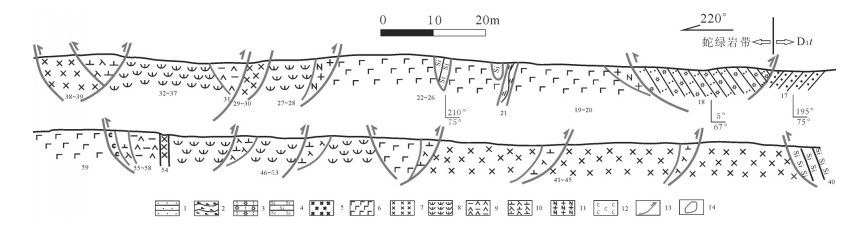
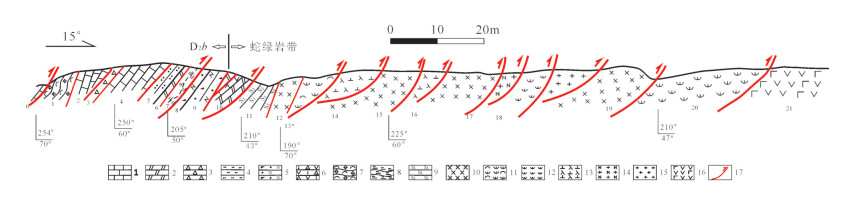
Geochemical characteristics and geological significance of basalt in the Armantai ophiolite, east Junggar, Xinjiang
-
摘要:
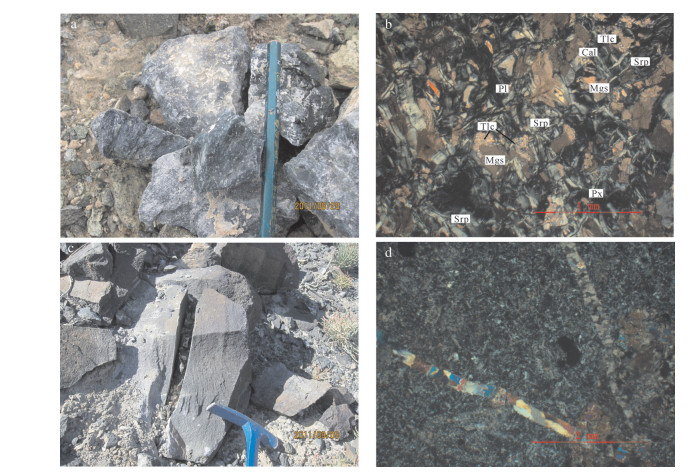
阿尔曼太蛇绿岩带位于新疆东准噶尔地区,蛇绿岩中变质橄榄岩、堆晶岩、基性火山岩较发育,层序组合虽受构造破坏,但从总体来看仍是一套组合比较完整的蛇绿岩,岩石变形变质强烈,普遍发生绿泥石化、绿帘石化。蛇绿岩中基性熔岩可分为3种类型,即洋岛玄武岩(OIB)、洋中脊玄武岩(MORB)和岛弧玄武岩(IAT)。其中洋岛玄武岩不属于蛇绿岩成分,是后期卷入蛇绿岩带随其他组分一同构造就位而成;基性熔岩主量和微量元素特征揭示岩浆源于亏损的地幔源区,且存在消减组分加入的交代作用,表明其成因与俯冲作用有关。结合岩石地球化学特征和构造环境判别图解,基性熔岩显示出IAT和MORB兼具并呈现过渡的特点,推断该蛇绿岩的形成与岛弧相关,其形成可能介于洋脊到海沟之间的偏海沟区域。
Abstract:The Armantai ophiolite belt is located in the east Junggar basin of Xinjiang. Metamorphic peridotite, cumulate rocks and basic volcanic rocks in the ophiolite belt are extensively developed. In spite of the fact that the sequence combination has been damaged by the structure, it on the whole remains a set of ophiolites with relatively complete assemblage. The rocks were deformed and experienced strong metamorphism, and have generally experienced chloritization and epidotization. The basic lava of Armantai ophiolite can be divided into three types, i.e., oceanic island basalt, oceanic ridge basalt and island arc basalt. Among them, oceanic island basalt did not belong to the ophiolite composition, it was involved in ophiolite belt at a later stage with other components into tectonic emplacement. The characteristics of major elements and trace elements of the basic lava show that the magma was derived from the depleted mantle and experienced metasomatism with the addition of the components of subduction zone. It is shown that its was related to the subduction. Combined with the tectonic setting and geochemical diagrams, the basic lava shows both IAT and MORB features and has the transitional characteristics. It can be inferred that the formation of the ophiolite was related to island arcs, and it probably occurred in partial oceanic trench region between oceanic ridge and oceanic trench.
-
Keywords:
- Armantai ophiolite /
- geochemical characteristics /
- tectonic environment /
- East Junggar /
- Xinjiang
-
致谢: 野外工作得到中国地质调查局西安地质调查中心王洪亮副主任、马中平研究员、朱涛等同事的指导与帮助,文章编写中得到西安地质调查中心冯益明、朱宝清等专家的帮助与指导,审稿专家提出宝贵的修改意见,岩石地球化学测试工作得到西安地质调查中心测试中心的帮助,在此一并致谢。
-
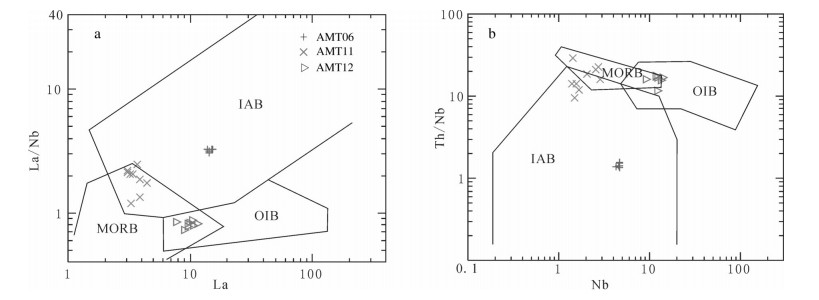
图 8 (Th/Nb)N-Nb/La图解(a)和Zr-Zr/Y图解[24](b)
WPB—板内玄武岩;MORB—洋中脊玄武岩;IAB—岛弧玄武岩
Figure 8. (Th/Nb)N-Nb/La(a)and Zr-Zr/Y(b)diagrams
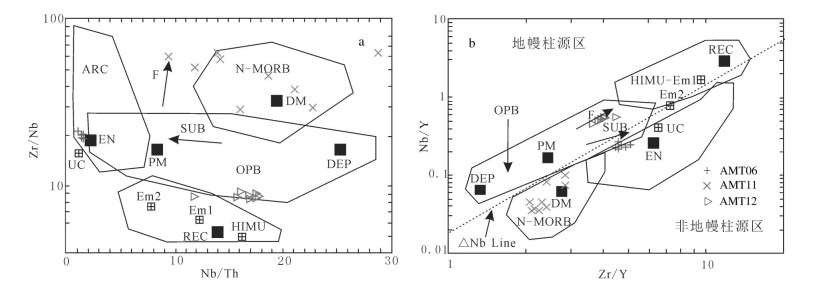
图 11 基性岩Zr/Nb-Nb/Th(a)和Nb/Y-Zr/Y(b)图解[27]
DEP—高度亏损地幔;EN—富集单元,包括上地壳和大陆岩石圈,后者可能具有消减带化学特征;REC—循环单元,包括Em1、Em2和HIMU;HIMU—高(U/Pb)地幔源区;Em1、Em2—富集地幔源区;UC—大陆上地壳;ARC—岛弧产生的玄武岩;N-MORB—洋脊玄武岩;OIB—洋岛玄武岩;OPB—洋底玄武岩;PM—原始地幔;DM—浅部亏损地幔单元。单箭头指示批次熔融(F)和俯冲流体(SUB)作用,△Nb线为地幔柱源区和非地幔柱源区的分界线
Figure 11. Zr/Nb-Nb/Th (a) and Nb/Y-Zr/Y (b) diagrams of basic lava
表 1 阿尔曼太基性岩主量、微量和稀土元素含量
Table 1 Major, trace and rare earth elements compositions
样品 SiO2 TiO2 Al2O3 Fe2O3 FeO MnO MgO CaO Na2O K2O P2O5 烧失量 总计 Mg# Cu Pb Zn Cr Ni Co Li Rb Cs Mo Sr Ba AMT06-1 47.11 0.77 15.92 3.53 5.19 0.15 8.51 4.85 3.68 4.29 0.2 5.79 99.99 0.65 57.8 5.29 76.1 406 131 36.3 23.4 170 11.8 0.2 91.2 162 AMT06-2 48.12 0.85 17.14 3.17 4.85 0.12 7.17 3.93 4.3 4.42 0.21 5.72 100 0.63 61.1 5.85 75.1 130 30.4 25.3 28.8 164 10.9 0.35 82.3 193 AMT06-3 47.9 0.88 17.23 3.31 5.1 0.13 7.04 3.96 3.86 4.79 0.22 5.57 99.99 0.61 63.1 3.02 72.2 132 27.5 25.3 32.8 165 11.3 0.64 67.8 273 AMT06-4 47.46 0.83 16.73 2.98 5.18 0.13 7.58 4.29 4.12 4.49 0.21 6.02 100.02 0.63 67.6 3.38 73.9 181 50 24.2 29.1 172 11.6 1.01 89.2 210 AMT06-5 48 0.8 16.57 3.21 4.93 0.14 7.44 4.45 4.34 3.95 0.22 5.96 100.01 0.63 71.5 4.88 72.1 191 66.2 28.9 26.3 146 9.65 0.67 108 175 AMT06-6 48.38 0.8 16.8 3.03 5.19 0.13 6.96 4.74 4.13 3.97 0.2 5.68 100.01 0.61 69.8 3.64 68.4 255 76.4 29.7 29.3 144 8.95 0.54 91.2 258 样品 V Sc Nb Ta Zr Hf Ga U Th La Ce Pr Nd Sm Eu Gd Tb Dy Ho Er Tm Yb Lu Y ΣREE δEu AMT06-1 219 26 4.24 0.35 85.5 1.85 16.9 0.96 3.07 13.9 30 3.88 16.2 3.64 0.96 3.5 0.51 3.52 0.72 2.02 0.29 1.77 0.28 18.9 81.2 0.81 AMT06-2 232 25.7 4.63 0.4 94.1 2.12 18 0.95 3.25 15.1 31.7 4.04 16.6 3.7 1.05 3.59 0.49 3.71 0.76 2.17 0.34 2 0.31 18.8 85.6 0.87 AMT06-3 245 27.4 4.69 0.36 96.9 2.03 18.2 0.87 3.05 14.3 30.9 4.01 17.1 3.99 1.08 3.6 0.55 4.07 0.77 2.34 0.32 2.18 0.35 20.3 85.6 0.85 AMT06-4 233 25.5 4.64 0.35 89.4 1.94 16.5 0.9 3 14.2 30.9 3.84 15.8 3.88 1.13 3.38 0.53 3.78 0.75 2.23 0.3 1.97 0.32 19.3 83 0.93 AMT06-5 212 24.1 4.64 0.4 94.8 2.15 17.4 1 3.4 15.2 32.2 4.07 16.8 3.96 1.19 3.66 0.54 3.5 0.76 2.19 0.3 2.02 0.33 19.7 86.7 0.94 AMT06-6 224 26.3 4.53 0.34 88.1 1.94 17.3 0.95 3.21 14.3 30.5 3.98 16.3 3.74 1.02 3.41 0.53 3.56 0.74 2.16 0.29 2.01 0.28 18.6 82.8 0.85 样品 SiO2 TiO2 Al2O3 Fe2O3 FeO MnO MgO CaO Na2O K2O P2O5 烧失量 总计 Mg# Cu Pb Zn Cr Ni Co Li Rb Cs Mo Sr Ba AMT11-1 45.24 1.55 12.61 4.22 7.93 0.22 4.13 13.26 3.93 0.52 0.15 6.18 99.94 0.39 93.3 1.86 91.8 166 76.9 43 14.2 12.2 1.67 0.8 343 139 AMT11-2 46.81 1.71 12.67 3.66 8.43 0.21 4.53 11.16 4.55 0.23 0.25 5.78 99.99 0.41 65.2 0.86 98.1 137 76.7 43.4 12.2 6.86 0.94 0.4 212 60 AMT11-3 48.04 1.62 12.72 3.39 8.18 0.19 4.85 10.82 4.52 0.22 0.23 5.2 99.98 0.44 62.8 1.55 101 132 51 37.6 13.1 5.67 0.64 0.87 269 93.5 AMT11-4 45.2 1.57 13.2 3.38 9.1 0.19 4.67 10.9 4.2 0.58 0.19 6.8 99.98 0.41 77.4 1.84 105 124 50.7 41.1 13 18.6 2.2 0.51 266 93.3 AMT11-5 47.45 1.65 12.77 3.76 8.08 0.2 4.8 10.98 4.39 0.33 0.24 5.34 99.99 0.43 53 2.53 99.9 129 45.5 37 12.3 9.3 0.97 0.85 276 113 AMT11-6 44.48 1.62 13.1 4.24 8.69 0.21 4.76 11.44 4.02 0.58 0.18 6.69 100.01 0.41 94 1.8 104 132 55.4 42.2 13.8 17.6 2.18 0.48 238 77.8 AMT11-7 45.21 1.57 13.8 3.65 7.48 0.18 4 12.54 4.1 0.61 0.2 6.64 99.98 0.4 110 2.31 87.1 125 61.1 42.8 13.6 14.8 1.96 0.28 353 140 AMT11-8 45.23 1.34 13.49 4.13 5.46 0.17 4 16.11 3.3 0.47 0.16 6.13 99.99 0.44 89 1.88 61 95.8 48.1 36 9.04 10 1.4 0.24 238 128 AMT11-9 46.42 1.44 10.65 3.62 9.45 0.34 5.06 14.44 3.22 0.35 0.16 4.84 99.99 0.42 62.8 0.61 97.3 105 50.7 44.8 12.9 7.94 0.92 0.09 176 78.2 样品 V Sc Nb Ta Zr Hf Ga U Th La Ce Pr Nd Sm Eu Gd Tb Dy Ho Er Tm Yb Lu Y ΣREE δEu AMT11-1 300 41.3 1.66 0.2 84.9 2.02 15.8 0.27 0.14 3.41 10.2 1.83 10.7 3.97 1.25 4.97 0.81 6.02 1.33 3.96 0.54 3.79 0.56 36.6 53.3 0.86 AMT11-2 314 45.8 2.06 0.17 94 2.29 14.8 0.24 0.11 3.86 11 2.13 12.3 4.51 1.51 5.97 0.95 7.12 1.64 4.78 0.69 4.62 0.7 45.1 61.8 0.89 AMT11-3 308 46.8 1.57 0.097 90.5 2.17 13.6 0.27 0.11 3.24 9.75 1.77 11.6 4.09 1.4 5.32 0.85 6.7 1.54 4.53 0.62 4.25 0.62 41.7 56.3 0.91 样品 V Sc Nb Ta Zr Hf Ga U Th La Ce Pr Nd Sm Eu Gd Tb Dy Ho Er Tm Yb Lu Y ΣREE δEu AMT11-4 319 44.6 1.4 0.11 88.3 2.06 15.1 0.21 0.1 3.06 9.39 1.79 10.6 3.96 1.3 5.18 0.8 6.23 1.46 4.35 0.62 4.07 0.6 39 53.4 0.87 AMT11-5 299 45.5 1.51 0.11 89.9 1.98 13.7 0.31 0.16 3.7 10.5 1.97 11.5 3.9 1.29 5.55 0.88 6.78 1.45 4.64 0.66 4.2 0.62 42.3 57.6 0.84 AMT11-6 312 43.3 1.44 0.14 90.2 1.97 17.8 0.23 0.05 3.08 9.4 1.73 10.8 3.88 1.18 5.09 0.82 6.08 1.28 4.1 0.6 3.62 0.54 37.2 52.2 0.81 AMT11-7 286 41.6 2.53 0.15 96.4 2.15 18.6 0.27 0.12 4.39 12 2.04 11.3 3.93 1.05 4.8 0.74 5.56 1.24 3.83 0.51 3.25 0.48 33.6 55.1 0.74 AMT11-8 264 36.9 2.89 0.21 83.4 1.71 19.5 0.26 0.18 3.89 10.4 1.7 10.2 3.22 0.99 4.16 0.67 4.75 1.03 3.27 0.49 3 0.44 29.1 48.2 0.82 AMT11-9 301 42 2.74 0.19 80.5 1.79 13.8 0.24 0.12 3.26 9.38 1.54 9.29 3.72 1 4.39 0.7 5.34 1.16 3.74 0.5 3.31 0.48 33.2 47.8 0.75 样品 SiO2 TiO2 Al2O3 Fe2O3 FeO MnO MgO CaO Na2O K2O P2O5 烧失量 总计 Mg# Cu Pb Zn Cr Ni Co Li Rb Cs Mo Sr Ba AMT12-1 47.69 1.62 14.04 2.1 9.36 0.16 8.56 8.58 3.49 0.2 0.17 4.01 99.98 0.58 87.3 1.19 99.2 528 285 56.8 24.6 3.9 0.33 0.3 309 102 AMT12-2 48.25 1.63 13.51 2.24 8.71 0.16 8.86 8.75 3.44 0.31 0.18 3.96 100 0.6 80 1.45 85 540 269 52.4 25.5 3.58 0.33 0.29 282 191 AMT12-3 47.4 1.48 14.08 1.78 7.6 0.14 7.27 9.75 3.88 0.58 0.19 5.85 100 0.59 66.1 1.04 81 431 192 46.2 25.7 6.15 0.48 0.22 225 439 AMT12-4 46.05 1.2 12.65 1.61 6.45 0.14 6.15 13.37 3.54 1.04 0.14 7.65 99.99 0.58 76.8 1.23 64.9 351 161 38.8 18.9 8.17 0.4 0.5 207 122
0AMT12-5 46.67 1.52 13.99 3.19 6.8 0.14 7.43 13.59 2.47 0.21 0.17 3.79 99.97 0.58 101 1.36 73.6 452 231 50.7 20.7 3.14 0.34 0.2 375 127 AMT12-6 44.58 1.4 13.1 1.86 8.34 0.16 8.12 11.85 2.98 0.6 0.16 6.83 99.98 0.59 71.9 1.2 81.4 443 214 49.2 28.8 6.49 0.56 0.18 234 554 AMT12-7 45.72 1.43 12.96 1.62 7.53 0.15 7.12 12.52 3.45 0.51 0.18 6.82 100.01 0.59 78.2 0.96 70.4 411 219 50 21.2 5.29 0.28 0.3 270 418 AMT12-9 47.3 1.39 14.91 2.85 7.59 0.14 7.3 11.19 2.69 0.34 0.14 4.14 99.98 0.56 48.1 1.05 79.9 422 200 45 24.9 3.66 0.19 0.33 381 273 样品 V Sc Nb Ta Zr Hf Ga U Th La Ce Pr Nd Sm Eu Gd Tb Dy Ho Er Tm Yb Lu Y ΣREE δEu AMT12-1 268 33.2 14.3 1.01 106 2.16 18.7 0.32 0.85 11.6 26.6 3.64 16.5 4.31 1.4 4.95 0.79 4.79 1 2.69 0.44 2.63 0.36 26.1 81.7 0.92 AMT12-2 267 34.3 13.6 1.01 104 2.16 17.7 0.32 0.87 10.8 24.7 3.51 16.2 3.79 1.33 4.68 0.75 4.68 0.97 2.68 0.44 2.45 0.34 25.4 77.3 0.96 AMT12-3 235 30 12 0.88 96.1 1.97 14.5 0.45 0.69 10.5 23.2 3.09 14.8 3.47 1.11 4.23 0.74 4.54 0.94 2.51 0.41 2.5 0.31 24.7 72.4 0.88 AMT12-4 196 24.7 9.29 0.78 75.9 1.56 13.1 0.3 0.58 7.83 18 2.44 11.3 2.74 1.2 3.59 0.59 3.65 0.8 2.1 0.34 2.12 0.28 20.5 57 1.17 AMT12-5 253 29.6 12.4 0.98 97.2 2.06 17.7 0.42 0.74 9.02 21.4 3.17 13.9 3.61 1.43 4.4 0.72 4.57 0.92 2.54 0.4 2.47 0.33 24.4 68.9 1.09 AMT12-6 233 29.4 12 0.87 90.3 1.83 15.6 0.56 0.69 10 23 3.16 13.7 3.52 1.26 4.28 0.69 4.17 0.84 2.25 0.37 2.34 0.31 22.7 69.9 0.99 AMT12-7 226 27.4 12 0.93 92 1.72 15.4 0.5 0.68 9.73 21.8 3.01 14.6 3.34 1.19 4.11 0.65 4.29 0.89 2.29 0.42 2.42 0.32 23.8 69.1 0.98 AMT12-9 212 27.8 12.6 0.87 104 2.13 21.6 0.39 1.09 9.76 23.5 3.15 14.3 3.41 1.41 4.2 0.67 4.3 0.87 2.33 0.39 2.57 0.29 22.9 71.2 1.13 注:Mg#=MgO/(MgO+TFeO)(分子数);主量元素含量单位为%,微量和稀土元素含量单位为10-6 表 2 阿尔曼太基性熔岩微量元素比值与不同地幔端元的对比
Table 2 Comparative studies of the trace element ratio in lava and different mantle elements
样品 Zr/Nb La/Nb Ba/Nb Ba/Th Rb/Nb Th/Nb Th/La Ba/La Th/U 原始地幔 14.8 0.94 9.0 77 0.91 0.117 0.125 9.6 4.1 亏损地幔 30.0 1.07 4.3 60 0.36 0.070 0.070 4.0 大陆地壳 16.2 2.20 54.0 124 4.70 0.440 0.200 25.0 3.8 HIMU 2.7~5.5 0.66~0.77 4.9~6.5 39~85 0.30~0.43 0.078~0.101 0.107~0.133 6.8~8.7 3.5~3.8 Em1 5.3~11.5 0.86~1.19 11.4~17.8 103~154 0.88~1.17 0.105~0.122 0.107~0.128 13.2~16.9 4.50~4.86 Em2 12.0~15.35 0.89~1.09 7.3~11.0 67~84 0.59~0.85 0.111~0.157 0.122~0.163 8.3~11.3 阿尔曼太基性熔岩对应不同地幔端元微量元素比值平均值 阿尔曼太
基性熔岩AMT06 20.05 3.18 46.34 67.25 35.17 0.69 0.22 14.65 3.37 AMT11 48.45 1.89 55.12 901.45 6.46 0.06 0.03 28.92 0.47 AMT12 7.82 0.81 37.75 614.86 0.43 0.06 0.08 45.56 2.00 注:HIMU为高(U/Pb)值地幔端元;Em1、Em2为富集地幔端元1和2;元素含量为平均值;地幔端元数据据贾大成等[28] -
张旗, 周国庆.中国蛇绿岩[M].北京:科学出版社, 2001:1-200. Dewey J F, Bird J M. Origin and emplacement of the ophiolite suite:Appalachian ophiolitesin Newfoundland[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1971, 76:3179-3206. doi: 10.1029/JB076i014p03179
Gass I G. Is the Troodos massif of Cyprus a fragment of Mesozoic ocean floor?[J]Nature, 1986, 220:39-42.
Coleman R G. Plate tectonic emplacement of upper mantle peridotites along continental edges[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1971, 76:1212-1222. doi: 10.1029/JB076i005p01212
Moores E M, Vine F J. The Troodos massif, Cyprus, and other ophiolites as oceanic crust:Evaluation and implications[J]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London, 1971, 268A:443-466.
Kidd R G W. A model for the process of formation of the upper oceanic crust[J]. Geophysical Journal of the Royal Astronmical Society, 1977, 50:149-183. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.1977.tb01328.x
Coleman R. Continental growth of Northwest China[J]. Tectonics, 1989, 8:621-635. doi: 10.1029/TC008i003p00621
Feng Y, Coleman R G, Tilton G, et al. Tectonic evolution of the west Junggar region, Xinjiang, China[J]. Tectonics, 1989, 8:729-752. doi: 10.1029/TC008i004p00729
李锦轶, 肖序常, 汤耀庆, 等.新疆东准噶尔卡拉麦里地区晚古生代板块构造的基本特征[J].地质论评, 1990, 36(4):305-316. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.1990.04.003 李锦轶.新疆东准噶尔蛇绿岩的基本特征和侵位历史[J].岩石学报, 1995, 11(增刊):73-84. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-YSXB5S1.005.htm 肖序常, 汤耀庆.古中亚复合巨型缝合带南缘构造演化[M].北京:科学出版社, 1991. 舒良树, 卢华复, 印栋浩, 等.新疆北部古生代大陆增生构造[J].新疆地质, 2001, 19(1):59-63. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8845.2001.01.011 Xiao W J, Windley B F, Badarch G, et al. Palaeozoic accretionary and convergent tectonics of the southern Altaids:implications for the lateral growth of Central Asia[J]. J. Geol. Soc., London, 2004, 161:339-342. doi: 10.1144/0016-764903-165
Xiao W J, Zhang L C, Qin K Z, et al. Paleozoic accretionary and collisional tectonics of the Eastern Tianshan (China):Implications for the continental growth of central Asia[J]. Am. J. Sci., 2004, 304:370-395. doi: 10.2475/ajs.304.4.370
刘伟, 张湘炳.乌伦古-斋桑泊构造杂岩带特征及其地质意义[C]//涂光炽.新疆北部固体地球科学新进展.北京: 科学出版社, 1993: 217-228. 黄萱, 金成伟, 孙宝山, 等.新疆阿尔曼太蛇绿岩时代的Nd、Sr同位素研究[J].岩石学报, 1997, 13(1):85-91. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0569.1997.01.007 Wang Z H, Sun S, Li J L, et al. Paleozoic tectonic evolution of the northern Xinjiang, China:Geochemical and geochronolgical constrains from the ophiolites[J]. Tectonics, 2003, 22(2):1014.
孙桂华, 李锦铁, 高立明, 等.新疆东部哈尔里克山闪长岩锆石SHRIMP U-Pb定年及其地质意义[J].地质论评, 2005, 51(4):463-469. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.2005.04.015 何国琦, 李茂松, 刘德权, 等.中国新疆古生代地壳演化与成矿[M].乌鲁木齐:新疆人民出版社, 香港文化教育出版社, 1994. Pearce, J A, Lippard S J, Roberts S. Characteristics and tectonic significance of supra-subduction zone ophiolites[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publication, 1984, 16:77-94. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.1984.016.01.06
Wilson M. Igneous Petrogenesis[M]. London:Unwin Hyman, 1989:21-22.
Melson W G, Vallier T L, Wright T L. Chemical diversity of abyssal volcanic glass erupted along Pacific, Atlantic and Indian Ocean sea-floor spreading centers[C]//The geophysics of the Pacific Ocean Basin and its Margin. Washington D C. Am. Geophys. Union, 1976: 351-367.
Sun S S, McDonough W F. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalt: Implications for mantle composition and process[C]//Saunders A D, Norry M J. Magmatism in the Ocean Basins. Spc. Publ. Geol. Soc. Lond., 1989, 42: 313-345.
夏林圻, 夏祖春, 徐学义, 等.利用地球化学方法判别大陆玄武岩和岛弧玄武岩[J].岩石矿物学杂志, 2007, 26(1):77-89. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2007.01.011 Elthon D. Geochemical evidence for formation of the Bay of Islands ophiolite above a subduction zone[J]. Nature, 1991, 354:140-143. doi: 10.1038/354140a0
周国庆.蛇绿岩的概念及其演变[C]//张旗.蛇绿岩与地球动力学研究[M].北京: 地质出版社, 1996: 15-20 Condie K C. High field strenches element ratios in Archean basalts:a window to evolving sources of mantle plumes?[J]. Lithos, 2005, 79:491-504. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2004.09.014
贾大成, 胡瑞忠, 卢焱, 等.湘东北钠质煌斑岩地幔源区特征及成岩构造环境[J].中国科学(D辑), 2003, 33(4):344-352. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgkx-cd200304007




 下载:
下载: