Petrogenesis of the Zhagadang O-type adakite in Naidong County of Tibet: Constraints from its geochemistry and Sr-Nd-Pb isotopic compositions
-
摘要:
埃达克岩是具有特定地球化学性质的一套中酸性火成岩组合,具有多种成因模式和特殊的构造意义。位于西藏泽当一带的泽当蛇绿岩对研究新特提斯洋的演化具有重要的意义,选取泽当蛇绿岩内出露的奥长花岗岩为研究对象,开展了岩石学、岩石地球化学、Sr-Nd-Pb同位素等研究。研究显示,扎嘎当奥长花岗岩地球化学特征表现为高硅、高铝、富钠(Na2O/K2O>2)、低镁,准铝质钙碱性,同时具高Sr和Sr/Y值,低Y、Yb,属O型埃达克岩。岩石稀土元素总量偏低,富集轻稀土元素和大离子亲石元素Rb、K、Ba,亏损高场强元素Nb、Ti、P,Eu具微弱的正异常。岩石具有较高的Sr、Sm、Nd、Pb含量,ISr=0.704251~0.704329,INd=0.512776~0.512807,εNd(t)=6.61~7.22。岩石铅同位素组成较均一,206Pb/204Pb=18.378~18.495,207Pb/204Pb=15.542~15.554和208Pb/204Pb=38.336~38.406。研究表明,扎嘎当奥长花岗岩源区来源于具有地幔特征的洋壳,由消减大洋板片在一定深度部分熔融形成。综合泽当地区的地质特征和前人研究成果,认为泽当洋内弧是存在的。
-
关键词:
- 扎嘎当 /
- 奥长花岗岩 /
- O型埃达克岩 /
- Sr-Nd-Pb同位素 /
- 洋内弧
Abstract:Adakite, as a set of intermediate-acid igneous rock assemblages with special geochemical characteristics, has a variety of genetic models and special tectonic significance.The Zedang ophiolite is of great significance to the study of the evolution of the Neo-Tethys Ocean.The trondhjemite outcropped in the Zedang ophiolite was selected to study its petrology, petrochemistry and Sr-Nd-Pb isotopes.The results show that the Zhagadang trondhjemite is a high SiO2 and Al2O3, rich Na2O(Na2O/K2O>2), low MgO, and para-aluminous calc-alkaline series.It is characterized by high Sr and Sr/Y, low Y and Yb.These geochemical characteristics are comparable with those of O-type adakite.The Zhagadang trondhjemite is rich in large ion lithophile elements(e.g., Rb, K and Ba), poor in high field-strength elements(e.g., Nb, Ti and P) and rare earth elements, and exhibits a weak positive Eu anomaly.The Sr-Nd-Pb isotopic compositions indicate that the Zhagadang trondhjemite is characterized by high Sr, Sm, Nd and Pb contents, with ISr of 0.704251~0.704329, INd of 0.512776~0.512807, positive εNd(t) values(6.61~7.22) and relatively uniform lead isotopic composition(206Pb/204Pb=18.378~18.495, 207Pb/204Pb=15.542~15.554 and 208Pb/204Pb=38.336~38.406).The study indicates that the Zhagadang trondhjemite bearing mantle characteristics was formed by partial melting of the subducting oceanic slab at a certain depth.The result confirms the existence of the Zedang intra-oceanic.
-
Keywords:
- Zhagadang /
- trondhjemite /
- O-type adakite /
- Sr-Nd-Pb isotopic /
- intra-oceanic arc
-
致谢: 审稿专家及吉林大学地球科学学院解超明副教授对本文提出了宝贵的修改意见,在此深表感谢。
-
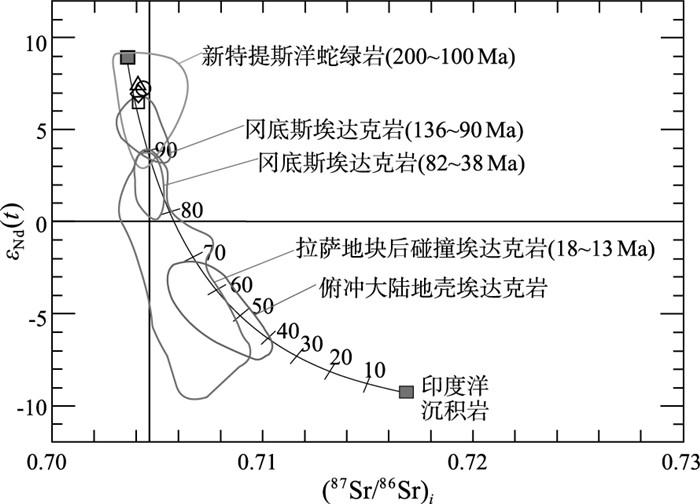
图 6 扎嘎当奥长花岗岩(87Sr/86Sr)i-εNd(t)判别图解[29]
Figure 6. Disriminant diamgram of εNd(t)vs(87Sr/86Sr)i of Zhagadang trondhjemite
图 7 扎嘎当奥长花岗岩SiO2-Al2O3图解[31]
Figure 7. SiO2-Al2O3 diagram of Zhagadang trondhjemite
图 8 扎嘎当奥长花岗岩SiO2-Yb图解[3]
Figure 8. SiO2-Yb diagram of Zhagadang trondhjemite
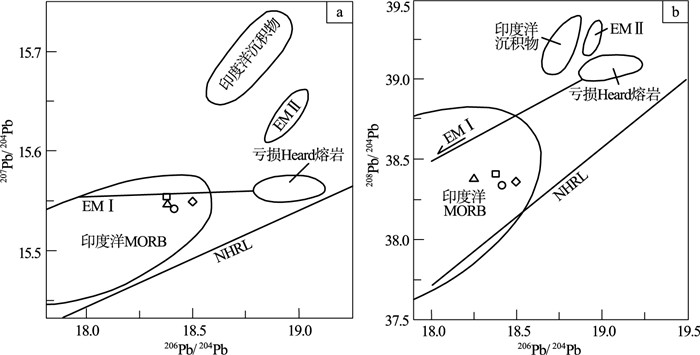
图 9 扎嘎当奥长花岗岩207Pb/204Pb-206Pb/204Pb(a)和208Pb/204Pb-206Pb/204Pb(b)同位素判别图解[32]
EMⅠ—第Ⅰ类富集地幔组分;EMⅡ—第Ⅱ类富集地幔组分;NHRL—北半球参考线;Heard熔岩—赫德岛屿熔岩;MORB—洋中脊玄武岩
Figure 9. Plots of 207Pb/204Pb-206Pb/204Pb(a)and 208Pb/204Pb-206Pb/204Pb(b)of Zhagadang trondhjemite
表 1 扎嘎当奥长花岗岩主量、微量和稀土元素组成及其特征参数
Table 1 Compositions and characteristic parameters of major, trace element and REE of Zhagadang trondhjemite
样品编号 D5958 -3-3 D5958 -4-5 D5959 -1-1 D5959-2-3 样品编号 D5958 -3-3 D5958 -4-5 D5959 -1-1 D5959-2-3 SiO2 66.87 65.65 64.4 66.73 Sc 4.92 4.13 4.42 3.78 TiO2 0.17 0.16 0.2 0.15 Li 3.05 6.29 4.94 10.68 Al2O3 17.58 18.39 18.74 17.83 Cs 0.75 0.73 0.74 1.6 TFe2O3 1.62 1.47 1.87 1.36 Be 2.39 2.46 3.03 1.65 MnO 0.06 0.05 0.06 0.07 Ga 17.66 16.95 19.43 17.76 MgO 0.87 0.81 0.99 0.72 Tl 0.29 0.28 0.27 0.32 CaO 2.64 3.25 4.11 3.67 Pb 29.86 29.28 20.54 31.4 Na2O 6.37 6.8 6.58 5.8 As 0.68 0.72 0.44 1.82 K2O 2.52 2.05 1.72 2.09 Bi 0.01 0.01 0.03 0.06 P2O5 0.11 0.1 0.14 0.09 Ge 0.79 0.81 0.71 0.9 烧失量 1.17 1.24 1.29 1.21 W 0.09 0.16 0.09 0.12 总计 99.98 99.97 100.1 99.7 La 18.03 22.35 18.24 24.26 An 12.06 13.76 16.74 16.72 Ce 27.65 34.86 29.02 35.54 Ab 54.6 58.32 56.39 49.83 Pr 2.54 2.96 2.68 3.36 Or 15.1 12.29 10.31 12.53 Nd 8.23 9.83 8.6 10.12 A/NK 1.33 1.371 1.477 1.511 Sm 1.37 1.5 1.44 1.63 A/CNK 0.976 0.952 0.93 0.966 Eu 0.43 0.46 0.45 0.46 Mg# 51.82 52.3 51.29 51.26 Gd 1.28 1.26 1.18 1.17 Na2O/K2O 2.53 3.31 3.82 2.78 Tb 0.17 0.17 0.17 0.16 Rb 56.89 47.7 47.76 58.06 Dy 0.93 0.87 0.84 0.98 Sr 688.1 842.16 853.44 1058.21 Ho 0.19 0.19 0.16 0.2 Ba 1796.65 908.89 700.86 1457.97 Er 0.49 0.53 0.45 0.54 Th 6.89 9.02 6.29 10.44 Tm 0.09 0.08 0.09 0.09 U 1.2 1.96 1.48 2.18 Yb 0.58 0.63 0.61 0.7 Nb 6.09 5.89 5.34 6.05 Lu 0.11 0.12 0.11 0.12 Ta 0.4 0.34 0.36 0.33 Y 6.29 6.55 5.78 6.64 Zr 82.39 102.4 97.51 103.91 ΣREE 62.08 75.82 64.04 79.34 Hf 2.25 2.45 2.54 2.7 LREE/HREE 15.24 18.63 16.75 18.99 Co 2.57 1.52 1.52 1.26 (La/Yb)N 20.7 23.28 19.82 22.83 Ni 6.6 5.06 6.02 3.63 (La/Sm)N 8 9.1 7.73 9.09 Cr 10.09 8.78 13.17 7.16 δEu 1.01 1.04 1.08 1.03 V 39.21 30.62 47.84 27.12 δCe 0.96 1 0.97 0.92 注:Mg#=100(Mg/Mg+Fe2+);主量元素含量单位为%,微量和稀土元素含量单位为10-6 表 2 扎嘎当奥长花岗岩Sr-Nd-Pb同位素组成
Table 2 Sr、Nd and Pb isotope data of Zhagadang trondhjemite
同位素组成 D5958-3-3 D5958-4-5 D5959-1-1 D5959-2-3 同位素组成 D5958-3-3 D5958-4-5 D5959-1-1 D5959-2-3 Rb 56.89 47.70 47.76 58.06 T2DM/Ma 6291 6876 6240 6538 Sr 688.10 842.12 853.44 1058.21 87Rb/86Sr 0.23915 0.16385 0.16189 0.15871 Sm 8.23 9.83 8.60 10.12 87Sr/86Sr 0.70486 0.70468 0.70461 0.70466 Nd 1.37 1.50 1.44 1.63 Isr 0.704329 0.704329 0.704251 0.704303 U 1.20 1.96 1.48 2.18 INd 0.512799 0.512776 0.512807 0.512779 Th 6.89 9.02 6.29 10.44 εSr(t) 0.2 0.1 -1 -0.2 Pb 29.86 29.28 20.54 31.40 206Pb/204Pb 18.413 18.378 18.495 18.382 147Sm/144Nd 3.64769 3.99721 3.63911 3.78579 207Pb/204Pb 15.542 15.554 15.549 15.547 143Nd/144Nd 0.512694 0.512682 0.512745 0.512708 208Pb/204Pb 38.336 38.406 38.358 38.374 εNd(t) 7.06377 6.61278 7.22183 6.67386 206Pb/207Pb 1.1847 1.1816 1.1895 1.1824 注:Sm、Rb、Sr、Nd、U、Th和Pb单位为10-6 -
Defant M J, Drummond M S. Derivation of some modern arc magmas by melting of young subducted lithosphere[J]. Nature, 1990, 347(6294): 662-665. doi: 10.1038/347662a0
朱弟成, 莫宣学, 王立全, 等. 西藏冈底斯东部察隅高分异Ⅰ型花岗岩的成因: 错石U-Pb年代学、地球化学和Sr-Nd-Hf同位素约束[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 2009, 39(7): 833-848. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK200907001.htm 赵珍, 胡道功, 陆露, 等. 西藏泽当地区晚白垩世埃达克岩的发现及其成矿意义[J]. 地质力学学报, 2013, 19(1): 45-52. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2013.01.005 Zheng Y C, Hou Z Q, Gong Y L, et al. Petrogenesis of Cretaceous adakite-like intrusions of the Gangdese plutonic Belt, southern Tibet: Implications for mid-ocean ridge subduction and crustal growth[J]. Lithos, 2014, 190/191: 240-263. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2013.12.013
Chen L, Qin K Z, Li G M, et al. Zircon U-Pb ages, geochemistry, and Sr-Nd-Pb-Hf isotopes of the Nuri intrusive rocks in the Gangdese area, southern Tibet: Constraints on timing, petrogenesis, and tectonic transformation[J]. Lithos, 2015, 212/215: 379-396. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2014.11.014
Muir R J, Weaver S D, Bradshaw J D, et al. The Cretaceous separation point batholith, New Zealand: Granitoid magmas formed by melting of mafic lithosphere[J]. Journal of the Geological Society, 1995, 152(4): 689-701. doi: 10.1144/gsjgs.152.4.0689
Wen D R, Chung S L, Song B, et al. Late Cretaceous Gangdese intrusions of adakitic geochemical characteristics, SE Tibet: petrogenesis and tectonic implications[J]. Lithos, 2008, 105(1/2): 1-11.
管琪, 朱弟成, 赵志丹, 等. 西藏南部冈底斯带东段晚白垩世埃达克岩: 新特提斯洋脊俯冲的产物?[J]. 岩石学报, 2010, 26(7): 2165-2179. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201007019.htm Gao S, Rudnick R L, Yuan H L, et al. Recycling lower continental crust in the North China Craton[J]. Nature, 2004, 432(7019): 892-897. doi: 10.1038/nature03162
Macpherson C G, Dreher S T, Thirlwall M F. Adakites without slab melting: High pressure differentiation of island arc magma, Mindanao, the Philippines[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2006, 243(3/4): 581-593. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0012821X06000082
张旗, 金惟俊, 熊小林, 等. 中国不同时代O型埃达克岩的特征及其意义[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2009, 33(3): 432-447. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1552.2009.03.015 朱弟成, 段丽萍, 廖忠礼, 等. 两类埃达克岩(Adakite) 的判别[J]. 矿物岩石, 2002, 22(3): 5-9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6872.2002.03.002 Allegre C J, Courtillot V, Tapponnier P, et al. Structure and evolution of the Himalaya Tibet orogenic belt[J]. Nature, 1984, 307: 17-22. doi: 10.1038/307017a0
Aitchison J C, Badengzhu, Davis A M, et al. Remnants of a Cretaceous intra-oceanic subduction system within the Yarlung-Zangbo suture(southern Tibet)[J]. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 2000, 183: 23l-244. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(00)00287-9
McDermid I R C, Aitchison J C, Davis A M, et al. The Zedong terrane: a Late Jurassic intra-oceanic magmatic arc within the Yarlung-Tsangpo suture zone, southeastern Tibet[J]. Chem. Geol., 2002, 187: 267-277. doi: 10.1016/S0009-2541(02)00040-2
韦栋梁, 夏斌, 周国庆, 等. 西藏泽当英云闪长岩的地球化学和Sr-Nd同位素特征: 特提斯洋内俯冲的新证据[J]. 中国科学, 2007, 42(5): 1515-1534. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK200704001.htm 吴福元, 王建刚, 刘传周, 等. 大洋岛弧的前世今生[J]. 岩石学报, 2019, 35(1): 1-15. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201901002.htm Song S G, Su L, Li X H, et al. Tracing the 850Ma continental flood basalts from a piece of subducted continental crust in the North Qaidam UHPM belt, NW China[J]. Precambrian Research, 2010, 183(4): 805-816. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2010.09.008
Chen F, Siebel W, Satir M, et al. Geochronology of the Karaderebasement(NW Turkey) and implications for the geological evolution of the Istanbul zone[J]. International Journal of Earth Sciences, 2002, 91(3): 469-481. doi: 10.1007/s00531-001-0239-6
Russell W A, Papanastassiou D A, Tombrello T A. Ca isotope fractionation on the Earth and other solar system materials[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1978, 42(8): 1075-1090. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(78)90105-9
Baker J, Peate D, Waight T, et al. Pb isotopic analysis of standards and samples using a 207Pb-204Pb double spike and thallium to correct for mass bias with a double-focusing MCICP-MS[J]. Chemical Geology, 2004, 211(3/4): 275-303. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0009254104002529
Middlemost E A K. Naming materials in the magma igneous rock system[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 1994, 37: 215-224. doi: 10.1016/0012-8252(94)90029-9
Barker F. Trondhjemite: definition, environment and hypotheses of origin[C]//Barker F. Trondhjemites, dacites and related rocks. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 1979: 1-12.
Middlemost E A K. Magas and magmatic rocks[M]. London: Longman, 1985: 1-266.
Maniar P D, Piccoli P M. Tectonic discrimination of granitoids[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 1989, 101: 635-643. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1989)101<0635:TDOG>2.3.CO;2
Martin H, Smithies R H, Rapp R, et al. An oveview of adakite, tonalite-trondhjemite-granodiorite(TTG), and sanukitoid: relationships and some implications for crustal evolution[J]. Lithos, 2005, 79(1/2): 1-24. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S002449370400266X
Mcdonough W F, Sun S S. The composition of the Earth[J]. Chemical Geology, 1995, 120(3/4): 223-253. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0009254194001404
Boynton W V. Cosmochemistry of the rare earth elements: meteorite studies[J]. Developments in Geochemistry, 1984, 2(2): 63-114. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780444421487500083
Jiang Z Q, Wang Q, Derek A. Wyman, et al. Transition from oceanic to continental lithosphere subduction in southern Tibet: Evidence from the Late Cretaceous-Early Oligocene(~91-30Ma) intrusive rocks in the Chanang-Zedong area, southern Gangdese[J]. Lithos, 2014, 196/197: 213-231. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2014.03.001
钟立峰, 夏斌, 周国庆, 等. 藏南罗布莎蛇绿岩成因: 壳层熔岩的Sr-Nd-Pb同位素制约[J]. 矿物岩石, 2006, 26(1): 57-63. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6872.2006.01.011 张旗, 王焰, 熊小林, 等. 埃达克岩和花岗岩: 挑战与机遇[M]. 北京: 中国大地出版社, 2008. Edwards C M, Menies M A, Thirlwall M F, et al. The transition to potassic volcanism in island arcs the Ringgit-Beser complex, east Jast Java, Indonesia[J]. J. Petology, 1994, 35: 1557-1595. doi: 10.1093/petrology/35.6.1557
张旗, 王焰, 刘伟, 等. 埃达克岩的特征及其意义[J]. 地质通报, 2002, 21(7): 431-435. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2002.07.012 Rapp R P, Watson E B, Miller C F. Partial melting of amphibolite/eclogite and the origin of Archean trondhjemites and tonalites[J]. Precambrian Res., 1991, 51: 1-25. doi: 10.1016/0301-9268(91)90092-O
Peacock S M, Rushmer T, Thompson A B. Partial melting of subducting oceanic crust[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1994, 121: 227-244. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(94)90042-6
Atherton M P, Petford N. Generation of sodium-rich magmas from newly underplated basaltic crust[J]. Nature, 1993, 362: 144-146. doi: 10.1038/362144a0
于涛, 徐佳丽, 高强, 等. 藏东卡贡地区早侏罗世似斑状钾长花岗岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄及地球化学特征[J]. 地质通报, 2020, 39(5): 621-630. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20200503&flag=1 董瀚, 张志平, 魏学平, 等. 西藏泽当蛇绿岩物质组成、年代格架及地质意义[J]. 矿产勘查, 2019, 10(6): 1265-1273. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7801.2019.06.003 Shervais J W. Birth, death and resurrection: the life cycle of suprasubduction zone ophiolites[J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2001, DOI: 10.1029/2000GC000080.
Stern R J. Subduction zones[J]. Reviews of Geophysics, 2002, 40(4): 1012, DOI: 10.1029/2001RG000108.
肖庆辉, 李廷栋, 潘桂棠, 等. 识别洋陆转换的岩石学思路——洋内弧与初始俯冲的识别[J]. 中国地质, 2016, 43(3): 721-737. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201603003.htm 赵珍, 吴珍, 胡道功, 等. 青藏高原冈底斯带南缘泽当多金属矿田多期岩浆活动及年代意义[J]. 地球学报, 2014, 35(6): 703-712. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB201406007.htm 西藏自治区地质矿产勘查开发局第五地质大队. 西藏桑耶地区1∶5万区域地质调查(H46E016005、H46E016006、H46E017005、H46E017006)报告. 2019.




 下载:
下载: