Petrogenesis and tectonic setting of Middle Silurian A-type granite in Kaerqueka area, East Kunlun
-
摘要:
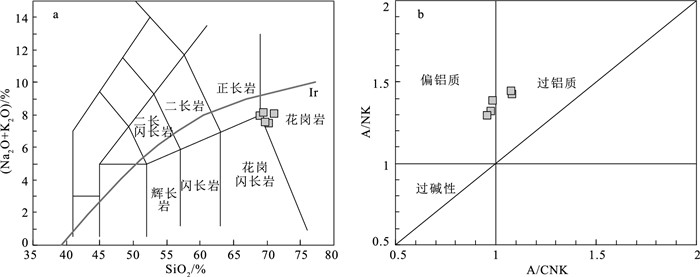
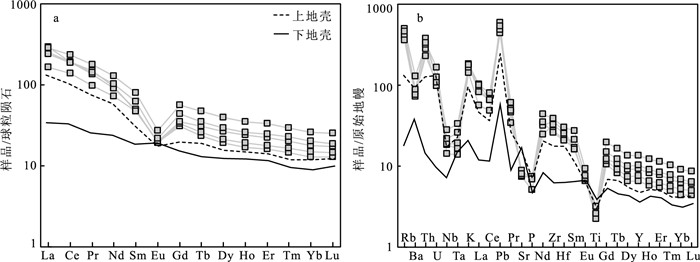
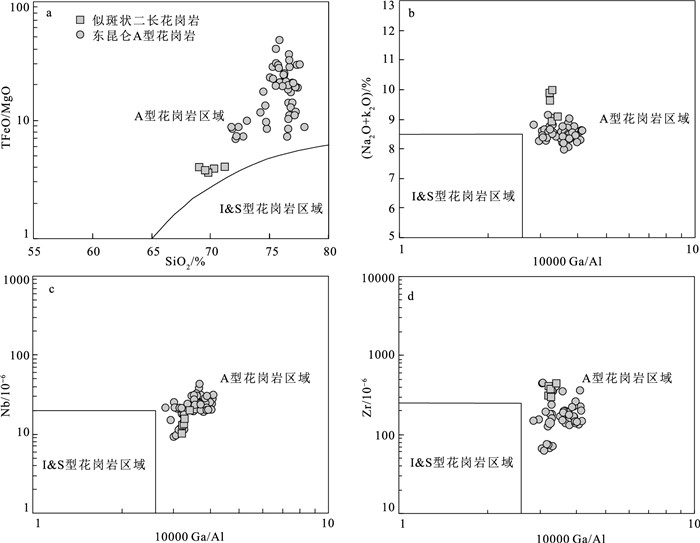
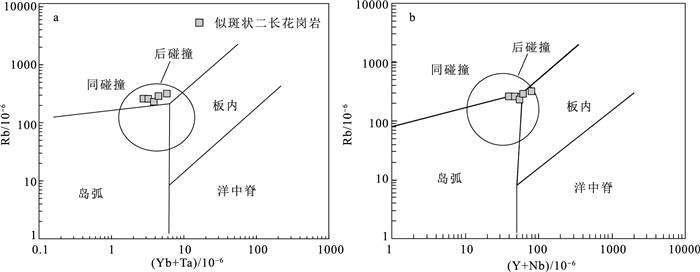
东昆仑造山带西部卡尔却卡地区出露大量似斑状二长花岗岩,对其展开岩相特征、锆石U-Pb年龄和岩石地球化学研究,结果显示,似斑状二长花岗岩年龄为425±2.3 Ma,表明其形成于中志留世。岩石具有高SiO2(69.0%~71.2%)和K2O(4.3%~5.54 %)含量,富集大离子亲石元素(Rb、K、Th和U),亏损高场强元素(Nb、Ta和Ti),强烈的负Eu异常(Eu/Eu*=0.40~0.51)特征。岩石较低的Cr、Ni含量(Cr=13.81×10-6~32.9×10-6,Ni=5.48×106~12.05×10-6)、低的Ce/Pb(2.01~4.19)和Nb/U(4.1~7.57)值,表明该岩体来自上地壳的部分熔融。岩体高10000Ga/Al值(3.22~3.42)、Zr+Nb+Ce+Y元素含量(459×10-6~656×10-6)和锆石饱和温度(827~881℃),表明其为A型花岗岩。构造图解和高的Y/Nb值(2.93~3.15)指示,该岩体为A2型花岗岩,形成于碰撞后伸展背景。结合区域岩浆岩的时空分布,表明东昆仑造山带从中志留世开始进入碰撞后伸展阶段。
Abstract:A lot of porphyritic monzogranites are outcropped in the Kaerqueka area, west of the East Kunlun orogenic belt.Zircon U-Pb age and geochemistry of the porphyritic monzonites were studied.Zircon U-Pb dating yields an age of 425±2.3 Ma, indicating Middle Silurian.The rocks are characterized by high contents of SiO2(69.0%~71.2%) and K2O(4.3%~5.54%), enrichment of large ion lithophile element(Rb, K, Th and U), depletion of high field strength element(Nb, Ta and Ti), and strong Eu negative anomaly(Eu/Eu*=0.40~0.51).Their lower content of Cr, Ni(Cr=13.81×10-6~32.9×10-6, Ni=5.48×10-6~12.05×10-6) and the lower Ce/Pb (2.01~4.19) and Nb/U(4.1~7.57) values indicate that they were originated from partial melting of the upper crust.The high ratio of 10000Ga/Al (3.22~3.42), high contents of Zr+Nb+Ce+Y(459×10-6~656×10-6) and zircon saturation temperature(827~881℃) imply they belong to A-type granite.Tectonic diagram and high Y/Nb ratio(2.93~3.15) indicate that they are A2 type granites, and were formed in the post-collision extension setting.Combined with the spatial and temporal distribution of magmatic rocks in the region, it is suggested that the East Kunlun Orogen entered the post-collision extension stage from the Middle Silurian period.
-
Keywords:
- A-type granite /
- Middle Silurian /
- post-collision extension /
- Kaerqueka area /
- East Kunlun orogen
-
致谢: 野外地质工作得到了青海地质矿产勘查三院大力帮助,吉林大学地球科学学院肖国拾、李予晋、霍亮研究员在地球化学测试与岩矿鉴定方面提供了帮助,审稿专家给出了建设性的修改意见,在此一并表示诚挚的感谢。
-
图 6 似斑状二长花岗岩TAS图解(a)和A/CNK-A/NK图解(b)[29]
Figure 6. TAS(a)and A/CNK-A/NK(b)diagrams of the porphyritic monzogranite
图 7 似斑状二长花岗岩稀土元素球粒陨石标准化图(a)和微量元素原始地幔标准化蛛网图(b)[30]
Figure 7. Chondrite-normalized REE patterns(a)and primitive mantle-normalized trace element patterns(b)of the porphyritic monzogranite
图 10 花岗岩构造环境判别图解[44]
Figure 10. Tectonic setting discriminant diagrams of granite
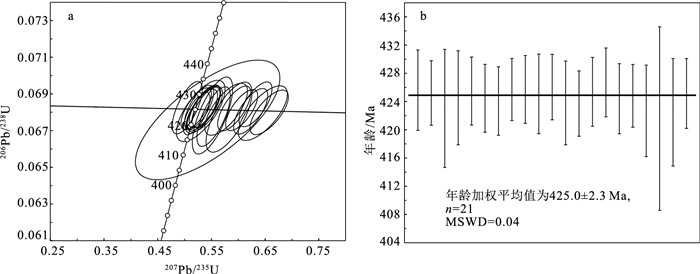
表 1 卡尔却卡地区似斑状二长花岗岩锆石U-Th-Pb测年分析结果
Table 1 Zircon U-Th-Pb dating results of the porphyritic monzogranite in Kaerqueka area
样品点 Th/10-6 U/10-6 Th/U 207Pb/206Pb 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ 207Pb/206Pb 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ KEQK-1 644 2185 0.29 0.05346 0.00205 0.50514 0.01851 0.06825 0.00094 350 85 415 12 425.6 5.7 KEQK-2 444 1845 0.24 0.05523 0.00210 0.52174 0.01873 0.06818 0.00076 420 81 426 13 425.2 4.6 KEQK-3 598 1286 0.46 0.05968 0.00296 0.55212 0.02483 0.06782 0.00139 591 107 446 16 423.0 8.4 KEQK-4 324 553 0.58 0.05610 0.00318 0.53019 0.02990 0.06807 0.00110 457 126 432 20 424.5 6.7 KEQK-5 445 1654 0.27 0.05650 0.00215 0.53636 0.02045 0.06823 0.00080 472 85 436 13 424.5 4.8 KEQK-6 652 1834 0.36 0.05649 0.00218 0.53195 0.01948 0.06806 0.00080 472 83 433 14 425.5 4.8 KEQK-7 1189 3249 0.37 0.06934 0.00238 0.65760 0.02360 0.06799 0.00080 909 76 513 14 424.1 4.8 KEQK-8 851 2870 0.30 0.05678 0.00179 0.53991 0.01729 0.06826 0.00073 483 69 438 11 425.7 4.4 KEQK-9 872 2648 0.33 0.05577 0.00196 0.52723 0.01799 0.06827 0.00080 443 80 430 12 425.7 4.8 KEQK-10 570 1254 0.45 0.06093 0.00269 0.57766 0.02628 0.06816 0.00093 635 94 463 17 425.1 5.6 KEQK-11 477 1184 0.40 0.05676 0.00205 0.53761 0.01909 0.06832 0.00077 483 47 437 13 426.0 4.6 KEQK-12 918 2493 0.37 0.06719 0.00260 0.64587 0.03016 0.06795 0.00098 843 80 506 19 423.8 5.9 KEQK-13 1092 3152 0.35 0.05545 0.00174 0.52268 0.01634 0.06794 0.00077 432 66 427 11 423.7 4.6 KEQK-14 541 3258 0.17 0.06240 0.00205 0.59267 0.02036 0.06821 0.00081 687 75 473 13 425.4 4.9 KEQK-15 821 2765 0.30 0.06650 0.00207 0.63209 0.02030 0.06843 0.00081 833 60 497 13 426.7 4.9 KEQK-16 549 1694 0.32 0.06627 0.00226 0.62327 0.02098 0.06805 0.00082 817 71 492 13 424.4 5.0 KEQK-17 1124 2801 0.40 0.06431 0.00209 0.60648 0.01969 0.06812 0.00074 754 69 481 12 424.8 4.4 KEQK-18 656 1248 0.53 0.05982 0.00219 0.55415 0.02052 0.06776 0.00107 598 80 448 13 422.7 6.5 KEQK-19 262 738 0.36 0.05798 0.00897 0.54309 0.08881 0.06758 0.00215 528 343 440 58 421.6 13.0 KEQK-20 313 1057 0.30 0.06212 0.00286 0.58292 0.02830 0.06773 0.00126 680 98 466 18 422.5 7.6 KEQK-21 513 1385 0.37 0.05674 0.00224 0.53783 0.02165 0.06817 0.00082 480 87 437 14 425.1 4.9 表 2 卡尔却卡地区似斑状二长花岗岩全岩主量、微量和稀土元素数据
Table 2 Major, trace elements and RRE composition of the porphyritic monzogranite in Kaerqueka area
元素 KE-1 KE-2 KE-3 KE-4 KE-5 元素 KE-1 KE-2 KE-3 KE-4 KE-5 SiO2 71.16 68.99 70.26 69.77 69.5 Cd 1.76 2.35 2.15 2.35 1.67 Al2O3 13.37 13.91 14.05 13.9 13.39 Sn 4.22 4.27 4.65 6.55 5.18 Fe2O3 0.93 1.3 1.07 1.11 1.05 Sb 2.63 1.72 1.43 1.41 1.49 FeO 2.08 2.56 2.43 2.28 2.46 Cs 7.23 8.86 5.72 6.04 7.83 CaO 1.94 2.25 1.71 1.8 2 Ba 580.1 498.9 531.7 900.7 612.3 MgO 0.73 0.94 0.88 0.92 0.91 La 70.12 60.25 39.06 68.07 56.59 K2O 5.54 5.24 4.3 4.96 5.37 Ce 116 117.1 85.1 142.9 115.4 Na2O 2.52 2.66 3.16 2.6 2.75 Pr 14.03 12.72 9.31 16.74 13.4 TiO2 0.39 0.6 0.49 0.42 0.52 Nd 44.56 42.55 33.55 59.84 47.77 P2O5 0.11 0.16 0.15 0.16 0.15 Sm 7.14 7.55 7.14 12.22 9.47 MnO 0.08 0.09 0.08 0.07 0.1 Eu 1.15 1.1 1.17 1.57 1.27 烧失量 0.96 0.98 1.06 1.55 1.52 Gd 6.31 6.84 7.2 11.62 8.93 Li 30.11 35.55 28.78 25.5 27.38 Tb 0.88 0.97 1.15 1.77 1.32 Be 3.38 3.66 3.96 3.38 3.84 Dy 4.86 5.41 6.72 9.97 7.38 B 37.43 14.57 14.9 13.83 14.19 Ho 0.96 1.07 1.35 1.98 1.48 Sc 4.69 7.96 7.68 9.49 7.24 Er 2.64 2.98 3.72 5.44 4.06 Ti 2908 4115 3324 4103 3375 Tm 0.37 0.42 0.51 0.75 0.58 V 28.84 45.12 30.18 31.79 26.42 Yb 2.18 2.54 3.04 4.42 3.38 Cr 28.84 32.9 15.54 16.88 13.81 Lu 0.32 0.37 0.44 0.63 0.48 Mn 748 740 733 852 645 Hf 6.72 8.46 7.89 9.28 6.4 Co 6.15 8.02 5.96 4.44 5.83 Ta 0.57 0.67 0.79 1.38 1.07 Ni 7.22 12.05 6.3 5.48 5.53 W 1.09 1.09 1.77 1.56 1.32 Cu 17.2 12.57 8.66 5.92 15.69 Tl 1.31 1.28 1.23 1.53 1.45 Zn 61.43 83.04 77.18 77.66 66.08 Pb 34.79 31.12 42.3 34.13 37.69 Ga 22.76 23.74 24.33 25.2 23.28 Bi 0.26 0.31 0.29 0.2 0.46 Ge 4.2 4.69 3.82 4.19 4.15 Th 32.03 23.46 19.29 26.61 28.37 As 5.31 3.77 8.21 2.86 4.32 U 2.45 2.03 2.26 2.62 3.45 Se 3.06 3.74 3.1 4.8 3.68 10000Ga/Al 3.22 3.22 3.27 3.42 3.28 Rb 260.6 259.7 230 317.9 288.8 Zr+Nb+Ce+Y 458.65 564.61 507.56 655.58 467.12 Sr 154.7 155.5 188.3 159.9 167.7 TZr/℃ 836 860 865 881 827 Y 29.48 34.74 42.16 60.73 46.65 ΣREE 271.51 261.86 199.46 337.92 271.5 Zr 303.1 399.9 366.9 432.1 289.6 (La/Yb)N 21.68 15.97 8.67 10.38 11.27 Nb 10.07 12.87 13.39 19.85 15.47 Eu/Eu* 0.51 0.46 0.49 0.4 0.42 Mo 1.16 1.43 1.64 0.98 1.14 Mg# 34.42 34.58 35.23 37.04 35.92 Ag 0.31 0.37 0.34 0.38 0.35 A/CNK 0.98 0.98 1.08 1.08 0.96 注:主量元素含量单位为%,微量和稀土元素含量单位为10-6 表 3 东昆仑造山带岩浆岩记录
Table 3 Magmatic records in East Kunlun orogen
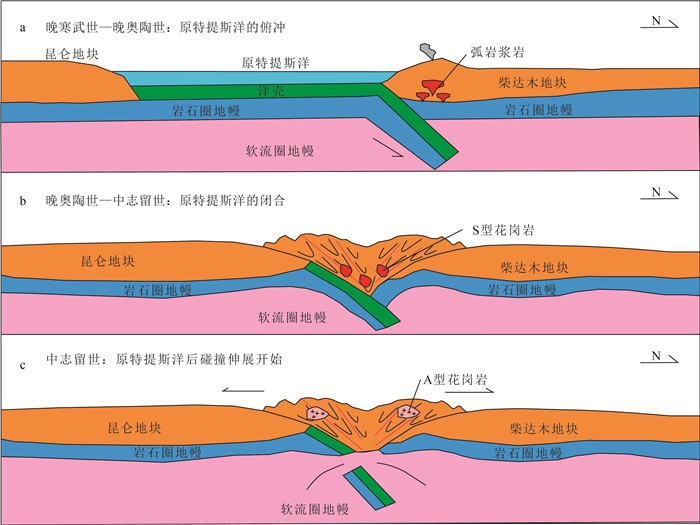
岩性 年龄/Ma 地球化学特征 采样地区 构造背景 闪长岩 493±6[47] 钙碱性 祁漫塔格 俯冲 闪长岩 480±3[47] 钙碱性 祁漫塔格 闪长岩 474±2[51] 拉班玄武岩 加当 玄武岩 474±8[52] 拉班钙碱玄武岩 纳赤台 花岗岩 454±2[53] 埃达克岩 沟里 花岗岩 452±3[54] 钙碱性 祁漫塔格 花岗闪长岩 441±6[45] 埃达克岩 布青山 花岗闪长岩 439±2[55] 埃达克岩 清水泉 流纹岩 438±3[45] 钙碱玄武岩 布青山 蓝闪石片岩 445[3] 吐木勒克 同碰撞 二长花岗岩 444[49] S型 哈日扎 榴辉岩 438~436[23] 夏日哈木 闪长岩、花岗闪长岩 432±2,432±2,427±3[14] 三铜沟 榴辉岩 450~410[56] 阿确墩 榴辉岩 432±2[17] 浪日木 榴辉岩 428±2[22] 温泉 似斑状二长花岗岩 425±2 A2型 卡尔缺卡 后碰撞伸展 花岗岩 425±2, 424±2, 426±3, 424±2[15] A2型 五龙 花岗岩 422~421[50] A2型 白干湖 花岗岩 421±2[48] 高钾钙碱性 祁漫塔格 花岗岩 420±3[48] 高钾钙碱性 祁漫塔格 二长花岗岩 419±2[20] A2型 五龙沟 花岗闪长岩 404±3[48] 高钾钙碱性 祁漫塔格 正长花岗岩 396±2[21] A2型 拉陵灶火 正长花岗岩 392±2[8] A2型 大干沟 正长花岗岩 391±1[19] A2型 夏日哈木 斑状花岗岩 391±3[57] 高钾钙碱性 祁漫塔格 正长花岗岩 391±3[10] A2型 哈拉郭勒 正长花岗岩 389±4[16] A2型 祁漫塔格山乌兰乌珠尔 花岗岩 381±1[48] 高钾钙碱性 祁漫塔格 -
许志琴, 杨经绥, 李海兵, 等. 中央造山带早古生代地体构架与高压/超高压变质带的形成[J]. 地质学报, 2006, 80(12): 1793-1806. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2006.12.002 杨经绥, 许志琴, 马昌前, 等. 复合造山作用和中国中央造山带的科学问题[J]. 中国地质, 2010, 37(1): 1-11. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201001004.htm 莫宣学, 罗照华, 邓晋福, 等. 东昆仑造山带花岗岩及地壳生长[J]. 高校地质学报, 2007, 13(3): 403-414. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2007.03.010 Yang J S, Robinson P T, Jiang C F, et al. Ophiolites of the Kunlun Mountains, China and their tectonic implications[J]. Tectonophysics, 1996, 258(1/4): 215-231. http://ci.nii.ac.jp/naid/80009051528
陆松年. 青藏高原北部前寒武纪地质初探[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2002: 1-125. 张亚峰, 裴先治, 丁仨平, 等. 东昆仑都兰县可可沙地区加里东期石英闪长岩锆石LAICP-MS U-Pb年龄及其意义[J]. 地质通报, 2010, 29(1): 79-85 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2010.01.010 赵振明, 马华东, 王秉璋, 等. 东昆仑早泥盆世碰撞造山的侵入岩证据[J]. 地质论评, 2008, 54(1): 49-58. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP200801007.htm 田广阔, 孟繁聪, 范亚洲, 等. 东昆仑早古生代造山后花岗岩的特征——以大干沟花岗岩为例[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2016, 35(3): 371-390. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2016.03.001 王晓霞, 胡能高, 王涛, 等. 柴达木盆地南缘晚奥陶世万宝沟花岗岩: 锆石SHRIMP U-Pb年龄、Hf同位素和元素地球化学[J]. 岩石学报, 2011, 28(9): 2950-2962. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201209023.htm 刘彬, 马昌前, 蒋红安, 等. 东昆仑早古生代洋壳俯冲与碰撞造山作用的转换: 来自胡晓钦镁铁质岩石的证据[J]. 岩石学报, 2013, 29(6): 2093-2106. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201306018.htm Collins W J, Beams S D, White A J R, et al. Nature and origin of A-type granites with particular reference to southeastern Australia[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy & Petrology, 1982, 80(2): 189-200. doi: 10.1007/BF00374895
King P L, White A J R, Chappell B W, et al. Characterization and Origin of Aluminous A-type Granites from the Lachlan Fold Belt, Southeastern Australia[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1997, 38(3): 371-391. doi: 10.1093/petroj/38.3.371
Loiselle M C, Wones D R. Characterization and origin of anorogenic granites[J]. Geological Society of America, Abstracts with Programs, 1979, 11(2): 448-468. http://ci.nii.ac.jp/naid/10019593683
Zhang J, Ma C Q, Xiong F H, et al. Early Paleozoic high-Mg diorite-granodiorite in the eastern Kunlun Orogen, western China: Response to continental collision and slab break-off[J]. Lithos, 2014, 210/211: 129-146. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2014.10.003
Xin Wei, Sun F Y, Li L, et al. The Wulonggou metaluminous A2-type granites in the Eastern Kunlun Orogenic Belt, NW China: Rejuvenation of subduction-related felsic crust and implications for post-collision extension[J]. Lithos, 2018: 108-127. http://smartsearch.nstl.gov.cn/paper_detail.html?id=3ed4324ec0c74cecc12ec531ab59bf7d
郭通珍, 刘荣, 陈发彬, 等. 青海祁漫塔格山乌兰乌珠尔斑状正长花岗岩LA-MC-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年及地质意义[J]. 地质通报, 2011, 30(8): 1203-1211. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2011.08.004 祁晓鹏, 范显刚, 杨杰, 等. 东昆仑东段浪木日上游早古生代榴辉岩的发现及其意义[J]. 地质通报, 2016, 35(11): 1771-1783. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2016.11.002 王艺龙, 李艳军, 魏俊浩, 等. 东昆仑五龙沟地区晚志留世A型花岗岩成因: U-Pb年代学、地球化学、Nd及Hf同位素制约[J]. 地球科学——中国地质大学学报, 2018, 43(4): 1219-1236. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201804018.htm 王冠, 孙丰月, 李碧乐, 等. 东昆仑夏日哈木矿区早泥盆世正长花岗岩锆石U-Pb年代学、地球化学及其动力学意义[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2013(4): 127-139. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK201304013.htm 严威, 邱殿明, 丁清峰, 等. 东昆仑五龙沟地区猴头沟二长花岗岩年龄、成因、源区及其构造意义[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2016, 46(2): 443-460. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ201602012.htm 陈静, 谢智勇, 李彬, 等. 东昆仑拉陵灶火地区泥盆纪侵入岩成因及其地质意义[J]. 矿物岩石, 2013, 33(2): 28-36. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWYS201302005.htm Meng F, Zhang J, Cui M. Discovery of Early Paleozoic eclogite from the East Kunlun, Western China and its tectonic significance[J]. Gondwana Research, 2013, 23(2): 825-836. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2012.06.007
张照伟, 钱兵, 李文渊, 等. 东昆仑夏日哈木铜镍矿区发现早古生代榴辉岩: 锆石U-Pb定年证据[J]. 中国地质, 2017, 44(4): 816-817. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201704016.htm 贾丽辉, 孟繁聪, 冯惠彬. 榴辉岩相峰期流体活动: 来自东昆仑榴辉岩石英脉的证据[J]. 岩石学报, 2014, 30(8): 2339-2350. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201408016.htm 姜春发, 杨经绥, 冯秉贵. 昆仑开合构造[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1992: 59-78. Yuan H, Gao S, Liu X, et al. Accurate U-Pb Age and Trace Element Determinations of Zircon by Laser Ablation-Inductively Coupled Plasma-Mass Spectrometry[J]. Geostandards and Geoanalytical Research, 2010, 28(3): 353-370. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/284091867_Accurate_U-Pb_age_and_trace_element_determinations_of_zircon_by_laser_ablation-inductively_coupled_plasma-mass_spectrometry
Anderson T. Correction of common lead in U-Pb analyses that do not report 204Pb[J]. Chemical Geology, 2002, 192(1): 59-79. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S000925410200195X
Hoskin P W O. The Composition of Zircon and Igneous and Metamorphic Petrogenesis[J]. Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry, 2003, 53(1): 27-62. doi: 10.2113/0530027
Chappell B W. Aluminium saturation in I-and S-type granites and the characterization of fractionated haplogranites[J]. Lithos, 1999, 46(3): 535-551. doi: 10.1016/S0024-4937(98)00086-3
Sun S S, Mcdonough W F. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: Implications for mantle composition and processes[J]. Geological Society London Special Publications, 1989, 42(1): 313-345. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.1989.042.01.19
Whalen J B, Currie K L, Chappell B W. A-type granites: geochemical characteristics, discrimination and petrogenesis[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy & Petrology, 1987, 95(4): 407-419. http://www.tandfonline.com/servlet/linkout?suffix=CIT0102&dbid=16&doi=10.1080%2F00206814.2017.1377121&key=10.1007%2FBF00402202
Sun J L, Qian Y, Li Y J, et al. The Late Paleoproterozoic A-Type Granites in the Jiao-Liao-Ji Orogenic Belt, North China Craton: Petrogenesis and Implications for Post-Collision Extension[J]. Geochemistry International, 2021, 59(4), 388-412. doi: 10.1134/S0016702921040078
Mushkin A, Navon O, Halicz L, et al. The petrogenesis of A-type magmas from the Amram Massif, southern Israel[J]. Journal of Petrology, 2003, 44(5): 815-832 doi: 10.1093/petrology/44.5.815
Mingram B, Trumbull R B, Littman S, et al. A petrogenetic study of anorogenic felsic magmatism in the Cretaceous Paresis ring complex, Namibia: evidence for mixing of crust and mantle-derived components[J]. Lithos, 2000, 54(1): 1-22. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0024493700000335
Yang J H, Wu F Y, Chung S L, et al. A hybrid origin for the Qianshan A-type granite, Northeast China: Geochemical and Sr-Nd-Hf isotopic evidence[J]. Lithos, 2006, 89(1): 89-106. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0024493705002264
Douce A E P. Generation of metaluminous A-type granites by low-pressure melting of calc-alkaline granitoids[J]. Geology, 1997, 25(8): 743-746. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1997)025<0743:GOMATG>2.3.CO;2
Turner S P, Foden J D, Morrison R S. Derivation of some A-type magmas by fractionation of basaltic magma: An example from the Padthaway Ridge, South Australia[J]. Lithos, 1992, 28(2): 151-179. doi: 10.1016/0024-4937(92)90029-X
Hofmann A W, Jochum K P, Seufert M, et al. Nb and Pb in oceanic basalts: new constraints on mantle evolution[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1986, 79(1): 33-45. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0012821X86900385
Taylor S R, Mclennan S M. The Continental Crust: its Composition and Evolution. An Examination of the Geochemical Record Preserved in Sedimentary Rocks[J]. Geology, 1985, 94(4): 196-197. http://mariontongpere.files.wordpress.com/2017/05/the-continental-crust-its-composition-and-evolution-an-examination-of-the-geochemical-record-preserved-in-sedimentary-rocks-by-stuart-r.pdf
Wu F Y, Sun D Y, Li H, et al. A-type granites in northeastern China: age and geochemical constraints on their petrogenesis[J]. Chemical Geology, 2002, 187(1/2): 143-173. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0009254102000189
Rapp R P, Watson E B. Dehydration Melting of Metabasalt at 8-32 kbar: Implications for Continental Growth and Crust-Mantle Recycling[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1995, 36(4): 891-931. doi: 10.1093/petrology/36.4.891
Eby N G. Chemical subdivision of the A-type granitoids: Petrogenetic and tectonic implications[J]. Geology, 1992, 20(7): 641. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1992)020<0641:CSOTAT>2.3.CO;2
Whalen J B, Jenner G A, Longstaffe F J, et al. Geochemical and Isotopic(O, Nd, Pb and Sr) Constraints on A-type Granite Petrogenesis Based on the Topsails Igneous Suite, Newfoundland Appalachians[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1996, 37(6): 1463-1489. doi: 10.1093/petrology/37.6.1463
Pearce J. Sources and settings of granitic rocks[J]. Episodes, 1996, 19(4): 120-125. doi: 10.18814/epiiugs/1996/v19i4/005
刘战庆, 裴先治, 李瑞保, 等. 东昆仑南缘阿尼玛卿构造带布青山地区两期蛇绿岩的LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年及其构造意义[J]. 地质学报, 2011, 85(2): 185-194 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201102005.htm 李王晔, 李曙光, 郭安林, 等. 青海东昆南构造带苦海辉长岩和德尔尼闪长岩的锆石SHRIMP U-Pb年龄及痕量元素地球化学——对"祁-柴-昆"晚新元古代-早奥陶世多岛洋南界的制约[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 2007, 37(增刊Ⅰ): 288-294 崔美慧, 孟繁聪, 吴祥珂. 东昆仑祁漫塔格早奥陶世岛弧: 中基性火成岩地球化学、Sm-Nd同位素及年代学证据[J]. 岩石学报, 2011, 27(11): 3365-3379. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201111017.htm Hao N, Yuan W, Zhang A, et al. Evolution process of the late Silurian-late Devonian tectonic environment in Qimantagh in the western portion of East Kunlun, China: evidence from the geochronology and geochemistry of granitoids[J]. Journal of Earth System Science, 2015, 124: 171-196. doi: 10.1007/s12040-014-0531-z
Li J Y, Qian Y, Li H R, et al. The Late Ordovician granitoids in the East Kunlun Orogenic Belt, Northwestern China: petrogenesis and constraints for tectonic evolution of the Proto-Tethys Ocean[J]. International Journal of Earth Sciences, 2020, 109(1): 1439-1461. doi: 10.1007/s00531-019-01787-7
李国臣, 丰成友, 王瑞江, 等. 新疆白干湖钨锡矿田东北部花岗岩锆石SIMS U-Pb年龄, 地球化学特征及构造意义[J]. 地球学报, 2012, 33(2): 216-226. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB201202015.htm 孔会磊, 李金超, 栗亚芝, 等. 青海东昆仑东段加当辉长岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb测年及其地质意义[J]. 地质与勘探, 2017, 53(5): 0089-0902. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT201705006.htm 陈有炘, 裴先治, 李瑞保, 等. 东昆仑东段纳赤台岩群变火山岩锆石U-Pb年龄、地球化学特征及其构造意义[J]. 地学前缘, 2013, 20(6): 1215-1216. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201306032.htm 陈加杰, 付乐兵, 魏俊浩, 等. 东昆仑沟里地区晚奥陶世花岗闪长岩地球化学特征及其对原特提斯洋演化的制约[J]. 地球科学——中国地质大学学报, 2016, 41(11): 1863-1882. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201611004.htm 李瑶. 东昆仑祁漫塔格阿确礅地区古生代花岗岩成因及大地构造意义[D]. 中国地质大学(北京) 硕士学位论文, 2017. 李瑞保. 东昆仑造山带(东段) 晚古生代-早中生代造山作用研究[D]. 长安大学博士学位论文, 2012. 李猛, 查显锋, 胡朝斌, 等. 东昆仑西段阿确墩地区白沙河岩组锆石U-Pb年龄——对前寒武纪基底演化的约束[J]. 地质通报, 2021, 40(1): 41-57. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD202101006.htm 王冠. 东昆仑造山带镍矿成矿作用研究[D]. 吉林大学博士学位论文, 2014.




 下载:
下载: