Origin and stability of landslides in Chaya County, Lancang River Basin, Tibet
-
摘要:
地球内外动力耦合叠加人类工程活动下的大型滑坡灾害是青藏高原工程建设面临的工程地质问题之一。针对在澜沧江流域察雅县城南侧斜坡新发现的9处大型—特大型滑坡,采取野外调查、试验测试和数值计算,分析了滑坡的特征、成因和现状稳定性。结果表明:①察雅县城滑坡具有规模大、切割深、地形阻止系数大等特征,滑坡堆积体现状具有多期蠕滑变形,表现为牵引式滑移的变形破坏特点,再次活动主要与降雨、河流侵蚀、人类工程活动等因素有关;②综合滑坡的发育特征、运动特征、物质结构与组成、断层与历史地震4个方面,初步判断察雅县城滑坡的诱发因素为内动力地质作用,为历史地震滑坡;③古妥尔滑坡堆积体在天然状态下处于基本稳定-稳定状态,在强降雨状态下滑坡前缘局部或整体处于欠稳定状态,较易-易发生滑动。新发现的大型—特大型滑坡拓宽了青藏高原"三江"地区地震滑坡的分布范围,对研究昌都及周边地区的地震历史、断裂活动性、地貌形成演化等方面提供了重要的佐证资料,滑坡堆积体现状稳定性分析结果可为县城的扩建及地质灾害风险管控提供一些参考。
Abstract:Large-scale landslide disasters under the coupling of internal and external dynamics of the earth and human engineering activities are one of the engineering geological problems faced by major engineering constructions on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Based on the field investigation, experimental test and numerical calculation of the newly discovered 9 large-extra large landslides on the southern slope of Chaya County in the Lancang River Region, the characteristics, causes and current stability of the landslides were analyzed. The results show that the Chaya landslide has the characteristics of large scale, deep cutting, and large topographic blocking coefficient; the landslide accumulation is represented by multi-stage creep deformation characterized by traction slip; and the deformation is mainly related to factors such as rainfall, river erosion and human engineering activities. The integration of the development characteristics, movement features, material structure and composition, faults and historical earthquakes of the landslides indicates that the inducing factor of the landslide in Chaya County is internal dynamic earthquake action, and it is a historical earthquake landslide. The Guttor landslide accumulation body is basically stable or stable in its natural state, and the front edge of the landslide is in a partially or overall under-stable state under heavy rainfall conditions, which is relatively easy to slip. The newly discovered large-extra-large ancient landslide provides important supporting information for the study of the earthquake history, fault activity and geomorphological evolution of Changdu and surrounding areas. The evaluation results of current stability of landslide accumulations can provide some scientific basis for the expansion of the county and the risk management as well as control of geological disasters.
-
作为天山-兴蒙构造域枢纽部分的中国西北甘—蒙北山地区,不仅是天山-兴安金属成矿带的重要组成部分,更是了解中亚及中国西北地区古大陆地质构造演化历史的重要窗口,一直备受国内外地学界关注。
以往的研究工作,学者们[1-23]主要关注马鬃山地块及其以南的北山南带地区,对这一区域的地质构造演化历史提出了诸多观点,且认识逐渐趋于统一。而对于马鬃山地块以北的北山北带地区,受限于基础地质资料的匮乏,对其地质演化历史的认识相对模糊,尤其是关于古生代以来该地区洋-陆转换进程的认知,一直与出露的地质实体处于相互矛盾或不匹配的状态。目前,关于北山北带古生代以来的洋-陆转换历史,主要存在以下3种观点:①该区域自中奥陶世以来一直处于活动陆缘的演化阶段,这一过程一直持续到中泥盆世末期,早石炭世开始,区域上沿红石山—百合山一线发生裂解,形成“有限大洋”,并于早石炭世中晚期大洋向南、北两侧发生双向俯冲,约在晚石炭世洋盆闭合,发生弧-弧碰撞,自此结束了区域上的洋演化历史[6, 10-11, 13-14, 24-25];②该区域在奥陶纪之前存在一个巨大洋盆-古亚洲洋,自中奥陶世开始,古亚洲洋先后向洋盆南侧的马鬃山地块(志留纪前可能为冈瓦纳大陆的一部分)北缘及洋盆北侧的西伯利亚古板块南缘俯冲消减,经过长期多次的俯冲消减,洋盆逐渐缩小,最终于晚石炭世大洋闭合,西伯利亚板块与哈萨克斯坦板块(马鬃山地块)发生碰撞[8, 12];③该区域的洋-陆转化格局在早古生代已结束,石炭纪沿红石山—百合山一线重新拉张裂解形成裂谷小洋盆(红海型“海槽”)[3-5, 15-16, 26-27]。
以上3种观点,对北山北带地区早古生代的时空演化体制认识方面基本达成一致,均认为区域上的俯冲消减事件开始于早古生代(奥陶纪),但是对于这一演化过程的后续发展存在分歧:赵茹石等认为,区域自奥陶纪以来先后经历了两阶段相对独立的俯冲消减事件,并认为石炭纪以来是与红石山-百合山新生“有限洋盆”双向俯冲有关的新一轮演化体制[6, 10-11],但是对古生代以来的这2次俯冲消减体制的时空演化关系方面未做明确的阐述;刘雪亚等则认为区域上奥陶纪—石炭纪一直处于同一大洋(古亚洲洋)向两侧板块(南侧哈萨克斯坦板块,北侧西伯利亚板块)多幕次的俯冲消减体制下,并认为红石山-百合山洋盆是古亚洲洋盆俯冲缩小的残余洋盆[8, 12],但无法解释红石山-百合山蛇绿构造混杂岩带至今未发现早古生代蛇绿岩的地质事实;左国朝等认为区域上的洋演化体制在早古生代已结束[3-5, 16],但这与区域上晚古生代发育大量的弧火山岩建造及配套的弧侵入体组合相违背。无论上述哪一种观点,均无法很好地解释北山北带古生代地质体所代表的两阶段弧-盆演化体制及其时空演化关系。
本文主要基于近年在甘肃、内蒙古北山北带地区开展的1:5万大红山等6幅区域地质矿产调查项目①,在红石山-百合山-额勒根乌兰乌拉蛇绿构造混杂岩带南侧首次厘定出泥盆纪弧花岗岩,通过对其进行岩石学、岩石地球化学及同位素年代学分析,结合其特有的构造变形特征,探讨岩石成因及形成的构造背景,进而为北山北带地区的洋-陆转换进程认识提供新的思路和线索。
1. 研究区地质背景
研究区位于马鬃山地块(亦称明水-旱山微板块)北缘古生代活动陆缘增生带(图 1-b),发育古生代以来的弧-盆建造且不含古老的结晶基底,是研究区最主要的地质特征(图 1-a)。以横贯研究区中部的蛇绿构造混杂岩带(属区域上红石山-百合山蛇绿构造混杂岩带一部分)为界,区内地质体表现出明显的南北差异:混杂带以北由老至新主要可见以泥盆纪雀儿山群(D1-2h、D1-2q、D3y)为代表的陆缘岛弧建造及同时期的弧侵入体(δD1),继承于奥陶纪—泥盆纪陆缘弧-盆系基础上发育而来的石炭纪白山组北区(C1-2bN)继承弧建造,此外,还可见发育于蛇绿构造混杂岩带北缘的早石炭世绿条山组(C1l)弧盆边缘沉积建造,以及弧-弧或陆-陆碰撞引起的大洋岩石圈拆沉,导致软流圈地幔上涌,形成早中二叠世双堡塘组(P1-2s)及中二叠世金塔组(P2j)裂谷盆地建造,并可见伴随该期事件形成的双峰式侵入体(νP2+γ(γπ+ηγ)P2);混杂带以南由老至新依次可见象征区域晚奥陶世—中志留世弧后有限海盆扩张至最大程度的志留系小红山岩组(S2x.)含BIF基性火山(MORB-LIKE)+复理石建造,以晚石炭世白山组南区(C2bS)陆相弧火山岩建造和早石炭世晚期—早二叠世早期高成熟度弧侵入体(δοC1+δοC2+γ(TTG+ηγ)C2+ δοP1)为代表的陆缘山弧体系。此外,还可见大量早—中二叠世碰撞-拆沉型裂谷盆地阶段之后,陆内造山机制下形成的一系列造山型花岗岩(γ(mηγβ+ηγβ)P2+ γ(ηγ)P3)。
![]() 图 1 甘蒙北山北带大红山地区地质图(a)及研究区位置图(b,据参考文献[15]修改)图a:1—(硅质)长英质糜棱岩;2—强面理化泥质岩;3—强面理化砂质岩;4—变质辉长岩、辉长闪长岩;5—变质玄武岩;6—砂岩;7—灰岩;8—蛇绿构造混杂岩带边界;9—晚二叠世花岗岩;10—中二叠世花岗岩;11—中二叠世辉长岩;12—早二叠世石英闪长岩;13—晚石炭世石英闪长岩;14—晚石炭世花岗岩;15—早石炭世石英闪长岩;16—中泥盆世花岗闪长岩;17—中泥盆世英云闪长岩;18—早泥盆世闪长岩;19—脉岩;20—推覆构造断裂;21—实测断层;22—早华力西期强变形面理;23—早华力西期糜棱面理;24—晚华力西期糜棱面理;25—英云闪长岩类采样位置;26—花岗闪长岩类采样位置;27—石英二长岩类采样位置;CZ—新生界;K1c—赤金堡组;P2j—金塔组;P1-2s—双堡塘组;C2bS—白山组南区;C1-2bN—白山组北区;C1-2l—绿条山组;D3y—雀儿山群圆锥山组;D1-2q—雀儿山群清河沟组;D1-2h—雀儿山群红尖山组;S2x.—志留系小红山岩组;图b:1—国境线;2—省界;3—构造分区界线;4—蛇绿混杂岩带;5—研究区;Ⅰ-1—雀儿山-狐狸山古生代岩浆弧;A—红石山-百合山-额勒根乌兰乌拉晚古生代SSZ型蛇绿构造混杂岩带;Ⅰ-2—黑鹰山-路井古生代岩浆弧;Ⅰ-3—马鬃山地块;Ⅰ-4—公婆泉早古生代岩浆弧;B—牛圈子-洗肠井早古生代MOR型蛇绿构造混杂岩带;Ⅱ-1—营毛沱-鹰嘴红山早古生带被动陆缘;Ⅱ-2—花牛山早古生带陆缘裂谷;Ⅱ-3—红柳园-白山堂晚古生带陆内裂谷;Ⅱ-4—敦煌地块Figure 1. Geological map in Dahong Mountain, the north belt of Beishan area, Gansu-Inner Mongolia(a)and the location of the study area(b)
图 1 甘蒙北山北带大红山地区地质图(a)及研究区位置图(b,据参考文献[15]修改)图a:1—(硅质)长英质糜棱岩;2—强面理化泥质岩;3—强面理化砂质岩;4—变质辉长岩、辉长闪长岩;5—变质玄武岩;6—砂岩;7—灰岩;8—蛇绿构造混杂岩带边界;9—晚二叠世花岗岩;10—中二叠世花岗岩;11—中二叠世辉长岩;12—早二叠世石英闪长岩;13—晚石炭世石英闪长岩;14—晚石炭世花岗岩;15—早石炭世石英闪长岩;16—中泥盆世花岗闪长岩;17—中泥盆世英云闪长岩;18—早泥盆世闪长岩;19—脉岩;20—推覆构造断裂;21—实测断层;22—早华力西期强变形面理;23—早华力西期糜棱面理;24—晚华力西期糜棱面理;25—英云闪长岩类采样位置;26—花岗闪长岩类采样位置;27—石英二长岩类采样位置;CZ—新生界;K1c—赤金堡组;P2j—金塔组;P1-2s—双堡塘组;C2bS—白山组南区;C1-2bN—白山组北区;C1-2l—绿条山组;D3y—雀儿山群圆锥山组;D1-2q—雀儿山群清河沟组;D1-2h—雀儿山群红尖山组;S2x.—志留系小红山岩组;图b:1—国境线;2—省界;3—构造分区界线;4—蛇绿混杂岩带;5—研究区;Ⅰ-1—雀儿山-狐狸山古生代岩浆弧;A—红石山-百合山-额勒根乌兰乌拉晚古生代SSZ型蛇绿构造混杂岩带;Ⅰ-2—黑鹰山-路井古生代岩浆弧;Ⅰ-3—马鬃山地块;Ⅰ-4—公婆泉早古生代岩浆弧;B—牛圈子-洗肠井早古生代MOR型蛇绿构造混杂岩带;Ⅱ-1—营毛沱-鹰嘴红山早古生带被动陆缘;Ⅱ-2—花牛山早古生带陆缘裂谷;Ⅱ-3—红柳园-白山堂晚古生带陆内裂谷;Ⅱ-4—敦煌地块Figure 1. Geological map in Dahong Mountain, the north belt of Beishan area, Gansu-Inner Mongolia(a)and the location of the study area(b)本次研究的弧花岗岩组合在空间上位于研究区中南部大红山南西一带,区域上红石山-百合山-额勒根乌兰乌拉蛇绿构造混杂岩带南侧,宏观上呈不规则岩株侵入其北侧的中志留世小红山岩组中,其内局部可见小红山岩组的捕虏体(图版Ⅰ-f),并被附近早石炭世晚期—早二叠世早期的弧侵入体(δοC1+δοC2+γ(TTG+ηγ)C2+δοP1)及晚期的造山型花岗岩(γ(mηγβ+ηγβ)P2+γ(ηγ)P3)侵入,向南可延伸至研究区南侧的少斜沟北一带,研究区出露面积约110 km2。前人1:20万红石山幅②曾将其划分为混合岩化石炭系白山组,1:25万红宝石幅③则将其厘定为新太古代片麻岩(深成岩)。本次实地调查发现,这是一套经历了强烈区域动热变质作用的弧花岗岩(英云闪长岩、花岗闪长岩、石英二长岩),发育透入性片麻理构造,其中,花岗闪长岩颜色较深,多呈深灰色-灰色,粒度整体较细,普遍变形强烈,发育强度不一的糜棱面理,露头多呈板状、板片状(图版Ⅰ-a),岩石中局部可见有深熔长英质条带(图版Ⅰ-b)发育;英云闪长岩颜色较浅,多呈灰色-浅灰色,粒度较粗,变形较弱且强弱不一,变形强者露头呈板片状、板状,发育一组糜棱面理(图版Ⅰ-c、d),变形弱者露头呈块状,仅可见岩石内矿物有弱定向排列(图版Ⅰ-e)。空间产出状态上,二者呈“你中有我,我中有你”的共生关系。
另外,石英二长岩多以共熔体的形式分别与花岗闪长岩类和英云闪长岩类紧密相伴产出,野外可填图性差,露头上难以将其与后二者区分,空间上3类岩石共同组成这套弧花岗岩。
2. 构造变形特征
强烈的多期次构造变形特征是该套弧花岗岩的一大特点,主要可识别出2期构造行迹。其中第一期构造主要为一系列的小型构造行迹,总体具有较深层次的构造变形特征,主要表现为发育的糜棱面理、固态流变褶皱、拉伸线理、粘滞型石香肠和同构造分泌脉一起组成的新生变质固态流变构造群落,进一步可划分为3类:①面状构造,以透入性糜棱面理为主,总体发育强、分布广,但不均一(图版Ⅱ-a、b);②线状构造,主要表现为矿物拉伸线理,线理倾伏向一般与糜棱面理倾向夹角在30°~45°之间,更接近于倾向线理,虽遭晚期构造影响变位明显,但其原始构造方位仍保留较好,与之相伴常可见顺层剪切褶皱,规模大小不一,但枢纽方位与同期矿物拉伸线理垂直或斜交,且二者共同参与了晚期叠加变形,属于“b”型线理(图版Ⅱ-c、d);③褶皱构造,均为露头尺度的小褶皱,较发育,多具固态流变紧闭压扁褶皱的特点,形成相似褶皱、平行褶皱和顶厚褶皱,局部还可见深熔柔流褶皱,表现为发育无根褶皱、肠状岩脉、钩状褶皱、构造透镜体,并伴有同期长英质熔出脉产出,形成褶皱脉岩同构造产出(图版Ⅱ-e~h),为S1面理构造置换的典型现象。
第二期构造行迹主要表现为叠加于早期片理面上的紧闭直立倾伏对称型褶皱(图 2-a),参与褶皱的面理为第一期构造形成的先成糜棱面理S1,相当于早期S1面理的重褶,主要见于该套弧花岗岩组合的北西端,褶皱长约5 km,宽约2.5 km,两翼产状相背产出,北翼代表性产状S1为340°∠60°~80°,南翼优势产状S1为145°∠50°~75°,转折端处产状为80°∠45°~60°,整体为一向北东东—东倾伏的背斜构造。在该褶皱两翼次级小褶皱较发育(图 2-b),褶皱较紧闭,枢纽近东西向,向东倾伏,为斜歪倾伏褶皱和直立倾伏褶皱。褶皱类型以ⅠB型的平行褶皱、尖棱褶皱为主,与主褶皱配套。
3. 岩石特征
岩石特征方面,该套弧花岗岩总体呈现三大类特征,分别对应3种不同的原岩类型:英云闪长岩、花岗闪长岩及石英二长岩。
黑云斜长糜棱片麻岩(英云闪长岩,图 3-a、b):呈麻灰色,具糜棱岩化结构、变余不等晶结构,定向构造、片麻状构造;主要由不等晶斜长石、石英、鳞片状变晶矿物黑云母组成,含少量白云母,并可见少量碎粒状矿物(主要为长石、石英),次生蚀变矿物主要包括绢云母、绿帘石、绿泥石、碳酸盐岩矿物,副矿物为微量锆石、磷灰石;主要矿物大小为0.05~2.2×4.5 mm,多为0.5~1.5×3 mm,矿物间呈弯曲齿状镶嵌,鳞片状矿物较均匀分布,矿物长径定向排列,部分斜长石呈半自形-较自形板状,并略显粗大。其中,斜长石(Pl)含量约50%,呈半自形-较自形板状,大小为0.05~2.2×4.5 mm,多为0.5~1.5×3 mm,较洁净-较污浊,表面具绢云母化、帘石化等,An=26~30,为更中长石;石英(Qtz)含量约25%,呈两向伸长粒状,大小为0.05~1×2.5 mm,多为0.25~1.5 mm,无色,洁净光亮,波状消光强烈,亚颗粒构造;黑云母(Bt)含量约20%,呈鳞片状,大小为0.1~0.75×2 mm,多为0.25~0.75×1.5 mm,浅黄色-棕黄多色性,部分具绿帘石化、绿泥石化、白云母化等,较均匀分布;白云母(Mu)含量3%~5%,呈鳞片状,无色,较鲜艳干涉色,较均匀分布,应属黑云母蚀变形成;碎粒长石、石英含量5%,以石英为主,大小为0.02~0.1 mm;副矿物锆石、磷灰石微量,前者呈浑圆粒状,d=0.05~0.1 mm,极高正突起,鲜艳干涉色,后者呈粒状、柱状,d=0.05~0.2 mm,无色,中正突起,一级灰干涉色。原岩为英云闪长岩,后受热动力变质作用,呈糜棱片麻岩。
片麻状英云闪长岩(图 3-c、d):岩石呈灰色,具弱糜棱岩化结构、变余半自形粒状结构,片麻状构造、块状构造;主要由斜长石、石英、黑云母组成,含少量白云母,次生蚀变矿物包括绢云母、绿帘石,副矿物为微量磷灰石、锆石、磁铁矿。其中,斜长石含量约60%,半自形板状、粒状,大小为0.05~1.5×2.8 mm,多为0.25~1.5 mm,较洁净-较污浊,可见聚片双晶、环带构造等,表面具轻微绢云母化,An=17,为更长石;石英含量约20%,呈两向伸长粒状,大小为0.05~1×2.5 mm,多为0.25~1.5 mm,无色,洁净光亮,波状消光强烈,亚颗粒构造;黑云母含量10%~15%,呈鳞片状,大小为0.1~0.75×2 mm,多为0.25~0.75×1.5 mm,浅黄色-棕黄多色性,部分具绿泥帘石化、白云母化等,较均匀分布,常具弯曲揉皱变形;白云母含量3%~5%,呈鳞片状,无色,较鲜艳干涉色,较均匀分布,应属黑云母蚀变形成;碎粒含量2%,以石英为主,长石少量,压碎、重结晶,大小为0.05~0.1 mm;副矿物锆石、磷灰石微量,前者呈浑圆粒状,d=0.05~0.1 mm,极高正突起,鲜艳干涉色,后者呈粒状、柱状,d=0.05~0.2 mm,无色,中正突起,一级灰干涉色;此外,还可见少于1%的磁铁矿,呈黑色立方体,具褐铁矿化,大小为0.08 mm。
黑云二长糜棱片麻岩(花岗闪长岩,图 4-a、b):岩石风化面呈深灰色,新鲜面呈灰绿色,具中细粒鳞片粒状变晶结构、碎斑结构、糜棱结构,定向构造、片麻状构造;主要由碎斑和碎基组成,其中碎斑包括半自形板状或碎斑状的斜长石、钾长石、石英、片状黑云母,而碎基主要由碎粒状的上述矿物组成,次生蚀变矿物可见绿泥石、绿帘石、绢云母、碳酸盐矿物,副矿物为微量磷灰石、榍石等;粒状矿物呈两向伸长状、透镜状,矿物间呈弯曲齿状镶嵌,鳞片状黑云母呈云母鱼状,矿物长径定向排列。其中,斜长石含量大于等于40%,板状、碎斑状、两向伸长粒状,大小为1×3.75~0.75 mm,绢云母化、帘石化,斜长石双晶扭折、弯曲、变形,碳酸盐化;石英含量15%,拉长、重结晶,沿长轴定向排列,大小为0.3×1.6 mm,重结晶大小为0.2~0.5 mm,无色,洁净光亮,波状消光强烈,亚颗粒构造;钾长石(Kf)含量10%~15%,碎斑状、两向伸长粒状,透镜状,边缘细粒化,具格子双晶,大小为1.5 mm;黑云母含量大于等于10%,棕黄色,片状,常具弯曲揉皱变形,部分呈云母鱼状,大小为1.5~0.5 mm,部分绿泥石化、绿帘石化或被绿泥石替代,一些帘石呈细脉状分布;碎粒含量20%,以长石、石英为主,次为黑云母,大小为0.01~0.05 mm,条纹状;磷灰石少见,无色,柱状,大小为0.03×0.07 mm;锆石少见,柱状,大小为0.04×0.07 mm;榍石少见,柱状,大小为0.75 mm。原岩为花岗闪长岩,后受热动力变质作用,呈糜棱片麻岩。
黑云二长糜棱片麻岩(石英二长岩,图 4-c、d):岩石呈灰色,具糜棱岩化结构、细粒鳞片粒状变晶结构,片麻状构造,定向构造;主要由板状、粒状变晶矿物斜长石、石英、钾长石、片状变晶矿物黑云母组成,含少量碎粒状矿物(以长石、石英为主),次生蚀变矿物为白云母、绢云母、绿帘石、绿泥石,副矿物主要为磷灰石、锆石等;主要矿物粒径为0.05~1.2× 2 mm,多为0.5~1 mm,粒状矿物呈两向伸长状,压扁透镜状,鳞片状黑云母部分弯曲变形,呈云母鱼状,矿物颗粒间呈弯曲状镶嵌,长径定向排列,碎粒状长石、石英呈细纹状,定向分布;其中,斜长石含量大于40%,呈半自形板状、两向伸长状、压扁透镜状,大小为0.05~1.2×2 mm,多为0.5~1 mm,较洁净,可见聚片双晶,轻微绢云母化,An=10~16;钾长石含量25%~30%,呈粒状、两向伸长状、压扁透镜状,大小为0.05~1 mm,多为0.5~0.75 mm,较洁净,可见格子状双晶;石英含量15%~20%,呈粒状、两向伸长状,定向分布,大小为0.05~1.5 mm,多为0.5~0.75 mm,无色,洁净光亮,波状消光、缎带式消光,亚颗粒构造发育;黑云母含量10%~15%,呈鳞片状、略弯曲变形,呈云母鱼状,大小为0.1~0.5×1 mm,浅黄色-棕黄色强多色性,较鲜艳干涉色,少量轻微绿泥石化、绿帘石化、绢(白)云母化;碎粒状长石、石英含量2%,大小为0.005~0.1 mm,细纹状、集合体分布;副矿物磷灰石、锆石微量,锆石呈浑圆粒状,d=0.05~0.2 mm,极高正突起,鲜艳干涉色,磷灰石呈粒状、柱状,d=0.05~0.25 mm,无色,中正突起,一级灰干涉色。原岩为石英二长岩,后受热动力变质作用,呈糜棱片麻岩。
4. 分析方法
本次野外采集9件新鲜无蚀变的花岗岩样品,用水将其表面冲洗干净并晾干,机械破碎至200目后送实验室分析。其中主量元素在自然资源部太原矿产资源监督检测中心完成,采用原子吸收分光光度计测定,测定偏差优于5%;微量和稀土元素在自然资源部武汉矿产资源监督检测中心完成,采用电感耦合等离子体质谱法(ICP-MS)测定,检测限优于5×10-9,相对标准偏差优于5%。
锆石分选在河北省地矿局廊坊区调队实验室完成,对所采的3件花岗岩样品进行清洗后,粉碎至80~100目,用常规的重液浮选和电磁分离方法进行分选。锆石的阴极发光(CL)图像研究和原位U-Pb同位素年龄分析在中国地质调查局天津地质调查中心(天津地质矿产研究所实验测试室)完成,锆石定年分析所用仪器为Thermo Fisher公司制造的Neptune型MC-ICP-MS及与之配套的Newwave UP 193激光剥蚀系统(ESI制造)。激光剥蚀斑束直径为35 μm,激光剥蚀样品的深度为20~40 μm。锆石年龄计算采用标准锆石91500为外标,元素含量采用美国国家标准物质局人工合成硅酸盐玻璃NIST SRM610为外标,29Si为内标元素进行校正。数据处理采用ICPMSDataCal 4.3程序[28],并采用软件[29]对测试数据进行普通铅校正,年龄计算及谐和图绘制采用Isoplot(3.0版)[30]完成。
5. 分析结果
5.1 岩石地球化学特征
从岩石地球化学数据(表 1)看,这套弧花岗岩总体可分为两大类:富钠的T1G1和富钾的QM(石英二长岩)。
表 1 大红山南弧花岗岩主量、微量和稀土分析结果Table 1. The analytical results of the major, trace and rare earth elements of the arc granite in the south of Dahong Mountain样品号 5034Gs-1 5418Gs-1 6045Gs-1 7903 Gs-1 6021Gs-1 5024Gs-1 6080Gs-1 6017Gs-1 5021Gs-1 原岩类型 英云闪长岩 花岗闪长岩 石英二长岩 SiO2 65.34 69.64 69.80 67.62 67.42 66.19 68.65 63.52 62.74 Al2O3 16.61 15.09 15.95 15.09 13.37 15.46 14.20 14.92 17.89 Fe2O3 1.64 1.23 1.26 1.70 1.59 1.04 1.54 1.76 1.87 FeO 2.11 1.12 1.16 2.48 1.79 4.28 2.42 4.34 4.43 TiO2 0.42 0.36 0.24 0.51 0.52 0.68 0.54 0.78 0.77 CaO 4.21 3.28 3.74 4.03 4.21 2.03 2.65 2.11 0.75 MgO 1.57 1.01 0.90 1.95 1.57 2.45 1.35 2.58 2.80 K2O 2.08 1.96 1.88 1.89 2.91 2.74 3.38 3.75 4.10 Na2O 3.61 4.39 3.38 3.10 3.30 1.85 2.74 1.10 0.91 MnO 0.10 0.05 0.16 0.08 0.08 0.08 0.08 0.09 0.32 P2O5 0.27 0.13 0.16 0.22 0.16 0.24 0.14 0.16 0.11 H2O+ 0.84 0.50 0.62 0.64 1.28 1.97 0.71 2.01 2.60 CO2 0.53 0.58 0.53 0.23 1.60 0.23 0.15 0.91 0.08 总计 99.33 99.34 99.78 99.54 99.80 99.24 98.55 98.03 99.37 Na2O/K2O 1.74 2.24 1.80 1.64 1.13 0.68 0.81 0.29 0.22 TFeO 3.58 2.23 2.29 4.01 3.22 5.21 3.80 5.92 6.11 Mg# 0.44 0.45 0.41 0.47 0.47 0.46 0.39 0.44 0.45 石英(Q) 26.46 29.80 34.93 31.07 30.13 36.49 32.49 36.33 34.93 钙长石(An) 16.02 11.90 14.28 17.30 9.88 7.25 11.53 3.82 2.61 钠长石(Ab) 31.02 37.59 28.85 26.53 28.35 16.09 23.70 9.69 7.96 正长石(Or) 12.48 11.72 11.21 11.30 17.46 16.65 20.42 23.08 25.04 Sc 9.46 4.84 3.82 9.75 10.51 15.13 10.30 16.88 19.43 Co 9.20 5.11 2.71 10.25 9.95 16.28 9.31 16.69 15.41 Ga 17.66 19.43 16.46 17.51 14.68 21.58 16.60 20.94 22.49 Rb 79.31 62.38 65.66 89.41 68.88 89.63 115.40 153.60 144.00 Zr 60.43 160.20 95.45 162.60 115.90 153.60 194.70 200.10 179.50 Nb 8.86 3.85 7.41 8.45 6.24 14.78 10.03 15.50 13.88 Cs 7.12 4.71 3.05 6.25 1.61 6.61 6.09 15.19 10.86 Hf 1.70 4.20 2.40 4.00 3.10 3.80 4.80 4.90 4.30 Ta 0.96 0.67 0.93 0.92 0.72 2.21 0.96 1.38 1.31 Th 2.66 6.28 6.34 1.74 25.34 12.18 16.10 15.40 14.68 U 0.64 2.43 1.02 0.81 2.82 2.06 1.25 2.88 3.14 Ba 451.00 200.20 395.30 310.10 613.10 489.70 755.40 907.80 599.00 Cr 11.19 10.79 7.21 30.89 34.38 63.37 31.11 78.29 87.56 Ni 9.94 5.89 1.58 19.52 16.73 39.43 22.73 40.74 43.05 Sr 321.30 241.00 347.40 210.10 238.90 141.50 175.70 103.10 66.27 V 66.23 37.27 11.83 69.82 80.50 104.00 72.73 127.80 124.40 La 11.31 16.33 20.48 12.06 19.69 33.72 31.01 42.18 37.56 Ce 20.71 31.16 38.10 21.04 37.68 65.04 58.42 82.41 75.16 Pr 2.69 4.08 4.87 2.69 4.95 8.15 7.39 10.42 9.15 Nd 10.50 15.85 18.06 10.66 19.19 30.69 27.65 39.39 34.28 Sm 2.50 3.20 3.66 2.68 4.03 6.21 5.55 7.74 6.80 Eu 1.12 0.86 1.02 1.00 0.95 1.20 1.15 1.48 1.22 Gd 2.54 2.79 3.13 2.92 3.55 5.36 4.85 6.65 6.19 Tb 0.44 0.42 0.48 0.53 0.55 0.87 0.75 1.06 0.97 Dy 2.79 2.37 2.77 3.38 3.27 5.29 4.30 6.24 5.90 Ho 0.54 0.44 0.55 0.72 0.64 1.03 0.79 1.23 1.21 Er 1.40 1.14 1.53 2.03 1.76 2.81 2.11 3.34 3.38 Tm 0.21 0.17 0.25 0.31 0.30 0.44 0.31 0.55 0.54 Yb 1.32 1.07 1.72 1.84 1.79 2.83 2.01 3.54 3.43 Lu 0.19 0.16 0.27 0.26 0.26 0.42 0.29 0.52 0.51 Y 13.53 11.85 15.44 18.79 17.28 27.07 21.44 32.31 33.22 ∑REE 58.26 80.03 96.89 62.13 98.59 164.06 146.57 206.75 186.30 LREE/HREE 5.18 8.35 8.05 4.18 7.14 7.62 8.51 7.94 7.42 (La/Yb)N 5.77 10.29 8.04 4.41 7.41 8.04 10.40 8.03 7.38 (La/Sm)N 2.85 3.21 3.52 2.83 3.08 3.41 3.52 3.43 3.47 (Gd/Yb)N 1.55 2.11 1.47 1.28 1.60 1.53 1.95 1.52 1.46 δEu 1.34 0.86 0.90 1.09 0.75 0.62 0.66 0.62 0.56 注:主量元素含量单位为%,微量和稀土元素含量单位为10-6;全铁TFeO= FeO+0.899×Fe2O3(wt%);Mg#=Mg/(Mg+Fe2+)(原子数比) 主量元素特征方面,T1类(英云闪长岩)SiO2含量为65.34%~69.80%,平均值为68.26%,整体为酸性岩石;Na2O含量为3.38%~4.39%,平均值为3.79%,K2O含量为1.88%~2.08%,平均值为1.97%,Na2O/K2O值为1.80~ 2.24,平均值为1.92,岩石明显富钠;CaO含量为3.28%~4.21%,平均值为3.74%;Al2O3含量中等,为15.09%~16.61%,平均值为15.88%;MgO含量为0.90%~ 1.57%,平均值为1.16%,Mg#平均值为0.43;全铁TFeO含量为2.23%~3.58%,平均值为2.70%;TiO2含量为0.24%~0.42%,平均值为0.34%。
G1类(花岗闪长岩)SiO2含量为67.42%~67.62%,平均值为67.52%,也为酸性岩石;Na2O含量为3.1%~3.3%,平均值为3.2%,K2O含量为1.89%~2.91%,平均2.4%,Na2O/K2O值为1.13~1.64,岩石总体富钠,但钾含量明显变高;CaO含量略高,为4.03%~ 4.21%,平均值为4.12%;Al2O3含量中等偏低,为13.37%~ 15.09%,平均值为14.23%;MgO含量为1.57%~1.95%,平均值为1.76%,Mg#=0.47;TFeO含量为3.22%~4.01%,平均值为3.61%;TiO2含量为0.51%~0.52%,平均值为0.52%。
总体而言,T1G1类表现出较富硅、富钠、略富钙的特点,且其整体在Al2O3含量方面与典型TTG高铝(Al2O3大于15%)的特征相符[31-36],其Al2O3平均值为15.22%,但不同类型的岩石还存在差异,T1类岩石Al2O3平均值为15.88%,相对富铝,而G1类岩石Al2O3平均值为14.23%,相对贫铝;此外,该岩套中的G1类岩石比T1类岩石更富钾。这些特征可能暗示,该岩系在源区残留相组成和源岩部分熔融程度上并不均一。
钾质的QM类岩石的SiO2含量为62.74%~68.65%,平均值为65.27%;Na2O含量为0.91%~2.74%,平均值为1.65%,K2O含量为2.74%~4.10%,平均值为3.49%,Na2O/K2O值为0.22~0.81,平均值为0.50,岩石明显富钾;CaO含量较低,为0.75%~2.65%,平均值为1.88%;Al2O3含量变化较大,为14.20%~17.89%,平均值为15.62%;MgO含量为1.35%~2.80%,平均值为2.29%,Mg#平均值为0.43;较富全铁,TFeO含量为3.81%~6.11%,平均值为5.26%;TiO2含量为0.54%~0.78%,平均值为0.69%。对比钠质的T1G1,该类型岩石表现出明显的富钾、贫钙、富铁特征。
在TAS图解(图 5)中,该套弧花岗岩主体落入花岗闪长岩区,岩石均为亚碱性系列;通过CIPW标准矿物计算,所有岩石的石英均大于10%,在TTG岩套CIPW标准矿物An-Ab-Or图解(图 6)中,T1类岩石主体落入英云闪长岩区, G1类岩石则落入花岗闪长岩区,而QM类岩石主体落入石英二长岩区;在CIPW标准矿物的Q-Ab-Or和K-Na-Ca图解(图 7)中,T1G1整体遵循奥长花岗岩演化趋势(Td或Tdj),向富钠的方向演化,而QM整体显示出钙碱性演化趋势(CA),向富钾的方向演化;在TFeO/MgO-SiO2图解(图 8-a)中,所有岩石整体落入钙碱系列区域,在FAM(图 8-b)图解中,岩石也均落在钙碱系列区域;SiO2-(K2O+Na2O-CaO)图解(图 9-a)中,T1G1整体落入C区,整体为钙性(Peacock碱-钙指数),而QM整体落入CA-AC区,整体为钙碱性-碱钙性;在SiO2-K2O图解(图 9-b)中,T1G1主体落入中钾钙碱性系列(MKCA)区,而QM整体落入高钾钙碱性系列(HKCA)。
![]() 图 6 大红山南弧花岗岩An-Ab-Or图解[37]T1—英云闪长岩;T2—奥长花岗岩;G1—花岗闪长岩;G2—花岗岩(狭义);QM—石英二长岩Figure 6. The An-Ab-Or diagram of arc granite in the south of Dahong Mountain
图 6 大红山南弧花岗岩An-Ab-Or图解[37]T1—英云闪长岩;T2—奥长花岗岩;G1—花岗闪长岩;G2—花岗岩(狭义);QM—石英二长岩Figure 6. The An-Ab-Or diagram of arc granite in the south of Dahong Mountain综上可以看出,钠质的T1G1和钾质的QM类岩石具有不同的属性,属于不同的系列,并遵循不同的演化趋势,反映二者可能具有不同的成因。
稀土元素特征方面,钠质T1G1中的T1类岩石稀土元素总量(∑REE)较低,∑REE =58.26×10-6~ 96.89×10-6,平均值为78.40×10-6;LREE/HREE=5.18~8.35,平均值为7.19,(La/Yb)N=5.77~10.29,平均值为8.03,轻、重稀土元素分馏十分明显,相对富集轻稀土元素(LREE),亏损重稀土元素(HREE),在稀土元素配分图(图 10-a)上总体表现为向右陡倾形态;(La/Sm)N值为2.85~3.52,平均值为3.19,(Gd/Yb)N值为1.47~2.11,平均值为1.71,轻稀土元素较重稀土元素分馏强;δEu值为0.86~1.34,平均值为1.03,以弱负Eu异常或正Eu异常为特征,反映源区残留相中基本不含(或含少量)斜长石;其Y(Y=11.85×10-6~15.44×10-6,小于20×10-6)、Yb(Yb=1.07×10-6~1.72×10-6,小于2×10-6)含量较低,反映源区残留相中含有石榴子石;配分曲线后半段相对平坦,中稀土元素(MREE)与重稀土元素(HREE,狭义)分馏不明显,反映源区残留相中含有角闪石。
G1类岩石的稀土元素总量也较低,∑REE =62.13×10-6~98.59×10-6,平均值为80.36×10-6;LREE/HREE=4.18~7.14,平均值为5.66,(La/Yb)N=4.41~7.91,平均值为5.91,轻、重稀土元素分馏明显,但程度较T1类岩石弱,相对富集轻稀土元素,亏损重稀土元素,在稀土元素配分图(图 10-a)上总体虽表现为右倾形态,但明显比T1类平缓;(La/Sm)N值为2.82~3.07,平均值为2.95,(Gd/Yb)N值为1.28~1.60,平均值为1.44,轻稀土元素较重稀土元素分馏强;δEu值为0.75~1.09,平均值为0.92,总体以弱负Eu异常为特征,反映源区残留相中含少量斜长石;其Y(Y=17.28×10-6~18.79×10-6,小于20×10-6)、Yb(Yb=1.79×10-6~1.84×10-6,小于2×10-6)含量较低,反映源区残留相中含石榴子石;配分曲线后半段相对平坦,中稀土元素与重稀土元素分馏不明显,反映源区残留相中含有角闪石。
钾质的QM类岩石的稀土元素总量明显较高,∑REE=146.57×10-6~206.75×10-6,平均值为175.92×10-6;LREE/HREE=7.42~8.51,平均值为7.87,(La/Yb)N=7.38~10.40,平均值为8.46,轻、重稀土元素分馏十分明显,相对富集轻稀土元素,贫重稀土元素(HREE,广义),在稀土元素配分图(图 10-a)上总体表现为向右陡倾形态;(La/Sm)N值为3.41~3.51,平均值为3.46,(Gd/Yb)N值为1.46~1.95,平均值为1.61,轻稀土元素分馏程度较重稀土元素强;δEu值为0.56~0.66,平均值为0.62,以明显的负Eu异常特征,反映源区残留相中多数斜长石能稳定存在;其Y(Y=21.44×10-6~33.22×10-6,大于20×10-6)、Yb(Yb=2.01×10-6~3.54×10-6,大于2×10-6)含量较高,反映源区残留相中不含石榴子石;配分曲线后半段相对平坦,中稀土元素与重稀土元素(狭义)分馏不明显,反映源区残留相中含有角闪石。
对比上述岩石的稀土元素含量特征可以发现,钠质T1G1的稀土元素总量较低,以弱的负Eu异常或正Eu异常为特征,且HREE含量较低,这其中T1类岩石整体以弱负或明显正的Eu异常为特征,G1类岩石则以弱的负Eu异常为特征。钾质的QM具有明显较高的稀土元素总量,并以明显的负Eu异常区别于前两类钠质系列岩石,且其HREE含量总体较高。进一步说明,钠质T1G1和钾质QM的源岩成分和源区残留相组成不同,它们来源于源岩在不同温压条件下的不同程度部分熔融。此外,钠质的T1和G1类岩石尽管可能具有相似的源岩成分,但是二者的残留相存在区别,说明它们经历的温压条件有差异,且部分熔融程度也有区别。
在微量元素原始地幔标准化蛛网图(图 10-b)中,该套弧花岗岩总体表现为富集大离子亲石元素(LILEs),亏损高场强元素(HFSEs),配分曲线整体右倾,并表现出作为岛弧花岗岩重要标志的“TNT”异常(Nb、Ta、Ti亏损)[45-47]。其中,钠质T1G1和钾质QM岩石还表现出明显不同的特征:钠质T1G1各元素的含量总体偏低,表现为其曲线整体在钾质QM的下方;而钾质QM元素含量总体较高,曲线位于钠质T1G1上方,此外,还表现出明显且相对一致的Th、La、Nd正异常和Ba、Sr、P负异常。这也从另一个角度说明,钠质T1G1和钾质QM可能具有截然不同的成因模式。
5.2 同位素测年结果
本次针对这套弧花岗岩中的英云闪长岩(D6045Rz-1)、花岗闪长岩(D6021Rz-1)及石英二长岩(D5021Rz-1)采集了3件同位素样品进行LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb测年(表 2)。
表 2 样品LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Th-Pb测年分析结果Table 2. The results of LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Th-Pb dating analysis of samples测点号 元素含量/10-6 Th/U 同位素比值及误差 表面年龄及误差/Ma Pb* Th U 207Pb/206Pb 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ 207Pb/206Pb 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ D6021Rz-1号样品 1 351 610 1291 0.47 0.1127 0.0010 3.788 0.054 0.2438 0.0026 1843 15 1590 22 1406 15 2 171 575 1706 0.34 0.0830 0.0013 1.046 0.022 0.0915 0.0015 1269 30 727 15 564 10 3 111 309 413 0.75 0.0973 0.0012 3.026 0.052 0.2256 0.0026 1573 23 1414 24 1311 15 4 86 484 1178 0.41 0.0723 0.0010 0.6664 0.0136 0.0669 0.0011 994 28 519 11 417 7 5 48 204 313 0.65 0.3097 0.0049 4.018 0.079 0.0941 0.0014 3519 25 1638 32 580 9 6 72 338 835 0.40 0.1031 0.0015 1.033 0.019 0.0726 0.0008 1681 27 720 13 452 5 7 80 321 837 0.38 0.0703 0.0013 0.8911 0.0178 0.0919 0.0014 937 38 647 13 567 9 8 261 167 1887 0.09 0.1229 0.0017 2.049 0.058 0.1209 0.0030 1999 24 1132 32 736 18 9 206 1109 1193 0.93 0.1553 0.0037 1.761 0.053 0.0822 0.0022 2406 40 1031 31 509 14 10 101 213 856 0.25 0.0797 0.0011 1.225 0.020 0.1115 0.0019 1190 26 812 13 681 11 11 194 425 760 0.56 0.1030 0.0010 3.215 0.056 0.2264 0.0034 1679 18 1461 26 1316 20 12 37 142 432 0.33 0.1067 0.0033 1.082 0.034 0.0735 0.0013 1744 56 744 23 457 8 13 173 1180 1931 0.61 0.1102 0.0028 1.120 0.029 0.0737 0.0008 1803 46 763 20 458 5 14 61 309 742 0.42 0.1011 0.0025 1.006 0.029 0.0722 0.0009 1645 46 707 20 449 6 15 399 1290 1925 0.67 0.0824 0.0007 2.081 0.030 0.1832 0.0022 1255 18 1143 17 1084 13 16 115 178 603 0.30 0.0936 0.0009 2.340 0.039 0.1812 0.0025 1501 19 1224 21 1074 15 17 154 340 587 0.58 0.1028 0.0011 3.236 0.049 0.2283 0.0024 1675 19 1466 22 1325 14 18 352 844 2436 0.35 0.1085 0.0013 1.923 0.034 0.1286 0.0019 1774 21 1089 19 780 12 19 39 210 548 0.38 0.0729 0.0023 0.6772 0.0245 0.0674 0.0017 1011 65 525 19 420 10 20 81 108 363 0.30 0.1272 0.0019 3.510 0.064 0.2001 0.0027 2060 26 1530 28 1176 16 21 157 241 830 0.29 0.0866 0.0007 2.196 0.033 0.1838 0.0021 1353 16 1180 18 1088 13 22 64 136 321 0.42 0.0945 0.0017 2.367 0.061 0.1817 0.0022 1518 34 1233 32 1076 13 23 29 97 468 0.21 0.0569 0.0013 0.4965 0.0125 0.0633 0.0010 488 51 409 10 396 6 24 47 492 605 0.81 0.0726 0.0019 0.6693 0.0218 0.0669 0.0015 1001 53 520 17 418 9 25 117 417 1667 0.25 0.0711 0.0009 0.6531 0.0106 0.0666 0.0007 960 27 510 8 416 4 26 181 413 620 0.67 0.1030 0.0013 3.670 0.072 0.2583 0.0041 1680 23 1565 31 1481 24 27 162 207 665 0.31 0.1294 0.0012 3.970 0.058 0.2226 0.0025 2089 16 1628 24 1295 15 28 69 528 856 0.62 0.0768 0.0015 0.7166 0.0168 0.0677 0.0009 1115 39 549 13 422 6 29 62 307 811 0.38 0.0927 0.0035 0.9002 0.0357 0.0704 0.0008 1481 72 652 26 439 5 30 219 1699 2721 0.62 0.0853 0.0014 0.8119 0.0158 0.0691 0.0006 1322 32 604 12 430 4 D5021Rz-1号样品 1 25 151 416 0.36 0.0688 0.0022 0.5449 0.0172 0.0574 0.0008 894 65 442 14 360 5 2 29 162 349 0.46 0.1664 0.0043 1.531 0.042 0.0667 0.0012 2522 43 943 26 416 8 3 24 234 355 0.66 0.1139 0.0038 0.9037 0.0236 0.0575 0.0017 1863 60 654 17 361 10 4 57 505 915 0.55 0.0601 0.0025 0.4808 0.0208 0.0581 0.0010 606 89 399 17 364 6 5 24 132 392 0.34 0.0797 0.0022 0.6351 0.0188 0.0578 0.0008 1191 56 499 15 362 5 6 27 230 419 0.55 0.0645 0.0033 0.5148 0.0250 0.0579 0.0016 757 108 422 20 363 10 7 78 337 1301 0.26 0.1499 0.0021 0.9623 0.0161 0.0466 0.0006 2345 24 684 11 293 4 8 65 153 445 0.34 0.1094 0.0017 1.893 0.035 0.1255 0.0016 1790 29 1079 20 762 10 9 46 173 748 0.23 0.0834 0.0018 0.6655 0.0151 0.0579 0.0009 1279 41 518 12 363 5 10 30 296 453 0.65 0.0751 0.0012 0.6001 0.0124 0.0580 0.0009 1070 32 477 10 363 6 11 57 526 813 0.65 0.1025 0.0017 0.8205 0.0180 0.0581 0.0008 1670 31 608 13 364 5 12 140 447 1672 0.27 0.1913 0.0026 1.517 0.030 0.0575 0.0013 2753 22 937 19 361 8 13 344 984 1998 0.49 0.1278 0.0016 2.474 0.038 0.1404 0.0023 2068 22 1264 20 847 14 14 24 199 355 0.56 0.0664 0.0017 0.5315 0.0145 0.0581 0.0008 819 53 433 12 364 5 15 34 236 528 0.45 0.0620 0.0019 0.4951 0.0160 0.0579 0.0008 675 65 408 13 363 5 16 153 220 1000 0.22 0.1184 0.0046 2.308 0.058 0.1414 0.0039 1932 69 1215 31 853 23 17 59 298 818 0.36 0.0690 0.0024 0.6514 0.0245 0.0685 0.0024 898 72 509 19 427 15 18 82 205 645 0.32 0.1549 0.0049 2.141 0.068 0.1002 0.0020 2401 54 1162 37 616 13 19 16 133 238 0.56 0.0986 0.0029 0.7842 0.0277 0.0577 0.0020 1597 54 588 21 362 12 20 25 124 316 0.39 0.1360 0.0032 1.184 0.034 0.0631 0.0010 2177 41 793 23 395 6 21 40 551 591 0.93 0.0596 0.0010 0.4812 0.0089 0.0586 0.0006 589 36 399 7 367 4 22 64 710 994 0.71 0.0582 0.0007 0.4656 0.0077 0.0580 0.0006 537 26 388 6 364 4 23 91 86 441 0.19 0.0820 0.0011 2.366 0.046 0.2092 0.0031 1245 26 1232 24 1225 18 24 32 342 333 1.03 0.0831 0.0037 0.6073 0.0345 0.0530 0.0016 1270 87 482 27 333 10 D6045Rz-1号样品 1 22 94 361 0.26 0.0564 0.0010 0.4716 0.0094 0.0606 0.0006 470 41 392 8 379 4 2 65 223 1093 0.20 0.0555 0.0007 0.4708 0.0078 0.0615 0.0007 432 28 392 7 385 4 3 41 184 686 0.27 0.0555 0.0016 0.4698 0.0140 0.0614 0.0007 433 63 391 12 384 5 4 83 122 1441 0.08 0.0579 0.0007 0.4851 0.0077 0.0608 0.0006 525 27 402 6 380 4 5 31 183 501 0.36 0.0552 0.0011 0.4635 0.0100 0.0609 0.0007 420 43 387 8 381 5 6 34 166 580 0.29 0.0559 0.0009 0.4701 0.0092 0.0610 0.0006 450 36 391 8 381 4 7 30 158 500 0.32 0.0554 0.0010 0.4662 0.0098 0.0610 0.0007 429 41 389 8 382 4 8 42 73 724 0.10 0.0556 0.0008 0.4676 0.0089 0.0610 0.0008 437 34 390 7 382 5 9 128 103 2222 0.05 0.0549 0.0006 0.4694 0.0074 0.0620 0.0008 409 24 391 6 388 5 10 25 187 393 0.48 0.0549 0.0013 0.4668 0.0123 0.0616 0.0009 409 53 389 10 386 6 11 46 93 793 0.12 0.0558 0.0009 0.4680 0.0103 0.0609 0.0010 443 38 390 9 381 6 12 43 128 745 0.17 0.0555 0.0010 0.4656 0.0109 0.0608 0.0010 434 39 388 9 381 6 13 43 200 705 0.28 0.0561 0.0010 0.4731 0.0103 0.0611 0.0010 458 41 393 9 382 6 14 30 207 482 0.43 0.0557 0.0011 0.4697 0.0101 0.0612 0.0007 440 45 391 8 383 4 15 27 31 479 0.06 0.0557 0.0010 0.4697 0.0102 0.0611 0.0008 442 40 391 9 382 5 16 51 242 803 0.30 0.0676 0.0021 0.5890 0.0189 0.0632 0.0008 855 65 470 15 395 5 17 56 71 500 0.14 0.0828 0.0016 1.278 0.027 0.1119 0.0018 1264 38 836 17 684 11 18 41 78 771 0.10 0.0539 0.0010 0.4167 0.0086 0.0561 0.0005 366 41 354 7 352 3 19 28 138 450 0.31 0.0547 0.0010 0.4679 0.0092 0.0620 0.0007 401 41 390 8 388 4 20 45 91 777 0.12 0.0548 0.0010 0.4641 0.0090 0.0614 0.0006 404 40 387 7 384 4 21 42 58 721 0.08 0.0549 0.0009 0.4677 0.0084 0.0617 0.0006 409 35 390 7 386 3 22 40 110 675 0.16 0.0563 0.0009 0.4814 0.0088 0.0620 0.0006 465 35 399 7 388 3 23 107 202 1691 0.12 0.0641 0.0010 0.5800 0.0101 0.0656 0.0007 746 32 464 8 410 4 24 41 84 782 0.11 0.0550 0.0012 0.4226 0.0093 0.0557 0.0006 412 50 358 8 350 4 在阴极发光图像(图 11-a、b)上,花岗闪长岩与石英二长岩的锆石多呈次圆状-次棱角状,颗粒较小,粒径多在40~60 μm之间,晶形多不完整且残碎,不少锆石内部可见振荡环带发育,显示岩浆锆石的特征,且多数锆石内未见明显的变质增生、重结晶、熔蚀等变质锆石特征,但许多锆石颜色较深,反映锆石U、Th含量较高。而英云闪长岩的锆石(图 11-c)多呈柱状-短柱状,颗粒较大,粒径多大于100 μm,晶形整体较完整,部分锆石有残缺,多数锆石内部也可见清晰细密的振荡环带发育,为典型岩浆锆石的特征。多数锆石内未见明显的变质增生、重结晶、熔蚀等变质锆石特征,个别锆石内部可见残留的继承锆石晶核。
本次在花岗闪长岩和石英二长岩的锆石中分别测得30个测点(D6021Rz-1)和24个测点(D5021Rz-1),测点的Th/U值多大于0.4,平均值分别为0.604(D6021Rz-1)和0.607(D5021Rz-1),为岩浆锆石的特征。在谐和图(图 12)上,多数锆石测点位于谐和线之下,说明锆石内发生过明显的铅丢失,而造成锆石内铅丢失的原因可能主要与锆石内U、Th含量较高导致蜕晶质化有关[48]。2类样品中少部分测点分布较散,但多数测点沿不一致线分布,其与谐和线的交点年龄分别为399±3 Ma(D6017Rz-1)和364.2±2.2 Ma(D5021Rz-1),可近似代表二者的形成年龄。
在英云闪长岩(D6045Rz-1)中共测试24个测点,测点的Th/U值多大于0.1,部分大于0.4,平均值为0.23,为岩浆锆石的特征。在谐和图(图 13)上,多数锆石测点位于谐和线附近略偏下的位置,说明锆石内发生过较弱的铅丢失,其反映的年龄信息精度较高。其中谐和度较高的测点组成的不一致线与谐和线的交点年龄为387.0±2.2 Ma,可近似代表锆石的结晶年龄。
由前文可知,研究区该套弧花岗岩侵入于志留系小红山岩组中,其中可见小红山岩组捕虏体,且被周围石炭纪弧侵入体侵入,说明其形成时代可能介于中志留世—早石炭世之间。而在野外的空间产出状态上,该套弧花岗岩中的英云闪长岩与花岗闪长岩显示紧密共生关系,岩石地球化学特征上存在“亲缘性”,说明二者的形成时代相近,这一点从二者获得较相近的锆石年龄信息可以印证。而花岗闪长岩(399±3 Ma)年龄略大于英云闪长岩(387.0±2.2 Ma)的原因,可能与其锆石内发生过明显的铅丢失而造成的年龄误差有关。因此综合认为,在锆石封闭体系相对完整的英云闪长岩中获得的年龄信息相对可靠,可代表这套弧花岗岩系中T1G1组合的形成时代,为中泥盆世。对于石英二长岩,空间产出状态上其呈共熔体的形式分别与花岗闪长岩类和英云闪长岩类紧密相伴产出,成因上其源自于TTG源岩在特殊条件下的部分熔融。因此综合认为,364.2±2.2 Ma的交点年龄信息大致反映其形成于晚泥盆世。
综上所述,笔者认为,研究区这套空间产出状态和内在成因上具有密切联系的弧花岗岩总体形成时代为中晚泥盆世。
6. 讨论
6.1 岩石成因
本次研究的这套中泥盆世弧花岗岩中的钠质T1G1和钾质QM类岩石在时空上混杂共生,在野外露头尺度上二者几乎不存在区别,但在岩石学特征及岩石地球化学特征方面,二者表现出明显的不同,说明这套弧花岗岩可能为同一(或类似)构造机制下,不同源岩在不同温压和水动力条件下,经过不同程度的部分熔融而成。
其中,钠质T1G1中的T1类岩石富Sr(241.0×10-6~347.4×10-6,平均值为303.22×10-6)、贫Y(11.85×10-6~15.44×10-6,平均值为13.617×10-6)、贫Yb(1.07×10-6~1.72×10-6,平均值为1.37×10-6),具中等较高的Al2O3含量(15.09%~16.61%,平均值为15.88%)和整体较高的Eu异常(δEu=0.86~1.34,平均值为1.03),主体符合张旗等[49-50]定义的埃达克(质)岩石,其对应的源区残留相组成为辉石+角闪石+石榴子石,属高压的角闪榴辉岩相;而G1类岩石贫Sr(210.1×10-6~238.9×10-6,平均值为224.53×10-6)、贫Y(17.28×10-6~18.79×10-6,平均值为18.03×10-6)、贫Yb(1.79×10-6~1.84×10-6,平均值为1.82×10-6),具有中等偏低的Al2O3含量(13.37%~15.09%,平均值为14.23%)和弱的负Eu异常(δEu为0.75~1.09,平均值为0.92),符合张旗等[49-50]定义的喜马拉雅型花岗岩,其对应的源区残留相组成为辉石+角闪石+石榴子石+斜长石,属中压的麻粒岩相(或石榴角闪岩相)。此外,T1类岩石的Na2O/K2O值为1.80~2.24,平均值为1.92,而G1类岩石Na2O/K2O值为1.13~1.64,平均值为1.39,但G1类岩石相对T1类岩石更富钾,说明相比于T1类岩石,G1类岩石的源岩部分熔融程度较低。
总体上,这套T1G1类岩石的地球化学特征与典型的TTG富铝(Al2O3>15%),HREE强烈亏损、轻重稀土元素分异明显且无明显负Eu异常的特征接近[31-35],但也不完全一致,其中存在相对高铝、高压型的T1类岩石和相对低铝、中压型的G1类岩石,且二者在部分熔融程度上存在区别,说明这套T1G1的源区可能跨越了不同的p-T范围。
关于TTG岩套的成因,前人提出过多种模式,目前认同度较高的有:来自变质到榴辉岩相或石榴角闪岩相的含水玄武质岩石的部分熔融[51-56]。考虑到该套T1G1尽管并不十分富镁,但其Mg#值不低(Mg#=0.41~0.47,平均值为0.45),且其在高镁闪长岩(HMA)-镁闪长岩(MA)的相关判别图解(图 14)中,主体显示镁闪长岩特征。因此,推测该T1G1可能来自达到石榴角闪岩相-榴辉岩相的俯冲洋壳板片在含水的条件下的部分熔融,由于其源区跨越了不同的p-T范围,形成了2种不同源区残留相组成、不同熔融程度下的产物,即高压高熔的T1和相对低压低熔的G1。之后熔浆在向上运移过程中通过俯冲板片上覆地幔楔,并与那里的富镁地幔橄榄岩进行一定程度的交代作用[32, 57],发生物质交换,导致该T1G1具有较明显的MA特征。
![]() 图 14 大红山南弧花岗岩MA的SiO2-MgO(a)和TFeO/MgO-SiO2(b)判别图[57]a:PQ线为HMA/MA边界,RS为MA/非MA边界;b:直线为Miyashiro的CA与TH分界线(上为CA,下为TH),双点划线为Arculus低Fe(LF-CA)与中Fe界线;HMA—高镁安山岩/闪长岩类;MA—镁安山岩/闪长岩类;LF-CA—低铁钙碱趋势Figure 14. The SiO2-MgO (a) and TFeO/MgO-SiO2 (b) discrimination diagrams of MA of arc granite in the south of Dahong Mountai
图 14 大红山南弧花岗岩MA的SiO2-MgO(a)和TFeO/MgO-SiO2(b)判别图[57]a:PQ线为HMA/MA边界,RS为MA/非MA边界;b:直线为Miyashiro的CA与TH分界线(上为CA,下为TH),双点划线为Arculus低Fe(LF-CA)与中Fe界线;HMA—高镁安山岩/闪长岩类;MA—镁安山岩/闪长岩类;LF-CA—低铁钙碱趋势Figure 14. The SiO2-MgO (a) and TFeO/MgO-SiO2 (b) discrimination diagrams of MA of arc granite in the south of Dahong Mountai对于该弧花岗岩中的钾质QM,其贫Sr(66.27×10-6~175.7×10-6,平均值为121.64×10-6)、富Y(21.44×10-6~33.22×10-6,平均值为28.51×10-6)、富Yb(2.01×10-6~3.54×10-6,平均值为2.95×10-6),具有中等含量且变化的Al2O3(14.20%~17.89%,平均值为15.62%)和明显的负Eu异常(δEu值为0.56~0.66,平均值为0.62),符合张旗等[49-50]定义的浙闽型花岗岩,其对应的源区残留相组成主要为斜长石+角闪石,属相对低压的斜长角闪岩相。此外,该类岩石还具有富钾(Na2O/K2O值为0.22~0.81,平均值为0.50)、富轻稀土元素(131.15×10-6~183.61×10-6,平均值为155.99×10-6)、明显的正Th异常等壳源属性。对于TTG岩套中QM岩浆的来源,许多学者认为其源于TTG源岩的局部熔融[37, 58-61]。但是本文中的QM类岩石较前述T1G1组合更富镁,MgO含量为1.35%~2.80%,平均值为2.30%(T1G1平均值为1.40%),高镁闪长岩-镁闪长岩相关判别图解(图 15)显示,其也具备镁闪长岩特质。同时,该类岩石的SiO2含量为62.74%~68.65%,平均值为65.27%(T1G1平均值为67.96%)。可以看出,单纯的TTG源岩部分熔融似乎难以达到。
邓晋福等[61, 64]认为,俯冲带岩浆的形成是多源的,或来源于俯冲洋壳的脱水熔融,或来源于洋壳上覆地幔橄榄岩的局部熔融,或来源于地幔楔上面地壳的局部熔融,亦或是上述2种或3种岩浆的混合或反应。因此,综合以上信息推断,本次研究的QM类岩石可能是下地壳TTG源岩在低压低熔条件下形成的富钾融浆,与来自地幔的富镁玄武质岩浆发生一定程度混合或反应的产物。
6.2 构造环境
在(Yb+Ta)-Rb、(Y+Nb)-Rb图解(图 15)中,中晚泥盆世花岗岩总体落在弧花岗岩范围,为一套具备MA性质的T1G1+QM弧侵入体。Maniar等[65]认为,TTG岩石组合既可以形成于岛弧环境,也可以发育于大陆边缘弧;不同的是,岛弧组合中除TTG外,还有大量的石英二长岩(QM)和少量的二长花岗岩,而大陆边缘弧组合中除有TTG外,还有较多的二长花岗岩和少量的石英二长岩(QM)。此外,再考虑到该弧花岗岩中T1G1普遍并均一的MA特征,说明熔浆与板片上覆地幔楔的物质交换较充分,而岛弧高角度俯冲机制下形成的较厚地幔楔恰好能为之提供有利的条件。由此认为,该套弧花岗岩可能形成于岛弧环境。
同时,该套弧花岗岩以钙性-钙碱性-碱钙性岩石为主,并表现出明显富钾的QM端元,整体属于中钾钙碱性(MKCA)-高钾钙碱性(HKCA)系列,为一套高成熟度的岛弧侵入体,为区域上奥陶纪开始的陆缘岛弧发育到成熟阶段的产物。
6.3 北山北带晚古生代洋-陆转换进程的新启示
通过近年(2014—2018年)在北山北带地区陆续开展的相关区调工作④~⑪,区域上逐渐达成共识,那就是从奥陶纪以来发育两阶段弧-盆体制。
其中,第一阶段为奥陶纪—泥盆纪,该弧-盆体制以咸水湖组(O1-2x)低成熟度岛弧火山岩建造、雀儿山群(SDQ)高成熟度岛弧火山-沉积建造(及相配套的弧侵入体)和相关弧盆建造(乌兰布拉格组(O3w)、圆包山组(S1b)、小红山岩组)为代表,有效记录了区域上陆缘岛弧从“幼年期”向“成熟期”演化发育,同时伴随弧后有限海盆不断扩张变深的弧盆演化早期进程。
第二阶段为石炭纪—早二叠世早期,该弧-盆体制以白山组北区(C1-2bN)弧火山岩建造(及配套弧侵入体)继承弧地体、白山组南区(C2bS)弧火山岩建造(及配套的弧侵入体)陆缘山弧地体和二者之间的红石山-百合山弧间洋盆地体(红石山-百合山蛇绿混杂岩带及绿条山组弧盆边缘沉积建造及配套弧侵入体)为代表。进一步,由相关资料④-⑪可知,红石山-百合山蛇绿岩带北侧的继承弧地体是继承奥陶纪—泥盆纪陆缘弧-盆系基底发育而来的,而南侧的陆缘山弧地体则是在红石山-百合山弧间洋盆向南侧马鬃山陆块北缘俯冲消减机制下形成的。但是,区域上古生代以来的这两阶段弧-盆体制的时空演化关系,即奥陶纪—泥盆纪的弧-盆体制是如何演化转变至石炭纪—早二叠世早期的弧-盆体制,一直是一个悬而未决的问题。
区域上,以往研究发现的奥陶纪—泥盆纪陆缘弧-盆演化记录,均位于红石山-百合山蛇绿构造混杂岩带北侧。而本次研究的这套弧花岗岩,位于区域上红石山-百合山蛇绿构造混杂岩带南侧,是该区泥盆纪弧记录的首次发现。此外,研究区蛇绿混杂岩带南侧还存在一套标志早期弧后有限海盆扩张发展至最大程度的志留系小红山岩组含BIF基性火山-复理石沉积建造。随之而来的问题是,作为北山北带早期弧-盆演化记录的相关地质体,为何会存在于晚期蛇绿混杂岩带的两侧?此外,作为同一构造背景,但不同构造阶段的早期弧-盆体制的产物,奥陶纪—泥盆纪地质体以区域上的蛇绿混杂岩带为界,南北表现出截然不同的变质变形面貌:以北的奥陶纪—泥盆纪地质体总体以低级变质作用为特征(最高达绿片岩相变质,多数表现为埋深变质),且具有较浅层次的构造变形特征(以透入性的糜棱面理、片理、板劈理、层理交织共存为主要特征,不发育线理构造,新生面理置换原生面理不均一、不彻底);而以南的小红山岩组和本文弧花岗岩整体经历了高绿片岩-低角闪岩相变质,具有较深层次的构造变形特征(发育的糜棱面理、固态流变褶皱、拉伸线理、粘滞型石香肠和同构造分泌脉一起共同组成一个新生的变质固态流变构造群落)。造成这种差异的机制又是什么?欲回答上述问题,需要对区域上呈近东西向,横贯北山北带的红石山-百合山蛇绿构造混杂岩带有深入了解。
6.3.1 红石山-百合山-蛇绿构造混杂岩带构造属性
从前人[3, 5, 14, 16, 25-27, 66-69]和近年在该地区陆续开展的相关区调项目①⑧⑨⑪对红石山-百合山蛇绿混杂岩带的调查研究可知:①其蛇绿岩组合属俯冲作用有关的SSZ型(俯冲带上盘型)[70-72];②蛇绿岩的活动时代可能从早石炭世已开始,并一直持续到早二叠世早期(347~280 Ma);③该蛇绿混杂岩带代表了奥陶纪—泥盆纪岛弧裂离发育而来的石炭纪(延续到早二叠世早期)弧间盆地残迹,作为一个三级构造单元的边界,其分割了石炭纪在弧盆两侧不同基底相继发育的2个弧,即北侧继承岛弧和南侧陆缘山弧。
6.3.2 北山北带古生代弧-盆演化模式
综上所述,笔者对北山北带古生代以来的洋-陆演化进程提出了初步的设想。北山北带的洋-陆转换过程可能始于奥陶纪(或更早)北侧主洋(古亚洲洋?)对南侧马鬃山地块北缘俯冲消减背景下形成的陆缘岛弧“幼年期”演化(以咸水湖组为代表,图 16-a),伴随俯冲作用的进行,弧开始向洋侧迁移,导致弧后产生张性营力,在此背景下区域上从晚奥陶世开始进入弧岩浆活动的“匮乏期”或“平静期”,拉开了弧后有限海盆的演化序幕,相继产出以乌兰布拉格组(O1w)、圆包山组(S1y)为代表的弧后盆地沉积组合,这一过程一直持续到中志留世末期,以象征弧后海盆拉张至最大程度的小红山岩组(S2x.)变基性火山岩(MORB-LIKE)+BIF+复理石建造的产出为节点,宣告这一阶段区域上早期有限海盆演化的结束。从晚志留世开始,以雀儿山区弧火山-沉积建造及相配套的弧侵入体(如本文的弧花岗岩)为代表,岛弧又恢复了生命,开始其“成熟期”演化发育的阶段(图 16-b)。上述弧-盆演化体制于泥盆纪末期走向终点。
石炭纪初期,伴随早期陆缘岛弧的南北向裂离(图 16-c),拉开了区域上新一轮的弧-盆演化序幕。在弧间盆地快速扩张发育过程中,漂移向北侧早期弧-盆地质体继续接受北侧主洋向南的俯冲消减,形成区域上混杂带以北的继承岛弧(图 16-c);以残留弧形式停滞于南侧马鬃山地块北缘的早期弧(以本文弧花岗岩为代表)-盆地质体则接受了早石炭世晚期,百合山弧间洋盆向南的俯冲消减,形成区域上混杂岩带以南的陆缘山弧(图 16-d)。在上述过程中,作为北侧继承弧基底的早期弧-盆地质体,由于其处于弧后缘,远离北侧主洋俯冲前峰,因而其俯冲消减过程中仅发生了浅层次的变质变形;与之不同,作为南侧陆缘山弧基底的早期弧-盆地质体,处于陆缘山弧的俯冲前缘,以“弧根”的形式存在,直接遭受百合山弧间洋盆向南的俯冲消减作用,因而其发生了深层次的变形变质,本文弧花岗岩组合中第一期构韧性构造行迹就是最好的例证。
上述弧-盆体制一直持续到早二叠世早期,伴随百合山弧间洋盆的俯冲闭合,开启了区域上二叠纪以来的碰撞-造山演化进程。在此过程中,由于陆内块体之间相互的挤压、碰撞等作用,造就了本次研究的弧花岗岩中叠加于早期变形面理之上的紧闭褶皱。
7. 结论
(1) 北山北带红石山-百合山-额勒根乌兰乌拉蛇绿构造混杂岩带南侧首次发现的一套弧花岗岩为T1G1+QM,具备MA(镁闪长岩)特质,以钙碱系列(贫铁)的钙-钙碱性-碱钙性岩石为主,整体属于中钾钙碱性(MKCA)-高钾钙碱性(HKCA)系列;LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb测年结果显示其形成于中晚泥盆世。综合说明,其为区域上奥陶纪开始的陆缘岛弧发育到相对成熟阶段的产物。
(2) 结合区域上整体的时空配置及该弧花岗岩组合的变形变质特征,认为其可能为早期陆缘岛弧在石炭纪开始的岛弧裂离-弧间盆地扩张过程中残留于南侧马鬃山地块北缘的残留弧代表。该认识的提出,为北山北带地区古生代弧盆演化体制提供了新的证据和线索。
致谢: 中国地质调查局应用地质研究中心熊德清高级工程师、西华大学刘建康副教授、中国地质科学院探矿工艺研究所李洪梁工程师在研究工作中给予了帮助,西南石油大学李旭德硕士生、西南交通大学肖克锋硕士生协助完成了野外调查工作,审稿专家在文章修改过程中提出了宝贵意见,在此一并表示感谢。 -
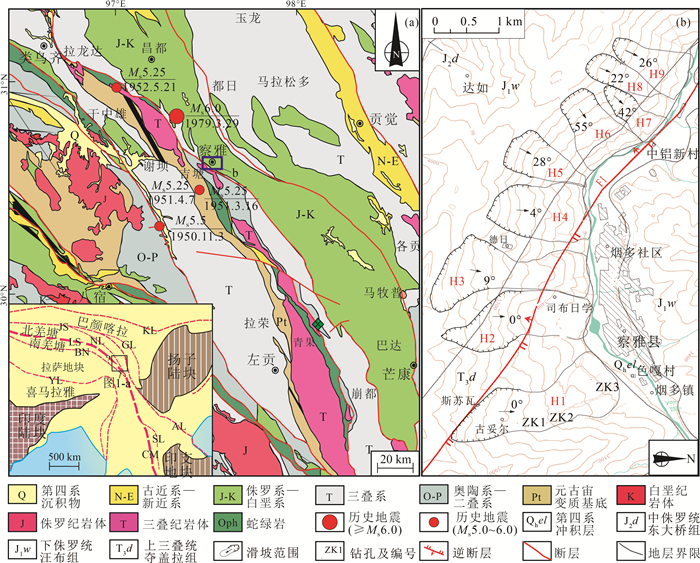
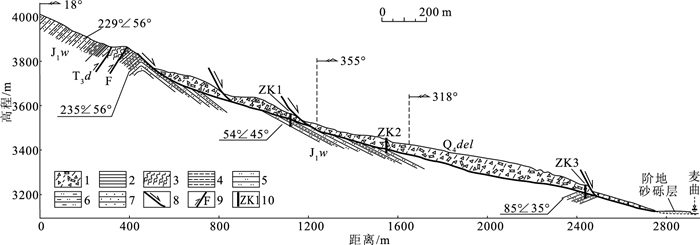
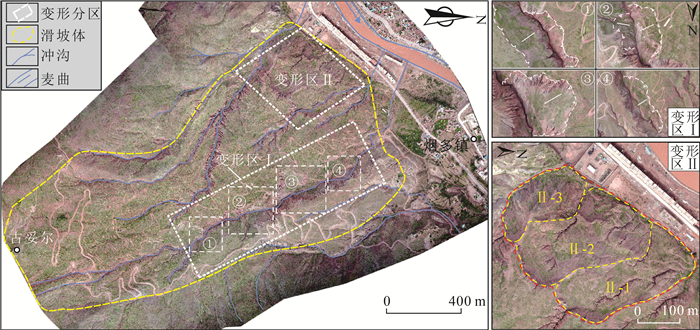
图 1 西藏昌都地区地质地震简图(a,据参考文献[20]修改)及研究区滑坡分布图(b) (历史地震数据据参考文献[21-22])
KL—阿尼玛卿-昆仑结合带;GL—甘孜-理塘结合带;JS—金沙江结合带;AL—哀牢山结合带;NL—北澜沧江结合带;SL—南澜沧江结合带;LS—龙木错-双湖结合带;CM—昌宁-孟连结合带;BN—班公湖-怒江结合带;YL—印度河-雅鲁藏布江结合带
Figure 1. Geological and history earthquake distribution of Changdu (a) and landslide distribution of the study area (b)
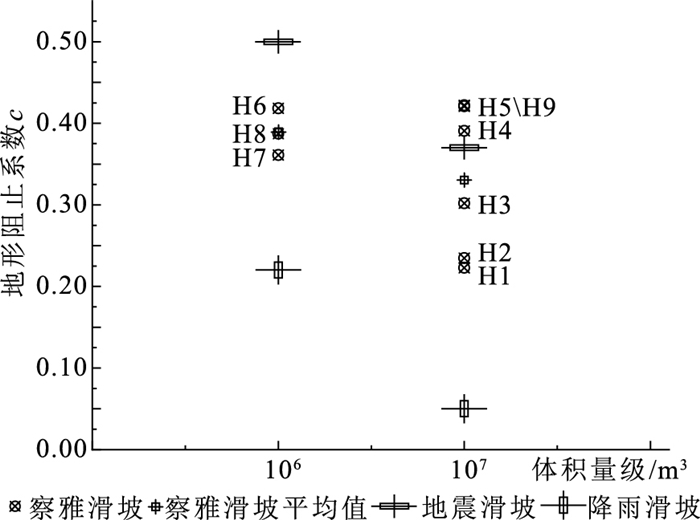
图 9 地震与非地震滑坡体积与地形阻止系数关系[18]及与察雅滑坡的对比
Figure 9. The volume and topographic blocking coefficient relation between seismic and non-seismic landslides, and the comparison with Chaya landslides
表 1 察雅县城滑坡群各滑坡基本特征
Table 1 Basic characteristics of the landslides in Chaya County
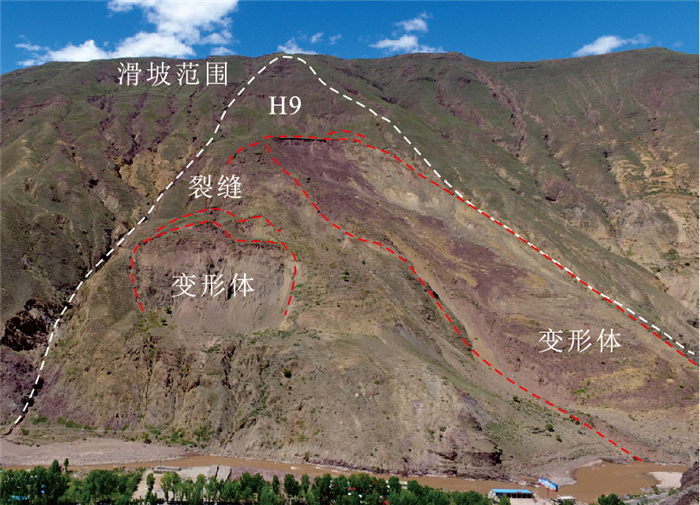
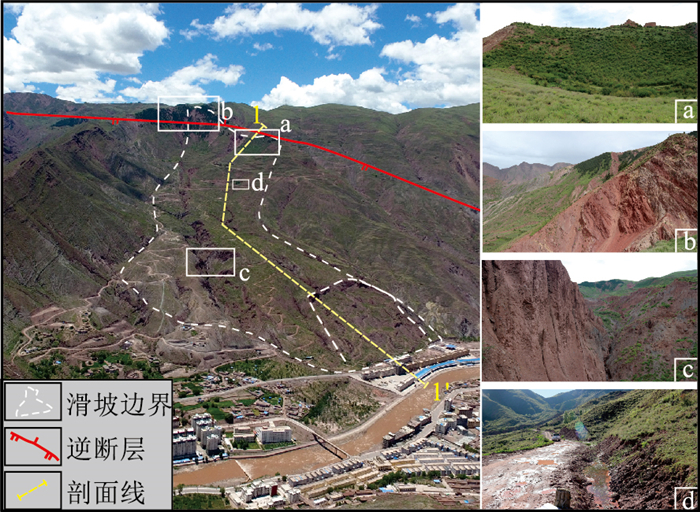
编号 滑坡名称 滑动方向 最大滑移距离/m 前后缘最大高差/m 质心高度/m 长×宽/m 长宽比 堆积体平均厚度/m 体积/m3 平均坡度 后缘距分水岭距离/m 地形阻止系数 H1 古妥尔滑坡 0° 2200 880 490 2200×500 3.7 30 2300×104 9° 280 0.22 H2 司布日学滑坡 0° 2300 960 310 1200×650 1.8 35 2200×104 8° 310 0.23 H3 德日东滑坡 9° 2400 1040 550 2100×500 4.2 40 3360×104 25° 250 0.30 H4 德日西滑坡 4° 1600 820 430 1070×850 1.3 35 2400×104 31° 610 0.39 H5 察雅县中学南侧滑坡 28° 1340 760 370 1000×500 2.0 35 1130×104 30° 150 0.42 H6 中铝新村南东侧滑坡 55° 1170 680 380 630×690 0.9 20 600×104 28° 370 0.42 H7 中铝新村南西侧1#滑坡 42° 1070 560 320 900×325 2.8 40 880×104 29° 630 0.36 H8 中铝新村南西侧2#滑坡 22° 1200 660 390 850×375 2.3 30 620×104 23° 120 0.39 H9 中铝新村南西侧3#滑坡 26° 1300 720 330 1100×510 2.2 40 1900×104 29° 250 0.42 表 2 研究区不同降雨频率下的年最大日降雨量估算结果
Table 2 Calculated results of maximum daily rainfall in a year at different frequencies
P/% KP H24P/mm 1 1.436 55.14 2 1.374 52.76 10 1.212 46.54 表 3 模型物理力学参数
Table 3 Physical and mechanical parameters of the model
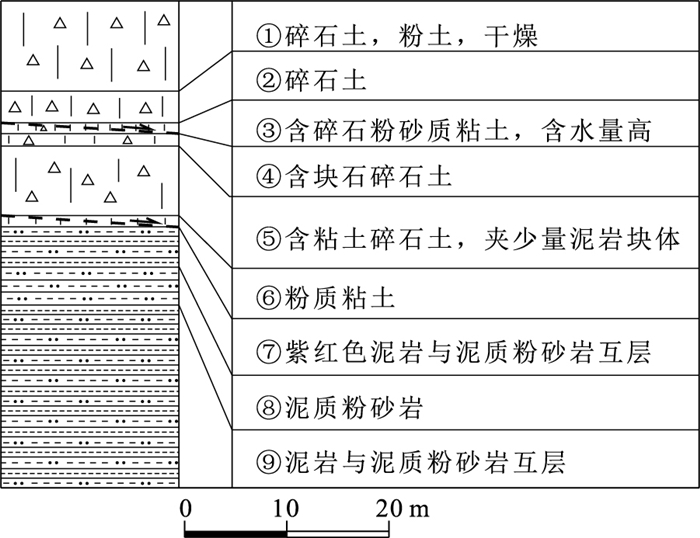
材料 天然容重/(kN·m-3) C/kPa φ/° 后部滑坡体 26.2 9.8 25.6 中前部滑坡体 25.8 10.3 25.2 前部滑坡体 25.5 10.5 24.6 基岩层(泥质粉砂岩) 24 16.2 8.5 表 4 古妥尔滑坡堆积体稳定性计算结果
Table 4 Calculation results of stability for Gutour landslide
滑坡体编号 L1 L2 L3 L4 L5 工况一 天然状态 1.939 1.722 1.109 1.18 1.101 工况二 10年一遇降雨 1.933 1.592 1.113 1.147 1.077 工况三 50年一遇降雨 1.915 1.575 1.104 1.066 1.032 工况四 100年一遇降雨 1.903 1.487 1.099 1.059 1.006 -
王思敬. 地球内外动力耦合作用与重大地质灾害的成因初探[J]. 工程地质学报, 2002, 10(2): 115-117. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2002.02.001 Scheidegger A E. Tectonic Predesign of Mass Movements, with Examples from the Chinese Himalaya[J]. Geomorphology, 1998, 26(1/2/3): 37-46. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0169555X98000506
Martel S J. Mechanics of Landslide Initiation as a Shear F racture Phenomenon[J]. Marine Geology, 2004, 203(3/4): 319-339. http://www.soest.hawaii.edu/martel/Martel.pubs.pdf/Martel_2004_Marine_Geo.pdf
居恢扬. 断裂构造对滑坡的控制意义[C]//滑坡文集: 第三集. 北京: 中国铁道出版社, 1982: 47-55. 吴玮江, 王念秦. 甘肃滑坡灾害[M]. 兰州: 兰州大学出版社, 2006: 82-87. Scheidegger A E, 艾南山. 武都地区的滑坡和泥石流[J]. 水土保持学报, 1987, 1(2): 19-27. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQS198702002.htm 张永双, 苏生瑞, 吴树仁, 等. 强震区断裂活动与大型滑坡关系研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2011, 30(增刊2): 3503-3513. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX2011S2020.htm 许强, 黄润秋. 5·12汶川大地震诱发大型崩滑灾害动力特征初探[J]. 工程地质学报, 2008, 16(6): 721-729. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2008.06.001 黄润秋, 李为乐. 5·12汶川大地震触发地质灾害的发育分布规律研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2008, 27(12): 2585-2592. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2008.12.028 杨为民, 黄晓, 张春山, 等. 白龙江流域坪定-化马断裂带滑坡特征及其形成演化[J]. 吉林大学学报: 地球科学版, 2014, 44(2): 574-583. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ201402017.htm 李晓, 李守定, 陈剑, 等. 地质灾害形成的内外动力耦合作用机制[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2008, 27(9): 1792-1806. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2008.09.006 吴树仁, 王涛, 石玲, 等. 2008汶川大地震极端滑坡事件初步研究[J]. 工程地质学报, 2010, 18(2): 145-159. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2010.02.001 邹谨敞, 邵顺妹. 海原地震滑坡及其分布特征探讨[J]. 内陆地震, 1996, (1): 1-6. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LLDZ601.000.htm 乔彦肖, 马中社, 吕凤军. 汶川地震地质灾害发育特点及动因机制分析[J]. 中国地质, 2009, 36(3): 736-741. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2009.03.020 邓龙胜, 范文. 宁夏海原8.5级地震诱发黄土滑坡的变形破坏特征及发育机理[J]. 灾害学, 2013, 28(3): 30-37. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-811X.2013.03.007 蒋瑶, 吴中海, 李家存, 等. 2010年玉树7.1级地震诱发滑坡特征及其地震地质意义[J]. 地质学报, 2014, 88(6): 1157-1176. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201406016.htm 殷跃平. 汶川八级地震滑坡特征分析[J]. 工程地质学报, 2009, 17(1): 29-38. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2009.01.004 樊晓一. 地震与非地震诱发滑坡的运动特征对比研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2010, 31(S2): 31-37. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX2010S2008.htm 潘桂棠, 李兴振, 王立全, 等. 青藏高原及邻区大地构造单元初步划分[J]. 地质通报, 2002, 21(11): 701-707. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2002.11.002 安显银, 王启宇, 李勇, 等. 西藏昌都市察雅地区侏罗纪恐龙化石新发现[J]. 地质通报, 2021, 40(1): 189-193. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20210115&flag=1 秦四清, 李国梁, 薛雷, 等. 中国西南地区某些地震区未来震情研判[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2013, 28(5): 2407-2432. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWJ201305022.htm 秦四清, 薛雷, 黄鑫, 等. 西藏地区未来强震预测[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2010, 25(6): 1879-1886. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2903.2010.06.001 钟康惠, 刘肇昌, 舒良树, 等. 澜沧江断裂带的新生代走滑运动学特点[J]. 地质论评, 2004, (1): 1-8. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.2004.01.001 郭长宝, 吴瑞安, 蒋良文, 等. 川藏铁路雅安-林芝段典型地质灾害与工程地质问题[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(1): 1-17. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ202101002.htm 王腾, 孙晓光, 李白萍. 昌都市近36a暴雨气候特征分析[J]. 暴雨灾害, 2017, 36(1): 75-80. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9045.2017.01.010 张树轩, 杨为民, 程小杰, 等. 甘肃天水红旗山黄土滑坡群成因及稳定性分析[J]. 中国地质, 2017, 44(5): 924-937. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201705008.htm 陈永明, 石玉成. 中国西北黄土地区地震滑坡基本特征[J]. 地震研究, 2006, 29(3): 276-280. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0666.2006.03.012 孟庆华, 孙炜锋, 张春山, 等. 陕西宝鸡地区胡家山滑坡风险性评价[J]. 地质通报, 2011, 30(7): 1155-1165. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2011.07.018




 下载:
下载: