Late Pliocene oblique thrusting and regional stress field changes in southern Longmen Mountain, eastern Tibet
-
摘要:
2008年汶川地震(Mw 7.9)同震滑移结果表明,今地壳缩短为近EW向,与龙门山褶皱冲断带斜交。这一斜向逆冲作用的准确起始时间一直未得到很好的约束。基于龙门山南段山前大邑背斜区三维地震解释和构造建模,结合野外地质调查和年代学数据,确定了晚新生代存在NE向和近NS向2期构造变形。120km长的NS向构造切割了NE向构造,表明近NS向构造形成时间较晚。山前大邑和邛西背斜区近NS向断层和褶皱的活动,均反映了龙门山南段局部或区域上水平最大主应力方向的转换过程,渐新世-早上新世的NW-SE向转变为晚上新世-全新世的近EW向。龙门山南段山前发育的NS向构造和汶川地震同震变形均反映出青藏高原东缘最新的EW向地壳缩短过程,为理解青藏高原东缘的隆升机制提供了新的视角。
Abstract:The co-seismic slip sense of the 2008 Wenchuan earthquake (Mw 7.9) has demonstrated the present east-west (E-W) crustal shortening and oblique thrusting across the Longmen Mountain. However, the oblique thrusting and its initial time remain poorly investigated. By using 3-D seismic reflection data, field investigation, and published dating results, the authors investigated the E-W crustal shortening in the Dayi Fault System (DYFS), and determined tectonic stress field changes during the Late Cenozoic. Two-period tectonic deformations were found in the DYFS, which correspond to the NE-and NS-trending structures, respectively. The activities of the DYFS and Qiongxi Fault System reflect a change in the direction of the tectonic stress, from NW-SE during the Oligocene and Early Pliocene to E-W from the Late Pliocene to Holocene. The 120km NS-trending structures in the southern Longmen Mountain range front as well as the Wenchuan earthquake co-seismic ruptures are assumed to reflect the active, E-W crustal shortening in Longmen Mountain, eastern Tibet plateau. The results obtained by the authors provide a new perspective for the uplift mechanisms of eastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau.
-
延长组长6油层组是鄂尔多斯盆地的主要产油层系,多年来,相继在盆地内安塞油田、姬塬油田、华庆油田等区域的长6油层组石油勘探中取得了显著的成果。20世纪70年代对该盆地东南部进行了地质普查,局部地区进行了地质详查及细致勘探,在多处发现较好的油气显示,但由于种种原因,勘探开发曾一度停滞,很多认识都停留在90年代研究的基础上。盆地南部现有的认识很难满足勘探工作的需要,且自2000年以后,由于全球资源和能源的紧张,各地油气勘探的力度逐步加强,该区的勘探开发再一次被提上了议程。
本文以研究区长6储层为目的层,通过岩心观察、油层物性、扫描电镜等分析测试手段,对目的层成岩作用进行了研究,意在揭示成岩作用对储层孔隙的影响作用,为后期勘探开发提供依据。
1. 地质背景
研究区位于鄂尔多斯盆地东南部,北起甘泉,南至铜川,西抵正宁,东达宜川(图 1),横跨陕北斜坡和渭北隆起2个构造单元。其北部在西倾单斜的背景上发育一系列的鼻褶构造,呈近南北向展布;南部以逆冲断层为主,呈南翘北倾的东西向排带状分布。晚三叠世受印支期秦岭造山活动的影响,延长期长6沉积期湖盆基底逐渐抬升,湖区逐渐缩小,形成湖退砂进的三角洲沉积,同时受东北、西南两大物源的控制。研究区东北和西南地区分别发育三角洲前缘沉积和深湖浊流沉积,三角洲前缘水下分流河道砂体和深湖浊积砂体广泛发育,形成延长组的主要产油层之一[1]。
2. 储层岩石学特征
砂岩薄片显微镜下鉴定结果表明,鄂尔多斯盆地东南部延长组长6储层砂岩以长石砂岩和岩屑质长石砂岩为主(图 2)。研究区长6砂岩的碎屑含量较高,碎屑中石英含量占碎屑总量的2%~21.5%,平均29.13%,长石含量较高,在5%~59.5%之间,平均值达37.31%,储层砂岩中的自生长石以钠长石为主,另外还见少量钾长石。受东北方向中下太古界—元古宇多套变质岩系组成的深变质岩物源的影响,长6油层组矿物成熟度由东北向西南逐渐增高,岩屑以千枚岩、片岩、板岩等变质岩岩屑为主,岩屑含量在2%~37.8%之间,平均值为11.83%,杂基主要为粘土矿物,包括伊利石、绿泥石、高岭石及少量泥质杂基,胶结物主要为绿泥石、方解石、铁方解石、铁白云石、硅质、白云石等,砂岩颗粒多呈次圆-次棱状、磨圆度中-好,分选性中等。
3. 成岩作用及其对孔隙演化的影响
通过镜下观察,研究区砂岩储集层在埋藏成岩过程中发生的成岩作用主要为压实作用、胶结作用、溶解作用和交代作用,不同成岩作用对储层孔隙演化具有显著的影响[2-3]。根据成岩作用对砂体孔隙演化的影响,分为建设性和破坏性两大类。
3.1 降低储层孔渗性的成岩作用
3.1.1 机械压实作用
压实作用是砂岩原生粒间孔减少的主要原因之一,对孔隙度的影响很大。研究区长6砂岩在埋藏成岩过程中经历了不同程度的压实作用,镜下观察颗粒呈定向或半定向排列,杂基等柔性矿物被压弯或折断,碎屑间的接触方式以线接触或点-线接触为主(图版Ⅰ-A)。一般压实作用的程度随可塑性岩石碎屑的比例增大而增强,但从研究区长6储层镜下薄片观察发现,研究区碎屑颗粒间呈点-线状接触,机械压实作用强度较弱,残余粒间孔隙较发育[4-5]。另外通过统计对比发现,由于东北部向西南部杂基等柔性易压实矿物依次增加,而相应的浊沸石、方解石、绿泥石等抗压能力强的胶结物含量依次减少,造成其压实作用后孔隙损失依次增大。
3.1.2 胶结作用
胶结作用是导致储层孔隙度降低的重要因素,其成岩效应是堵塞孔隙,但不减小粒间体积,这与压实作用有着本质上的差别。通过镜下观察,本区主要有碳酸盐胶结、硅质胶结及粘土矿物胶结3种,胶结类型以孔隙式胶结、孔隙-薄膜式胶结和孔隙-加大式胶结为主。
(1)碳酸盐胶结
研究区长6储层碳酸盐胶结物含量介于0%~ 23.4%之间,平均为5.28%,类型有早成岩期形成的方解石、晚成岩期生成的铁方解石胶结、铁白云石胶结和白云石胶结4种,以铁方解石、铁白云石胶结为主(图版Ⅰ-B)。方解石胶结充填于碎屑颗粒间,呈连生式胶结,在阴极发光下显示橙黄色[6-9],仅在研究区北部分布,铁方解石以嵌晶式、薄膜式呈漂浮状充填于原生孔隙和长石溶蚀产生的次生孔隙中,在阴极发光下颜色较暗,白云石多呈自形菱面体充填于粒间孔中(图版Ⅰ-L)。由于白云石胶结物与该区碳酸盐岩岩屑含量高有一定相关性[10-11],铁白云石和白云石多发育在研究区西南地区。另外,受沉积相影响,在开阔深湖相中的砂岩铁白云石及铁方解石的含量较多[12],研究区西南部铁白云石和铁方解石含量高于东北部。
由于区内碳酸盐胶结物主要形成于晚成岩阶段,中成岩阶段A期出现大量含铁碳酸盐胶结物,溶蚀交代作用较弱,影响储层物性的主要作用为原生孔隙之间的胶结作用,且其含量与孔隙度及渗透率具有一定的负相关性[13]。
(2)长英质胶结
长英质胶结包括自生石英胶结和自生长石胶结,在研究区长6砂岩中通常以石英次生加大和自生石英长石微晶的形式存在。石英的次生加大对砂岩储层孔隙度的影响取决于石英次生加大的强度,薄片观察表明,研究区长6石英次生加大多为Ⅰ级加大,偶见Ⅱ级加大,石英具有窄的加大边或小的自形晶,可见研究区硅质胶结作用较弱,对降低砂岩的孔隙度仅起次要作用(图版Ⅰ-C),自生长石常以自生加大边和半自形粒状长石充填孔隙出现,在研究区内不常见(图版Ⅰ-D)。
(3)粘土胶结
研究区长6粘土矿物胶结物有绿泥石、高岭石、伊利石、伊蒙混层等,其中以绿泥石和伊蒙混层为主。
受沉积相影响,该区长6绿泥石胶结分布普遍,含量最高[5, 11],以薄膜(栉壳)方式包裹颗粒,或以针状或玫瑰花状、绒球状集合体形成环边绿泥石充填于孔隙中(图版Ⅰ-E)。伊利石和伊/蒙混层,在扫描电镜下多呈片状或丝缕状和蜂窝状充填于孔隙中(图版Ⅰ-F),绿泥石薄膜和伊利石充填原生孔隙,使孔隙度降低,但增强砂岩的抗压实程度,同时也阻碍孔隙水与颗粒的反应,限制石英次生加大,有利于原生孔隙的保存,起到了保护粒间孔的作用[14]。研究区长6储层砂岩薄片长石高岭石化现象不常见(图版Ⅰ-H),常呈薄膜状出现在颗粒表面,部分出现绒球状充填孔隙,高岭石的含量和孔隙度之间一般呈正相关关系[8],因此研究区长6储层高岭石的含量较低,对孔隙度的增加影响较小。
3.1.3 压实作用及胶结作用对储层孔隙的影响
胶结作用虽然引起孔隙堵塞,但不减少粒间体积,这些自生胶结物在后期孔隙流体作用下可被溶解成为孔隙,同时胶结作用可阻止压实作用。依据Housknechet评价图[15],假设砂层原始孔隙度为40%,通过计算得知(图 3),研究区延长组长6储集层中压实作用不可逆地减小岩石的粒间体积,其仍然是造成孔隙度下降最直接、最重要的因素,减少的原始孔隙百分比达68.8%,胶结作用消除的原始孔隙百分比可达16.9%。
3.2 增加储层孔渗性的成岩作用
3.2.1 溶解作用
研究区长6储层中有大量的长石、岩屑等易溶组分,其溶解作用主要为长石被酸性流体溶蚀而形成的粒间和粒内溶蚀孔隙,呈网状、岛弧状,在扫描电镜下多见长石沿解理缝进行(图版Ⅰ-I),另外,在含有成岩高岭石的碎屑岩中,随着孔隙溶液酸碱度的变化,高岭石稳定性变差,继而转变成伊/蒙混层、伊利石、绿泥石等。
3.2.2 交代作用
研究区长6储层内交代作用是方解石对长石的交代(图版Ⅰ-J),主要表现为成岩早期长石溶孔形成的粒内溶孔被后期的方解石胶结物充填。由于研究区内方解石胶结不常见,而晚期铁方解石胶结对长石、石英等碎屑颗粒的交代作用也仅存在于局部,交代作用虽堵塞孔隙,使渗透率降低,但交代过程并未减小粒间孔隙的体积,事实上对储层的影响不大。
3.2.3 溶解作用对孔隙的影响
由于交代作用对储层的影响不大,增加砂体孔、渗性的成岩作用主要为溶解作用对储层的影响而形成的次生孔隙,通过定量化计算,研究区延长组长6由溶解作用增加的孔隙度平均值为3.67%。
4. 成岩序列及成岩阶段的确定
根据显微镜、扫描电镜、阴极发光等镜下的成岩现象及成岩作用特征,结合自生矿物的产出状况、生成条件和演化过程,揭示成岩矿物的接触关系,归纳研究区的典型成岩序列特征。自生粘土矿物胶结物包绕碎屑颗粒,如绿泥石、伊利石等,石英的次生加大覆盖并包裹绿泥石薄膜和自生伊利石,被晚期方解石包围,说明其形成早于晚期方解石,但晚于绿泥石薄膜的形成时间,方解石、铁方解石和高岭石充填于粒间孔隙及长石、岩屑溶孔内,或可见其交代其他碎屑颗粒,因此方解石、铁方解石和高岭石的沉淀发生在长石、岩屑颗粒的溶蚀作用之后。
根据上述分析,初步确定鄂尔多斯盆地东南部延长组长6储层的成岩序列为:压实作用→早期粘土膜(绿泥石膜)形成→石英次生加大→(早期)碳酸盐沉淀→伊/蒙混层和绿/蒙混层-孔隙充填伊利石及绿泥石形成→长石和岩屑颗粒溶解→自生高岭石形成→(晚期)铁方解石充填→晚期白云石充填或交代碎屑颗粒。
鄂尔多斯盆地东部延长组含油砂岩的古温度范围介于88~110℃之间,其中长6油层组的古温度为95~100℃,Ro值为0.77%~0.99% [16-17],长6油层组的伊/蒙混层中蒙脱石含量为10%~35%,平均含量16.9%(表 1)。结合上述成岩作用研究,长6油层组砂岩经历了较强的压实作用,原生孔隙大量丧失,石英多为Ⅰ级加大,偶见Ⅱ级加大,铁方解石-晚期白云石充填在次生溶蚀孔隙中或交代碎屑颗粒,长石、岩屑等溶蚀明显,伊/蒙混层、伊利石、高岭石、绿泥石等自生粘土矿物比较常见。从上述成岩特征综合判断,根据石油天然气行业标准(2003),研究区长6段储集砂岩的成岩阶段主要处于中成岩阶段A期。
表 1 研究区长6油层组粘土矿物X衍射数据统计Table 1. X-ray diffraction data of clay minerals from Chang 6 sandstone in the study area伊利石(I)/% 高岭石(K)/% 绿泥石(Ch)/% 伊/蒙(I/S)/% 层间比(S)/% 最小值 2.6 1.0 5.0 2.1 10.0 最大值 65.0 26.0 98.0 86.0 35.0 平均值 22.5 8.3 34.2 38.7 16.9 5. 结论
(1)鄂尔多斯盆地东南部延长组长6储层砂岩为典型的低孔低渗储集岩,以长石砂岩和岩屑质长石砂岩为主,砂岩颗粒多呈次圆-次棱状、磨圆度中-好,分选性中等。
(2)依据对储层的贡献,包括成岩作用降低储层孔渗性的压实作用、胶结作用和增加储层孔渗性的溶蚀作用、交代作用,其中压实作用、胶结作用、溶蚀作用最为重要,起建设性的成岩作用为溶蚀作用、高岭石化作用、环边绿泥石作用。
(3)通过量化各成岩作用对孔隙演化的影响,计算出压实作用和胶结作用分别使储层孔隙损失了原始孔隙的68.8%和16.90%,储层成为致密型储层,而后期的溶蚀作用使储层孔隙增加了原始孔隙的3.67%,为油气聚集空间贡献一定的作用。
(4)鄂尔多斯盆地东南部延长组长6储层的成岩序列为:压实作用→早期粘土膜(绿泥石膜)形成→石英次生加大→(早期)碳酸盐沉淀→伊/蒙混层和绿/蒙混层-孔隙充填伊利石及绿泥石形成→长石和岩屑颗粒溶解→自生高岭石形成→(晚期)铁方解石充填→晚期白云石充填或交代碎屑颗粒,其成岩阶段主要处于中成岩阶段A期。
致谢: 中国石化西南油气分公司提供石油地震反射剖面和钻井数据,西南石油大学陈伟教授给予的宝贵建议,审稿人提出的建设性意见,在此表示衷心的感谢。 -
图 1 青藏高原东缘主要活动断层和大地震分布
a-青藏高原东缘周缘GPS位移场(据参考文献[22]修改);b-青藏高原东缘龙门山褶皱冲断带和四川盆地西部区域构造位置,2008年汶川地震震中位置和震源机制解,同震地表破裂和未破裂的主断层[30, 38-39], 1970年大邑地震、1976年松潘地震和2013年芦山地震震源机制解[34, 42-43]和区域地震剖面位置均在图中标明(最大水平主应力数据修改据参考文献[39, 44]);c-小鱼洞断层地表破裂和同震滑移场(数据修改据参考文献[45-46])。WMF-汶川-茂汶断裂;YBF-映秀-北川断裂;PGF-彭县-灌县断裂;QCF-青川断裂;MJF-岷江断裂;HYF-虎牙断裂;LRBF-龙日坝断裂;WLF-武龙断裂;BXF-宝兴断裂;DYF-大邑断层;QXF-邛西断层;PLF-平罗坝断层;LQF-龙泉断层;XPF-熊坡断层
Figure 1. Main active faults and earthquake events on the eastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau
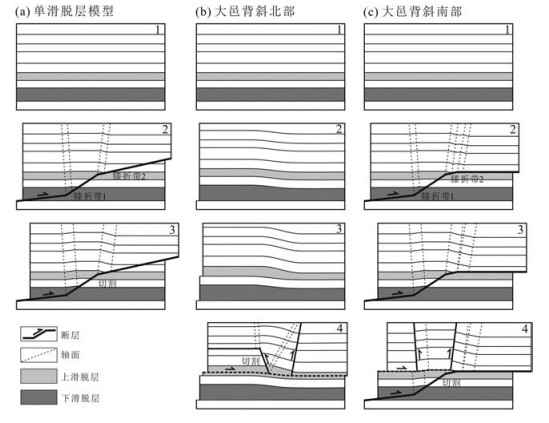
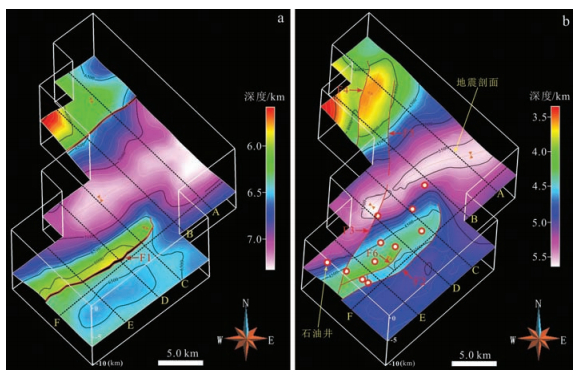
图 4 过崇州构造北翼的地震剖面A解释方案(剖面位置见图 2)
Pre-P-前二叠系;P-二叠系;T1j-下三叠统嘉陵江组;T2l-中三叠统雷口坡组;T3m-上三叠统马鞍塘组;T3x-上三叠统须家河组;J1-下侏罗统;J2-上侏罗统;K-白垩系;E-古近系;N2-Q1-大邑砾岩;Q-第四系
Figure 4. Interpreted seismic profile A across the Chongzhou structure
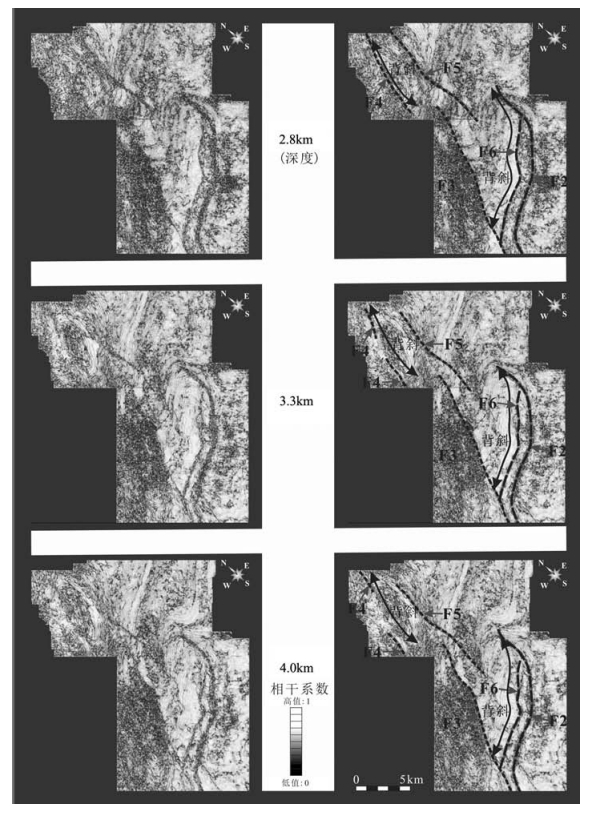
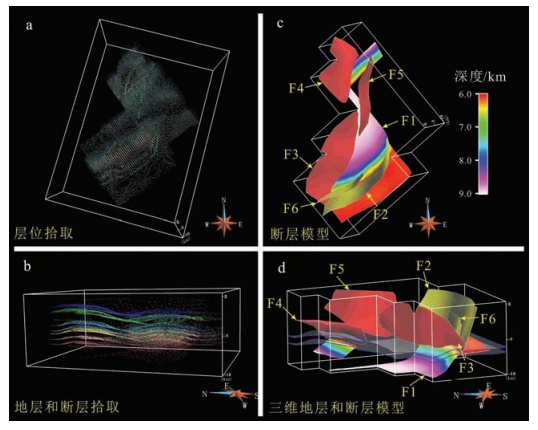
图 9 沿走向地震剖面F,展示滑脱层厚度在走向上的变化和F5断层的侧断坡(剖面位置见图 2)
Figure 9. Along-strike NE-trending seismic profile F across the Dayiand Chongzhou structures, showing the along-strike changes of the thickness and lateral ramp of F5 fault
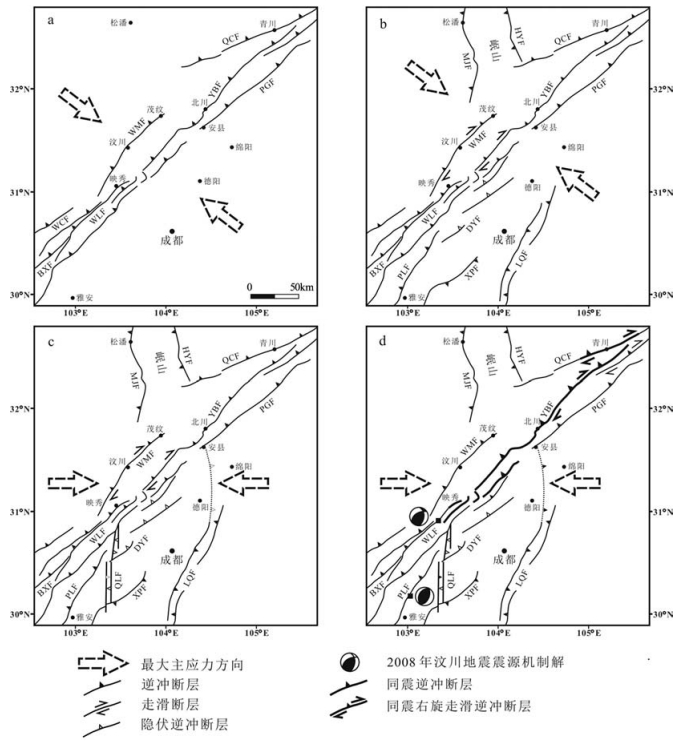
图 14 青藏高原东缘龙门山褶皱冲断带及其邻区构造应力场演化
a-晚三叠世水平最大主压应力(σhmax)方向为NW-SE向;b-渐新世-早上新世σhmax为NW-SE向;c-晚上新世-全新世为EW向挤压过程;d-现今测量的和汶川地震反演的近EW向挤压应力场。WMF-汶川-茂汶断裂;YBF-映秀-北川断裂;PGF-彭县-灌县断裂;QCF-青川断裂;MJF-岷江断裂;HYF-虎牙断裂;LRBF-龙日坝断裂;WLF-武龙断裂;BXF-宝兴断裂;DYF-大邑断层;QXF-邛西断层;PLF-平罗坝断层;LQF-龙泉断层;XPF-熊坡断层
Figure 14. The evolution of the tectonic stress field in Longmen Mountain and adjacent areas
-
Kuncoro A K, Cubas N, Singh S C, et al. Tsunamigenic potential due to frontal rupturing in the Sumatra locked zone[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2015, 432:311-322. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2015.10.007 Kuncoro A K, Cubas N, Singh S C, et al. Tsunamigenic potential due to frontal rupturing in the Sumatra locked zone[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2015, 432:311-322. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2015.10.007
Wang K L, He J H. Mechanics of low-stress forearcs:Nankai and Cascadia[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1999, 104(B7):15191-15205. doi: 10.1029/1999JB900103 Wang K L, He J H. Mechanics of low-stress forearcs:Nankai and Cascadia[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1999, 104(B7):15191-15205. doi: 10.1029/1999JB900103
Tsuji T, Ashi J, Strasser M, et al. Identification of the static backstop and its influence on the evolution of the accretionary prism in the Nankai Trough[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2015, 431:15-25. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2015.09.011 Tsuji T, Ashi J, Strasser M, et al. Identification of the static backstop and its influence on the evolution of the accretionary prism in the Nankai Trough[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2015, 431:15-25. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2015.09.011
Angermann D, Klotz J, Reigber C. Space-geodetic estimation of the Nazca-South America Euler vector[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1999, 171:329-324. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(99)00173-9 Angermann D, Klotz J, Reigber C. Space-geodetic estimation of the Nazca-South America Euler vector[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1999, 171:329-324. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(99)00173-9
Ader T, Avouac J P, Liu-Zeng J, et al. Convergence rate across the Nepal Himalaya and interseismic coupling on the Main Himalayan Thrust:Implications for seismic hazard[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 2012, 117:1-16. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/258661893_Convergence_rate_across_the_Nepal_Himalaya_and_interseismic_coupling_on_the_Main_Himalayan_Thrust_Implications_for_seismic_hazard Ader T, Avouac J P, Liu-Zeng J, et al. Convergence rate across the Nepal Himalaya and interseismic coupling on the Main Himalayan Thrust:Implications for seismic hazard[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 2012, 117:1-16. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/258661893_Convergence_rate_across_the_Nepal_Himalaya_and_interseismic_coupling_on_the_Main_Himalayan_Thrust_Implications_for_seismic_hazard
Kundu B, Yadav R K, Bali B S, et al. Oblique convergence and slip partitioning in the NW Himalaya:Implications from GPS measurements[J]. Tectonics, 2014, 33, doi: 10.1002/2014TC003633. Kundu B, Yadav R K, Bali B S, et al. Oblique convergence and slip partitioning in the NW Himalaya:Implications from GPS measurements[J]. Tectonics, 2014, 33, doi: 10.1002/2014TC003633.
Rosenberg C L, Brun J P, Cagnard F, et al. Oblique indentation in the Eastern Alps:Insights from laboratory experiments[J]. Tectonics, 2007, 26:TC2003, doi: 10.1029/2006TC001960. Rosenberg C L, Brun J P, Cagnard F, et al. Oblique indentation in the Eastern Alps:Insights from laboratory experiments[J]. Tectonics, 2007, 26:TC2003, doi: 10.1029/2006TC001960.
Castelltort S, Goren L, Willett S D, et al. River drainage patterns in the New Zealand Alps primarily controlled by plate tectonic strain[J]. Nature Geoscience, 2012, doi: 10.1038/NGEO1582. Castelltort S, Goren L, Willett S D, et al. River drainage patterns in the New Zealand Alps primarily controlled by plate tectonic strain[J]. Nature Geoscience, 2012, doi: 10.1038/NGEO1582.
Chang C P, Chang T Y, Angelier J, et al. Strain and stress field in Taiwan oblique convergent system:constraints from GPS observation and tectonic data[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2003, 214:115-127. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(03)00360-1 Chang C P, Chang T Y, Angelier J, et al. Strain and stress field in Taiwan oblique convergent system:constraints from GPS observation and tectonic data[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2003, 214:115-127. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(03)00360-1
Chen Y G, Lai K Y, Lee Y H, et al. Coseismic fold scarps and their kinematic behavior in the 1999 Chi-Chi earthquake Taiwan[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 2007, 112:B03S02, doi: 10.1029/2006JB004388. Chen Y G, Lai K Y, Lee Y H, et al. Coseismic fold scarps and their kinematic behavior in the 1999 Chi-Chi earthquake Taiwan[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 2007, 112:B03S02, doi: 10.1029/2006JB004388.
Norabuena E, Leffler-Griffin L, Mao L, et al. Space Geodetic Observations of Nazca-South America Convergence Across the Central Andes[J]. Science, 1998, 279, doi: 10.1126/science.279.5349.358. Norabuena E, Leffler-Griffin L, Mao L, et al. Space Geodetic Observations of Nazca-South America Convergence Across the Central Andes[J]. Science, 1998, 279, doi: 10.1126/science.279.5349.358.
Vargas G, Klinger Y, Rockwell T K, et al. Probing large intraplate earthquakes at the west flank of the Andes[J]. Geology, 2014, 42, 1083-1086. doi: 10.1130/G35741.1 Vargas G, Klinger Y, Rockwell T K, et al. Probing large intraplate earthquakes at the west flank of the Andes[J]. Geology, 2014, 42, 1083-1086. doi: 10.1130/G35741.1
Authemayou C, Chardon D, Bellier O, et al. Late Cenozoic partitioning of oblique plate convergence in the Zagros fold-andthrust belt (Iran)[J]. Tectonics, 2006, 25, doi: 10.1029/2005TC001860. Authemayou C, Chardon D, Bellier O, et al. Late Cenozoic partitioning of oblique plate convergence in the Zagros fold-andthrust belt (Iran)[J]. Tectonics, 2006, 25, doi: 10.1029/2005TC001860.
Tavakoli F, Walpersdorf A, Authemayou C, et al. Distribution of the right-lateral strike-slip motion from the Main Recent Fault to the Kazerun Fault System (Zagros, Iran):Evidence from presentday GPS velocities[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2008, 275:342-347. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2008.08.030 Tavakoli F, Walpersdorf A, Authemayou C, et al. Distribution of the right-lateral strike-slip motion from the Main Recent Fault to the Kazerun Fault System (Zagros, Iran):Evidence from presentday GPS velocities[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2008, 275:342-347. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2008.08.030
Bilham R, Gaur V K, Molnar P. Himalayan seismic hazard[J]. Science, 2001, 293:1442-1444. doi: 10.1126/science.1062584 Bilham R, Gaur V K, Molnar P. Himalayan seismic hazard[J]. Science, 2001, 293:1442-1444. doi: 10.1126/science.1062584
Subarya C, Chlieh M, Prawirodirdjo L, et al. Plate-boundary deformation associated with the great Sumatra-Andaman earthquake[J]. Nature, 2006, 440:46-51. doi: 10.1038/nature04522 Subarya C, Chlieh M, Prawirodirdjo L, et al. Plate-boundary deformation associated with the great Sumatra-Andaman earthquake[J]. Nature, 2006, 440:46-51. doi: 10.1038/nature04522
Murphy M A, Taylor M H, Gosse J, et al. Limit of strain partitioning in the Himalaya marked by large earthquakes in western Nepal[J]. Nature Geoscience, 2014, 7:38-42. http://www.nature.com/ngeo/journal/v7/n1/abs/ngeo2017.html Murphy M A, Taylor M H, Gosse J, et al. Limit of strain partitioning in the Himalaya marked by large earthquakes in western Nepal[J]. Nature Geoscience, 2014, 7:38-42. http://www.nature.com/ngeo/journal/v7/n1/abs/ngeo2017.html
McClay K R, Whitehouse P S, Dooley T, et al. 3D evolution of fold and thrust belts formed by oblique convergence[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2004, 21:857-877. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2004.03.009 McClay K R, Whitehouse P S, Dooley T, et al. 3D evolution of fold and thrust belts formed by oblique convergence[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2004, 21:857-877. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2004.03.009
Upton P, Craw D. Coeval emplacement and orogen-parallel transport of gold in oblique convergent orogens[J]. Tectonophysics, 2016, http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.tecto.2016.01.015. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2016.01.015 Upton P, Craw D. Coeval emplacement and orogen-parallel transport of gold in oblique convergent orogens[J]. Tectonophysics, 2016, http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.tecto.2016.01.015. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2016.01.015
Burchfiel B C, Chen Z L, Liu Y P, et al. Tectonics of the Longmen Shan and adjacent regions, central China[J]. International Geology Review, 1995, 37:661-735. doi: 10.1080/00206819509465424 Burchfiel B C, Chen Z L, Liu Y P, et al. Tectonics of the Longmen Shan and adjacent regions, central China[J]. International Geology Review, 1995, 37:661-735. doi: 10.1080/00206819509465424
Robert A, Pubellier M, de Sigoyer J, et al. Structural and thermal characters of the Longmen Shan (Sichuan, China)[J]. Tectonophysics, 2010, 491:165-173. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2010.03.018 Robert A, Pubellier M, de Sigoyer J, et al. Structural and thermal characters of the Longmen Shan (Sichuan, China)[J]. Tectonophysics, 2010, 491:165-173. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2010.03.018
Wang Q, Zhang P Z, Freymueller J T, et al. Present-Day crustal deformation in China constrained by Global Positioning System measurements[J]. Science, 2001, 294:574-577. doi: 10.1126/science.1063647 Wang Q, Zhang P Z, Freymueller J T, et al. Present-Day crustal deformation in China constrained by Global Positioning System measurements[J]. Science, 2001, 294:574-577. doi: 10.1126/science.1063647
Burchfiel B C, Royden L H, van der Hilst R D, et al. A geological and geophysical context for the Wenchuan earthquake of 12 May 2008, Sichuan, People's Republic of China[J]. GSA Today, 2008, 18:4-11. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK_NSTL_QKJJ0213989097.aspx Burchfiel B C, Royden L H, van der Hilst R D, et al. A geological and geophysical context for the Wenchuan earthquake of 12 May 2008, Sichuan, People's Republic of China[J]. GSA Today, 2008, 18:4-11. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK_NSTL_QKJJ0213989097.aspx
Jia D, Wei G Q, Chen Z X, et al. Longmen Shan fold-thrust belt and its relation to the western Basin in Central China:New insights from hydrocarbon exploration[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2006, 90:1425-1447. doi: 10.1306/03230605076 Jia D, Wei G Q, Chen Z X, et al. Longmen Shan fold-thrust belt and its relation to the western Basin in Central China:New insights from hydrocarbon exploration[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2006, 90:1425-1447. doi: 10.1306/03230605076
李勇, 周荣军, Densmore A L, 等.青藏高原东缘龙门山晚新生代走滑挤压作用的沉积响应[J].地质学报, 2006, 24:153-164. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB200602000.htm Royden L H, Burchfiel B C, King R W, et al. Surface deformation and lower crustal flow in Eastern Tibet[J]. Science, 1997, 276:788-790. doi: 10.1126/science.276.5313.788 Royden L H, Burchfiel B C, King R W, et al. Surface deformation and lower crustal flow in Eastern Tibet[J]. Science, 1997, 276:788-790. doi: 10.1126/science.276.5313.788
Royden L H, Burchfiel B C, Hilst R D, et al. The geological evolution of the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Science, 2008, 321:1054-1058. doi: 10.1126/science.1155371 Royden L H, Burchfiel B C, Hilst R D, et al. The geological evolution of the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Science, 2008, 321:1054-1058. doi: 10.1126/science.1155371
Clark M K, Royden L H. Topographic ooze:building the eastern margin of Tibet by lower crustal flow[J]. Geology, 2000, 28:703-706. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(2000)28<703:TOBTEM>2.0.CO;2 Clark M K, Royden L H. Topographic ooze:building the eastern margin of Tibet by lower crustal flow[J]. Geology, 2000, 28:703-706. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(2000)28<703:TOBTEM>2.0.CO;2
Hubbard J, Shaw J H. Uplift of the Longmen Shan and Tibetan plateau, and the 2008 Wenchuan (M=7.9) earthquake[J]. Nature, 2009, 458:194-197. doi: 10.1038/nature07837 Hubbard J, Shaw J H. Uplift of the Longmen Shan and Tibetan plateau, and the 2008 Wenchuan (M=7.9) earthquake[J]. Nature, 2009, 458:194-197. doi: 10.1038/nature07837
Liuzeng J, Zhang Z, Wen L, et al. Co-seismic ruptures of the 12 May 2008, Ms 8.0 Wenchuan earthquake, Sichuan:East-west crustal shortening on oblique, parallel thrusts along the eastern edge of Tibet[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2009, 286:355-370. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2009.07.017 Liuzeng J, Zhang Z, Wen L, et al. Co-seismic ruptures of the 12 May 2008, Ms 8.0 Wenchuan earthquake, Sichuan:East-west crustal shortening on oblique, parallel thrusts along the eastern edge of Tibet[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2009, 286:355-370. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2009.07.017
Zhang P Z, Wen X Z, Shen Z K, et al. Oblique, High-angle, listric-reverse faulting and associated development of strain:The Wenchuan earthquake of May 12, 2008, Sichuan, China[J]. Annual Review Earth and Planetary Sciences, 2010, 38:353-382. doi: 10.1146/annurev-earth-040809-152602 Zhang P Z, Wen X Z, Shen Z K, et al. Oblique, High-angle, listric-reverse faulting and associated development of strain:The Wenchuan earthquake of May 12, 2008, Sichuan, China[J]. Annual Review Earth and Planetary Sciences, 2010, 38:353-382. doi: 10.1146/annurev-earth-040809-152602
Tapponnier P, Xu Z Q, Roger F, et al. Oblique stepwise rise and growth of the Tibet Plateau[J]. Science, 2001, 294:1671-1677. doi: 10.1126/science.105978 Tapponnier P, Xu Z Q, Roger F, et al. Oblique stepwise rise and growth of the Tibet Plateau[J]. Science, 2001, 294:1671-1677. doi: 10.1126/science.105978
Guo X Y, Gao R, Keller G R, et al. Imaging the crustal structure beneath the eastern Tibetan Plateau and implications for the uplift of the Longmen Shan range[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2013, 379:72-80. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2013.08.005 Guo X Y, Gao R, Keller G R, et al. Imaging the crustal structure beneath the eastern Tibetan Plateau and implications for the uplift of the Longmen Shan range[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2013, 379:72-80. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2013.08.005
Zhang P Z. A review on active tectonics and deep crustal processes of the Western Sichuan region, eastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Tectonophysics, 2013, 584:7-22. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2012.02.021 Zhang P Z. A review on active tectonics and deep crustal processes of the Western Sichuan region, eastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Tectonophysics, 2013, 584:7-22. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2012.02.021
Liu Q Y, van der Hilst R D, Li Y, et al. Eastward expansion of the Tibetan Plateau by crustal fl ow and strain partitioning across faults[J]. Nature Geoscience, 2014, 7:361-365. doi: 10.1038/ngeo2130 Liu Q Y, van der Hilst R D, Li Y, et al. Eastward expansion of the Tibetan Plateau by crustal fl ow and strain partitioning across faults[J]. Nature Geoscience, 2014, 7:361-365. doi: 10.1038/ngeo2130
Avouac J P, Tapponnier P. Kinematical model of active deformation in central Asia[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 1993, 20:895-898. doi: 10.1029/93GL00128 Avouac J P, Tapponnier P. Kinematical model of active deformation in central Asia[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 1993, 20:895-898. doi: 10.1029/93GL00128
Zhang P Z, Shen Z K, Wang M, et al. Continuous deformation of the Tibetan Plateau from global positioning system data[J]. Geology, 2004, 32:809-812. doi: 10.1130/G20554.1 Zhang P Z, Shen Z K, Wang M, et al. Continuous deformation of the Tibetan Plateau from global positioning system data[J]. Geology, 2004, 32:809-812. doi: 10.1130/G20554.1
Xu X W, Wen X Z, Yu G H, et al. Coseismic reverse-and oblique-slip surface faulting generated by the 2008 Mw 7.9 Wenchuan earthquake, China[J]. Geology, 2009, 37:515-518. doi: 10.1130/G25462A.1 Xu X W, Wen X Z, Yu G H, et al. Coseismic reverse-and oblique-slip surface faulting generated by the 2008 Mw 7.9 Wenchuan earthquake, China[J]. Geology, 2009, 37:515-518. doi: 10.1130/G25462A.1
Wang Q, Qiao X J, Lan Q G, et al. Rupture of deep faults in the 2008 Wenchuan earthquake and uplift of the Longmen Shan[J]. Nature Geoscience, 2011, 4:634-640. doi: 10.1038/ngeo1210 Wang Q, Qiao X J, Lan Q G, et al. Rupture of deep faults in the 2008 Wenchuan earthquake and uplift of the Longmen Shan[J]. Nature Geoscience, 2011, 4:634-640. doi: 10.1038/ngeo1210
Chen S F, Wilson C J L. Emplacement of the Longmen Shan thrustnappe belt along the eastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 1996, 18:413-430. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/280800842_Emplacement_of_the_Longmen_Shan_Thrust-Nappe_Belt_along_the_eastern_margin_of_the_Tibetan_Plateau Chen S F, Wilson C J L. Emplacement of the Longmen Shan thrustnappe belt along the eastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 1996, 18:413-430. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/280800842_Emplacement_of_the_Longmen_Shan_Thrust-Nappe_Belt_along_the_eastern_margin_of_the_Tibetan_Plateau
Li Y, Allen P A, Densmore A L, et al. Evolution of the Longmen Shan foreland basin (western Sichuan, China) during the late Triassic Indosinian orogeny[J]. Basin Research, 2003, 15:117-138. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2117.2003.00197.x Li Y, Allen P A, Densmore A L, et al. Evolution of the Longmen Shan foreland basin (western Sichuan, China) during the late Triassic Indosinian orogeny[J]. Basin Research, 2003, 15:117-138. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2117.2003.00197.x
Jones L M, Han W B, Hausson E, et al. Focal mechanism and aftershock locations of the Songpan earthquakes of August 1976 in Sichuan, China[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1984, 89:7697-7707. doi: 10.1029/JB089iB09p07697 Jones L M, Han W B, Hausson E, et al. Focal mechanism and aftershock locations of the Songpan earthquakes of August 1976 in Sichuan, China[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1984, 89:7697-7707. doi: 10.1029/JB089iB09p07697
Li Z G, Jia D, Chen W, et al. Late Cenozoic east-west crustal shortening in the southern Longmen Shan, eastern Tibet:Implications for regional stress field changes[J]. Tectonophysics, 2014, 623:169-186. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2014.03.033 Li Z G, Jia D, Chen W, et al. Late Cenozoic east-west crustal shortening in the southern Longmen Shan, eastern Tibet:Implications for regional stress field changes[J]. Tectonophysics, 2014, 623:169-186. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2014.03.033
Du Y, Xie F R, Zhang X L, et al. The mechanics of fault slip of Ms 8.0 Wenchuan earthquake[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysical, 2009, 52:464-473. http://manu39.magtech.com.cn/Geophy/EN/abstract/abstract926.shtml Du Y, Xie F R, Zhang X L, et al. The mechanics of fault slip of Ms 8.0 Wenchuan earthquake[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysical, 2009, 52:464-473. http://manu39.magtech.com.cn/Geophy/EN/abstract/abstract926.shtml
Shen Z K, Sun J B, Zhang Z P, et al. Slip maxima at fault junctions and rupturing of barriers during the 2008 Wenchuan earthquake[J]. Nature Geoscience, 2009, 2:718-724. doi: 10.1038/ngeo636 Shen Z K, Sun J B, Zhang Z P, et al. Slip maxima at fault junctions and rupturing of barriers during the 2008 Wenchuan earthquake[J]. Nature Geoscience, 2009, 2:718-724. doi: 10.1038/ngeo636
Liu Z J, Sun J, Wang P, et al. Surface ruptures on the transverse Xiaoyudong fault:A significant segment boundary breached during the 2008 Wenchuan earthquake, China[J]. Tectonophysics, 2012, 580:218-241. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2012.09.024 Liu Z J, Sun J, Wang P, et al. Surface ruptures on the transverse Xiaoyudong fault:A significant segment boundary breached during the 2008 Wenchuan earthquake, China[J]. Tectonophysics, 2012, 580:218-241. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2012.09.024
Jia D, Li Y Q, Lin A M, et al. Structural model of 2008 Mw 7.9 Wenchuan earthquake in the rejuvenated Longmen Shan thrust belt, China[J]. Tectonophysics, 2010, 491:174-184. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2009.08.040 Jia D, Li Y Q, Lin A M, et al. Structural model of 2008 Mw 7.9 Wenchuan earthquake in the rejuvenated Longmen Shan thrust belt, China[J]. Tectonophysics, 2010, 491:174-184. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2009.08.040
Li Y Q, Jia D, Shaw J H, et al. Structural interpretation of the coseismic faults of the Wenchuan earthquake:Three-dimensional modeling of the Longmen Shan fold-and-thrust belt[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 2010, 115:1-26. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/248805410_Structural_interpretation_of_the_coseismic_faults_of_the_Wenchuan_earthquake_Three-dimensional_modeling_of_the_Longmen_Shan_fold-and-thrust_belt Li Y Q, Jia D, Shaw J H, et al. Structural interpretation of the coseismic faults of the Wenchuan earthquake:Three-dimensional modeling of the Longmen Shan fold-and-thrust belt[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 2010, 115:1-26. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/248805410_Structural_interpretation_of_the_coseismic_faults_of_the_Wenchuan_earthquake_Three-dimensional_modeling_of_the_Longmen_Shan_fold-and-thrust_belt
Jin W Z, Tang L J, Yang K M, et al. Segmentation of the Longmen Mountains thrust belt, Western Sichuan Foreland Basin, SW China[J]. Tectonophysics, 2010, 485:107-121. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2009.12.007 Jin W Z, Tang L J, Yang K M, et al. Segmentation of the Longmen Mountains thrust belt, Western Sichuan Foreland Basin, SW China[J]. Tectonophysics, 2010, 485:107-121. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2009.12.007
Hubbard J, Shaw J H, Klinger Y. Structural setting of the 2008Mw 7.9 Wenchuan, China, earthquake[J]. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 2010, 100:2713-2735. doi: 10.1785/0120090341 Hubbard J, Shaw J H, Klinger Y. Structural setting of the 2008Mw 7.9 Wenchuan, China, earthquake[J]. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 2010, 100:2713-2735. doi: 10.1785/0120090341
Li Z G, Jia D, Chen W, et al. Structural geometry and deformation mechanism of the Longquan anticline in the Longmen Shan foldand-thrust belt, eastern Tibet[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2013, 64:223-234. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2012.12.022 Li Z G, Jia D, Chen W, et al. Structural geometry and deformation mechanism of the Longquan anticline in the Longmen Shan foldand-thrust belt, eastern Tibet[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2013, 64:223-234. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2012.12.022
Wang M M, Jia D, Lin A M, et al. Active fault-related folding beneath an alluvial terrace in the southern Longmen Shan range front, Sichuan basin, China:Implications for seismic hazard[J]. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 2013, 103:2369-2385. doi: 10.1785/0120120188 Wang M M, Jia D, Lin A M, et al. Active fault-related folding beneath an alluvial terrace in the southern Longmen Shan range front, Sichuan basin, China:Implications for seismic hazard[J]. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 2013, 103:2369-2385. doi: 10.1785/0120120188
Densmore A L, Ellis M A, Li Y, et al. Active tectonics of the Beichuan and Pengguan faults at the eastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Tectonics, 2007, 26:1-17. http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DZYC200802002.htm Densmore A L, Ellis M A, Li Y, et al. Active tectonics of the Beichuan and Pengguan faults at the eastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Tectonics, 2007, 26:1-17. http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DZYC200802002.htm
Tang R, Han W. Active Faults and Earthquakes in Sichuan Province[M]. Seismological Press, Beijing, 1993. Tang R, Han W. Active Faults and Earthquakes in Sichuan Province[M]. Seismological Press, Beijing, 1993.
Richardson N J, Densmore A L, Seward D, et al. Extraordinary denudation in the Sichuan Basin:Insights from low-temperature thermochronology adjacent to the eastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 2008, 113:1-23. doi: 10.1029/2006JB004739/full Richardson N J, Densmore A L, Seward D, et al. Extraordinary denudation in the Sichuan Basin:Insights from low-temperature thermochronology adjacent to the eastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 2008, 113:1-23. doi: 10.1029/2006JB004739/full
黎兵, 李勇, 张开均, 等.青藏高原东缘晚新生代大邑砾岩的物源分析与水系变迁[J].第四纪研究, 2007, 27:64-73. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DSJJ200701007.htm Li Z W, Liu S G, Chen H D, et al. Spatial variation in Meso-Cenozoic exhumation history of the Longmen Shan thrust belt (eastern Tibetan Plateau) and the adjacent western Sichuan basin:Constraints from fi ssion track thermochronology[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2012, 47:185-203. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2011.10.016 Li Z W, Liu S G, Chen H D, et al. Spatial variation in Meso-Cenozoic exhumation history of the Longmen Shan thrust belt (eastern Tibetan Plateau) and the adjacent western Sichuan basin:Constraints from fi ssion track thermochronology[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2012, 47:185-203. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2011.10.016
Kong P, Zheng Y, Fu B H. Cosmogenic nuclide burial ages and provenance of Late Cenozoic deposits in the Sichuan Basin:Implications for Early Quaternary glaciations in east Tibet[J]. Quaternary Geochronology, 2011, 6:304-312. doi: 10.1016/j.quageo.2011.03.006 Kong P, Zheng Y, Fu B H. Cosmogenic nuclide burial ages and provenance of Late Cenozoic deposits in the Sichuan Basin:Implications for Early Quaternary glaciations in east Tibet[J]. Quaternary Geochronology, 2011, 6:304-312. doi: 10.1016/j.quageo.2011.03.006
董绍鹏, 韩竹军, 尹金辉, 等.龙门山山前大邑断裂活动时代与最新构造变形样式初步研究[J].地震地质, 2008, 30:996-1003. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDZ200804018.htm 李永昭, 郭兵.成都平原的晚新生代构造[J].成都理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2008, 35:371-376. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CDLG200804004.htm Suppe J, Connors C D, Zhang Y K, et al. Shear fault-bend folding[C]//McClay K R. Thrust Tectonics and Hydrocarbon Systems:AAPG Memoir, 2004, 82:303-323. Suppe J, Connors C D, Zhang Y K, et al. Shear fault-bend folding[C]//McClay K R. Thrust Tectonics and Hydrocarbon Systems:AAPG Memoir, 2004, 82:303-323.
Shaw J H, Connors C D, Suppe J, et al. Seismic interpretation of contractional fault-related folds[M]. An AAPG Seismic Atlas Studies in Geology #53, 2005:8-56. Shaw J H, Connors C D, Suppe J, et al. Seismic interpretation of contractional fault-related folds[M]. An AAPG Seismic Atlas Studies in Geology #53, 2005:8-56.
Graveleau F, Malavieille J, Dominguez S. Experimental modelling of orogenic wedges:A review[J]. Tectonophysics, 2012, 538/540:1-66. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2012.01.027 Graveleau F, Malavieille J, Dominguez S. Experimental modelling of orogenic wedges:A review[J]. Tectonophysics, 2012, 538/540:1-66. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2012.01.027
Couzens-Schultz B A, Vendeville B C, Wiltschko D V. Duplex style and triangle zone formation:insights from physical modeling[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 2003, 25:1623-1644. doi: 10.1016/S0191-8141(03)00004-X Couzens-Schultz B A, Vendeville B C, Wiltschko D V. Duplex style and triangle zone formation:insights from physical modeling[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 2003, 25:1623-1644. doi: 10.1016/S0191-8141(03)00004-X
Ruh J B, Kaus B J P, Burg J P, et al. Numerical investigation of deformation mechanics in fold-and-thrust belts:Influence of rheology of single and multiple décollements[J]. Tectonics, 2012, 31:1-32. https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Boris_Kaus/publication/233906712_Numerical_investigation_of_deformation_mechanics_in_fold-and-thrust_belts_Influence_of_rheology_of_single_and_multiple_decollements/links/0deec52714ad361ff9000000.pdf Ruh J B, Kaus B J P, Burg J P, et al. Numerical investigation of deformation mechanics in fold-and-thrust belts:Influence of rheology of single and multiple décollements[J]. Tectonics, 2012, 31:1-32. https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Boris_Kaus/publication/233906712_Numerical_investigation_of_deformation_mechanics_in_fold-and-thrust_belts_Influence_of_rheology_of_single_and_multiple_decollements/links/0deec52714ad361ff9000000.pdf
Medwedeff D A, Suppe J. Multibend fault-bend folding[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 1997, 19:279-292. doi: 10.1016/S0191-8141(97)83026-X Medwedeff D A, Suppe J. Multibend fault-bend folding[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 1997, 19:279-292. doi: 10.1016/S0191-8141(97)83026-X
Bahorich M S, Farmer S L. 3-D seismic discontinuity for faults and stratigraphic features[J]. The Leading Edge, 1995, 14:1053-1058. doi: 10.1190/1.1437077 Bahorich M S, Farmer S L. 3-D seismic discontinuity for faults and stratigraphic features[J]. The Leading Edge, 1995, 14:1053-1058. doi: 10.1190/1.1437077
Bahorich M S, Farmer S L. Methods of seismic signal processing and exploration[J]. U.S. Patent No. 5, 1996, 563:949. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=1849907805&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn Bahorich M S, Farmer S L. Methods of seismic signal processing and exploration[J]. U.S. Patent No. 5, 1996, 563:949. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=1849907805&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Mallet J L. Discrete smooth interpolation in geometric modeling[J]. Computer Aided Design, 1992, 24:178-191. doi: 10.1016/0010-4485(92)90054-E Mallet J L. Discrete smooth interpolation in geometric modeling[J]. Computer Aided Design, 1992, 24:178-191. doi: 10.1016/0010-4485(92)90054-E
Plesch A, Shaw J H, Benson C, et al. Community fault model (CFM) for southern California[J]. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 2007, 97:1793-1802. doi: 10.1785/0120050211 Plesch A, Shaw J H, Benson C, et al. Community fault model (CFM) for southern California[J]. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 2007, 97:1793-1802. doi: 10.1785/0120050211
Luna L M, Hetland E A. Regional stresses inferred from coseismic slip models of the 2008 Mw 7.9 Wenchuan, China, earthquake[J]. Tectonophysics, 2013, 584:43-53. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2012.03.027 Luna L M, Hetland E A. Regional stresses inferred from coseismic slip models of the 2008 Mw 7.9 Wenchuan, China, earthquake[J]. Tectonophysics, 2013, 584:43-53. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2012.03.027
Arne D, Worley B, Wilson C, et al. Differential exhumation in response to episodic thrusting along the eastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Tectonophysics, 1997, 280:239-256. doi: 10.1016/S0040-1951(97)00040-1 Arne D, Worley B, Wilson C, et al. Differential exhumation in response to episodic thrusting along the eastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Tectonophysics, 1997, 280:239-256. doi: 10.1016/S0040-1951(97)00040-1
Kirby E, Reiners P W, Krol M A, et al. Late Cenozoic evolution of the eastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau:Inferences from 40Ar/39Ar and (U-Th)/He thermochronology[J]. Tectonics, 2002, 21:1-20. Kirby E, Reiners P W, Krol M A, et al. Late Cenozoic evolution of the eastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau:Inferences from 40Ar/39Ar and (U-Th)/He thermochronology[J]. Tectonics, 2002, 21:1-20.
Zhang Y Q, Dong S W, Yang N, et al. Active faulting pattern, present-day tectonic stress field and block kinematics in the east Tibetan Plateau[J]. Acta geological Sincia, 2009, 83:694-712. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-6724.2009.00093.x Zhang Y Q, Dong S W, Yang N, et al. Active faulting pattern, present-day tectonic stress field and block kinematics in the east Tibetan Plateau[J]. Acta geological Sincia, 2009, 83:694-712. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-6724.2009.00093.x
Zhu A L, Xu X W, Zhou Y S, et al. Relocation of small earthquakes in western Sichuan, China and its implications for active tectonics[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2005, 48:629-636. http://manu39.magtech.com.cn/Geophy/EN/abstract/abstract721.shtml Zhu A L, Xu X W, Zhou Y S, et al. Relocation of small earthquakes in western Sichuan, China and its implications for active tectonics[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2005, 48:629-636. http://manu39.magtech.com.cn/Geophy/EN/abstract/abstract721.shtml




 下载:
下载: