Electron microprobe analysis of sulfide and its implication on genesis of Jinding lead zinc deposit in Yunnan Province
-
摘要:
金顶铅锌矿床位于滇西兰坪思茅盆地北部,为世界级超大型铅锌矿床。应用电子探针分析(EPMA)技术测定了金顶铅锌矿床中不同矿段(北厂、跑马坪、白草坪)黄铁矿、闪锌矿的微量元素组成,探讨金属硫化物的地球化学特征、矿床成矿环境,从而为研究区矿床成因提供依据。结果表明,各个矿段不同寄主岩石中黄铁矿相对富集Pb、Zn、Co,贫Cu、Cd、Ni、Sb、Te等微量元素,闪锌矿相对富集Cd、Pb等微量元素,贫Fe、Mn、Ag、Cu、Sb等。微量元素Cd、Fe、Mn、Sb、Cu、Pb、Co、Zn等可能以类质同象、矿物包体及多种形式赋存于金属硫化物中。硫化物微量元素特征显示其主要形成于中低温,成矿温度自白草坪-北厂-跑马坪呈现上升特征,具盆地卤水特征。综合矿床地质特征及微量元素特征,表明金顶铅锌矿床应属于密西西比河谷型(MVT)矿床一类。
Abstract:The Jinding lead-zinc deposit is located in the northern of the Lanping-Simao Basin in western Yunnan, which is a world-class super large lead-zinc deposit.The electron probe microanalysis (EPMA)technology was used to determine the trace element composition of pyrite and sphalerite in different ore sections of the Jinding lead-zinc deposit in this paper (Beichang, Paomaping and Baicaoping).This paper discusses the geochemical characteristics of metal sulfide and the metallogenic environment of the deposit, which provide a basis for the genesis of the deposit in the study area.The results show that the different host rocks in each ore section are relatively enriched in Pb, Zn and Co, but poor in trace elements, such as Cu, Cd, Ni, Sb and Te, while sphalerite is relatively enriched in Cd and Pb, but poor in trace elements, such as Fe, Mn, Ag, Cu and Sb.Trace elements, such as Cd, Fe, Mn, Ni, Sb, Cu, Pb, Co and Zn, could occur in sulfides as isomorphism, mineral inclusions or various forms.The characteristics of trace elements of sulfides show that there are mainly formed at medium and low temperature.The mineralization temperature shows rising characteristics from Baicaoping to Beichang to Paomaping, which has the characteristics of basin brine.According to the geological and trace element characteristics of the deposit, Jinding lead-zinc deposit should belong to MVT deposit.
-
Keywords:
- Jinding lead-zinc deposite /
- lectron probe /
- genesis of the deposit /
- sulfide /
- Yunnan Province
-
致谢: 诚挚感谢中色紫金地质勘察有限责任公司蒋斌斌工程师在野外工作中的大力支持和帮助。
-
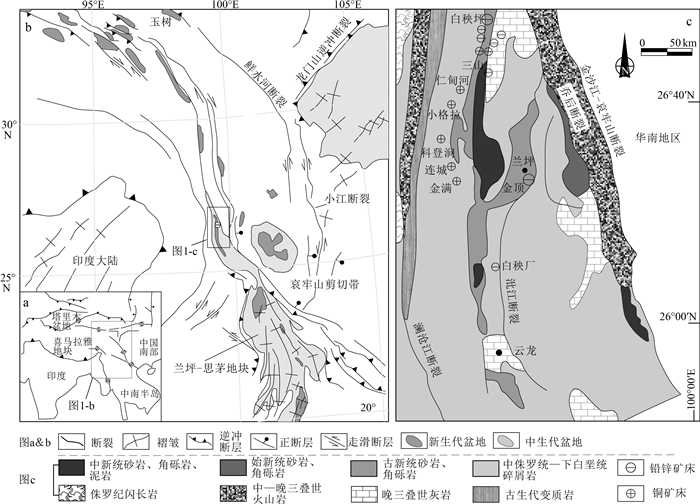
图 1 喜马拉雅造山带中新生代盆地构造(a)、兰坪-思茅地块金顶铅锌矿床位置(b)与兰坪盆地北部区域地质简图(c)(据参考文献[1, 22-23]修改)
Figure 1. The generalized structure and distribution of Mesozoic-Cenozoic basins in Himalayan orogenic (a), the location of Jinding lead-zinc deposit in Lanping-Simao block (b), and the geological sketch map of the northern part of Lanping basin (c)
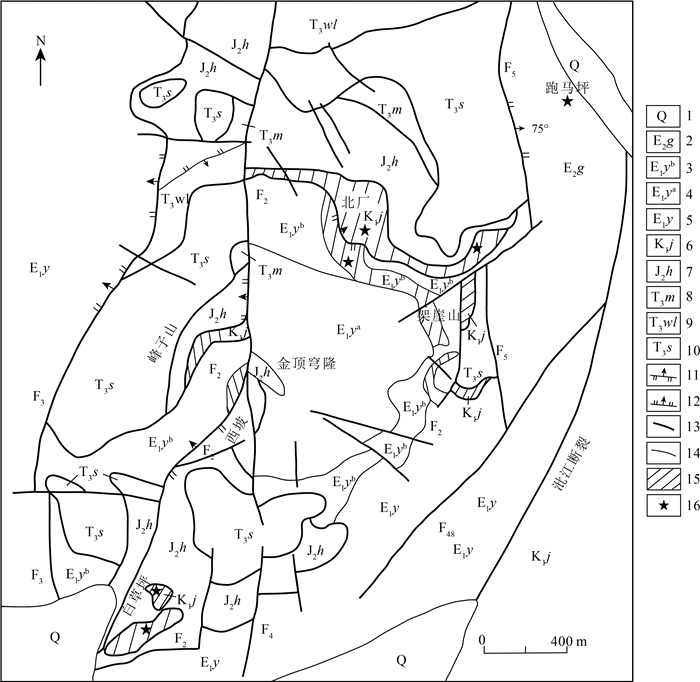
图 2 金顶铅锌矿床地质图(据参考文献①修改)
1—第四系砾石及砂土; 2—古新统果郎组泥质粉砂岩、细砂岩; 3—古新统云龙组含石膏灰岩角砾岩、含砾砂岩、粉砂岩; 4—古新统云龙组含砾的砂岩、粉砂岩; 5—古新统云龙组泥砾岩,夹石膏和粉砂岩; 6—下白垩统景星组石英砂岩; 7—中侏罗统花开佐组粉砂岩及细砂岩; 8—上三叠统麦初菁组粉砂质泥岩; 9—上三叠统挖鲁八组泥岩及粉砂岩; 10—上三叠统三合洞组泥灰岩、含燧石、沥青白云质灰岩; 11—正断层; 12—逆断层; 13—断裂; 14—地质界线; 15—矿体; 16—采样位置
Figure 2. The geological map of the Jinding lead-zinc deposit
表 1 金顶铅锌矿床黄铁矿电子探针分析结果
Table 1 The analytical results of price from the Jinding lead-znic deposit using electron probe
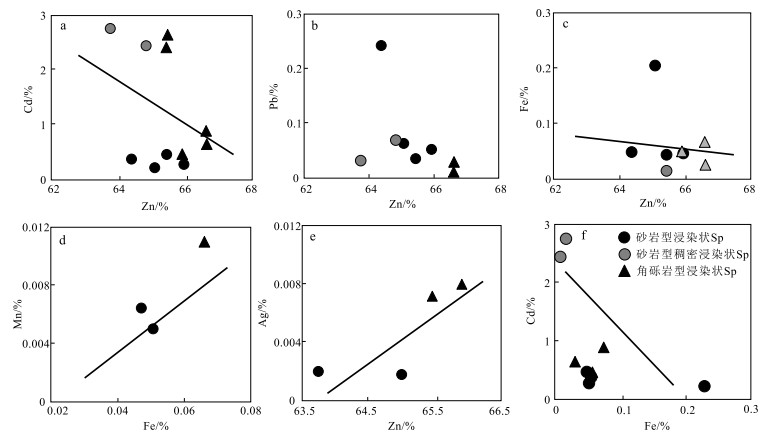
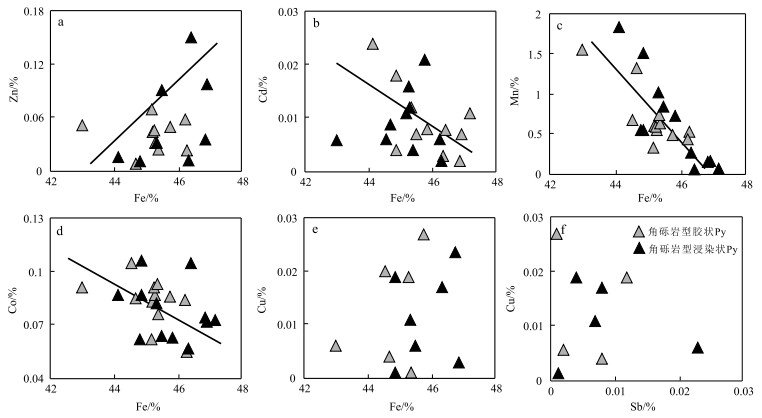
% 样品编号 矿石类型及矿物特征 Zn Fe S Pb Sb Cd Ag Cu Ni Co Mn 总计 跑马坪 JZB26-2 灰岩角砾岩型,浸染状矿化 0.016 44.135 52.851 0.044 - 0.024 - - - 0.087 1.84 99.009 JZB26-2 灰岩角砾岩型,浸染状矿化 0.032 45.332 53.048 - 0.007 0.012 - 0.011 - 0.082 1.019 99.584 JZB26-2 灰岩角砾岩型,浸染状矿化 - 45.837 53.302 0.057 0.005 0.008 - - - 0.063 0.726 100.009 JZB26-2 灰岩角砾岩型,浸染状矿化 0.011 44.804 52.135 0.037 - - 0.003 - 0.015 0.062 0.549 97.655 JZB26-2 灰岩角砾岩型,浸染状矿化 - 44.869 53.293 0.135 0.004 0.018 - 0.019 0.003 0.087 1.515 99.943 JZB26-2 灰岩角砾岩型,浸染状矿化 - 47.178 52.951 - - 0.011 0.005 - - 0.073 0.065 100.372 JZB26-2 灰岩角砾岩型,浸染状矿化 0.091 45.494 52.795 0.076 0.023 0.007 0.007 0.006 - 0.064 0.848 99.411 JKB817-1 灰岩角砾岩型,浸染状矿化 0.15 46.423 52.996 0.456 0.003 0.008 - - - 0.105 0.06 100.211 JKB817-1 灰岩角砾岩型,浸染状矿化 0.098 46.907 53.248 0.393 - 0.007 - - 0.016 0.072 0.159 100.9 JKB817-1 灰岩角砾岩型,浸染状矿化 0.035 46.848 53.227 0.227 - 0.002 0.027 0.003 - 0.074 0.149 100.62 JKB817-1 灰岩角砾岩型,浸染状矿化 - 44.864 51.12 0.785 0.001 0.004 0.007 0.001 0.004 0.106 0.547 97.439 JKB817-1 灰岩角砾岩型,浸染状矿化 0.012 46.333 52.843 0.177 0.008 0.003 0.004 0.017 0.007 0.057 0.266 99.758 JDB18-17 灰岩角砾岩型,胶状矿化 0.051 43.014 52.009 1.01 0.002 0.006 0.016 0.006 0.022 0.091 1.558 97.797 JDB18-17 灰岩角砾岩型,胶状矿化 0.044 45.195 52.261 0.011 - - - - - 0.083 0.6 98.197 JDB18-17 灰岩角砾岩型,胶状矿化 0.032 45.276 53.045 - 0.012 0.012 - 0.019 - 0.087 0.552 99.054 JDB18-17 灰岩角砾岩型,胶状矿化 0.069 45.183 52.756 0.071 0.014 0.011 - - - 0.062 0.327 98.507 JDB18-17 灰岩角砾岩型,胶状矿化 0.046 45.257 52.957 0.066 - 0.016 0.004 - 0.002 0.091 0.592 99.031 JDB18-17 灰岩角砾岩型,胶状矿化 - 44.542 52.729 - - 0.006 - 0.02 - 0.105 0.677 98.08 JDB18-17 灰岩角砾岩型,胶状矿化 0.023 46.284 53.281 0.11 0.002 0.002 - - 0.008 0.055 0.53 100.338 JDB18-17 灰岩角砾岩型,胶状矿化 0.05 45.753 53.012 - 0.001 0.021 0.008 0.027 - 0.086 0.487 99.451 JDB18-17 灰岩角砾岩型,胶状矿化 0.024 45.384 52.674 - 0.003 0.004 0.004 - 0.005 0.076 0.637 98.894 JDB18-17 灰岩角砾岩型,胶状矿化 0.058 46.217 52.585 0.096 0.002 0.006 0.006 - 0.001 0.084 0.433 99.488 JDB18-17 灰岩角砾岩型,胶状矿化 0.008 44.673 52.896 - 0.008 0.009 - 0.004 0.007 0.085 1.321 99.031 JDB18-17 灰岩角砾岩型,胶状矿化 - 45.356 53.304 0.032 - - 0.006 0.001 - 0.093 0.744 99.542 北厂 JDB402-1 砂岩型,浸染状矿化 - 46.728 52.995 - 0.012 0.011 - 0.013 - 0.096 0.012 99.879 JDB402-1 砂岩型,浸染状矿化 0.021 47.135 52.595 0.096 - 0.011 0.01 - - 0.077 0.028 99.976 JDB402-1 砂岩型,浸染状矿化 0.015 46.893 53.742 0.132 0.006 0.013 - 0.017 0.006 0.093 - 100.917 JDB402-1 砂岩型,浸染状矿化 - 46.615 53.122 0.021 - - - 0.011 0.004 0.087 - 99.895 JDB402-1 砂岩型,浸染状矿化 0.01 46.262 53.011 0.21 0.015 0.017 0.002 - - 0.086 - 99.624 JDB402-1 砂岩型,浸染状矿化 0.01 45.462 53.909 0.03 0.005 0.017 0.004 0.02 - 0.086 0.008 99.587 JZB21-14 砂岩型,浸染状矿化 0.027 45.883 52.773 0.123 - 0.024 0.01 - - 0.034 - 98.906 JZB21-14 砂岩型,浸染状矿化 - 45.853 52.486 0.622 0.004 0.022 - 0.012 - 0.005 0.014 99.018 JDB412-2 含灰岩角砾砂岩型,浸染状 0.035 47.106 53.395 - 0.002 0.01 0.005 0.003 - 0.072 0.18 100.808 JDB412-2 含灰岩角砾砂岩型,浸染状 0.117 46.611 54.261 0.082 - 0.016 0.01 0.003 - 0.078 0.347 101.525 注:“-”代表低于检测下限 表 2 金顶铅锌矿床中闪锌矿电子探针分析结果
Table 2 The analytical results of sphalerites from the Jinding Pb-Zn deposit using electron probe
% 样品编号 矿石类型及矿物特征 Zn Fe S Pb Sb Cd Ag Cu Ni Co Mn 总计 跑马坪 JZB18-31 灰岩角砾岩型,蠕虫状矿化 66.505 0.012 32.787 - - 0.229 0.005 - - - 0.006 99.587 JZB18-31 灰岩角砾岩型,蠕虫状矿化 65.847 0.033 33.438 0.043 - 0.297 - 0.018 0.005 - 0.007 99.707 JZB18-31 灰岩角砾岩型,蠕虫状矿化 65.506 0.042 33.243 0.033 - 0.588 0.002 - - 0.009 0.001 99.439 JZB18-31 灰岩角砾岩型,蠕虫状矿化 66.255 0.021 33.456 0.028 - 0.367 - - - - - 100.151 JZB18-31-1 灰岩角砾岩型,胶状矿化 66.868 0.016 32.566 0.076 0.014 0.545 - 0.006 - - 0.007 100.154 JZB18-31-2 灰岩角砾岩型,胶状矿化 66.23 0.039 32.108 0.258 - 0.274 - 0.032 - - 0.012 98.955 JZB18-31-3 灰岩角砾岩型,胶状矿化 66.904 0.025 32.57 0.177 - 0.416 - 0.042 0.001 0.001 0.013 100.167 JZB18-31-4 灰岩角砾岩型,胶状矿化 65.256 0.083 32.2 0.685 0.006 0.248 - - - 0.002 0.052 98.542 JZB18-31-5 灰岩角砾岩型,胶状矿化 65.791 0.109 32.543 0.303 - 0.234 - - - - 0.044 99.057 JZB18-31-6 灰岩角砾岩型,胶状矿化 64.851 0.116 32.14 0.254 - 2.534 0.011 - 0.007 0.023 0.002 99.938 JZB18-31-7 灰岩角砾岩型,胶状矿化 66.133 0.164 32.646 0.071 - 0.218 - - 0.004 0.011 0.087 99.334 JZB18-31-8 灰岩角砾岩型,胶状矿化 63.727 1.635 32.233 0.447 - 0.133 0.003 - 0.006 0.014 0.182 98.432 JZB18-31-9 灰岩角砾岩型,胶状矿化 64.835 0.388 32.105 0.632 0.005 0.251 - - 0.009 0.004 0.043 98.586 JZB18-31-10 灰岩角砾岩型,胶状矿化 65.718 0.081 32.88 0.313 - 0.309 0.025 - - 0.008 0.044 99.382 JZB18-31-11 灰岩角砾岩型,胶状矿化 65.917 0.303 32.792 0.662 - 0.102 0.003 0.051 - 0.011 0.134 99.998 JZB18-31-12 灰岩角砾岩型,胶状矿化 65.573 0.054 32.713 - - 0.298 0.006 - - - 0.002 98.664 JZB18-27 灰岩角砾岩型,胶状矿化 66.381 0.059 32.339 0.271 - 0.158 - 0.11 0.012 0.002 0.019 99.351 JZB18-27 灰岩角砾岩型,胶状矿化 67.338 0.029 32.779 0.223 - 0.317 - 0.068 - 0.011 0.013 100.816 JDB18-17-1 灰岩角砾岩型,胶状矿化 66.24 0.043 32.534 0.401 0.001 0.362 0.017 - - 0.008 0.031 99.637 JDB18-17-2 灰岩角砾岩型,胶状矿化 65.892 0.019 31.987 0.379 - 0.292 - - - - 0.043 98.612 JDB18-17-3 灰岩角砾岩型,胶状矿化 65.546 0.036 32.361 0.373 - 0.38 - - - 0.007 0.026 98.731 JDB18-17-4 灰岩角砾岩型,胶状矿化 65.675 0.032 32.393 0.366 0.021 0.384 - - - - 0.022 98.923 JDB18-17-5 灰岩角砾岩型,胶状矿化 65.749 0.028 32.201 0.356 0.001 0.323 - - 0.012 0.013 0.063 98.746 JDB18-17-6 灰岩角砾岩型,胶状矿化 66.393 0.067 32.52 0.344 - 0.247 - - 0.001 - 0.024 99.638 JDB18-17-7 灰岩角砾岩型,胶状矿化 66.456 0.263 33.263 0.115 - 0.184 - - - 0.007 0.027 100.323 JDB18-22 灰岩角砾岩型,浸染状矿化 65.347 1.134 32.085 0.269 0.027 0.003 0.011 0.122 - - 0.038 99.036 JZB26-2-1 灰岩角砾岩型,浸染状矿化 66.431 0.083 32.661 0.497 - 0.334 - - 0.014 0.03 0.051 100.121 JZB26-2-2 灰岩角砾岩型,浸染状矿化 64.616 0.028 32.159 0.058 0.009 2.369 - 0.003 - 0.006 0.034 99.282 JDB44-8 灰岩角砾岩型,浸染状矿化 66.622 0.256 32.586 0.058 - 0.852 - - - - 0.028 JDB44-8 灰岩角砾岩型,浸染状矿化 65.565 0.159 32.407 0.003 0.004 0.318 - - 0.001 0.013 0.015 98.517 JKB817-1 灰岩角砾岩型,浸染状矿化 63.374 0.779 32.604 0.092 0.01 2.08 0.001 - - 0.005 0.044 98.989 JKB817-1 灰岩角砾岩型,浸染状矿化 63.185 0.857 32.307 0.117 - 3.245 0.021 0.043 0.003 0.043 0.034 99.865 JKB817-1 灰岩角砾岩型,浸染状矿化 62.465 2.279 32.041 0.507 - 0.29 0.008 0.064 - - 0.086 97.756 JKB817-1 灰岩角砾岩型,浸染状矿化 61.43 0.02 31.681 0.042 0.039 6.696 - 0.022 0.002 0.009 0.01 99.957 JKB817-1 灰岩角砾岩型,浸染状矿化 65.639 0.092 31.157 0.043 0.011 1.978 - - 0.007 0.017 0.036 98.98 JKB817-1 灰岩角砾岩型,浸染状矿化 65.657 0.662 32.14 0.003 - 0.205 - 0.003 - 0.004 0.166 98.901 北厂 JDB402-1 砂岩型,浸染状矿化 65.947 0.047 32.172 0.053 - 0.279 - - - - 0.006 98.504 JDB402-1 砂岩型,浸染状矿化 65.088 0.206 32.172 0.063 - 0.222 0.001 - - - 0.005 97.757 JZB21-14 砂岩型,浸染状矿化 65.45 0.044 32.222 0.035 0.002 0.467 - - 0.001 - - 98.221 JZB21-14 砂岩型,浸染状矿化 64.391 0.05 32.799 0.242 - 0.376 - - - 0.007 0.004 97.876 JDB413-2 砂岩型,稠密浸染状矿化 64.823 - 32.009 0.07 - 2.443 - - 0.018 - 0.002 99.365 JDB413-2 砂岩型,稠密浸染状矿化 63.752 0.015 32.175 0.032 - 2.762 0.002 - 0.002 - - 98.751 JDB412-2 含灰岩角砾砂岩型,浸染状 65.46 - 32.345 - 0.024 2.656 0.007 - - - - 100.498 JDB412-2 含灰岩角砾砂岩型,浸染状 65.904 0.051 32.489 - - 0.473 0.008 - 0.017 0.006 - 98.97 JDB412-2 含灰岩角砾砂岩型,浸染状 65.423 - 32.75 - 0.015 2.43 - - - - 0.006 100.648 JDB412-2 含灰岩角砾砂岩型,浸染状 66.61 0.067 32.629 0.003 - 0.898 - - 0.013 0.006 0.011 100.246 JDB412-2 含灰岩角砾砂岩型,浸染状 66.635 0.027 32.933 0.03 - 0.657 - - - - - 100.282 白草坪 JDB401-1 砂岩型,浸染状矿化 63.583 0.03 32.377 0.173 0.005 1.258 - - 0.008 0.032 0.001 97.502 JDB401-1 砂岩型,浸染状矿化 63.943 0.063 32.17 0.158 - 1.685 - 0.011 0.006 - - 98.036 JDB401-1 砂岩型,浸染状矿化 63.522 0.023 32.068 0.208 - 1.26 - - 0.011 - - 97.099 JDB401-2 含灰岩角砾砂岩型,浸染状 64.059 0.046 32.257 0.023 0.009 1.492 - 0.03 0.01 - 0.006 97.94 JDB401-2 含灰岩角砾砂岩型,浸染状 62.261 1.423 32.398 0.1 0.008 0.641 - 0.255 - 0.004 0.012 97.102 JDB404-3 含灰岩角砾砂岩型,浸染状 56.855 0.052 31.017 0.039 0.012 12.289 - 0.013 - - - 100.277 JDB404-3 含灰岩角砾砂岩型,浸染状 59.682 0.012 28.766 0.007 0.013 10.062 - 0.035 - - - 98.577 注:“-”代表低于检测下限 -
Song Y, Hou Z, Xue C, et al. New mapping of the world-class Jinding Zn-Pb deposit, Lanping Basin, Southwest China: Genesis of ore host rocks and records of hydrocarbon-rock interaction[J]. Economic Geology, 2020, 115(5): 981-1002. doi: 10.5382/econgeo.4721
Song Y, Liu Y, Hou Z, et al. Sediment-hosted Pb-Zn deposits in the Tethyan domain from China to Iran: Characteristics, tectonic setting, and ore controls[J]. Gondwana Research, 2019, 75: 249-281. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2019.05.005
施加辛, 易凤煌, 文启錞. 兰坪金顶铅锌矿床的岩矿特征及成因[J]. 云南地质, 1983, (3): 179-194, 276-280. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YNZD198303000.htm 白嘉芬, 王长怀, 纳荣仙. 云南金顶铅锌矿床地质特征及成因初探[J]. 矿床地质, 1985, (1): 1-10. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ198501000.htm 张乾. 云南金顶铅锌矿床成因研究[J]. 地质找矿论丛, 1991, (2): 47-58. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZZK199102004.htm 张乾. 云南金顶超大型铅锌矿床的铅同位素组成及铅来源探讨[J]. 地质与勘探, 1993, (5): 21-28. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT199305005.htm 覃功炯, 朱上庆. 金顶铅锌矿床成因模式及找矿预测[J]. 云南地质, 1991, (2): 145-190, 205. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YNZD199102001.htm Kyle J K, Li N. Jinding: a giant tertiary sandstone-hosted Zn-Pb deposit, Yunnan, China[J]. SEG Newsletter, 2002, 50(1): 9-16.
薛春纪, 陈毓川, 杨建民, 等. 滇西兰坪盆地构造体制和成矿背景分析[J]. 矿床地质, 2002, (1): 36-44. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2002.01.005 薛春纪, 陈毓川, 王登红, 等. 滇西北金顶和白秧坪矿床: 地质和He, Ne, Xe同位素组成及成矿时代[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 2003, (4): 315-322. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK200304003.htm Xue C, Zeng R, Liu S, et al. Geologic, fluid inclusion and isotopic characteristics of the Jinding Zn-Pb deposit, western Yunnan, South China: A review[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2007, 31(1/4): 337-359.
王京彬, 李朝阳, 陈晓钟. 金顶超大型铅锌矿喷流沉积成因初探[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通讯, 1990, (2): 122-123. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYDH199002013.htm 赵兴元. 云南金顶铅锌矿床成因研究[J]. 地球科学, 1989, (5): 523-530. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX198905008.htm 曾荣, 薛春纪, 刘淑文, 等. 金顶超大型铅锌矿床成矿条件分析[J]. 地球科学与环境学报, 2005, (2): 21-25. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6561.2005.02.005 王安建, 曹殿华, 管烨, 等. 西南三江成矿带中南段金属矿床成矿规律与若干问题探讨[J]. 地质学报, 2009, 83(10): 1365-1375. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2009.10.001 罗君烈. 滇西特提斯的演化及主要金属矿床成矿作用[J]. 云南地质, 1991, (1): 1-10. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YNZD199101001.htm 叶庆同, 胡云中, 杨岳清. 三江地区区域地球化学背景和金银铅锌成矿作用[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1992. 曾荣, 薛春纪, 刘淑文, 等. 云南金顶铅锌矿床成矿流体与流体的稀土元素研究[J]. 地质与勘探, 2007, (2): 55-61. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT200702012.htm 王安建, 曹殿华, 高兰, 等. 论云南兰坪金顶超大型铅锌矿床的成因[J]. 地质学报, 2009, 83(1): 43-54. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE200901005.htm Leach D L, Song Y C, Hou Z Q. The world-classJinding Zn-Pb deposit: ore formation in an evaporite dome, Lanping Basin, Yunnan, China[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 2017, 52(3): 281-296. doi: 10.1007/s00126-016-0668-6
龚玉爽, 胡斌, 付山岭, 等. 电子探针分析技术(EPMA)在地学中的应用综述[J]. 化学工程与装备, 2011, (6): 166-168. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FJHG201106062.htm Tang YY, Bi X W, Fayek M, et al. Microscale sulfur isotopic compositions of sulfide minerals from the Jinding Zn-Pb deposit, Yunnan Province, Southwest China[J]. Gondwana Research, 2014, 26(2): 594-607.
Wang J H, Yin A, Harrison T M, et al. A tectonic model for Cenozoic igneous activities in the eastern Indo-Asian collision zone[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2001, 188(1/2): 123-133.
范金伟, 杨天南, 梁明娟, 等. 滇西兰坪盆地西缘火山岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年代学、地球化学特征及其大地构造意义[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2014, 33(3): 471-490. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSKW201403005.htm Chunji X, Shuwen L, Yuchuan C, et al. Giant mineral deposits and their geodynamic setting in the Lanping basin, Yunnan, China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2004, 78(2): 368-374.
Yalikun Y, Xue C, Symons D T A. Paleomagnetic age and tectonic constraints on the genesis of the giant Jinding Zn-Pb deposit, Yunnan, China[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 2018, 53(2): 245-259.
Xue C, Chi G, Fayek M. Micro-textures and in situ sulfur isotopic analysis of spheroidal and zonal sulfides in the giant Jinding Zn-Pb deposit, Yunnan, China: Implications for biogenic processes[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2015, 103: 288-304.
李胜荣, 许虹, 申俊峰. 结晶学与矿物学[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2008. Bajwah Z U, Seccombe P K, Offler R. Trace element distribution, Co: Ni ratios and genesis of the Big Cadia iron-copper deposit, New South Wales, Australia[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 1987, 22(4): 292-300.
李志丹, 薛春纪, 董新丰, 等. 新疆霍什布拉克铅锌矿床微量元素地球化学[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2014, 33(3): 540-550. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSKW201403012.htm Ye L, Cook N J, Ciobanu C L, et al. Trace and minor elements in sphalerite from base metal deposits in South China: A LA-ICPMS study[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2011, 39(4): 188-217.
Burke E A J, Kieft C. Roquesite and Cu-In-bearing sphalerite from Långban, Bergslagen, Sweden[J]. The Canadian Mineralogist, 1980, 18(3): 361-363.
Sverjensky D A. The origin of a Mississippi Valley-type deposit in the Viburnum Trend, southeast Missouri[J]. Economic Geology, 1981, 76(7): 1848-1872.
Bernardini G P, Borgheresi M, Cipriani C, et al. Mn distribution in sphalerite: an EPR study[J]. Physics and Chemistry of Minerals, 2004, 31(2): 80-84.
刘铁庚, 叶霖, 沈能平, 等. 闪锌矿的Cd含量与颜色关系[J]. 矿物学报, 2015, 35(1): 51-55. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWXB201501009.htm 叶庆同. 闪锌矿的化学成分特征及其地质意义[C]//中国地质科学院矿床地质研究所文集(14), 1985. Misra K C. Understanding mineral deposits[M]. Kluwer Academic Publishers, 2000.
Schwartz M O. Cadmium in zinc deposits: economic geology of a polluting element[J]. International Geology Review, 2000, 42(5): 445-469.
印修章, 胡爱珍. 以闪锌矿标型特征浅论豫西若干铅锌矿成因[J]. 物探与化探, 2004, (5): 413-414, 417. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTYH200405009.htm Cook N J, Ciobanu C L, Pring A, et al. Trace and minor elements in sphalerite: A LA-ICPMS study[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2009, 73(16): 4761-4791.
Yuan B, Zhang C, Yu H, et al. Element enrichment characteristics: Insights from element geochemistry of sphalerite inDaliangzi Pb-Zn deposit, Sichuan, Southwest China[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2018, 186: 187-201.
代鸿章. 云南省太平铅锌矿床地质地球化学特征与成矿机制[D]. 中国地质大学(北京)博士学位论文, 2016. 李季霖, 章永梅, 顾雪祥, 等. 云南西邑MVT型铅锌矿床地质特征与硫化物电子探针分析[J]. 地质与勘探, 2017, 53(1): 23-34. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT201701004.htm 王建飞, 许东, 尹光候. 云南金顶铅锌矿成矿流体特征与成矿作用[J]. 现代地质, 2014, 28(4): 701-710. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ201404005.htm 徐国风, 邵洁涟. 黄铁矿的标型特征及其实际意义[J]. 地质论评, 1980, (6): 541-546. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP198006015.htm Cook N J, Ciobanu C L, Mao J. Textural control on gold distribution in As-free pyrite from theDongping, Huangtuliang and Hougou gold deposits, North China Craton (Hebei Province, China)[J]. Chemical Geology, 2009, 264(1/4): 101-121.
Price B J. Minor elements in pyrites from thesmithers map area, bc and exploration applications of minor element studies[D]. Doctoral dissertation, University of British Columbia, 1972.
范世家, 王安建, 刘汉斌, 等. 论兰坪盆地白秧坪铜(钴)矿床成因的氦氩同位素证据[J]. 地质论评, 2006, (5): 628-635. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP200605009.htm 刘家军, 翟德高, 李志明, 等. 兰坪盆地白秧坪银铜多金属矿集区中银、钴、铋、镍的赋存状态与成因意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2010, 26(6): 1646-1660. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201006002.htm 王哲. 云南金顶铅锌矿床成矿流体与矿化机制研究[D]. 中国地质大学(北京)硕士学位论文, 2013. Wang C, Yang L, Bagas L, et al. Mineralization processes at the giant Jinding Zn-Pb deposit, Lanping Basin, Sanjiang Tethys Orogen: Evidence from in situ trace element analysis of pyrite and marcasite[J]. Geological Journal, 2018, 53(4): 1279-1294.
Qian Z. Trace elements in galena and sphalerite and their geochemical significance in distinguishing the genetic types of Pb-Zn ore deposits[J]. Chinese Journal of Geochemistry, 1987, 6(2): 177-190.
郭飞, 王智琳, 许德如, 等. 湖南栗山铅锌铜多金属矿床闪锌矿微量元素特征及成矿指示意义[J]. 地学前缘, 2020, 27(4): 66-81. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY202004006.htm 胡宇思, 叶霖, 黄智龙, 等. 滇东北麻栗坪铅锌矿床微量元素分布与赋存状态: LA-ICPMS研究[J]. 岩石学报, 2019, 35(11): 3477-3495. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201911014.htm 王光辉, 刘兵, 匡爱兵. 铅锌矿床中闪锌矿Cd含量及Zn/Cd值的地质意义[J]. 西北地质, 2016, 49(3): 132-140. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBDI201603015.htm 云南地质三大队. 云南省兰坪县金顶铅锌矿详细勘探地质报告. 昆明: 云南省地质与矿产局, 1984.



 下载:
下载: