Correction of heat storage temperature Mg2+ and analysis of heat damage mechanism of hydrothermal system in central and eastern Tibetan Plateau
-
摘要:
隧道作为铁路穿越青藏高原中东部水热活动区的重要工程形式,探讨其遭受水热灾害的影响因素在隧道热害研究方面是有必要的。隧道热害预测手段是综合性的,其中水文地球化学方法因易实施、性价比高而被广泛应用。热储温度是水热系统研究的重要参数,热储温度的推算因体系的复杂性很难全面考虑其地球化学作用过程而发生偏差。热储温度的Mg2+校正受热水作用的岩石类型、运移速率和热储构造条件的影响,因此采用Mg2+校正可以辅助分析多类型水热循环机制,据此可对隧道穿越水热体系遭遇的热害特征进行辨识。利用温标平衡理论,构建富Mg体系平衡判定的Na-K-Ca三角图,基于水热体系作用地质背景进行平衡点梳理,探讨青藏高原中东部典型水热体系中Mg2+校正特征与影响因素的关系,对多类型水热循环条件、水岩作用、传热传质机制进行分析、比较,辅助对工程中地热带来的高岩温、热水涌突、围岩裂化等危害的分析。此方法是水文地球化学对工程热害预测的方法性讨论,也能为青藏高原中东部及未来在该区域实施交通干线的热害防控提供理论分析基础。
Abstract:Tunnel is an important engineering form of railway crossing the middle and eastern part of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau.It is necessary to discuss the influencing factors of tunnel thermal disaster.The methods of tunnel heat damage prediction are comprehensive, among which the hydrogeochemical method is widely used because of its easy implementation and high cost performance.Heat storage temperature is an important parameter in the study of hydrothermal system.Due to the complexity of the heat storage system, it is difficult to fully consider the geochemical process in the calculation of heat storage temperature, and deviation may take place in heat storage temperature calculation.The Mg2+ correction of heat storage temperature is affected by the rock type, migration rate and structural conditions of heat storage under the action of hot water.Therefore, the Mg2+ correction can be used to assist the analysis of multi-type hydrothermal cycling mechanism.Based on this, the characteristics of heat damage encountered by the tunnel through the hydrothermal system can be identified.The Na-K-Ca triangle diagram of equilibrium judgment of Mg-rich system was constructed by using the equilibrium theory of temperature scale.Based on the geological background of hydrothermal system action, the equilibrium sample points were combed to discuss the relationship between the correction characteristics of Mg2+ and the influencing factors in the typical hydrothermal system in western Sichuan and eastern Tibet.The various types of hydrothermal cycling conditions, water-rock interaction, heat and mass transfer mechanism in central and eastern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau were analyzed and compared, which can assist in the analysis of hazards such as high rock temperature, hot water inrush and surrounding rock cracking caused by geothermal in engineering.This method is a methodological discussion about hydrogeochemical prediction of engineering heat damage, and can also provide a theoretical basis for heat damage prevention and control in the middle and eastern part of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau and in the future.
-
致谢: 本文在成都理工大学地质灾害防治与地质环境保护国家重点实验室、中铁二院工程集团有限公司和中铁第一勘察设计院集团有限公司的支持下完成,同时感谢相关技术人员对文章问题分析的大力帮助。
-
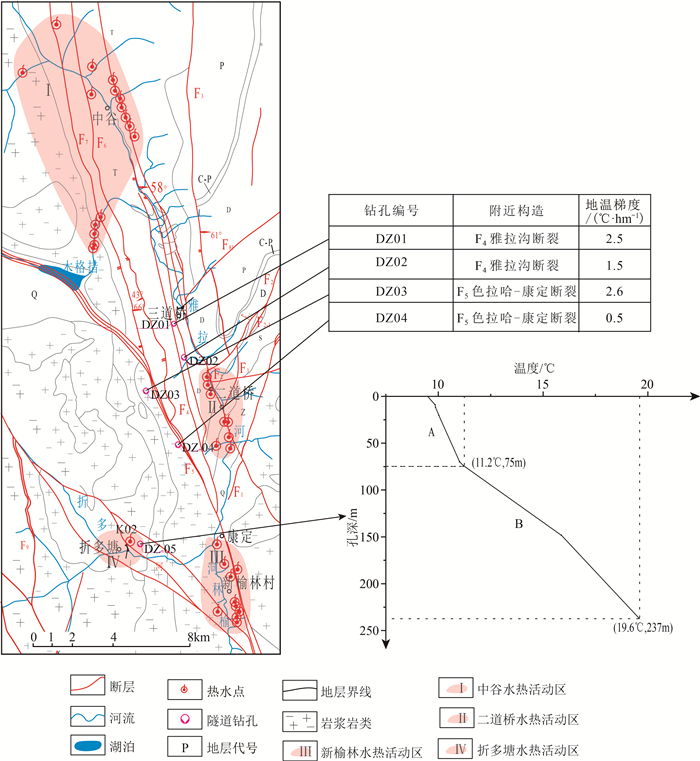
图 1 研究区区域构造及地热异常区(据参考文献[26]修改)
Ⅰ—炉霍-道孚-康定水热活动区;Ⅱ—甘孜-新龙-理塘水热活动区;Ⅲ—德格-巴塘-乡城水热活动区;Ⅳ—贡觉-芒康水热活动区;Ⅴ—昌都-察雅-左贡水热活动区;Ⅵ—洛隆-八宿水热活动区;Ⅶ—雅鲁藏布江水热活动区
Figure 1. Regional structure and geothermal anomaly map of the study area
图 7 鲜水河断裂带热水成因模型(据参考文献[29]修改)
Figure 7. Hydrothermal genesis model of Xianshuihe fault
图 9 澜沧江断裂带南段盐井热水成因演化过程示意图[28]
Figure 9. Hydrothermal genesis and evolution of salt wells in the southern part of Lancang River fault
表 1 Na-K-Ca温标计算平衡样点的温度及其Mg2+温度校正
Table 1 Calculation temperature of the equilibrium sample point and Mg2+ temperature correction by the Na-K-Ca temperature scale
地点 编号 名称 Ca Mg K Na SO4 HCO3 Cl 出露温度 Na-K-Ca温标计算温度 ΔtMg 最终计算温度 Mg2+校正幅度 温泉出露点岩性 /(mg·L-1) /℃ /% 三江地区 S01 章柯沸泉群 0.05 0.04 27.9 392.9 34.63 963.8 39.7 94.5 238 0 238 0.0 主要为碎屑岩、变质岩、花岗岩,部分地区含少量碳酸盐岩 S02 查洛间歇泉 0.2 0.04 21.0 250.7 58.269 489.574 40.0 87.6 226.5 0 227 0.0 S03 索绒北麓 3.8 0.02 4.8 71.9 24.13 150.8 17.4 87.1 159.1 0 159 0.0 S04 仁措热泉 10.3 0.3 9.3 201.7 49.97 490.85 16.9 66.5 150.1 0 150 0.0 S05 曲色热泉 16.2 1.2 36.3 555.2 92.29 1366.4 77.0 80.4 181 0 181 0.0 康定—挖角 K01 灌顶 55.2 15.9 40.2 310.3 / / 341.8 82.5 197 77.8 119.2 39.5 片岩、花岗岩、白云灰岩 K02 折多塘 4.3 1.2 5.6 260.7 8.5 610.82 54.7 54.0 126.4 11.1 115.3 8.8 花岗岩 K03 灌木林 61.5 17.0 12.7 299.4 88.9 613.0 200.7 47.0 94.6 3.7 90.9 3.9 片岩 K04 海螺沟1 30.2 8.6 13.8 390.7 18.3 867.6 126.7 59.0 139.7 43.2 96.5 30.9 灰岩、白云岩 K05 海螺沟2 31.7 1.3 9.8 246.4 132.7 607.5 44.0 62.0 98.8 0 98.8 0.0 板岩、灰岩 K06 湾东 59.8 7.6 9.8 326.5 138.0 668.5 102.5 61.4 87.1 0 97.1 0.0 绿片岩 K07 明香 43.1 12.8 9.2 290.8 134.8 857.2 56.1 61.2 91.3 2.5 88.8 2.7 绿片岩 K08 什月河 35.2 7.0 15.8 357.1 57.7 807.5 158.6 52.3 147.3 32.1 115.2 21.8 绿片岩与结晶灰岩界线 K09 什月河谷 48.1 9.9 11.3 211.1 76.5 514.8 102.3 50.0 92.2 0 92.2 0.0 绿片岩 K10 挖角 55.3 10.8 12.3 319.7 147.4 659.4 106.2 35.2 96.8 0 96.8 0.0 绿片岩 K11 草料 41.3 4.5 6.1 351.2 151.8 946.2 8.6 41.1 80.4 0 80.4 0.0 绿片岩 ZK1 一号钻孔 3.5 1.9 96.5 954 22.2 895.4 875.1 209 233.9 2.6 231.3 1.1 片岩与花岗岩界线 ZK2 二号钻孔 0.2 0.6 100.1 963 24.4 909.2 895.7 172.0 269.0 2 267.0 0.7 片岩与花岗岩界线 ZK3 三号钻孔 0.1 1.9 86.5 840.1 39.9 1006.9 705.7 210.0 273.2 8.5 264.7 3.1 片岩与花岗岩界线 ZK4 四号钻孔 80.5 10.0 65.4 890.1 1.8 896.3 83.6 65.0 181.3 23.6 157.7 13.0 灰岩、白云岩 拉月 L01 0.4 0.5 96 594 199.8 / 404.5 86.8 265.9 4.6 261.3 1.7 片麻岩、蛇绿岩 盐井 Y01 澜沧江左岸盐井村 4180 185 1450 25200 341 400 39000 37.1 180.4 4.5 175.9 2.5 以砂岩和泥岩为主 Y02 4150 183 1220 24700 341 441 37200 35.2 172.0 3.2 168.8 1.9 Y03 3710 159 1390 23400 394 820 34400 47.5 181.9 3.9 178.0 2.1 Y04 4870 234 2740 29000 647 162 47000 50.3 210.3 9.1 201.2 4.3 Y05 3060 151 854 13700 335 372 19200 24.5 176.6 6.7 169.9 3.8 Y06 4500 248 2040 32700 687 165 50600 40.5 189.0 9.5 179.5 5.0 Y07 4700 227 1600 30300 706 41 46800 55.2 178.1 5.7 172.4 3.2 Y08 292 38.4 234 1830 132 335 2390 35.3 201.3 34.1 167.2 16.9 Y09 5240 264 1660 33400 1400 117 51400 27.3 175.6 6.3 169.3 3.6 Y10 5200 278 1360 27400 706 141 41900 37.5 172.1 7.4 164.7 4.3 Y11 澜沧江右岸家大村 3220 164 511 7980 282 93 10500 25.0 168.1 7 161.1 4.2 Y12 2060 46.4 241 4160 225 414 6970 25.3 156.0 0 156.0 0.0 Y13 2640 139 316 5090 225 379 6030 38.1 160.7 5.9 154.8 3.7 Y15 澜沧江左岸 1920 50.6 1130 11600 369 708 22600 23.5 203.1 0 203.1 0.0 Y16 澜沧江右岸 1040 91.2 686 9660 577 478 15200 54.5 187.2 17.2 170.0 9.2 Y17 1040 92.3 774 11700 482 460 18300 32.4 186.8 16.6 170.2 8.9 注:上述数据均为课题组在不同时段测试所得或公开发表:三江地区数据据参考文献[27];盐井地区数据据参考文献[28] 表 2 各研究区Mg2+校正的影响因素与其校正特征
Table 2 The influencing factors of Mg2+ correction and its correction characteristics in each study area
取样地点 编号 岩性条件 运移速率 构造条件(浅层构造水) Mg2+校正幅度 热储岩性 出露岩性 三江 S01~S05 硅酸盐岩、碳酸盐岩均有 硅酸盐岩 较快 无浅层水混合 小(< 10%) 康定 K01、K04、K08 硅酸盐岩 硅酸盐岩、碳酸盐岩均有出露 相对ZK4慢 与浅层水混合 大(>20%) ZK4 硅酸盐岩 相对天然温泉快 几乎无浅层水混合 中等(10%~20%) 其余 相对ZK4慢 几乎无浅层水混合 小(< 10%) 拉月 L01 片麻岩 片麻岩 较快 无浅层水混合 小(< 10%) 盐井 Y08 碳酸盐岩 硅酸盐岩 相对该区其他点较慢 与浅层水混合 中等(10%~20%) -
高芳芳, 邓睿, 陈伟, 等. 瓦纳温泉发育特征及其对隧道工程影响分析[J]. 铁道标准设计, 2019, 63(2): 115-119. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDBS201902024.htm 马鑫, 付雷, 李铁锋, 等. 喜马拉雅东构造结地区地热成因分析[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(1): 209-219. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ202101023.htm 孙会肖, 郎旭娟, 男达瓦, 等. 西藏萨迦冲曲流域地下热水成因及工程效应分析[J]. 安全与环境工程, 2021, 28(3): 147-155. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTAQ202103020.htm 孙杨艳, 刘声凯, 景营利. 郴州地热田地热温标的选取和热储温度计算[J]. 资源信息与工程, 2020, 35(1): 36-39. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSJW202001010.htm 马致远, 李嘉祺, 翟美静, 等. 沉积型和火山型地热流体的同位素水文地球化学对比研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2019, 46(6): 9-18. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG201906003.htm 王轶, 童珏, 李晓龙, 等. 青海省曲乃亥温泉地质特征及成因分析[J]. 华东理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 43(3): 248-256. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HDDZ202003007.htm 王莹, 周训, 于湲, 等. 应用地热温标计算地下热储温度[J]. 现代地质, 2007, 21(4): 605-612. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2007.04.003 郭静, 毛绪美, 童晟, 等. 水化学温度计计算粤西沿海深部地热系统热交换温度[J]. 地球科学, 2016, 41(12): 2075-2087. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201612011.htm 卢丽, 王喆, 邹胜章, 等. 四川昭觉县地热温度解析及成因模式[J]. 地质通报, 2021, 40(2/3): 434-441. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=2021020324&flag=1 Fournier R O, Truesdell A H. An empirical Na-K-Ca geothermometer for natural waters[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1973, 37(5): 1255-1275. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(73)90060-4
Arnórsson S, Gunnlaugsson E, Svavarsson H. The chemistry of geothermal waters in Iceland III. Chemical geothermometry in geothermal investigations[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1983, 47(3): 567-577. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(83)90278-8
Arnórsson S, Sigurdsson S, Svavarsson H. The chemistry of geothermal waters in Iceland. I. Calculation of aqueous speciation from 0℃ to 370℃[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1982, 46: 1513-1532. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(82)90311-8
Arnórsson S, Gunnlaugsson E, Svavarsson H. The chemistry of geothermal waters in Iceland Ⅱ. Mineral equilibria and independent variables controlling water compositions[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1982, 47: 547-566. http://www.onacademic.com/detail/journal_1000035676113310_3ffe.html
Nieva D, Nieva R. Developments in geothe-rmal energy in Mexico-part twelve. A cationic geothermometer for prospecting of geothermal resources[J]. Heat Recovery Systems and CHP, 1987, 7(3): 243-258. doi: 10.1016/0890-4332(87)90138-4
Giggenbach W F. Geothermal solute equilibria Derivation of Na-K-Mg-Ca geoindicators[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1988, 52(12): 2749-2765. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(88)90143-3
Giggenbach W F. Mass transfer in hydrothe-rmal alteration systems[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1984, 48: 2693-2711. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(84)90317-X
夏跃珍, 王飞, 姚晶娟, 等. 地热系统热储温度评价方法探讨[J]. 能源与环境, 2014, (2): 10-11, 13. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9064.2014.02.004 Fournier R O, Potter II R W. Magnesium correction to the Na-K-Ca chemical geothermometer[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1979, 43(9): 1543-1550. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(79)90147-9
Rybach L, Muffler L J P. 地热系统——原理和典型地热系统分析[M]. 北京大学地质学系地热研究室, 译. 北京: 地质出版社, 1986: 87-88. 郑西来, 刘鸿俊. 地热温标中的水-岩平衡状态研究[J]. 西安地质学院学报, 1996, 18(1): 74-79. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XAGX601.014.htm 刘军强. 应用地热温标计算热储温度——以嵊州崇仁热水为例[J]. 西部探矿工程, 2014, 26(5): 129-132. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5716.2014.05.043 周立岱, 郭宇. 阳离子温标在中地温地热中的应用[J]. 黑龙江科技学院学报, 2006, (1): 27-30. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HLJI200601007.htm 陈履安. 贵州热矿水热储温度的计算[J]. 贵州地质, 1995, 12(1): 69-77. 汪集旸, 熊亮萍, 庞忠和. 中低温对流地热系统[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1993. 吴红梅, 周立岱, 郭宇. 阳离子温标在中低温地热中的应用研究[J]. 黑龙江科技学院学报, 2006, 16(1): 27-30. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HLJI200601007.htm 郭长宝, 王保弟, 刘建康, 等. 川藏铁路交通廊道地质调查工程主要进展与成果[J]. 中国地质调查, 2020, 7(6): 1-12. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDC202006001.htm Yi L, Qi J H, Li X, et al. Geochemical characteristics and genesis of the high-temperature geothermal systems in the north section of the Sanjiang Orogenic belt in southeast Tibetan Plateau[J]. Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, 2021, 414: 107244. doi: 10.1016/j.jvolgeores.2021.107244
Qi J H, Li X, Xu M, et al. Origin of saline springs in Yanjing, Tibet: Hydrochemical and isotopic characteristics[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2018, 96: 164-176. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2018.06.013
Tian J, Pang Z H, Liao D W, et al. Fluid geochemistry and its implications on the role of deep faults in the genesis of high temperature systems in the eastern edge of the Qinghai Tibet Plateau[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2021, 131: 105036. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2021.105036
安成蛟. 康定-磨西断裂带地下热水水文地球化学特征及成因模式研究[D]. 成都理工大学硕士学位论文, 2017. 李洁祥, 郭清海, 王焰新. 高温热田深部母地热流体的温度计算及其升流后经历的冷却过程: 以腾冲热海热田为例[J]. 地球科学-中国地质大学学报, 2015, 40(9): 1576-1584. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201509013.htm 王补宣. 工程传热传质学(上册)[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2015: 12-14. 余恒昌. 矿山地热与热害治理[M]. 北京: 煤炭工业出版社, 1991: 54-55.




 下载:
下载: