Structural analysis of multi-stage superimposed deformation in the southwestern Sichuan Basin: An example from the Ziliujing anticline
-
摘要:
四川盆地西南部地区由于受到周缘造山带构造隆升及变形扩展作用的影响,构造变形样式复杂,演化期次缺乏准确的时间约束。为了进一步探究该地区的构造演化过程,本次研究选取构造变形幅度相对较小的自流井背斜为研究对象,基于高品质地震反射资料,依据断层相关褶皱理论,精细解析其构造几何样式和运动学特征。研究结果表明,区内构造变形分层特征明显,深部以寒武系膏盐层为滑脱层,发育断层传播褶皱和滑脱褶皱,中部逆冲褶皱变形主要限制在志留系泥页岩顶界不整合面和下三叠统膏盐岩滑脱层之间,而浅部主要在上三叠统及以上地层发育宽缓褶皱和局部小位移断层。其中,深部寒武系滑脱层对区域构造样式控制起到关键作用。识别出的生长地层及构造平衡恢复结果揭示,自流井背斜带主要经历了加里东期、印支期,以及燕山期—喜马拉雅期3期主要挤压构造变形。而上三叠统中发育的北西向断裂指示后期在不同方向构造应力场下发生了叠加变形,可能是受到青藏高原东缘往东向四川盆地扩展作用的影响。
Abstract:Due to the tectonic uplift and deformation propagation of adjacent orogens, complex structural styles have developed in the southwestern Sichuan Basin. However, there is still a lack of precise age constraints on their evolution history. Based on high−quality seismic reflection data, we conduct a structural analysis on the structural geometry and kinematic features of the low−amplitude Ziliujing anticline as an example using fault−related folding theory for exploring the history of structural evolution in the study area. The results demonstrate distinct stratified tectonic deformation. In the deep, fault− propagation folds and detachment folds develop above the Cambrian salt. Folds and thrusts in the intermediate are primarily confined between the top of the Silurian shales and soils and the lower Triassic salt layer. In the shallow, it is primarily characterized by gentle folds and minor faults. Significantly, the regional structural styles in this area are controlled by the deep Cambrian detachment. The identified growth strata, in conjunction with the results of balanced structural restorations, indicate that the study area has undergone three main stages of tectonic compression; late Caledonian, Indosinian, and Yanshanian and Himalayan epochs. Furthermore, the development of NW−directed faults in the upper Triassic strata implies a structural imposition likely resulting from the propagation of deformation due to eastward movement of the eastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau.
-
-
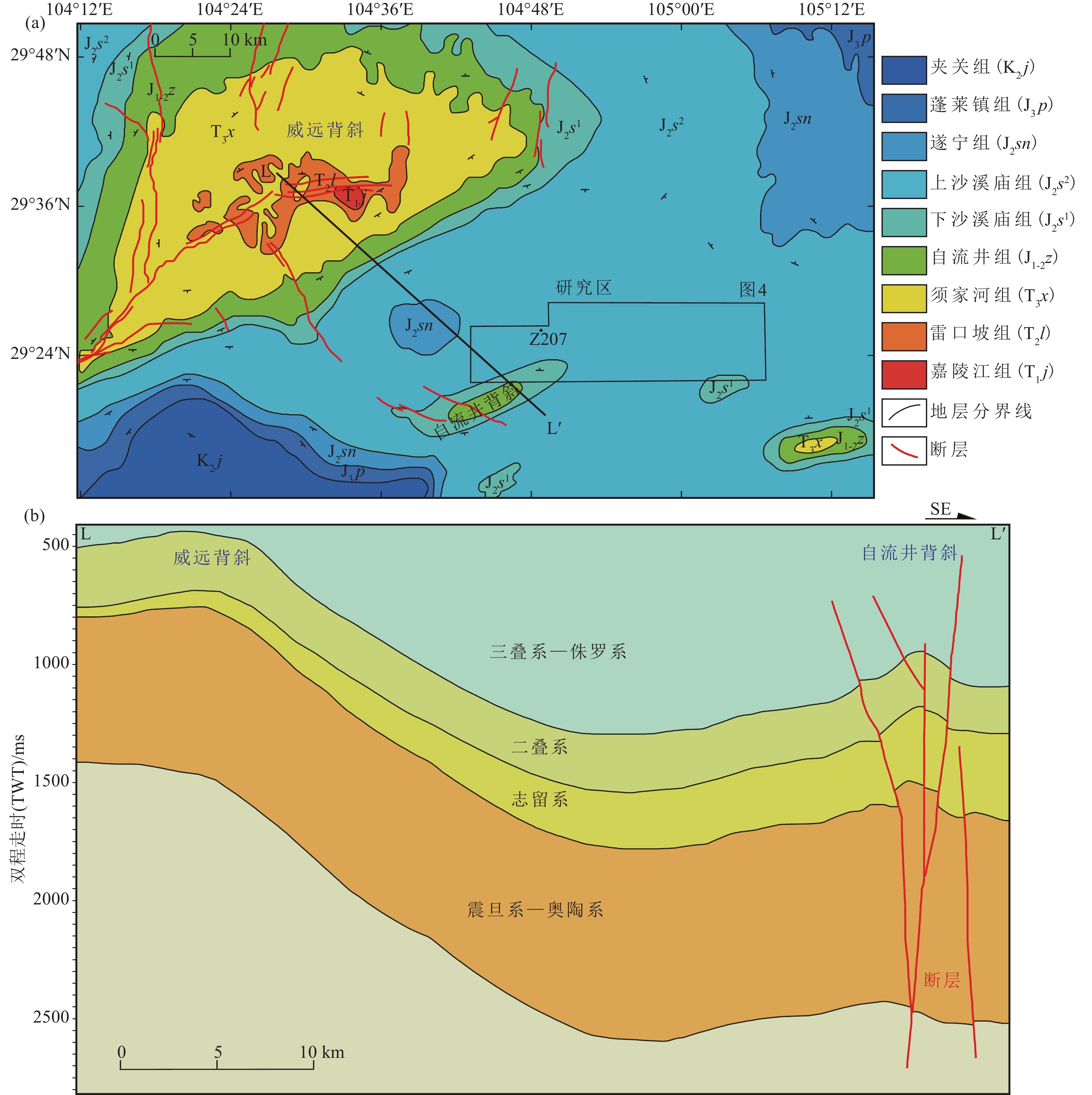
图 1 川西南地区地质背景(据郑志红等, 2017修改)
Figure 1. Geological background of the southwestern Sichuan Basin
图 2 区域地质图(a)和L-L´测线构造解释剖面(b)(据张宏祥等, 2023修改)
Figure 2. Regional geological map (a) and structural interpretations of line L-L´(b)
图 3 区域综合地层柱状图(据李洪奎等, 2020修改)
Figure 3. Comprehensive stratigraphic column of the study area
图 5 A−A′地震解释剖面(剖面位置见图4)
T3x—须家河组;T1j2—嘉陵江组二段;T1f—飞仙关组;P2l—龙潭组;P1l—梁山组;S1l11—龙马溪组一段1小层;O3w—五峰组
Figure 5. Interpreted seismic section A-A′
图 10 平衡剖面恢复结果揭示的三期主要挤压构造变形(地层代号注释同图5)
Figure 10. Balanced cross-section restoration reveals three-stage tectonic compression
-
Chen Z X, Lei Y L, Hu Y. 2018. Structural analysis of multi−level detachments and identification of deep−seated anticline[J]. Petroleum Exploration & Development, 45(2): 281−289.
Chen Z X, Li W, Wang L L, et al. 2019. Structural geology and favorable exploration prospect belts in northwestern Sichuan Basin, SW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 46(2): 397−408(in Chinese with English abstract).
Chen Z X, Wang L L, Yang G, et al. 2020. Geological structures and potential petroleum exploration areas in the southwestern Sichuan fold−thrust belt, SW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 47(4): 653−667(in Chinese with English abstract).
Costa E, Vendeville B C. 2002. Experimental insights on the geometry and kinematics of fold−and−thrust belts above weak, viscos evaporitic décollement[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 24: 1729−1739. doi: 10.1016/S0191-8141(01)00169-9
Cotton J T, Koyi H A. 2000. Modeling of thrust fronts above ductile and frictional detachments: Application to structures in the Salt Range and Potwar Plateau, Pakistan[J]. GSA Bulletin, 112(3): 351−363. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(2000)112<351:MOTFAD>2.0.CO;2
Davis D M, Engelder T. 1985. The role of salt in fold−and−thrust belts[J]. Tectonophysics, 119: 67−88. doi: 10.1016/0040-1951(85)90033-2
Epard J L, Groshong Jr R H. 1995. Kinematic mode of detachment folding including limb rotation, fixed hinges and layer−parallel strain[J]. Tectonophysics, 247: 85−103. doi: 10.1016/0040-1951(94)00266-C
Gao L, Rao G, Tang P C, et al. 2020. Structural development at the leading edge of the salt−bearing Kuqa fold−and−thrust belt, southern Tian Shan, NW China[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 140: 104184. doi: 10.1016/j.jsg.2020.104184
Gu M F, Liu R, Zhang H, et al. 2023. Characteristics and geological response of Caledonian tectonic movement in the Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 43(2): 32−43(in Chinese with English abstract).
Gu Z D, Lonergan L, Zhai X F, et al. 2021a. The formation of the Sichuan Basin, South China, during the Late Ediacaran to Early Cambrian[J]. Basin Research, 33: 2328−2357. doi: 10.1111/bre.12559
Gu Z D, Wang X, Nunns A, et al. 2021b. Structural styles and evolution of a thin−skinned fold−and−thrust belt with multiple detachments in the eastern Sichuan Basin, South China[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 142: 104191. doi: 10.1016/j.jsg.2020.104191
Gu Z D, Yan S Y, Zhang B, et al. 2012. Triassic tectonic decoupling in Weiyuan uplift (Sichuan) and its implications[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Pekinensis, 48(2): 262−272(in Chinese with English abstract).
Guo W X, Tang J M, Ouyang J S, et al. 2021. Characteristics of structural deformation in the southern Sichuan Basin and its relationship with the storage condition of shale gas[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 51(5): 11−19(in Chinese with English abstract).
He D F, Li D S, Zhang G W, et al. 2011. Formation and evolution of multi−cycle superposed Sichuan Basin, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology (Scientia Geologica Sinica), 51(5): 11−19(in Chinese with English abstract).
Hu J, Jia D, Wei G Q, et al. 2022. Seismic reflection analysis of the deeply buried Neoproterozoic rift basin beneath Sichuan Basin, Southern China[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 106(4): 759−782. doi: 10.1306/10212120127
Huang H Y, He D F, Li Y Q, et al. 2019. Determination and formation mechanism of the Luzhou paleo−uplift in the southeastern Sichuan Basin[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 26(1): 102−120(in Chinese with English abstract).
Hubert−Ferrari A, Suppe J, Gonzalez−Mieres R, et al. 2007. Mechanisms of active folding of the landscape (southern Tian Shan, China)[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 12: B03S09.
Jia D, Li Y Q, Lin A M, et al. 2010. Structural model of 2008 Mw 7.9 Wenchuan earthquake in the rejuvenated Longmen Shan thrust belt, China[J]. Tectonophysics, 491: 174−184. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2009.08.040
Jia D, Wei G Q, Chen Z X, et al. 2006. Longmen Shan fold−thrust belt and its relation to the western Sichuan Basin in central China: New insights from hydrocarbon exploration[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 90(9): 1425−1447. doi: 10.1306/03230605076
Li H K, Li Z Q, Long W, et al. 2020. Vertical configuration of Sichuan Basin and its superimposed characteristics of the prototype basin[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology (Science & Technology Edition), 46(3): 257−267(in Chinese with English abstract).
Li S J, Sun D S, Zheng M L, et al. 2014. Salt−related structure and its control on hydrocarbon of the Cambrian in Sichuan Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 35(5): 622−631,638(in Chinese with English abstract).
Li Y Q, Jia D, Wang M M, et al. 2014. Structural geometry of the source region for the 2013 Mw 6.6 Lushan earthquake: Implication for earthquake hazard assessment along the Longmen Shan[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 390: 275−286. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2014.01.018
Li Y, Allen P A, Densmore A L, et al. 2003. Evolution of the Longmen Shan foreland basin (western Sichuan, China) during the Late Triassic Indosinian orogeny[J]. Basin Research, 15: 117−138. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2117.2003.00197.x
Li Z G, Zheng W J, Zhang P Z, et al. 2019. Evidence for three Cenozoic phases of upper crustal shortening of the Xiongpo structure in the Longmen Shan fold−and−thrust belt, China: Implications for the eastward growth of the eastern Tibetan Plateau[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 179: 138−148. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2019.04.017
Li Z W, Liu S G, Chen H D, et al. 2011. Structural superimposition and conjunction and its effects on hydrocarbon accumulation in the western Sichuan Depression[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 35(5): 538−551.
Liang H, Wen L, Ran Q, et al. 2022. Structural characteristics and implications on oil/gas accumulation in north segment of the Longmenshan piedmont, northwestern Sichuan Basin[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 49(3): 478−490(in Chinese with English abstract).
Liu S G, Yang Y, Deng B, et al. 2021. Tectonic evolution of the Sichuan Basin, southwest China[J]. Earth−Science Reviews, 213: 103470. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2020.103470
Liu S G, Deng B, Li Z W, et al. 2011. The texture of sedimentary basin−orogenic belt system and its influence on oil/gas distribution: A case study from Sichuan basin[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 27(3): 621−635(in Chinese with English abstract).
Mei Q H, He D F, Wen Z, et al. 2014. Geologic structure and tectonic evolution of Leshan−Longnvsi paleo−uplift in Sichuan Basin, China[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 35(1): 11−25(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.1038/aps.2013.142
Pei Y W, Sheng S Z, Mao Z S, et al. Sandbox physical modelling with multiple detachment layers and its implication on structural evolution of East Sichuan Fold Belt[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum (Edition of Natural Science), 46(2): 38–49(in Chinese with English abstract).
Poblet J, Mcclay K, Storti F, et al. 1997. Geometries of syntectonic sediments associated with single−layer detachment folds[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 19(3/4): 369−381. doi: 10.1016/S0191-8141(96)00113-7
Qiu J H, Rao G, Wang X, et al. 2019. Effects of fault slip distribution on the geometry and kinematics of the southern Junggar fold−and−thrust belt, northern Tian Shan[J]. Tectonophysics, 722: 228209.
Rao G, Chen W, Yan D P, et al. 2024. Editorial: Lithosphere and surface processes of the Sichuan Basin and surrounding areas: Resources and environmental effects[J/OL]. Frontiers in Earth Science. doi: 10.3389/feart.2024.1435918.
Shaw J H, Connors C D, Suppe J. 2005. Seismic interpretation of contractional fault−related folds[M]. AAPG Studies in Geology, 53: 156.
Song W H. 1996. Research on reservoir−formed conditions of large−medium gas fields of Leshan−Longnvsi palaeohigh[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 16(suppl.): 13−26(in Chinese with English abstract).
Sun C, Li Z, Wu S, et al. 2021. Structural significance of the mid−level decollement within the western Sichuan fold−and−thrust belt (WSFTB), insights from sandbox modeling[J]. Frontiers in Earth Science, 9: 631405.
Suppe J, Chou G T, Hook S C. 1992. Rates of folding and faulting determined from growth strata[C]//McClay K R. Thrust Tectonics, 105–121. Chapman and Hall, London.
Suppe J, Medwedeff D A. 1990. Geometry and kinematics of fault−propagation folding[J]. Eclogae Geologicae Helvetiae, 83(3): 409−454.
Suppe J. 1983. Geometry and kinematics of fault−bend folding[J]. American Journal of Science, 283: 684−721. doi: 10.2475/ajs.283.7.684
Tang L J, Guo T L, Yu Y X, et al. 2007. Salt−related structures in the foreland fold−thrust belt of the Northeastern Sichuan Basin, South China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 81(8): 1048−1056(in Chinese with English abstract).
Tang L J, Yang K M, Jin Z W, et al. 2008. Multi−level detachment zone and detachment structural deformation in Longmenshan thrust belt[J]. Scientia Sinica (Terrae), 38(suppl.): 30−40(in Chinese with English abstract).
Tang P C, Rao G, Li S Q, et al. 2017. Lateral structural variations and drainage response along the Misikantage anticline in the western Kuqa fold−and−thrust belt, southern Tianshan, NW China[J]. Tectonophysics, 721: 196−210. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2017.10.007
Wang M M, Feng W, Jiang D Q, et al. 2020. Interactions between thin− and thick−skinned tectonics at the western Sichuan Basin, China[J]. Tectonophysics, 796: 228628. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2020.228628
Wang M M, Jia D, Shaw J H, et al. 2014. The 2013 Lushan earthquake: Implications for seismic hazards posed by the Range Front blind thrust in the Sichuan Basin, China[J]. Geology, 42(10): 915−918. doi: 10.1130/G35809.1
Wang M M, Lin A M. 2017. Active thrusting of the Longquan fault in the central Sichuan Basin, China, and the seismogenic behavior in the Longmen Shan fold−and−thrust belt[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 122: 5639−5662. doi: 10.1002/2016JB013391
Wu H, Qiu N S, Chang J, et al. 2019. Physical simulation on development of multilayer detachment fold belt in Eastern Sichuan[J]. Earth Science, 44(3): 784−797(in Chinese with English abstract).
Xu W Q, Yin H W, Jia D, et al. 2021. Structural features and evolution of the northwestern Sichuan Basin: Insights from discrete numerical simulations[J]. Frontiers in Earth Science, 9: 653395. doi: 10.3389/feart.2021.653395
Xu W Q, Yin H W, Zhao S X, et al. 2024. Influence of multiple detachments on structural vergence and evolution of the thin−skinned fold−and−thrust belt in the eastern Sichuan Basin: Insights from numerical modeling[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 180: 105068. doi: 10.1016/j.jsg.2024.105068
Xu X W, Wen X Z, Yu G H, et al. 2009. Coseismic reverse− and oblique−slip surface faulting generated by the 2008 Mw 7.9 Wenchuan earthquake, China[J]. Geology, 37(3): 515−518.
Yan D P, Zhou Y, Qiu L, et al. 2018. The Longmenshan tectonic complex and adjacent tectonic units in the eastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 164: 33−57. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2018.06.017
Zhai Y H, Chen Z X, Zhang Y Q, et al. 2023. A new superimposed model of the Tongnanba anticline in northeastern Sichuan and its exploration implications[J]. Frontiers in Earth Science, 11: 1162586. doi: 10.3389/feart.2023.1162586
Zhang H X, Tong H M, He Y B, et al. 2023. Structural analysis of superimposed deformation under oblique compression: A case study of the Weiyuan area, Sichuan Province[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 97(5): 1630−1640(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang Y Q, Dong S W, Li J H, et al. 2011. Mesozoic multi−directional compressional tectonics and formation−reformation of Sichuan basin[J]. Geology in China, 38(2): 233−250(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang Y Q. 2020. Seismogenic structures of the south Sichuan basin seismic zone and its neotectonic setting[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 94(11): 3161−3177(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang Y, Li Y J, Pan L, et al. 2023. The influence of structural characteristics on the preservation conditions of shale gas in Nanchuan area, Chongqing[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 42(5): 680−686(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zheng Z H, Li D H, Bai S S, et al. 2023. Resource potentials of natural gas in Sichuan Basin[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 22(3): 12−20(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhu Z, Yin H W, Jia D, et al. 2015. Impact of gypsolith on the preservation and exploration prospect of shale gas in Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 26(8): 1472−1480(in Chinese with English abstract).
陈竹新, 李伟, 王丽宁, 等. 2019. 川西北地区构造地质结构与深层勘探层系分区[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 46(2): 397−408. doi: 10.11698/PED.2019.02.21 陈竹新, 王丽宁, 杨光, 等. 2020. 川西南冲断带深层地质构造与潜在油气勘探领域[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 47(4): 653−667. doi: 10.11698/PED.2020.04.02 谷明峰, 刘冉, 张豪, 等. 2023. 四川盆地加里东期构造运动特征及其地质响应[J]. 天然气工业, 43(2): 32−43. 谷志东, 闫淑玉, 张波, 等. 2012. 川中威远低缓隆起区三叠系地层中的构造解耦记录及其构造暗示[J]. 北京大学学报(自然科学版), 48(2): 262−272. 郭卫星, 唐建明, 欧阳嘉穗, 等. 2021. 四川盆地南部构造变形特征及其与页岩气保存条件的关系[J]. 天然气工业, 51(5): 11−19. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2021.05.002 何登发, 李德生, 张国伟, 等. 2011. 四川多旋回叠合盆地的形成与演化[J]. 地质科学, 46(3): 589−606. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0563-5020.2011.03.001 黄涵宇, 何登发, 李英强, 等. 2019. 四川盆地东南部泸州古隆起的厘定及其成因机制[J]. 地学前缘, 26(1): 102−120. 李洪奎, 李忠权, 龙伟, 等. 2020. 四川盆地纵向结构及原型盆地叠合特征[J]. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版), 46(3): 257−267. 李双建, 孙冬胜, 郑孟林, 等. 2014. 四川盆地寒武系盐相关构造及其控油气作用[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 35(5): 622−631+638. doi: 10.11743/ogg20140506 梁瀚, 文龙, 冉崎, 等. 2022. 四川盆地龙门山前北段构造演化特征及其油气地质意义[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 49(3): 478−490. doi: 10.11698/PED.20210452 刘树根, 邓宾, 李智武, 等. 2011. 盆山结构与油气分布——以四川盆地为例[J]. 岩石学报, 27(3): 621−635. 梅庆华, 何登发, 文竹, 等. 2014. 四川盆地乐山—龙女寺古隆起地质结构及构造演化[J]. 石油学报, 35(1): 11−25. doi: 10.7623/syxb201401002 裴仰文, 盛受政, 苗正硕, 等. 2022. 多滑脱层构造物理模拟试验及其对川东褶皱带形成演化的指示意义[J]. 中国石油大学学报(自然科学版), 46(2): 38−49. 宋文海. 1996. 乐山−龙女寺古隆起大中型气田成藏条件研究[J]. 天然气工业, 16(增刊): 13−26. 汤良杰, 郭彤楼, 余一欣, 等. 2007. 四川盆地东北部前陆褶皱-冲断带盐相关构造[J]. 地质学报, 81(8): 1048−1056. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2007.08.004 汤良杰, 杨克明, 金文正, 等. 2008. 龙门山冲断带多层次滑脱带与滑脱构造变形[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 38(增刊I): 30−40. 吴航, 邱楠生, 常健, 等. 2019. 川东多套滑脱层褶皱构造带形成物理模拟[J]. 地球科学, 44(3): 784−797. 张宏祥, 童亨茂, 何昀宾, 等. 2023. 斜向挤压叠加变形的构造解析——以四川威远地区为例[J]. 地质学报, 97(5): 1630−1640. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2023.05.018 张勇, 李彦婧, 潘兰, 等. 2023. 构造特征对重庆南川地区页岩气保存条件的影响[J]. 地质通报, 42(5): 680−686. doi: 10.12097/j.issn.1671-2552.2023.05.002 张岳桥, 董树文, 李建华, 等. 2011. 中生代多向挤压构造作用与四川盆地的形成和改造[J]. 中国地质, 38(2): 233−250. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2011.02.001 张岳桥. 2020. 四川盆地南部地震区发震构造及其新构造背景[J]. 地质学报, 94(11): 3161−3177. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2020.11.001 郑志红, 李登华, 白森舒, 等. 2017. 四川盆地天然气资源潜力[J]. 中国石油勘探, 22(3): 12−20. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2017.03.002 朱臻, 尹宏伟, 贾东, 等. 2015. 四川盆地膏盐岩层对页岩气保存及勘探前景的影响[J]. 天然气地球科学, 26(8): 1472−1480.




 下载:
下载: