A discussion on the calculation method of instability probability of landslide due to rainfall
-
摘要:
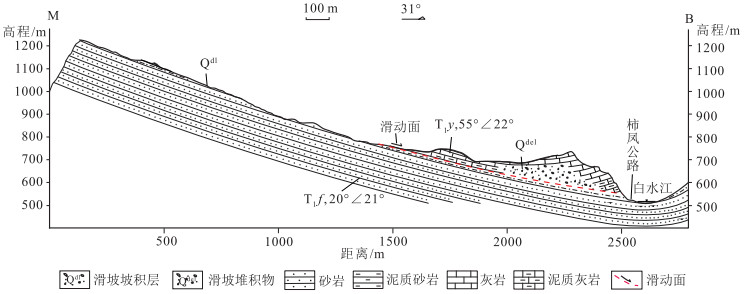
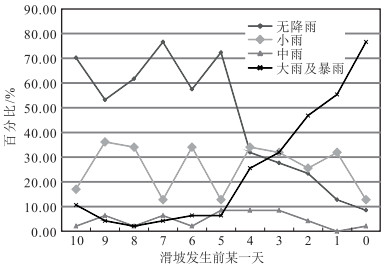
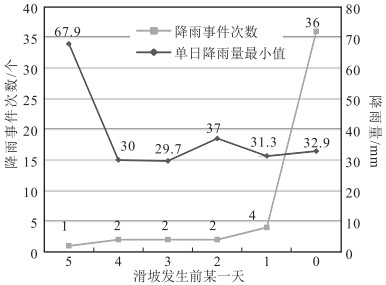
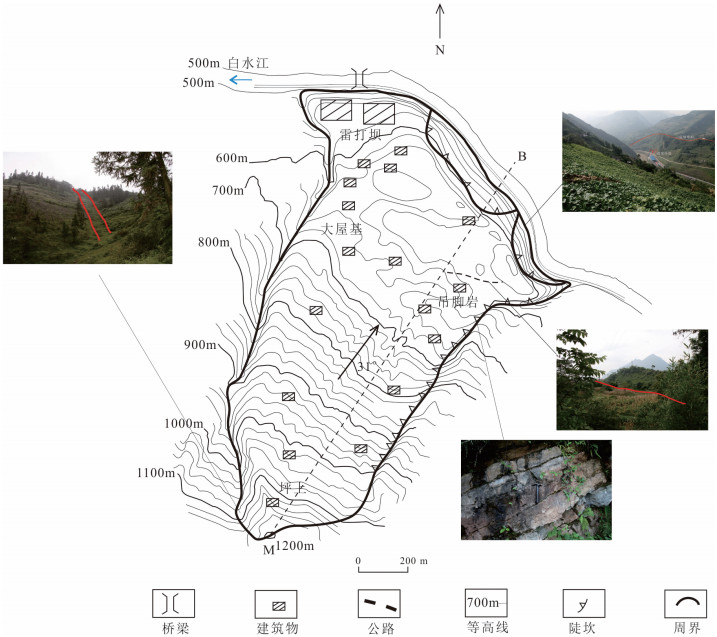
为了解决滑坡风险评价中的滑坡失稳概率计算问题,利用前人在降雨阈值的研究成果,结合气象学中降雨概率分布理论,以云南省盐津县庙坝滑坡为例进行计算,建立降雨型滑坡失稳概率计算模型。结果表明,盐津县降雨型滑坡的降雨阈值类型为累积降雨量-历时关系阈值,即为单日降雨阈值,降雨阈值为29.7 mm;盐津县在当日降雨量达到或超过阈值水平时可能诱发滑坡,对滑坡影响的滞后天数最大为5天;庙坝滑坡在8月20—25日6天内单日降雨达到或超过29.7 mm的降雨概率为46.49%;庙坝滑坡在8月25日因前5天或当天单日降雨量超过29.7 mm而失稳的概率为0.2853%。
Abstract:In order to solve the landslide risk evaluation of landslide failure instability probability calculation problem, this paper summarizes the research achievements of previous researchers in rainfall threshold and, in combination with the previous research results in a threshold rainfall, uses the theory of statistical to perform coupling analysis of the historical record of the rainfall landslide and rainfall data, so as to create a rainfall landslide failure instability probability calculation model, with Miaoba landslide in Yanjin County of Yunnan Province as an example for demonstration.The results show that the rainfall threshold type of Yanjin County rainfall landslide is cumulative rainfall duration threshold, which means the one-day rainfall threshold, with the rainfall threshold being 29.7 mm; most of rainfall landslide in Yanjin County is caused by the daily rainfall which reaches rainfall threshold within 5 days; the possibility that the rain reaches or exceeds 29.7 mm from August 20th to 25th is 46.49%;the possibility of the failure of Miaoba landslide in August 25th is 0.2853%.
-
致谢: 感谢云南省昭通气象局提供气象数据,感谢盐津县提供地质灾害记录。审稿专家提出的建议和意见使得本文得以完善。
-
表 1 三种常用降雨概率分布函数及统计参数
Table 1 Three commonly used rainfall probability distribution function and statistical parameter
概率曲线及统计参数 公式 参数 P-Ⅲ型 P(X≥x)=βαΓ(α)+∞∫x(x−a0)α−1e−β(x−a0)dx a0=E(x)(1−2CVCS) α=4C2S β=2E(x)CVCS 指数分布 P(X≥x)=+∞∫xf(x)dx=+∞∫xαe−α(x−β)dx=e−α(x−β) \alpha = \frac{1}{b} = \frac{1}{{E(x)}}, {\rm{ \mathit{ β} = (}}{{\rm{X}}_{\rm{i}}}{{\rm{)}}_{\min }} 耿贝尔分布 P(X \ge x) = 1 - {e^{[ - {e^{ - a(x - b)}}]}} a = \frac{{1.2825}}{\sigma }, b = E(x) - 0.45005\sigma 统计参数 E(x) = x = \frac{1}{n}, \sum\limits_{i = 1}^n {{x_i}, {K_i} = \frac{{{x_i}}}{x}} {C_v} = \sqrt {\frac{1}{{n - 1}}\sum\limits_{i = 1}^n {{{({K_i} - 1)}^2}} } , {C_S} = \frac{{\sum\limits_{i = 1}^n {{{({K_i} - 1)}^3}} }}{{\left( {n - 3} \right)C_v^3}}, \sigma = \sqrt {\frac{{\sum\limits_{i = 1}^n {{{({x_i} - x)}^2}} }}{{n - 1}}} 表 2 8月20—25日降雨概率分布曲线拟合参数结果
Table 2 Fitting parameter results of rainfall probability distribution curve from August 20th to 25th
分布类型及参数 8月20日 8月21日 8月22日 8月23日 8月24日 8月25日 皮尔逊Ⅲ型分布 E(x) 6.3 3.6 9.4 8.6 7.8 7.6 Cv 0.6 0.6 0.6 0.6 0.6 0.6 Cs 1.2 1.2 1.2 1.2 1.2 1.2 s 12.6 8.9 15.8 17.9 19.4 10.8 指数分布 a 0 0 0 0 0 0 b 6.4 3.6 9.5 8.5 7.9 7.7 s 10.8 7.8 7.8 15.2 9.9 8.3 耿贝尔分布 a 0.08366 0.12396 0.06349 0.05908 0.07936 0.0885 b -0.4682 -1.04356 0.44242 -1.00348 0.65429 1.1432 s 9.9 7.1 11 13.3 8.4 6.9 统计参数 E(Si) 6.3 3.6 9.6 8.6 7.8 7.6 D(Si) 235.0 107.0 408.0 471.2 261.2 210.2 Max(Si) 97.2 60.7 103.8 103.9 84.0 52.4 Min(Si) 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 表 3 8月20—25日降雨概率分布曲线及超过阈值概率
Table 3 The probability distribution curve of rainfall and the threshold exceeding the probability from August 20th to 25th
日期 超过概率分布公式 P(X≥x=29.7) 8月20日 P(X \ge x) = 1 - {e^{[ - {e^{ - 0.08366(x + 0.46820)}}]}} 0.07702 8月21日 P(X \ge x) = 1 - {e^{[ - {e^{ - 0.12396(x + 1.04356)}}]}} 0.02188 8月22日 P(X \ge x) = 1 - {e^{ - 0.10526x}} 0.04388 8月23日 P(X \ge x) = 1 - {e^{[ - {e^{ - 0.05908(x + 1.00348)}}]}} 0.15041 8月24日 P(X \ge x) = 1 - {e^{[ - {e^{ - 0.07936(x + 0.65429)}}]}} 0.09494 8月25日 P(X \ge x) = 1 - {e^{[ - {e^{ - 0.08850(x + 1014320)}}]}} 0.07677 -
王涛, 吴树仁, 石菊松.国际滑坡风险评估与管理指南研究综述[J].地质通报, 2009, 28(8):1006-1019. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2009.08.002 石菊松, 石玲, 吴树仁, 等.滑坡风险评估实践中的难点与对策[J].地质通报, 2009, 28(8):1020-1030. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2009.08.003 吴树仁, 石菊松, 张春山, 等.滑坡风险评估理论与技术[M].北京:科学出版社, 2012. 李媛, 孟晖, 董颖, 等.中国地质灾害类型及其特征——基于全国县市地质灾害调查成果分析[J].中国地质灾害与防治学报, 2004, 15(2):29-34. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8035.2004.02.005 陈洪凯, 魏来, 谭玲.降雨型滑坡经验性降雨阈值研究综述[J].重庆交通大学学报(自然科学版), 2012, 31(5):990-996. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=cqjtxyxb201205018 谢剑明, 刘礼领, 殷坤龙, 等.浙江省滑坡灾害预警预报的降雨阀值研究[J].地质科技情报, 2004, 22(4):101-105. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzkjqb200304019 陈洪凯, 魏来, 谭玲.降雨型滑坡经验性降雨阈值研究综述[J].重庆交通大学学报(自然科学版), 2012, 31(5):990-996. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=cqjtxyxb201205018 Maitir M.Assessing the triggering rainfall-induced landslip events in the ShivKhola Watershed of DARJILING Himalaya, west Bengal[J].European Journal of Geography, 2013, 4(3):21-37. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/264903246_ASSESSING_THE_TRIGGERING_RAINFALL-INDUCED_LANDSLIP_EVENTS_IN_THE_SHIVKHOLAWATERSHED_OF_DARJILING_HIMALAYA_WEST_BENGAL
Galeandro A, Doglioni A, Simeone V, et al.Analysis of infiltration processes into fractured and swelling soils as triggering factors of landslides[J].Environmental earth sciences, 2014, 71(6):2911-2923. doi: 10.1007/s12665-013-2666-7
Capparelli G, Versace P.Analysis of landslide triggering conditions in the Sarno area using a physically based model[J].Hydrology and Earth System Sciences, 2014, 18(8):3225-3237. doi: 10.5194/hess-18-3225-2014
Chien Yuan C, Tien Chien C, Fan Chieh Y, et al.Analysis of time-varying rainfall infiltration induced landslide[J].Environmental Geology, 2005, 48(4/5):466-479. doi: 10.1007/s00254-005-1289-z
Muntohar A S, Liao H J.Rainfall infiltration:infinite slope model for landslides triggering by rainstorm[J].Natural hazards, 2010, 54(3):967-984. doi: 10.1007/s11069-010-9518-5
魏来.降雨诱发滑坡预测模型研究[D].重庆交通大学硕士学位论文, 2013. 高华喜, 殷坤龙.降雨与滑坡灾害相关性分析及预警预报阀值之探讨[J].岩土力学, 2007, 28(5):1055-1060. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2007.05.039 张珍, 李世海, 马力.重庆地区滑坡与降雨关系的概率分析[J].岩石力学与工程学报, 2005, 24(17):3185-3191. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2005.17.029 陈剑, 杨志法, 李晓.三峡库区滑坡发生概率与降水条件的关系[J].岩石力学与工程学报, 2005, 24(17):3052-3056. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2005.17.008 陈正洪, 孟斌.湖北省降雨型滑坡泥石流及其降雨因子的时空分布, 相关性浅析[J].岩土力学, 1995, 16(3):62-69. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-YTLX503.009.htm 陈丽霞, 殷坤龙, 刘长春.降雨重现期及其用于滑坡概率分析的探讨[J].工程地质学报, 2012, 20(5):745-750. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2012.05.013 陈丽霞, 殷坤龙, 刘礼领, 等.江西省滑坡与降雨的关系研究[J].岩土力学, 2008, 29(4):1114-1120. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2008.04.049 张桂荣, 殷坤龙, 陈丽霞, 等.滑坡预测预报的地质-气象耦合模型研究[J].水利水电技术, 2005, 36(3):5-18. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=slsdjs200503005 殷坤龙, 陈丽霞, 张桂荣.区域滑坡灾害预测预警与风险评价[J].地学前缘, 2008, 14(6):85-97. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dxqy200706011 杜娟.单体滑坡灾害风险评价研究[D].中国地质大学(北京)博士学位论文, 2012. 黄振平.水文统计学[M].南京:河海大学出版社, 2003. Caine N.The rainfall intensity-duration control of shallow landslides and debris flows[J].Geografiska Annaler:Series A, Physical Geography, 1980, 62(1/2):23-27. doi: 10.2307/520449
Guzzetti F, Peruccacci S, Rossi M, et al.The rainfall intensity-duration control of shallow landslides and debris flows:an update[J].Landslides, 2008, 5(1):3-17. doi: 10.1007/s10346-007-0112-1
Huang Q X, Xu X T, Kulatilake P H S W, et al.Formation mechanism of a rainfall triggered complex landslide in southwest China[J].Journal of Mountain Science, 2020, 17(5):1128-1142. doi: 10.1007/s11629-019-5736-9
周伟杰, 徐卫亚, 王如宾, 等.暴雨及久雨作用下东岭信滑坡堆积体的渗流特性及稳定性分析[J].三峡大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 42(2):28-33. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=whsldldxxb-yc202002006 张勇, 温智, 程英建.四川巴中市滑坡灾害与降雨雨型关系探讨[J].水文地质工程地质, 2020, 47(2):178-182. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=swdzgcdz202002023 甘建军, 储小东.中低山台风暴雨型泥石流形成机制和动力特征——以江西德安杜家沟泥石流为例[J].灾害学, 2020, 35(1):150-155. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-811X.2020.01.027 向小龙, 孙炜锋, 李国伟, 等.云南盐津地区地质灾害影响因素分析[J].地质力学学报, 2015, 21(1):97-105. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2015.01.011



 下载:
下载: