision zone: Insights from late Paleozoic magmatism suites of the eastern Central Asian Orogenic Belt[J]. Geoscience Frontiers, 14(1): 101−117.
Zhou J B, Wilde S A, Zhang X Z, et al. 2011. Early Paleozoic metamorphic rocks of the Erguna block in the Great Xing'an Range, NE China: Evidence for the timing of magmatic and metamorphic events and their tectonic implications[J]. Tectonophysics, 499: 105−117. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2010.12.009
Zhou J B, Zeng W S, Cao J L, et al. 2012. The Tectonic Framework and Evolution of the NE China: From ~500 Ma to ~180 Ma[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Earth Science Edition), 42(5): 1298−1316(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhou J B, Wang B, Zeng WS, et al. 2014. Detrital zircon U−Pb dating of the Zhalantun Metamorphic Complex and its tectonic implications, Great Xing'an, NE China, Acta Petrologica Sinica[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 30(7): 1879−1888(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhou X M, Ren S M, Zhang X Z, et al. 2013. Deep Structural Study on Gravity−Magneto−Electricity Profile of Alar−Handagai in Hailar Basin and Its Geological Significance[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Earth Science Edition), 43(5): 1630−1638(in Chinese with English abstract).
董树文, 李廷栋, 高锐, 等. 2013. 我国深部探测技术与实验研究与国际同步[J]. 地球学报, 34(1): 7−23. doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2013.01.02 杜琦, 马晓阳, 韩成满, 等. 2008. 斑岩铜矿成因探讨[M]. 北京: 地质出版社: 1-91. 杜英杰. 2012. 黑龙江省多宝山Cu−Au成矿带成矿特征及找矿方向[D]. 吉林大学硕士学位论文. 冯志强, 刘永江, 金巍, 等. 2019. 东北大兴安岭北段蛇绿岩的时空分布及与区域构造演化关系的研究[J]. 地学前缘, 26(2): 120−136. 高俊, 朱明田, 王信水, 等. 2019. 中亚成矿域斑岩大规模成矿特征: 大地构造背景、流体作用与成矿深部动力学机制[J]. 地质学报, 93(1): 24−71. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2019.01.004 高锐, 卢占武, 刘金凯, 等. 2010. 庐−枞金属矿集区深地震反射剖面解释结果——揭露地壳精细结构, 追踪成矿深部过程[J]. 岩石学报, 26(9): 2543−2552. 高锐, 王海燕, 张忠杰, 等. 2011. 切开地壳上地幔, 揭露大陆深部结构与资源环境效应—深部探测技术实验与集成(SinoProbe−02)项目简介与关键科学问题[J]. 地球学报, 32(C1): 34−48. 郝宇杰. 2015. 黑龙江省多宝山矿集区成矿作用与成矿规律研究[D]. 吉林大学博士学位论文. 侯贺晟, 高锐, 卢占武, 等. 2010. 庐枞铁多金属矿集区龙桥铁矿反射地震初至波层析成像与隐伏矿床预测[J]. 岩石学报, 26(9): 2623−2629. 黄汲清, 曾莫休, 龚素玉. 1954. 中国主要地质构造单位[M]. 北京: 地质出版社. 黄汲清, 姜春发. 1962. 从多旋回构造运动观点初步探讨地壳发展规律[J]. 地质学报, (2): 105−152. 金昌抖. 1976. 黑龙江省多宝山−卧都河幅铜矿区域成矿特征及其找矿方向[Z]. 黑龙江省地质科研所. 李成禄. 2018. 黑龙江省嫩江−黑河构造混杂岩带金矿成矿作用及找矿预测[D]. 中国地质大学(北京)博士学位论文. 李春昱, 王荃. 1983. 中国北方板块构造文集(第一集)[M]. 北京: 地质出版社: 3−17. 李德荣, 吕福林, 刘素颖, 等. 2011. 黑龙江省嫩江县三矿沟矿区地质特征及找矿方向[J]. 中国地质, 38(2): 415−426. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2011.02.016 李锦轶. 1986. 内蒙古东部中朝板块与西伯利亚板块之间古缝合带的初步研究[J]. 科学通报, (14): 1093−1096. 李锦轶. 1998. 中国东北及邻区若干地质构造问题的新认识[J]. 地质论评, (4): 339−347. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.1998.04.002 李锦轶, 曲军峰, 张进, 等. 2013. 中国北方造山区显生宙地质历史重建与成矿地质背景研究进展[J]. 地质通报, 32(2): 207−219. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2013.02.001 李锦轶, 刘建峰, 曲军峰, 等. 2019. 中国东北地区古生代构造单元: 地块还是造山带?[J]. 地球科学, 44: 3157−3177. 李廷栋, 刘勇, 丁孝忠, 等. 2022. 中国区域地质研究的十大进展[J]. 地质学报, 96(5): 1544−1581. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2022.05.004 梁宏达, 高锐, 侯贺晟, 等. 2016. 大兴安岭与两侧盆地结合地带深部电性结构与岩石圈尺度构造关系[J]. 地球物理学报, 59(5): 1696−1704. doi: 10.6038/cjg20160514 刘财, 杨宝俊, 王兆国, 等. 2011. 松辽盆地西边界带深部构造: 地电学证据[J]. 地球物理学报, 54(2): 401−406. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2011.02.016 刘敦一, 简平, 张旗, 等. 2003. 内蒙古图林凯蛇绿岩中埃达克岩SHRIMP测年: 早古生代洋壳消减的证据[J]. 地质学报, (3): 317−327, 435−437. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2003.03.004 刘永江, 张兴洲, 金巍, 等. 2010. 东北地区晚古生代区域构造演化[J]. 中国地质, 37(4): 943−951. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2010.04.010 刘永江, 冯志强, 蒋立伟, 等. 2019. 中国东北地区蛇绿岩[J]. 岩石学报, 35(10): 3017−3047. 卢造勋, 姜德禄, 白云, 等. 2005. 东北地区地壳上地幔结构的探测与研究[J]. 东北地震研究, (1): 1−8. 吕庆田, 侯增谦, 赵金花, 等. 2003. 深地震反射剖面揭示的铜陵矿集区复杂地壳结构形态[J]. 中国科学(D辑), (5): 442−449. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-9267.2003.05.006 那福超, 付俊彧, 汪岩, 等. 2014. 内蒙古莫力达瓦旗哈达阳绿泥石白云母构造片岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄及其地质意义[J]. 地质通报, 33(9): 1326−1332. 那福超, 宋维民, 刘英才, 等. 2018. 大兴安岭扎兰屯地区前寒武纪变质岩系年龄及其构造意义[J]. 地质通报, 37(9): 1607−1619. 庞雪娇, 付俊彧, 钱程, 等. 2024. 大兴安岭中段内蒙古扎赉特旗地区石炭纪高镁闪长岩、埃达克岩的发现及其对嫩江洋俯冲作用的指示[J]. 地质通报, 43(8): 1430−1445. doi: 10.12097/gbc.2023.09.019 钱程, 陆露, 秦涛等. 2018. 大兴安岭北段扎兰屯地区晚古生代早期花岗质岩浆作用——对额尔古纳−兴安地块和松嫩地块拼合时限的制约[J]. 地质学报, 92(11): 2190−2214. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2018.11.002 秦克章, 翟明国, 李光明, 等. 2017. 中国陆壳演化、多块体拼合造山与特色成矿的关系[J]. 岩石学报, 33(2): 305−325. 秦克章, 赵俊兴, 范宏瑞, 等. 2021. 试论主要类型矿床的形成深度与最大延深垂幅[J]. 地学前缘, 28(3): 271−294. 权京玉. 2013. 松嫩地块东部新元古代—早古生代构造属性研究[D]. 吉林大学硕士学位论文. 任纪舜, 牛宝贵, 刘志刚. 1999. 软碰撞、叠覆造山和多旋回缝合作用[J]. 地学前缘, (3): 85−93. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.1999.03.008 邵济安, 牟保磊, 何国琦, 等. 1997. 华北北部在古亚洲域与古太平洋域构造叠加过程中的地质作用[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 27(5): 390−394. 孙德有, 吴福元, 张艳斌, 等. 2004. 西拉木伦河−长春−延吉板块缝合带的最后闭合时间——来自吉林大玉山花岗岩体的证据[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), (2): 174−181. 谭成印, 王根厚, 李永胜. 2010. 黑龙江多宝山成矿区找矿新进展及其地质意义[J]. 地质通报, 29(2/3): 436−445. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2010.02.031 唐克东, 王莹, 何国琦, 等. 1995. 中国东北及邻区大陆边缘构造[J]. 地质学报, 69(1): 16−30. 唐克东, 苏养正. 1966. 小兴安岭西北部古生代地层的新资料及其意义[J]. 地质学报, (1): 14−28. 王涛, 张磊, 郭磊, 等. 2014. 亚洲中生代花岗岩图初步编制及若干研究进展[J]. 地球学报, 35(6): 655−672. 王喜臣, 王训练, 王琳, 等. 2007. 黑龙江多宝山超大型斑岩铜矿的成矿作用和后期改造[J]. 地质科学, 42(1): 124−133. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0563-5020.2007.01.011 汪岩, 付俊彧, 杨帆, 等. 2015. 嫩江黑河构造带收缩与伸展源自晚古生代花岗岩类的地球化学证据[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 45(2): 374−388. 肖文交, 宋东方, Brian F. W, 等. 2019. 中亚增生造山过程与成矿作用研究进展[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 49(10): 1512−1545. 徐备, 赵盼, 鲍庆中, 等. 2014. 兴蒙造山带前中生代构造单元划分初探[J]. 岩石学报, 30(7): 1841−1857. 许文良, 孙晨阳, 唐杰, 等. 2019. 兴蒙造山带的基底属性与构造演化过程[J]. 地球科学, 44(5): 1620−1646. 杨宝俊, 穆石敏, 金旭, 等. 1996. 中国满洲里—绥芬河地学断面地球物理综合研究[J]. 地球物理学报, (6): 772−782. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5733.1996.06.007 杨福深, 李成禄, 李文龙, 等. 2020. 黑龙江省多宝山矿集区基底残块的发现及大地构造意义[J]. 地球科学前沿, 10(12): 1212−1225. 杨晓平, 钟辉, 杨雅军, 等. 2022. 大兴安岭地区古生代构造格架重建: 来自俯冲增生杂岩研究进展[J]. 地学前缘, 29(2): 94−114. 叶茂, 张世红, 吴福元. 1994. 中国满洲里—绥芬河地学断面域古生代构造单元及其地质演化[J]. 长春地质学院学报, (3): 241−245. 章凤奇, 陈汉林, 董传万, 等. 2008. 松辽盆地北部存在前寒武纪基底的证据[J]. 中国地质, (3): 421−428. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2008.03.006 张梅生, 彭向东, 孙晓猛. 1998. 中国东北区古生代构造古地理格局[J]. 辽宁地质, (2): 12−17. 张兴洲, 杨宝俊, 吴福元, 等. 2006. 中国兴蒙—吉黑地区岩石圈结构基本特征[J]. 中国地质, (4): 816−823. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2006.04.011 张兴洲, 周建波, 迟效国, 等. 2008. 东北地区晚古生代构造−沉积特征与油气资源[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), (5): 719−725. 张兴洲, 曾振, 高锐, 等. 2015. 佳木斯地块与松嫩地块俯冲碰撞的深反射地震剖面证据[J]. 地球物理学报, 58(12): 4415−4424. doi: 10.6038/cjg20151207 赵理芳, 李希元, 李成立, 等. 2022. 基于重, 磁, 电法的多宝山矿集区隐伏斑岩体识别与深部找矿实践[J]. 矿床地质, 41(6): 1217−1231. 赵元艺, 王江朋, 赵广江, 等. 2011. 黑龙江多宝山矿集区成矿规律与找矿方向[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 41(6): 1676−1688. 赵芝, 迟效国, 刘建峰, 等. 2010. 内蒙古牙克石地区晚古生代弧岩浆岩: 年代学及地球化学证据[J]. 岩石学报, 26(11): 3245−3258. 赵忠海, 郑卫政, 曲晖, 等. 2012. 黑龙江多宝山地区铜金成矿作用及成矿规律[J]. 矿床地质, 31(3): 601−614. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2012.03.017 周建波, 曾维顺, 曹嘉麟, 等. 2012. 中国东北地区的构造格局与演化: 从500 Ma到180 Ma[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 42(5): 1298−1316. 周建波, 王斌, 曾维顺, 等. 2014. 大兴安岭地区扎兰屯变质杂岩的碎屑锆石U−Pb年龄及其大地构造意义[J]. 岩石学报, 30(7): 1879−1888. -
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 徐大兴,邵兆刚,陈宣华,张进江,徐盛林,李冰,张义平,余苇,邓文兵,丁奕文. 贺兰山构造带深部电性结构与动力学机制. 地质通报. 2024(11): 1921-1936 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(0)




 下载:
下载: