Chemical speciation and bioavailability of five heavy metals in soil of Beijing plain area in two years
-
摘要:
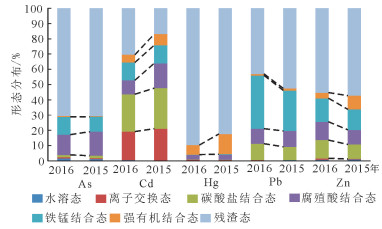
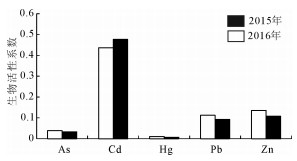
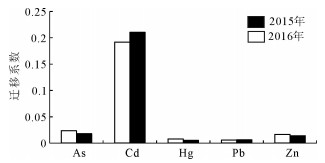
为了监测北京市平原区2015年和2016年土壤中5种重金属As、Cd、Hg、Pb、Zn化学形态的变化趋势,运用Tessier连续提取法对土壤重金属进行了形态分析,并对影响重金属元素生物有效性的因素进行研究。结果表明,2年内研究区表层土壤重金属元素的形态变化微弱,有效态含量以Cd元素最高,达到45.67%,故潜在生态危害性最大;其次为Zn元素,达12.16%,其中碳酸盐结合态占比虽大,但由于研究区土壤呈偏碱性,Zn元素的迁移能力较弱,潜在危害性较小;As、Hg、Pb均以难迁移态存在,故潜在危害性也较小。土壤重金属元素的生物活性系数及迁移系数分别为:Cd > Zn > Pb > As > Hg和Cd > As > Zn > Pb=Hg,其中Cd元素2年的生物活性系数和迁移系数最高,展现出较强的生物活性和迁移能力,其余重金属元素的活性系数和迁移系数较低,潜在危害性较弱。影响重金属元素生物有效性的因素较复杂,以重金属元素全量为主,pH、有机质、CEC等理化性质次之。
Abstract:To effectively monitor the overall variation trend of the chemical forms for 5 heavy metals (As, Cd, Hg, Pb and Zn) in the soil in Beijing plain area during the year 2015 and 2016, the authors employed the Tessier sequential extraction method to ana-lyze the morphological characteristics of these soil heavy minerals. The authors studied the factors controlling the bio-availability of these heavy minerals. The results show that there is only minor change in the morphology of soil heavy metals in these 2 years. The element with highest effective concentration is Cd (45.67%), which thus poses greatest potential ecological risk. The following ele-ment is Zn with concentration of 12.16%. Though Zn is largely incorporated in carbonates, the mobility of Zn is reduced by the al-kaline soil, thus having less ecologically hazardous effect. The elements As, Hg and Pb are immobile with little potential hazards on ecology. The orders of activity coefficients and migration coefficients of the heavy metal elements in topsoil in the study area are Cd > Zn > Pb > As > Hg and Cd > As > Zn > Pb=Hg respectively. This suggests that Cd has the highest values in both the 2-year biological activity coefficient and transfer coefficient, implying a strong biological activity and migration capability, while other soil heavy metals have smaller activity coefficients and migration coefficients, indicating relatively low potential ecological risks. In the study area, the factors that affect the bio-availability of heavy metals are complex, and the dominant one is the total amount of heavy metal elements, followed by pH, organic matter, CEC, and other physical and chemical properties, and the connections of these factors are complicated.
-
Keywords:
- Beijing /
- soil /
- heavy metal /
- morphology /
- bioavailability
-
-
表 1 供试土壤基本理化性质
Table 1 Basic physico-chemical properties of studied soils
年份 理化参数 范围 平均值±标准差 中值 2015年 有机质/% 0.24~6.59 1.07±0.83 0.95 PH 7.2~8.34 7.9±0.26 7.99 CEC/(cmol·kg-1) 4.88~18.16 11.81±3.04 11.76 2016年 有机质/% 0.17~8.59 1.38±1.22 1.17 PH 7.23~9.08 8.1±0.38 8.20 CEC/(cmol·kg-1) 3.63~23.36 11.28±3.67 11.38 粒径/% 砂粒(2~0.2mm) 0.6~69.8 14.85±13.27 10.15 粘粒(< 0.002mm) 3.1~25.3 13.68±4.19 13.95 注:CEC代表阳离子交换量 表 2 表层土壤中重金属元素不同形态统计参数(n=120)
Table 2 Statistical parameters of different forms of heavy metal elements in topsoil
mg/kg 元素 年份 参数 水溶态 离子交换态 碳酸盐结合态 腐殖酸结合态 铁锰结合态 强有机结合态 残渣态 As 2016年 范围 0.03~0.55 0.01~0.17 0.01~0.51 0.21~2.58 0.36~2.49 0.01~0.38 1.4~12.3 平均值±标准差 0.147±0.093 0.061±0.038 0.134±0.099 1.170±0.513 1.034±0.423 0.050±0.094 6.228±2.217 变异系数 0.63 0.62 0.74 0.44 0.41 1.89 0.36 2015年 范围 0.009~0.36 0~0.318 0.018~0.85 0.285~3.331 0.138~2.558 0~0.321 1.098~13.92 平均值±标准差 0.114±0.079 0.046±0.045 0.135±0.145 1.397±0.528 0.873±0.468 0.036±0.059 6.249±1.967 变异系数 0.69 0.99 1.08 0.38 0.54 1.63 0.31 Cd 2016年 范围 0.0006~0.008 0.009~0.41 0.01~0.44 0.003~0.340 0.003~0.42 0.006~0.048 0.02~0.28 平均值±标准差 0.002±0.002 0.062±0.070 0.082±0.090 0.031±0.052 0.039±0.065 0.017±0.008 0.102±0.0517 变异系数 0.73 1.13 1.10 1.69 1.68 0.50 0.51 2015年 范围 0.001~0.005 0.007~0.91 0.02~1.05 0.001~0.684 0.005~0.21 0.002~0.108 0.008~0.135 平均值±标准差 0.001±0.001 0.059±0.122 0.077±0.147 0.047±0.101 0.034±0.041 0.021±0.021 0.049±0.025 变异系数 0.68 2.06 1.91 2.14 1.2 0.98 0.51 Hg 2016年 范围 0.0005~2.4022 0.0006~2.0355 0.00001~.58646 0.0034~1.9066 0.0004~.7146 0.0011~3.3235 0.0039~1.655 平均值±标准差 0.003±0.007 0.0034±0.0068 0.0022±0.0034 0.0230±0.0438 0.00176±.0013 0.0507±0.1687 0.7265±.2198 变异系数 2.40 2.04 1.59 1.91 0.71 3.32 4.43 2015年 范围 0.0002~0.0239 0.0001~0.0035 0.0001~0.0107 0.0003~0.2382 0~0.0207 0.0003~2.511 0.0053~14.9496 平均值±标准差 0.0029±0.0042 0.0005±0.0006 0.0013±0.0019 0.022±0.0377 0.0015±0.0029 0.0862±0.4097 0.5366±.4705 变异系数 1.43 1.14 1.48 1.72 1.89 4.75 4.6 Pb 2016年 范围 0.003~1.02 0.001~0.22 0.46~22.9 0.3~24.3 2.32~53.5 0.012~3.24 7.45~41.9 平均值±标准差 0.133±0.160 0.053±0.0580 3.577±3.863 3.291±3.934 11.688±8.937 0.330±0.472 14.392±6.917 变异系数 1.20 1.10 1.08 1.20 0.76 1.43 0.48 2015年 范围 0.0019~1.21 0.0001~0.22 0.06~25.65 0.51~31.68 1.98~45.5 0.06~1.84 9.54~41.5 平均值±标准差 0.172±0.255 0.029±0.044 2.683±4.189 3.248±4.48 8.333±7.918 0.425±0.439 16.438±6.81 变异系数 1.48 1.49 1.56 1.38 0.95 1.03 0.41 Zn 2016年 范围 0.010~3.95 0.005~18.8 0.2~170 1.85~265 2.08~173 0.57~16.4 29.5~106 平均值±标准差 0.741±0.620 0.935±2.537 12.099±23.299 12.226±33.851 15.663±24.414 3.725±2.730 56.08±14.781 变异系数 0.84 2.71 1.93 2.77 1.56 0.73 0.26 2015年 范围 0.02~9.009 0.1~1.53 0.18~63.6 1.88~39.95 2.66~76.78 1.11~39 26.9~184 平均值±标准差 0.893±1.317 0.386±0.282 8.445±11.914 8.706±7.592 12.124±10.793 8.149±7.03 51.84±21.084 变异系数 1.48 0.73 1.41 0.87 0.89 0.86 0.41 表 3 不同形态重金属元素所占比例与土壤理化性质的相关分析(n=120)
Table 3 Correlation coefficients between percentage of heavy metal fractions and soil properties
元素 形态 全量 pH Corg CEC 砂粒(2~0.2mm) 粘粒(< 0.002mm) As 水溶态 0.534** -0.170 0.209* 0.159 -0.082 0.119 离子交换态 0.144 0.199* 0.160 -0.133 -0.223* -0.077 碳酸盐结合态 0.389** -0.161 0.244** 0.148 -0.099 -0.015 Cd 水溶态 0.582** -0.048 0.287** 0.102 -0.088 0.107 离子交换态 0.955** -0.297** 0.292** 0.251** 0.033 -0.022 碳酸盐结合态 0.942** -0.199* 0.333** 0.144 0.008 -0.069 Hg 水溶态 0.472** -0.067 0.082 0.091 0.024 0.076 离子交换态 0.020 0.090 0.046 -0.093 -0.096 0.193 碳酸盐结合态 0.042 -0.327** 0.105 0.205* -0.048 0.176 Pb 水溶态 0.609** -0.145 0.112 0.124 0.112 0.054 离子交换态 0.567** -0.203* 0.310** 0.173 -0.035 0.187 碳酸盐结合态 0.828** 0.265** 0.386** 0.002 -0.152 -0.011 Zn 水溶态 0.203* -0.235** 0.141 0.221* -0.158 0.121 离子交换态 0.823** -0.311** 0.263** 0.231* 0.015 0.144 碳酸盐结合态 0.928** -0.315** 0.412** 0.208* -0.019 0.186 注:**表示显著性水平为0.01;*表示显著性水平为0.05; Corg代表有机质; CEC代表阳离子交换量 -
Zhong X L, Zhou S L, Zhu Q, et al. Fraction distribution and bioavailability of soil heavy metals in the Yangtze River Delta:A case study of Kunshan City in Jiangsu province, China[J]. Journal of haz-ardous materials, 2011, 198(30):13-21. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=54c013fb2633f4b60da97e8375fabe1d&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
陈涛, 常庆瑞, 刘京.长期污灌农田土壤Cd赋存形态及其有效性的空间变异研究[J].农业环境科学学报, 2014, 33(7):1322-1327. doi: 10.11654/jaes.2014.07.010 覃朝科, 农泽喜, 黄伟, 等.广西某铅锌矿区农田土壤重金属形态分布特征[J].安徽农业科学, 2016, 44(15):146-149. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2016.15.051 陈怀满.环境土壤学(第二版)[M].北京:科学出版社, 2005:187-193. 郭世鸿, 侯晓龙, 邱海源, 等.基于形态学分析铅锌矿不同功能区土壤重金属元素的分布特征及污染评价[J].地质通报, 2015, 34(11):2047-2053. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2015.11.008 Bhuiyan M A H, Parvez L, Islam M A, et al. Heavy metal pollution of coal mine-affected agricultural soils in the northern part of Bangladesh[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2010, 173:384-392. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.08.085
Yenilmez F, Kuter N, Emil M K, et al. Evaluation of pollution levels at an abandoned coal mine site in Turkey with the aid of GIS[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology, 2011, 86:12-19. doi: 10.1016/j.coal.2010.11.012
贾赵恒, 罗瑶, 沈友刚, 等.大冶龙角山矿区农田土壤重金属形态分布及其来源[J].农业环境科学学报, 2017, 36(2):264-271. doi: 10.11654/jaes.2016-1116 崔邢涛, 王学求, 栾文楼.河北中南部平原土壤重金属元素存在形态及生物有效性分析[J].中国地质, 2015, 42(2):655-663. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgdizhi201502023 庞文品, 秦樊鑫, 吕亚超, 等.贵州兴仁煤矿区农田土壤重金属化学形态及风险评估[J].应用生态学报, 2016, 27(5):1468-1478. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-YYSB201605017.htm Tessier A, Campbell P G C, Blsson M. Sequential Extraction Procedure for the Speciation of Partculate Trace Metals[J].Analytical Chemistry, 1979, 51(7):844-851. doi: 10.1021/ac50043a017
Adriano D C. Trace Elements in Terrestrial Environments:Biogeochemistry, Bioavailability and Risk of Metals, 2nd ed[M]. Springer, New York, 2001.
胡绵好, 袁菊红, 黄和平.南昌市城市污泥重金属形态分布及其生物活性研究[J].水土保持通报, 2010, 30(5):63-67. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-HJKZ201304021.htm Kidd P S, Dominguez-Rodriguez M J, Diez J, et al. Bioavailability and plant accumulation of heavy metals and phosphorus in agricultural soils amended by long-term application of sewage sludge[J]. Chemosphere, 2007, 66:1458-1467. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2006.09.007
Pueyo M, Lopex-Sanchez J F, Rauret G. Assessment of CaCl2, Na-NO3 and NH4NO3 Extraction Procedures for the Study of Cd, Cu, Pb and Zn Extraction in Contaminated Soils[J]. Analytica Chimiea Acta, 2004, 504(2):217-226. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2003.10.047
张萌, 毋燕妮, 解静芳, 等.太原市污灌区土壤镉存在形态与生物可利用性研究[J].环境科学学报, 2015, 35(10):3276-3283. http://www.oalib.com/paper/4506003 孙海, 张亚玉, 孙长伟, 等.林下参土壤中重金属形态分布及生态风险评估[J].农业环境科学学报, 2014, 33(5):928-934. doi: 10.11654/jaes.2014.05.015 刘勇, 岳玲玲, 李晋昌.太原市土壤重金属污染及其潜在生态风险评价[J].环境科学学报, 2011, 31(6):1285-1293. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NHBH201211016.htm 王振中, 张友梅, 邓继福, 等.重金属在土壤生态系统中的富集及毒性效应[J].应用生态学报, 2006, 17(10):1948-1952. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-9332.2006.10.033 傅晓文, 陈贯虹, 迟建国, 等.胜利油田石油污染土壤中重金属的形态分析[J].山东科学, 2015, 28(4):58-64. doi: 10.3976/j.issn.1002-4026.2015.04.011 成杭新, 庄广民, 赵传冬, 等.北京市土壤Hg污染的区域生态地球化学评价[J].地学前缘, 2008, 15(5):126-145. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-BJLY201301027.htm 吴昆明, 朱立新, 马生明, 等.冲积平原区土壤中重金属元素的存在形态分析[J].分析测试学报, 2004, 23(2), 41-43. http://www.cqvip.com/qk/95913A/200402/9460482.html McCarty L S, Mackay D. Enhancing eco-toxicological modeling and assessment, body residues and modes of action[J]. Environmental Science and Technology, 1993, 27:1719-1728. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/246073230_Enhancing_Ecotoxicological_Modeling_and_Assessment_Body_Residues_and_Modes_of_Toxic_Action
安永龙, 黄勇, 刘清俊, 等.苹果产地土壤环境与地质背景研究[J].城市地质, 2016, 11(3):36-43. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/88732X/201603/7000036592.html 栾文楼, 刘洪微, 温小亚, 等.冀东平原土壤重金属元素的存在形态及有效性分析[J].中国地质, 2010, 37(2):508-514. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/90050X/201502/664376534.html 刘清俊, 黄勇, 胡省英, 等.北京城区土壤中Hg、Pb、Cd、Cu及Zn化学形态及环境效应[J].城市地质, 2015, 10(4):11-15. http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/magadetail/CSDZ201504.htm Li J X, Yang X E, He Z L, et al. Fractionation of lead in paddy soils and its bioavailability to rice plants[J]. Geoderma., 2007, 141(3/4):174-180. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=1305ad0817c82e8b8035c424559878f8&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
叶宏萌, 李国平, 郑茂钟, 等.武夷山茶园土壤中五种重金属的化学形态和生物有效性[J].环境化学, 2016, 35(10):2071-2078. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2016.10.2016022304 徐聪珑, 贾丽, 张文卿, 等.吉林省镍矿区土壤重金属Cu、Ni、Pb、Zn的形态分布特征及活性[J].吉林农业大学学报, 2016, 38(3):313-319. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-JLNY201603011.htm 张江华, 王葵颖, 李皓, 等.陕西潼关金矿区土壤Pb和Cd生物有效性的影响因素及其意义[J].地质通报, 2014, 33(8):1188-1195. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20140812&flag=1 黄碧捷.土壤重金属生物可利用性研究趋势展望[J].江汉大学学报(自然科学版), 2013, 41(6):38-43. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JLNK200905010.htm 胡宁静, 骆永明, 黄朋, 等.碱性土壤对Pb的吸附特性:内圈吸附和形成沉淀的XAFS证据[J].光谱学与光谱分析, 2011, 33(2):560-564. http://www.docin.com/p-1016807942.html 周国华.土壤重金属生物有效性研究进展[J].物探与化探, 2014, 38(6):1097-1106. doi: 10.11720/wtyht.2014.6.01 蔡奎, 段亚敏, 栾文楼, 等.石家庄农田区土壤重金属Cd、Cr、Pb、As、Hg形态分布特征及其影响因素[J].地球与环境, 2014, 42(6):742-749. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzdqhx201406006 戴前进, 冯新斌, 仇广乐, 等.陕西省潼关采金地区汞污染的初步研究[J].环境化学, 2004, 23(4):460-464. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/95665X/200404/10895522.html



 下载:
下载: