Genesis of Xinli gold deposit in Jiaodong Peninsula, Shandong Province
-
摘要:
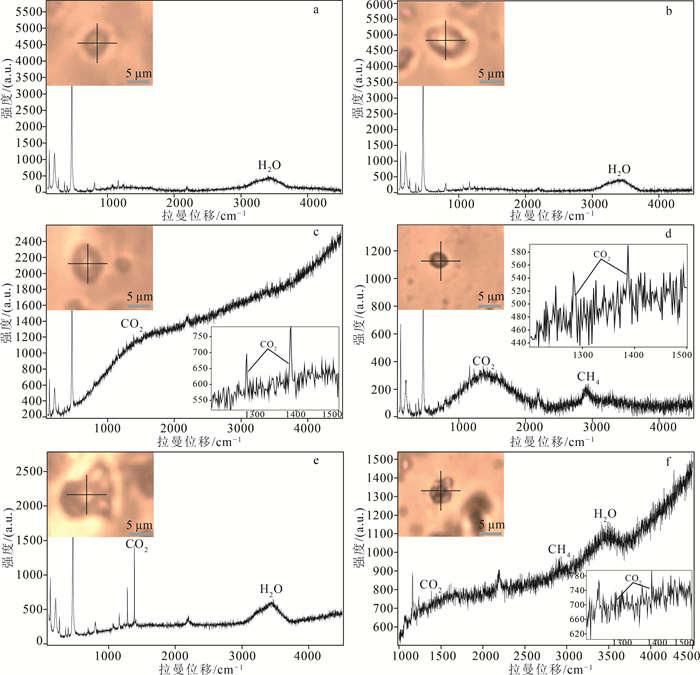
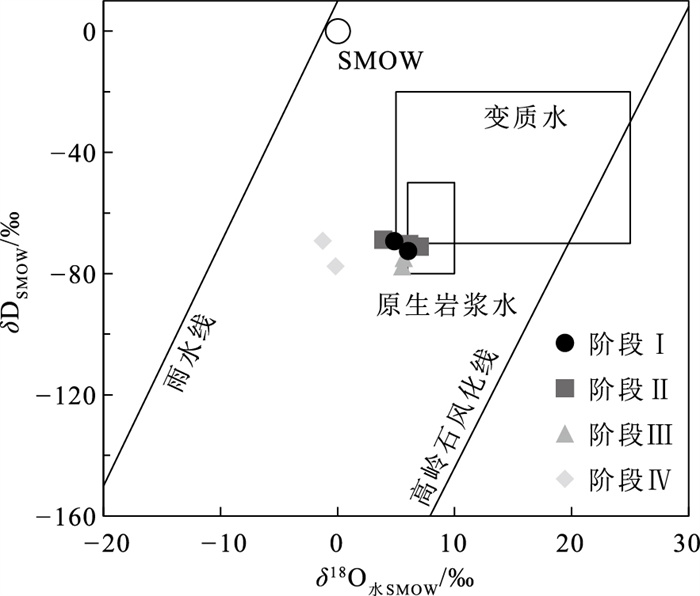
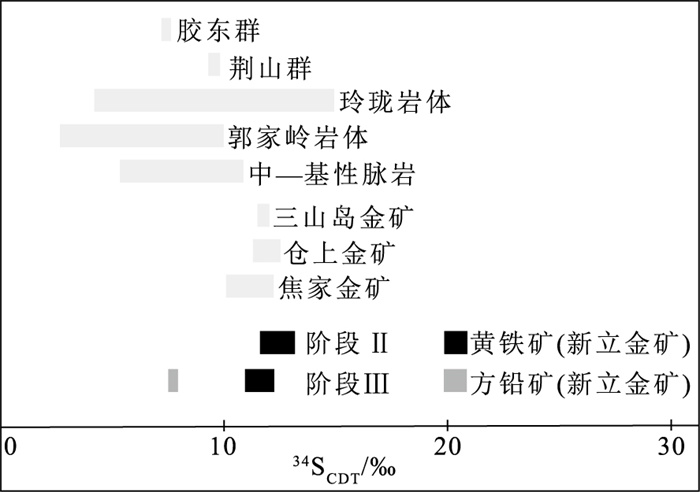
胶东半岛西北部三山岛-仓上断裂带的新立金矿床是典型的蚀变岩型金矿床。对新立金矿床的矿床地质特征和流体包裹体特征开展研究, 分析了新立金矿床的成矿流体特征, 明确新立金矿床的成因。矿床的矿化阶段划分为Ⅰ黄铁绢英岩阶段、Ⅱ石英-黄铁矿阶段、Ⅲ石英-多金属硫化物阶段和Ⅳ石英-碳酸盐阶段。将新立金矿床中的流体包裹体划分为单相液相包裹体(Ⅰ-l型)、单相气相包裹体(Ⅰ-g型)、两相富液相包裹体(Ⅱ-l型, V/V+L < 50%)、两相富气相包裹体(Ⅱ-g型, V/V+L>50%)和CO2-H2O三相包裹体(Ⅲ型, VCO2+LCO2+LH2O)。阶段Ⅰ中发育Ⅰ-l、Ⅰ-g、Ⅱ-l、Ⅱ-g和Ⅲ型流体包裹体, 均一温度为201~378℃, 盐度变化为3.06%~13.83%NaCl.eqv.; 阶段Ⅱ中发育Ⅰ-l、Ⅱ-l、Ⅱ-g和Ⅲ型流体包裹体, 均一温度为144~355℃, 盐度变化为2.07%~13.45%NaCl.eqv.; 阶段Ⅲ中发育Ⅰ-l、Ⅱ-l、Ⅱ-g和Ⅲ型流体包裹体, 均一温度为108~299℃, 盐度变化为0.35%~11.61%NaCl.eqv.; 阶段Ⅳ中发育Ⅱ-l、Ⅱ-g和Ⅲ型流体包裹体, 均一温度为102~236℃, 盐度变化为0.35%~10.49%NaCl.eqv.。激光拉曼光谱分析表明, 流体包裹体的成分为CO2、H2O和少量的CH4, 成矿流体为中-低温、低盐度的NaCl-CO2-H2O±CH4流体体系。新立金矿床阶段Ⅰ中δ18O水SMOW为4.86‰~6.04‰, δDSMOW为-72.49‰~-69.27‰, 表明成矿流体主要来自岩浆水。黄铁矿中δ34SCDT为10.8‰~13.2‰, 方铅矿中δ34SCDT为7.7‰, 新立金矿床的成矿物质硫元素可能直接来源于郭家岭花岗岩。成矿过程中随着成矿流体温度的降低, 成矿流体与围岩发生反应及流体的不混溶作用使流体发生相分离作用导致金的沉淀, 成因类型是与岩浆热液有关的脉状金矿床。
Abstract:The Xinli gold deposit in the Sanshandao-Cangshang fault zone in the northwest Jiaodong Peninsula is a typical altered-rock type gold deposit.This paper studies the geological characteristics and fluid inclusion characteristics of Xinli gold deposit, analyzes the ore-forming fluid characteristics of Xinli gold deposit, and defines the genesis of Xinli gold deposit.The hydrothermal mineralization period of Xinli gold deposit can be divided into Ⅰ beresitization stage, Ⅱ quartz-pyrite stage, Ⅲ quartz-polymetallic sulfide stage and Ⅳ quartz-calcite stage.The fluid inclusions in Xinli gold deposit can be divided into single-phase liquid inclusions(Ⅰ-l type), single-phase gas inclusions(Ⅰ-g type), two-phase liquid rich inclusions(Ⅱ-l type, V/V+L < 50%), two-phase gas rich inclusions(Ⅱ-g type, V/V+L>50%)and CO2-H2O three-phase inclusions(Ⅲ type, VCO2+LCO2+ LH2O).In stage I, type Ⅰ-l, Ⅰ-g, Ⅱ-l, Ⅱ-g and Ⅲ fluid inclusions are developed, with homogenization temperature ranging from 201℃ to 378℃, and the salinity ranging from 3.06%NaCl.eqv. to 13.83% NaCl.eqv.. In stage Ⅱ, type Ⅰ-l, Ⅱ-l, Ⅱ-g and Ⅲ fluid inclusions are developed, with homogenization temperature ranging from 144℃ to 355℃, and the salinity ranging from 2.07%NaCl.eqv. to 13.45% NaCl.eqv.; In stage Ⅲ, type Ⅰ-l, Ⅱ-l, Ⅱ-g and Ⅲ fluid inclusions are developed, with homogenization temperature ranging from 108℃ to 299℃, and the salinity ranging from 0.35%NaCl.eqv. to 11.61% NaCl.eqv.; In stage Ⅳ, type Ⅱ-l, Ⅱ-g and Ⅲ fluid inclusions are developed, with homogenization temperature ranging from 102℃ to 236℃, and the salinity ranging from 0.35%NaCl.eqv. to 10.49% NaCl.eqv.Laser Raman spectroscopy shows that the fluid inclusions are composed of CO2, H2O and a small amount of CH4.The ore-forming fluid is a medium-low temperature and low salinity NaCl-CO2-H2O±CH4 fluid system.In the stage Ⅰ of Xinli gold deposit, δ18Owater SMOW=4.86‰~6.04‰, δDSMOW=-72.49‰~-69.27‰, indicating that ore-forming fluids mainly come from magmatic water.The δ34SCDT values of pyrite range from 10.8‰ to 13.2‰, and the δ34SCDT values of galena is 7.7‰.The sulfur element of xinli gold deposit may be directly derived from Guojialing granite.With the decrease of ore-forming fluid temperature, the ore-forming fluid reacts with the surrounding rock and the immiscibility of the fluid leads to the phase separation of the fluid, which leads to the precipitation of gold.The genetic type is vein gold deposit related to magmatic hydrothermal solution.
-
Keywords:
- Jiaodong Peninsula /
- Xinli gold deposit /
- fluid inclusion /
- ore-forming fluid /
- ore genesis /
- Shandong Province
-
致谢: 样品采集得到山东黄金地质矿产勘查有限公司与山东黄金集团有限公司三山岛金矿的大力协助,显微激光拉曼光谱分析中得到实验室相关人员的悉心指导,审稿专家对本文提出建设性意见,在此一并致谢。
-
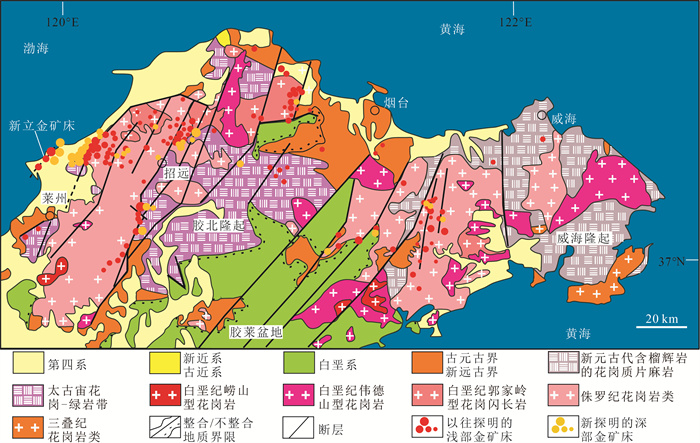
图 1 胶东地区区域地质及金矿床分布图[2](底图以标准地图绘制,审图号为GS(2019)3333)
Figure 1. Regional geology and distribution of gold deposits in Jiaodong area
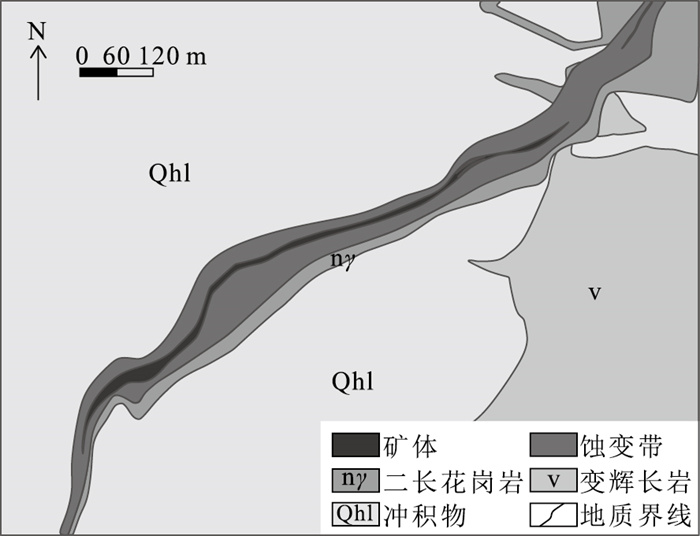
图 2 新立金矿床地形地质图①
Figure 2. Topographic geological map of Xinli gold deposit
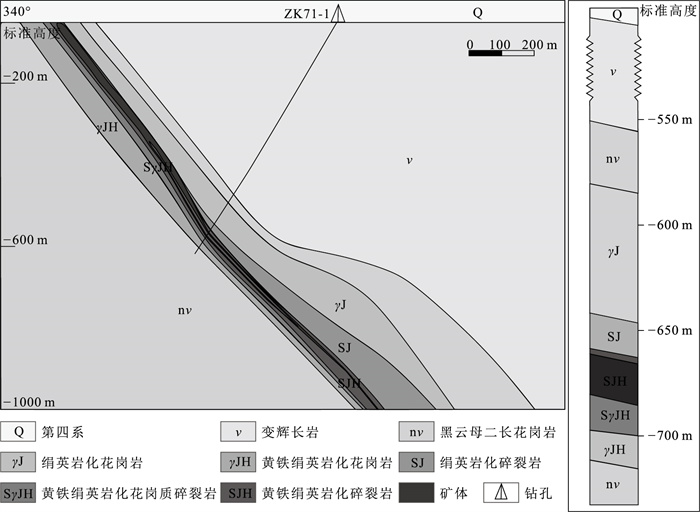
图 3 新立金矿床71号勘探线地质剖面图与钻孔ZK71-1柱状图①
Figure 3. Geological profile of No.71 exploration line and ZK71-1 histogram of borehole in Xinli gold deposit
表 1 新立金矿床流体包裹体显微测温数据
Table 1 Microthermometry data of fluid inclusions in Xinli gold deposit
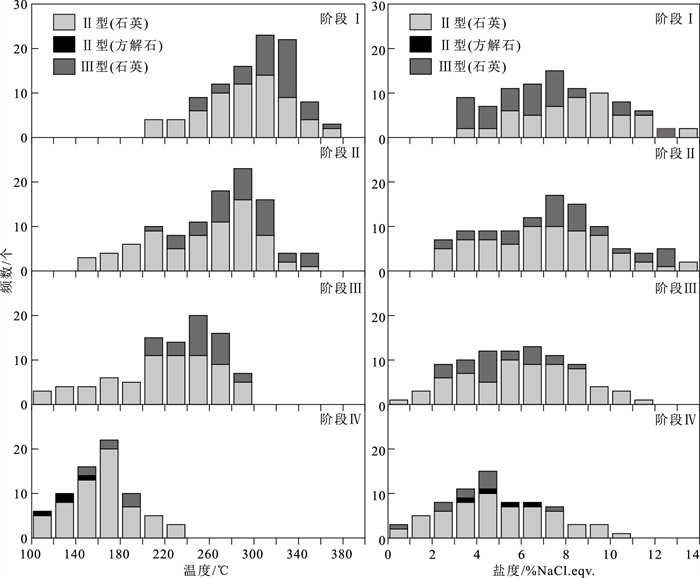
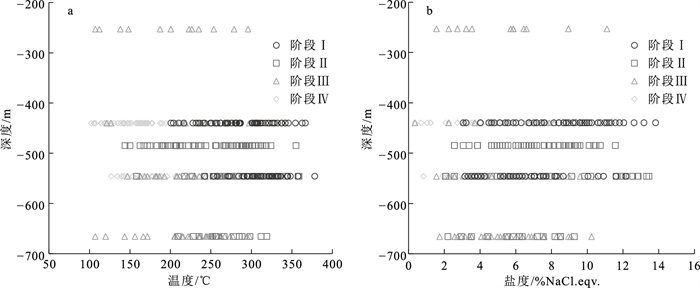
样品编号 矿化阶段 测试矿物 包裹体类型 Tm.CO2/℃ Tm.ice/℃ Tm.clath/℃ Th.CO2/℃ Th.TOT/℃ 均一方式 XL44000-11 Ⅰ 石英 Ⅱ/Ⅲ -61.6~-56.8 -9.9~-1.4 3.9~8.2 23.7~28.6 201~348 液相/气相 XL44000-12 Ⅰ 石英 Ⅱ/Ⅲ -58.8~-56.9 -7.7~-4.2 3.2~6.3 23.2~30.0 204~378 液相/气相 XL54671-11 Ⅰ 石英 Ⅱ/Ⅲ -58.8~-56.8 -8.3~-3.6 2.8~8.4 24.5~31.1 268~367 液相 XL54671-12 Ⅰ 石英 Ⅱ/Ⅲ -59.2~-56.9 -5.4~-1.8 6.0~8.3 23.8~31.0 254~358 液相/气相 XL48508-21 Ⅱ 石英 Ⅱ/Ⅲ -58.2~-56.8 -7.9~-0.8 2.3~7.3 16.8~29.7 144~359 液相/气相 XL48508-22 Ⅱ 石英 Ⅱ/Ⅲ -57.1-~56.8 -7.2~-1.1 1.8~7.8 17.1~28.3 197~355 液相 XL54671-21 Ⅱ 石英 Ⅱ/Ⅲ -57.9~-57.1 -6.4~-0.3 4.8~6.1 19.6~24.9 150~319 液相/气相 XL54671-22 Ⅱ 石英 Ⅱ/Ⅲ -57.3 -9.0~-1.2 5.9~7.7 27.3~29.8 167~325 液相 XL66679-21 Ⅱ 石英 Ⅱ/Ⅲ -58.9~-58.3 -8.2~-1.2 5.3~8.9 21.2~26.1 158~298 液相 XL25375-31 Ⅲ 石英 Ⅱ -7.5~-0.9 108~296 液相/气相 XL44000-31 Ⅲ 石英 Ⅱ/Ⅲ -59.1~-56.9 -5.9~-1.3 6.2~8.7 19.5~31.0 206~286 液相/气相 XL54671-31 Ⅲ 石英 Ⅱ/Ⅲ -59.2~-56.8 -6.4~-0.2 7.4~8.2 26.7~29.8 122~297 液相/气相 XL54671-32 Ⅲ 石英 Ⅱ/Ⅲ -59.3~-56.8 -5.5~-0.9 5.3~7.9 27.0~30.7 168~298 液相 XL66679-31 Ⅲ 石英 Ⅱ -7.0~-1.5 172~299 液相 XL66679-32 Ⅲ 石英 Ⅱ/Ⅲ -58.6~-56.7 -6.8~-1.0 6.4~8.7 30.1~30.6 107~295 液相/气相 XL44000-41 Ⅳ 石英 Ⅱ/Ⅲ -58.2~-56.9 -7.0~-0.4 7.1~8.9 16.9~24.5 102~227 液相/气相 XL44000-41 Ⅳ 方解石 Ⅱ -4.5~-2.0 107~147 液相 XL44000-42 Ⅳ 石英 Ⅱ -6.2~-0.2 119~212 液相 XL54671-41 Ⅳ 石英 Ⅱ/Ⅲ -59.5~-56.9 -5.1~-1.2 6.2~9.6 21.3~29.9 106~236 液相/气相 XL54671-42 Ⅳ 石英 Ⅱ -6.0~-1.1 142~207 液相 注:Tm.CO2—CO2冰点温度;Tm.ice—冰点温度;Tm.clath—笼合物温度;Th.CO2—CO2部分均一温度;Th.TOT—完全均一温度 表 2 新立金矿床氢、氧同位素测试数据
Table 2 H and O isotope data of Xinli gold deposit
样品编号 成矿阶段 测试矿物 δDSMOW/‰ δ18O矿物SMOW/‰ 计算温度/℃ δ18O水SMOW/‰ XL44000-11 Ⅰ 石英 -72.49 12.80 305 6.04 XL54671-11 Ⅰ 石英 -69.27 11.40 310 4.86 XL48508-21 Ⅱ 石英 -71.16 14.70 280 7.02 XL54671-22 Ⅱ 石英 -68.77 11.96 270 3.90 XL66679-21 Ⅱ 石英 -70.30 14.17 270 6.11 XL44000-31 Ⅲ 石英 -77.63 14.70 245 5.53 XL66679-31 Ⅲ 石英 -74.77 14.80 245 5.64 XL44000-41 Ⅳ 石英 -69.20 12.90 165 -1.28 XL54671-41 Ⅳ 石英 -77.63 13.60 170 -0.17 表 3 新立金矿床S同位素测试数据
Table 3 S isotope test data of Xinli gold deposit
样品编号 矿化阶段 矿物 δ34SCDT/‰ XL48508-21 Ⅱ 黄铁矿 13.2 XL66679-21 Ⅱ 黄铁矿 11.6 XL25375-31 Ⅲ 黄铁矿 10.8 XL44000-31 Ⅲ 黄铁矿 12.1 XL66679-31 Ⅲ 黄铁矿 11.2 XL66679-31 Ⅲ 方铅矿 7.7 表 4 新立金矿床与胶东地区其他蚀变岩型金矿床地质特征、成矿流体特征对比
Table 4 Comparison of geological characteristics and ore-forming fluid characteristics between Xinli gold deposit and other alteration rock type gold deposits in Jiaodong area
对比项目 造山型金矿[51] 三山岛金矿床[52] 焦家金矿床[53] 新立金矿床 矿床类型 造山型金矿 蚀变岩型金矿 蚀变岩型金矿 蚀变岩型金矿 赋矿围岩 变质岩 花岗岩 花岗岩 花岗岩 控矿构造 韧脆性剪切带 三山岛-仓上断裂带 焦家-新城断裂带 三山岛-仓上断裂带 矿体形态 脉状 脉状、透镜状、似层状 脉状、透镜状、似层状 脉状、透镜状、似层状 矿石类型 石英脉型、蚀变岩型 石英脉型、蚀变岩型 石英脉型、蚀变岩型 石英脉型、蚀变岩型 金属矿物 黄铁矿为主 黄铁矿、方铅矿、黄铜矿、闪锌矿 黄铁矿、方铅矿、黄铜矿、 黄铁矿、方铅矿、黄铜矿、闪锌矿 载金矿物 主要为黄铁矿 主要为黄铁矿 黄铁矿、方铅矿、黄铜矿、 主要为黄铁矿 主成矿温度 220~500℃ 207~336℃ 170~358℃ 200~320℃ 流体盐度 < 6% NaCl.eqv. 0.2%~18.4% NaCl.eqv. 2.04%~10.0% NaCl.eqv. 0.35%~13.83% NaCl.eqv. 流体不混溶现象 有 有 有 有 流体来源 变质流体 岩浆流体 岩浆流体 岩浆流体 成矿流体体系 含CO2水溶液 NaCl-CO2-H2O±CH4 NaCl-CO2-H2O±CH4 NaCl-CO2-H2O±CH4 -
Deng J, Liu X, Wang Q, et al. Origin of theJiaodong-type Xinli gold deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula, China: Constraints from fluid inclusion and C-D-O-S-Sr isotope compositions[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2015, 65: 674-686. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2014.04.018
宋明春, 李三忠, 伊丕厚, 等. 中国胶东焦家式金矿类型及其成矿理论[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2014, 44(1): 87-104. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ201401008.htm 孙宗锋, 于海新, 郭天庆, 等. 莱州新立金矿床的发现及其地质特征[J]. 山东地质, 1999, (2): 34-39. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDDI902.004.htm 邓军, 王庆飞, 杨立强, 等. 胶西北金矿集区成矿作用发生的地质背景[J]. 地学前缘, 2004, (4): 527-533. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2004.04.019 郭彬, 刘自成, 李威, 等. 三山岛金矿床成矿地质特征与找矿预测[J]. 矿业工程, 2008, (4): 14-16. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-8550.2008.04.006 赵冬冬, 金刚, 李海松, 等. 山东省莱州市三山岛金矿床地质特征及成因探讨[J]. 地质找矿论丛, 2013, 28(4): 546-551. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZZK201304008.htm 翟明国, 杨进辉, 刘文军. 胶东大型黄金矿集区及大规模成矿作用[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 2001, (7): 545-552. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK200107002.htm 杨林, 王庆飞, 刘学飞, 等. 胶东控矿断裂断层泥形成与演化: 以新立金矿床为例[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2014, 38(4): 908-918. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1552.2014.04.016 赵睿, 刘学飞, 潘瑞广, 等. 胶东新立构造蚀变岩型金矿床元素地球化学行为[J]. 岩石学报, 2015, 31(11): 3420-3440. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201511018.htm 智云宝, 孙海瑞, 李风华. 山东栖霞笏山金矿床成因-元素地球化学与流体包裹体证据[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2020, 50(5): 1552-1569. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ202005019.htm 邓军, 王庆飞, 杨立强, 等. 胶东西北部金热液成矿系统内部结构解析[J]. 地球科学, 2005, (1): 102-108. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX200501014.htm 范宏瑞, 胡芳芳, 杨进辉, 等. 胶东中生代构造体制转折过程中流体演化和金的大规模成矿[J]. 岩石学报, 2005, (5): 1317-1328. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200505000.htm 毛景文, 谢桂青, 张作衡, 等. 中国北方中生代大规模成矿作用的期次及其地球动力学背景[J]. 岩石学报, 2005, 21(1): 171-190. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200501018.htm 宋明春, 崔书学, 周明岭, 等. 山东焦家矿区深部超大型金矿床及其对"焦家式"金矿的启示[J]. 地质学报, 2010, 84(9): 1349-1358. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201009009.htm 宋英昕, 宋明春, 焦秀美, 等. 胶东金矿集区深部找矿重要进展及特征[J]. 黄金科学技术, 2017, 25(3): 4-18. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKJ201703003.htm Deng J, Yang L Q, Groves D I, et al. An integrated mineral system model for the gold deposits of the giantJiaodong province, eastern China[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2020, 208(2): 103274.
林文蔚, 赵一鸣, 赵国红, 等. 胶东金矿铅同位素地质特征及成矿年代讨论[J]. 长春科技大学学报, 1999, (2): 116-121. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ199902003.htm 张军进, 邹键, 林大伟, 等. 胶东金矿集中区金矿成矿年代学分析[J]. 硅谷, 2013, 6(16): 148, 162. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GGYT201316111.htm 李洪奎, 时文革, 李逸凡, 等. 山东胶东地区金矿成矿时代研究[J]. 黄金科学技术, 2013, 21(3): 1-9. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKJ201303002.htm 宋雪龙, 李俊建, 李秀章, 等. 胶东金矿床成矿流体、稳定同位素及成矿时代研究进展[J]. 地质找矿论丛, 2014, 29(1): 13-19. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZZK201401002.htm 张良. 胶西北金成矿系统热年代学[D]. 中国地质大学(北京)博士学位论文, 2016. 杜泽忠, 程志中, 姚晓峰, 等. 胶东谢家沟金矿床蚀变钾长石40Ar-39Ar年龄及地质意义[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2020, 50(5): 1570-1581. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ202005020.htm Goldfarb R J, Groves D I, Gardoll S. Orogenic gold and geologic time: a global synthesis[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2001, 18(1/2): 1-75.
朱日祥, 范宏瑞, 李建威, 等. 克拉通破坏型金矿床[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2015, 45(8): 1153-1168+1-4. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK201508006.htm Li S R, Santosh M. Metallogeny and craton destruction: records from the North China Craton[J]. Ore Geology Reviews. 2014, 56: 376-414.
Song M C, Li S Z, Santosh M, et al. Types, characteristics andmetallogenesis of gold deposits in the Jiaodong Peninsula, Eastern North China Craton[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2015, 65: 612-625.
宋明春. 胶东金矿深部找矿主要成果和关键理论技术进展[J]. 地质通报, 2015, 34(9): 1758-1771. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20150917&flag=1 Gong B, Zheng Y F, Chen R X. An online method combining a thermal conversion elemental analyzer with isotope ratio mass spectrometry for the determination of hydrogen isotope composition and water concentration in geological samples[J]. Rapid Communications in Mass Spectrometry, 2007, 21(8): 1386-1392.
Clayton R N, Mayeda T K. The use of bromine pentafluoride in the extraction of oxygen from oxides and silicates for isotopic analysis[J]. Geochimica Et Cosmochimica Acta, 1963, 27(1): 43-52.
Studley S A, Ripley E M, Elswick E R, et al. Analysis of sulfides in whole rock matrices by elemental analyzer-continuous flow isotope ratio mass spectrometry[J]. Chemical Geology, 2002, 192(1): 141-148.
卢焕章. 流体包裹体[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2004: 11-325. Hall D L, Sterner S M, Bodnar R J. Freezing point depression of NaCl-H2O solution[J]. Economic Geology, 1988, 83(1): 197-202.
Roedder E. Fluid Inclusions. Reviews in Mineralogy[J]. Mineral. Soc. Amer., 1984: 12.
郑永飞. 稳定同位素地球化学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2000: 62-118. Hollister L S, Burruss R C. Phase equilibria in fluid inclusions from the Khtada Lake metamorphic complex[J]. Geochim. cosmochim. acta, 1976, 40(2): 163-175.
Fan H R, Ming G Z, Xie Y H, et al. Ore-forming fluids associated with granite-hosted gold mineralization at the Sanshandao deposit, Jiaodong gold province, China[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 2003, 38(6): 739-750.
Yang L Q, Zhang L, Wang Y, et al. Thermochronologic constrains on the processes of formation and exhumation of the Xinli orogenic gold deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula, eastern China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews: Journal for Comprehensive Studies of Ore Genesis and Ore Exploration, 2017, 81(Pt. 1): 140-153.
陈衍景, 倪培, 范宏瑞, 等. 不同类型热液金矿系统的流体包裹体特征[J]. 岩石学报, 2007, 23(9): 2085-2108. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200709009.htm Chai P, Sun J G, Hou Z Q, et al. Geological, fluid inclusion, H-O-S-Pb isotope, and Ar-Ar geochronology constraints on the genesis of the Nancha gold deposit, southern Jilin Province, northeast China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2016, 72: 1053-1071.
Taylor H P. The Application of Oxygen and Hydrogen Isotope Studies to Problems of Hydrothermal Alteration and Ore Deposition[J]. Economic Geology, 1974, 69(6): 843-883.
黄德业. 胶东金矿成矿系列硫同位素研究[J]. 矿床地质, 1994, (1): 75-87. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ401.007.htm 李治平. 胶东乳山金矿床成因[J]. 矿床地质, 1992, (2): 165-178. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ199202007.htm 杨敏之. 金矿床围岩蚀变带地球化学: 以胶东金矿床为例[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1998: 100-105. Mao J W, Wang Y T, Li H M, et al. The relationship of mantle-derived fluids to gold metallogenesis in the Jiaodong Peninsula: Evidence from D-O-C-S isotope systematics[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2008, 33(3/4): 361-381.
侯建华, 任天龙, 王来明, 等. 胶东地区晚侏罗世玲珑期花岗岩[J]. 山东国土资源, 2021, 37(9): 1-11. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDDI202109001.htm 蔡亚春. 胶东地区白垩纪中-基性脉岩岩浆作用与典型金矿床研究[D]. 中国科学院大学博士后论文, 2014. 常裕林, 郑小礼, 王晖. 胶东西北部玲珑、郭家岭超单元花岗岩成因探讨[J]. 地质找矿论丛, 2006, (S1): 90-94. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZZK2006S1022.htm 姜晓辉, 范宏瑞, 胡芳芳, 等. 胶东三山岛金矿中深部成矿流体对比及矿床成因[J]. 岩石学报, 2011, 27(5): 1327-1340. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201105009.htm Li R H, Chen B H, Goldfarb R J, et al. A comparison of Jiaojia- and Linglong-type gold deposit ore-forming fluids: Do they differ?[J]. Ore Geology Reviews: Journal for Comprehensive Studies of Ore Genesis and Ore Exploration, 2017, 88: 511-533.
Phillips G N, Evans K A. Role of CO2 in the formation of gold deposits[J]. Nature, 2004, 429(6994): 860-863.
Kerrich R, Goldfarb R, Groves D, et al. The characteristics, origins, and geodynamic settings of supergiant gold metallogenic provinces[J]. Science in China Series D, 2000, (43): 1-68.
Wen B J, Fan H R, Hu F F, et al. Fluid evolution and ore genesis of the giant Sanshandao gold deposit, Jiaodong gold province, China: Constrains from geology, fluid inclusions and H-O-S-He-Ar isotopic compositions[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2016, 171: 96-112.
陈阳阳. 山东焦家金矿床地球化学特征及矿床成因探讨[D]. 长安大学硕士学位论文, 2017. 刘日富, 许延波, 沈少莹, 等. 山东省莱州市新立村矿区深部及外围金矿勘探报告. 山东黄金地质矿产勘查有限公司, 2015.



 下载:
下载: