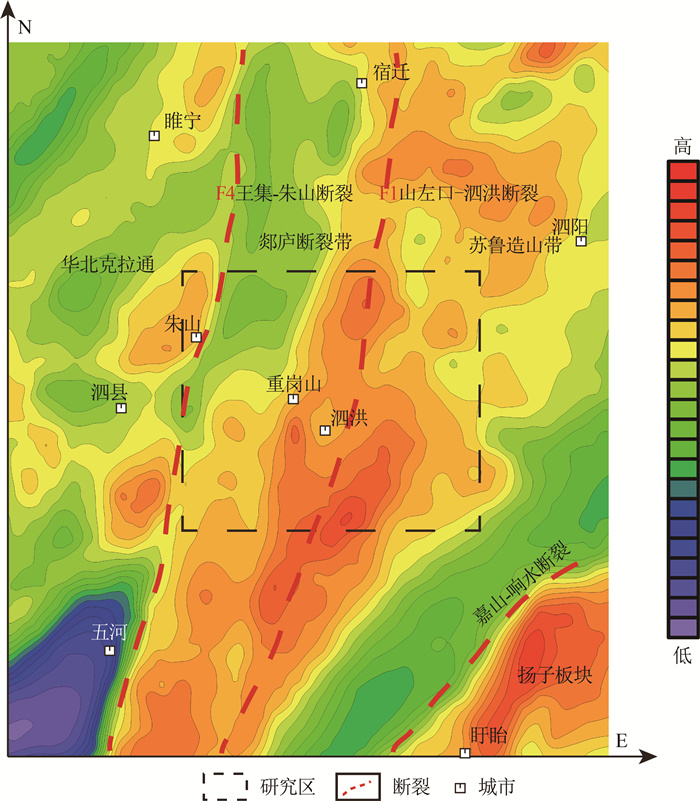
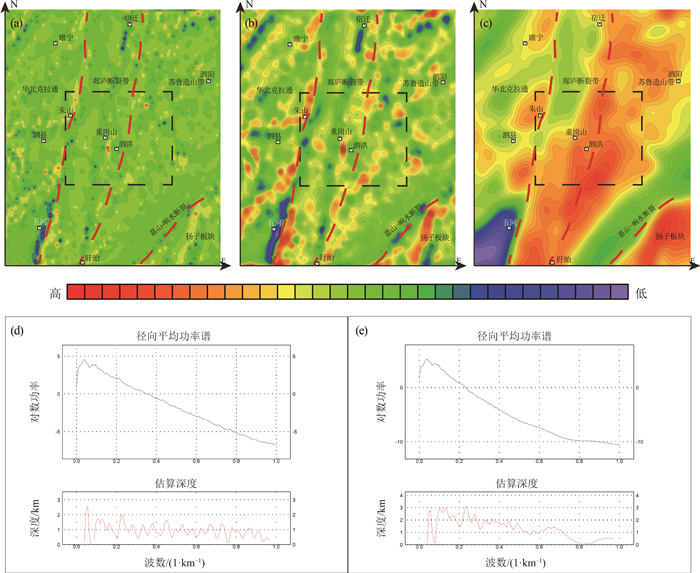
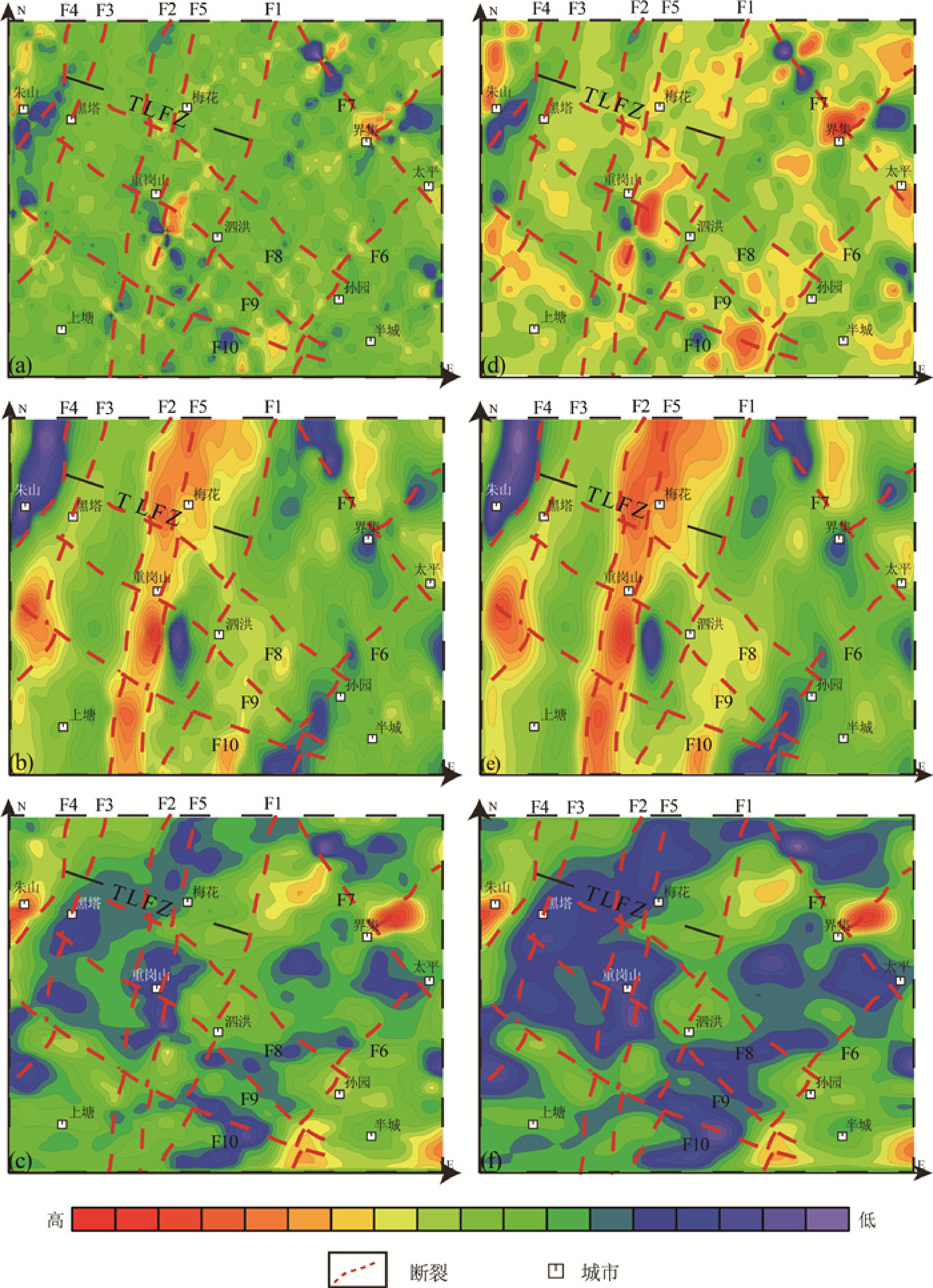
Construction of bedrock geological model in shallow overburden area: Application of a joint inversion of gravity anomaly and borehole data in the Tanlu Fault Zone, Sihong area
-
摘要:
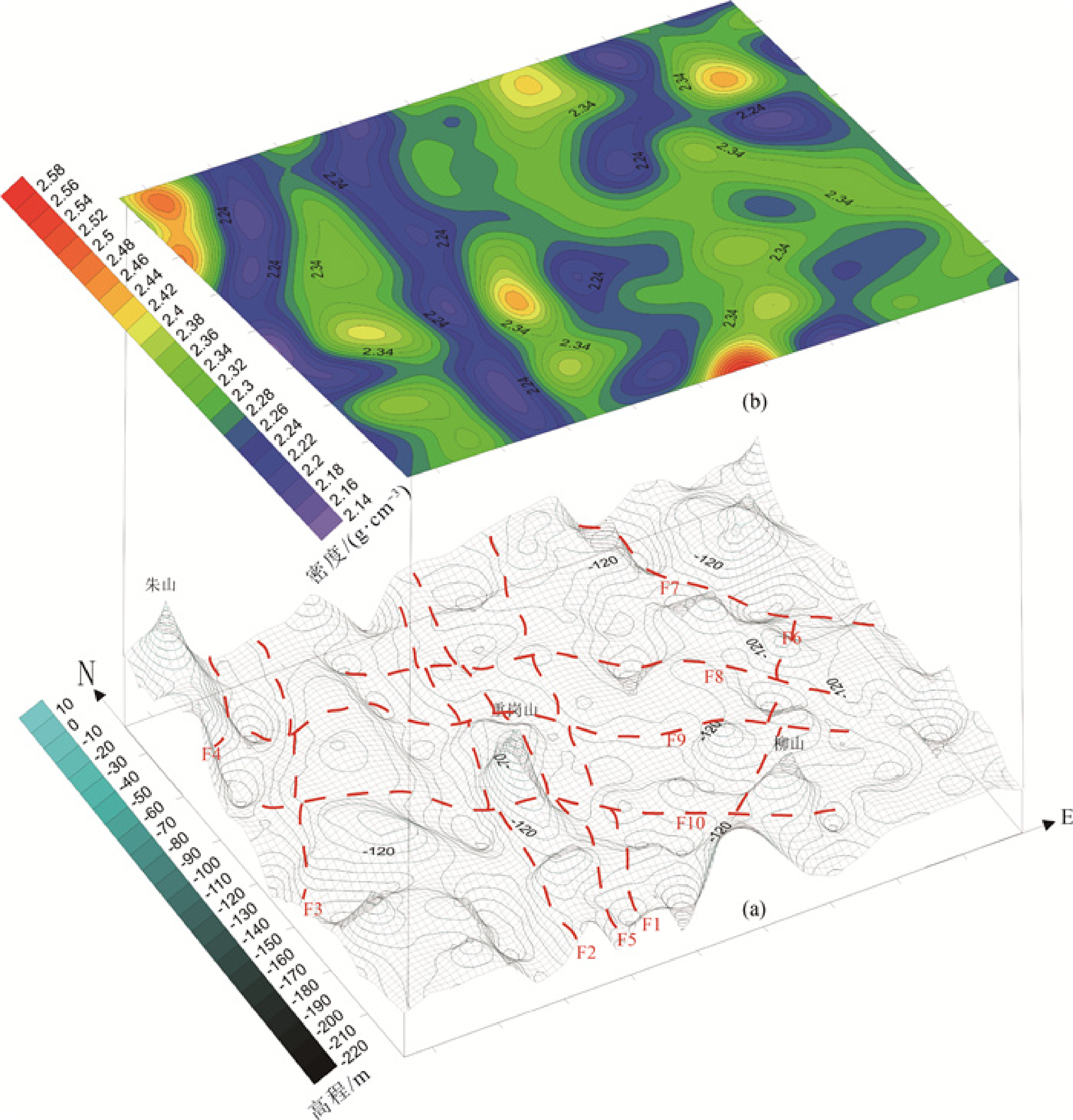
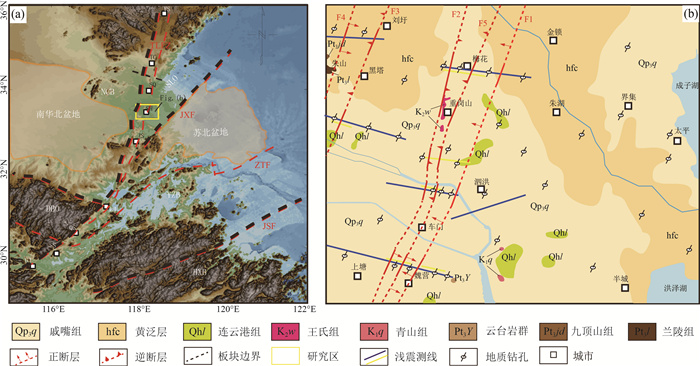
利用重力异常数据建立覆盖区的基岩地质模型往往需要大量的地质与岩石物性资料,同时受地质先验信息、人为因素等干扰严重。运用重力异常钻孔约束反演的方法尝试构建浅覆盖区基岩地质模型,探讨在人为介入较少的情况下快速高效构建包含基岩面起伏特征、断裂展布、密度分布等要素的地质模型的可行性。在郯庐断裂泗洪地区的地质调查实际应用中,对区内布格重力异常采用小波多尺度分解的方法进行基岩面异常场提取,随后联合运用小波断裂分析、线性回归反演、视密度填图等方法构建了该区域的隐伏基岩地质模型。结果显示,在不需要大量地质先验信息的情况下,该系列方法能够快速高效地构建覆盖区地质模型。结果模型能够较好地反映基岩面构造及物性特征,并且细化郯庐断裂带泗洪地区的区域构造特征,对于郯庐断裂地区的构造演化研究具有一定的参考意义,同时为探索较少人为干预的地球物理数据反演覆盖区隐伏基岩的方法研究提供一定的实践价值。
Abstract:The establishment of the bedrock geological model with gravity anomaly data in the covered area usually requires a lot of geological and rock-physical data.The results are often disturbed by geological prior information and human factors.A joint inversion method of gravity anomaly and borehole data for constructing the geological bedrock model in shallow overburden area was introduced to explore the feasibility of rapidly and efficiently constructing the geological model of bedrock surface undulation, fault distribution and density distribution in the case of less human intervention.In the practical application of the Tanlu Fault Zone, Sihong area, the wavelet multi-scale decomposition method was used to extract the gravity anomaly field of bedrock surface; furthermore, the geological model of bedrock in this region was constructed by means of wavelet fault analysis, linear regression inversion and apparent density mapping.The results show that this method can construct the geological model of overburden area quickly and efficiently without requiring a lot of geological prior information.This model can truthfully reflect the structural and physical characteristics of the bedrock surface, and refine the regional tectonic characteristics of the Tanlu Fault, which is meaningful for the better understanding of the regional tectonic evolution and geophysical data inversion of buried bedrock.
-
致谢: 感谢两位审稿专家提出的宝贵意见及中国地质调查局地质力学研究所胡健民研究员在本文写作过程中的帮助。
-
表 1 基岩填图单位
Table 1 The mapping units of the bedrock
中新生代盖层 华北板块 苏鲁造山带 时代 古近纪(缺失) 白垩纪 新元古代 新元古代—中元古代 中元古代—古元古代 地层及代号 三垛组(E2-3s) 戴南组(E2d) 阜宁组(E1f) 泰州组(E1t) 王氏组(K2w) 青山群(K1qs) 淮河群 八公山群 云台岩群(Pt2-3Y) 锦屏岩群 九顶山组(Pt3jd) 张渠组(Pt3zh) 魏集组(Pt3wj) 兰陵组(Pt3l) 石英岩片麻岩组(Pt1-2Jqg) 磷灰岩片麻岩组(Pt1-2Jpg) 表 2 泗洪地区部分岩石密度参数
Table 2 The densities of the bedrock in the Sihong area
年代 岩性 标本数/块 密度/(103 kg·m-3) 最小值 最大值 平均值 标准差 白垩纪 粉砂岩 13 2.033 2.346 2.191 0.131 白垩纪 砂岩 43 2.243 2.535 2.330 0.048 白垩纪 火山岩 23 2.254 2.368 2.330 0.028 元古宙 花岗片麻岩 19 2.426 2.669 2.585 0.065 元古宙 片麻岩 24 2.545 2.806 2.658 0.062 元古宙 灰岩 32 2.616 2.857 2.800 0.050 元古宙 石英岩 34 2.598 2.676 2.643 0.014 元古宙 斜长角闪岩 3 2.456 2.616 2.552 0.069 表 3 用于线性回归反演的地质钻孔信息
Table 3 The geological boreholes for linear regression inversion
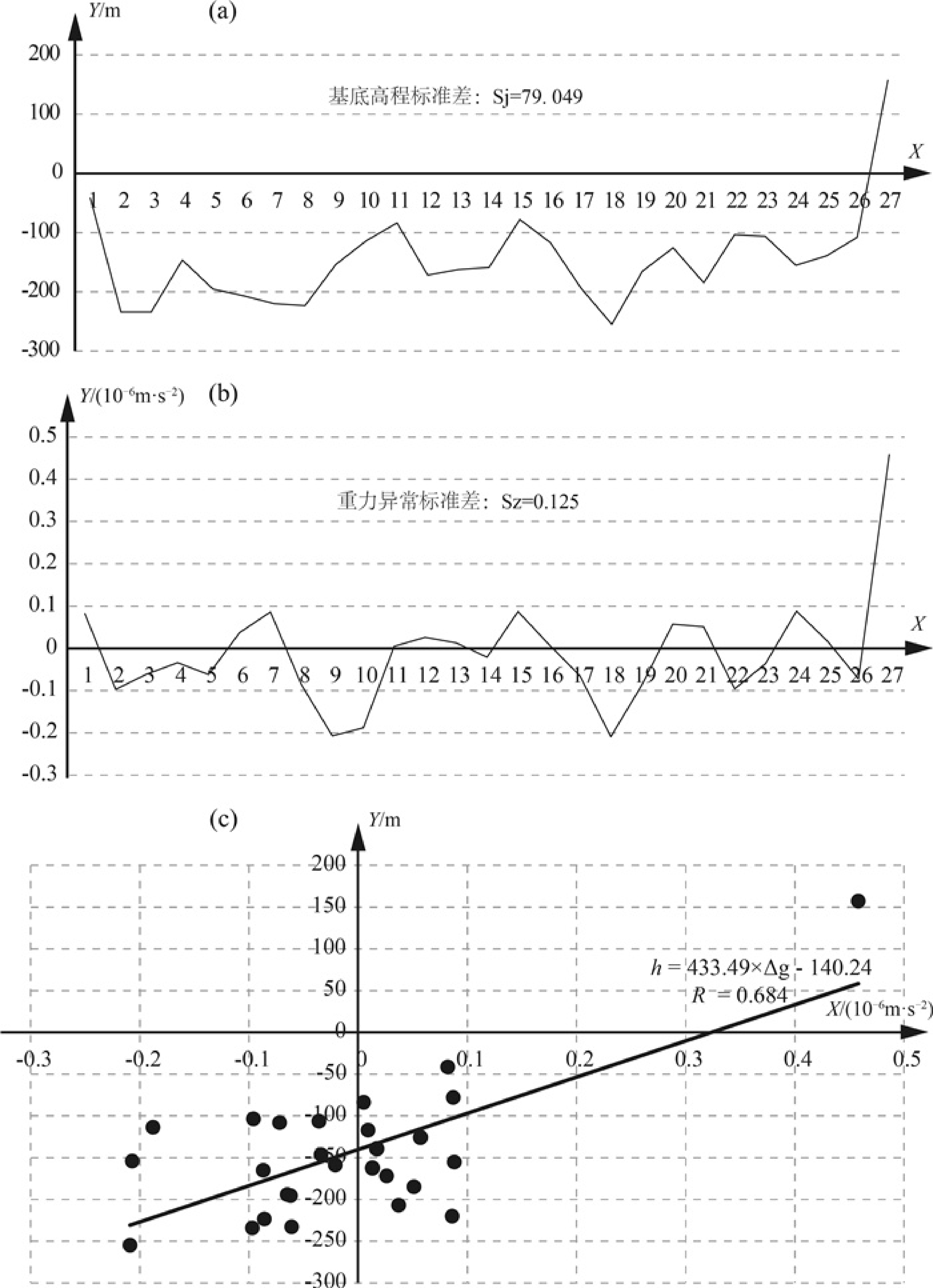
序号 钻孔编号及基岩出露点 钻孔高程/m 基岩面高程/m Δg值/(10-6 m·s-2) 1 SHJ01 18.88 -41.4 0.082 2 SHJ03 18.47 -234.11 -0.097 3 SHJ05 18.12 -232.78 -0.061 4 SHJ07 22.47 -146.31 -0.034 5 SHJ08 19.59 -195.38 -0.062 6 SHJ09 18.71 -206.85 0.037 7 SHJ10 18.69 -220 0.086 8 SHJ11 18.13 -223.4 -0.086 9 SHJ14 16.37 -154 -0.207 10 SHJ15 16.71 -113.6 -0.188 11 SHJ17 16.09 -83.65 0.005 12 SHJ18 18.82 -171.8 0.026 13 SHJ19 46.04 -162.36 0.013 14 SHJ20 22.77 -158.72 -0.021 15 SHJ21 16.47 -77.86 0.087 16 SHJ22 15.46 -117 0.009 17 SHJ23 13.02 -194.1 -0.065 18 SHJ24 20.42 -254.77 -0.209 19 SHJ25 20.86 -165.05 -0.087 20 SHJ26 18.39 -125.67 0.057 21 SHJ28 15.32 -184.8 0.051 22 SHJ31 16.73 -103.49 -0.096 23 SHJ34 15.03 -106.3 -0.036 24 SHJ35 19.63 -155.18 0.088 25 SHJ37 16.38 -139.25 0.017 26 SHJ38 26.07 -108 -0.072 27 朱山 / 157.2 0.458 -
刘保金, 酆少英, 姬计法, 等. 郯庐断裂带中南段的岩石圈精细结构[J]. 地球物理学报, 2015, 58(5): 1610-1621. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX201505013.htm 张鹏, 王良书, 钟锴, 等. 郯庐断裂带的分段性研究[J]. 地质论评, 2007, 53(5): 721-722. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP200705001.htm 徐嘉炜. 郯城-庐江平移断裂系统[J]. 构造地质论丛, 1984, 3: 19-22. 王小凤, 李中坚, 陈柏林, 等. 郯庐断裂带[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2000. 朱光, 王道轩, 刘国生, 等. 郯庐断裂带的演化及其对西太平洋板块运动的响应[J]. 地质科学, 2004, 40(1): 36-49. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0563-5020.2004.01.005 张鹏, 李丽梅, 张景发, 等. 郯庐断裂带江苏段第四纪活动特征及其动力学背景探讨[J]. 防灾减灾工程学报, 2011, 31(4): 389-396. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXK201104008.htm 刘备, 朱光, 胡红雷, 等. 郯庐断裂带江苏段新构造活动规律分析[J]. 地质学报, 2015, 89(8): 1352-1366. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2015.08.002 朱光, 刘国生, 牛漫兰, 等. 郯庐断裂带的平移运动与成因[J]. 地质通报, 2003, 22(3): 200-207. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2003.03.009 朱光, 牛漫兰, 刘国生, 等. 郯庐断裂带早白垩世走滑运动中的构造、岩浆、沉积事件[J]. 地质学报, 2002, 76(3): 325-334. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2002.03.005 朱光, 王道轩, 刘国生, 等. 郯庐断裂带的伸展活动及其动力学背景[J]. 地质科学, 2001, 36(3): 269-278. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0563-5020.2001.03.002 朱光, 张力, 谢成龙, 等. 郯庐断裂带构造演化的同位素年代学制约[J]. 地质科学, 2009, 44(4): 1327-1342. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0563-5020.2009.04.019 刘国生, 朱光, 牛漫兰, 等. 合肥盆地对郯庐断裂带同造山走滑活动的沉积响应[J]. 合肥工业大学学报(自然科学版), 2005, 28(10): 1233-1237. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-5060.2005.10.001 刘国生, 朱光, 宋传中, 等. 郯庐断裂带新近纪以来的挤压构造与合肥盆地的反转[J]. 安徽地质, 2002, 12(2): 81-85. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6157.2002.02.001 侯明金, 朱光, Mercier J. 郯庐断裂带(安徽段)及邻区的动力学分析与区域构造演化[J]. 地质科学, 2007, 42(2): 362-381. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0563-5020.2007.02.010 Grimmer J C, Jonckheere R, Enkelmann E, et al. Cretaceous-Cenozoic history of the southern Tan-Lu Fault Zone: apatite fission-track and structural constraints from the Dabie Shan(eastern China)[J]. Tectonophysics, 2002, 359(3): 225-253.
牛漫兰, 朱光, 刘国生. 郯庐断裂带中-南段中生代岩浆活动的构造背景与深部过程[J]. 地质科学, 2002, 37(4): 393-404. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0563-5020.2002.04.002 孙卫东, 凌明星, 汪方跃, 等. 太平洋板块俯冲与中国东部中生代地质事件[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2007, 27(s1): 218-225. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYDH200803003.htm 王勇生, 朱光, 宋传中, 等. 大别山东端郯庐断裂带由走滑向伸展运动转换的40Ar-39Ar年代学记录[J]. 地质科学, 2006, 41(2): 242-255. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0563-5020.2006.02.007 万天丰, 朱鸿, 赵磊, 等. 郯庐断裂带的形成与演化: 综述[J]. 现代地质, 1996, 10(2): 159-168. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ602.002.htm 张岳桥, 董树文. 郯庐断裂带中生代构造演化史: 进展与新认识[J]. 地质通报, 2008, 27(9): 1371-1390. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2008.09.002 Li C B, Jiang R, Zeng J W, et al. Deep structures underneath the Sihong Segment of the Tan-Lu Fault Zone, Eastern China: Interpretations of gravity anomaly and seismic profiles[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2019, 176: 229-243. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2019.02.014
Sun B, Wang L, Dong P, et al. Integrated analysis on gravity and magnetic fields of the Hailar Basin, NE China: Implications for basement structure and deep tectonics[J]. Pure and Applied Geophysics, 2012, 169(11): 2011-2029. doi: 10.1007/s00024-012-0452-1
喻劲松, 荆磊, 王乔林, 等. 特殊地质地貌区填图物化探技术应用[J]. 地质力学学报, 2016, 22(4): 893-906. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2016.04.008 刘彦, 严加永, 吴明安, 等. 基于重力异常分离方法寻找深部隐伏铁矿——以安徽泥河铁矿为例[J]. 地球物理学报, 2012, 55(12): 4181-4193. doi: 10.6038/j.issn.0001-5733.2012.12.030 邓震, 孟贵祥, 汤贺军, 等. 浅覆盖区1:5万基岩地质填图实践探索——以准噶尔北缘克什克涅绍喀尔(L45E009020)图幅为例[J]. 地球学报, 2019(5): 651-660. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB201905002.htm Beltrão J F, Silva J B C, Costa J C. Robust polynomial fitting method for regional gravity estimation[J]. Geophysics, 1991, 56(1): 80-89. doi: 10.1190/1.1442960
Mickus K L, Aiken C L V, Kennedy W D. Regional-residual gravity anomaly separation using the minimum-curvature technique[J]. Geophysics, 1991, 56(2): 279-283. doi: 10.1190/1.1443041
Mallick K, Sharma K K. A finite element method for computation of the regional gravity anomaly[J]. Geophysics, 1999, 64(2): 461-469. doi: 10.1190/1.1444551
侯遵泽, 杨文采. 中国重力异常的小波变换与多尺度分析[J]. 地球物理学报, 1997, 40(1): 85-95. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5733.1997.01.010 刘天佑, 吴招才, 詹应林, 等. 磁异常小波多尺度分解及危机矿山的深部找矿: 以大冶铁矿为例[J]. 地球科学——中国地质大学学报, 2007, (1): 135-140. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX200701020.htm Xu Y, Hao T, Li Z, et al. Regional gravity anomaly separation using wavelet transform and spectrum analysis[J]. Journal of Geophysics & Engineering, 2009, (3): 279-287.
杨文采, 施志群, 侯遵泽, 等. 离散小波变换与重力异常多重分解[J]. 地球物理学报, 2001, 44(4): 534-541. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5733.2001.04.012 牟力, 陈召曦. 重力资料多尺度分析最优小波基的选择[J]. 物探与化探, 2015, 39(5): 1013-1019. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTYH201505022.htm Daubechies I. Orthonormal base of compactly supported wavelets[J]. Communications on Pure and Applied Mathematics, 1998, XLI: 909-996.
Mallat S, Hwang W L. Singularity detection and processing with wavelets[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2002, 38(2): 617-643.
Spector A, Grant F S. Statistical models for interpreting aeromagnetic data[J]. Geophysics, 1970, 35(2): 293-302. doi: 10.1190/1.1440092
Cook R D. Detection of influential observation in linear regression[J]. Technometrics, 1977, 42(1): 65-68.
Fan D, Li S, Meng S, et al. Predicting submarine topography by linear regression analysis[J]. Journal of Chinese Inertial Technology, 2018, 26(1): 2018.
汪冬华. 多元统计分析与SPSS应用[M]. 上海: 华东理工大学出版社, 2010. 王谦身, 安玉林, 张赤军, 等. 重力学[M]. 北京: 地震出版社, 2003. Jiang R, Cao K, Zeng J, et al. Late Cenozoic tectonic evolution of the southern segment of the Tan-Lu fault zone, Eastern China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2019, 182: 103932. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2019.103932



 下载:
下载: