Deformation and failure mechanism of rainfall-induced shallow loess landslide
-
摘要:
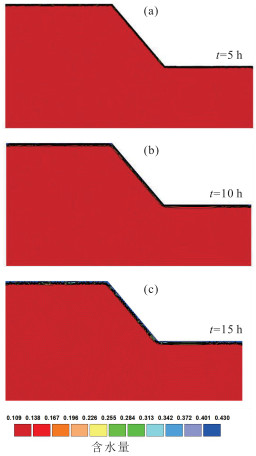
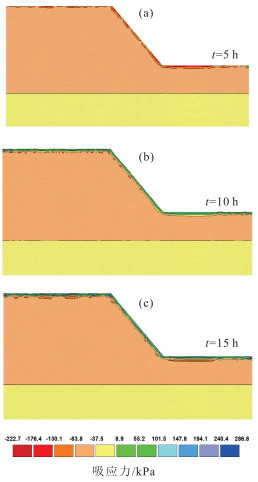
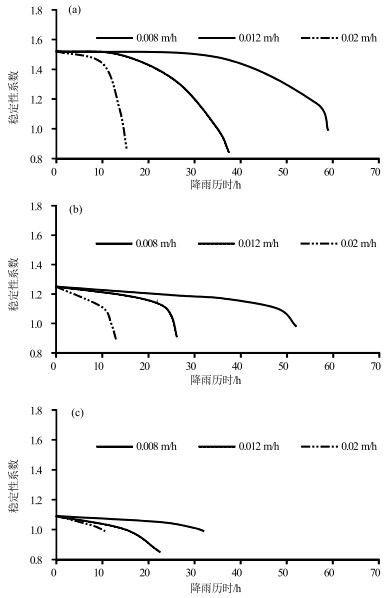
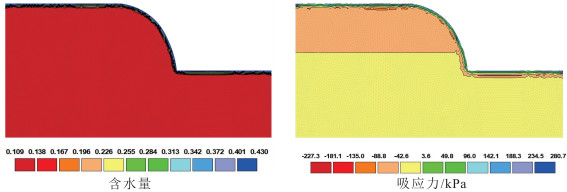
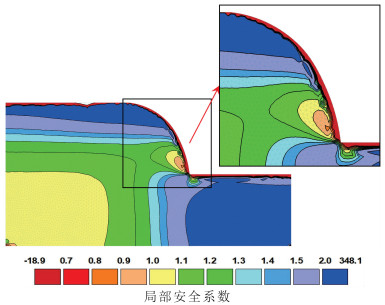
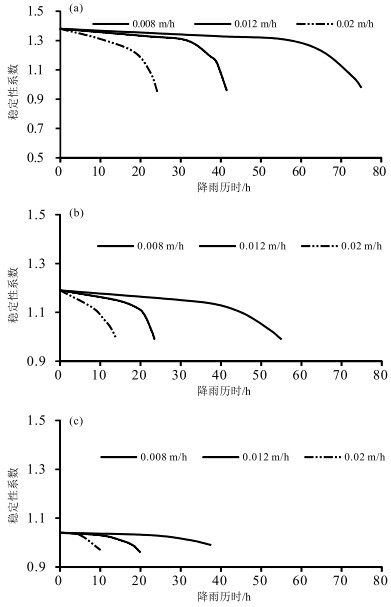
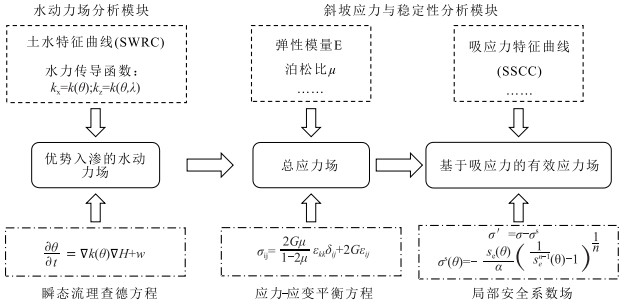
由降雨引发的浅层黄土滑坡灾害具有致灾性强、范围广、影响面积大等特点,是黄土高原地区危害严重的地质灾害类型。经典算法采用安全系数描述坡体稳定性,难以对坡体变形破坏的起始位置和实际失效面加以识别,限制了滑坡变形过程的描述和滑坡有效预测。以非饱和土吸应力理论为指导,基于Hydrus中的Slope Cube模块,建立黄土斜坡水-力耦合模型,结合黄土地区易滑坡形态统计数据,针对凸型、凹型、直线型3种坡型与30°、40°、50°三种坡度组合,计算了不同降雨条件下的坡体稳定性响应。结果表明,不同坡型的黄土斜坡对降雨条件具有明显的响应。相同降雨量、相同坡度条件下直线型坡发生浅表层破坏的可能性最低,凹型坡次之、凸型坡的稳定性最差。与之相对应的,相同条件下凸型坡失稳时间最短、凹型坡次之、直线型坡最长。本研究可为浅层滑坡的早期识别和预报提供支撑。
Abstract:The shallow loess landslides, triggered by precipitation has the characteristics of serious catastrophability, wide range of influence and large impact area, is one of the serious disaster in the Loess Plateau.It is difficult to identify the initial failure position and actual failure surface with the classical analysis method by using one safety factor to describe the slope stability, which limits the description of the failure process of slopes and consequently influence the effective prediction of landslides.Guided by the theory of unsaturated soil matric suction, the water- stress coupling model of loess slope was established based on the Slope Cube module with the Hydrus software.According to the statistics of slide-prone morphology of loess slopes, the slope stability response to rainfall conditions was calculated under different conbinations of convex, concave and linear, and the three slope gradients of 30°, 40° and 50°.The results show that different loess slopes have obvious responses to precipitation, and its influence is controlled by the slope types.Under the condition of the same rainfall and the same slope, the possibility of superficial surface damage occurs on the linear slope is the lowest, followed by the concave slope and the convex slope.Correspondingly, the time consuming of instability is the shortest for convex slopes, the second for the concave slopes, and the longest for the linear slopes under the same conditions.This study can provide support for early identification and prediction of shallow loess landslides.
-
Keywords:
- loess /
- precipitation /
- shallow landslides /
- failure mechanism
-
致谢: 本文是在延安地区大量调查与监测工作的基础上完成的,调查工作由项目成员程秀娟、薛强、王虎、王益民、郭怀军等共同完成,软件计算和分析过程中得到中国科学院武汉岩土力学研究所陈盼副研究员的指导和帮助,成文过程中得到长安大学李同录教授、西北大学谷天峰教授的悉心指导,在此一并表示衷心的感谢。
-
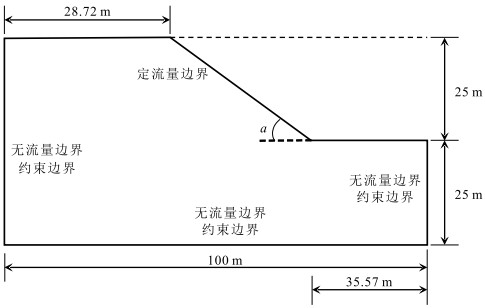
表 1 模型主要参数取值
Table 1 Main parameters selected for modeling
参数 量纲 参数取值 饱和含水量(θs) - 0.4 残余含水量(θr) - 0.078 饱和渗透系数(Ks) m/h 0.00104 进气值参数(α) 1/m 3.6 有效粘聚力(c`) kPa 45 摩擦系数(Φ`) ° 28.5 重度(Gs) - 2.6 空间参数(n) - 1.56 干密度(ρd) g/cm3 1.43 液性指数(wL) % 28.8 塑性指数(wP) % 9.5 -
李同录, 习羽, 侯晓坤. 水致黄土深层滑坡灾变机理[J]. 工程地质学报, 2018, 26(5): 1113-1120. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ201805001.htm Ng C W W, Pang Y W. Influence of stress state on soils-water charateristics and slope stability[J]. J. Geotech Geoenviron., 2000, 126(2): 157-166. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)1090-0241(2000)126:2(157)
Zhang M S, Dong Y, Sun P P. Impact of reservoir impoundment-caused groundwater level changes on regional slope stability: a case study in the Loess Plateau of Western China[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2012, 66: 1715-1725. doi: 10.1007/s12665-012-1728-6
杨宗佶, 蔡焕, 雷小芹, 等. 非饱和地震滑坡堆积体降雨破坏水-力耦合行为的试验研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2019, 40(5), doi: 10.16285/j.rsm.2018.0045. 向小龙, 孙炜锋, 谭成轩, 等. 降雨型滑坡失稳概率计算方法[J]. 地质通报, 2020, 39(7): 1115-1120. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20200716&flag=1 张茂省. 引水灌区黄土地质灾害成因机制与防控技术——以黄河三峡库区甘肃黑方台移民灌区为例[J]. 地质通报, 2013, 32(6): 833-839. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20130602&flag=1 金艳丽, 戴福初. 地下水位上升下黄土斜坡稳定性分析[J]. 工程地质学报, 2007, 15(5): 599-606. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2007.05.004 汪发武. 高速滑坡形成机制_土粒子破碎导致超孔隙水压力的产生[J]. 长春科技大学学报, 2001, 31(1): 64-69. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-5888.2001.01.013 邢鲜丽, 李同录, 李萍, 等. 黄土抗剪强度与含水率的变化规律[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2014, 41(3): 53-59. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG201403012.htm Duncan J M., Wright S G. Soil strength and slope stability[M]. John Wiley & Sons, Hoboken, , 2005.
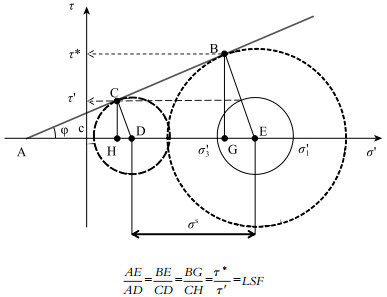
Lu N, Likos W J. Suction stress characteristic curve for unsaturated soil[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geo-environmental Engineering, 2006, 48(9): 131-142. http://www.researchgate.net/profile/Ning_Lu5/publication/228662948_Suction_Stress_Characteristic_Curve_for_Unsaturated_Soil/links/54621cfa0cf27487b455833d/Suction-Stress-Characteristic-Curve-for-Unsaturated-Soil.pdf
Lu N, Basak S, Alexandra W, et al. Analysis of rainfall-induced slope instability using a field of local factor of safety[J]. Water Resources, Research, 2012, 48: W09524. doi: 10.1029/2012WR011830.
Lu N, Jonathan W G. Hillslope hydrology and stability[M]. Cambridge, 2013.
孙萍萍, 张茂省, 程秀娟, 等. 黄土高原地质灾害发生规律[J]. 山地学报, 2019, 37(5), Doi: 10.16089/j.cnki.1008-2786.000455. 黄玉华, 冯卫, 李政国. 陕北延安地区2013年"7·3"暴雨特征及地质灾害成灾模式浅析[J]. 灾害学, 2014, 29(2): 54-59. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHXU201402012.htm 张茂省, 孙萍萍, 程秀娟, 等.西北黄土高原区地质灾害综合研究报告.中国地质调查局西安地质调查中心, 2015.



 下载:
下载: