Discovery of hydrothermal beryllium deposit in the Changshan area of Northwest Zhejiang Province
-
摘要:研究目的
铍属于国家战略关键金属,其成矿机制、成矿规律及资源潜力研究对于寻找铍矿具有重要意义。
研究方法通过对浙西北常山地区进行铍矿调查与找矿,结合电子探针化学成分分析,
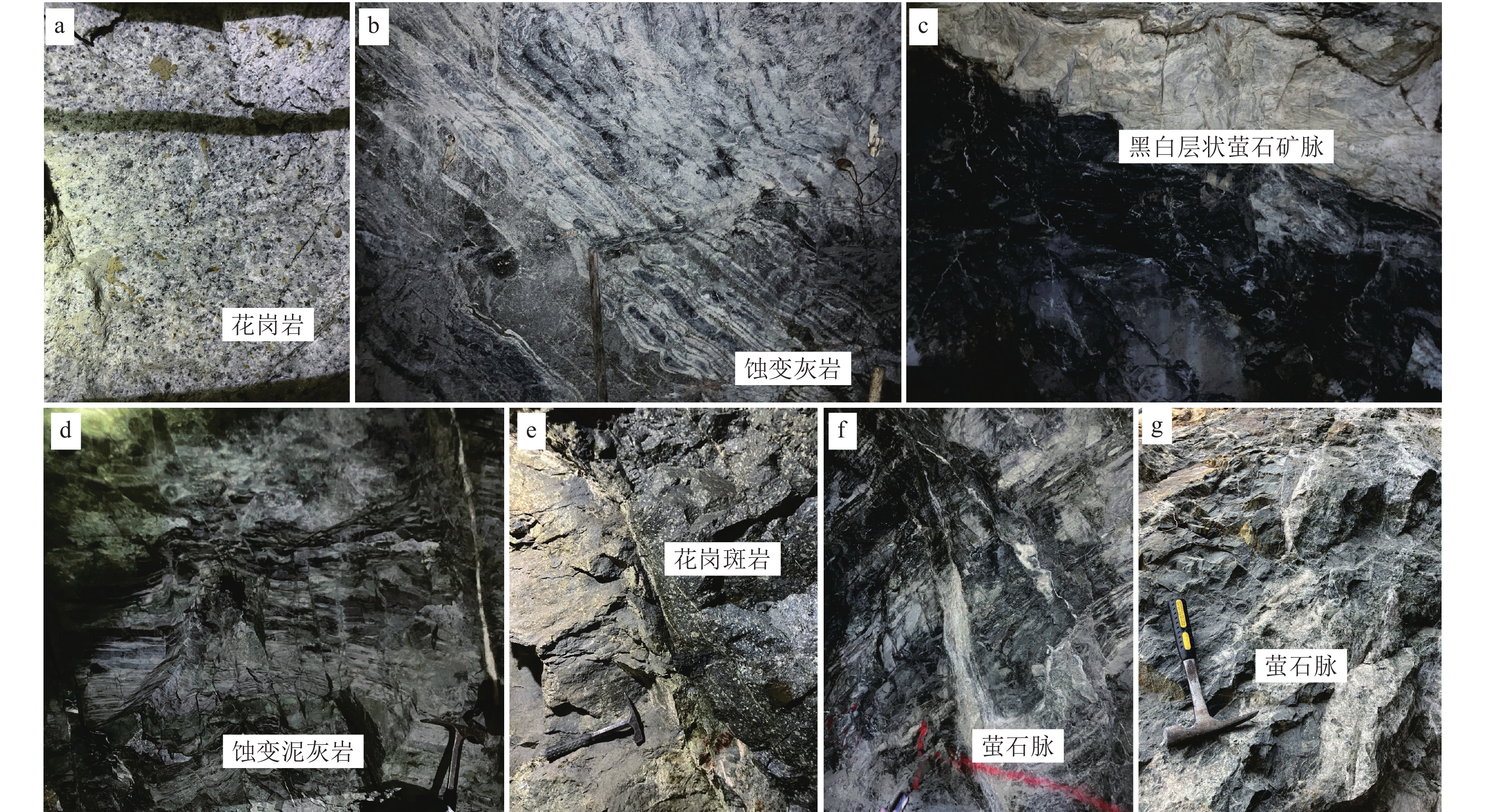
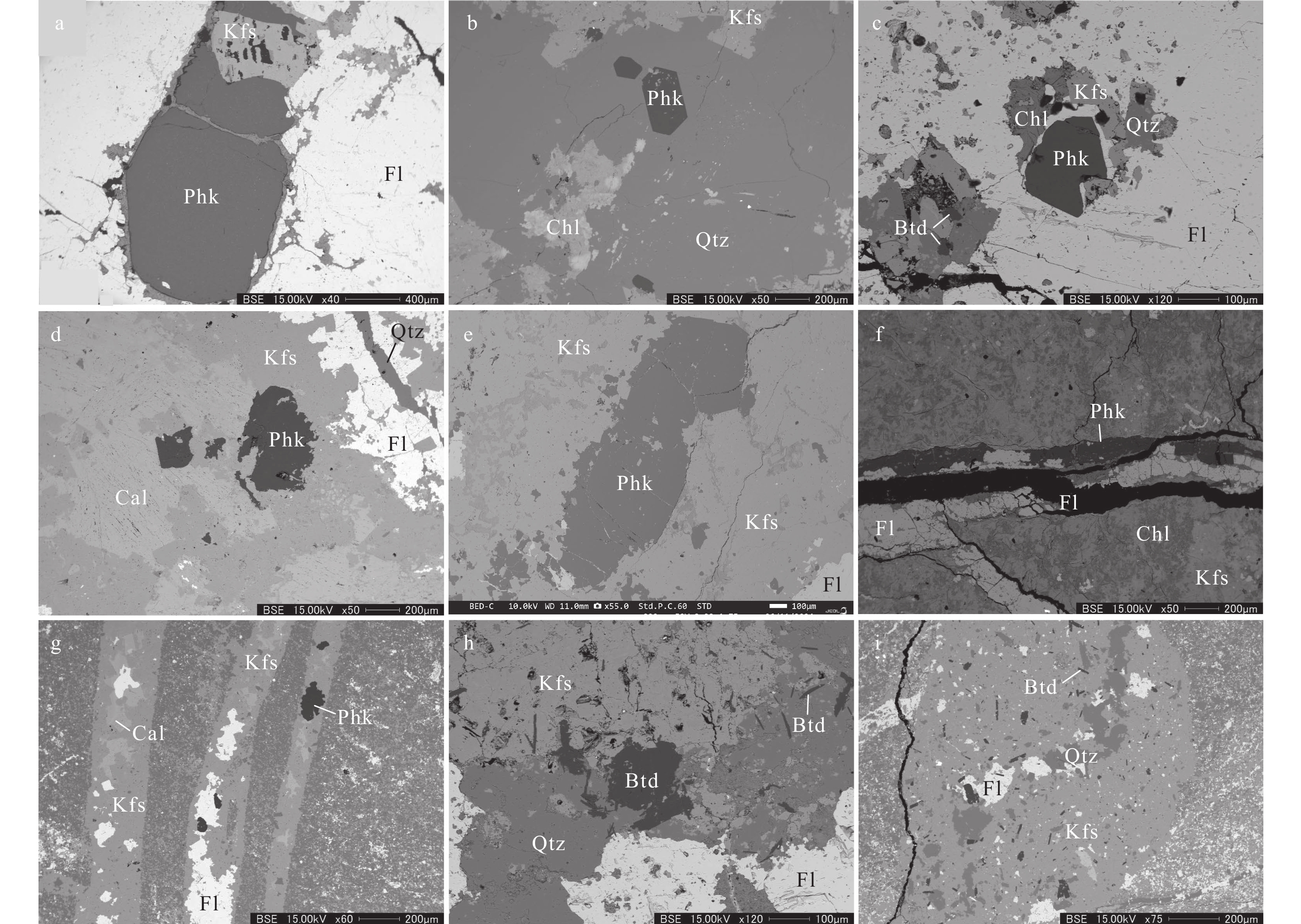
研究结果在高坞山和蕉坑坞萤石矿中发现了新的铍矿床。该矿床中可含高达4400×10−6 Be,矿石矿物主要为硅铍石和羟硅铍石,与萤石、钾长石、石英、方解石等形成矿物组合。硅铍石晶体颗粒较大,个别可达厘米级。该铍矿与萤石矿一起充填于构造裂隙或层间裂隙中,是岩前花岗岩岩浆-热液与围岩发生反应所致,属于热液型铍矿。
结论高坞山和蕉坑坞铍矿的发现及周边地区铍地球化学异常显示,常山地区具有较大的铍成矿潜力,应作为铍资源找矿勘查的重点区域。
Abstract:ObjectiveBeryllium, a nationally strategic critical metal, plays an indispensable role in modern technology and defense industries.
MethodsInvestigating its mineralization mechanisms, patterns, and resource potential is of paramount importance.
ResultsRecent explorations in the Changshan area of northwest Zhejiang have unveiled promising beryllium deposits within the Gaowushan and Jiaokengwu fluorite occurrences. These deposits exhibit notable concentrations of up to 4400 ×10−6 Be, with phenakite and bertrandite being the principal ore minerals. These minerals are intimately associated with fluorite, K−feldspar, quartz, and calcite. A remarkable feature of these deposits is the relatively large size of phenakite crystals, some exceeding centimeters in length. The beryllium−bearing minerals are predominantly found filling structural fractures or interlayer fissures adjacent to fluorite ore bodies, which suggests that these are hydrothermal−type deposits formed through the interaction of granite−derived magmatic hydrothermal fluids with host rocks.
ConclusionsThe identification of significant Be mineralization at Gaowushan and Jiaokengwu, coupled with the detection of beryllium geochemical anomalies in nearby regions, underscores the substantial mineralization potential of the Changshan district. Consequently, this area should be prioritized for further exploration aimed at assessing and developing its beryllium resources.
-
Keywords:
- beryllium-bearing minerals /
- beryllium resources /
- fluorite deposit /
- metallogenic mechanism /
- Gaowushan /
- Jiaokengwu /
- Zhejiang
创新点在浙江常山地区新发现了热液型铍矿。
-
-
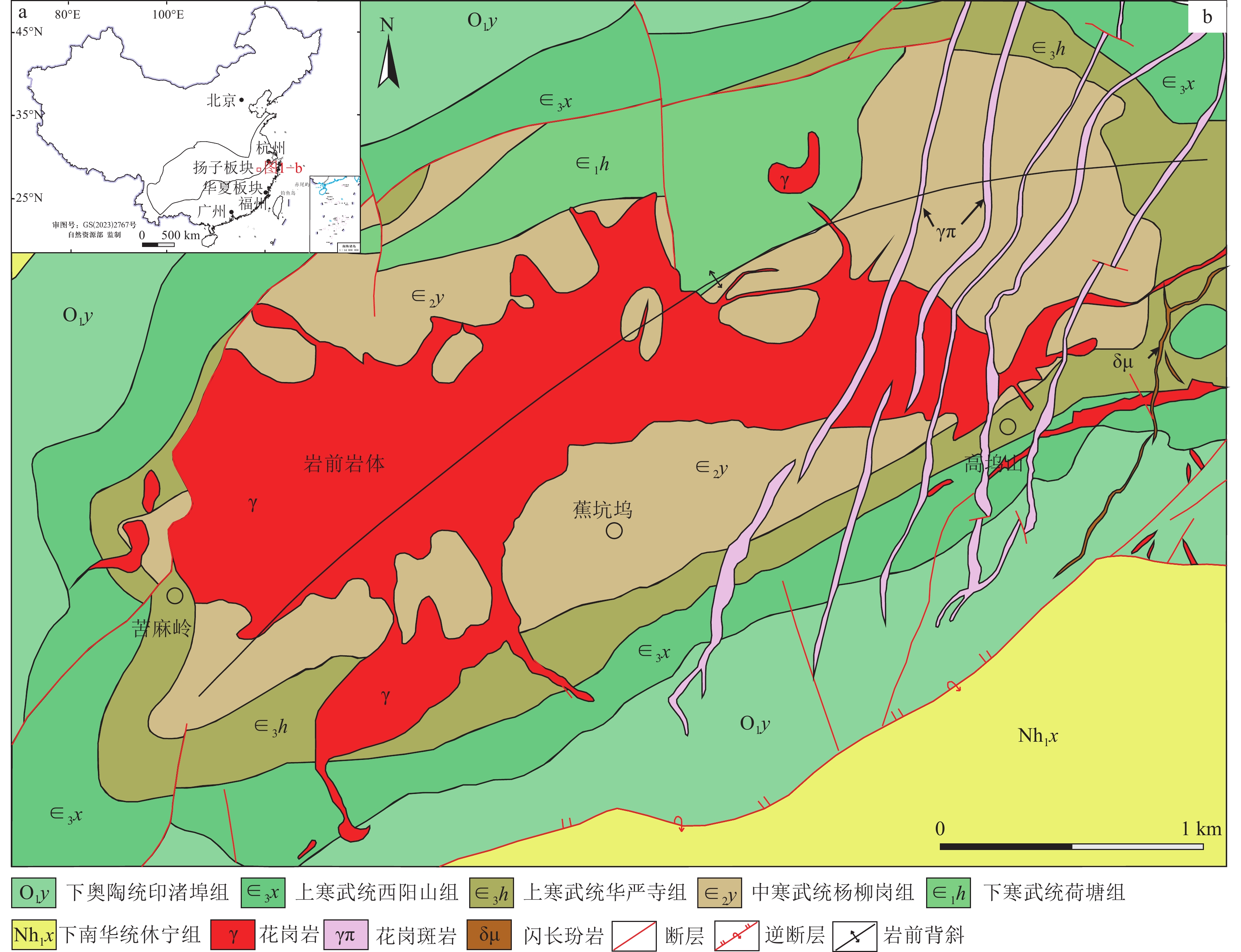
图 1 浙西北高坞山—蕉坑坞地区地质简图 (据刘道荣等,2013修改)
Figure 1. Geological map of Gaowushan-Jiaokengwu area in Northwest Zhejiang
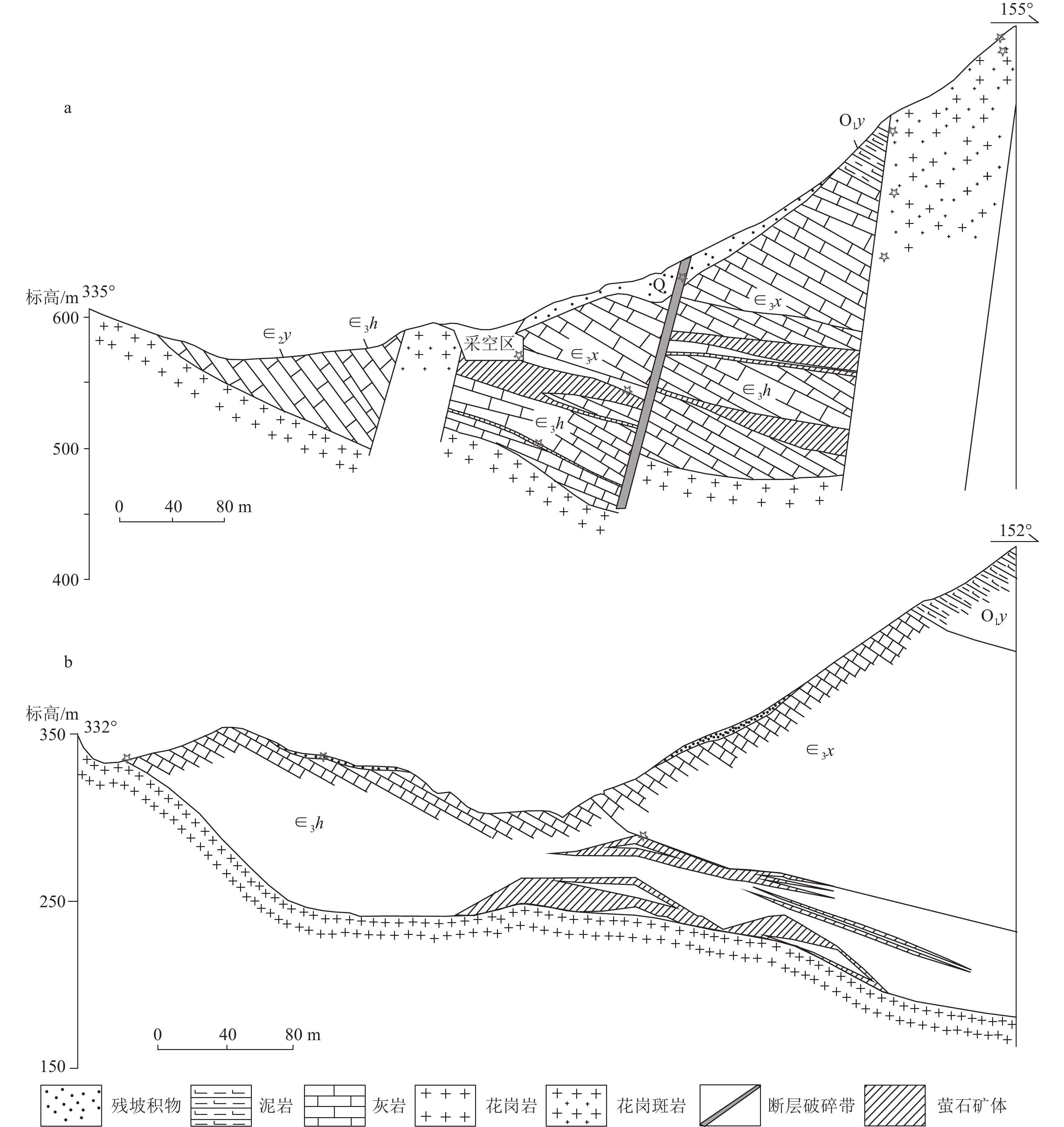
图 2 高坞山萤石矿矿体剖面图(a)和蕉坑坞萤石矿矿体剖面图(b) (据刘道荣等,2013修改;其中星号为采样点)
Q—第四系;O1y—下奥陶统印渚埠组;∈3x—上寒武统西阳山组;∈3h—上寒武统华严寺组;∈2y—中寒武统杨柳岗组
Figure 2. Profile of Gaowushan fluorite deposit(a) and Jiaokengwu fluorite deposit (b)
表 1 浙西北高坞山和蕉坑坞萤石矿围岩主量元素及Be含量
Table 1 The whole rock major elements and beryllium content of host rocks of Gaowushan and Jiaokengwu fluorite deposit in Northwest Zhejiang Province
样品号 SiO2 Al2O3 CaO TFe2O3 MgO MnO BaO K2O Na2O P2O5 SnO2 SO3 TiO2 F 烧失量 Be/10−6 GWS 740-1 57.62 11.88 10.65 2.67 1.75 0.04 0.10 6.99 0.99 0.04 <0.01 <0.01 0.33 6.2 4.35 305 GWS 740-2 55.67 10.52 13.90 2.28 1.82 0.03 0.09 5.70 0.06 0.07 0.01 0.04 0.28 6.2 6.77 550 GWS 740-3 42.29 12.33 21.1 2.51 2.23 0.04 0.05 5.52 2.29 0.03 0.02 <0.01 0.40 12.9 4.06 148.5 GWS 740-4 52.44 9.47 14.80 3.12 3.93 0.07 <0.01 5.02 0.75 <0.01 0.01 0.05 0.22 8.0 6.43 31.8 GWS 740-5 37.13 10.62 28.7 2.08 1.85 0.03 0.02 2.36 3.50 0.01 0.02 <0.01 0.21 17.2 4.45 146.0 GWS 695 35.38 10.26 23.0 4.19 4.10 0.09 0.16 4.65 0.48 0.07 0.01 0.09 0.40 5.5 14.52 117.5 GWS 645-1 43.21 11.77 21.8 1.34 1.22 0.04 0.06 9.28 0.13 <0.01 0.02 <0.01 0.05 13.2 4.22 4400 GWS 645-2 71.10 14.42 0.17 0.63 0.97 0.02 0.22 9.97 0.09 0.01 <0.01 <0.01 0.11 0.1 1.43 1100 GWS 645-3 34.02 10.74 28.2 3.32 2.42 0.06 0.05 6.48 0.10 0.01 0.03 0.93 0.19 16.5 5.40 589 GWS 595-1 71.89 14.50 0.48 1.78 0.03 0.08 0.01 4.84 4.32 <0.01 <0.01 0.08 0.01 0.8 0.97 18.60 GWS 545-1 12.90 3.81 56.5 0.57 1.40 0.02 0.06 2.25 0.07 <0.01 0.05 0.01 0.05 33.7 2.54 85.8 GWS 545-2 16.40 6.96 45.0 1.86 6.32 0.05 0.15 2.58 0.07 0.07 0.05 0.02 0.28 27.9 3.94 1300 GWS 490-2 73.74 12.14 0.85 2.52 0.09 0.03 0.01 5.62 2.90 0.01 <0.01 0.03 0.17 0.4 1.01 19.60 GWS 400-1 9.81 2.65 43.2 1.15 5.92 0.04 0.07 1.44 0.03 0.01 0.02 0.39 0.10 0.6 35.42 15.75 JKW 330-3 28.47 7.46 25.9 22.98 4.82 0.46 0.05 1.16 0.68 0.07 0.23 0.04 0.05 8.6 3.07 168.0 JKW-1 20.47 2.54 53.2 0.61 0.70 0.01 0.04 1.69 0.05 0.02 0.04 <0.01 0.01 31.8 2.90 73.5 JKW-3 26.06 4.70 43.9 1.09 2.92 0.02 0.05 3.73 0.05 0.01 0.03 <0.01 0.08 25.7 3.19 1300 注:主量元素含量单位为% -
Barton M D, Young S. 2002. Non−pegmatitic deposits of beryllium−Mineralogy, geology, phase equilibria and origin[C]//Grew E S. Beryllium−Mineralogy, petrology and geochemistry. Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry, 50: 591−691.
Černý P. 2002. Mineralogy of beryllium in granitic pegmatites[C]//Grew E S. Chapter 10 of Beryllium−Mineralogy, petrology, and geochemistry. Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry, 50: 405−444.
Damdinova L B, Damdinov B B, Rampilov M O, et al. 2019. Ore Formation Conditions of the Aunik F−Be Deposit (Western Transbaikalia)[J]. Geol. Ore Deposits, 61: 14−37.
Foley N K, Hofstra A H, Lindsey D A S, et al. 2012. Occurrence model for volcanogenic beryllium deposits[C]// Chapter F : Mineral deposit models for resource assessment. U. S. Geological Survey Scientific Investigations Report 2010−5070−F: 1−43.
Foley N K, Jaskula B W, Piatak N M, et al. 2017. Beryllium[C]// Schulz K J, De Young J H Jr, Seal R R, et al. Chapter E: Critical mineral resources of the United States−Economic and environmental geology and prospects for future supply. U. S. Geological Survey Professional Paper, 1802: E1−E32.
Freiman S W. 2008. Minerals, critical minerals, and the U. S. economy[EB/OL]. Science and Technology Committee, Subcommittee on Investigations and Oversight, also see the House Science, Space, and Technology Committee's Web site. https://doi.org/10.17226/12034.
Gu L F. 2013. The research of metallogenic characteristics and mechanism in Gaowushan fluorite deposite, Zhejiang[D]. Master Thesis of China University of Geosciences (Beijing) (in Chinese with English Abstract).
Han W B, Ma C A, Wang Y R, et al. 1991. Geological and geochemical characteristics of fluorite deposits: A case study of the Wuyi ore field in Zhejiang Province [M]. Beijing: Geological Press: 82−92 (in Chinese).
Huang Y H, Du S H, Zhou X Z. 1988. Xianghualing rock deposit and minerals [M]. Beijing: Science and Technology Press (in Chinese).
Jiang S Y, Wen H J, Xu C, et al. 2019. Multi cycle and enrichment mechanism of key metal elements: major scientific issues and future research directions[J]. Chinese Science Foundation, 33(2): 112−118 (in Chinese with English Abstract).
Lederer G W, Foley N K, Jaskula B W, et al. 2016. Beryllium − A critical mineral commodity − resources, production, and supply chain[R]. U. S. Geological Survey, FS 2016−3081: 1−4.
Li J K, Zou T R, Wang D H, et al. 2017. The metallogenic regularity of beryllium in China[J]. Geology of Mineral Deposits, 36(4): 951−978 (in Chinese with English Abstract).
Li L C, Zhou Y, Chen C F, et al. 2017. Investigation and evaluation report on lead and zinc polymetallic mineral resources in Fangcun area, Changshan County, Zhejiang Province[R]. Zhejiang Geological Exploration Institute of China National Chemical Corporation Geological and Mining Administration: 1−125 (in Chinese)
Li W C, Li J W, Xie G Q, et al. 2022. Current status, research content, and resource strategy analysis of key mineral resources in China[J]. Frontiers of Geosciences, 29(1): 1−13 (in Chinese with English Abstract).
Liang F, Zhao T, Wang D H, et al. 2018. Prediction of supply and demand of beryllium resources in China and development Strategy[J]. China Mining, 27(11): 6−10 (in Chinese with English Abstract).
Liu D R. 2013. Geological characteristics and mineralization laws of Gaowushan Jiaokengwu fluorite deposit in Bamianshan ore field, Changshan, Zhejiang Province[D]. Master Thesis of China University of Geosciences (Beijing) (in Chinese with English Abstract).
Liu D R, Wang M H, Chen Y, et al. 2012. Detailed survey report on fluorite ore in Gaowushan Jiaokengwu mining area of Bamianshan ore field in Changshan County, Zhejiang Province[R]. Zhejiang Geological Exploration Institute of China National Chemical Corporation Geological and Mining Administration: 1−122 (in Chinese with English Abstract).
Lykhin D A, Yarmolyuk V V. 2014. Magmatism and formation conditions of the Urma helvite−bertrandite deposit, West Transbaikal berillium province[J]. Geol. Ore Deposits, 56: 281−301. doi: 10.1134/S1075701514040059
Mao J W, Cheng Y B, Chen M H, et al. 2013. Major types and time−space distribution of Mesozoic ore deposits in South China and their geodynamic settings[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 48: 267−294. doi: 10.1007/s00126-012-0446-z
Rao C, Wang R C, Wu F Y, et al. 2022. Preliminary study on the beryllium mineralization belt of volcanic intrusive complex type along the southeast coast of China[J]. Chinese Science, Earth Science Edition, 52(8): 1547-1561 (in Chinese with English Abstract).
Rohe R, Tranter T N. 2011. Managing Beryllium in Nuclear Facility Applications[J]. Nuclear Technology, 176(3): 430−441. doi: 10.13182/NT11-A13318
Snead L L, Zinkle S J. 2005. Use of beryllium and beryllium oxide in space reactors[C]//Space Technology and Applications International Forum. American Institute of Physics Conf. Proc., 746: 768−775.
Tang C Y, Liu F J. 2010. Geological characteristics and structural mineralization analysis of the Yanling Lanshan fault zone in southern Hunan Province[J]. Mineral Resources and Geology, 24(1): 1−8 (in Chinese with EnglishAbstract).
Taylor T P, Ding M, Ehler D S, et al. 2003. Beryllium in the envirroment: a review[J]. J. Environ. Sci. Health A, 38: 439−469. doi: 10.1081/ESE-120016906
Tomberlin T A. 2004. Beryllium−A unique material in nuclear applications[C]//36th international SAMPE Technical Conference, INEEL/CON-04-01869.
Wang W. 2014. Analysis of production and application prospects of beryllium copper alloy[J]. Nonferrous metal processing, 43(2): 9−12 (in Chinese with EnglishAbstract).
Wang R C, Xing J Y, Peng H. 2014. Strategic Implications for Beryllium Resources in the United States[J]. China Mining, 23(10): 21−24 (in Chinese with EnglishAbstract).
Wood S A. 1992. Theoretical prediction of speciation and solubility of beryllium in hydrothermal solution to 300℃ at saturated vapor pressure: Application to bertrandite/phenakite deposits[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 7(4): 249−278. doi: 10.1016/0169-1368(92)90012-A
Zhao Y M, Feng C Y, Li D X, et al. 2017. Li and Be striped rocks and related metasomatism rocks in Xianghualing tin beryllium polymetallic mining area, Hunan Province[J]. Geology of Mineral Deposits, 36(6): 1245−1262 (in Chinese with EnglishAbstract).
Zheng X Q, He H J, Zhu Q T. 1990. Survey and evaluation report on yanqian Duiwu Tungsten Tin polymetallic mine in Changshan County, Zhejiang Province[R]. Zhejiang Geological Exploration Institute of China National Chemical Geology and Mining Administration: 1−88 (in Chinese).
古立峰. 2013. 浙江常山高坞山萤石矿的成矿机制研究[D]. 中国地质大学(北京)硕士学位论文. 韩文彬, 马承安, 王玉荣, 等. 1991. 萤石矿床地质及地球化学特征——以浙江武义矿田为例[M]. 北京: 地质出版社: 82−92. 黄蕴慧, 杜绍华, 周秀仲. 1988. 香花岭岩石矿床与矿物[M]. 北京: 科学技术出版社. 蒋少涌, 温汉捷, 许成, 等. 2019. 关键金属元素的多圈层循环与富集机理: 主要科学问题及未来研究方向[J]. 中国科学基金, 33(2): 112−118. 李建康, 邹天人, 王登红, 等. 2017. 中国铍成矿规律[J]. 矿床地质, 36(4): 951−978. 李良传, 周漪, 陈春发, 等. 2017. 浙江省常山县芳村地区铅、锌多金属矿资源调查评价报告[R]. 中化地质矿山总局浙江地质勘查院: 1−125. 李文昌, 李建威, 谢桂青, 等. 2022. 中国关键矿产现状、研究内容与资源战略分析[J]. 地学前缘, 29(1): 1−13. 梁飞, 赵汀, 王登红, 等. 2018. 中国铍资源供需预测与发展战略[J]. 中国矿业, 27(11): 6−10. 刘道荣, 2013. 浙江常山八面山矿田高坞山-蕉坑坞萤石矿床地质特征及成矿规律研究[D]. 中国地质大学(北京)硕士学位论文. 刘道荣, 王美华, 陈荫等. 2012. 浙江省常山县八面山矿田高坞山-蕉坑坞矿区萤石矿详查报告[R]. 中化地质矿山总局浙江地质勘查院: 1−122. 饶灿, 王汝成, 吴福元, 等. 2022. 我国东南沿海火山-侵入杂岩型铍成矿带初步研究[J]. 中国科学(地球科学版), 52(8): 1547−1561. doi: 10.1360/SSTe-2021-0252 唐朝永, 柳凤娟. 2010. 湘南炎陵-蓝山断裂带地质特征及其构造成矿作用分析[J]. 矿产与地质, 24(1): 1−8. 王伟. 2014. 铍铜合金的生产和应用前景分析[J]. 有色金属加工, 43(2): 9−12. 王仁财, 邢佳韵, 彭浩. 2014. 美国铍资源战略启示[J]. 中国矿业, 23(10): 21−24. 赵一鸣, 丰成友, 李大新, 等. 2017. 湖南香花岭锡铍多金属矿区的含Li、Be条纹岩和有关交代岩[J]. 矿床地质, 36(6): 1245−1262. 郑兴泉, 何华军, 朱全棠. 1990. 浙江省常山县岩前——对坞钨锡多金属矿普查评价报告[R]. 中化地质矿山总局浙江地质勘查院: 1−88.



 下载:
下载: