Zircon U-Pb age, petrogenesis and teceonic setting of the Yabulai adakite, northern Alxa Block, Inner Mongolia
-
摘要:
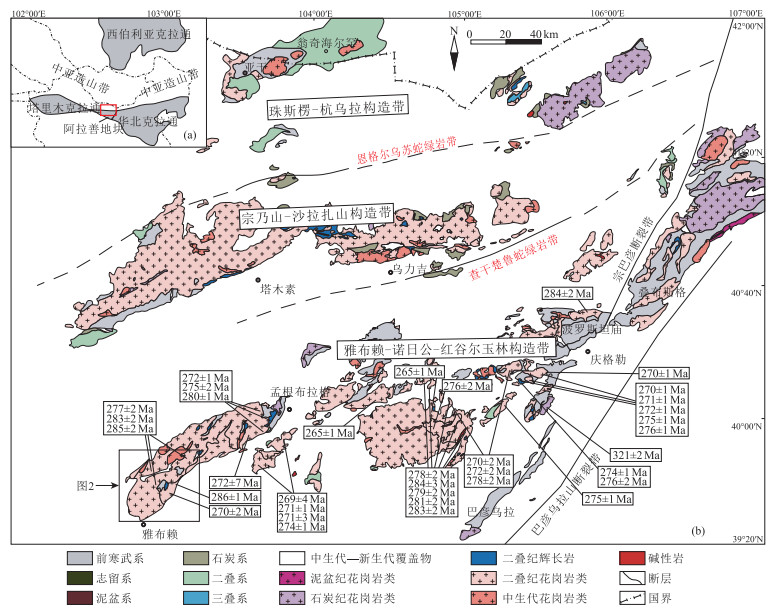
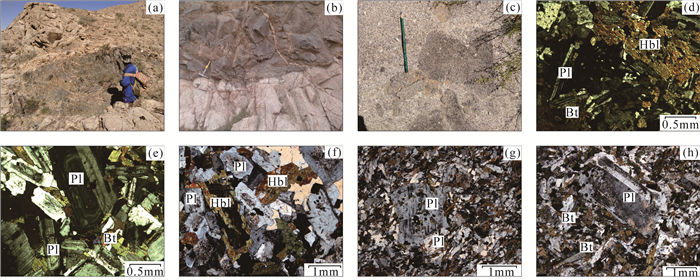
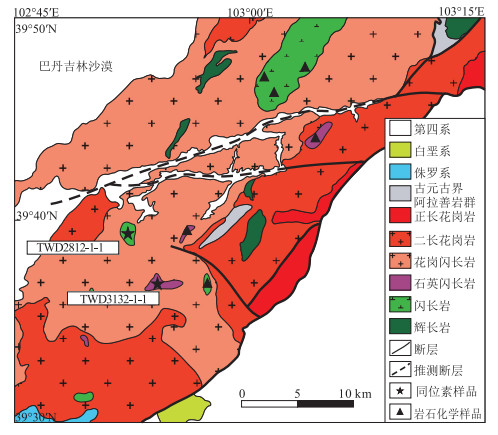
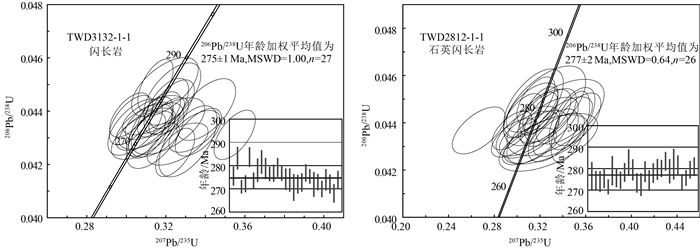
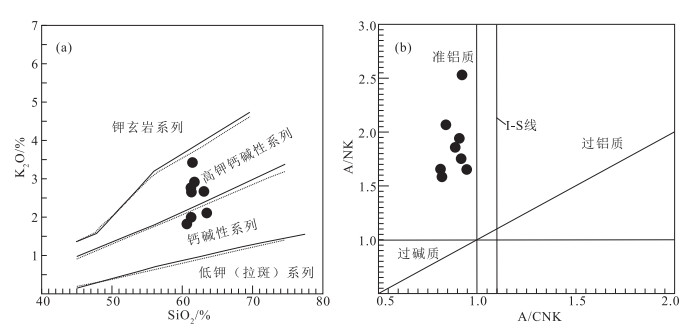
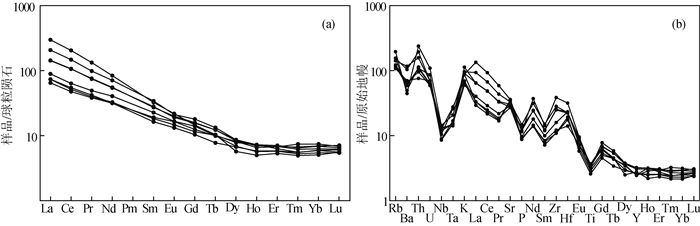
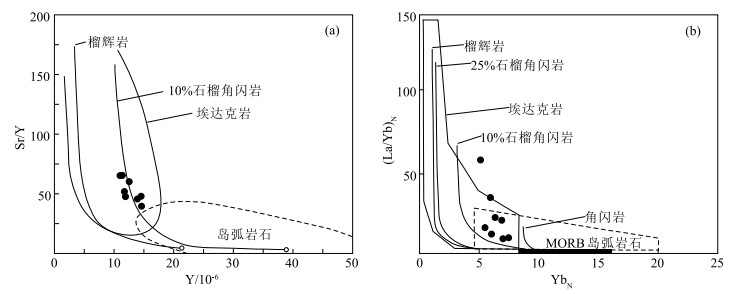
雅布赖地区位于阿拉善地块北缘,埃达克岩岩石类型主要为闪长岩和石英闪长岩。用LA-ICP-MS方法测得埃达克岩中的锆石206Pb/238U年龄为275±1 Ma(MSWD=1.00,n=27,闪长岩)和277±2 Ma(MSWD=0.64,n=26,石英闪长岩),故认为雅布赖地区埃达克岩侵位年龄为275±1~277±2 Ma,形成时代为早二叠世。地球化学特征表明,该岩体具有较高的SiO2(60.56%~63.41%)、Al2O3(15.86%~17.33%)、Sr(572×10-6~758×10-6)含量,较低的MgO(1.45%~3.06%)、Y(11.10×10-6~14.7×10-6)、Yb(1.06×10-6~1.55×10-6)含量,富集大离子亲石元素K、Rb、Ba、Sr等,亏损高场强元素Ta、Nb、Ti、P等。岩石重稀土元素强烈亏损,轻、重稀土元素分馏明显,Eu异常较弱(0.81 < δEu < 1.04),Mg#值较高(38~53),Y/Yb值为7.35~11.89,Na2O/K2O值为1.18~1.77,具有C型埃达克岩特征,为拆沉下地売部分熔融产生的流体与地幔橄榄岩相互作用形成的产物。结合前人研究,其可能形成于碰撞后伸展环境。
Abstract:Yabulai adakite is located in the western part of Yabulai-Nuorigong-Honggueryulin belt, northern Alxa Block.The main rock types of the Yabulai adakite are diorite and quartz diorite.The LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb dating results are 275±1 Ma(MSWD=1.00, n=27, diorite) and 277±2 Ma(MSWD=0.64, n=26, quartz diorite), which shows that the ages of the adakite are between 275 Ma and 277 Ma, suggesting a product of Early Permian.Geochemical characteristics show that the Yabulai adakite with high content of SiO2(60.56%~63.41%), Al2O3 (15.86%~17.33%), Sr(572×10-6~758×10-6) and low content of MgO(1.45%~3.06%), Y(11.1×10-6~14.7×10-6), Yb(1.06×10-6~1.55×10-6), enrichment of large ion lithophile elements(such as K, Rb, Ba and Sr), and depletion of high field-strength elements(such as Ta, Nb, Ti and P).The Yabulai adakite is typical C-type adakite with high content of Mg#(38~53), the ratio of Y/Yb is between 7.35 and 11.89, and Na2O/K2O is between 1.18 and 1.77;in addition, it exhibits significant fractionation between LREE and HREE and is depleted in HREE with slight Eu anomaly(0.81 < δEu < 1.04).The authors hold that the Yabulai adakite was formed by partial melting of delaminated lower crust and interaction with the mantle peridotite, and magmatic mixing was experienced during diagenesis.Combined with previous studies, the authors hold that the Yabulai adakite might have been formed in a post-collision extension stage.
-
Keywords:
- adakite /
- zircon U-Pb dating /
- Yabulai /
- magma mixing /
- Alxa Block
-
早中新世后,随着青藏高原隆升,亚洲季风增强,中国北方大部地区逐渐脱离原有的行星气候控制的干旱气候状况,向今天的暖温带季风气候系统转变[1-2],其生态系统也由原来的草原及荒漠草原为主的植被景观,转变为森林草原-落叶阔叶林为主[2]。亚洲季风区的典型暖温带植被系统不仅对全球周期性气候变化具有明显的指示意义,而且对过去数百万年时间的气候转型具有较好的响应,因此,是近年来研究过去全球变化的重点[3-4]。
晚新近纪以来,全球气候经历了几次重要的调整过程,其中最重要的就是中更新世时期全球气候格局的调整,又称中更新世转型[5-6]。其特征为从“高频低幅”的早更新世气候向中更新世以来“低频高幅”的气候波动,其气候变化周期由40ka的地轴倾斜度周期,转变为100ka 的轨道偏心率周期[7]。期间全球气候降温,陆地表面大部分地区因此变得更加寒冷干燥,冰期时,形成北美、欧洲的冰盖,非洲撒哈拉沙漠形成,亚洲内陆环境进一步干旱化,冬季季风强度增加等[7-9]。研究中更新世气候格局的重新调整,以及转型前后气候周期性对华北地区植被的影响,有利于了解不同区域植被对全球气候环境变化的响应特征,为研究重大气候转型中的生态环境效应提供重要对比参照物[10]。
华北平原主要包括淮北平原、黄河平原和海河平原三大区块,位于中国北方地区的东部,属典型的季风区。华北平原北部海河下游地区的凹陷盆地中沉积了厚度大于5000m 的新生带地层[11],其中第四系厚280~410m,最厚约450m。目前,基于这些新生带地层,华北地区的古植被研究已有较多积累,如河北黄骅HB1、衡水HS1 及天津CQJ1 孔花粉谱[12-14],天津G2 孔[15]。但是由于地层中花粉鉴定数量偏少、地层年代学不完善,以及区域地貌、沉积环境等多元因素的影响,用高质量孢粉数据来探讨更新世以来华北地区植被转型与气候变化问题的研究并不多见。本次研究利用华北地区东部天津滨海新区沉积凹陷中G3 钻孔的岩心材料,通过古地磁年代序列及较高质量的孢粉分析数据重建区域植被历史,并结合已有的植被重建资料,探讨第四纪以来华北地区的植被演变特征及气候变化过程。
1. 研究区自然地理概况
位于北纬32°~40°、东经114°~121°的华北平原是中国东部最主要的平原,平均海拔低于50m,由黄河、海河、淮河等带来的泥沙沉积而成。华北平原属暖温带季风气候,四季变化明显,冬季寒冷、少雪;春季干旱,夏季气温高、湿度大、降水集中;全年平均气温8~15℃。年平均降水量南部淮河区800~1000mm,黄河下游600~700mm,海河下游为500~600mm,年降水量分配不平衡,多年平均水面蒸发量为1625mm,降水随季节变化显著,冬、春季少,夏季集中[16]。
研究区自然植被主要由暖温带落叶阔叶林组成。在现代植被中,阔叶类的落叶栎(Quercus)植被组成受纬向的温度效应控制非常明显,在南部为麻栎(Quercus acutissima)、栓皮栎(Quercus variabilis),向北逐渐过渡为蒙古栎(Quercus mongolica)和辽东栎(Quercus liaotungensis)。针叶类以松属(Pinus)占主要地位,以赤松(Pinus densiflora)为主。另外常见温带的枫桦(Betula costata)、五加(Eleutherococcussenticosus)、核桃楸(Juglans mandshurica Max.)、椴属(Tilia)等。华北平原,尤其是海河平原,湖泊和沼泽广布,沼泽植被以芦苇(Phragmites)、香蒲(Ty⁃pha)、水葱(Scirpus)、苔草(Carex)等为主[17]。
全新世晚期以来,由于人类活动的持续加强,华北地区原生落叶阔叶林遭到大规模破坏,形成了今天普遍的灌丛及灌丛草原,其中灌木以荆条、酸枣为主,草丛以黄背草和白羊草为建群种。
2. 研究材料与研究方法
2.1 钻孔地理位置与磁性地层
天津G3 钻孔(孔口坐标:北纬117°25′59.5″、东经38°49′57.6″)位于华北平原东部天津滨海地区的海河南侧,构造上属于黄骅坳陷中的板桥凹陷。孔口高程2.65m,孔深905m(图 1)。岩心直径100mm,全孔取心率90.0%以上。因此,取心率和岩心状况满足磁性地层学及其他研究的要求。
G3 孔200m 以上磁性地层中共有6 个极性段,包括3 个正极性段(N1~N3)和3 个负极性段(R1~R3),正极性段分别为N1(0~85.0m)、N2(95.5~105.9m)和N3(177~191.8m),负极性段分别为R1(85.0~95.5m)、R2(105.9~177.0m)和R3(191.8~212.5m)。其中N1(0~85.0m)以正极性为主,并且包含明显的全新世海相层,对应布容极性时(Brunhes),故确定N1(0~85.0m)对应C1n(0~0.781Ma)。85.0~212.5m(R1~R3)以负极性为主,对应松山极性时(Matuyama),其中,N2(95.5~105.9m)对应C1r.1n(0.988~1.072Ma),为贾拉米罗(Jaramillo)正极性亚时,奥尔都微(Olduvai)正极性亚时持续事件长,且强度大,在渤海湾沿岸其他钻孔中亦有出现,因此推断N3(177~191.8m)对应C2n(1.778~1.945Ma),为Olduvai正极性亚时(图 2)。
2.2 花粉分析方法
天津滨海新区大港G3 钻孔花粉样品取样深度在0~905m 之间,取样间隔岩性为粘土、亚粘土、亚砂土和砂。每个样品重量为100g,经盐酸和氢氟酸处理、直径7μm 筛网筛选提取花粉化石。花粉鉴定统计在400 倍日本OLYMPUS 光学生物显微镜下进行,每个样品鉴定统计的花粉数是观察统计3 个玻片以上得到的。
在取得的165 个样品的大部分中发现了花粉化石,但仅在160m 以上发现连续而丰富的花粉,160m以下花粉数量稀少,绝大多数样品中不足50 粒。160m 以上共42 个样品中花粉相对丰富,其中绝大多数样品鉴定粒数高于100 粒,样品平均粒数为218粒。本文选择具有连续有效花粉数据的0~160m 地层(0~1.7Ma),用Tilia 软件对花粉图谱进行百分比图谱的绘制(图 3)。
2.3 研究结果
在42 个有效样品中,共鉴定了9167 粒花粉,分属48 个科属。其中针叶乔木花粉有铁杉属(Tsu⁃ga)、冷杉属(Abies)、云杉属(Picea)和松属(Pinus),落叶阔叶乔木花粉有桦属(Betula)、鹅耳枥属(Car⁃pinus)、桤木属(Alnus)、栗属(Castanea)、落叶栎属(Quercus)、椴属(Tilia)、胡桃属(Juglans)、榆属(Ul⁃mus)、糙叶树属(Aphananthe)、枫香属(Liquidanber)、山核桃属(Carya)、无患子科(Sapindaceae),灌木植物花粉有嚼床科(Acanthaceae)、胡秃子科(Elaeagna⁃ceae)、榛属(Corylus)、虎榛子属(Ostryopsis)、麻黄属(Ephedra)、忍冬科(Caprifoliaceae)、蔷薇科(Rosace⁃ae)。草本植物花粉有旱生的地榆属(Sangnisorba)、葎草属(Humulus)、藜科(Chenopodiaceae)、菊科(Compositea)、蒿属(Artemisia)、茜草科(Rubiace⁃ae)、唇形科(Labiatea)、豆科(Leguminosae)、茄科(Solanaceae)、蓼属(Polygonum)、十字花科(Crcife⁃rae)、石竹科(Caryophllaceae)、伞形花科(Umbella⁃les)等,水生植物有禾本科(Gramineae)、泽泻科(Alismataceae)、香蒲属(Typha)、莎草科(Cyperace⁃ae)、荇菜属(Nymphoides)。蕨类植物孢子有石松科(Lycopodiaceae)、水龙骨属(Polypodium)、凤尾蕨属(Pteridium)、卷柏属(Selaginella)、水蕨科(Parkeria⁃ceae)、单缝孢子(Monolites)和三缝孢子(Trilites)。
通过Canoco 4.5 软件对G3 孔中孢粉属种排序(图 4),发现所有属种可分为4 个类群:①以云杉、松为代表的温性针叶林;②以栎属、榛属、栗属、胡桃等为主的落叶阔叶林;③以蒿属、藜科、禾本科和桦属为主的草原及疏林草原;④以榆属、蔷薇科、胡颓子和铁杉为主的暖温性灌丛。根据属种的分布规律推断,图 4 中第一主轴(横轴)指示湿度,第二主轴(纵轴)指示温度。
如图 3 所示,根据孢粉聚类分析结果,将G3 孔中花粉百分比图谱分为4 个带。
(1)孢粉带Ⅰ:松属-云杉属-藜属-菊科-蕨类组合(1.6~1.2Ma)
乔木平均为58.6%,以松(12.7%~84.2%)和云杉(0~10.6%)为主,早期有少量铁杉,后过渡为云杉,此外还包含含量较低的栎属、榆属、椴属、桦属、胡桃属等常见暖温性阔叶乔木;草本中藜科最多,平均为8.1%,菊科含量平均4.3%,最高14.3%,蒿属含量少于菊科,平均仅2.8%。蕨类孢子在本带含量较丰富,以石松为主,另外还有水龙骨、凤尾蕨等蕨类。
本段组合指示暖温带针阔叶混交林的特点,其中松属为主要建群种,其花粉的突出代表性使松属在此时具有绝对优势。其中重要的变化在1.5Ma 前后,针叶林成分由铁杉向云杉转变的过程,显示一次降温事件,由此又可以划分出2 个阶段,即Ⅰ -1(1.6~1.5Ma)和Ⅰ -2(1.5~1.2Ma)。草本组合显示,1.5Ma 以前,菊科含量较高,而到后期,禾本科含量逐渐增加,菊科花粉基本消失,显示了区域草地环境由湿转干的过程。
(2)孢粉带Ⅱ:松属-栎属-藜-蒿组合(1.2~0.7Ma)
本段乔木花粉整体比例下降,松属比例由上段的平均51%下降至15%左右,云杉、铁杉等针叶树基本消失,但落叶栎属比例由带Ⅰ的1.2%,显著上升为13.0%,同时桦属花粉也显著增加,另有少量栗属、榆属、胡桃属等阔叶树。草本花粉组成也发生重要改变,藜科、蒿属比例大幅度增加,并伴随禾本科与香蒲属花粉的增加。蒿属平均值由原来的2.7%增加为20.7%。
本段孢粉组合指示暖温带落叶阔叶林的植被特征。草本花粉,尤其是蒿属的比例大幅度增加,显示华北地区在该阶段林地消退与草原发展,指示该时期气候干旱化。
(3)孢粉带Ⅲ:栎属-松属-藜-蒿-香蒲组合(0.7~0.3Ma)
本段乔木花粉比例最低,松属平均值由15%进一步下降,栎属略有下降,伴随较多的桦属与少量云杉属、铁杉属,并出现了零星的枫香属、山核桃属花粉。草本中藜科和蒿属依然占据主导地位,显示草原继续发展,而香蒲比例大幅度上升,显示周边地区湖泊湿地的扩展。本段孢粉组合指示疏林草原的植被景观,同时,湖泊湿地开始大规模发育。
(4)孢粉带Ⅳ:松属-栎属-藜-蒿-香蒲组合(0.3~0Ma)
本段针叶乔木花粉比例回升,松属增加至22.1%,云杉、铁杉花粉含量也有显著增加,而阔叶类乔木比例下降,栎属略微下降,枫香属、山核桃属消失,出现少量椴属、栗属、榆属、胡桃属等阔叶树。草本主要变化为藜科比例下降和香蒲比例升高。本段孢粉组合指示以暖温带落叶阔叶林为主的植被景观,湖泊湿地持续发育。
3. 讨论
3.1 演变趋势
中更新世气候转型期间,全球冰量整体增加了约15%,平均温度显著下降。对于其转型时间,大部分研究显示其大约开始于1.2Ma[6],另一些研究认为稍晚,在约1.05Ma,或是0.9Ma 前后,另外有人认为这种转型也可能是以一种渐进的方式进行的,始于1.2Ma,到约0.6Ma 才完成转型[18]。
G3 孔指示的中国华北平原地区中更新世植被转型期,对应上述的孢粉带Ⅱ,显示华北地区植被转型开始发生于1.2Ma,主要表现为林地减少,喜湿的针叶林比例下降,较为干旱的落叶阔叶林增加,同时藜科、蒿属、禾本科等草地面积显著增加。这种变化在1.2Ma 左右的某个时间点发生,大致相当于深海O 同位素36 阶段。
黄骅HB1、衡水HS1、天津CQJ2 孔、天津G2 孔的1.28~2.80Ma 为暖温带落叶阔叶林的景观,整体上较暖湿。1.28Ma以来,典型暖温带阔叶乔木花粉比例减小,华北平原草地扩张,而黄骅HB1 孔与衡水HS1 孔在中更新世前后也发生了类似事件[12-15]。
尽管由于孢粉数据分辨率的问题,所有这些钻孔的花粉百分比变化在时间上没有完好吻合,但是1.2Ma 前后,中更新世转型期推动华北平原地区植被整体向干旱类型发展是具有普遍性的。
此后,大约在0.7Ma 前后又发生一次重大转型,林地进一步退化,区域植被由原来的落叶阔叶林向疏林草原转变,对应深海O 同位素18 阶段。之后这种趋势一直延续到0.3Ma 左右才发生转变。黄骅HB1 孔中,0.8~0.7Ma 以后以蒿属和香蒲属为主,草本花粉出现,并分别达到12.5% 和10.9%,衡水HS1孔中以蒿和藜科为代表的草本花粉在0.78Ma 后也显著增长,显示华北平原0.7~0.8Ma 前后草地植被显著扩张[12-14]。此后,在约0.3Ma,即大约O 同位素8 阶段以后,华北地区植被中林地比例再度增加,可能与深海O 同位素11 阶段以后的7 阶段,5 阶段等几次典型的高温期有关。
3.2 周期性气候变化的区域植被响应
尽管由于样品分辨率的问题,周期性气候变化导致的区域植被变化未能完全被花粉谱记录,以致花粉谱更多地指示了区域植被在万年尺度的长期发展趋势。但是,不论是1.2Ma 之前的40ka 轨道倾斜度周期性,还是1.2Ma 之后的100ka 轨道偏心率周期,周期性气候变化对植被的影响,在花粉谱中确有一定表现。
例如在孢粉带Ⅰ中,以松为代表的乔木花粉比例的波动变化为10%~80%,可能对应该时期由地轴倾斜度40ka 周期变化导致的区域植被的变化。在带Ⅳ 也有类似的波动响应。由此可见,不论是1.2Ma 之前40ka 周期的“ 高频低幅”变化,还是1.2Ma 之后,100ka 周期的“低频高幅”变化,对华北地区的植被都有显著影响。
如图 3 所示,华北地区植被在1.6~1.2Ma 期间在40ka 气候周期“高频低幅”的变化中,主要表现为松属、常绿栎、铁杉属、胡桃属的交替变化,指示了区域暖温性与温性植被林地类型的交替变化。而1.2Ma 之后随着草原植被的扩张,100ka 周期的“低频高幅”变化造成的华北地区区域植被的响应更多地表现为草原与森林的交替发展。
4. 结论
华北平原东北部天津G3 孔孢粉数据及周边地区已有花粉研究表明,华北平原地区1.6Ma 以来的植被演化主要可以分为4 个阶段:①1.6~1.2Ma 密闭度较高的暖温带针阔叶混交林;②1.2~0.7Ma 开阔的暖温带落叶阔叶林;③0.7~0.3Ma,阔叶疏林草原;④0.3Ma 至今,暖温带落叶阔叶林。
中国华北平原地区中更新世植被转型期对应于孢粉带Ⅱ,显示该转型始于1.2Ma,大致对应深海O 同位素36 阶段。主要特征为林地减少、喜湿的针叶林比例下降,较为干旱的落叶阔叶林增加,同时,藜科、蒿属、禾本科等草地面积显著增加。
大约在0.7Ma 前后又发生一次重大转型,林地进一步退化,区域植被由原来的落叶阔叶林向疏林草原转变,对应深海O 同位素18 阶段。
G3 孔代表的花粉谱显示,1.6Ma 以来气候周期性的变化对华北地区区域植被有较显著的影响。
在1.2Ma 之前,受40ka 轨道倾斜度气候周期性的影响,主要表现为植被林地类型的交替发展;在1.2Ma之后,受100ka 轨道偏心率气候周期性影响,主要表现为草原与森林交替发展。
致谢: 在项目实施和成文过程中,天津地质调查中心辛后田教授级高工,滕学建、张永高级工程师给予大力支持,在此表示衷心感谢。 -
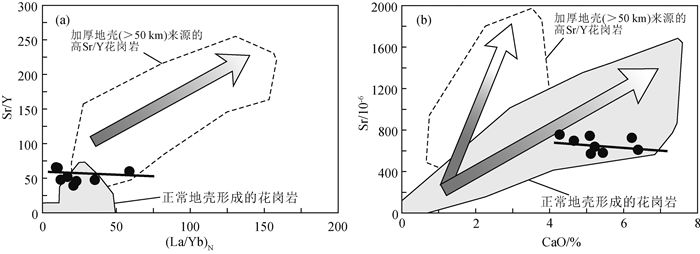
图 8 雅布赖地区埃达克岩Y-Sr/Y(a)和YbN-(La/Yb)N(b)图解[1]
MORB—大洋中脊玄武岩
Figure 8. Y-Sr/Y(a) and YbN-(La/Yb)N(b) diagrams for the Yabulai adakite
图 9 雅布赖地区埃达克岩(La/Yb)N-Sr/Y(a)和CaO-Sr(b)[52]图解
Figure 9. (La/Yb)N-Sr/Y(a) and CaO-Sr(b) diagrams for the Yabulai Adakite
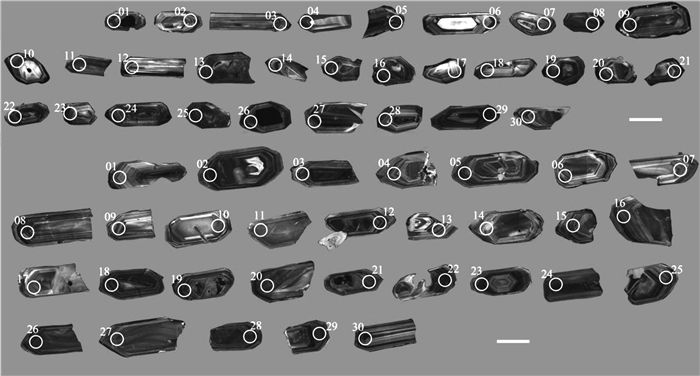
表 1 雅布赖地区埃达克岩闪长岩和石英闪长岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Th-Pb同位素测试结果
Table 1 LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Th-Pb data of diorite and quartz diorite of the Yabulai adakite
测点号 元素含量/10-6 Th/U 同位素比值 同位素年龄/Ma Pb Th U 207Pb/
206Pb1σ 207Pb/
235U1σ 206Pb/
238U1σ 207Pb/
206Pb1σ 207Pb/
235U1σ 206Pb/
238U1σ 谐和
度/%TWD3132-1-1闪长岩 1 35.3 664 588 1.13 0.0504 0.0012 0.3024 0.0073 0.0437 0.0006 213 90 268 5.7 276 3.8 97 2 13.8 181 234 0.77 0.0517 0.0017 0.3195 0.0111 0.0449 0.0007 333 74 282 8.6 283 4.5 99 3 21.9 334 382 0.87 0.0532 0.0013 0.3148 0.0080 0.0429 0.0004 345 56 278 6.1 271 2.6 97 4 21.2 330 367 0.90 0.0521 0.0010 0.3099 0.0066 0.0431 0.0005 300 44 274 5.1 272 3.3 99 5 35.4 467 606 0.77 0.0507 0.0007 0.3148 0.0059 0.0450 0.0006 228 33 278 4.5 284 4.0 97 6 17.0 197 271 0.73 0.0518 0.0010 0.3446 0.0101 0.0482 0.0011 280 43 301 7.6 303 6.9 99 7 12.4 149 228 0.65 0.0519 0.0015 0.3106 0.0094 0.0433 0.0005 283 65 275 7.3 274 3.1 99 8 29.5 553 464 1.19 0.0702 0.0012 0.4280 0.0114 0.0440 0.0006 1000 35 362 8.1 277 4.0 73 9 18.5 199 346 0.57 0.0561 0.0015 0.3404 0.0098 0.0441 0.0008 457 62 297 7.4 278 4.7 93 10 16.9 198 312 0.63 0.0524 0.0012 0.3233 0.0095 0.0446 0.0008 302 52 284 7.3 282 4.8 98 11 22.9 273 413 0.66 0.0527 0.0012 0.3202 0.0074 0.0442 0.0007 322 50 282 5.7 279 4.3 98 12 11.8 164 171 0.96 0.0560 0.0028 0.3888 0.0192 0.0505 0.0011 454 108 333 14 318 6.7 95 13 20.4 236 370 0.64 0.0532 0.0010 0.3214 0.0066 0.0438 0.0005 345 44 283 5.1 276 2.8 97 14 16.6 257 283 0.91 0.0501 0.0012 0.3016 0.0066 0.0439 0.0005 211 54 268 5.2 277 3.4 96 15 21.1 286 370 0.77 0.0529 0.0010 0.3232 0.0074 0.0443 0.0006 324 43 284 5.7 279 3.7 98 16 15.7 225 271 0.83 0.0519 0.0016 0.3137 0.0104 0.0439 0.0005 280 70 277 8.0 277 3.0 99 17 8.9 90.2 171 0.53 0.0537 0.0019 0.3211 0.0123 0.0434 0.0007 367 80 283 9.4 274 4.3 96 18 29.4 493 505 0.98 0.0524 0.0011 0.3124 0.0075 0.0434 0.0008 302 46 276 5.8 274 4.7 99 19 27.4 375 484 0.78 0.0561 0.0012 0.3312 0.0097 0.0429 0.0009 454 48 290 7.4 271 5.5 92 20 12.0 115 226 0.51 0.0520 0.0017 0.3085 0.0106 0.0431 0.0006 287 78 273 8.2 272 3.7 99 21 21.4 303 370 0.82 0.0566 0.0011 0.3364 0.0077 0.0432 0.0006 476 43 294 5.9 273 3.6 92 22 31.0 439 533 0.82 0.0524 0.0011 0.3165 0.0072 0.0439 0.0006 302 46 279 5.5 277 3.5 99 23 21.3 248 382 0.65 0.0518 0.0012 0.3114 0.0079 0.0436 0.0005 280 56 275 6.1 275 2.9 99 24 29.3 427 502 0.85 0.0528 0.0012 0.3146 0.0096 0.0431 0.0008 320 50 278 7.4 272 5.0 97 25 22.7 277 404 0.69 0.0561 0.0012 0.3344 0.0085 0.0432 0.0005 457 50 293 6.5 273 3.2 92 26 14.2 172 254 0.68 0.0554 0.0016 0.3260 0.0102 0.0428 0.0005 428 69 286 7.8 270 3.2 94 27 22.3 303 392 0.77 0.0511 0.0014 0.3044 0.0091 0.0434 0.0007 243 60 270 7.1 274 4.3 98 28 24.6 363 403 0.90 0.0600 0.0012 0.3548 0.0069 0.0431 0.0006 606 47 308 5.2 272 3.8 87 29 36.2 478 641 0.75 0.0555 0.0009 0.3247 0.0065 0.0425 0.0006 432 35 286 5.0 268 3.7 93 30 14.3 208 239 0.87 0.0517 0.0015 0.3089 0.0095 0.0434 0.0006 333 67 273 7.4 274 3.6 99 TWD2812-1-1石英闪长岩 1 10.6 118 212 0.55 0.0534 0.0023 0.3033 0.0137 0.0416 0.0010 346 100 269 11 263 6.4 97 2 25.5 400 471 0.85 0.0479 0.0014 0.2777 0.0092 0.0421 0.0007 100 70 249 7.3 266 4.6 93 3 21.7 246 400 0.61 0.0576 0.0017 0.3463 0.0112 0.0438 0.0010 517 69 302 8.4 277 6.1 91 4 15.4 222 301 0.74 0.0530 0.0023 0.3004 0.0135 0.0412 0.0006 328 103 267 11 261 3.8 97 5 13.3 162 257 0.63 0.0520 0.0028 0.3100 0.0174 0.0435 0.0007 287 119 274 13 275 4.0 99 6 13.2 176 245 0.72 0.0532 0.0031 0.3170 0.0176 0.0434 0.0007 345 125 280 14 274 4.5 97 7 10.2 123 198 0.62 0.0524 0.0032 0.3089 0.0184 0.0437 0.0007 302 136 273 14 275 4.3 99 8 18.4 240 349 0.69 0.0522 0.0025 0.3101 0.0157 0.0430 0.0005 295 107 274 12 272 3.2 98 9 11.5 164 217 0.76 0.0542 0.0042 0.3332 0.0283 0.0442 0.0011 376 174 292 22 279 6.5 95 10 11.8 160 228 0.70 0.0499 0.0040 0.2851 0.0240 0.0417 0.0006 191 178 255 19 264 3.9 96 11 14.9 255 265 0.96 0.0447 0.0027 0.2654 0.0154 0.0437 0.0007 error 239 12 276 4.0 85 12 18.5 233 352 0.66 0.0562 0.0024 0.3360 0.0148 0.0435 0.0006 461 96 294 11 275 3.7 93 13 15.8 192 299 0.64 0.0558 0.0025 0.3411 0.0164 0.0441 0.0007 443 98 298 12 278 4.0 93 14 7.6 87.4 144 0.60 0.0513 0.0030 0.3138 0.0172 0.0448 0.0009 254 133 277 13 283 5.9 97 15 16.4 220 300 0.73 0.0527 0.0023 0.3234 0.0153 0.0443 0.0007 317 98 285 12 279 4.6 98 16 14.2 190 264 0.72 0.0545 0.0040 0.3247 0.0244 0.0433 0.0007 391 163 286 19 273 4.2 95 17 10.0 137 187 0.73 0.0555 0.0050 0.3269 0.0286 0.0432 0.0008 432 204 287 22 273 5.0 94 18 21.2 310 389 0.80 0.0582 0.0023 0.3524 0.0138 0.0442 0.0007 539 85 306 10 279 4.5 90 19 21.5 344 393 0.88 0.0555 0.0024 0.3310 0.0145 0.0435 0.0007 432 98 290 11 274 4.5 94 20 13.6 189 248 0.76 0.0540 0.0027 0.3277 0.0167 0.0441 0.0007 369 113 288 13 278 4.2 96 21 16.1 229 297 0.77 0.0541 0.0025 0.3287 0.0151 0.0443 0.0007 376 71 289 12 280 4.6 96 22 31.1 445 564 0.79 0.0518 0.0015 0.3183 0.0110 0.0444 0.0006 276 69 281 8.5 280 3.7 99 23 33.4 425 614 0.69 0.0510 0.0017 0.3157 0.0110 0.0449 0.0007 243 79 279 8.5 283 4.0 98 24 45.1 559 827 0.68 0.0575 0.0023 0.3477 0.0134 0.0442 0.0009 509 89 303 10 279 5.3 91 25 13.0 167 250 0.67 0.0524 0.0037 0.3237 0.0238 0.0447 0.0011 302 127 285 18 282 6.8 99 26 19.1 296 342 0.86 0.0505 0.0021 0.3127 0.0150 0.0447 0.0007 217 103 276 12 282 4.2 98 27 11.5 154 213 0.72 0.0500 0.0024 0.2971 0.0134 0.0434 0.0005 195 111 264 10 274 3.3 96 28 18.7 266 344 0.77 0.0489 0.0018 0.2948 0.0115 0.0437 0.0005 143 87 262 9.0 276 3.3 95 29 18.3 247 341 0.73 0.0502 0.0019 0.3046 0.0114 0.0443 0.0006 211 95 270 8.8 279 3.8 96 30 26.4 570 430 1.33 0.0522 0.0016 0.3199 0.0102 0.0445 0.0006 300 72 282 7.8 281 4.0 99 表 2 雅布赖地区埃达克岩主量、微量和稀土元素分析结果
Table 2 Content of major, trace elements, and REE of the Yabulai adakite
样号 PM001-20-1 D5483-1-1 D5865-1-1 D3132-1-1 PM021-10-1 D2812-1-1 D0605-1-1 D7135-1-1 岩性 闪长岩 闪长岩 闪长岩 闪长岩 闪长岩 石英闪长岩 石英闪长岩 石英闪长岩 SiO2 61.23 63.41 61.21 61.63 62.98 61.32 61.12 60.56 TiO2 0.74 0.62 0.68 0.70 0.56 0.71 0.79 0.80 Al2O3 17.33 16.00 16.18 16.38 15.86 16.35 16.02 16.99 Fe2O3 2.31 1.23 1.60 1.86 1.67 1.80 1.94 1.89 FeO 3.37 4.19 4.00 3.92 3.00 3.51 3.79 4.36 MnO 0.10 0.09 0.10 0.12 0.09 0.10 0.11 0.11 MgO 1.45 2.52 2.99 1.65 2.34 1.78 1.95 3.06 CaO 4.26 5.08 6.22 4.65 5.11 5.21 5.43 6.39 Na2O 4.62 3.63 3.50 3.78 3.48 4.02 4.06 2.93 K2O 2.63 2.09 1.98 2.89 2.65 3.40 2.74 1.80 P2O5 0.25 0.19 0.20 0.32 0.20 0.26 0.29 0.21 H2O+ 0.78 0.19 0.6 0.82 0.46 0.74 0.85 0.28 CO2 0.4 0.12 0.27 0.74 0.37 0.51 0.62 0.45 烧失量 1.24 0.36 0.96 1.69 1.49 1.33 1.56 0.78 总计 99.53 99.41 99.62 99.59 99.43 99.79 99.80 99.88 Na2O/K2O 1.76 1.74 1.77 1.31 1.31 1.18 1.48 1.63 Mg# 38 49 53 38 53 43 43 51 A/CNK 0.95 0.91 0.85 0.92 0.89 0.82 0.82 0.93 σ 2.88 1.60 1.65 2.39 1.88 3.01 2.55 1.27 Cs 3.03 2.03 2.52 1.80 2.02 1.31 1.43 3.38 Rb 124 98.2 74.2 98.6 89.9 77.4 73.5 68.2 Sr 758 746 725 697 572 640 581 611 Ba 310 345 423 725 816 457 412 489 Nb 10.2 8.96 6.33 9.55 7.44 8.46 9.14 6.10 Ta 0.85 1.13 0.69 0.58 1.06 0.63 0.62 0.62 Zr 432 122 136 316 123 285 278 178 Hf 9.78 5.41 4.34 6.95 5.96 7.04 6.85 7.20 Th 20.2 9.63 9.23 16.5 13.4 8.12 9.14 6.44 V 48.3 102 113 57.5 90.1 70.7 76.7 127 Cr 6.70 63.6 35.5 14.7 17.0 11.7 9.94 13.8 Co 8.56 21.6 15.2 9.33 11.7 10.5 10.5 17.7 Ni 5.53 34.2 17.2 7.25 12.3 7.19 5.53 9.86 Li 26.4 16.3 16.5 16.2 17.8 9.67 11.1 24.6 U 2.29 1.32 1.81 1.45 1.44 1.24 1.30 1.46 La 92.2 22.8 20.1 64.1 22.8 44.1 44.5 27.6 Ce 165 41.6 38.4 119 44.1 85.5 86.2 51.3 Pr 16.2 4.85 4.67 12.0 5.13 9.24 9.07 6.00 Nd 50.2 19.6 18.9 42.5 19.0 33.1 32.6 24.3 Sm 6.32 3.56 3.72 6.65 3.19 5.30 5.45 4.42 Eu 1.60 1.08 1.21 1.55 0.97 1.46 1.40 1.22 Gd 3.76 2.98 3.23 4.64 2.69 4.10 4.03 3.62 Tb 0.49 0.48 0.47 0.63 0.37 0.58 0.58 0.47 Dy 1.84 2.52 2.62 2.78 2.16 2.68 2.74 2.20 Ho 0.36 0.52 0.47 0.52 0.42 0.50 0.52 0.41 Er 1.12 1.41 1.42 1.32 1.22 1.43 1.48 1.21 Tm 0.16 0.24 0.22 0.18 0.18 0.20 0.21 0.17 Yb 1.06 1.55 1.45 1.23 1.25 1.31 1.43 1.13 Lu 0.18 0.22 0.23 0.18 0.19 0.20 0.21 0.17 Y 12.6 11.4 11.1 14.6 12.0 14.0 14.7 11.8 ∑REE 353.1 114.8 108.2 271.9 115.6 203.7 205.1 136.0 LREE/HREE 37.0 9.42 8.61 21.4 11.2 16.3 16.0 12.2 δEu 0.93 0.99 1.04 0.81 0.99 0.92 0.88 0.91 (La/Yb) N 58.7 9.91 9.34 35.1 12.3 22.7 21.0 16.4 Sr/Y 60.2 65.4 65.3 47.7 47.8 45.7 39.5 51.8 La/Nb 9.04 2.54 3.17 6.71 3.06 5.21 4.87 4.52 Y/Yb 11.9 7.35 7.66 11.9 9.58 10.7 10.3 10.4 Rb/Sr 0.16 0.13 0.10 0.14 0.16 0.12 0.13 0.11 La/Sm 14.6 6.40 5.40 9.64 7.16 8.32 8.17 6.24 La/Yb 87.0 14.7 13.9 52.1 18.2 33.7 31.1 24.3 注:主量元素含量单位为%,微量和稀土元素含量单位为10-6 表 3 雅布赖地区埃达克岩中斜长石电子探针分析结果
Table 3 Electron microprobe data of plagioclase from the Yabulai adakite
% 测点 D5822-1-1闪长岩 D7135-1-1石英闪长岩 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Na2O 6.42 6.44 6.10 8.48 8.10 5.87 6.05 5.33 5.67 5.40 5.68 1.65 2.55 2.93 6.15 MgO 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.03 0.00 0.00 0.01 0.02 0.00 0.02 0.00 0.02 0.06 0.00 0.00 Al2O3 26.02 25.92 26.17 24.48 24.90 27.45 27.33 27.85 26.59 27.01 26.10 31.39 30.50 29.71 26.13 SiO2 58.84 58.51 58.27 64.32 64.03 57.30 58.22 56.11 56.32 56.30 56.71 47.32 49.36 50.33 58.72 FeO 0.05 0.05 0.04 0.00 0.01 0.09 0.08 0.16 0.18 0.12 0.08 0.16 0.18 0.10 0.05 MnO 0.00 0.01 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.06 0.00 0.04 0.03 0.00 0.00 0.02 0.00 0.00 0.00 TiO2 0.03 0.09 0.05 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.05 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.03 0.00 0.00 0.00 Cr2O3 0.01 0.06 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.03 0.02 0.00 0.01 0.00 0.03 0.00 0.00 0.03 0.00 K2O 0.08 0.05 0.05 0.02 0.01 0.06 0.09 0.03 0.07 0.03 0.06 0.02 0.04 0.02 0.03 CaO 7.86 8.41 8.76 2.71 2.04 8.19 7.96 10.25 10.63 10.81 10.55 18.49 17.13 15.99 8.75 P2O5 0.01 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.00 0.00 0.01 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.01 0.00 0.03 0.05 NiO 0.00 0.00 0.02 0.01 0.00 0.01 0.02 0.01 0.00 0.05 0.02 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 V2O3 0.00 0.00 0.02 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.02 0.02 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.02 总计 99.32 99.55 99.51 100.06 99.09 99.06 99.78 99.84 99.50 99.76 99.23 99.12 99.83 99.14 99.90 An 40 42 44 15 12 43 42 51 51 52 51 86 79 75 44 Ab 59 58 56 85 88 56 58 48 49 47 49 14 21 25 56 Or 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 -
Defant M J, Drummond M S. Derivation of some modern arc magmas by melting of young subducted lithosphere[J]. Nuture, 1990, 347(18): 662-665. http://www.nature.com/articles/347662a0
Rapp R P, Watson E B, Miller C F. Partial melting of amphiboliteeclogite and the origin of Archean trondhjemites and tonalities[J]. Precambrian Research, 1991, 51: 1-25. doi: 10.1016/0301-9268(91)90092-O
Kay S M, Ramos V A, Marquez M. Evidence in Cerro Pampa volcanic rocks for slab-melting prior to ridge-trench collision in southern South America[J]. Journal of Geology, 1993, 101(6): 703-714. doi: 10.1086/648269
Atherton M P, Petferd N. Generation of sodium-rich magmas from newly underplated basaltic crust[J]. Nature, 1993, 362(6416): 144-146. doi: 10.1038/362144a0
Atherton M P, Petford N. Plutonism and the growth of Andean crust at 9°S from 100 to 3 Ma[J]. Journal of South American Earth Sciences, 1996, 9(1): 1-9. http://www.researchgate.net/profile/Nick_Petford/publication/32975166_Plutonism_and_the_growth_of_Andean_Crust_at_9S_from_100_to_3_Ma/links/56125c6008aec422d117665a.pdf
王焰, 张旗, 钱青. 埃达克岩(adakite)的地球化学特征及其构造意义[J]. 地质科学, 2000, 35(2): 251-256. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0563-5020.2000.02.016 张旗, 王焰, 钱青, 等. 中国东部燕山期埃达克岩的特征及其构造-成矿意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2001, 17(2): 236-244. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200102007.htm 张旗, 王焰, 刘伟, 等. 埃达克岩的特征及其意义[J]. 地质通报, 2002, 21(7): 431-435. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2002.07.012 张旗, 王焰, 王元龙. 埃达克岩与构造环境[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2003, 27(2): 101-108. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1552.2003.02.001 王强, 许继锋, 赵振华. 一种新的火成岩——埃达克岩的研究综述[J]. 地球科学进展, 2001, 16(2): 201-208. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2001.02.010 王强, 许继峰, 赵振华, 等. 埃达克质岩的构造背景与岩石组合[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2008, 27(4): 344-350. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2008.04.003 朱弟成, 段丽萍, 廖忠礼, 等. 两类埃达克岩(Adakite)的判别[J]. 矿物岩石, 2002, 22(3): 5-9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6872.2002.03.002 罗照华, 柯珊, 谌宏伟. 埃达克岩的特征、成因及构造意义[J]. 地质通报, 2002, 21(7): 436-440. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2002.07.013 董申保, 田伟. 埃达克岩的原义、特征与成因[J]. 地学前缘, 2004, 11(4): 585-594. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2004.04.025 邱士东, 董增产, 辜平阳. 柴达木盆地北缘西端埃达克质花岗岩的发现及地质意义[J]. 地质学报, 2015, 89(7): 1231-1243. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2015.07.007 翟明国. 埃达克岩和大陆下地壳重熔的花岗岩类[J]. 岩石学报, 2004, 20(2): 193-194. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200402000.htm Castillo P R. Adakite petrogenesis[J]. Lithos, 2012, 134(3): 304-316. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S002449371100274X
Muir R J, Ireland T R, Weaver S D, et al. Ion microprobe dating of Paleozoic granitoids: Devonian magmatism in New Zealand and correlations with Australia and Antarctica[J]. Chemical Geology, 1996, 127(1/3): 191-210. http://people.rses.anu.edu.au/ireland_t/All_Publications_files/037_1996_MuirA.pdf
张旗, 许继峰, 王焰, 等. 埃达克岩的多样性[J]. 地质通报, 2004, 23(9): 959-965. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2004.09.020 唐卓, 王国强, 李向民, 等. 北祁连走廊南山西水地区加里东期大野口埃达克质闪长玢岩的成因及其地质意义[J]. 地质通报, 2018, 37(4): 716-723. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20180418&flag=1 Feng J Y, Xiao W J, Brian Windley, et al. Field geology, geochronology and geochemistry of mafic-ultramafic rocks from Alxa, China: Implications for Late Permian accretionary tectonics in the southern Altaids[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2013, 78(78): 114-142. http://www.zhangqiaokeyan.com/academic-journal-foreign_other_thesis/0204112273423.html
叶珂, 张磊, 王涛, 等. 阿拉善雅布赖山二叠纪中酸性岩浆岩年代学、地球化学、锆石Hf同位素特征及构造意义[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2016, 35(6): 901-928. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2016.06.001 王凯垒, 张家兴, 张学萌, 等. 阿拉善地块北缘西段雅布赖岩体暗色微粒包体的岩浆混合成因[J]. 地质论评, 2020, 66(1): 13-34. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP202001002.htm 仵康林. 阿拉善地区华力西晚期花岗岩类岩石地球化学特征及其构造意义[D]. 长安大学硕士学位论文, 2011. 张建军, 张磊, 王涛, 等. 内蒙古阿拉善地区二叠纪曼德林乌拉岩体年龄、成因及其地质意义[J]. 地质通报, 2019, 38(10): 1675-1690. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20191009&flag=1 史兴俊, 童英, 王涛, 等. 内蒙古西部阿拉善地区哈里努登花岗岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄和地球化学特征[J]. 地质通报, 2012, 31(5): 662-670. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2012.05.003 Dan W, Li X H, Wang Q, et al. An Early Permian(ca. 280 Ma) silicic igneous province in the Alxa Block; NW China: A magmatic flare-up triggered by a mantle-plume?[J]. Lithos, 2014, 204: 144-158. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2014.01.018
Dan W, Wang Q, Wang X C, et al. Overlapping Sr-Nd-Hf-O isotopic compositions in Permian mafic enclaves and host granitoids in Alxa Block, NW China: Evidence for crust-mantle interaction and implications for the generation of silicic igneous Provinces[J]. Lithos, 2015, 230: 133-145. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2015.05.016
张建军. 阿拉善地块北部二叠纪花岗岩类成因及地质意义[D]. 中国地质大学(北京)博士学位论文, 2015. 肖进, 孙萍, 徐琳. 阿拉善北部诺尔公地区早二叠世辉长岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄、地球化学特征及成因[J]. 西部资源, 2016, (4): 55-60. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBZY201604021.htm 张磊, 史兴俊, 张建军, 等. 内蒙古阿拉善北部陶豪托西圈辉长岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄和地球化学特征[J]. 地质通报, 2013, 32(10): 1536-1547. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2013.10.005 王廷印, 王金荣, 刘金坤, 等. 宗乃山-沙拉扎山陆壳基底火山弧火成岩组合及地球化学特征[J]. 地球化学, 1994, 23(S1): 162-172. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX4S1.018.htm 吴泰然, 何国琦. 内蒙古阿拉善地块北缘的构造单元划分及各单元的基本特征[J]. 地质学报, 1993, 67(2): 97-108. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE199302000.htm 田健, 滕学建, 刘洋, 等. 内蒙古狼山地区早石炭世石英闪长岩U-Pb年龄、地球化学特征及其对古亚洲洋俯冲的指示[J]. 地质通报, 2020, 39(7): 1035-1045. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20200710&flag=1 Zheng R G, Wu T R, Zhang W, et al. Late Paleozoic subduction system in the northern margin of the Alxa block, Altaids: Geochronological and geochemical evidences from ophiolites[J]. Gondwana Research, 2014, 25(2): 842-858. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2013.05.011
耿元生, 周喜文. 阿拉善变质基底中的早二叠世岩浆热事件——来自同位素年代学的证据[J]. 岩石学报, 2012, 28(9): 2667-2685. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201209002.htm Zhang J J, Wang T, Zhang L, et al. Tracking deep crust by zircon xenocrysts within igneous rocks from the northern Alxa, China: Constraints on the southern boundary of the Central Asian Orogenic Belt[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2015, 108(108): 150-169. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1367912015002163
张家兴, 王凯垒. 阿拉善地块北缘雅布赖地区辉长岩的锆石U-Pb定年及地球化学特征[J]. 地质学刊, 2021, 45(1): 13-20. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-3636.2021.01.003 王德滋, 谢磊. 岩浆混合作用: 来自岩石包体的证据[J]. 高校地质学报, 2008, 14(1): 16-21. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2008.01.002 Liu Y S, Gao S, Hu Z C, et al. Continental and oceanic crust recycling-induced melt-peridotite interactions in the Trans-North China Orogen: U-Pb dating, Hf isotopes and trace elements in zircons from mantle xenoliths[J]. Journal of Petrology, 2010, 51(1/2): 537-571. http://www.ingentaconnect.com/content/oup/petroj/2010/00000051/F0020001/art00023
Frost B R, Barnes C G, Collins W J, et al. A geochemical classification for granitic rocks[J]. Journal of Petrology, 2001, 42(11): 2033-2048. doi: 10.1093/petrology/42.11.2033
Maniar P D, Piccoli P M. Tectonic discrimination of granitoids[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 1989, 101(5): 635-643. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1989)101<0635:TDOG>2.3.CO;2
Boynton W V. Geochemistry of the rare earth elements: meteorite studies[C]//Henderson P. Rare Earth Element Geochemistry. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 1984: 63-114.
Sun S S, Mcdonough W F. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: implications for mantle composition and processes[J]. Geological Society London Special Publications, 1989, 42(1): 313-345. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.1989.042.01.19
葛小月, 李献华, 陈志刚, 等. 中国东部燕山期高Sr低Y型中酸性火成岩的地球化学特征及成因: 对中国东部地壳厚度的制约[J]. 科学通报, 2002, 47(6): 474-480. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2002.06.018 Prouteau G, Scaillet B, Pichavant M, et al. Evidence for mantle metasomatism by hydrous silicic melts derived from subducted oceanic crust[J]. Nature, 2001, 410: 197-200. doi: 10.1038/35065583
王文龙, 滕学建, 刘洋, 等. 内蒙古狼山地区中三叠世早期C型埃达克岩的发现及其构造意义[J]. 地球科学, 2019, 44(1): 220-233. Wang Q, Mcdermott F, Xu J F, et al. Cenozoic K-rich adakitic volcanic rocks in the Hohxil area, northern Tibet: Lower-crustal melting in an intracontinental setting[J]. Geology, 2005, 33(6): 465-468. doi: 10.1130/G21522.1
Gao S, Rudnick R L, Yuan H L, er al. Recycling lower continental crust in the North China craton[J]. Nature, 2004, 432(7019): 892-897. doi: 10.1038/nature03162
霍腾飞, 杨德彬, 师江朋, 等. 徐淮地区早白垩世丰山和蔡山高镁埃达克质岩: 拆沉下地壳熔融的熔体与地幔橄榄岩的反应[J]. 岩石学报, 2018, 34(6): 1669-1684. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201806008.htm 黄雄飞, 莫宣学, 喻学惠, 等. 西秦岭印支期高Sr/Y花岗岩类的成因及动力学背景——以同仁地区舍哈力吉岩体为例[J]. 岩石学报, 2014, 30(11): 3255-3270. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201411012.htm He Y S, Li S G, Hoefs J, et al. Post-collisional granitoids from the Dabie orogen: New evidence for partial melting of a thickened continental crust[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2011, 75(13): 3815-3838. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2011.04.011
Kay R W, Kay S M. Delamination and delamination magmatism[J]. Tectonophysics, 1993, 219(219): 177-189. http://www.researchgate.net/profile/Suzanne_Kay/publication/257656451_Delamination_and_delamination_magmatism/links/549334a40cf286fe31268c1f.pdf
Rapp R P, Watson E B. Dehydration melting of metabasalt at 8-32 kbar: Implications for continental growth and crust-mantle recycling[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1995, 36(4): 891-931. doi: 10.1093/petrology/36.4.891
赵宏刚, 梁积伟, 王驹, 等. 甘肃北山算井子埃达克质花岗岩年代学、地球化学特征及其构造意义[J]. 地质学报, 2019, 93(2): 329-352. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2019.02.005 史兴俊, 张磊, 王涛, 等. 内蒙古阿拉善盟北部宗乃山中酸性侵入岩年代学、地球化学及构造意义[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2014, 33(6): 989-1007. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2014.06.001 Shi X J, Wang T, Zhang L, et al. Timing, petrogenesis and tectonic setting of the Late Paleozoic gabbro-granodiorite-granite intrusions in the Shalazhashan of northern Alxa: Constraints on the southernmost boundary of the Central Asian Orogenic Belt[J]. Lithos, 2014, 208/209(208/209): 158-177. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0024493714003314




 下载:
下载: