Zircon U–Pb age, Hf isotope composition, and their constraints on tectonic setting of the Saima alkaling complex in the eastern Liaoning Province
-
摘要:
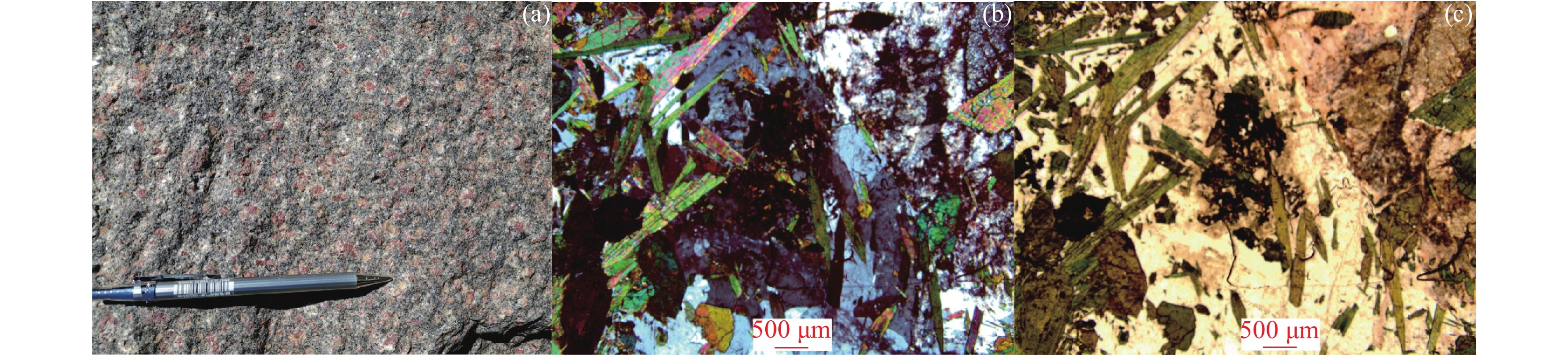
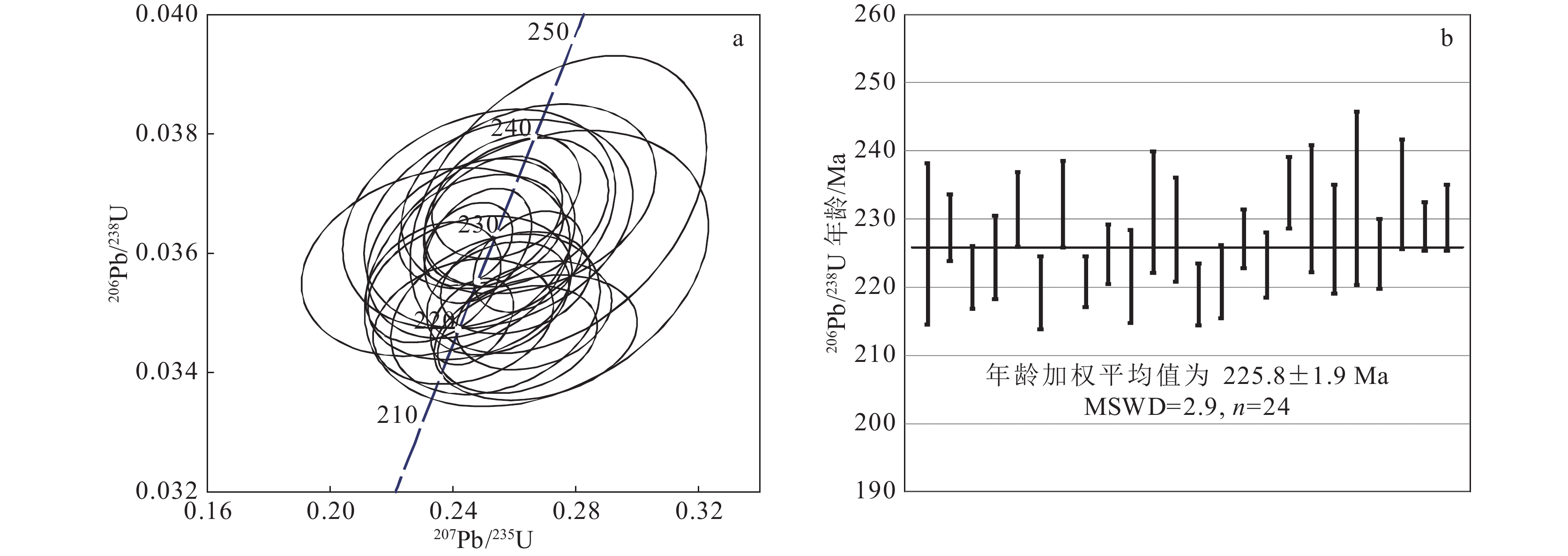
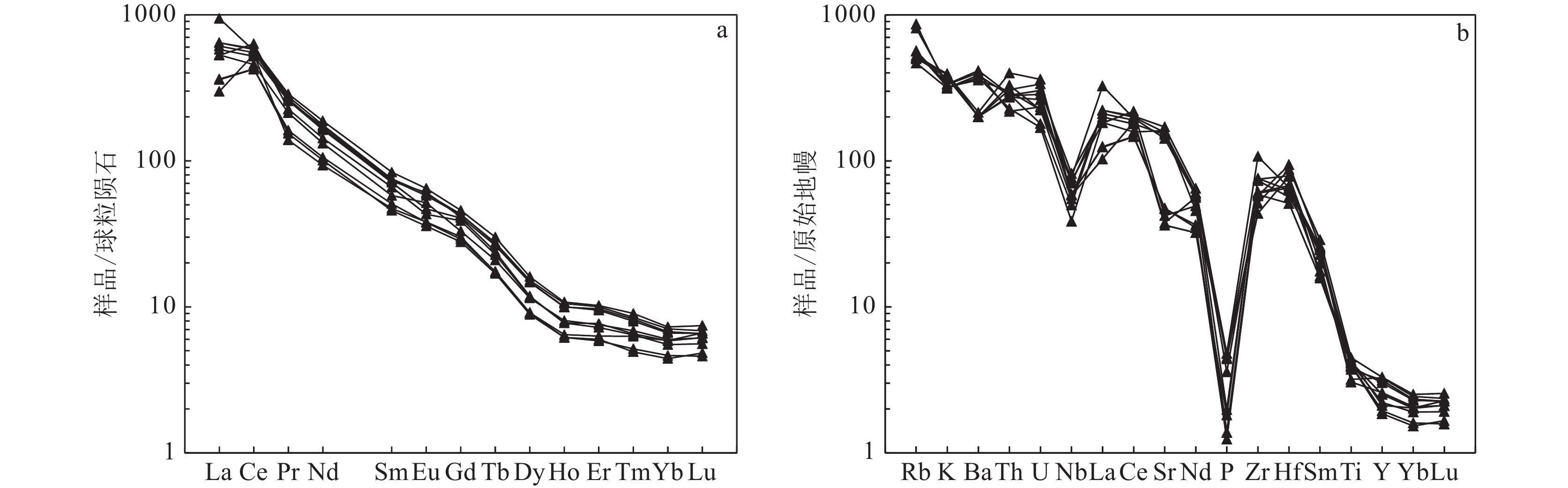
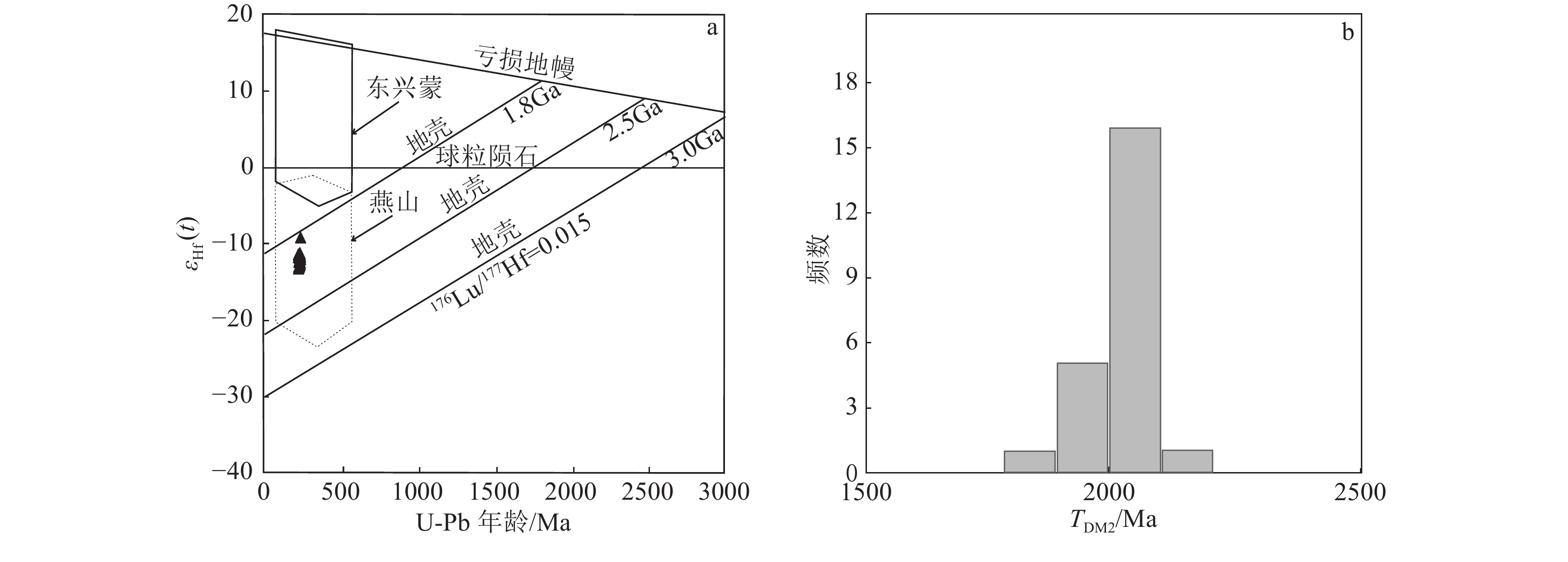
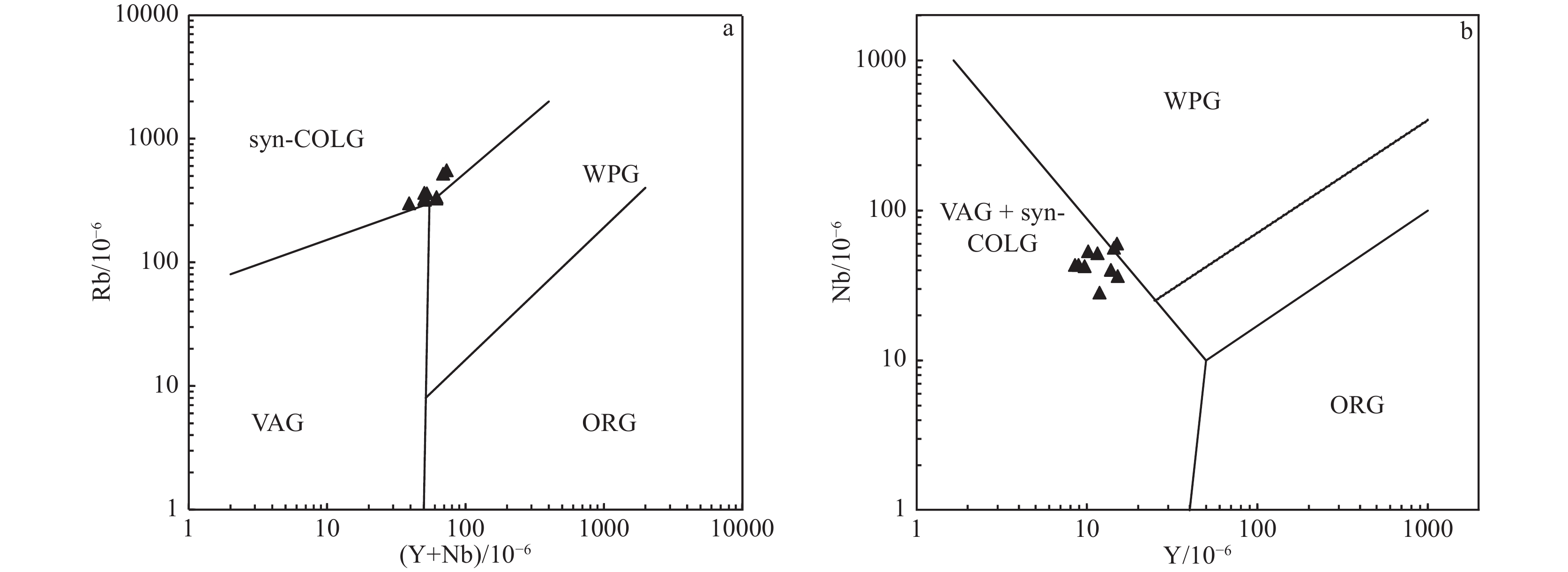
通过LA-ICP-MS测得辽宁赛马地区浅肉红色霞霓正长岩中的锆石U-Pb年龄为225.8±1.9 Ma,赛马碱性杂岩的侵位时代为晚三叠世。地球化学分析表明,霞霓正长岩SiO2含量为55.87% ~ 60.88%,Na2O为0.41% ~ 5.32%,Al2O3为17.81% ~ 19.53%,K2O为9.46% ~ 11.91%,MgO为0.46% ~ 1.36%,里特曼指数为7.54 ~ 17.01;稀土元素总量较高,高于300×10−6,强烈富集轻稀土元素,(La/Yb)N值大于10,个别达到100以上;亏损Nb、Ta、P等高场强元素,富集Rb、Th等大离子亲石元素,总体表现出富碱性岩石特征。锆石εHf(t)值为−13.37 ~ −9.30,对应的两阶段Hf模式年龄TDM2为2102 ~ 1855 Ma。通过岩石成因分析和构造环境判别,赛马碱性杂岩可能形成于由俯冲挤压向陆内伸展、拉张转换的动力背景下的下地壳(或上地幔)部分熔融。赛马碱性杂岩侵位时代(225.8±1.9 Ma)可能代表了华北克拉通北缘岩石圈开始伸展减薄的时间,也是郯庐断裂形成的时间。
-
关键词:
- LA-ICP-MS U-Pb年龄 /
- Hf同位素组成 /
- 晚三叠世 /
- 赛马碱性杂岩 /
- 辽东地区
Abstract:The light-red aegirine nepheline syenite in Liaoning Saima area has a LA-ICP-MS U-Pb age of 225.8 ± 1.9 Ma, and the emplacement age of the Saima alkaline complex is the Late Triassic. Aegirine nepheline syenite shows SiO2 of 55.87%~60.88%, Na2O of 0.41%~5.32%, Al2O3 of 17.81%~19.53%, K2O of 9.46%~11.91%, MgO of 0.46%~1.36%, σ43 of 7.54~17.01.The total amount of rare earth elements is higher than 300×10−6, and it is strongly enriched with light rare earth elements. Depletion of high field strength elements such as Nb, Ta, P, and enrichment of large ion lithophilic elements such as Rb, Th, shows the characteristics of alkaline rich rocks. The zircon εHf (t) value is −13.37 ~ −9.30, the corresponding two-stage Hf model age TDM2 is 2102~1855 Ma. The Saima alkaline complex may be formed by the partial melting of the lower crust (or upper mantle) under the dynamic background of subduction-squeezing to inland extension and extension conversion. The age of emplacement (225.8 ± 1.9 Ma) may represent the time when the lithosphere began to stretch and thin on the northern margin of the North China Craton, and also the time when the Tanlu fault was formed.
-
油页岩属于非常规油气资源,利用蒸馏等技术处理后能够获得页岩气及页岩油,是一种前景非常好的油气资源,被列为21世纪非常重要的接替能源(侯祥麟,1994;赵政璋等,2005;刘招君等,2006;王红岩等,2009)。中国油页岩资源丰富,资源潜力大,其中松辽盆地是油页岩资源极丰富的地区,占东北地区油页岩资源总量的96%(刘招君等,2009)。松辽盆地是一个大型陆相薄互层沉积盆地,岩石物性横向变化大,地层平缓且构造幅度小,油页岩单层厚度薄,这种复杂的沉积结构增加了地震勘探的难度(李桂林,2009)。大地电磁法由于天然场源的随机性及信号微弱精度和效率较低,电阻率法则存在探测深度浅、高阻层屏蔽等缺点。测井技术在识别和评价油页岩方面较成熟(丰莉等,2016;刘同庆,2020),已被广泛应用于油页岩矿区,但是由于其空间探测范围的局限性,存在横向范围内描述储层物性变化能力很弱的缺陷。
测井具有较高的纵向地层分辨率,将测井数据作为先验信息进行电磁法约束反演,可以提高反演结果的纵向分辨率。朱宇启等(2021)在南黄海中部隆起区对海洋CSEM实测数据进行测井约束反演,突出了垂向发生明显变化的层位。Brown et al.(2012)发现,利用测井数据进行正则化约束反演比常规反演结果更紧凑地估计了储层结构。余年等(2012)利用测井数据作为先验信息开展大地电磁约束反演,与常规反演结果相比,约束反演结果对岩溶、断层、褶皱等地质构造的反映与实际吻合更好。自20世纪80年代以来,可控源音频大地电磁法和仪器都得到了很大发展,具有设备轻便、勘探深度相对较大、不受高阻层屏蔽、横向分辨率高等特点(何梅兴,2006;余年等,2012),在勘探石油、天然气、金属矿床、地热等领域得到广泛应用(秦伟,2013;李致君等,2018;李英宾等,2019)。地球物理方法和测井技术在联合研究油页岩储层特征方面几乎还是空白,本文通过松辽盆地采集的可控源音频大地电磁数据,利用测井资料作为先验信息,开展可控源音频大地电磁法和测井联合约束反演技术应用研究,将油页岩与泥页岩互层整体作为相对高阻层,进行划分识别,取得较好的效果,初步查明研究区油页岩的展布特征,为进一步勘探工作指明了有利方向。
1. 地质地球物理背景
1.1 地质条件
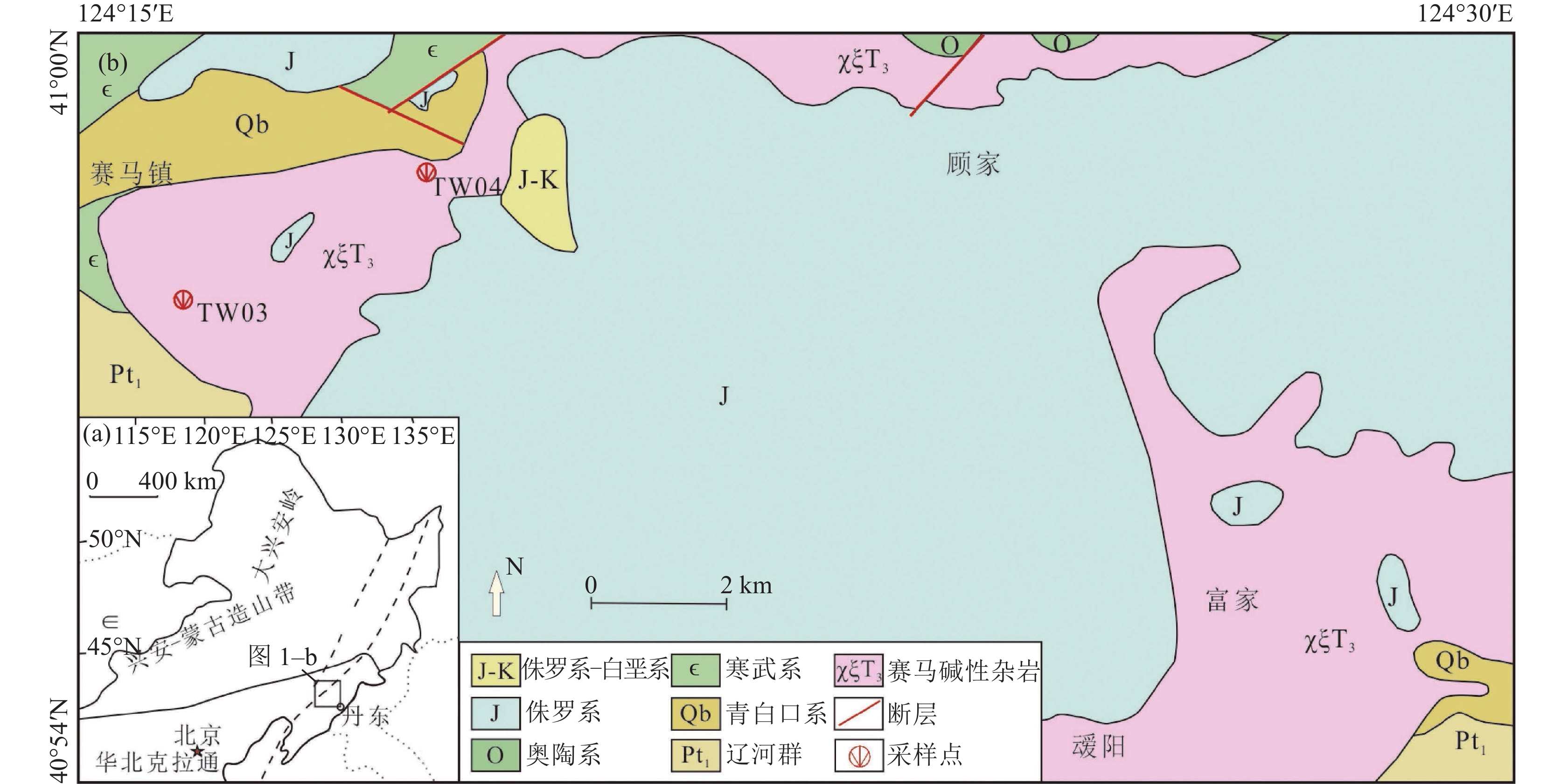
研究区位于松辽盆地东南隆起区(图1)。松辽盆地形成于印支运动末期—燕山运动早期,经历了多期构造运动,盆地内部划分出西部斜坡区、北部倾没区、东北隆起区、中央坳陷区、东南隆起区和西南隆起区6个一级构造单元(张利,2020)。
东南隆起区位于盆地边部,自西向东分为次一级背斜、向斜构造,主要有登娄库背斜、哈拉海向斜、农安背斜、德惠向斜、青山口背斜、杨大城子背斜;主要发育中、新生代地层,自下而上依次为白垩系火石岭组、沙河子组、营城组、登娄库组、泉头组、青山口组、姚家组、嫩江组,新近系大安组及第四系(高立新,2008;李宝毅等,2012;李翔等,2014),油页岩主要存在于白垩系青山口组一段和嫩江组一段、二段,油页岩矿层单层厚度较薄,与沉积岩地层呈互层关系。
1.2 地层电性特征
根据研究区及周缘物性资料分析,第四系为表层高阻层,古近系—新近系大安组−青山口组为低阻层,泉头组−登楼库组为中阻层,营城组−火石岭层为次高阻层,局部发育火山岩为高阻,石炭系—二叠系为基底高阻层(表1)。地层电性特征分析表明,白垩系嫩江组、青山口组电阻率整体呈现低阻特征。
表 1 研究区及周缘地区岩层电性特征Table 1. The electrical characteristics of rock strata in the study area and surrounding areas系 统 组 符号 岩性特征 ρ/(Ω·m) 电性 第四系 Q 粘土、亚粘土、砂砾石 37.9 表层高阻 古近系—新近系 大安组 Nd 泥岩、粉砂质泥岩、泥质粉砂岩 3.2 低阻层 白垩系 上统 嫩江组 K2n 砂砾岩、粉砂岩、细砂岩、泥质粉砂岩、粉砂质泥岩、泥岩、油页岩 3.9 姚家组 K2y 泥岩、粉砂质泥岩、泥质粉砂岩、粉砂岩 6.8 青山口组 K2qs 质粉砂岩、粉砂岩、粉砂质泥岩、油页岩 22.8 下统 泉头组 K1q 粉砂质泥岩、泥岩、粉砂岩、泥质粉砂岩、细砂岩、砂岩 28.2 中阻层 登楼库组 K1d 砂砾岩夹泥岩 71.5 营城组 K1yc 泥岩与火山岩间互夹煤层 211.7 次高阻层 沙河子组 K1sh 火山岩、砂泥岩夹煤线 220.0 火石岭组 K1h 火山碎屑岩、火山喷发岩 240.0 石炭系—二叠系 293.0 基底高阻 1.3 油页岩物性特征
油页岩含丰富的有机质,有机质具有低密度、高电阻率特征,在含油页岩的沉积地层中,油页岩层与围岩存在电阻率、密度等物性差异(Constable et al.,1987;贺君玲等,2006;王永明等,2007)。
综合分析研究区不同测井曲线发现,油页岩呈现中高电阻率、高自然伽马、高声波时差和低密度特征;泥岩呈现低电阻率、高自然伽马、高声波时差和高密度特征;粉砂岩具有中高电阻率、低自然伽马、低声波时差、低密度特征;粉砂质泥岩相对于泥岩电阻率偏高、自然伽马偏低、声波时差偏低、密度偏低;泥质粉砂岩相对于粉砂岩电阻率偏低、自然伽马偏高、声波时差偏高、密度高。油页岩与粉砂岩、粉砂质泥岩及泥质粉砂岩在电阻率和密度方面均呈现高电阻率、低密度特征,但与围岩泥岩存在明显的电阻率和密度差异(表2;图2),油页岩有机质含量越高,这种特征越明显。因此,根据不同测井曲线形态和曲线值可以判断出不同岩性,划分识别油页岩。
表 2 研究区白垩系不同岩性测井曲线响应分布范围Table 2. Logging response distribution range table of Cretaceous different lithology in the study area测井识别岩性 电阻率平均值/(Ω·m) 声波时差平均值/(μs·m−1) 补偿密度平均值/(g·cm−3) 自然伽马平均值/API 粉砂岩 10 ~ 13 250 ~ 430 2.15 ~ 2.62 50 ~ 115 泥质粉砂岩 6.5 ~ 17.5 240 ~ 450 2.20 ~ 2.50 75 ~ 140 粉砂质泥岩 5.5 ~ 12 275 ~ 500 2.25 ~ 2.55 90 ~ 135 泥岩 5 ~ 9 330 ~ 450 2.25 ~ 2.50 110 ~ 150 油页岩 7.5 ~ 15 ≥375 ≤2.35 ≥130 2. 勘探方法
2.1 方法原理
CSAMT法全称是可控源音频大地电磁测深法,属于人工源频率域电磁测深法,以有限长接地电偶极子为场源,其核心是采用大小随着频率改变的音频电流来建立人工电磁场,激发地下空间产生电磁感应,当电磁场变为谐变场时通过改变电磁场的频率来达到测深目的,采集电磁场参数,求取视电阻率、阻抗相位等电磁响应数据,具有工作效率高、勘探深度范围大、水平方向分辨能力高、地形影响小、高阻层的屏蔽作用小等特点。
2.2 数据采集与处理
研究区CSAMT测线均过钻井(图1),测线总长80 km,点距100 m,采用美国Zonge公司生产的GDP-3224多功能电法仪,发电输出功率30 kW。数据采用赤道偶极装置进行标量测量,发射偶极AB与测线平行布设,长度为1 ~ 2 km,接收偶极100 m,发射源接地电阻要求20 ~ 40 Ω,接收端接地电阻不大于2000 Ω;同时观测与场源平行的电场水平分量Ex和与场源正交的磁场水平分量Hy,采集频率范围为 0.125 ~ 8192 Hz。
数据处理采用人机交互的方式进行,包括去噪、静态校正、近场校正、视电阻率、相位拟断面分析等。近场校正采用过渡三角形法,消除卡尼亚电阻率在近区由于非平面波效应产生的畸变,采用空间滤波、中值滤波、曲线平移等方法进行静态位移综合校正。图3为SL-01线视电阻率和阻抗相位断面图,视电阻率、阻抗相位等值线连续光滑,噪声、近场效应及静位移影响得到较好的压制,断面图上电性层由高频到低频呈现高、低、次低、高的变化特征。
2.3 约束反演技术
常规二维正则化OCCAM反演方法是一种由电磁测深数据产生光滑模型的实用算法,体现了正则化反演优点,在保证电性分布连续或光滑的条件下,寻求有极小可能构造意义下拟合数据的模型(Constable et al.,1987),该方法收敛稳定,对初始模型依赖度低,成像效果好,被广泛应用于电磁数据处理中。研究区存在人文干扰,受干扰的数据不能真实反映地下电性结构,对地质解释的可靠性存在影响,同时可控源音频大地电磁反演存在多解性、非唯一性的问题,为此在二维正则化OCCAM反演的基础上,将研究区测井信息融入到可控源音频大地电磁资料的反演处理中,减少反演结果的非唯一性,提高成果解释的精度和合理性(孟翠贤,2003;张凯飞,2016)。二维OCCAM地电约束反演主要包括地电模型建立、反演算法与正则化因子、模型粗糙度及迭代误差分析。
(1)地电模型建立
对研究区可控源音频大地电磁测线周边测井资料进行处理分析,根据不同物性特征对钻孔处地层进行划分,重点对嫩江组和青山口组油页岩及附近地层进行划分,建立可控源音频大地电磁资料处理所需要的电阻率分布先验地电模型,数据反演过程中加入先验地电信息开展约束反演。表3、表4为SL-03线先验约束信息。
表 3 吉扶地3井油页岩及附近地层约束信息Table 3. Constraint information of oil shale and nearby strata in Well Jifudi 3序号 顶部深度/m 底部深度/m 厚度/m 电阻率/(Ω·m) 岩性 序号 顶部深度/m 底部深度/m 厚度/m 电阻率/(Ω·m) 岩性 1 258.2 268.6 10.4 9.19 泥岩 15 469.8 476.9 7.1 6.23 泥岩 2 268.6 281.4 12.8 10.70 粉砂质泥岩 16 476.9 478.0 1.1 6.99 油页岩 3 281.4 289.0 7.6 9.55 泥岩 17 478.0 483.2 5.2 5.70 泥岩 4 289.0 294.1 5.1 12.90 粉砂质泥岩 18 483.2 484.1 0.9 6.27 油页岩 5 294.1 298.3 4.2 9.44 泥岩 19 484.1 487.3 3.2 6.22 泥岩 6 298.3 306.6 8.3 11.61 粉砂质泥岩 20 487.3 489.5 2.2 8.38 粉砂质泥岩 7 306.6 312.4 5.8 9.55 泥岩 21 489.5 494.2 4.7 6.06 油页岩 8 312.4 341.0 28.6 10.92 粉砂质泥岩 22 494.2 503.2 9.0 5.25 泥岩 9 341.0 382.3 41.3 6.49 泥岩 23 503.2 507.1 3.9 12.73 油页岩 10 382.3 383.2 0.9 6.45 油页岩 24 507.1 514.0 6.9 7.19 泥岩 11 383.2 462.2 79.0 5.95 泥岩 25 514.0 519.3 5.3 11.22 油页岩 12 462.2 463.4 1.2 7.19 油页岩 26 519.3 523.1 3.8 5.91 泥岩 13 463.4 468.0 4.6 6.10 泥岩 27 523.1 524.0 0.9 10.72 油页岩 14 468.0 469.8 1.8 7.65 油页岩 28 524.0 528.7 4.7 8.34 粉砂质泥岩 表 4 吉扶地8井油页岩及附近地层约束信息Table 4. Constraint information of oil shale and nearby strata in Well Jifudi 8序号 顶部深度/m 底部深度/m 厚度/m 电阻率/(Ω·m) 岩性 序号 顶部深度/m 底部深度/m 厚度/m 电阻率/(Ω·m) 岩性 1 258.2 268.6 10.4 9.19 泥岩 15 469.8 476.9 7.1 6.23 泥岩 2 268.6 281.4 12.8 10.70 粉砂质泥岩 16 476.9 478.0 1.1 6.99 油页岩 3 281.4 289.0 7.6 9.55 泥岩 17 478.0 483.2 5.2 5.70 泥岩 4 289.0 294.1 5.1 12.90 粉砂质泥岩 18 483.2 484.1 0.9 6.27 油页岩 5 294.1 298.3 4.2 9.44 泥岩 19 484.1 487.3 3.2 6.22 泥岩 6 298.3 306.6 8.3 11.61 粉砂质泥岩 20 487.3 489.5 2.2 8.38 粉砂质泥岩 7 306.6 312.4 5.8 9.55 泥岩 21 489.5 494.2 4.7 6.06 油页岩 8 312.4 341.0 28.6 10.92 粉砂质泥岩 22 494.2 503.2 9.0 5.25 泥岩 9 341.0 382.3 41.3 6.49 泥岩 23 503.2 507.1 3.9 12.73 油页岩 10 382.3 383.2 0.9 6.45 油页岩 24 507.1 514.0 6.9 7.19 泥岩 11 383.2 462.2 79.0 5.95 泥岩 25 514.0 519.3 5.3 11.22 油页岩 12 462.2 463.4 1.2 7.19 油页岩 26 519.3 523.1 3.8 5.91 泥岩 13 463.4 468.0 4.6 6.10 泥岩 27 523.1 524.0 0.9 10.72 油页岩 14 468.0 469.8 1.8 7.65 油页岩 28 524.0 528.7 4.7 8.34 粉砂质泥岩 (2)反演算法
二维Occam地电约束反演重点是对目标函数中的模型粗糙度进行修改,推导出修改后目标函数的迭代格式,形成以地电参数作为先验信息的约束反演算法。反演过程中在目标函数中加入利用测井等资料建立的先验地电模型,在已知电性分布区域修正模型,不断地向先验地电模型靠拢,提高反演结果与实测数据的拟合度。具体流程如下:
① 建立可控源音频大地电磁反演目标函数,在目标函数模型粗糙度中加入模型约束项。
U=‖ (1) 式中, {\left\|{\partial }_{y}m\right\|}^{2}+{\left\|{\partial }_{z}m\right\|}^{2} 为模型粗糙度,μ为拉格朗日乘子,即正则化因子, W 为归一化计算后 M\times M 的对角加权矩阵, F(m) 模型为 m 在一定的激发作用下正演后取得的响应,X*2为反演拟合差。
② 根据已知钻孔及测井数据建立初始模型,构造二维粗糙度矩阵:
{R}_{1}=\alpha {\left\|C(m-{m}_{0})\right\|}^{2}+{\left\|{\partial }_{y}m\right\|}^{2}+{\left\|{\partial }_{z}m\right\|}^{2} (2) 式中, \alpha {\left\|C(m-{m}_{0})\right\|}^{2} 为先验模型的约束项, \alpha 为权重系数, {m}_{0} 为先验模型, m 为迭代过程中当前模型, C 为约束矩阵。
③ 根据约束后的目标函数,计算推导迭代格式,开展反演迭代计算。
\begin{split} &{m}_{k+1}\left(\mu \right)={\left[\alpha \mu {C}^{T}+\mu \left({\partial }_{x}^{T}{\partial }_{x}+{\partial }_{z}^{T}{\partial }_{z}\right)+ {\left(W{J}_{k}\right)}^{T}W{J}_{k}\right]}^{-1}.\\ &\qquad \left[{\left(W{J}_{k}\right)}^{T}W{d}_{k}+\alpha \mu {C}^{T}C{m}_{0}\right]\\[-1pt]\end{split} (3) 式中 ,{J}_{k} 为雅可比矩阵, {d}_{k}=d-F\left[{m}_{k}\right]+{J}_{k}{m}_{k} ,拉格朗日乘子μ为待求值。
④ 求取模型 {m}_{k+1}\left(\mu \right) 的一系列μ值,根据 \mu 值计算模型 {m}_{k+1}\left(\mu \right) 拟合差,选取数据残差平方最小的 \mu 值。
(3)正则化因子、模型粗糙度及迭代误差分析
本次约束反演正则化因子初始值为1000,模型粗糙度随正则化因子增大呈现波动变化,当正则化因子增大到一定值时,逐步变小,最后趋于稳定(图4)。经过15次迭代计算,二维地电约束反演结果趋近稳定,图5为SL-01线约束前后迭代反演曲线误差对比图,拟合差分别为0.77和0.78,拟合初期约束反演拟合误差比常规反演拟合误差大,拟合后期常规反演提前趋于稳定。
3. 效果分析
(1)常规二维OCCAM反演能够反映出规模较大的异常体,但是对于规模较小的异常体分辨能力不足,由SL-01线二维OCCAM反演与二维OCCAM约束反演剖面对比图(图6)可以看出,二维OCCAM地电约束反演剖面纵向上地层电性变化特征清楚,横向分辨率也有很大的提高,能够明显提高对异常体的分辨率,地电信息更丰富,较好地反映了研究区地层平缓、构造幅度小、岩石物性横向变化大的地质特征,油页岩与泥岩作为整体得到较好反映。
(2)以二维OCCAM地电约束反演剖面为主,结合测井、以往物探地质资料进行综合解释,可以对油页岩与泥页整体进行有效识别。图7为SL-01线二维地电约束反演及地质解释剖面,二维地电约束反演剖面纵向上呈现高—低—中—次高—高变化特征,电性结构变化与电测井曲线吻合较好。表层高阻层反映了第四系沉积地层分布与厚度变化特征,电阻率值为15 ~ 55 Ω·m,厚度10 ~ 50 m;中浅部低阻层主要反映了白垩系嫩江组、姚家组及青山口组的分布,电阻率值为3 ~ 12 Ω·m,厚度180 ~ 750 m,局部存在相对高阻异常,与电测井曲线上粉砂质泥岩、泥质粉砂岩、粉砂岩、油页岩和泥岩互层基本对应;下部中阻层代表白垩系泉头组,电阻率值为6 ~ 17 Ω·m,厚度50 ~ 100 m;下部次高阻层代表白垩系火石岭组—登楼库组,电阻率值为7 ~ 22 Ω·m,厚度400 ~ 1000 m;底部分布的高阻层代表了变质岩或侵入体基底,顶面最大埋深范围大于1000 m。利用电测井曲线及分层数据,结合约束反演剖面电阻率变化特征,将中浅部低阻层进一步划分为嫩江组、姚家组和青山口组,在嫩江组、青山口组划分的基础上,油页岩与泥岩整体作为相对高阻层可划分识别。
(3)通过研究区采集的可控源音频电磁测线地电约束反演及综合解释,对研究区地层、构造及油页岩矿层展布特征获得了整体认识:① 研究区横跨登楼库背斜和哈拉海向斜2个构造,背斜核部地层以白垩系泉头组、青山口组为主,翼部为姚家组、嫩江组,向斜核部地层以白垩系嫩江组为主,翼部为姚家组、青山口组。以登楼库背斜轴为界,两翼地层倾角均为1° ~ 6°,核部近水平,呈宽缓的背斜构造,整体控制白垩系的分布,影响油页岩矿层的空间展布。②登楼库背斜地层较哈拉海向斜整体抬升,导致研究区背斜所在区域的嫩江组基本缺失,嫩江组油页岩主要分布在哈拉海向斜,仅在背斜西部局部沉积,油页岩与泥岩互层厚度为25 ~ 100 m,埋深50 ~ 250 m。青山口组油页岩分布范围广,登楼库背斜、哈拉海向斜均有分布,油页岩与泥岩互层厚度为30 ~ 200 m,埋深400 ~ 800 m,整体呈沿登楼库背斜轴高、沿背斜轴两翼逐渐减薄的特征。
4. 结 论
(1)可控源音频大地电磁和测井联合约束反演技术能够提高对异常体的分辨率,油页岩与泥岩互层作为整体只要具有一定的规模,利用可控源音频大地电磁和测井联合约束反演技术就可以划分识别。
(2)油页岩单层厚度薄,单一地球物理方法划分识别油页岩存在很大的局限性,基于测井综合曲线分析技术的地球物理方法是油页岩勘探方法发展的方向。
(3)油页岩与砂岩、粉砂岩和粉砂质泥岩均呈现相对高电阻率特征,区分困难,可以开展可控源音频电磁法、时频电磁法等多种方法试验,利用电阻率、极化率等多参数综合分析研究。
-
图 5 辽东赛马地区碱性杂岩稀土元素配分曲线(a)和微量元素蛛网图(b)(标准值据Sun et al., 1989)
Figure 5. Rare earth element distribution curves (a) and trace element spider diagrams (b) for alkaline complex sampled from Saima area in the eastern Liaoning Province
图 6 辽东赛马地区霞霓正长岩锆石Lu-Hf同位素特征(底图据Yang et al.,2006)
Figure 6. Zircon Lu-Hf isotope characteristics diagram of aegirine nepheline syenite from Saima area in the eastern Liaoning Province
图 7 辽东赛马地区碱性杂岩构造环境图解(底图据Pearce et al.,1984)
WPG—板内环境;ORG—洋中脊环境;VAG—火山弧环境;syn-COLG—同碰撞环境
Figure 7. Structure environment diagram of alkaline complex from Saima area in the eastern Liaoning Province
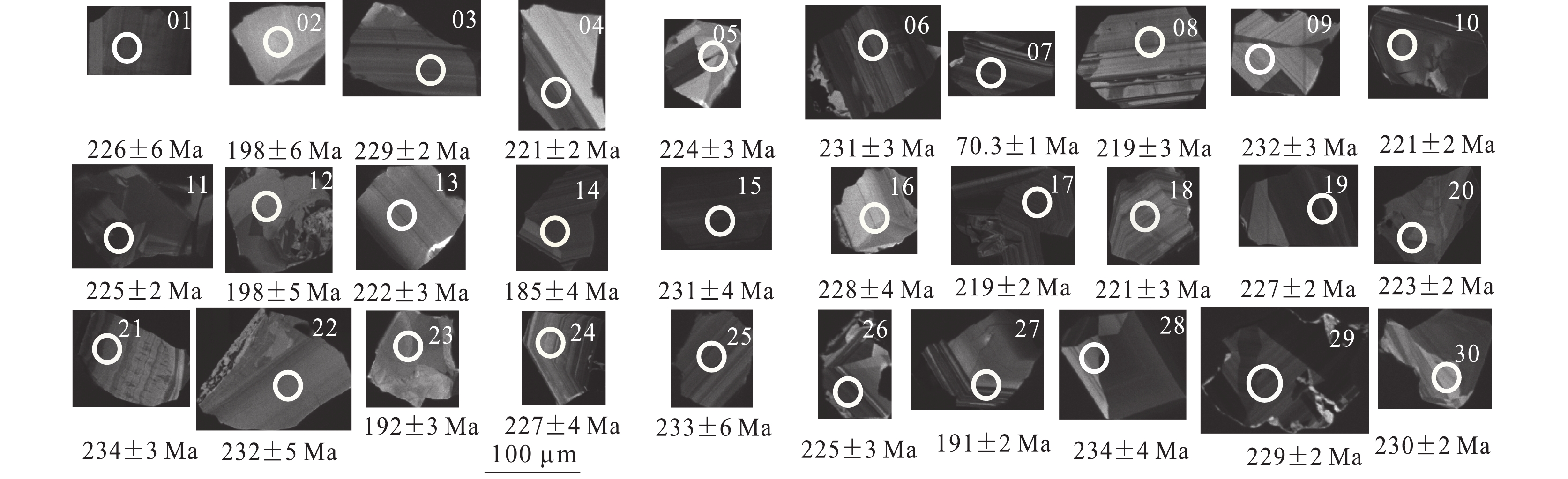
表 1 辽东赛马地区霞霓正长岩(TW04)锆石U-Th-Pb同位素数据
Table 1 The U-Th-Pb isotope compositions of zircons from aegirine nepheline syenite (TW04)from Saima area in the eastern Liaoning Province
点编号 含量/10−6 232Th/238U 207Pb*/206Pb* 1σ 206Pb*/238U 1σ 207Pb*/235U 1σ 误差 206Pb/238U 207Pb/235U 谐和度 206Pbc U Th /% /% /% 相关系数 年龄/Ma 年龄/Ma 01 0.21 21 1679 18.38 78.39 0.06 0.0068 0.04 0.0009 0.27 0.0229 0.3083 226 6 241 18 93% 02 0.22 33 218 3.65 6.61 0.08 0.0142 0.03 0.0010 0.29 0.0352 0.2616 198 6 258 28 73% 03 0.44 280 262 13.62 0.94 0.05 0.0014 0.04 0.0004 0.25 0.0072 0.3767 229 2 225 6 98% 04 0.00 150 396 10.02 2.64 0.06 0.0022 0.04 0.0004 0.27 0.0104 0.2730 221 2 240 8 92% 05 0.15 87 78 4.14 0.90 0.05 0.0029 0.04 0.0005 0.25 0.0136 0.2504 224 3 223 11 99% 06 0.00 247 194 11.66 0.78 0.05 0.0019 0.04 0.0004 0.25 0.0092 0.3273 231 3 229 7 98% 07 4.20 266 3051 36.25 11.45 0.28 0.0080 0.01 0.0002 0.43 0.0136 0.5663 70.3 1 364 10 -36% 08 0.00 116 73 5.06 0.62 0.06 0.0029 0.03 0.0004 0.27 0.0135 0.2440 219 3 240 11 90% 09 0.69 108 61 4.85 0.56 0.05 0.0027 0.04 0.0005 0.26 0.0123 0.2958 232 3 235 10 98% 10 0.03 737 217 29.94 0.29 0.05 0.0012 0.03 0.0003 0.25 0.0055 0.3791 221 2 224 4 98% 11 0.26 243 1829 27.46 7.53 0.05 0.0019 0.04 0.0003 0.26 0.0100 0.2575 225 2 235 8 95% 12 0.07 28 903 11.56 32.00 0.06 0.0059 0.03 0.0008 0.25 0.0189 0.3280 198 5 223 15 87% 13 0.08 92 347 7.54 3.79 0.05 0.0030 0.04 0.0005 0.25 0.0139 0.2852 222 3 230 11 96% 14 0.15 164 759 13.56 4.64 0.07 0.0033 0.03 0.0006 0.26 0.0098 0.5694 185 4 235 8 76% 15 0.00 44 4858 53.05 111.50 0.05 0.0035 0.04 0.0007 0.25 0.0179 0.2788 231 4 231 14 99% 16 0.18 62 37 2.79 0.60 0.05 0.0035 0.04 0.0006 0.25 0.0138 0.3036 228 4 223 11 97% 17 1.00 199 156 8.95 0.78 0.06 0.0023 0.03 0.0004 0.26 0.0106 0.2607 219 2 236 9 92% 18 0.00 134 41 5.31 0.31 0.05 0.0025 0.03 0.0004 0.24 0.0120 0.2493 221 3 221 10 99% 19 0.01 315 57 12.42 0.18 0.05 0.0015 0.04 0.0003 0.26 0.0073 0.3494 227 2 238 6 95% 20 1.34 192 40 7.55 0.21 0.05 0.0020 0.04 0.0004 0.25 0.0095 0.2934 223 2 230 8 96% 21 0.00 219 335 12.49 1.53 0.05 0.0021 0.04 0.0004 0.26 0.0099 0.2998 234 3 233 8 99% 22 0.65 29 686 9.20 23.50 0.05 0.0046 0.04 0.0007 0.25 0.0182 0.2802 232 5 225 15 97% 23 0.23 103 658 11.15 6.36 0.09 0.0059 0.03 0.0005 0.36 0.0188 0.3467 192 3 314 14 51% 24 0.63 40 258 4.45 6.49 0.05 0.0042 0.04 0.0006 0.23 0.0179 0.2356 227 4 214 15 94% 25 0.35 21 2915 31.11 135.98 0.06 0.0059 0.04 0.0010 0.27 0.0197 0.3842 233 6 246 16 94% 26 0.00 170 1372 20.78 8.09 0.05 0.0019 0.04 0.0004 0.24 0.0090 0.3030 225 3 214 7 95% 27 1.27 126 602 12.03 4.79 0.10 0.0038 0.03 0.0003 0.41 0.0147 0.3132 191 2 346 11 42% 28 0.61 64 279 5.53 4.40 0.05 0.0036 0.04 0.0006 0.26 0.0169 0.2743 234 4 238 14 97% 29 1.08 592 65 22.78 0.11 0.05 0.0011 0.04 0.0003 0.25 0.0059 0.3256 229 2 223 5 97% 30 0.28 169 98 7.50 0.58 0.05 0.0022 0.04 0.0004 0.25 0.0110 0.2436 230 2 226 9 98% 表 2 辽东赛马地区碱性杂岩主量、微量和稀土元素含量
Table 2 Major, trace and rare earth elements data for the alkaline complex from Saima area in the eastern Liaoning Province
样品号 TW03-YQ1 TW03-YQ2 TW03-YQ3 TW03-YQ4 TW03-YQ5 TW04-YQ1 TW04-YQ2 TW04-YQ3 TW04-YQ4 TW04-YQ5 SiO2 57.27 56.95 56.49 55.87 56.01 60.85 60.60 60.42 60.88 59.81 TiO2 0.81 0.66 0.84 0.97 0.69 0.86 0.91 0.86 0.89 0.94 Al2O3 19.18 18.75 18.84 18.53 19.53 18.38 18.26 17.93 18.66 17.81 Fe2O3 1.85 1.92 2.09 2.40 1.73 4.94 5.03 5.09 4.62 6.22 MnO 0.08 0.08 0.08 0.09 0.07 0.08 0.09 0.08 0.08 0.09 MgO 0.64 0.86 0.59 0.58 0.75 0.62 1.36 0.84 0.46 0.47 CaO 0.76 0.78 0.85 0.94 0.90 0.04 0.25 0.04 0.04 0.09 Na2O 4.40 4.87 5.32 5.16 4.97 0.46 0.54 0.47 0.45 0.41 K2O 10.03 9.46 9.68 10.09 9.50 11.76 11.11 11.91 11.69 11.78 P2O5 0.10 0.10 0.08 0.10 0.10 0.03 0.04 0.03 0.03 0.04 FeO 2.29 2.35 2.31 2.46 2.15 0.42 0.47 0.54 0.58 0.49 烧失量 2.08 2.67 2.42 2.28 2.58 1.24 1.34 1.13 1.37 1.52 A/CNK 0.99 0.95 0.91 0.88 0.97 1.35 1.37 1.31 1.39 1.31 σ43 13.89 13.83 15.73 17.01 14.91 8.18 7.54 8.55 8.04 8.57 总计 99.49 99.45 99.59 99.47 98.98 99.68 100 99.34 99.75 99.67 Cr 8.94 7.92 8.56 7.98 9.34 10.9 8.53 8.63 9.39 9.28 Ni 1.95 1.79 2.21 0.96 4.14 2.41 3.56 2.52 2.73 2.95 Rb 515 297 358 360 549 317 324 323 334 323 Sr 3000 3400 3300 3600 3200 1000 794 989 889 765 Zr 819 489 644 573 1200 658 850 672 683 838 Nb 54.7 27.5 39.0 35.5 58.4 42.1 50.3 42.0 51.8 41.3 Ba 2800 2600 2500 2900 2700 1400 1400 1400 1400 1500 Hf 17.5 24.2 29.1 27.0 20.2 15.8 19.4 20.1 20.9 24.4 Ta 2.13 1.53 1.64 2.23 2.40 1.85 1.95 2.31 2.45 1.85 Th 18.6 19.4 25.4 24.3 23.9 23.2 26.2 23.7 28.0 34.0 U 4.92 3.54 4.68 3.77 6.37 5.51 7.06 6.00 4.68 7.59 Li 50.8 54.6 48.9 50.7 48.6 55.0 63.6 41.5 35.1 45.2 Be 10.3 9.64 10.4 10.8 11.6 5.48 5.47 6.23 6.36 6.72 Co 6.12 6.70 6.20 6.43 5.39 7.23 7.79 5.97 5.33 8.72 V 53.0 56.6 57.1 56.5 53.5 69.9 79.0 70.7 77.3 81.1 Ga 28.4 29.4 29.2 30.9 27.5 29.3 29.9 28.8 27.0 29.2 Sc 3.19 3.01 3.16 3.06 3.59 3.37 3.39 3.30 3.54 3.40 Pb 69.9 86.6 84.0 111 77.5 103 106 119 121 124 Y 14.3 11.8 13.7 15.0 14.9 8.84 11.4 8.43 10.1 9.62 La 224 126 152 153 137 86.0 145 85.2 125 70.8 Ce 347 280 354 359 318 261 337 259 388 327 Pr 25.2 20.2 26.2 27.2 24.4 14.6 24.5 15.4 21.4 13.2 Nd 78.0 61.6 81.9 87.7 80.2 47.1 76.2 49.3 66.6 43.5 Sm 11.1 8.85 11.5 12.8 11.3 6.99 10.9 7.78 10.1 7.22 Eu 3.53 3.00 3.46 3.75 3.35 2.07 2.72 2.20 2.50 2.21 Gd 8.49 6.78 8.86 9.40 8.79 5.72 8.35 5.98 7.99 6.20 Tb 0.99 0.78 1.01 1.12 1.03 0.63 0.89 0.65 0.85 0.65 Dy 3.74 2.92 3.76 4.09 3.86 2.25 3.01 2.32 2.97 2.32 Ho 0.56 0.46 0.57 0.61 0.60 0.35 0.44 0.35 0.44 0.36 Er 1.61 1.25 1.57 1.69 1.66 0.97 1.27 0.99 1.20 1.04 Tm 0.21 0.18 0.20 0.23 0.22 0.13 0.17 0.13 0.16 0.16 Yb 1.15 1.02 1.13 1.24 1.20 0.79 1.00 0.75 0.94 1.00 Lu 0.17 0.16 0.17 0.19 0.17 0.12 0.16 0.12 0.14 0.17 ΣREE 706 513 647 661 592 428 611 430 628 476 LREE 689 499 629 643 574 418 596 419 613 464 HREE 16.91 13.54 17.27 18.57 17.53 10.97 15.28 11.29 14.69 11.90 LREE/HREE 40.73 36.86 36.44 34.62 32.75 38.08 39.02 37.13 41.74 39.01 (La/Yb)N 140 88.5 96.9 88.3 81.9 78.1 104 81.2 95.6 50.9 δEu 1.11 1.18 1.05 1.05 1.03 1.00 0.87 0.98 0.85 1.01 注:σ43为里特曼指数,σ43=[w(Na2O+K2O)]2/[w(SiO2)]−43 表 3 辽东赛马地区霞霓正长岩(TW04)锆石Hf同位素含量
Table 3 Hf isotope data of aegirine nepheline syenite (TW04) from Saima area in the eastern Liaoning Province
测点编号 年龄/Ma 176Yb/177Hf 176Lu/177Hf 176Hf/177Hf 1σ 176Hf/177Hfi εHf(0) εHf(t) TDM1 /Ma TDM2 /Ma fLu/Hf 01 226 0.053437 0.001291 0.282290 0.000013 0.282267 −17.86 −13.09 1402 2088 −0.96 03 229 0.000917 0.000021 0.282333 0.000012 0.282310 −16.34 −11.32 1297 1979 −1.00 04 221 0.001844 0.000041 0.282333 0.000013 0.282310 −16.34 −11.50 1298 1984 −1.00 05 224 0.001043 0.000023 0.282302 0.000012 0.282279 −17.43 −12.52 1340 2051 −1.00 08 219 0.001057 0.000018 0.282333 0.000019 0.282310 −16.34 −11.54 1297 1985 −1.00 09 232 0.000687 0.000016 0.282293 0.000015 0.282270 −17.75 −12.67 1352 2066 −1.00 10 221 0.003449 0.000068 0.282322 0.000016 0.282299 −16.73 −11.89 1314 2009 −1.00 11 225 0.001295 0.000030 0.282306 0.000019 0.282283 −17.29 −12.36 1335 2042 −1.00 13 222 0.000242 0.000004 0.282286 0.000013 0.282263 −18.00 −13.13 1361 2088 −1.00 15 231 0.042501 0.000941 0.282331 0.000012 0.282308 −16.41 −11.48 1332 1990 −0.97 16 228 0.000353 0.000008 0.282301 0.000012 0.282278 −17.47 −12.47 1341 2051 −1.00 17 219 0.000479 0.000010 0.282323 0.000013 0.282300 −16.69 −11.89 1311 2007 −1.00 18 221 0.000507 0.000011 0.282280 0.000017 0.282257 −18.21 −13.37 1369 2102 −1.00 19 227 0.001331 0.000032 0.282315 0.000018 0.282292 −16.97 −12.00 1322 2020 −1.00 20 223 0.000626 0.000016 0.282284 0.000015 0.282261 −18.07 −13.18 1364 2092 −1.00 21 234 0.029693 0.000765 0.282310 0.000015 0.282287 −17.15 −12.14 1355 2034 −0.98 22 232 0.035978 0.000832 0.282320 0.000012 0.282297 −16.80 −11.84 1343 2013 −0.97 24 227 0.000551 0.000012 0.282286 0.000010 0.282263 −18.00 −13.02 1361 2085 −1.00 25 233 0.144341 0.003151 0.282332 0.000015 0.282309 −16.37 −11.75 1413 2008 −0.91 26 225 0.001419 0.000023 0.282330 0.000013 0.282307 −16.44 −11.51 1302 1988 −1.00 28 234 0.001903 0.000044 0.282387 0.000014 0.282364 −14.43 −9.30 1224 1855 −1.00 29 229 0.003627 0.000085 0.282304 0.000016 0.282281 −17.36 −12.35 1339 2044 −1.00 30 230 0.000404 0.000010 0.282288 0.000012 0.282265 −17.93 −12.89 1358 2078 −1.00 注:TDM1=ln[(176Hf/177Hf样品−176Hf/177HfDM)/(176Lu/177Hf样品−176Lu/177HfDM)+1]/λ,TDM2=ln{[176Hf/177Hf样品−176Hf/177HfDM−(176Lu/177Hf样品−176Lu/177HfCrust) ×(eλt−1)] /(176Lu/177HfCrust−176Lu/177HfDM) +1}/λ -
Belousova E, Griffin W, O'Reilly S Y, et al. 2002. Igneous zircon: Trace element composition as an indicator of source rock type[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 143(5): 602−622. doi: 10.1007/s00410-002-0364-7
Green T H. 1995. Significance of Nb/Ta as an indicator of geochemical processes in the crust-mantle system[J]. Chemical Geology, 120(3/4): 347−359.
Huang X L, Wang R C, Chen X M, et al. 2002. Vertical variations in the mineralogy of the Yichun topaz lepidolite granite, Jiangxi Province, southern China[J]. Can. Miner., 40: 1047−1068. doi: 10.2113/gscanmin.40.4.1047
Kaeter D, Barros R, Menuge J F, et al. 2018. The magmatic-hydrothermal transition in rare-element pegmatites from southeast Ireland: LA-ICP-MS chemical mapping of muscoviteand columbite-tantalite[J]. Geochimet Cosmochim Acta, 240: 98−130. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2018.08.024
Linnen R L. 2014. Geochemistry of the rare-earth element, Nb, Ta, Hf, and Zr deposits[C]//Holland H D, Turekian K K. Treatise on geochemistry. Amsterdam: Elsevier Ltd., 13: 543–568.
Liu Y S, Hu Z C, Gao S, et al. 2008. In situ analysis of major and trace elements of anhydrous minerals by LA-ICP-MS without applying an internalstandard[J]. Chemical Geology, 257: 34−43. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2008.08.004
Pearce J A, Harris N B W, Tindle A G. 1984. Trace element discrimination diagrams for the tectonic interpretation of granitic rocks[J]. Journal of Petrology, 25(4): 956−983. doi: 10.1093/petrology/25.4.956
Rollison H R. 1993. Using geochemical data: Evaluation, pre-Sentation, interpretation[M]. London, Longman Group UK: 1–20.
Sun S S, McDonough, W F. 1989. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: Implications for mantle composition and processes[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 42(1): 313−345. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.1989.042.01.19
Wang R C, Hu H, Zhang A C, et al. 2004. Pollucite and the cesiumdominant analogue of polylithionite as expressions of extreme Cs enrichment in the Yichun topaz-lepidolite granite, southern China[J]. Can. Miner., 42: 883−896. doi: 10.2113/gscanmin.42.3.883
Xie L, Wang R C, Che X D, et al. 2016. Tracking magmatic and hydrothermal Nb-Ta-W -Sn fractionation using mineral textures and composition: A case study from the late Cretaceous Jiepailing ore district in the Nanling Range in South China[J]. Ore Geol. Rev., 78: 300−321. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2016.04.003
Xie L, Wang Z, Wang R, et al. 2018. Mineral ogical constraints onthe genesis of W-Nb-T a mineralization in the Laiziling granite (Xianghua ling District, South China)[J]. Ore Geol. Rev., 95: 695−712. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2018.03.021
Yang J, Wu F, Shao J, et al. 2006. Constraints on the timing of uplift of the Yanshan Fold and Thrust Belt, North China[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 246(3/4): 336−352.
Zhu Z Y, Wang R C, Che X D, et al. 2015. Magmatic-hydrothermal rare-element mineralization in the Songshugang granite (northeastern Jiangxi, China): Insights from an electron-microprobe study of Nb-Ta-Zr minerals[J]. Ore Geol. Rev., 65: 749−760. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2014.07.021
Zhu Z Y, Wang R C, Marignac C, et al. 2018. The Early Cretaceous Huangshan rare metalgranite complex, northeast Jiangxi Province, southeast China: A new style of Nb-rich rare metalgranite[J]. Am. Mineral, 65: 1−11.
常翔, 孙景贵, 陈旭, 等. 2023. 吉林省南部集安大石湖-大台子铜矿化区中生代中酸性杂岩岩石成因与地球动力学背景[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 53(3): 920−945. 高永宝, 李文渊, 钱兵, 等. 2014. 东昆仑野马泉铁矿相关花岗质岩体年代学、地球化学及Hf同位素特征[J]. 岩石学报, 30(6): 1647−1665. 景立珍, 郭裕嘉, 丁彩霞. 1995. 辽宁赛马碱性岩的年代学及碱性岩桨的形成[J]. 辽宁地质, 4: 257−271. 鞠楠, 张森, 毕中伟, 等. 2019. 辽宁凤城赛马铌矿床成矿岩体地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 世界地质, 38(1): 130−153. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5589.2019.01.012 李建康, 李鹏, 王登红, 等. 2019. 中国铌钽矿成矿规律[J]. 科学通报, 64: 1545−1566. 李梦玲, 孙珍军, 于赫楠, 等. 2022. 秦皇岛茹各庄火山碎屑岩地球化学、锆石U-Pb定年、Hf同位素组成及其地质意义[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 52(5): 1688−1706. 李石. 1992. 论碱性岩的定义和碱性花岗岩的分标[J]. 湖北地质, 6(1): 70−78. 罗晨皓, 周晔, 沈阳. 2019. 云南姚安Au-Pb-Ag矿床含矿富碱岩浆岩地球化学特征及岩石成因[J]. 地球科学, 44(6): 2063−2083. 邱家骧. 1993. 秦巴碱性岩[M]. 北京: 地质出版社: 139–141. 任康绪. 2003. 碱性岩研究进展述评[J]. 化工矿产地质, 25(3): 151−163. 宋运红, 郝立波, 杨凤超, 等. 2015. 辽东三叠纪弟兄山岩体SHRIMP U-Pb年龄、地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 地质与资源, 24(5): 444−452. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1947.2015.05.009 孙雷, 曾振, 崔维龙, 等. 2021. 黑龙江省东部晚三叠世—中侏罗世硅质岩地球化学特征及形成环境[J]. 地质与资源, 30(6): 637−645. doi: 10.13686/j.cnki.dzyzy.2021.06.001 涂光炽. 1989. 关于富碱侵入岩[J]. 矿产与地质, 13: 1−4. 邬斌, 王汝成, 郭国林, 等. 2020. 辽宁赛马碱性岩体层硅铈钛矿化学成分变化及其对碱性岩浆演化的指示意义[J]. 地球科学, 45(2): 467−478. 吴福元, 杨进辉, 柳小明. 2005. 辽东半岛中生代花岗质岩浆作用的年代学格架[J]. 高校地质学报, 11(3): 305−317. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2005.03.003 阎国翰, 牟保磊, 许保良, 等. 2002. 中国北方显生宙富碱侵入岩年代学和Nd、Pb、Sr同位素特征及其意义[J]. 地质论评, 48(增刊): 69−76. 杨凤超, 孙景贵, 宋运红, 等. 2016. 辽东连山关地区新太古代花岗杂岩SHRIMP U-Pb年龄、Hf同位素组成及地质意义[J]. 地球科学, 41(12): 2008−2018. 于喜洹, 李新鹏, 陈旭峰, 等. 2022. 大兴安岭潮满林场地区新元古代花岗质片麻岩——锆石U-Pb测年、地球化学特征及构造环境探讨[J]. 地质与资源, 31(2): 123−130. doi: 10.13686/j.cnki.dzyzy.2022.02.001 赵振华. 1994. 富碱侵入岩-窥探地慢成分的窗口[C]//欧阳自远. 中国矿物岩石地球化学研究进展. 兰州: 兰州大学出版社: 113–114. 钟军, 范洪海, 陈金勇, 等. 2020. 辽宁赛马霓霞正长岩黑云母地球化学特征、40Ar−39Ar 年龄及其地质意义[J]. 地球科学, 45(1): 131−144. 周玲棣, 赵振华. 1994. 我国富碱侵入岩的岩石学和岩石化学特征[J]. 中国科学(B辑), 20(10): 1093−1101. -
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 徐大兴,邵兆刚,陈宣华,张进江,徐盛林,李冰,张义平,余苇,邓文兵,丁奕文. 贺兰山构造带深部电性结构与动力学机制. 地质通报. 2024(11): 1921-1936 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(0)




 下载:
下载: