LA−ICP−MS trace element analysis of pyrite from Jiaodingshan cobalt deposits in Sichuan,and its constraints on the ore genesis
-
摘要:
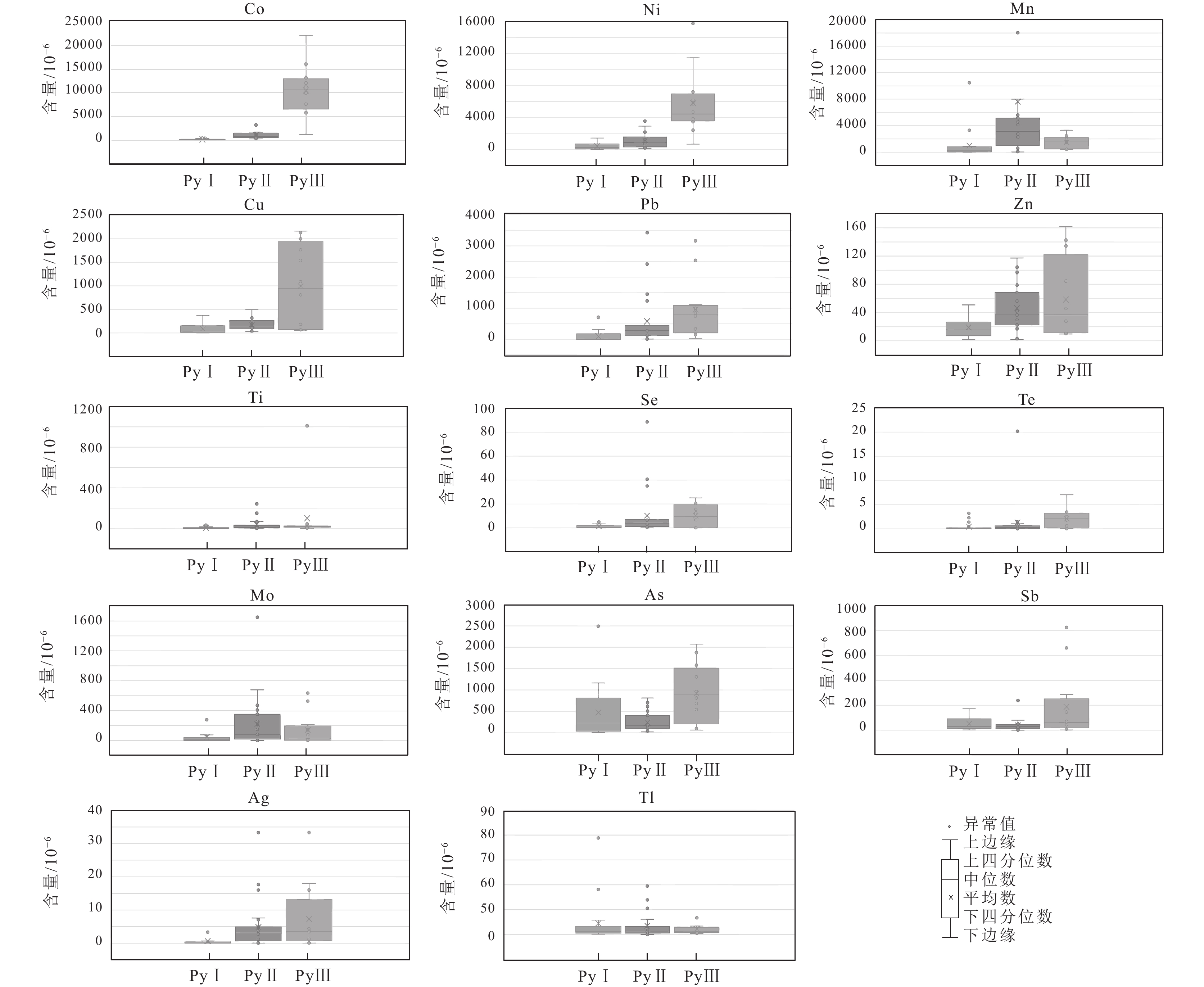
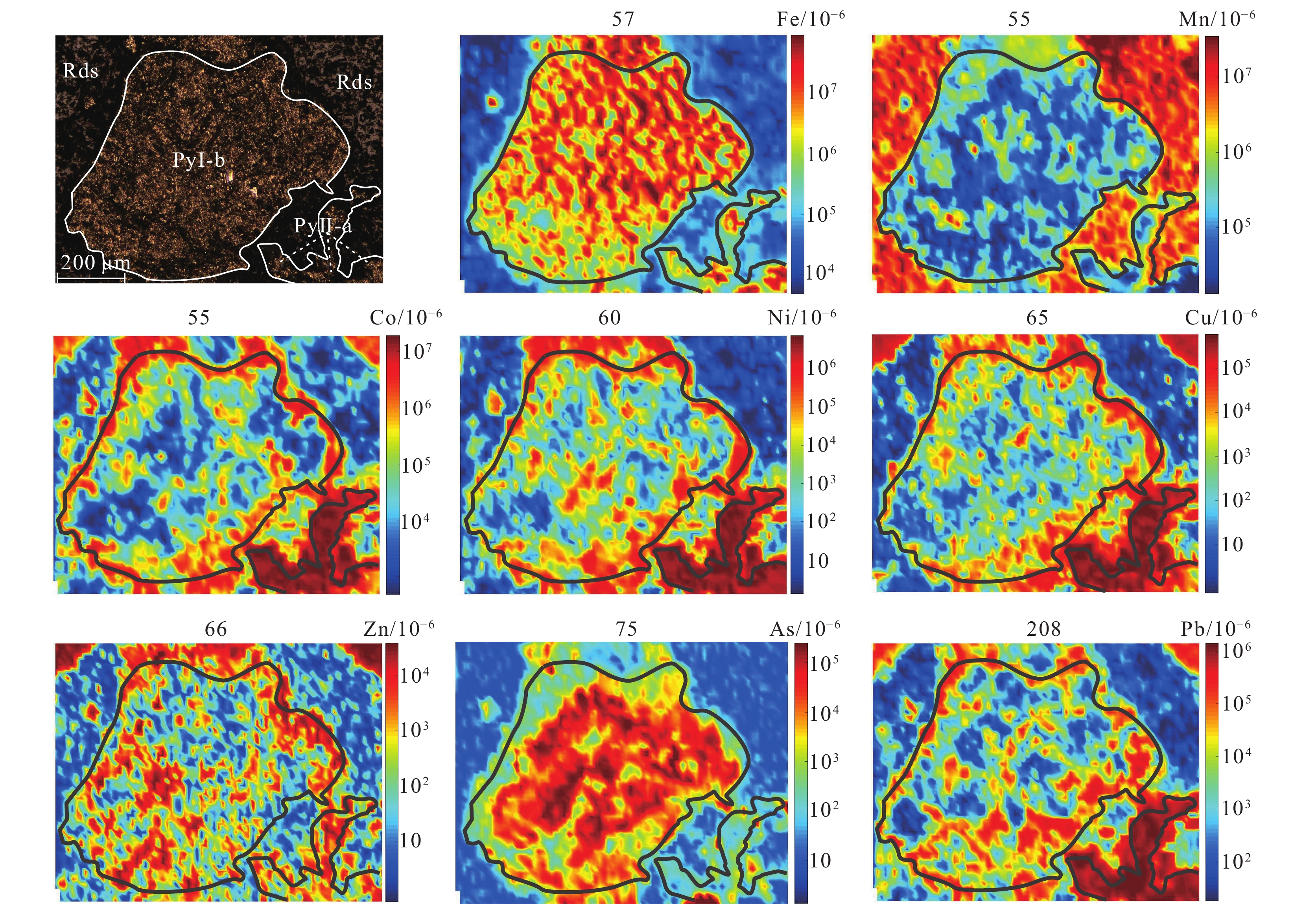
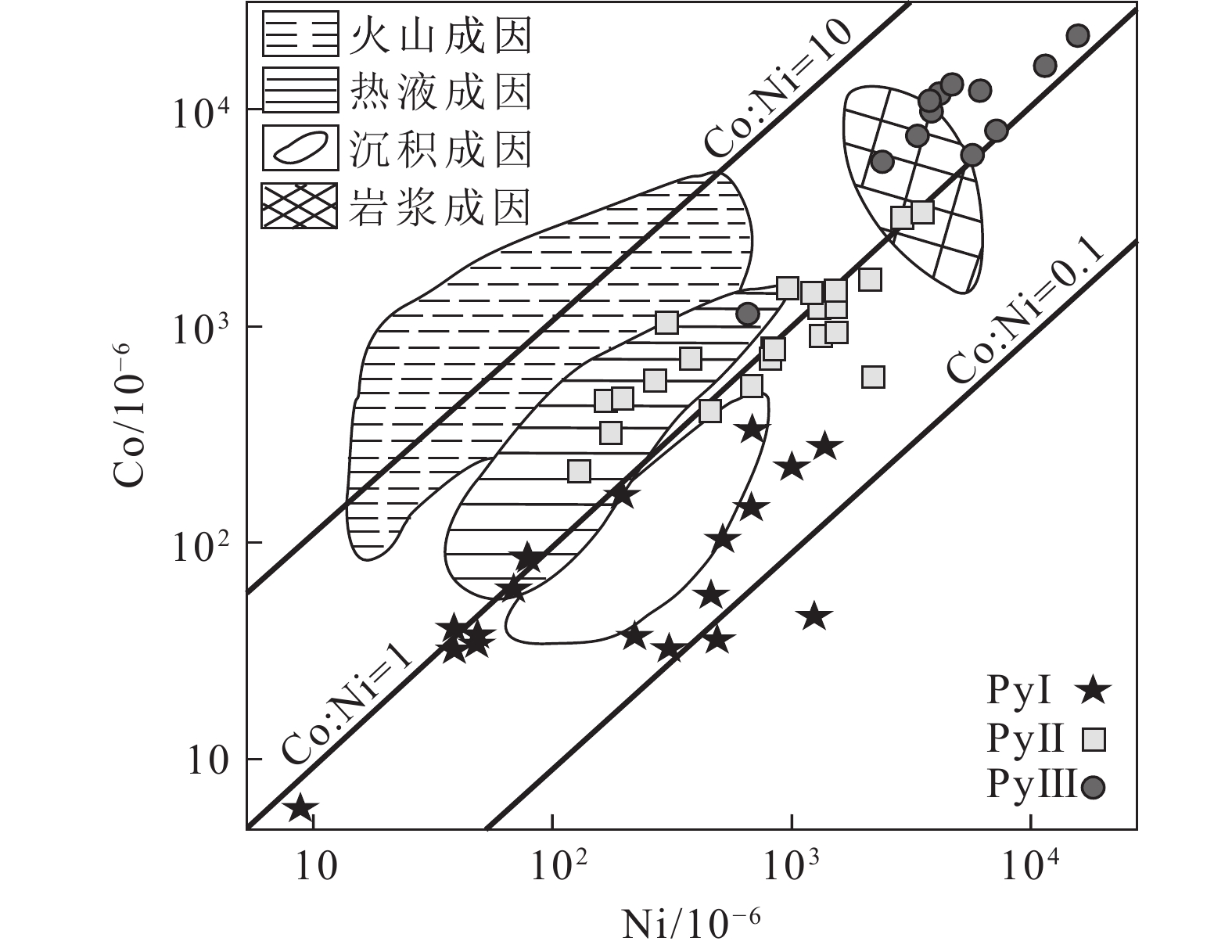
轿顶山钴矿床位于四川盆地西南缘,其矿床成矿物质来源及矿床成因鲜有研究,由于Co元素具有亲铁和亲硫的双重特性,使其在硫化物中富集明显。以轿顶山钴矿床中的黄铁矿为研究对象,在黄铁矿显微结构研究基础上,利用LA−ICP−MS对黄铁矿微量元素进行原位测试分析,为探讨矿床成因提供制约。根据黄铁矿的显微组构特征,可将轿顶山钴矿床中的黄铁矿划分为3个世代。PyⅠ为原始沉积型黄铁矿,包括少量半自形状黄铁矿(PyⅠ-a)、胶状黄铁矿(PyⅠ-b)及莓状黄铁矿(PyⅠ-c),其Co/Ni值基本上都小于1(平均值0.53),成矿元素(Co)平均含量99.8×10−6。PyⅡ受构造变形及热液叠加作用影响,常具有交代残余结构(PyⅡ-a)及变形重结晶结构(PyⅡ-b),其Co/Ni>1(平均值1.31),成矿元素(Co)平均含量为1060.8×10−6;PyⅢ为细粒散砂状及细粒胶状集合体形式,强金属光泽,并与硫钴矿、硫镍钴矿、黄铜矿共生,Co/Ni平均值为2.05,成矿元素Co平均含量为10453.5×10−6,PyⅢ中Co、Ni元素可能以硫钴镍矿的微细物包裹体形式存在于黄铁矿内部。综合分析认为,早期沉积型PyⅠ成矿元素背景值较高,受后期构造变形-热液叠加改造作用影响,PyⅡ中成矿元素逐渐富集,而主成矿期PyⅢ为后期热液对PyⅡ进一步叠加改造,最终形成了现有的钴矿床。
Abstract:The Jiaodingshan cobalt deposit is situated in the southwestern of Sichuan basin, and the source of the ore materials and fluids is still under debated. Cobalt is enriched in vulcanized species because of its double properties of iron and sulfur affinity. In order to analyse the genesis of the deposit, this study investigates the pyrite microstructure and the geochemical compositions of pyrite based on LA−ICP−MS. The results show that three generations of pyrite were identified according to its microstructure characteristics in Jiaodingshan cobalt deposit. The first generation (pyrite Ⅰ)is identified as original sedimentary pyrite, including colloform pyrite, subhedral pyrite and framboidal pyrite. The pyrite Ⅰ is characterized by low Co/ Ni ratio (<1 and the average ratio is 0.53) and low Co content (99.8 × 10−6). Due to the influence of tectonic deformation and hydrothermal superimposition, the pyrite Ⅱ often presents the structure with metasomatic relict texture(pyrite Ⅱ−a) and recrystallization(pyrite Ⅱ−b), which is characterized by high Co/ Ni ratios (Co/ Ni >1, the average ratios is 1.31) and middle Co content (1060.8 × 10−6). Pyrite Ⅲ exists in the form of fine sand−like and fine colloidal aggregates, along with strong metal luster. Such pyrite is often associated with linnaeite, siegenite and chalcopyrite, with the ratios of Co/ Ni higher than 1(the average ratios is 2.05) and the Co content being 10453.5×10−6. The Co and Ni contents in Py Ⅲ perhaps represented by siegenite inclusions enclosed in pyrite. Overall, the early sedimentary pyrite I with high ore−forming element background value may be affected by tectonic deformation−hydrothermal superposition transformation in the later period, resulting in further enrichment of ore−forming elements (Co) in pyrite Ⅱ. While the main ore−forming period of Py Ⅲ was hydrothermal superimposed on Py Ⅱ, and finally formed the existing cobalt deposit.
-
Keywords:
- LA−ICP−MS /
- pyrite /
- trace element /
- cobalt deposit /
- Jiaodingshan, Sichuan Province
-
油页岩属于非常规油气资源,利用蒸馏等技术处理后能够获得页岩气及页岩油,是一种前景非常好的油气资源,被列为21世纪非常重要的接替能源(侯祥麟,1994;赵政璋等,2005;刘招君等,2006;王红岩等,2009)。中国油页岩资源丰富,资源潜力大,其中松辽盆地是油页岩资源极丰富的地区,占东北地区油页岩资源总量的96%(刘招君等,2009)。松辽盆地是一个大型陆相薄互层沉积盆地,岩石物性横向变化大,地层平缓且构造幅度小,油页岩单层厚度薄,这种复杂的沉积结构增加了地震勘探的难度(李桂林,2009)。大地电磁法由于天然场源的随机性及信号微弱精度和效率较低,电阻率法则存在探测深度浅、高阻层屏蔽等缺点。测井技术在识别和评价油页岩方面较成熟(丰莉等,2016;刘同庆,2020),已被广泛应用于油页岩矿区,但是由于其空间探测范围的局限性,存在横向范围内描述储层物性变化能力很弱的缺陷。
测井具有较高的纵向地层分辨率,将测井数据作为先验信息进行电磁法约束反演,可以提高反演结果的纵向分辨率。朱宇启等(2021)在南黄海中部隆起区对海洋CSEM实测数据进行测井约束反演,突出了垂向发生明显变化的层位。Brown et al.(2012)发现,利用测井数据进行正则化约束反演比常规反演结果更紧凑地估计了储层结构。余年等(2012)利用测井数据作为先验信息开展大地电磁约束反演,与常规反演结果相比,约束反演结果对岩溶、断层、褶皱等地质构造的反映与实际吻合更好。自20世纪80年代以来,可控源音频大地电磁法和仪器都得到了很大发展,具有设备轻便、勘探深度相对较大、不受高阻层屏蔽、横向分辨率高等特点(何梅兴,2006;余年等,2012),在勘探石油、天然气、金属矿床、地热等领域得到广泛应用(秦伟,2013;李致君等,2018;李英宾等,2019)。地球物理方法和测井技术在联合研究油页岩储层特征方面几乎还是空白,本文通过松辽盆地采集的可控源音频大地电磁数据,利用测井资料作为先验信息,开展可控源音频大地电磁法和测井联合约束反演技术应用研究,将油页岩与泥页岩互层整体作为相对高阻层,进行划分识别,取得较好的效果,初步查明研究区油页岩的展布特征,为进一步勘探工作指明了有利方向。
1. 地质地球物理背景
1.1 地质条件
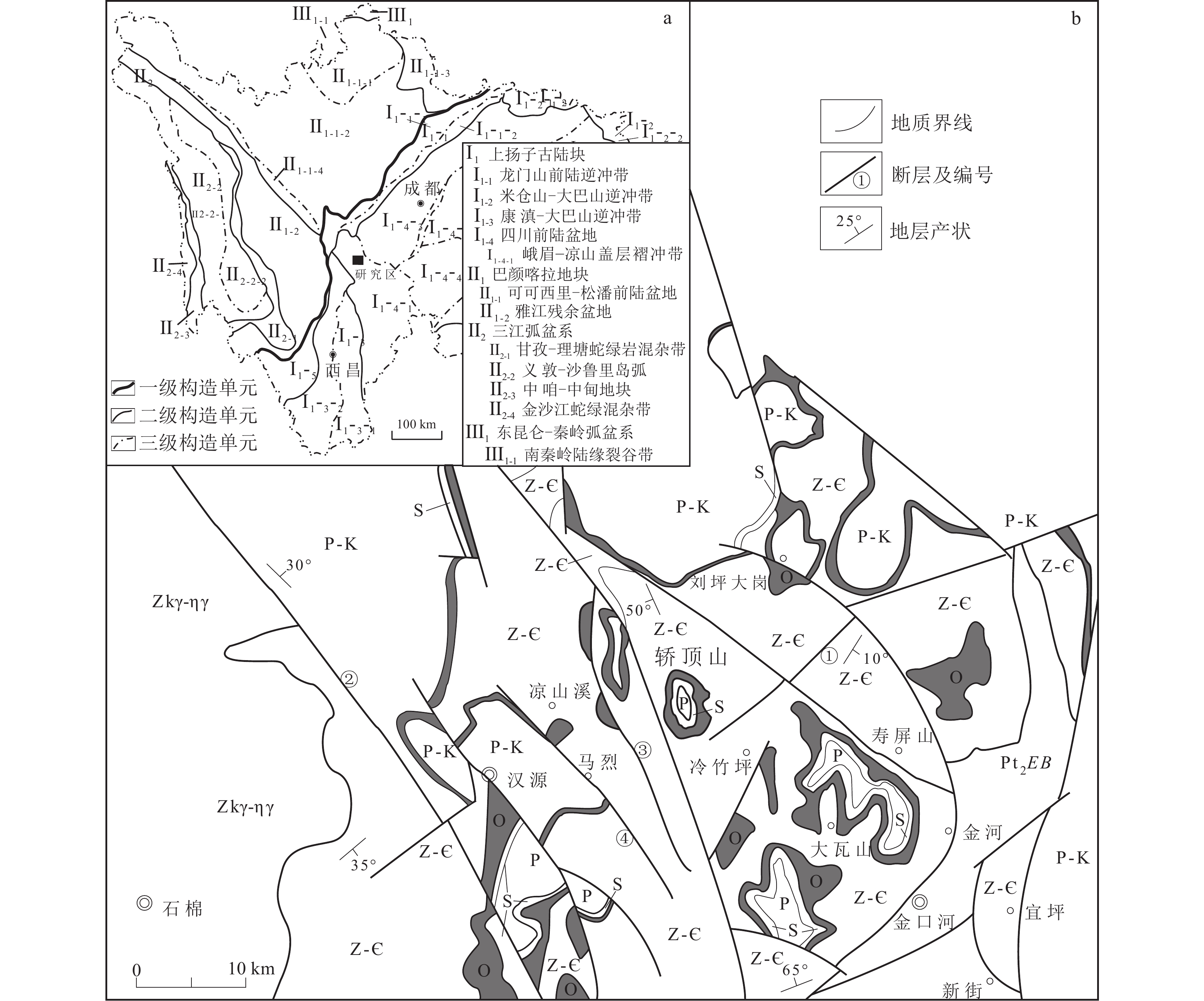
研究区位于松辽盆地东南隆起区(图1)。松辽盆地形成于印支运动末期—燕山运动早期,经历了多期构造运动,盆地内部划分出西部斜坡区、北部倾没区、东北隆起区、中央坳陷区、东南隆起区和西南隆起区6个一级构造单元(张利,2020)。
东南隆起区位于盆地边部,自西向东分为次一级背斜、向斜构造,主要有登娄库背斜、哈拉海向斜、农安背斜、德惠向斜、青山口背斜、杨大城子背斜;主要发育中、新生代地层,自下而上依次为白垩系火石岭组、沙河子组、营城组、登娄库组、泉头组、青山口组、姚家组、嫩江组,新近系大安组及第四系(高立新,2008;李宝毅等,2012;李翔等,2014),油页岩主要存在于白垩系青山口组一段和嫩江组一段、二段,油页岩矿层单层厚度较薄,与沉积岩地层呈互层关系。
1.2 地层电性特征
根据研究区及周缘物性资料分析,第四系为表层高阻层,古近系—新近系大安组−青山口组为低阻层,泉头组−登楼库组为中阻层,营城组−火石岭层为次高阻层,局部发育火山岩为高阻,石炭系—二叠系为基底高阻层(表1)。地层电性特征分析表明,白垩系嫩江组、青山口组电阻率整体呈现低阻特征。
表 1 研究区及周缘地区岩层电性特征Table 1. The electrical characteristics of rock strata in the study area and surrounding areas系 统 组 符号 岩性特征 ρ/(Ω·m) 电性 第四系 Q 粘土、亚粘土、砂砾石 37.9 表层高阻 古近系—新近系 大安组 Nd 泥岩、粉砂质泥岩、泥质粉砂岩 3.2 低阻层 白垩系 上统 嫩江组 K2n 砂砾岩、粉砂岩、细砂岩、泥质粉砂岩、粉砂质泥岩、泥岩、油页岩 3.9 姚家组 K2y 泥岩、粉砂质泥岩、泥质粉砂岩、粉砂岩 6.8 青山口组 K2qs 质粉砂岩、粉砂岩、粉砂质泥岩、油页岩 22.8 下统 泉头组 K1q 粉砂质泥岩、泥岩、粉砂岩、泥质粉砂岩、细砂岩、砂岩 28.2 中阻层 登楼库组 K1d 砂砾岩夹泥岩 71.5 营城组 K1yc 泥岩与火山岩间互夹煤层 211.7 次高阻层 沙河子组 K1sh 火山岩、砂泥岩夹煤线 220.0 火石岭组 K1h 火山碎屑岩、火山喷发岩 240.0 石炭系—二叠系 293.0 基底高阻 1.3 油页岩物性特征
油页岩含丰富的有机质,有机质具有低密度、高电阻率特征,在含油页岩的沉积地层中,油页岩层与围岩存在电阻率、密度等物性差异(Constable et al.,1987;贺君玲等,2006;王永明等,2007)。
综合分析研究区不同测井曲线发现,油页岩呈现中高电阻率、高自然伽马、高声波时差和低密度特征;泥岩呈现低电阻率、高自然伽马、高声波时差和高密度特征;粉砂岩具有中高电阻率、低自然伽马、低声波时差、低密度特征;粉砂质泥岩相对于泥岩电阻率偏高、自然伽马偏低、声波时差偏低、密度偏低;泥质粉砂岩相对于粉砂岩电阻率偏低、自然伽马偏高、声波时差偏高、密度高。油页岩与粉砂岩、粉砂质泥岩及泥质粉砂岩在电阻率和密度方面均呈现高电阻率、低密度特征,但与围岩泥岩存在明显的电阻率和密度差异(表2;图2),油页岩有机质含量越高,这种特征越明显。因此,根据不同测井曲线形态和曲线值可以判断出不同岩性,划分识别油页岩。
表 2 研究区白垩系不同岩性测井曲线响应分布范围Table 2. Logging response distribution range table of Cretaceous different lithology in the study area测井识别岩性 电阻率平均值/(Ω·m) 声波时差平均值/(μs·m−1) 补偿密度平均值/(g·cm−3) 自然伽马平均值/API 粉砂岩 10 ~ 13 250 ~ 430 2.15 ~ 2.62 50 ~ 115 泥质粉砂岩 6.5 ~ 17.5 240 ~ 450 2.20 ~ 2.50 75 ~ 140 粉砂质泥岩 5.5 ~ 12 275 ~ 500 2.25 ~ 2.55 90 ~ 135 泥岩 5 ~ 9 330 ~ 450 2.25 ~ 2.50 110 ~ 150 油页岩 7.5 ~ 15 ≥375 ≤2.35 ≥130 2. 勘探方法
2.1 方法原理
CSAMT法全称是可控源音频大地电磁测深法,属于人工源频率域电磁测深法,以有限长接地电偶极子为场源,其核心是采用大小随着频率改变的音频电流来建立人工电磁场,激发地下空间产生电磁感应,当电磁场变为谐变场时通过改变电磁场的频率来达到测深目的,采集电磁场参数,求取视电阻率、阻抗相位等电磁响应数据,具有工作效率高、勘探深度范围大、水平方向分辨能力高、地形影响小、高阻层的屏蔽作用小等特点。
2.2 数据采集与处理
研究区CSAMT测线均过钻井(图1),测线总长80 km,点距100 m,采用美国Zonge公司生产的GDP-3224多功能电法仪,发电输出功率30 kW。数据采用赤道偶极装置进行标量测量,发射偶极AB与测线平行布设,长度为1 ~ 2 km,接收偶极100 m,发射源接地电阻要求20 ~ 40 Ω,接收端接地电阻不大于2000 Ω;同时观测与场源平行的电场水平分量Ex和与场源正交的磁场水平分量Hy,采集频率范围为 0.125 ~ 8192 Hz。
数据处理采用人机交互的方式进行,包括去噪、静态校正、近场校正、视电阻率、相位拟断面分析等。近场校正采用过渡三角形法,消除卡尼亚电阻率在近区由于非平面波效应产生的畸变,采用空间滤波、中值滤波、曲线平移等方法进行静态位移综合校正。图3为SL-01线视电阻率和阻抗相位断面图,视电阻率、阻抗相位等值线连续光滑,噪声、近场效应及静位移影响得到较好的压制,断面图上电性层由高频到低频呈现高、低、次低、高的变化特征。
2.3 约束反演技术
常规二维正则化OCCAM反演方法是一种由电磁测深数据产生光滑模型的实用算法,体现了正则化反演优点,在保证电性分布连续或光滑的条件下,寻求有极小可能构造意义下拟合数据的模型(Constable et al.,1987),该方法收敛稳定,对初始模型依赖度低,成像效果好,被广泛应用于电磁数据处理中。研究区存在人文干扰,受干扰的数据不能真实反映地下电性结构,对地质解释的可靠性存在影响,同时可控源音频大地电磁反演存在多解性、非唯一性的问题,为此在二维正则化OCCAM反演的基础上,将研究区测井信息融入到可控源音频大地电磁资料的反演处理中,减少反演结果的非唯一性,提高成果解释的精度和合理性(孟翠贤,2003;张凯飞,2016)。二维OCCAM地电约束反演主要包括地电模型建立、反演算法与正则化因子、模型粗糙度及迭代误差分析。
(1)地电模型建立
对研究区可控源音频大地电磁测线周边测井资料进行处理分析,根据不同物性特征对钻孔处地层进行划分,重点对嫩江组和青山口组油页岩及附近地层进行划分,建立可控源音频大地电磁资料处理所需要的电阻率分布先验地电模型,数据反演过程中加入先验地电信息开展约束反演。表3、表4为SL-03线先验约束信息。
表 3 吉扶地3井油页岩及附近地层约束信息Table 3. Constraint information of oil shale and nearby strata in Well Jifudi 3序号 顶部深度/m 底部深度/m 厚度/m 电阻率/(Ω·m) 岩性 序号 顶部深度/m 底部深度/m 厚度/m 电阻率/(Ω·m) 岩性 1 258.2 268.6 10.4 9.19 泥岩 15 469.8 476.9 7.1 6.23 泥岩 2 268.6 281.4 12.8 10.70 粉砂质泥岩 16 476.9 478.0 1.1 6.99 油页岩 3 281.4 289.0 7.6 9.55 泥岩 17 478.0 483.2 5.2 5.70 泥岩 4 289.0 294.1 5.1 12.90 粉砂质泥岩 18 483.2 484.1 0.9 6.27 油页岩 5 294.1 298.3 4.2 9.44 泥岩 19 484.1 487.3 3.2 6.22 泥岩 6 298.3 306.6 8.3 11.61 粉砂质泥岩 20 487.3 489.5 2.2 8.38 粉砂质泥岩 7 306.6 312.4 5.8 9.55 泥岩 21 489.5 494.2 4.7 6.06 油页岩 8 312.4 341.0 28.6 10.92 粉砂质泥岩 22 494.2 503.2 9.0 5.25 泥岩 9 341.0 382.3 41.3 6.49 泥岩 23 503.2 507.1 3.9 12.73 油页岩 10 382.3 383.2 0.9 6.45 油页岩 24 507.1 514.0 6.9 7.19 泥岩 11 383.2 462.2 79.0 5.95 泥岩 25 514.0 519.3 5.3 11.22 油页岩 12 462.2 463.4 1.2 7.19 油页岩 26 519.3 523.1 3.8 5.91 泥岩 13 463.4 468.0 4.6 6.10 泥岩 27 523.1 524.0 0.9 10.72 油页岩 14 468.0 469.8 1.8 7.65 油页岩 28 524.0 528.7 4.7 8.34 粉砂质泥岩 表 4 吉扶地8井油页岩及附近地层约束信息Table 4. Constraint information of oil shale and nearby strata in Well Jifudi 8序号 顶部深度/m 底部深度/m 厚度/m 电阻率/(Ω·m) 岩性 序号 顶部深度/m 底部深度/m 厚度/m 电阻率/(Ω·m) 岩性 1 258.2 268.6 10.4 9.19 泥岩 15 469.8 476.9 7.1 6.23 泥岩 2 268.6 281.4 12.8 10.70 粉砂质泥岩 16 476.9 478.0 1.1 6.99 油页岩 3 281.4 289.0 7.6 9.55 泥岩 17 478.0 483.2 5.2 5.70 泥岩 4 289.0 294.1 5.1 12.90 粉砂质泥岩 18 483.2 484.1 0.9 6.27 油页岩 5 294.1 298.3 4.2 9.44 泥岩 19 484.1 487.3 3.2 6.22 泥岩 6 298.3 306.6 8.3 11.61 粉砂质泥岩 20 487.3 489.5 2.2 8.38 粉砂质泥岩 7 306.6 312.4 5.8 9.55 泥岩 21 489.5 494.2 4.7 6.06 油页岩 8 312.4 341.0 28.6 10.92 粉砂质泥岩 22 494.2 503.2 9.0 5.25 泥岩 9 341.0 382.3 41.3 6.49 泥岩 23 503.2 507.1 3.9 12.73 油页岩 10 382.3 383.2 0.9 6.45 油页岩 24 507.1 514.0 6.9 7.19 泥岩 11 383.2 462.2 79.0 5.95 泥岩 25 514.0 519.3 5.3 11.22 油页岩 12 462.2 463.4 1.2 7.19 油页岩 26 519.3 523.1 3.8 5.91 泥岩 13 463.4 468.0 4.6 6.10 泥岩 27 523.1 524.0 0.9 10.72 油页岩 14 468.0 469.8 1.8 7.65 油页岩 28 524.0 528.7 4.7 8.34 粉砂质泥岩 (2)反演算法
二维Occam地电约束反演重点是对目标函数中的模型粗糙度进行修改,推导出修改后目标函数的迭代格式,形成以地电参数作为先验信息的约束反演算法。反演过程中在目标函数中加入利用测井等资料建立的先验地电模型,在已知电性分布区域修正模型,不断地向先验地电模型靠拢,提高反演结果与实测数据的拟合度。具体流程如下:
① 建立可控源音频大地电磁反演目标函数,在目标函数模型粗糙度中加入模型约束项。
U=‖ (1) 式中, {\left\|{\partial }_{y}m\right\|}^{2}+{\left\|{\partial }_{z}m\right\|}^{2} 为模型粗糙度,μ为拉格朗日乘子,即正则化因子, W 为归一化计算后 M\times M 的对角加权矩阵, F(m) 模型为 m 在一定的激发作用下正演后取得的响应,X*2为反演拟合差。
② 根据已知钻孔及测井数据建立初始模型,构造二维粗糙度矩阵:
{R}_{1}=\alpha {\left\|C(m-{m}_{0})\right\|}^{2}+{\left\|{\partial }_{y}m\right\|}^{2}+{\left\|{\partial }_{z}m\right\|}^{2} (2) 式中, \alpha {\left\|C(m-{m}_{0})\right\|}^{2} 为先验模型的约束项, \alpha 为权重系数, {m}_{0} 为先验模型, m 为迭代过程中当前模型, C 为约束矩阵。
③ 根据约束后的目标函数,计算推导迭代格式,开展反演迭代计算。
\begin{split} &{m}_{k+1}\left(\mu \right)={\left[\alpha \mu {C}^{T}+\mu \left({\partial }_{x}^{T}{\partial }_{x}+{\partial }_{z}^{T}{\partial }_{z}\right)+ {\left(W{J}_{k}\right)}^{T}W{J}_{k}\right]}^{-1}.\\ &\qquad \left[{\left(W{J}_{k}\right)}^{T}W{d}_{k}+\alpha \mu {C}^{T}C{m}_{0}\right]\\[-1pt]\end{split} (3) 式中 ,{J}_{k} 为雅可比矩阵, {d}_{k}=d-F\left[{m}_{k}\right]+{J}_{k}{m}_{k} ,拉格朗日乘子μ为待求值。
④ 求取模型 {m}_{k+1}\left(\mu \right) 的一系列μ值,根据 \mu 值计算模型 {m}_{k+1}\left(\mu \right) 拟合差,选取数据残差平方最小的 \mu 值。
(3)正则化因子、模型粗糙度及迭代误差分析
本次约束反演正则化因子初始值为1000,模型粗糙度随正则化因子增大呈现波动变化,当正则化因子增大到一定值时,逐步变小,最后趋于稳定(图4)。经过15次迭代计算,二维地电约束反演结果趋近稳定,图5为SL-01线约束前后迭代反演曲线误差对比图,拟合差分别为0.77和0.78,拟合初期约束反演拟合误差比常规反演拟合误差大,拟合后期常规反演提前趋于稳定。
3. 效果分析
(1)常规二维OCCAM反演能够反映出规模较大的异常体,但是对于规模较小的异常体分辨能力不足,由SL-01线二维OCCAM反演与二维OCCAM约束反演剖面对比图(图6)可以看出,二维OCCAM地电约束反演剖面纵向上地层电性变化特征清楚,横向分辨率也有很大的提高,能够明显提高对异常体的分辨率,地电信息更丰富,较好地反映了研究区地层平缓、构造幅度小、岩石物性横向变化大的地质特征,油页岩与泥岩作为整体得到较好反映。
(2)以二维OCCAM地电约束反演剖面为主,结合测井、以往物探地质资料进行综合解释,可以对油页岩与泥页整体进行有效识别。图7为SL-01线二维地电约束反演及地质解释剖面,二维地电约束反演剖面纵向上呈现高—低—中—次高—高变化特征,电性结构变化与电测井曲线吻合较好。表层高阻层反映了第四系沉积地层分布与厚度变化特征,电阻率值为15 ~ 55 Ω·m,厚度10 ~ 50 m;中浅部低阻层主要反映了白垩系嫩江组、姚家组及青山口组的分布,电阻率值为3 ~ 12 Ω·m,厚度180 ~ 750 m,局部存在相对高阻异常,与电测井曲线上粉砂质泥岩、泥质粉砂岩、粉砂岩、油页岩和泥岩互层基本对应;下部中阻层代表白垩系泉头组,电阻率值为6 ~ 17 Ω·m,厚度50 ~ 100 m;下部次高阻层代表白垩系火石岭组—登楼库组,电阻率值为7 ~ 22 Ω·m,厚度400 ~ 1000 m;底部分布的高阻层代表了变质岩或侵入体基底,顶面最大埋深范围大于1000 m。利用电测井曲线及分层数据,结合约束反演剖面电阻率变化特征,将中浅部低阻层进一步划分为嫩江组、姚家组和青山口组,在嫩江组、青山口组划分的基础上,油页岩与泥岩整体作为相对高阻层可划分识别。
(3)通过研究区采集的可控源音频电磁测线地电约束反演及综合解释,对研究区地层、构造及油页岩矿层展布特征获得了整体认识:① 研究区横跨登楼库背斜和哈拉海向斜2个构造,背斜核部地层以白垩系泉头组、青山口组为主,翼部为姚家组、嫩江组,向斜核部地层以白垩系嫩江组为主,翼部为姚家组、青山口组。以登楼库背斜轴为界,两翼地层倾角均为1° ~ 6°,核部近水平,呈宽缓的背斜构造,整体控制白垩系的分布,影响油页岩矿层的空间展布。②登楼库背斜地层较哈拉海向斜整体抬升,导致研究区背斜所在区域的嫩江组基本缺失,嫩江组油页岩主要分布在哈拉海向斜,仅在背斜西部局部沉积,油页岩与泥岩互层厚度为25 ~ 100 m,埋深50 ~ 250 m。青山口组油页岩分布范围广,登楼库背斜、哈拉海向斜均有分布,油页岩与泥岩互层厚度为30 ~ 200 m,埋深400 ~ 800 m,整体呈沿登楼库背斜轴高、沿背斜轴两翼逐渐减薄的特征。
4. 结 论
(1)可控源音频大地电磁和测井联合约束反演技术能够提高对异常体的分辨率,油页岩与泥岩互层作为整体只要具有一定的规模,利用可控源音频大地电磁和测井联合约束反演技术就可以划分识别。
(2)油页岩单层厚度薄,单一地球物理方法划分识别油页岩存在很大的局限性,基于测井综合曲线分析技术的地球物理方法是油页岩勘探方法发展的方向。
(3)油页岩与砂岩、粉砂岩和粉砂质泥岩均呈现相对高电阻率特征,区分困难,可以开展可控源音频电磁法、时频电磁法等多种方法试验,利用电阻率、极化率等多参数综合分析研究。
-
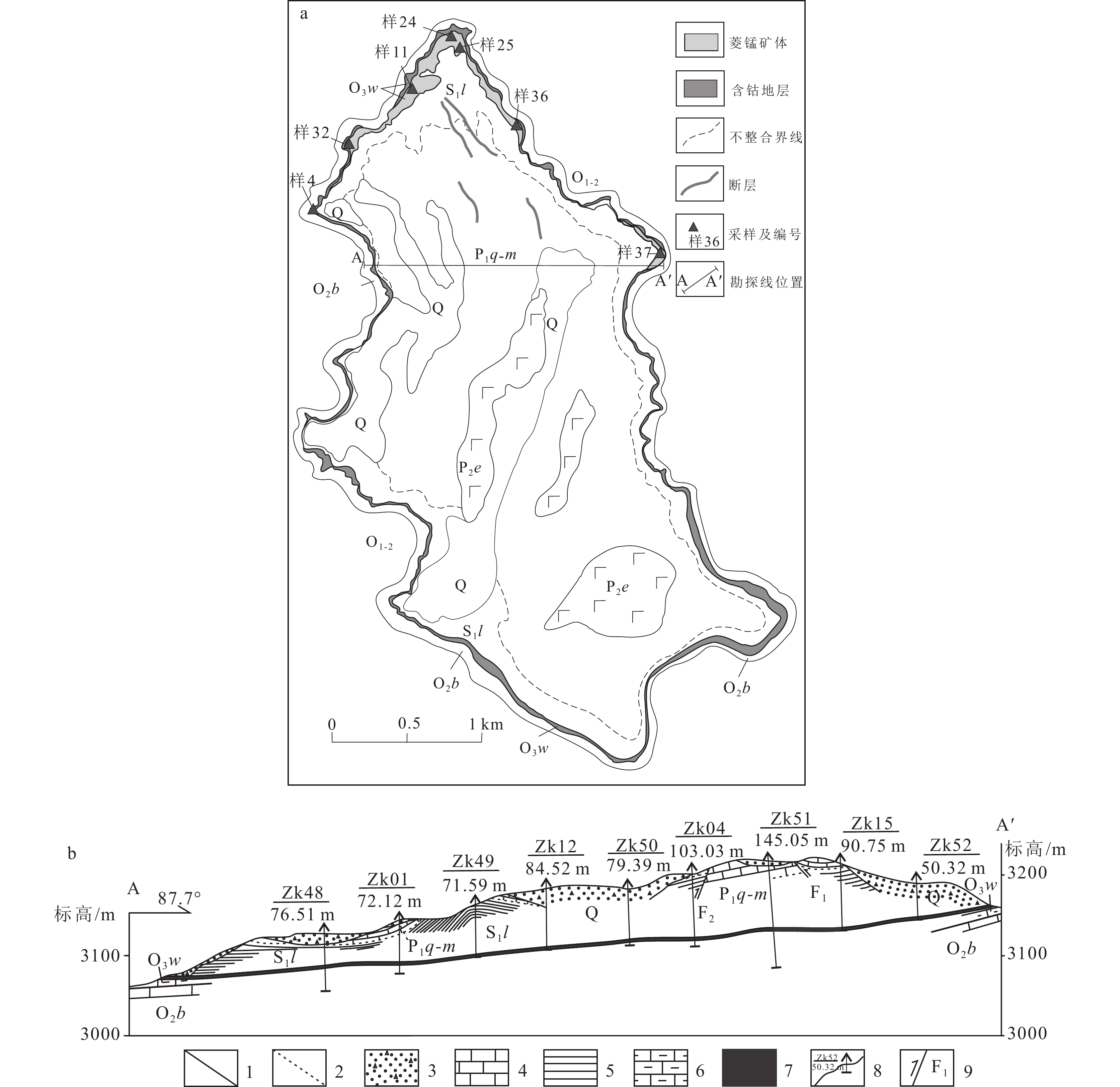
图 2 轿顶山钴矿床地质简图(a)和6号勘探线线剖面(b)
1—地质界线;2—不整合界线;3—浮土;4—灰岩;5—页岩;6—泥灰岩;7—锰钴矿体;8—钻孔机编号及孔深;9—断层及编号;Q—第四系;P2e—峨眉山玄武岩;P1q—下二叠统栖霞组;P1q-m—下二叠统栖霞组 + 茅口组;S1l—下志留统龙马溪组;O3w—上奥陶统五峰组;O2b—中奥陶统宝塔组
Figure 2. A geological sketch map (a) and No.6 geological section along exploratory line (b) of the Jiaodingshan Co deposit
图 6 轿顶山钴矿床中黄铁矿Ni−Co 图解(不同地质环境边界的定义据 Bajwah et al., 1987; Brill, 1989)
Figure 6. Ni−Co diagram for pyrites from Jiaodingshan cobalt deposit
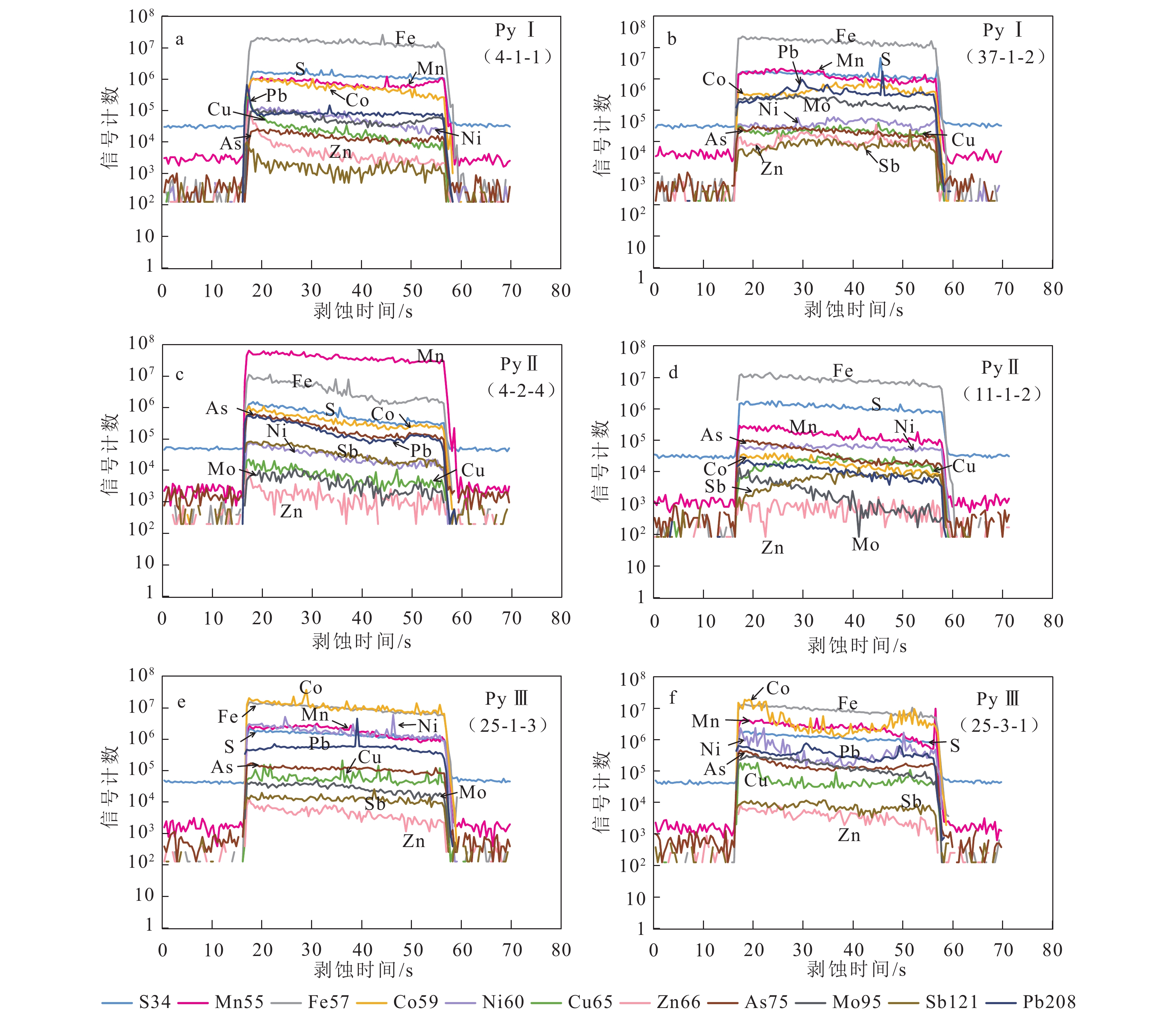
表 1 轿顶山钴矿床中黄铁矿微量元素分析结果
Table 1 Major and trace element analysis for pyrite from Jiaodingshan cobalt deposits
10−6 测试
点号样品
分类Co Ni Mn Cu Pb Zn Mo Sb As Se Te Tl Ba Cr Ti Sr Fe S Ag Au Co/Ni 25-4-1 PyⅠ-a 37.6 48.5 102.1 2.1 7.8 21.4 7.4 173.1 1162.7 0.8 0.1 3.8 11.6 0.5 9.9 2.6 510538.0 480491.3 0.0 0.0 0.8 4-1-1 145.9 680.3 36.4 143.4 7 12.2 10.4 11.2 225.7 0.6 0.1 12.4 0 0 2.6 0 498386 500318 0 0 0.2 4-1-2 293.1 1407 796 51 2.8 15.7 42 25.5 490.3 1.6 0 17.5 1.2 1.1 6.6 0.1 487055.4 508995.2 0.3 0 0.2 4-2-1 84.3 79.6 3318.7 48.3 2.1 14.1 7.6 14 140.8 0 0 12.2 0.1 0.1 7.3 0.1 499110.8 499801.3 0 0 1.1 4-2-2 41.8 38.6 60.8 1.1 7.9 26.9 10.9 87.8 819 0 0 1.5 0.5 33 0.3 0 511976.5 486825.9 0 0 1.1 4-2-3 62.8 68 743.1 3.4 19.2 44.1 8.1 122.8 1035.5 0 0 1.8 2 66.6 1.5 1 501070.7 495431.8 0 0 0.9 32-1-1 PyⅠ-b 60.2 464.8 210 16.8 6.6 15.6 278.7 98.2 355.6 0.1 0.2 2.8 7.5 0.3 0.6 10.2 500683.8 498914.8 0 0 0.1 32-1-2 37.2 493 229.3 2.1 0.9 8.6 70 13 37.4 0.9 0.1 1 0.4 0.3 0.3 0 496111.7 502492.6 0 0 0.1 32-1-3 176.3 199.6 153.5 14.5 11.8 19 295 91.4 807.8 1.2 0.4 3.2 9.8 1.5 4.3 3.2 496446.4 490436.1 0 0 0.9 32-1-4 348.7 663.1 234.9 113.6 180.6 2.6 0 91.1 34.9 1.7 0 194.1 5.4 0.8 1 3.1 538891.3 459341.9 0 0 0.5 32-4-3 225 997.5 18 18.9 4.3 7.2 76.2 10.9 649.7 3.2 0.1 4.1 4.4 0 5.3 0.9 498605.6 494173.1 0 0 0.2 32-4-4 33.7 308.2 11.5 371.6 43 21.8 0.4 71.6 53.9 0 0.1 6.8 19.1 115.9 2.6 5.1 484800.3 511250.6 0.1 0 0.1 4-6-1 6 8.8 80.3 6.6 66.6 21 27.4 47.2 2492 5 0 5.7 3.6 0 0.4 0.2 491000.8 506399 0.4 0 0.7 4-6-2 35.7 48.6 906.4 20.8 5.5 5 0 4.9 2.1 0.4 0 16.9 1.1 0.4 31.9 0.3 501249.4 496051.4 0 0 0.7 4-6-3 34.1 38.8 643.9 39.6 3.3 2 0 2 4.7 0.2 0.1 29.4 10.2 8.5 14.9 1.6 488879.5 504899.9 0.7 0 0.9 24-2-1 PyⅠ-c 86.1 78.6 816.6 360.6 319.2 26.4 32.7 29.6 234.6 3.4 3.2 11.6 4.1 0.4 1.5 4.2 535551.3 456069.5 3.3 0 1.1 36-4-4 103.9 515.9 10479.2 152.8 263.6 42.8 24 19.3 188.5 2.6 2.3 12.5 19 0.7 1.4 21.2 529972.5 461529.9 3.7 0 0.2 37-1-1 47.7 1240.8 28.6 162.9 249 50.9 13.5 15 189.7 1.8 1.4 4 2.2 0.4 0.6 4.2 528626.4 466949.1 0.1 0 0 37-1-2 36.5 233.4 2.7 220.2 706.5 2.1 0.1 65.3 23.8 0.8 0.1 91 2.3 0.7 38.7 0.2 529100.9 464039 0.1 0 0.2 11-1-2 PyⅡ-a 1426.4 1222.3 2511.8 116.9 17.7 31.8 148.6 0.3 74.1 0.6 0 1.1 0.2 0.4 69.7 0.1 518346.2 472749.1 4 0.1 1.2 11-2-1 1665.3 2152.8 5153.8 42.4 152.4 70.2 5.3 15.1 200.5 88.7 0.3 0.4 0.8 0 27.3 1.5 525837.6 472398.4 0.6 0 0.8 11-2-2 1228.2 1541.5 4968.6 76.1 217.5 22.6 23.5 14.6 102.9 1.2 1.6 3.1 1.4 0.5 12.2 4.5 511749.9 468869 17.7 0.2 0.8 11-3-1 706.1 805.3 5605.1 90.7 328.4 19 24.1 14.8 118.1 2.2 1 3.5 2.5 0 16.4 19.4 513564.7 477721.9 4.4 0 0.9 11-3-2 3168.5 2905 4897.7 54 290 2.9 0 36.4 106.2 35 0.2 0.2 0.1 0.2 241.3 0.4 470840.2 523082.3 0.1 0 1.1 11-3-3 525.2 693.7 5900.2 174.1 292.1 21.2 22.4 30.7 174.8 2.9 1.6 4.8 1.9 1.4 7 6.7 515775.2 470119.7 5.7 0.1 0.8 32-4-2 406.6 457.2 66.5 220.5 447 26.6 24.9 43.6 193.4 4.4 1.4 5.3 5.9 7.2 2.7 17.8 527139.7 459305.8 3.9 0.1 0.9 4-1-3 574.4 2254.5 9 89.9 281.8 36.9 20.9 25.3 187.1 2.7 0.4 3.7 1.5 0.3 3.4 2.5 523868.5 465509.8 4.2 0.1 0.3 4-2-5 707.2 379.5 18035.2 492.9 1237.2 41.7 14 40.7 166.8 7 20.2 53.1 6.7 2 66.7 13.1 517590.9 468341.3 4.9 0 1.9 11-1-1 PyⅡ-b 799 824.4 2954.6 150.7 211.6 36.5 113.7 17.5 133.1 2.5 0.5 5.7 4.2 833.1 32.4 29.7 507205.7 472810.2 0.9 0 1 11-1-3 779.9 846.9 2746.2 143.5 70.5 96.9 473 4.8 18.4 6.4 0.1 69.6 2.2 1.4 95.5 4.6 513090.9 475747.9 1.9 0 0.9 11-2-3 935.6 1547.9 4613.2 265.3 3425 30 36.9 28.1 225.4 4 0 31.1 623.8 0.3 10.2 56.2 477645.2 478784.3 7.6 0 0.6 11-5-1 1222.1 1304.5 3161.4 333.1 280.2 68.3 677.2 32.4 814.6 40.8 0.2 5.4 517.9 0.5 9.4 155 499377 479275.7 2.1 0 0.9 11-5-2 903.2 1327.2 4840.3 247.1 2418.2 56.2 81 46.5 405.1 6.9 0.2 14.5 127.3 0 2.2 48.6 494168.3 485255.5 7.1 0 0.7 11-5-3 1495.6 963.4 7997.7 320 280.5 104 210.9 37.6 613.1 6.6 0.4 5.9 880.2 0.7 6.3 564.6 500810.3 481794.7 2.7 0 1.6 24-1-1 462.3 197.2 2268.9 41.1 36 34 352 1.2 93.2 0 0 0.9 0.5 4.2 28.4 0.3 515725.5 482061.1 0.3 0 2.3 24-1-2 452.6 167.4 1012.5 28.6 34.6 38.2 378 1.4 104.2 0.9 0 1.1 1.1 0.3 32.6 0.4 515370.6 482188.7 0.4 0 2.7 24-1-3 555.4 270.4 587.7 112.7 160.7 78.6 408.2 9.6 41.2 3 0.1 58.2 4.7 411.3 4.7 5.9 516338.3 472389.2 1.5 0 2.1 24-2-2 214.2 129.9 993 107.5 131.1 2 0.7 79.9 62.3 0.6 0 97.5 2.8 0.8 11.1 0.4 464427 518579.2 0.2 0 1.6 24-2-3 321.9 176.4 703 108.1 12 17.2 1649.7 49.6 108 4.5 0.6 12.1 509 0.4 5.9 33 474591.6 509385.2 0.5 0 1.8 36-1-1 1461.5 1529.2 676.8 163.2 1448.7 117.3 255.8 52.5 700.8 6.5 0 6.3 561.3 1.1 24.1 153.2 499992.5 490368.3 1.7 0 1 36-4-3 3346.1 3536.3 4151.9 267.2 312.1 42.5 34.8 239.3 409.6 0.8 0.3 7.9 1245.6 0.4 8.8 103.6 483528.1 500825.2 4.1 0 0.9 4-2-4 1041.2 301.2 91445.4 331.8 1268.8 68.6 104 50.7 505.3 6.9 0.2 16.4 1462.3 3.9 150.8 499.8 473115.1 487336.7 5.1 0 3.5 25-1-1 PyⅢ 6178.8 5696.5 1960.7 1996.6 747.2 9.6 4.1 70.2 686.1 20.5 2.5 7 15.1 0.6 23.6 29.6 475018.8 470613.4 0.1 0 1.1 25-1-2 22101.9 15745.3 575 1089.4 2534.4 142.4 37.2 660 1310.1 12.6 7 36.8 1225.2 0.4 0.3 59.2 284684.1 349173.1 18 0 1.4 25-1-3 16017.6 11459.9 2122.2 808.5 1117.4 48.1 212.7 286.4 542.7 6.7 1.8 17.3 475.7 2 24.8 37.2 458582.7 523409.2 16 0.1 1.4 25-3-1 7595.2 3465.9 3301 182.9 377.5 161.8 634.9 11.8 96.9 0.1 0 3.5 8902.9 1.2 23.5 89.2 429153.6 538926.6 4.4 0.1 2.2 25-3-2 1144.6 656.9 2454.6 1540.2 846.2 10.6 4.5 48.3 813.8 15.6 2.5 6.6 51 1.3 16.7 18 444052.5 520007.4 33.3 0.2 1.7 25-3-3 5777.4 2391.2 1840.6 1766 1009.6 11 4.9 43.4 980.7 25.1 3.7 7.4 43.7 2.2 43.6 45.7 357317.2 371491.8 0.1 0 2.4 32-5-1 11284.3 3825.9 428.9 59.3 167.4 27.7 24.4 84.9 1874.3 1.6 0.9 3 42.8 0.6 20.1 91.9 421676.4 548614.1 3.7 0.1 2.9 32-5-2 9865 3852.3 393.3 2131.5 3164.1 84.4 79 824.8 1580.1 22.8 3.4 33.9 415.9 3.2 12.2 37.7 401941.7 557653.4 4.4 0.1 2.6 32-5-3 13116.8 4677.8 794.7 2162 997 12.4 4.9 54 967 16.3 2.5 8.2 46.6 0.8 15.5 12.7 524068.9 473604.1 0.7 0 2.8 32-5-4 12031.5 4158.8 447.8 68.1 336.8 12.6 10.8 145.4 2073.3 0 0.6 2.2 25.5 1.7 5.6 26.1 523301.1 462226 1.4 0 2.9 36-1-2 12293.7 6126.2 2223.2 70 36.2 45.8 143.3 1.7 63.3 0.2 0 6 0.1 116.5 13.1 0.2 526019.2 470265.5 1.2 0 2 36-4-1 8035 7198.2 1470.1 77.4 159.8 134.4 527.9 10.1 95.1 0.3 0 5.3 36.3 89.4 1010.9 1.2 438047 535648.9 3.5 0.1 1.1 -
Brill B A. 1989. Trance element contents and partitioning of elements inore minerals from the CSA Cu−Pb−Zn deposit , Aust ralia[J]. Can. Mineral., 27: 263−274.
Belousov I, Large R R, Meffre S, et al. 2016. Pyrite compositions from VHMS and orogenic Au deposits in the Yilgarn Craton, Western Australia: Implications for gold and copper exploration[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 79: 474−499. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2016.04.020
Bajwah Z U , Seccombe P K, Offler R. 1987. Trace element distribution, Co/Ni ratios and genesis of the Big Cadia iron copper deposit, New South wales, Australia[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 22: 292−303.
Craig J R, Vokes F M, Solberg T N. 1998. Pyrite: Physical and chemical textures. Mineralium Deposita, 34(1): 82–101.
Cook N J, Ciobanu C L, Mao J W. 2009. Textural control on gold distribution in As−free pyrite from the Dongping, Huangtuliang and Hougou gold deposits, North China raton (Hebei Province, China)[J]. Chemical Geology, 264(1/2/3/4): 101−121.
Hawley J E, Niehol L. 1961. Trace elements in pyrite, pyrrhotite and chalcopyrite of different ores[J]. Economic Geology, 56: 467−487. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.56.3.467
Keith M, Häckel F, Haase K M, et al. 2016. Trace element systematics of pyrite from submarine hydrothermal vents [J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 72(11): 728–745.
Koglin N, Frimmel H E, Minter W E L, et al. 2009. Trace−element characteristics of different pyrite types in Mesoarchaean to Palaeoproterozoic placer deposits[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 45(3): 259−280.
Large R R, Maslennikow V V, Robert F, et a1. 2007. Multistage sedimentary and metamorphic origin of pyrite and gold in the Giant Sukhoi Log Deposit, Lena gold province, Russia[J]. Economic Geology, 102: 1233−1267. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.102.7.1233
Palenik C S, Utsunomiya S, Reich M, et al. 2004. “Invisible” gold revealed: direct imaging of gold nanoparticles in a Carlin−type deposit[J]. American Mineralogist, 89(10): 1359−1366. doi: 10.2138/am-2004-1002
Springer G, Schachner−Korn D, Long J V P. 1964. Metastable solid solution relations in the system FeS2−CoS2−NiS2[J]. Economic Geology, 59: 475−491. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.59.3.475
白志强. 2015. 川西南地区五峰组−龙马溪组页岩特征研究[D]. 成都理工大学硕士学位论文. 陈多福, 陈先沛, 陈光谦, 等. 1997. 热水沉积作用与成矿效应[J]. 地质地球化学, (4): 7−12. 段士刚, 董满华, 张作衡, 等. 2014. 西天山敦德. 铁矿床磁铁矿原位LA−ICP−MS 元素分析及意义[J]. 矿床地质, 33(6): 1325−1337. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2014.06.011 丰成友, 张德全, 党兴彦. 2004. 中国钴资源及其开发利用概况[J]. 矿床地质, 23(1): 94−100. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2004.01.011 冷成彪. 2017. 滇西北红山铜多金属矿床的成因类型: 黄铁矿和磁黄铁矿LA−ICPMS 微量元素制约[J]. 地学前缘, 24(6): 162−175. 李红兵, 曾凡治. 2005. 金矿中的黄铁矿标型特征[J]. 地质找矿论丛, 21(3): 199−203. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1412.2005.03.011 梅建明. 2000. 浙江遂昌治岭头金矿床黄铁矿的化学成分标型研究[J]. 现代地质, 14(1): 51−55. 牟传龙, 葛祥英, 余谦, 等. 2019. 川西南地区五峰−龙马溪组黑色页岩古气候及物源特征: 来自新地2井地球化学记录[J]. 古地理学报, 21(5): 835−854. 曲红军. 1988. 轿顶山式锰矿岩相古地理特征及成矿规律探讨[J]. 地质与勘探, (11): 7−13. 盛继福, 李岩, 范书义. 1999. 大兴安岭中段铜多金属矿床矿物微量元素研究[J]. 矿床地质, 18(2): 57−64. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.1999.02.007 宋学信, 张景凯. 1986. 中国各种成因黄铁矿的微量元素特征[J]. 中国地质科学院矿床地质研究所所刊, 2: 166−175. 苏桂萍, 李忠权, 应丹琳, 等. 2020. 四川盆地加里东古隆起形成演化及动力学成因机理[J], 地质学报, 94(6): 1794−1811. 汤庆艳, 张铭杰, 余明, 等. 2013. 晚二叠世峨眉山地幔柱岩浆成矿作用[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 32(5): 681−692. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2013.05.010 徐国风, 邵洁涟. 1980. 黄铁矿的标型特征及其实际意义[J]. 地质论评, 26(6): 541−546. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.1980.06.017 徐志刚, 陈毓川, 王登红, 等. 2008. 中国成矿区代划分方案[M]. 北京: 地质出版社. 严育通, 李胜荣, 贾宝剑, 等. 2012. 中国不同成因类型金矿床的黄铁矿成分标型特征及统计分析[J]. 地学前缘, 19(4): 214−226. 叶甜, 李诺. 2015. 黄铁矿原位LA−ICP−MS 微量元素分析在金矿床中应用[J]. 地质科学, 50(4): 1178−1199. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0563-5020.2015.04.010 曾云, 贺金良, 王秀京, 等. 2015. 四川省成矿区带划分及区域成矿规律[M]. 北京: 地质出版社. 张靖宇, 陆永潮, 付孝悦, 等. 2017. 四川盆地涪陵地区五峰组−龙马溪组一段层序格架与沉积演化[J]. 地质科技情报, 36(4): 66−72. 赵俊兴, 李光明, 秦克章, 等. 2013. 富含钴矿床研究进展与问题分析[J]. 科学通报, 64(24): 2484−2500. 周涛发, 张乐骏, 袁峰, 等. 2010. 安徽铜陵新桥Cu−Au−S 矿床黄铁矿微量元素LA−ICP−MS 原位测定及其对矿床成因的制约[J]. 地学前缘, 17(2): 306−319. -
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 徐大兴,邵兆刚,陈宣华,张进江,徐盛林,李冰,张义平,余苇,邓文兵,丁奕文. 贺兰山构造带深部电性结构与动力学机制. 地质通报. 2024(11): 1921-1936 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(0)




 下载:
下载: