A study of the distribution regularity and development process of the energy metal deposits in "One Belt, One Road" region
-
摘要:
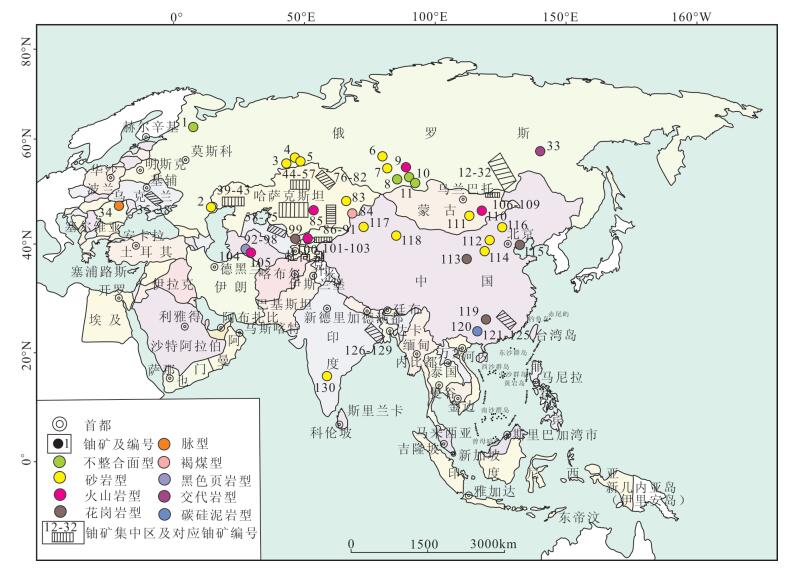
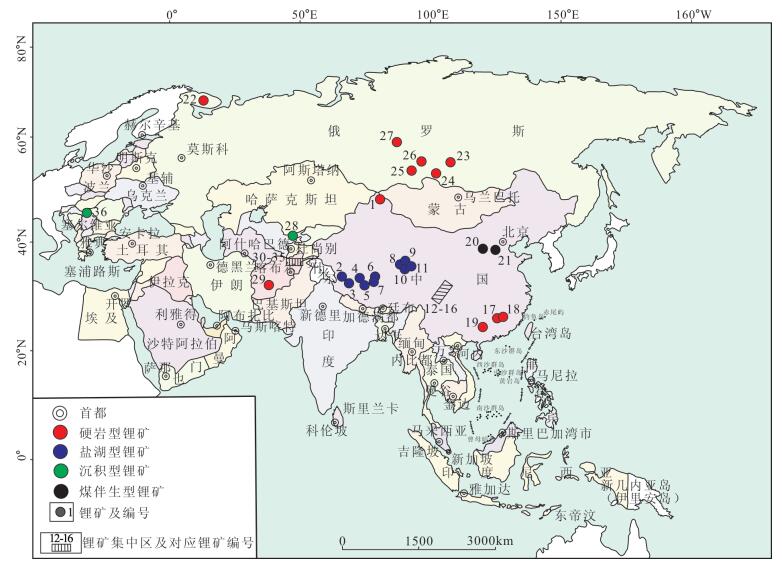
对“一带一路”地区的能源金属锂和铀的矿床分布规律进行统计,并对典型矿床的地质特征与开发工艺进行概述,为了解“一带一路”地区的锂矿和铀矿提供基础信息,同时为中国进行“能源金属”的开采提供科学依据。研究认为,“一带一路”地区共有大型及以上锂矿36个,成因类型有硬岩型、盐湖型、沉积型和煤伴生型4种,资源储量分别为784×104t、1702×104t、237.5×104t和623×104t。盐湖型锂矿分布于中国和阿富汗,硬岩型锂矿分布在俄罗斯等国家,沉积型锂矿分布在塞尔维亚等国家,煤伴生型锂矿只分布于中国。鉴于盐湖型锂矿开发的环境影响较小,建议有关国家加大对盐湖型锂资源的勘探与开发。“一带一路”地区共有大型及以上铀矿130个,成因类型主要为砂岩型和火山岩型,主要集中在哈萨克斯坦等国家,铀资源储量(可靠回收成本≤130$/kg)达181.94×104t,占“一带一路”地区总资源储量的92.12%,建议中国与相关国家进行交流与合作,加大对中国境内北方地区砂岩型铀矿的寻找力度,同时进行火山岩型铀矿的勘探开发。
Abstract:To fully understand the basic information of lithium deposits and uranium deposits, the authors performed statistical analysis for "energy metals" of lithium deposit and uranium deposit distribution in "One Belt, One Road" region and summarized geological characteristics and development process of the typical deposits on the basis of referring to a large number of relevant data. At the same time, this paper can provide some scientific basis for the exploitation of "energy metals" in China. Researches show that the "One Belt, One Road" region has 36 large and superlarge lithium deposits, which genetically include hard rock type, saline lake type, sedimentary type and coal associated type, with resource reserves being 7.84, 17.02, 2.375 and 6.23 million tons, respectively. Salt lake lithium deposits are distributed in China and Afghanistan, hard rock type lithium deposits are distributed in Russia and some other countries, sedimentary type lithium deposits are distributed in Serbia and some other countries, and coal associated lithium deposits are only distributed in China. In view of the fact that development of saline lake type lithium deposits will have low impact on the environment, the authors hold that the relevant countries should increase the exploration and development of saline lake lithium resources. The "One Belt, One Road" region has 130 large and superlarge uranium deposits mainly concentrated in Kazakhstan and some other countries, their genetic types are mainly of sandstone type and volcanic rock type, and their uranium resource reserves (reliable recovery cost≤130$/kg) are 1.8194 million tons, accounting for 92.12% of the total resource reserves of the "One Belt, One Road" region. It is suggested that China should expand exchange and cooperation with the relevant countries and increase the exploration of sandstone type uranium deposits in northern China. At the same time, the exploration and development of volcanic rock type uranium deposits should also be carried out.
-
Keywords:
- One Belt, One Road /
- lithium deposits /
- uranium deposit /
- energy metal
-
致谢: 中国地质科学院矿产资源研究所赵一鸣研究员提出建设性建议,绘制图件时得到了中国科学院油气资源研究重点实验室樊海龙硕士的帮助,在此一并感谢。
-
表 1 “一带一路”地区典型锂矿数据分布
Table 1 Data distribution of typical lithium deposits in "One Belt, One Road" region
序号 编号 矿床名称 经纬度(E/N) 国家 矿种 成因
类型矿物组合 伴生有
益元素品位
(Li2O%)资源储量(Li2O×104t) 开发
现状资料来源 1 4 西藏麻米措盐湖 83°30′ 32°10′ 中国 锂硼钟矿 盐湖型 - K、B 6.08 250 未开采 [45]③ 2 5 西藏扎布耶 84°04′ 31°21′ 中国 锂矿 盐湖型 扎布耶石、含锂白云石、石盐、钟石盐、硼砂、水碱、芒硝等 B、 K、 Br、Rb、Cs 南湖地表卤水2.55~4.31, 南湖晶间卤水5.59~9.78, 北湖地表卤水5.40~8.01 183 正在
开采[1, 45-46] 3 13 四川甲基卡锂铍铌钽铷矿床 101°48′ 30°21′ 中国 锂铍铌
钽矿硬岩型 锂辉石、锂云母、石英、白云母、长石等 Be、Nb、 Ta、Rb 1.2 90 正在
开采[2, 47]① 4 20 准格尔煤伴生锂矿 111°30′ 39°23′ 中国 锂矿 煤伴
生型515.7 未开采 [14, 17, 19] 5 23 Goltsovoe 104°30′ 54°20′ 俄罗斯 锂矿 硬岩型 锂辉石、微斜长石、钠长石、铯榴石、磷锂铝石 Ta、Cs 0.79 30 未开采 [20-23, 26-29] 6 27 Vishnyakovskoe 98°30′ 55°20′ 俄罗斯 锂矿 硬岩型 透锂长石、锂辉石 - 1.06 42 未开采 [21-22] 7 28 塔什干地区
沙瓦兹赛矿床68°31′ 41°21′ 乌兹別
克斯坦锂铷铯矿 沉积
岩型- Ce、Rb - 12 正在
开采[11-13, 48] 8 29 Taghawlor
塔哈卢尔66°42′ 33°21′ 阿富汗 锂矿 硬岩型 锂辉石、电气石、白云母、磷灰石、透锂长石、石英 Ni、Ta、Ce、
Pb、Zn0.08~2.8 146.4 未开采 [49]① 9 30 Drumgal 71°01′ 35°19′ 阿富汗 锂矿 硬岩型 - - 1.38~1.58 25.3 未开采 [49]① 10 36 贾达尔盆地超大型锂硼矿床 19°43′ 44°28′ 塞尔
维亚锂硼矿 沉积
岩型- - 1.8 225.5 未开采 [50]① 注:盐湖型锂矿大型以LiCl≥50×104t为界,其他类型锂矿以Li2O≥10×104t为界;序号1、2锂矿的品位和资源储量以LiCl计,品位单位以g/L计;表格中锂矿编号与图 1中锂矿编号一致;“-”表示数据无法获得 表 2 “一带一路”地区典型铀矿数据分布
Table 2 Data distribution of typical uranium deposits in "One Belt, One Road" region
序号 编号 矿床名称 经纬度(E/N) 国家 矿种 成因
类型矿物组合 伴生有
益元素品位
(%U)资源储量(铀t) 开发
现状资料
来源1 22 斯特列佐夫斯卡Strltssovskoye 118°00′ 50°00′ 俄罗斯 铀矿 火山
岩型铀石、沥青铀矿、钛铀矿、辉钼矿、黄铁矿、白铁矿、方铅矿 Li、Sb、Mo、Au, Zn, Hg 0.185 71000 正在
开采[4, 35] 2 34 Crucea,
Bihor and Crucea25°50′ 47°25′ 罗马
尼亚铀矿 脉型 - - 0.21 8769 正在
开采[4, 59] 3 36 Novokonstan-tinovskoe 31°50′ 48°25′ 乌克兰 铀矿 交代
岩型钛铀矿、晶质铀矿、沥青铀矿、水沥青铀矿、铀石、磷灰石、方解石等 Sc、V 0.139 93630 正在
开采[4, 59] 4 72 明库杜克
Mynkuduk68°30′ 46°00′ 哈萨克
斯坦铀矿 砂岩型 方解石、黄铁矿、荽铁矿、白铁矿、铀石、沥青铀矿 Se, Sc、Y, REE 0.015~0.15 127000 正在
开采[32] 5 94 苏格拉利
Sugraly64°11′ 41°39′ 乌兹別
克斯坦铀矿 砂岩型 铀石、沥青铀矿、钛铀矿、黄铁矿、白铁矿 Se、Mo、Re 0.2 60000 正在
开采[37] 6 102 图雅-姆云
Tyuya-Muyun72°12′ 40°15′ 吉尔吉
斯斯坦铀矿 碳酸
盐型沥青铀矿、乌黑沥青铀矿、赤铁矿、黄铁矿 Co、V、Cu、Ra 1.4 5000 正在
开采[33] 7 104 Baïlik 58°15′ 39°20′ 土库曼
斯坦铀矿 黑色页
岩型铀石、黄铁矿、荽铁矿、磷酸盐 Ag、Co、Mo、Ni、Pb、V、Au、Pt - 5000 未开采 [36] 8 111 Zoovch Ovoo
祖尔维奇敖包108°20′ 45°20′ 蒙古 铀矿 砂岩型 - - 0.022 67706 未开采 [34, 60] 9 124 相山
Xiangshan116°18′ 27°55′ 中国 铀矿 火山
岩型铀石、沥青铀矿、钛铀矿、辉钼矿、黄铁矿 REE、Mo、Pb、Zn、Ag、P、Be、Cd、Ni、Sr 0.1~0.3 26000 正在开采 [30, 61-65] 10 129 斯因布姆
Singhbhum86°29′ 22°29′ 印度 铀矿 砂岩型 铀石、沥青铀矿、黄铁矿、铜铀云母、钙铀云母 Co、Cu, Ni、Mo、Ni 0.012~0.041 56000 未开采 [31] 注:砂岩型铀矿大型以10000t为界,其他类型铀矿以3000t为界;表格中铀矿编号与图 2中铀矿编号一致;“-”表示数据无法获得 -
赵元艺.中国盐湖锂资源及其开发进程[J].矿床地质, 2003, 22(1):99-105. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ200301014.htm 李建康, 刘喜方, 王登红.中国锂矿成矿规律概要[J].地质学报, 2014, 88(12):2269-2276. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201412009.htm 王秋舒, 元春华, 许虹.全球锂矿资源分布与潜力分析[J].中国矿业, 2015, 24(2):11-13. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGKA201502004.htm Susan H, Margaret C. Critical analysis of world uranium resources:U.S. Scientific Investigations Report 2012-5239[M].U.S. Geological Survey, 2013:56.
OECD NEA & IAEA. Uranium 2014:Resources, Production and Demand[M]. OECD NEA & IAEA, 2014.
纪忠元, 项仁杰, 刘吉成, 等.世界矿情.独联体[M].北京:地质出版社, 2010:19-48, 89-120, 225-230. 李俊建, 刘晓阳, 唐文龙, 等.蒙古国矿产资源概况[C]//李俊建, 刘新秒编译.蒙古地质矿产研究进展.天津:天津科学技术出版社, 2013:59-64. 施俊法, 李友枝, 金庆花, 等.世界矿情.亚洲卷[M].北京:地质出版社, 2006:88-100, 360-378. 郑绵平.论中国盐湖[J].矿床地质, 2001, 20(2):181-185. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ200102010.htm OECD NEA & IAEA. Uranium 2009:Resources, production and demand[M]. OECD NEA & IAEA, 2010:456.
Richard M L, Glenn J W. 2006 Minerals Yearbook[M]. U.S.Geological Survey, 2009.
Richard M L, Mark B, Glenn J W. 2007 Minerals Yearbook[M].U. S.Geological Survey, 2010.
Richard M L, Glenn J W. 2008 Minerals Yearbook[M].U.S.Geological Survey, 2010.
Sun Y Z, Zhao C L, Li Y H, et al. Li distribution and mode of occurrences in Li-bearing coal seam #6 from the Guanbanwusu Mine, Inner Mongolia, northern China[J]. Energy Exploration & Exploition, 2012, 30(1):109-130.
Sun Y Z, Yang J J, Zhao C L. Minimum mining grade of associated Li deposits in coal seams[J]. Energy Exploration & Exploition, 2012, 30(2):167-170.
Sun Y Z, Zhao C L, Zhang Y Z, et al. Concentrations of valuable elements of the coals from the Pingshuo Mining District, Ningwu Coalfield, northern China[J]. Energy Exploration & Exploition, 2013, 31(5):727-744.
Sun Y Z, Zhao C L, Li Y H, et al. Further Information of the Associated Li Deposits in the No.6 Coal Seam at Jungar Coalfield, Inner Mongolia, Northern China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2013, 87(4):1097-1108. doi: 10.1111/acgs.2013.87.issue-4
Sun Y Z. China Geological Survey Proved the Existence of an Extra-large Coal-Associated Lithium Deposit[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2015, 89(1):311. doi: 10.1111/1755-6724.12418
Sun Y Z, Zhao C L, Qin S J, et al.Occurrence of some valuable elements in the unique 'high-aluminium coals' from the Jungar coalfield, China[J].Ore Geology Reviews, 2016, 72:659-668. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2015.09.015
Evans R K. An abundance of lithium[EB/OL] (2012-07-12)[2016-06-30]http://www.doc88.com/p-497333704749.html.2008.
Seltmann R, Soloviev S, Shatov V, et al. Metallogeny of Siberia:tectonic, geologic and metallogenic settings of selected significant deposits[J]. Australian Journal of Earth Sciences, 2010:687-690.
Stephen E K, Paul W G, Pablo A M, et al. Global lithium resources:Relative importance of pegmatite, brine and other deposits[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2012, 48:56-68.
Camille G, Pamela H M, Marion P, et al. Assessment of world lithium resources and consequences of their geographic distribution on the expected development of the electric vehicle industry[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2012, 16:1737-1744.
Stephen G P, Trude V V K, Thomas J M, et al.Summaries of Important Areas for Mineral Investment and Production Opportunities of Nonfuel Minerals in Afghanistan[M].U.S. Geological Survey, 2013:294-302.
Stephen G P, Summaries and Data Packages of Important Areas for Mineral Investment and Production Opportunities in Afghanistan:U.S. Geological Survey Fact Sheet 2011-3108[M]. U.S. Geological Survey, 2012.
Matviyenko A D. Geological and physical-chemical formation conditions of spodumene pegmatites of the Ukrainian Shield[J]. Arch. Mineralogiczne XLIX, 1993:143-144.
Ryabtsev V V, Chistov L B, Schuriga T N. Tantalum ores of Russia[M]. Mineral Resources 21, 2006.
Odintsova I V, Syzykh A I. Mineral raw material resources of rare and base metals in Eastern Siberia[C]//Geology and mineral deposits of Eastern Siberia. Irkutsk University Publishing, Irkutsk, 2007:95-101.
Ryabtsev V V, Kalish E A, Golovanov O G. The perspectives of the use of the mineral resource base of tantalum in Russia[C]//Mineral Resources 18(A Special Issue devoted to the current problems of the rare metal resource base of Russia (1956-2006)), 2006:40-61.
Dahlkamp F J. Chapter 1 China, Uranium deposits of the worldAsian[M].Berlin Heidelberg:Springer-Verlag, 2009:32-155.
Dahlkamp F J. Chapter 2 India, Uranium deposits of the worldAsian[M].Berlin Heidelberg:Springer-Verlag, 2009:157-173.
Dahlkamp F J. Chapter 6 Kazakhstan, Uranium deposits of the world-Asian[M].Berlin Heidelberg:Springer-Verlag, 2009:192-267.
Dahlkamp F J. Chapter 7 Kyrgyzstan, Uranium deposits of the world-Asian[M].Berlin Heidelberg:Springer-Verlag, 2009:269-284.
Dahlkamp F J. Chapter 8 Mongolia, Uranium deposits of the worldAsian[M].Berlin Heidelberg:Springer-Verlag, 2009:286-308.
Dahlkamp F J. Chapter 10 Russian Federation, Uranium deposits of the world-Asian[M].Berlin Heidelberg:Springer-Verlag, 2009:322-390.
Dahlkamp F J. Chapter 14Turkmenistan, Uranium deposits of the world-Asian[M].Berlin Heidelberg:Springer-Verlag, 2009:397-400.
Dahlkamp F J. Chapter 15 Uzbekistan, Uranium deposits of the world-Asian[M].Berlin Heidelberg:Springer-Verlag, 2009:402-446.
Dahlkamp F J. Chapter 16 Vietnam, Uranium deposits of the world-Asian[M].Berlin Heidelberg:Springer-Verlag, 2009:449-450.
张洪瑞, 侯增谦, 杨志明.特提斯成矿域主要金属矿床类型与成矿过程[J].矿床地质, 2010, 29(1):113-115. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ201001012.htm 任秉琛, 邬介人.古亚洲成矿域古生代矿床成矿系列组合与矿床成矿系列类型的初步划分[J].矿床地质, 2002, 21(增刊):219-221. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ2002S1063.htm 任秉琛, 邬介人.古亚洲成矿域重要金属矿床类型与区域成矿规律探讨[J].矿床地质, 2004, 23(增刊):112-120. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ2004S1016.htm 周飞飞."一带一路"点燃地质工作新梦想[N].中国国土资源报(第5版), 2015-01-01. 国土资源部信息中心.世界矿产资源年评[M].北京:地质出版社, 2014:250-254. Bradley D, Jaskula B. Lithium-For harnessing renewable energy:U. S. Geological Survey Fact Sheet 2014-3035[M].U.S. Geological Survey, 2014.
曹文虎, 吴蝉.卤水资源及其综合利用技术[M].北京:地质出版社, 2004:1-189, 249-279. 乜贞, 卜令忠, 郑绵平.中国盐湖锂资源的产业化现状--以西台吉乃尔盐湖和扎布耶盐湖为例[J].地球学报, 2010, 31(1):95-99. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB201001014.htm 《中国矿床发展史.四川卷》编委会.中国矿床发现史.四川卷[M].北京:地质出版社, 1996:131-133. 张立生.乌兹别克斯坦的矿产资源与投资前景--随中国科学家代表团访问乌兹别克斯坦考察报告之一[J].四川地质学报, 2001, 21(4):205-213. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SCDB200104002.htm British Geological Survey. Minerals in Afghanistan[EB/OL] (2016-12-03)[2016-12-03]http://www.bgs.ac.uk/afghanMinerals/docs/RareMetals_A4.pdf.2016.
赵元艺, 符家骏, 李运.塞尔维亚贾达尔盆地超大型锂硼矿床[J].地质论评, 2015, 61(1):34-43. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP201501003.htm Bray E L, Guberman D E, Edelstein D L, et al. Mineral commodity summaries 2016[M]. U.S. Geological Survey, 2016:100-101.
罗莎莎, 郑绵平.西藏地区盐湖锂资源的开发现状[J].地质与勘探, 2004, 40(3):10-14. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT200403003.htm 刘喜方, 郑绵平, 齐文, 等.西藏扎布耶盐湖超大型B、Li矿床成矿物质来源研究[J].地质学报, 2007, 81(12):1709-1714. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE200712012.htm 尹淑苹, 任玉峰.新矿物(2007.1~2007.12)[J].岩石矿物学杂志, 2010, 29(4):445-451. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSKW201004011.htm 纪志永, 焦朋朋, 袁俊生, 等.锂资源的开发利用现状与发展分析[J].轻金属, 2013, 5:2-5. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QJSS201305002.htm 雪晶, 胡山鹰.我国锂工业现状及前景分析[J].化工进展, 2011, 30(4):783-787. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HGJZ201104017.htm 杨晶晶, 秦身钧, 张健雅, 等.锂提取方法研究进展与展望[J].化工矿物与加工, 2012, 6:44-46. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HGKJ201206017.htm 赵元艺.西藏扎布耶盐湖碳酸锂提取盐田工艺及其相关技术研究[D].中国地质科学院博士后论文, 2000:1-9. Uranium Maps and Statistics[EB/OL](2016-12-01)[2016-12-03] http://www.wise-uranium.org/umaps.html.2016.
World Nuclear Association.Uranium in Mongolia[EB/OL](2016-04-01)[2016-12-03] http://www.world-nuclear.org/info/Country-Profiles/Countries-G-N/Mongolia/.2016.
方锡珩.相山铀矿田与斯特列利措夫铀矿田特征对比[J].铀矿地质, 2012, 28(5):265-272. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YKDZ201205001.htm 邱爱金, 郭令智, 郑大瑜, 等.江西相山地区中、新生代构造演化对富大铀矿形成的制约[J].高校地质学报, 1999, 5(4):418-424. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXDX199904008.htm 张万良, 余西垂.相山铀矿田成矿综合模式研究[J].大地构造与成矿学, 2011, 35(2):249-254. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK201102011.htm 张树明, 曹寿孙, 曾文乐, 等.江西相山矿田典型铀矿床流体包裹体特征及意义[J].矿床地质, 2012, 31(1):66-69. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ201201007.htm 张万良, 邹茂卿.相山矿田铀多金属成矿条件分析[J].铀矿地质, 2014, 30(3):172-174. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YKDZ201403008.htm 李有柱.俄罗斯东外贝加尔地区图鲁库伊破火山口铀矿床上的交代作用[J].国外铀金地质, 2000, 17(1):23-28. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GWYD200001006.htm 叶庆森.俄罗斯外贝加尔地区晚中生代Tulukuev破火山口铀矿床和蚀变作用[J].世界核地质科学, 2003, 20(3):153-154. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GWYD200303006.htm 谭克仁, 侯惠群, 蔡新平, 等.斯特列佐夫斯克铀矿床构造岩浆活化控矿特征及成矿规律[J].大地构造与成矿学, 2003, 27(1):91-95. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK200301013.htm 李海东, 钟福军, 张志勇, 等.我国火山岩型铀矿床中铀-多金属组合特征及其意义[J].矿产与地质, 2015, 29(3):283-286. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCYD201503003.htm 杨明桂, 梅勇文.钦-杭古板块结合带与成矿带的主要特征[J].华南地质与矿产, 1997, 3:52-56. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HNKC199703008.htm 陈雷, 赵元艺, 王宗起, 等.江西相山铀矿田山南矿区流纹英安岩和花岗斑岩的地球化学与Sr、Nd同位素特征[J].地质与勘探, 2013, 49(6):999-1001. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT201306001.htm 陈正乐, 王永, 周永贵, 等.江西相山火山-侵入杂岩体锆石SHRIMP定年及其地质意义[J].中国地质, 2013, 40(1):217-219. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201301017.htm 聂江涛, 李子颖, 王健, 等.江西相山矿田多金属成矿流体特征与成矿作用[J].地质通报, 2015, 34(2/3):535-537, 546. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=2015020328&journal_id=gbc 陈肇博, 谢佑新, 万国良, 等.华东南中生代火山岩中的铀矿床[J].地质学报, 1982, 3:235-242. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE198203004.htm 严冰, 严寒, 周莉, 等.江西相山火山岩型铀矿C、O、H、S同位素特征及意义[J].矿物岩石, 2013, 33(3):47-49. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWYS201303008.htm 陈小明, 陆建军, 刘昌实, 等.桐庐、相山火山-侵入杂岩单颗粒锆石U-Pb年龄[J].岩石学报, 1999, 15(2):272-277. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB902.013.htm 李学礼.论热源、水源、矿(铀) 源三源成矿问题[J].华东地质学院学报, 1992, 15(2):101-108. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HDDZ199202000.htm 陈迪云, 周文斌, 周鲁民, 等.相山铀矿田同位素地质学特征[J].矿床地质, 1993, 12(4):370-376. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ199304011.htm 姜耀辉, 蒋少涌, 凌洪飞.地幔流体与铀成矿作用[J].地学前缘, 2004, 11(2):493-496. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200402026.htm 钟福军, 潘家永, 夏菲, 等.我国火山岩型铀矿找矿预测地质模型的构建与应用[J].东华理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2015, 38(2):135-138. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HDDZ201502001.htm 施祖远.我国铀矿开采技术成就与发展对策[J].铀矿冶, 2011, 30(4):175-179. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YKYI201104004.htm 苏学斌, 杜志明.我国地浸采铀工艺技术发展现状与展望[J].中国矿业, 2012, 21(9):79-82. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGKA201209024.htm 黄群英.某砂岩铀矿酸法地浸溶质运移与酸化进程分析[J].有色金属(冶炼部分), 2015, (6):50-51. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-METE201506014.htm 蔡煜琦, 张金带, 李子颜, 等.中国铀矿资源特征及成矿规律概要[J].地质学报, 2015, 89(6):1052-1015. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201506005.htm 焦养泉, 吴立群, 彭云彪, 等.中国北方古亚洲构造域中沉积型铀矿形成发育的沉积-构造背景综合分析[J].地学前缘, 2015, 22(1):190-195. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201501018.htm 董永观, 邢怀学, 高卫华等.阿尔泰成矿带构造演化与成矿作用[J].矿床地质, 2010, 29(增刊):1-2. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ2010S1005.htm 付小方.四川甘孜甲基卡地区发现超大型规模锂辉石矿[EB/OL] (2015-03-25)[2016-06-30] http://www.cgs.gov.cn/xwl/cgkx/201603/t20160309_298929.html.2015. 王木清.中国北东部铀矿化与大地构造活动及演化的关系[J].铀矿地质, 2013, 29(4):193-198. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YKDZ201304000.htm 赵忠华, 彭志东, 张学元, 等.中国北东部火山岩型铀矿成矿地质特征及找矿方向[J].铀矿地质, 2007, 23(3):135-136. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YKDZ200703000.htm 姚振凯, 刘翔, 郑大瑜.亚欧东西向活化构造铀成矿带划分依据及铀成矿域分布[J].铀矿地质, 2014, 30(4):195. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YKDZ201404001.htm 姚振凯, 刘翔.中亚独联体五国铀成矿的大地构造背景[J].大地构造与成矿学, 2000, 24(1):1-5. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK200001000.htm 申军, 戴斌联.盐湖卤水锂矿资源开发利用及其展望[J].化工矿物与加工, 2009, 4:2-4. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HGKJ200904002.htm 袁于飞.我国地浸采铀新技术获得重大突破-盘活数万吨复杂砂岩型铀矿资源[N].光明日报, 2014-08-02. 于德福.我国实现硬岩型铀矿原地浸开采[N].中国国土资源报, 2015-08-05. 应对全球化:全球主要矿产资源研究系列报告(锂矿卷).中国地质调查局发展研究中心,2015. 乔东海,赵元艺,汪傲,等.“一带一路”地区36个锂矿数据统计表.中国地质大学(北京)、中国地质科学院矿产资源研究所,2016. 赵元艺.西藏麻米错盐湖卤水锂硼钾资源综合开发扩大试验.中国地质科学院矿产资源研究所研究报告.2013. 乔东海,赵元艺,汪傲,等.“一带一路”地区130个铀矿数据统计表.中国地质大学(北京)、中国地质科学院矿产资源研究所,2016.



 下载:
下载: