Geochronology, geochemistry and tectonic setting of the Dianzhong Formation volcanic rocks in the Riduo area, Eastern Gangdese belt, Tibet
-
摘要:
林子宗群火山岩为古近纪岩浆活动的典型代表,记录了印度与欧亚大陆碰撞造山过程。以冈底斯带东段日多地区林子宗群典中组火山岩为研究对象,对其基性和中酸性火山岩进行岩石地球化学、锆石U-Pb年代学和Lu-Hf同位素研究。LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb测年结果表明,典中组玄武岩、安山质晶屑凝灰岩锆石U-Pb年龄分别为57.9±1.2 Ma和57.4±1.2 Ma。典中组火山岩为钙碱性-高钾钙碱性岩石,其中,基性火山岩表现为低SiO2(48.67%~49.34%)、富Al2O3(15.25%~18.59%)、MgO(3.76%~8.69%),轻稀土元素相对富集和正Eu异常(δEu=1.15~1.37)特征;中酸性火山岩具有高SiO2(54.92%~64.16%)、富Al2O3(15.85%~16.72%)、K2O(0.65%~2.14%),低MgO(1.34%~3.67%)的特征,轻稀土元素富集,呈现出弱的负Eu异常(δEu=0.77~0.92)。两者不同程度富集Rb、Ba、Sr等大离子亲石元素,亏损Nb、Ta、Ti等高场强元素,球粒陨石标准化稀土元素配分模式图均呈现出右倾、轻稀土元素富集型曲线。锆石Lu-Hf同位素结果显示,基性火山岩(玄武岩)εHf(t)值为4.86~8.97,中酸性火山岩(安山质晶屑凝灰岩)εHf(t)值为0.26~6.37。结合前人研究成果,认为西藏日多地区典中组火山岩形成于古新世印度-欧亚大陆碰撞对接的同碰撞阶段,基性火山岩主要源自消减板片流体交代上覆地幔楔部分熔融的产物,中酸性火山岩主要为新生地壳的部分熔融,上升过程中均受到不同程度地壳物质的混染。
Abstract:The Linzizong Group is a typical Paleogene volcanic assemblage in the Gangdise belt, which records the orogenic history of subduction and collision between India and Eurasia.Zircon U-Pb chronology and Lu-Hf isotope studies were conducted on the Dianzhong Formation basic and intermediate volcanic rocks at the bottom of the Linzizong Group in the Riduo region of the Eastern Gangdese belt.LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb dating results show that ages of the Dianzhong Formation basalt and andesite crystalline tuff are 57.9±1.2 Ma and 57.4±1.2 Ma respectively, indicating that they were formed in the Late Paleozoic.Geochemically, the volcanic rocks generally belong to high-K(calc-alkaline) series.The basic volcanic rocks have low SiO2(48.67%~49.34%), high Al2O3(15.25%~18.59%) and high MgO(3.76%~8.69%).They are characterized by LREE enrichment and positive Eu anomalies(δEu=1.15~1.37).The intermediate volcanic rocks have high SiO2(54.92%~64.16%), high Al2O3(15.85%~16.72%), high K2O(0.65%~2.14%) and low MgO(1.34%~3.67%).They are relatively enriched in LREE and weak negative Eu anomalies(δEu=0.77~0.92).Both volcanic rocks exhibit fractionated REE and rightward patterns, strong enrichment of LILE(Rb, Ba, Sr), and depletion of HFSE(Nb, Ta, Ti).The zircon εHf(t) values of the basic volcanic rocks range from 4.86 to 8.97, and the εHf(t) values of the intermediate volcanic rocks are from 0.26 to 6.37.Based on previous results, it is suggested that the Dianzhong Formation volcanic rocks in Riduo area were formed in the syn-collision tectonic setting of the collision between India and Eurasia.The basic volcanic rocks were mainly derived from the partial melting of overlying mantle wedge metasomatized by the fluids of subducting plate, while the intermediate volcanic rocks were originated from partial melting of the juvenile crust materials, both of which were influenced by the contamination of old crustal materials to various degrees.
-
位于青藏高原南部的班公湖-怒江缝合带(BNSZ)和雅鲁藏布江缝合带(YZSZ)之间的冈底斯带岩浆活动强烈,其中林子宗群火山岩为古近纪岩浆活动的典型代表。林子宗群火山岩西起狮泉河一带,东至拉萨东部,延伸长度超过1200 km,角度不整合于中生代或更老地层之上。自下而上划分为典中组、年波组和帕那组[1-2],由具有典型弧火山岩地球化学特征的钙碱性岩石组成,其火山岩序列显示从低钾拉斑玄武岩向钙碱性-钾玄岩系列的变化特征[3-5]。该套火山岩与印度-欧亚大陆碰撞事件密切相关[6-9],记录了新特提斯洋北向俯冲到印度-欧亚大陆碰撞的过程[10],因此得到地质学者的广泛关注。前人对林子宗群火山岩的研究集中在地层学[11-12]、年代学[13-14]、岩石成因[1-5]、构造背景[3, 15]等方面,并认为林子宗群底部火山岩代表了印度-欧亚大陆碰撞的初始时间,但冈底斯东段、中段与西段火山岩形成时代差异较大,据此提出了印度与欧亚板块碰撞的多种模式,例如点-点同步碰撞[16]、由西往东或由西向东的斜向穿时性碰撞等[17-20]。林子宗群各组火山岩地球化学特征显示出同碰撞-后碰撞环境转变过程中产生的具岛弧或陆缘弧特点的火山岩[4]。
前人对冈底斯东段林子宗群火山岩的研究主要集中在林周盆地,获得典中组形成时代为64~59 Ma。例如,周肃等[14]厘定出林周盆地林子宗火山岩活动时期为64.43~43.93 Ma,典中组形成于64.43~60 Ma;陈贝贝等[21]限定的林周盆地典中组年龄范围为66~59 Ma;Huang等[22]获得典中组锆石U-Pb年龄为64~62 Ma等。但目前尚无林周盆地以东的日多地区林子宗群典中组精确的年龄报道,且研究区该套火山岩岩石成因的研究程度仍然很低,制约了对冈底斯东段同碰撞深部构造-岩浆过程的认识。
本文对日多地区林子宗群火山岩典中组进行了岩石地球化学、锆石U-Pb年代学及Lu-Hf同位素研究,厘定了火山岩的成岩时代,探讨了岩石成因与构造背景,为研究冈底斯东段印度-欧亚大陆碰撞过程提供新的证据。
1. 地质概况
冈底斯带为一巨型岩浆岩带,夹持于北部的班公湖-怒江缝合带(BNSZ)和南侧的印度河-雅鲁藏布江缝合带(YZSZ)之间(图 1-a)。自南向北,冈底斯带被划分为南冈底斯带、隆格尔-念青唐古拉带、措勤-多瓦后陆拗陷带、中冈底斯带和北冈底斯带(图 1-b)。
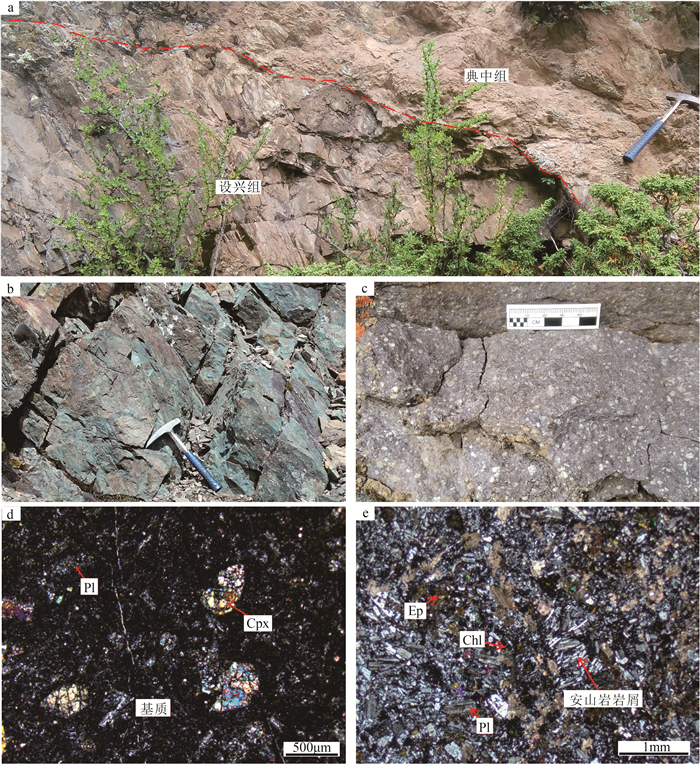
![]() 1—下中侏罗统叶巴组一段:粉砂质板岩、砂岩夹火山岩;2—下白垩统楚木龙组二段:粉砂岩、粉砂质板岩夹石英砂岩;3—下白垩统塔克那组:千枚岩、粉砂质板岩、泥晶-微晶灰岩;4—上白垩统设兴组一段:浅灰绿色绿泥绢云母化粉砂岩;5—古新统典中组火山岩;6—航木多二长花岗岩;7—逆断层/断层;8—地质界线;9—角度不整合界线;10—火山岩相界线;11—破火山口;12—安山岩;13—安山质晶屑凝灰岩;14—安山质火山角砾岩;15—安山质集块岩;16—英安质晶屑凝灰岩;17—玄武岩;18—测年样品位置(D0758/1-玄武岩,D2851/1-安山质晶屑凝灰岩);BNSZ—班公湖-怒江缝合带;YZSZ—印度河-雅鲁藏布江缝合带;SMLMF—沙莫勒-麦拉-洛巴堆-米拉山断裂;GLZCF—噶尔-隆格尔-扎日南木错-错麦断裂带;DMDF—达马错-马尔下-德庆断裂;JSSZ—金沙江缝合带;SLYNJOMZ—狮泉河-拉果错-永珠-嘉黎蛇绿混杂岩带;STDS—藏南拆离系;MBT—主边缘逆冲断层Figure 1. Tectonic position of Lhasa terrane(a, b)and geological map of the Riduo area(c)
1—下中侏罗统叶巴组一段:粉砂质板岩、砂岩夹火山岩;2—下白垩统楚木龙组二段:粉砂岩、粉砂质板岩夹石英砂岩;3—下白垩统塔克那组:千枚岩、粉砂质板岩、泥晶-微晶灰岩;4—上白垩统设兴组一段:浅灰绿色绿泥绢云母化粉砂岩;5—古新统典中组火山岩;6—航木多二长花岗岩;7—逆断层/断层;8—地质界线;9—角度不整合界线;10—火山岩相界线;11—破火山口;12—安山岩;13—安山质晶屑凝灰岩;14—安山质火山角砾岩;15—安山质集块岩;16—英安质晶屑凝灰岩;17—玄武岩;18—测年样品位置(D0758/1-玄武岩,D2851/1-安山质晶屑凝灰岩);BNSZ—班公湖-怒江缝合带;YZSZ—印度河-雅鲁藏布江缝合带;SMLMF—沙莫勒-麦拉-洛巴堆-米拉山断裂;GLZCF—噶尔-隆格尔-扎日南木错-错麦断裂带;DMDF—达马错-马尔下-德庆断裂;JSSZ—金沙江缝合带;SLYNJOMZ—狮泉河-拉果错-永珠-嘉黎蛇绿混杂岩带;STDS—藏南拆离系;MBT—主边缘逆冲断层Figure 1. Tectonic position of Lhasa terrane(a, b)and geological map of the Riduo area(c)研究区位于南冈底斯带东段的墨竹工卡县的日多地区,出露中下侏罗统叶巴组火山-沉积岩组合、下白垩统楚木龙组碎屑岩建造、下白垩统塔克那组细碎屑岩夹碳酸盐岩建造和上白垩统设兴组碎屑岩建造。这些地层普遍被古近系林子宗群典中组火山岩角度不整合覆盖。出露的侵入岩主要为古新世航木多二长花岗岩。区内断裂构造较发育,以北西向、近南北向为主[23]。
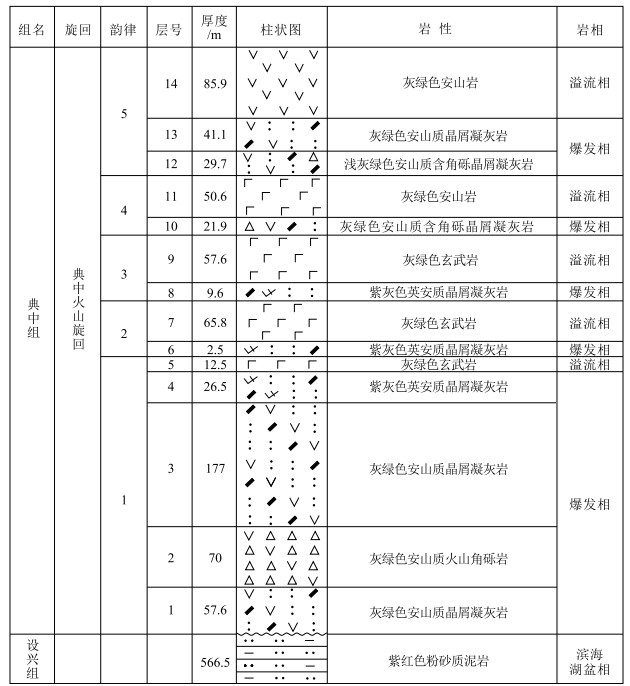
研究区典中组火山岩整体呈近东西向展布,为一套基性-中酸性陆相火山岩系,底部以角度不整合于早中侏罗世—晚白垩世地层之上(图 1-c)。根据尼龙拉一带的火山喷发旋回柱状图(图 2),典中组以中性火山碎屑岩为主,少量基性、中性火山熔岩,反映火山岩相以爆发相为主,溢流相次之。可划分为1个喷发旋回,5个喷发韵律,总厚度大于708 m,各韵律层的基本岩石组合为火山碎屑岩→火山熔岩,各韵律层间厚度由厚变薄再变厚,反映火山活动经历了一个由爆发→溢流多次脉动的活动过程,即具有火山喷发强度由强到弱的特点。底部以角度不整合于上白垩统设兴组之上(图 3-a)。岩石类型为灰绿色玄武岩、浅灰色-灰绿色玄武安山岩、安山岩、安山质(含角砾)晶屑岩屑凝灰岩、英安岩、英安质角砾晶屑凝灰岩等,少量安山质火山角砾岩、英安质集块角砾岩等。
2. 样品与分析方法
本文对典中组基性火山岩和中酸性火山岩进行了研究。2类岩石的代表性样品岩石学特征如下。
玄武岩:呈灰绿色,具斑状结构,块状构造,岩石由斑晶(20%)和基质(80%)组成。斑晶为基性斜长石和单斜辉石,斑晶斜长石粒径为0.25~1.50 mm,部分绿泥石化。单斜辉石主要为透辉石,粒径为0.25~1.60 mm,半自形-自形晶,发生绿泥石化、绿帘石化、碳酸盐化等蚀变,部分具交代假像结构或交代残余结构。基质主要由斜长石和暗色矿物组成,部分为隐晶质的火山玻璃,已次生变化(图 3-b、d)。
安山质晶屑凝灰岩:呈灰绿色,凝灰结构,块状构造,由岩屑(55%)、晶屑(25%)、火山灰(20%)组成。岩屑成分为安山质凝灰岩等,粒径小于2 mm,呈棱角状、不规则粒状;晶屑为斜长石,呈碎屑状、棱角状,粒径小于2 mm,聚片双晶发育,以拉长石和中长石为主;火山灰为中基性成分。岩石次生变化较强,主要为钠黝帘石化、绿泥石化、碳酸盐化等(图 3-c、e)。
在典中组中共采集7件火山岩样品。其中,对2件基性火山岩和5件中酸性火山岩进行了主量、微量元素测试;对其中1件基性火山岩(玄武岩)和1件中性火山岩(安山质晶屑凝灰岩)样品进行了LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb测年。
2.1 全岩化学分析
全岩主量、微量和稀土元素分析测试在核工业二○三研究所分析测试中心完成,测试结果见表 1。主量元素分析采用XRF法,在荷兰帕纳科制造的Ax-iosX射线光谱仪上测定,分析误差小于5%。经烧失量校正后,计算主要岩石地球化学参数。微量和稀土元素采用ICP-MS法,在ThermoFisherScientific制造的XSERIESⅡ型电感耦合等离子体发射光谱仪上测定,分析误差一般小于5%。分别对稀土和微量元素数据采用球粒陨石、原始地幔数据[27-28]进行标准化处理。
表 1 日多地区典中组火山岩主量、微量和稀土元素分析结果Table 1. Major, trace and rare earth element composition of the Dianzhong Formation volcanic rocks in the Riduo area样品编号 D0758/1 D2844/2 D1016/1 D3040/1 D4998/3 D4998/5 D4998/9 岩石分类 基性火山岩 中酸性火山岩 岩石名称 玄武岩 玄武安山岩 安山质晶屑凝灰岩 英安岩 SiO2 49.34 48.67 54.92 58.34 61.28 64.16 62.37 Al2O3 18.59 15.25 16.62 16.72 16.05 16.01 15.85 TFe2O3 9.14 9.98 10.44 7.45 6.13 4.95 6.31 MgO 3.76 8.69 3.67 2.82 1.70 1.34 1.66 CaO 9.44 9.30 9.36 5.23 4.04 4.11 4.40 Na2O 2.46 2.42 2.67 4.07 3.42 3.56 3.28 K2O 2.14 0.65 0.30 2.08 2.82 2.92 2.51 P2O5 0.27 0.12 0.22 0.24 0.24 0.22 0.25 MnO 0.21 0.19 0.19 0.13 0.12 0.10 0.11 TiO2 0.76 1.07 1.18 0.88 0.75 0.70 0.74 烧失量 4.00 4.21 0.32 1.92 3.30 1.91 2.36 总计 100.11 100.55 99.89 99.88 99.85 99.98 99.84 Mg# 49 67 45 47 39 37 38 里特曼指数(σ) 2.7 1.3 0.7 2.4 2 1.9 1.7 Sr 795 299 426 507 488 445 527 Zr 105 73.3 148 277 185 226 156 Ba 516 229 139 413 505 471 541 Rb 43.0 13.4 10.0 59.0 73.2 89.3 60.6 Th 6.90 1.30 6.43 7.24 5.52 9.25 7.57 U 1.45 0.68 1.13 1.5 1.45 2.51 1.43 Nb 7.31 2.40 13.45 6.27 7.01 9.67 7.12 Hf 1.86 2.02 2.95 5.29 3.91 4.91 4.13 Ta 0.72 0.38 0.80 0.50 0.66 0.70 0.52 Y 20.1 26.5 28.2 23.8 24.8 28.8 22.1 La 20.3 6.6 20.7 26.3 24.9 26.7 22.8 Ce 41.6 15.4 42.1 53.8 57.6 60.2 47.7 Pr 4.61 2.20 4.58 6.27 6.07 6.65 5.39 Nd 18.8 11.0 19.2 24.3 24.1 26.4 21.4 Sm 4.10 3.64 4.25 4.75 4.92 5.48 4.47 Eu 1.45 1.55 1.24 1.45 1.43 1.38 1.18 Gd 3.61 3.31 4.50 4.85 4.93 5.53 4.41 Tb 0.56 0.70 0.72 0.72 0.74 0.85 0.66 Dy 2.96 4.03 4.35 4.19 4.40 4.99 3.89 Ho 0.67 0.96 0.88 0.87 0.91 1.06 0.82 Er 1.74 2.17 2.69 2.62 2.71 3.14 2.42 Tm 0.25 0.42 0.37 0.39 0.39 0.46 0.36 Yb 1.58 2.21 2.49 2.51 2.65 3.00 2.38 Lu 0.24 0.30 0.38 0.43 0.43 0.48 0.37 ∑REE 102 55 108 133 136 146 118 ∑LREE/∑HREE 7.83 2.87 5.62 7.05 6.93 6.50 6.72 (La/Yb)N 9.22 2.16 5.96 7.52 6.73 6.38 6.87 δEu 1.15 1.37 0.87 0.92 0.89 0.77 0.81 注:Mg#=100×Mg2+/(Mg2++Fe2+);里特曼指数(σ)=[ω(K2O+Na2O)]2/[ω(SiO2-43)],主量元素含量单位为%,微量和稀土元素含量单位为10-6 2.2 LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb测年
分别对1件玄武岩(D0758/1)和1件安山质晶屑凝灰岩样品(D2851/1)进行锆石U-Pb年代学分析。锆石挑选由西安瑞石地质科技公司完成。LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb同位素年龄分析在西北大学大陆动力学国家重点实验室完成。将挑选出的锆石放置于环氧树脂中进行打磨,待锆石中心面露出后抛光,之后对处理好的样品进行反射光及阴极发光(CL)照相。阴极发光照相采用美国Gatan公司的MonoCL3+X型阴极荧光探头获得。锆石测试点的选择通过反射光照片和阴极发光照片反复对比,避开内部裂隙和包体,以期获得较准确的年龄数据。锆石U-Pb同位素分析在四极杆ICP-MSElan6100DRC上进行测定。激光剥蚀系统是德国MicroLas公司生产的GeoLas200M。激光束斑直径为30 μm,激光脉冲10 Hz,能量32~36 mJ。同位素组成采用澳大利亚锆石标样GEMOC GJ-1为内标进行校正,采用锆石标样Plesovice为外部标样进行监控,并采用Glitter和Isoplot进行数据处理和作图。在进行年龄数据分析时,结合206Pb/238U计算锆石各测点数据的谐和性,剔除谐和度小于90%的测点数据。
2.3 锆石Lu-Hf同位素
锆石Lu-Hf同位素分析在西北大学大陆动力学国家重点实验室完成。采用配备193 nm激光的Neptune多接收电感耦合等离子体质谱仪分析,分析过程中采用8 Hz的激光频率、100 mJ的激光强度和50 μm的激光束斑直径,以氦作为剥蚀物质的载气,采用标准锆石91500为外部标样。Hf同位素测定时采用176Lu/175Lu=0.02669和176Yb/172Yb=0.5886进行同量异位干扰校正,测定样品的176Lu/177Hf和176Hf/177Hf值。实验过程及数据处理方法见参考文献[29]。
3. 分析结果
3.1 岩石地球化学特征
3.1.1 主量元素
典中组火山岩主量元素测试结果见表 1。基性火山岩样品测试结果表明,SiO2含量为48.67%~49.34%(平均49.01%),Al2O3含量为15.25%~18.59%(平均16.92%),MgO含量为3.76%~8.69%(平均6.23%),TiO2含量为0.76%~1.07%(平均0.92%),K2O含量为0.65%~2.14%(平均1.40%),总碱量ALK为3.07%~4.60%,Mg#值为49~67,具有低SiO2、高Al2O3、富MgO的特征;中酸性火山岩样品SiO2含量为54.92%~64.16%(平均60.21%),Al2O3含量为15.85%~16.72%(平均16.25%),MgO含量为1.34%~3.67%(平均2.24%),TiO2含量为0.70%~1.18%(平均0.85%),K2O含量为0.30%~2.92%(平均2.13%),总碱量ALK为2.97%~6.48%,Mg#值介于38~47之间,表现为高SiO2、富Al2O3、K2O、低MgO的特征。
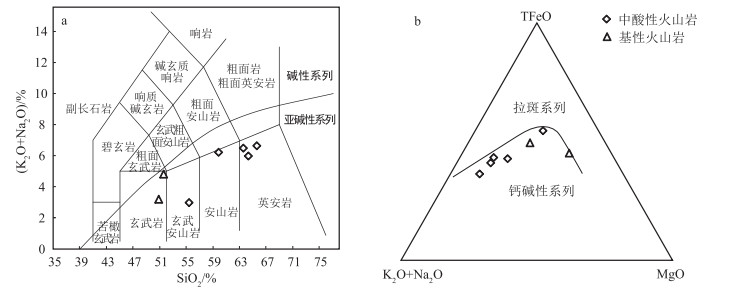
在TAS图解(图 4-a)中,基性岩和中酸性岩样品分别落入玄武岩、玄武安山岩、安山岩和英安岩区,且所有样品点均位于亚碱性系列。里特曼指数(σ)为0.7~2.7(均小于3.3),属钙碱性系列。在AFM图解(图 4-b)中,所有样品点落入钙碱性系列区。SiO2-K2O图解显示(图 5),大多数样品为高钾钙碱性系列,总体显示钙碱性-高钾钙碱性岩石特征。
3.1.2 稀土和微量元素
稀土元素分析结果显示,2件基性火山岩的稀土元素总量ΣREE为54.53×10-6~102.47×10-6,轻、重稀土元素比值ΣLREE/ΣHREE为2.87~7.83,(La/Yb)N值为2.16~9.22(平均5.69),具有正Eu异常(δEu=1.15~1.37);5件中酸性火山岩的稀土元素总量高于基性火山岩,含量为108.37×10-6~146.31×10-6,轻、重稀土元素比值为5.62~7.05,(La/Yb)N值为5.96~7.52(平均6.69),具弱的负Eu异常(δEu=0.77~0.92)。所有样品的球粒陨石标准化稀土元素配分模式图均呈现出右倾、轻稀土元素富集型曲线(图 6-a)。
在原始地幔标准化微量元素蛛网图(图 6-b)上,基性火山岩表现为Rb、Ba、Sr等大离子亲石元素相对富集,Nb、Ta、Ti等高场强元素相对亏损;中酸性火山岩表现与基性火山岩相似,但在微量元素含量及富集程度上存在明显差异,中酸性火山岩大离子亲石元素含量较基性火山岩高,其富集程度也明显高于基性火山岩,而中酸性火山岩高场强元素Nb、Ta等元素亏损程度较基性火山岩低。
3.2 LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄
典中组玄武岩(D0758/1)和安山质晶屑凝灰岩样品(D2851/1)的锆石颗粒均呈浅黄色-无色透明,多呈自形长柱状,部分呈短柱状,长宽比为1:1~2:1,粒径在50~100 μm之间,阴极发光图像显示明显的岩浆型锆石振荡环带结构(图 7)。锆石的Th/U值较高,介于0.67~2.16之间(平均1.23)(表 2),总体显示岩浆成因锆石的特点[30]。
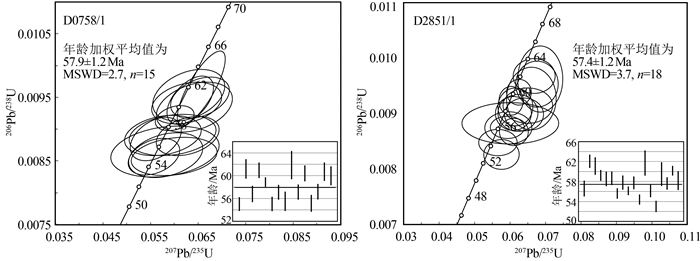
表 2 日多地区典中组火山岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Th-Pb同位素分析结果Table 2. LA-ICP-MS U-Th-Pb isotopic data of zircons from the Dianzhong Formation volcanic rocks in the Riduo area测点 含量/10-6 Th/U 同位素比值 年龄值/Ma Pb Th U 207Pb/206Pb 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ 207Pb/206Pb 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ D0758/1玄武岩 2 14.0 404 307 1.31 0.0471 0.0030 0.0558 0.0037 0.00857 0.00019 53.8 140.7 55.0 3.4 55.0 1.2 3 7.11 181 114 1.59 0.0475 0.0034 0.0630 0.0050 0.00954 0.00028 72.3 162.9 62.1 4.8 61.2 1.7 5 10.4 298 172 1.73 0.0463 0.0030 0.0560 0.0037 0.00885 0.00023 9.4 144.4 55.4 3.4 56.8 1.4 7 11.5 306 183 1.67 0.0499 0.0029 0.0653 0.0041 0.00950 0.00021 190.8 134.2 64.3 3.9 61.0 1.4 8 24.1 639 298 2.15 0.0475 0.0021 0.0600 0.0027 0.00918 0.00013 76.0 113.0 59.2 2.6 58.9 0.8 9 5.77 151 105 1.44 0.0515 0.0051 0.0599 0.0060 0.00857 0.00020 261.2 229.6 59.1 5.7 55.0 1.3 10 10.7 302 199 1.52 0.0521 0.0037 0.0628 0.0044 0.00890 0.00020 300.1 167.6 61.8 4.2 57.1 1.3 11 14.2 374 173 2.16 0.0488 0.0061 0.0580 0.0075 0.00865 0.00026 139.0 270.3 57.2 7.2 55.5 1.7 12 26.0 603 739 0.82 0.0494 0.0017 0.0656 0.0033 0.00964 0.00039 164.9 88.0 64.5 3.2 61.9 2.5 14 6.76 197 98 2.01 0.0468 0.0043 0.0575 0.0053 0.00890 0.00021 39.0 216.6 56.8 5.1 57.1 1.3 15 6.87 178 117 1.52 0.0477 0.0035 0.0626 0.0049 0.00942 0.00022 87.1 162.9 61.6 4.7 60.4 1.4 16 6.55 186 127 1.47 0.0505 0.0049 0.0582 0.0051 0.00859 0.00023 216.7 211.1 57.4 4.9 55.2 1.5 18 13.6 376 218 1.72 0.0479 0.0042 0.0596 0.0060 0.00891 0.00021 100.1 187.0 58.8 5.8 57.2 1.4 20 14.8 372 229 1.62 0.0488 0.0022 0.0633 0.0032 0.00946 0.00025 139.0 105.5 62.3 3.1 60.7 1.6 23 5.57 142 102 1.40 0.0499 0.0040 0.0642 0.0053 0.00935 0.00026 190.8 177.8 63.2 5.1 60.0 1.7 D2851/1安山质晶屑凝灰岩 1 13.6 87.9 75.7 1.16 0.0497 0.0072 0.0601 0.0090 0.00882 0.00025 189.0 298.1 59.3 8.6 56.6 1.6 4 24.1 187 260 0.72 0.0496 0.0024 0.0669 0.0039 0.00967 0.00021 172.3 116.7 65.7 3.7 62.1 1.3 5 37.0 307 417 0.74 0.0504 0.0020 0.0676 0.0039 0.00953 0.00027 216.7 88.9 66.4 3.7 61.1 1.7 8 23.1 206 259 0.79 0.0478 0.0018 0.0604 0.0023 0.00923 0.00017 100.1 -112.0 59.5 2.2 59.2 1.1 9 28.0 290 276 1.05 0.0491 0.0023 0.0616 0.0033 0.00912 0.00023 153.8 109.2 60.7 3.1 58.5 1.4 12 8.46 79.1 89.0 0.89 0.0529 0.0037 0.0650 0.0046 0.00914 0.00021 327.8 156.5 64.0 4.4 58.7 1.4 14 28.0 257 350 0.73 0.0512 0.0022 0.0611 0.0027 0.00866 0.00016 250.1 98.1 60.2 2.6 55.6 1.0 15 32.5 295 322 0.92 0.0496 0.0024 0.0623 0.0037 0.00901 0.00022 189.0 114.8 61.3 3.6 57.8 1.4 16 36.3 297 410 0.72 0.0492 0.0027 0.0593 0.0032 0.00875 0.00013 166.8 123.1 58.5 3.0 56.2 0.9 17 67.9 613 767 0.80 0.0484 0.0019 0.0610 0.0033 0.00900 0.00020 120.5 88.0 60.1 3.2 57.8 1.3 19 15.6 119 158 0.75 0.0482 0.0028 0.0567 0.0036 0.00848 0.00016 109.4 129.6 56.0 3.4 54.4 1.0 20 52.4 525 533 0.99 0.0512 0.0019 0.0685 0.0042 0.00962 0.00039 250.1 89.8 67.3 4.0 61.7 2.5 21 23.6 289 187 1.55 0.0494 0.0032 0.0595 0.0044 0.00874 0.00019 164.9 151.8 58.7 4.2 56.1 1.2 22 21.5 163 244 0.67 0.0513 0.0031 0.0576 0.0033 0.00826 0.00018 253.8 138.9 56.9 3.2 53.0 1.1 23 43.9 444 456 0.97 0.0520 0.0027 0.0660 0.0046 0.00927 0.00037 283.4 118.5 64.9 4.4 59.5 2.4 27 19.6 159 236 0.68 0.0520 0.0030 0.0639 0.0036 0.00898 0.00019 283.4 131.5 62.9 3.5 57.6 1.2 28 63.6 581 664 0.88 0.0480 0.0014 0.0626 0.0023 0.00938 0.00015 98.2 70.4 61.6 2.2 60.2 1.0 30 24.7 278 204 1.37 0.0506 0.0032 0.0624 0.0044 0.00907 0.00030 220.4 141.6 61.5 4.2 58.2 1.9 锆石U-Pb同位素测年结果显示,1件玄武岩样品(D0758/1)校正后有效测点为15个,206Pb/238U年龄值介于55.0~61.9 Ma之间,对应的加权平均值为57.9±1.2 Ma;1件安山质晶屑凝灰岩样品(D2851/1)校正后有效测点为18个,206Pb/238U年龄值介于53.0~62.1 Ma之间,加权平均值为57.4±1.2 Ma。2件样品锆石U-Pb定年结果在误差范围内一致,推测日多地区典中组火山岩形成时代为古新世。
3.3 锆石Lu-Hf同位素
在LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb测年的基础上,对玄武岩(D0758/1)和安山质晶屑凝灰岩(D2851/1)分别进行了锆石原位Lu-Hf同位素分析。测试及相关计算结果见表 3,所有测点均选取与锆石U-Pb年代学测试点相同部位(图 7)。所测锆石176Lu/177Hf值为0.001389~0.004568,表明放射性成因的Hf积累较少,可用于火山岩的成因研究[31-32]。玄武岩样品(D0758/1)的176Hf/177Hf值介于0.282879~0.282996之间,平均值为0.282947,εHf(t)值为4.86~8.97,平均值为7.26;安山质晶屑凝灰岩样品(D2851/1)的176Hf/177Hf值介于0.282752~0.282923之间,平均值为0.282827,εHf(t)值为0.26~6.37,平均值为2.99。
表 3 日多地区典中组火山岩锆石Lu-Hf同位素分析结果Table 3. Lu-Hf isotopic data of zircons from the Dianzhong Formation volcanic rocks in the Riduo area测点编号 t/Ma 176Yb/177Hf 2σ 176Lu/177Hf 2σ 176Hf/177Hf 2σ εHf(0) εHf(t) tDM1/Ma tDM2/Ma D0758/1玄武岩 3 61.2 0.078482 0.000488 0.003121 0.000009 0.282994 0.000030 7.74 8.96 392 558 7 61.0 0.068604 0.000780 0.002834 0.000025 0.282968 0.000028 6.81 8.03 429 618 8 58.9 0.085772 0.001875 0.003356 0.000059 0.282935 0.000026 5.64 6.80 485 695 9 55.0 0.048382 0.000772 0.002026 0.000030 0.282896 0.000026 4.31 5.45 522 778 11 55.5 0.062427 0.000684 0.002425 0.000024 0.282996 0.000023 7.84 8.97 381 553 12 61.9 0.117556 0.005751 0.004568 0.000219 0.282994 0.000022 7.66 8.83 413 567 14 57.1 0.052639 0.001068 0.002079 0.000037 0.282950 0.000020 6.23 7.40 444 655 15 60.4 0.078384 0.000460 0.003189 0.000016 0.282946 0.000028 6.02 7.21 467 669 16 55.2 0.062395 0.001212 0.002504 0.000052 0.282949 0.000029 6.17 7.29 451 661 18 57.2 0.058012 0.001090 0.002296 0.000038 0.282907 0.000027 4.70 5.87 510 753 20 60.7 0.073338 0.000904 0.002985 0.000033 0.282879 0.000027 3.65 4.86 564 820 23 60.0 0.044750 0.001483 0.001842 0.000057 0.282951 0.000028 6.26 7.50 440 651 D2851/2安山质晶屑凝灰岩 1 56.6 0.046272 0.001210 0.001941 0.000049 0.282858 0.000025 2.98 4.15 576 862 4 62.1 0.070582 0.001031 0.002887 0.000034 0.282824 0.000023 1.73 2.97 644 942 8 59.2 0.055712 0.000239 0.002192 0.000009 0.282866 0.000021 3.23 4.45 569 845 9 58.5 0.050771 0.000300 0.002027 0.000008 0.282830 0.000020 1.96 3.16 619 927 12 58.7 0.034924 0.000499 0.001389 0.000018 0.282822 0.000018 1.70 2.93 619 942 15 57.8 0.078208 0.000511 0.003208 0.000013 0.282923 0.000028 5.23 6.37 501 721 16 56.2 0.079574 0.000772 0.003205 0.000017 0.282814 0.000029 1.36 2.48 665 969 17 57.8 0.100605 0.001505 0.003989 0.000046 0.282832 0.000027 1.97 3.09 654 931 19 54.4 0.071036 0.000351 0.003005 0.000009 0.282752 0.000030 -0.83 0.26 754 1109 20 61.7 0.098993 0.000930 0.003906 0.000029 0.282816 0.000030 1.38 2.58 678 966 21 56.1 0.083099 0.002810 0.003230 0.000113 0.282764 0.000028 -0.39 0.72 740 1080 22 53.0 0.069312 0.001323 0.002846 0.000049 0.282787 0.000029 0.42 1.48 698 1030 23 59.5 0.074525 0.000991 0.002934 0.000029 0.282785 0.000029 0.35 1.53 703 1031 27 57.6 0.075913 0.001345 0.002986 0.000047 0.282868 0.000027 3.30 4.45 579 844 28 60.2 0.097575 0.001446 0.003906 0.000039 0.282859 0.000027 2.92 4.09 611 869 30 58.2 0.062287 0.000458 0.002584 0.000013 0.282829 0.000027 1.90 3.08 631 932 注:εHf(t) = 10, 000 × {[(176Hf/177Hf)s-(176Lu/177Hf)s × (eλt-1)]/[(176Hf/177Hf)CHUR, 0-(176Lu/177Hf)CHUR, 0 × (eλt-1)]-1}, tDM1 = (1/λ) ×ln{1+[(176Hf/177Hf)s-(176Hf/177Hf)DM]/[(176Lu/177Hf)s-(176Lu/177Hf)DM], tDM2 = t + (1/λ) × ln{1+[(176Hf/177Hf)s, t-(176Hf/177Hf)DM, t]/[(176Lu/177Hf)c-(176Lu/177Hf)DM]}。(176Hf/177Hf)s, (176Lu/177Hf)s为样品测量值, (176Hf/177Hf)CHUR, 0 = 0.282772, (176Lu/177Hf)CHUR, 0 = 0.0332, (176Hf/177Hf)DM = 0.28325, (176Lu/177Hf)DM = 0.0384, (176Lu/177Hf)c = 0.015, λ = 1.867 × 10-11/a, t为锆石结晶年龄 4. 讨论
4.1 成岩时代
日多地区位于林周盆地以东约120 km。本次研究显示,冈底斯东段日多地区典中组火山岩以基性-中酸性火山碎屑岩为主,具有与邻区林周盆地典中组相似的岩石组合[14],研究区可见典中组底部与设兴组呈角度不整合接触。本次采集的典中组玄武岩和安山质晶屑凝灰岩样品锆石206Pb/238U年龄加权平均值分别为57.9±1.2 Ma、57.4±1.2 Ma,与前人获得的林周盆地典中组形成时代(64.43~59 Ma)上限接近,表明日多地区典中组火山岩形成于古新世。
冈底斯带林子宗群典中组火山岩大量年代学研究结果表明(表 4),典中组火山岩形成时代由冈底斯带东段向西段存在明显差异,东段、中段、西段的年龄分别为60.6~70.9 Ma、64.8~83.4 Ma和61.9~82.2 Ma。其中,最老年龄出现在冈底斯西段的石巴罗和中段的申扎地区,最年轻年龄出现在冈底斯东段的林周盆地。印度与欧亚大陆板块碰撞具有穿时性,其碰撞可能开始于西段和中段,东段最后才发生碰撞。莫宣学等[8, 33]认为,林子宗群火山岩不整合覆盖于中生代褶皱构造层之上,是印度-欧亚陆块初始碰撞的证据和标志。本次获得的典中组年龄,可能代表了冈底斯东段印度-欧亚陆块的碰撞时间。
表 4 冈底斯带典中组火山岩形成时代Table 4. Formation age of the Dianzhong Formation volcanic rocks in the Gangdise belt位置 采样地点 岩性 年龄/Ma 测试方法 数据来源 冈底斯东段 南木林 英安岩、安山岩 60.6~64.4 Ar-Ar [34] 林周盆地 安山岩 65~57 Ar-Ar [35] 林周盆地 安山岩 60.6~64.4 Ar-Ar [14] 林周盆地 流纹岩 62.6~68.7 U-Pb [36] 林周盆地 辉石安山岩 62~64 U-Pb [22] 林周盆地 辉石安山岩 66.0 U-Pb [21] 林周盆地 黑云母安山岩 65.8 U-Pb [21] 新嘎果地区 流纹质晶屑凝灰岩 70.9 U-Pb [37] 日多地区 安山质晶屑凝灰岩、玄武岩 57.4~57.9 U-Pb 本文 冈底斯中段 朱诺地区 流纹质晶屑凝灰岩 64.8 U-Pb [38] 措麦地区 凝灰岩 65~70 U-Pb [39] 桑桑地区 凝灰岩 69.9 U-Pb [18] 申扎地区 78.5~83.4 K-Ar ② 查孜地区 流纹质晶屑凝灰岩 70.7 U-Pb [40] 冈底斯西段 狮泉河 流纹岩 64.5 U-Pb [41] 石巴罗地区 英安岩、火山角砾岩 77.1~79.2 U-Pb ③ 69.7~75.5 Ar-Ar 塔若错和仁多地区 英安岩和流纹岩 63.9~82.2 K-Ar ④ 4.2 岩石成因
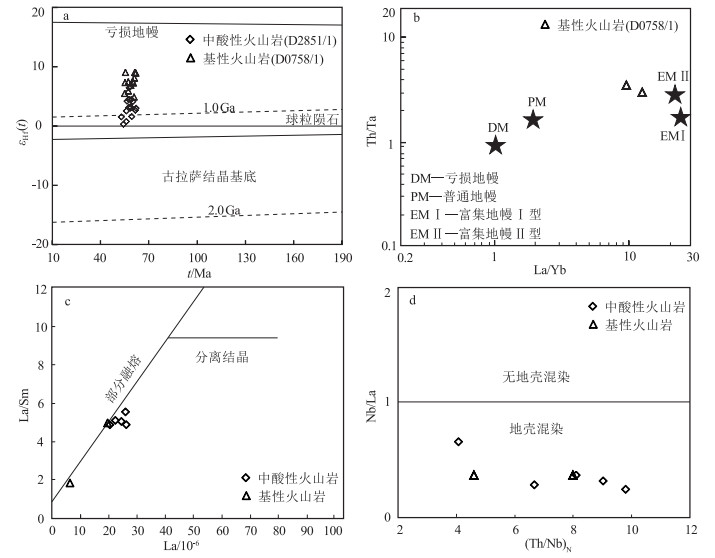
本次测得典中组玄武岩样品εHf(t)值介于4.86~8.97之间,在t-εHf(t)图解中,所有测点均落在球粒陨石和亏损地幔演化线之间(图 9-a),显示幔源属性特征。典中组玄武岩一阶段Hf模式年龄大于成岩年龄,表明岩浆源区受到地壳物质混染或来自富集地幔[32]。在La/Yb-Th/Ta图解(图 9-b)中,典中组基性火山岩偏离原始地幔而靠近富集地幔端元,岩石Nb/U值(平均值4.29)和Ta/U值(平均值0.53)偏低,都指示岩浆来源于遭受俯冲板片流体交代改造的地幔源区[42-43]。同时,典中组玄武岩具有大离子亲石元素(Rb、Ba、Sr)相对富集、高场强元素(Nb、Ta、Ti)相对亏损的地球化学特征,与典型弧玄武岩相似,指示岩浆源区存在俯冲流体的交代作用[44]。通常,幔源岩浆在上升及侵位过程中会受到不同程度地壳物质混染[45]。Th/Ta值可以有效指示基性岩在形成过程中是否存在混染的地壳物质。典中组玄武岩Th/Ta值(3.42~9.58)介于原始地幔(2.3)和大陆地壳(10)之间,且样品的Mg#值(49~67)略低于原生玄武岩变化范围(Mg#=68~75)[46],说明玄武质岩浆在上升或侵位过程中还可能受到一定程度的地壳物质混染。
中性火山岩的形成一般有2种模式:一是基性岩浆的结晶分异作用[47];二是来自幔源基性岩浆的热量使下地壳物质脱水发生重熔的产物[48-49]。安山质晶屑凝灰岩相对富集Rb、Sr等大离子亲石元素,明显亏损Nb、Ta、Ti等高场强元素,表明源区来自地壳物质。由t-εHf(t)图解(图 9-a)可见,安山质晶屑凝灰岩的εHf(t)值为0.26~6.37,接近并位于球粒陨石演化线之上,暗示岩浆在演化过程中有新端元组分的加入[32],其源区可能与新生地壳部分熔融有关。另外,在La-La/Sm图解(图 9-c)中,所有样品显示出部分熔融的特点。(Th/Nb) N-Nb/La图解(图 9-d)进一步表明,中性火山岩也经历了地壳混染作用。
此外,根据前人大量的Hf同位素数据,南部拉萨地体以新生地壳为主,中部拉萨地体存在古老结晶基底[50-51]。研究区典中组火山岩主要分布于南部拉萨地体,结合研究区岩石地球化学及Hf同位素特征,指示日多地区典中组中酸性火山岩可能为热的基性岩浆底侵到新生地壳使地壳岩石发生部分熔融而成,而基性火山岩可能起源于遭受板块俯冲流体交代的地幔源区,两者在上升过程中均受到不同程度地壳物质的混染。
4.3 构造环境
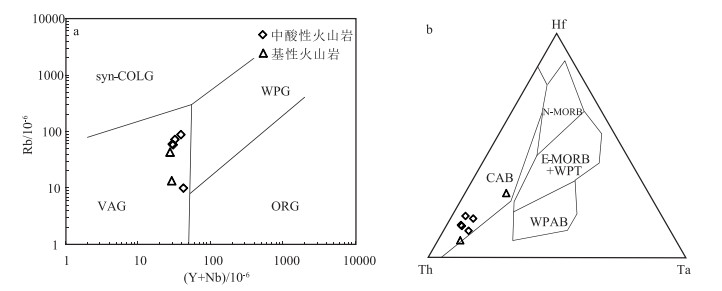
岩石地球化学特征表明,典中组火山岩在地球化学上属于钙碱性-高钾钙碱性岩石,球粒陨石标准化稀土元素配分模式图呈向右缓倾的轻稀土元素富集型曲线,相对富集Rb、Ba、Sr等大离子亲石元素,而相对亏损Nb、Ta、Ti等高场强元素,且基性火山岩TiO2含量(平均0.92%)与岛弧玄武岩接近(0.98%),总体显示出俯冲背景下弧火山岩的地球化学特征,与区域上典中组火山岩地球化学特征一致[7]。在(Y+Nb)-Rb图解(图 10-a)中,所有样品点均投入弧火山岩区;在Rb/30-Hf-3Ta图解(图 10-b)中,样品点亦投入钙碱性弧火山岩区。结合上述岩石的源区属性、岩石地球化学特征及构造环境判别图解,典中组火山岩为形成于俯冲消减构造背景下的弧火山岩,与俯冲板片脱水产生的流体交代地幔楔有关。
典中组火山岩中Ba和Sr含量明显偏低,且具有并不明显的负异常,与典型的岛弧或陆缘弧环境的钙碱性火山岩明显不同。Mo等[5]认为,洋壳蚀变作用加上成熟的地壳物质(如再生陆源沉积物)的参与,使熔体中Ba、Rb、Th、U、K、Pb的丰度增加,显示弧火山岩地球化学特征。同时也指示具有岛弧岩石地球化学特征的典中组火山岩的形成是俯冲洋壳陆-陆碰撞诱发的滞后的弧岩浆作用的效应[8, 33]。
印度-欧亚大陆碰撞经历了新特提斯洋俯冲消减-同碰撞过程。然而,基于对岩相古地理、古生物、古地磁学、区域岩石学的不同证据,印度-欧亚陆块碰撞的初始时间还存在较大争议,如莫宣学等[8]认为,印度-欧亚陆块初始碰撞的时间在西藏不晚于65 Ma,65~45 Ma处于印度和欧亚大陆从开始接触到完全接触的同碰撞阶段[7-8, 52-53];Chen等[54]通过古地磁等资料,将印度和欧亚大陆初始碰撞的时间限定在65~50 Ma之间;也有学者认为,新特提斯洋完全消亡到印度-欧亚主碰撞的时间应不早于56 Ma[55]。综合分析认为,日多地区典中组火山岩形成于57 Ma左右,应处于印度-欧亚大陆碰撞对接的同碰撞阶段,即古新世印度大陆向北漂移与欧亚大陆由西向东碰撞对接,连接在印度大陆前端的残留新特提斯洋壳滞留在欧亚大陆之下,随着俯冲深度增加、压力增大,原来低角度消减的新特提斯大洋板片阻力加大,发生回转,导致地幔楔对流增强并诱使残留的新特提斯大洋板片俯冲流体交代上覆地幔楔而发生部分熔融,产生一定量的基性岩浆,部分底侵于南拉萨地块之下,使新生地壳发生部分熔融产生中酸性火山岩,两者在上升过程中可能受到不同程度地壳物质的混染。
5. 结论
(1) LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb测年获得日多地区典中组火山岩锆石206Pb/238U年龄加权平均值为57.4±1.2 Ma、57.9±1.2 Ma,表明日多地区典中组火山岩形成时代为古新世。
(2) 典中组火山岩为钙碱性-高钾钙碱性岩石,具有弧火山岩地球化学特征。稀土元素配分曲线表现为轻稀土元素富集、重稀土元素亏损的右倾型,不同程度富集Rb、Ba、Sr等大离子亲石元素,亏损Nb、Ta、Ti等高场强元素。
(3) 冈底斯东段的日多地区典中组火山岩形成于印度-欧亚大陆同碰撞阶段。基性火山岩主要为滞留的消减板片流体诱发上覆地幔楔发生部分熔融的产物,中酸性火山岩主要源于新生地壳的部分熔融,上升过程中均受到不同程度地壳物质的混染。
致谢: 感谢审稿专家对本文提出建设性的修改意见;感谢野外工作中成都地质调查中心李光明研究员、张林奎高级工程师、西藏地勘局胡敬仁高级工程师的大力支持;感谢参与本文野外取样及数据处理的所有专家、同志。 -
图 1 拉萨地块大地构造位置(a、b)和日多地区地质简图(c)(据参考文献①[19, 24-26]修改)
1—下中侏罗统叶巴组一段:粉砂质板岩、砂岩夹火山岩;2—下白垩统楚木龙组二段:粉砂岩、粉砂质板岩夹石英砂岩;3—下白垩统塔克那组:千枚岩、粉砂质板岩、泥晶-微晶灰岩;4—上白垩统设兴组一段:浅灰绿色绿泥绢云母化粉砂岩;5—古新统典中组火山岩;6—航木多二长花岗岩;7—逆断层/断层;8—地质界线;9—角度不整合界线;10—火山岩相界线;11—破火山口;12—安山岩;13—安山质晶屑凝灰岩;14—安山质火山角砾岩;15—安山质集块岩;16—英安质晶屑凝灰岩;17—玄武岩;18—测年样品位置(D0758/1-玄武岩,D2851/1-安山质晶屑凝灰岩);BNSZ—班公湖-怒江缝合带;YZSZ—印度河-雅鲁藏布江缝合带;SMLMF—沙莫勒-麦拉-洛巴堆-米拉山断裂;GLZCF—噶尔-隆格尔-扎日南木错-错麦断裂带;DMDF—达马错-马尔下-德庆断裂;JSSZ—金沙江缝合带;SLYNJOMZ—狮泉河-拉果错-永珠-嘉黎蛇绿混杂岩带;STDS—藏南拆离系;MBT—主边缘逆冲断层
Figure 1. Tectonic position of Lhasa terrane(a, b)and geological map of the Riduo area(c)
表 1 日多地区典中组火山岩主量、微量和稀土元素分析结果
Table 1 Major, trace and rare earth element composition of the Dianzhong Formation volcanic rocks in the Riduo area
样品编号 D0758/1 D2844/2 D1016/1 D3040/1 D4998/3 D4998/5 D4998/9 岩石分类 基性火山岩 中酸性火山岩 岩石名称 玄武岩 玄武安山岩 安山质晶屑凝灰岩 英安岩 SiO2 49.34 48.67 54.92 58.34 61.28 64.16 62.37 Al2O3 18.59 15.25 16.62 16.72 16.05 16.01 15.85 TFe2O3 9.14 9.98 10.44 7.45 6.13 4.95 6.31 MgO 3.76 8.69 3.67 2.82 1.70 1.34 1.66 CaO 9.44 9.30 9.36 5.23 4.04 4.11 4.40 Na2O 2.46 2.42 2.67 4.07 3.42 3.56 3.28 K2O 2.14 0.65 0.30 2.08 2.82 2.92 2.51 P2O5 0.27 0.12 0.22 0.24 0.24 0.22 0.25 MnO 0.21 0.19 0.19 0.13 0.12 0.10 0.11 TiO2 0.76 1.07 1.18 0.88 0.75 0.70 0.74 烧失量 4.00 4.21 0.32 1.92 3.30 1.91 2.36 总计 100.11 100.55 99.89 99.88 99.85 99.98 99.84 Mg# 49 67 45 47 39 37 38 里特曼指数(σ) 2.7 1.3 0.7 2.4 2 1.9 1.7 Sr 795 299 426 507 488 445 527 Zr 105 73.3 148 277 185 226 156 Ba 516 229 139 413 505 471 541 Rb 43.0 13.4 10.0 59.0 73.2 89.3 60.6 Th 6.90 1.30 6.43 7.24 5.52 9.25 7.57 U 1.45 0.68 1.13 1.5 1.45 2.51 1.43 Nb 7.31 2.40 13.45 6.27 7.01 9.67 7.12 Hf 1.86 2.02 2.95 5.29 3.91 4.91 4.13 Ta 0.72 0.38 0.80 0.50 0.66 0.70 0.52 Y 20.1 26.5 28.2 23.8 24.8 28.8 22.1 La 20.3 6.6 20.7 26.3 24.9 26.7 22.8 Ce 41.6 15.4 42.1 53.8 57.6 60.2 47.7 Pr 4.61 2.20 4.58 6.27 6.07 6.65 5.39 Nd 18.8 11.0 19.2 24.3 24.1 26.4 21.4 Sm 4.10 3.64 4.25 4.75 4.92 5.48 4.47 Eu 1.45 1.55 1.24 1.45 1.43 1.38 1.18 Gd 3.61 3.31 4.50 4.85 4.93 5.53 4.41 Tb 0.56 0.70 0.72 0.72 0.74 0.85 0.66 Dy 2.96 4.03 4.35 4.19 4.40 4.99 3.89 Ho 0.67 0.96 0.88 0.87 0.91 1.06 0.82 Er 1.74 2.17 2.69 2.62 2.71 3.14 2.42 Tm 0.25 0.42 0.37 0.39 0.39 0.46 0.36 Yb 1.58 2.21 2.49 2.51 2.65 3.00 2.38 Lu 0.24 0.30 0.38 0.43 0.43 0.48 0.37 ∑REE 102 55 108 133 136 146 118 ∑LREE/∑HREE 7.83 2.87 5.62 7.05 6.93 6.50 6.72 (La/Yb)N 9.22 2.16 5.96 7.52 6.73 6.38 6.87 δEu 1.15 1.37 0.87 0.92 0.89 0.77 0.81 注:Mg#=100×Mg2+/(Mg2++Fe2+);里特曼指数(σ)=[ω(K2O+Na2O)]2/[ω(SiO2-43)],主量元素含量单位为%,微量和稀土元素含量单位为10-6 表 2 日多地区典中组火山岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Th-Pb同位素分析结果
Table 2 LA-ICP-MS U-Th-Pb isotopic data of zircons from the Dianzhong Formation volcanic rocks in the Riduo area
测点 含量/10-6 Th/U 同位素比值 年龄值/Ma Pb Th U 207Pb/206Pb 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ 207Pb/206Pb 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ D0758/1玄武岩 2 14.0 404 307 1.31 0.0471 0.0030 0.0558 0.0037 0.00857 0.00019 53.8 140.7 55.0 3.4 55.0 1.2 3 7.11 181 114 1.59 0.0475 0.0034 0.0630 0.0050 0.00954 0.00028 72.3 162.9 62.1 4.8 61.2 1.7 5 10.4 298 172 1.73 0.0463 0.0030 0.0560 0.0037 0.00885 0.00023 9.4 144.4 55.4 3.4 56.8 1.4 7 11.5 306 183 1.67 0.0499 0.0029 0.0653 0.0041 0.00950 0.00021 190.8 134.2 64.3 3.9 61.0 1.4 8 24.1 639 298 2.15 0.0475 0.0021 0.0600 0.0027 0.00918 0.00013 76.0 113.0 59.2 2.6 58.9 0.8 9 5.77 151 105 1.44 0.0515 0.0051 0.0599 0.0060 0.00857 0.00020 261.2 229.6 59.1 5.7 55.0 1.3 10 10.7 302 199 1.52 0.0521 0.0037 0.0628 0.0044 0.00890 0.00020 300.1 167.6 61.8 4.2 57.1 1.3 11 14.2 374 173 2.16 0.0488 0.0061 0.0580 0.0075 0.00865 0.00026 139.0 270.3 57.2 7.2 55.5 1.7 12 26.0 603 739 0.82 0.0494 0.0017 0.0656 0.0033 0.00964 0.00039 164.9 88.0 64.5 3.2 61.9 2.5 14 6.76 197 98 2.01 0.0468 0.0043 0.0575 0.0053 0.00890 0.00021 39.0 216.6 56.8 5.1 57.1 1.3 15 6.87 178 117 1.52 0.0477 0.0035 0.0626 0.0049 0.00942 0.00022 87.1 162.9 61.6 4.7 60.4 1.4 16 6.55 186 127 1.47 0.0505 0.0049 0.0582 0.0051 0.00859 0.00023 216.7 211.1 57.4 4.9 55.2 1.5 18 13.6 376 218 1.72 0.0479 0.0042 0.0596 0.0060 0.00891 0.00021 100.1 187.0 58.8 5.8 57.2 1.4 20 14.8 372 229 1.62 0.0488 0.0022 0.0633 0.0032 0.00946 0.00025 139.0 105.5 62.3 3.1 60.7 1.6 23 5.57 142 102 1.40 0.0499 0.0040 0.0642 0.0053 0.00935 0.00026 190.8 177.8 63.2 5.1 60.0 1.7 D2851/1安山质晶屑凝灰岩 1 13.6 87.9 75.7 1.16 0.0497 0.0072 0.0601 0.0090 0.00882 0.00025 189.0 298.1 59.3 8.6 56.6 1.6 4 24.1 187 260 0.72 0.0496 0.0024 0.0669 0.0039 0.00967 0.00021 172.3 116.7 65.7 3.7 62.1 1.3 5 37.0 307 417 0.74 0.0504 0.0020 0.0676 0.0039 0.00953 0.00027 216.7 88.9 66.4 3.7 61.1 1.7 8 23.1 206 259 0.79 0.0478 0.0018 0.0604 0.0023 0.00923 0.00017 100.1 -112.0 59.5 2.2 59.2 1.1 9 28.0 290 276 1.05 0.0491 0.0023 0.0616 0.0033 0.00912 0.00023 153.8 109.2 60.7 3.1 58.5 1.4 12 8.46 79.1 89.0 0.89 0.0529 0.0037 0.0650 0.0046 0.00914 0.00021 327.8 156.5 64.0 4.4 58.7 1.4 14 28.0 257 350 0.73 0.0512 0.0022 0.0611 0.0027 0.00866 0.00016 250.1 98.1 60.2 2.6 55.6 1.0 15 32.5 295 322 0.92 0.0496 0.0024 0.0623 0.0037 0.00901 0.00022 189.0 114.8 61.3 3.6 57.8 1.4 16 36.3 297 410 0.72 0.0492 0.0027 0.0593 0.0032 0.00875 0.00013 166.8 123.1 58.5 3.0 56.2 0.9 17 67.9 613 767 0.80 0.0484 0.0019 0.0610 0.0033 0.00900 0.00020 120.5 88.0 60.1 3.2 57.8 1.3 19 15.6 119 158 0.75 0.0482 0.0028 0.0567 0.0036 0.00848 0.00016 109.4 129.6 56.0 3.4 54.4 1.0 20 52.4 525 533 0.99 0.0512 0.0019 0.0685 0.0042 0.00962 0.00039 250.1 89.8 67.3 4.0 61.7 2.5 21 23.6 289 187 1.55 0.0494 0.0032 0.0595 0.0044 0.00874 0.00019 164.9 151.8 58.7 4.2 56.1 1.2 22 21.5 163 244 0.67 0.0513 0.0031 0.0576 0.0033 0.00826 0.00018 253.8 138.9 56.9 3.2 53.0 1.1 23 43.9 444 456 0.97 0.0520 0.0027 0.0660 0.0046 0.00927 0.00037 283.4 118.5 64.9 4.4 59.5 2.4 27 19.6 159 236 0.68 0.0520 0.0030 0.0639 0.0036 0.00898 0.00019 283.4 131.5 62.9 3.5 57.6 1.2 28 63.6 581 664 0.88 0.0480 0.0014 0.0626 0.0023 0.00938 0.00015 98.2 70.4 61.6 2.2 60.2 1.0 30 24.7 278 204 1.37 0.0506 0.0032 0.0624 0.0044 0.00907 0.00030 220.4 141.6 61.5 4.2 58.2 1.9 表 3 日多地区典中组火山岩锆石Lu-Hf同位素分析结果
Table 3 Lu-Hf isotopic data of zircons from the Dianzhong Formation volcanic rocks in the Riduo area
测点编号 t/Ma 176Yb/177Hf 2σ 176Lu/177Hf 2σ 176Hf/177Hf 2σ εHf(0) εHf(t) tDM1/Ma tDM2/Ma D0758/1玄武岩 3 61.2 0.078482 0.000488 0.003121 0.000009 0.282994 0.000030 7.74 8.96 392 558 7 61.0 0.068604 0.000780 0.002834 0.000025 0.282968 0.000028 6.81 8.03 429 618 8 58.9 0.085772 0.001875 0.003356 0.000059 0.282935 0.000026 5.64 6.80 485 695 9 55.0 0.048382 0.000772 0.002026 0.000030 0.282896 0.000026 4.31 5.45 522 778 11 55.5 0.062427 0.000684 0.002425 0.000024 0.282996 0.000023 7.84 8.97 381 553 12 61.9 0.117556 0.005751 0.004568 0.000219 0.282994 0.000022 7.66 8.83 413 567 14 57.1 0.052639 0.001068 0.002079 0.000037 0.282950 0.000020 6.23 7.40 444 655 15 60.4 0.078384 0.000460 0.003189 0.000016 0.282946 0.000028 6.02 7.21 467 669 16 55.2 0.062395 0.001212 0.002504 0.000052 0.282949 0.000029 6.17 7.29 451 661 18 57.2 0.058012 0.001090 0.002296 0.000038 0.282907 0.000027 4.70 5.87 510 753 20 60.7 0.073338 0.000904 0.002985 0.000033 0.282879 0.000027 3.65 4.86 564 820 23 60.0 0.044750 0.001483 0.001842 0.000057 0.282951 0.000028 6.26 7.50 440 651 D2851/2安山质晶屑凝灰岩 1 56.6 0.046272 0.001210 0.001941 0.000049 0.282858 0.000025 2.98 4.15 576 862 4 62.1 0.070582 0.001031 0.002887 0.000034 0.282824 0.000023 1.73 2.97 644 942 8 59.2 0.055712 0.000239 0.002192 0.000009 0.282866 0.000021 3.23 4.45 569 845 9 58.5 0.050771 0.000300 0.002027 0.000008 0.282830 0.000020 1.96 3.16 619 927 12 58.7 0.034924 0.000499 0.001389 0.000018 0.282822 0.000018 1.70 2.93 619 942 15 57.8 0.078208 0.000511 0.003208 0.000013 0.282923 0.000028 5.23 6.37 501 721 16 56.2 0.079574 0.000772 0.003205 0.000017 0.282814 0.000029 1.36 2.48 665 969 17 57.8 0.100605 0.001505 0.003989 0.000046 0.282832 0.000027 1.97 3.09 654 931 19 54.4 0.071036 0.000351 0.003005 0.000009 0.282752 0.000030 -0.83 0.26 754 1109 20 61.7 0.098993 0.000930 0.003906 0.000029 0.282816 0.000030 1.38 2.58 678 966 21 56.1 0.083099 0.002810 0.003230 0.000113 0.282764 0.000028 -0.39 0.72 740 1080 22 53.0 0.069312 0.001323 0.002846 0.000049 0.282787 0.000029 0.42 1.48 698 1030 23 59.5 0.074525 0.000991 0.002934 0.000029 0.282785 0.000029 0.35 1.53 703 1031 27 57.6 0.075913 0.001345 0.002986 0.000047 0.282868 0.000027 3.30 4.45 579 844 28 60.2 0.097575 0.001446 0.003906 0.000039 0.282859 0.000027 2.92 4.09 611 869 30 58.2 0.062287 0.000458 0.002584 0.000013 0.282829 0.000027 1.90 3.08 631 932 注:εHf(t) = 10, 000 × {[(176Hf/177Hf)s-(176Lu/177Hf)s × (eλt-1)]/[(176Hf/177Hf)CHUR, 0-(176Lu/177Hf)CHUR, 0 × (eλt-1)]-1}, tDM1 = (1/λ) ×ln{1+[(176Hf/177Hf)s-(176Hf/177Hf)DM]/[(176Lu/177Hf)s-(176Lu/177Hf)DM], tDM2 = t + (1/λ) × ln{1+[(176Hf/177Hf)s, t-(176Hf/177Hf)DM, t]/[(176Lu/177Hf)c-(176Lu/177Hf)DM]}。(176Hf/177Hf)s, (176Lu/177Hf)s为样品测量值, (176Hf/177Hf)CHUR, 0 = 0.282772, (176Lu/177Hf)CHUR, 0 = 0.0332, (176Hf/177Hf)DM = 0.28325, (176Lu/177Hf)DM = 0.0384, (176Lu/177Hf)c = 0.015, λ = 1.867 × 10-11/a, t为锆石结晶年龄 表 4 冈底斯带典中组火山岩形成时代
Table 4 Formation age of the Dianzhong Formation volcanic rocks in the Gangdise belt
位置 采样地点 岩性 年龄/Ma 测试方法 数据来源 冈底斯东段 南木林 英安岩、安山岩 60.6~64.4 Ar-Ar [34] 林周盆地 安山岩 65~57 Ar-Ar [35] 林周盆地 安山岩 60.6~64.4 Ar-Ar [14] 林周盆地 流纹岩 62.6~68.7 U-Pb [36] 林周盆地 辉石安山岩 62~64 U-Pb [22] 林周盆地 辉石安山岩 66.0 U-Pb [21] 林周盆地 黑云母安山岩 65.8 U-Pb [21] 新嘎果地区 流纹质晶屑凝灰岩 70.9 U-Pb [37] 日多地区 安山质晶屑凝灰岩、玄武岩 57.4~57.9 U-Pb 本文 冈底斯中段 朱诺地区 流纹质晶屑凝灰岩 64.8 U-Pb [38] 措麦地区 凝灰岩 65~70 U-Pb [39] 桑桑地区 凝灰岩 69.9 U-Pb [18] 申扎地区 78.5~83.4 K-Ar ② 查孜地区 流纹质晶屑凝灰岩 70.7 U-Pb [40] 冈底斯西段 狮泉河 流纹岩 64.5 U-Pb [41] 石巴罗地区 英安岩、火山角砾岩 77.1~79.2 U-Pb ③ 69.7~75.5 Ar-Ar 塔若错和仁多地区 英安岩和流纹岩 63.9~82.2 K-Ar ④ -
Lee H Y, Chung S L, Ji J, et al. Geochemical and Sr-Nd isotopic constraints on the genesis of the Cenozoic Linzizong volcanic successions, southern Tibet[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2012, 53(2): 96-114.
黄映聪, 杨德明, 郑常青, 等. 西藏林周县扎雪地区林子宗群帕那组火山岩的地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2005, 35(5): 576-580. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ200505004.htm Lee H Y, Chung S L, Lo C H, et al. Eocene Neotethyan slab breakoff in southern Tibet inferred from the Linzizong volcanic record[J]. Tec-tonophysics, 2009, 477(1): 20-35.
Mo X X, Hou Z Q, Niu Y L, et al. antle contributions to crustal thickening during continental collision: Evidence from Cenozoic igneous rocks in southern Tibet[J]. Lithos, 2007, 96(1): 225-242. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0024493706002933
Mo X X, Niu Y L, Dong G C, et al. Contribution of syncollisional felsic magmatism to continental crust growth: a case study of the Paleogene Linzizong volcanic succession in southern Tibet[J]. Chemical Geology, 2008, 250(1): 49-67. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0009254108000582
Zhu D C, Zhao Z D, Niu Y L, et al. The Lhasa Terrane: record of a microcontinent and its histories of drift and growth[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2011, 301(1): 241-255. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0012821X10007004
莫宣学, 赵志丹, 邓晋福. 印度-亚洲大陆主碰撞过程的火山作用响应[J]. 地学前缘, 2003, 10(3): 135-148. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2003.03.013 莫宣学, 董国臣, 赵志丹, 等. 西藏冈底斯带花岗岩的时空分布特征及地壳生长演化信息[J]. 高校地质学报, 2005, 11(3): 281-290. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2005.03.001 潘桂棠, 莫宣学, 侯增谦, 等. 冈底斯造山带的时空结构及演化[J]. 岩石学报, 2006, 22(3): 521-533. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200603001.htm 侯增谦, 杨竹森, 徐文艺, 等. 青藏高原碰撞造山带: Ⅰ. 主碰撞造山成矿作用[J]. 矿床地质, 2006, 25(4): 337-358. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2006.04.001 张博川, 范建军, 罗安波, 等. 拉萨地块东部米拉山地区中新世地层的特征及构造意义[J]. 地球科学, 2019, 44(7): 2392-2407. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201907015.htm 于云鹏, 解超明, 王伟, 等. 青藏高原陆相火山岩区填图新进展——以松多地区新生代火山机构为例[J]. 地质通报, 2018, 37(8): 129-135. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20180814&flag=1 刘安琳, 朱弟成, 王青, 等. 藏南米拉山地区林子宗火山岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄和起源[J]. 地质通报, 2015, 34(5): 826-833. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2015.05.003 周肃, 莫宣学, 董国臣, 等. 西藏林周盆地林子宗火山岩40Ar/39Ar年代格架[J]. 科学通报, 2004, 49(20): 2095-2103. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2004.20.014 Ran M L, Kang Z Q, Xu J F, et al. Evolution of the northward subduction of the Neo-Tethys: Implications of geochemistry of Cretaceous arc volcanics in Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2019, 515: 83-94. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2017.12.043
董树文, 武红岭, 刘晓春, 等. 陆-陆点碰撞与超高压变质作用[J]. 地质学报, 2002, 76(2): 163-172. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2002.02.003 韦天伟, 杨锋, 康志强, 等. 西藏拉萨地块东部尼木-加查地区林子宗群火山岩年代学, 地球化学特征及其构造意义[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(4): 715-726. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ201904004.htm 谢冰晶, 周肃, 谢国刚, 等. 西藏冈底斯中段孔隆至丁仁勒地区林子宗群火山岩锆石SHRIMP年龄和地球化学特征的区域对比[J]. 岩石学报, 2013, 29(11): 3803-3814. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201311013.htm 张运昌, 陈彦, 杨青, 等. 西藏冈底斯带中部南木林地区林子宗群火山岩锆石U-Pb年龄和地球化学特征[J]. 地质通报, 2019, 38(5): 719-732. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20190503&flag=1 周征宇, 廖宗廷. 印度板块向欧亚板块俯冲碰撞的新模式及其对青藏高原构造演化的影响[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 2005, 25(4): 826-833. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TTSD200504003.htm 陈贝贝, 丁林, 许强, 等. 西藏林周盆地林子宗群火山岩的精细年代框架[J]. 第四纪研究, 2016, 36(5): 1037-1054. Huang W T, Dupont-Nivet G, Lippert P C, et al. What was the Paleogene latitude of the Lhasa terrane? A reassessment of the geochronology and paleomagnetism of Linzizong volcanic rocks(Linzhou Basin, Tibet)[J]. Tectonics, 2015, 34: 594-622. doi: 10.1002/2014TC003787
王立全, 潘桂棠, 张万平, 等. 青藏高原及邻区大地构造图及说明书(1: 1 500 000)[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2013. 董宇超, 解超明, 于云鹏, 等. 西藏工布江达县龙崖松多榴辉岩的发现及意义[J]. 地质通报, 2018, 37(8): 1464-1471. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20180810&flag=1 董宇超, 解超明, 范建军, 等. 西藏松多地区榴辉岩的原岩属性探讨及其地质意义[J]. 地球科学, 2019, 44(7): 2234-2248. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201907004.htm 解超明, 李才, 李光明, 等. 西藏松多古特提斯洋研究进展与存在问题[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 2020, 40(2): 1-13. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TTSD202002002.htm Boynton W. Cosmochemistry of the Rare Earth Elements: Meteorite Studies[J]. Dev. Geochem., 1984, 2: 63-114. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780444421487500083
Sun S S, McDonough W F. Chemical and isotopic systematic of oceanic basalts: implications for mantle composition and processes[J]. Geological Society of London Special Publication, 1989, 42: 313-345. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.1989.042.01.19
Yuan H L, Gao S, Dai M N, et al. Simultaneous determinations of U-Pb age, Hf isotopes and trace element compositions of zircon by excimer laser ablation quadrupole and multiple collector ICP-MS[J]. Chemical Geology, 2008, 247: 100-117. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2007.10.003
Rubatto D. Zircon trace element geochemistry: partitioning with garnet and the link between U-Pb ages and metamorphism[J]. Chemical Geology, 2002, 184(1): 123-138. http://www.researchgate.net/profile/Daniela_Rubatto/publication/223526967_Rubatto_D._Zircon_trace_element_geochemistry_partitioning_with_garnet_and_the_link_between_U-Pb_ages_and_metamorphism._Chem._Geol._184_123138/links/0a85e537d3da6b9f3d000000.pdf
Griffin W L, Wang X, Jackson S E, et al. Zircon chemistry and magma mixing, SE China: In-situ analysis of Hf isotopes, Tonglu and Pingtan igneous complexes[J]. Lithos, 2002, 61(3): 237-269. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0024493702000828
吴福元, 李献华, 郑永飞, 等. Lu-Hf同位素体系及其岩石学应用[J]. 岩石学报, 2007, 23(2): 185-220. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200702002.htm 莫宣学. 青藏高原岩浆成因研究: 成果与展望[J]. 地质通报, 2009, 28(12): 1694-1703. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20091201&flag=1 莫宣学, 赵志丹, Depaolo D J, 等. 青藏高原拉萨地块碰撞-后碰撞岩浆作用的三种类型及其对大陆俯冲和成矿作用的启示: Sr-Nd同位素证据[J]. 岩石学报, 2006, 22(4): 795-803. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200604004.htm 董国臣. 西藏林周盆地林子宗火山岩及其所含的印度-欧亚大陆碰撞信息研究[D]. 中国地质大学(北京) 博士学位论文, 2002. He S D, Kapp P, Decelles P G, et al. Cretaceous-Tertiary geology of the Gangdese Arc in the Linzhou area, southern Tibet[J]. Tectonophysics, 2007, 433: 13-37.
唐攀, 唐菊兴, 郑文宝, 等. 西藏新嘎果地区典中组火山岩年代学、Hf同位素及地球化学特征[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2018, 37(1): 47-60. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2018.01.005 梁银平, 朱杰, 次邛, 等. 青藏高原冈底斯带中部朱诺地区林子宗群火山岩锆石U-Pb年龄和地球化学特征[J]. 地球科学(中国地质大学学报), 2010, 35(2): 211-223. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201002004.htm 于枫, 李志国, 赵志丹, 等. 西藏冈底斯带中西部措麦地区林子宗火山岩地球化学特征及意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2010, 26(7): 2217-2225. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201007023.htm 李勇, 张士贞, 李奋其, 等. 拉萨地块中段查孜地区典中组火山岩锆石U-Pb年龄及地质意义[J]. 地球科学, 2018, 43(8): 2755-2766. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201808017.htm 王乔林. 冈底斯西部林子宗群火山岩的地球化学特征及锆石年代学研究[D]. 中国地质大学(北京) 硕士学位论文, 2011. Ayers J. Trace element modeling of aqueous fluid-peridotite interaction in the mantle wedge of subduction zones[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1998, 132(4): 390-404. doi: 10.1007/s004100050431
Regelous M, Collerson K, Ewart A, et al. Trace element transport rates in subduction zones: Evidence from Th, Sr and Pb isotope data for Tonga-Kermadec arc lavas[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1997, 150: 291-302. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(97)00107-6
徐义刚, 王强, 唐功建, 等. 弧玄武岩的成因: 进展与问题[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2020, 50(12): 1818-1844. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK202012009.htm Mohr P A. Crustal Contamination in mafic Sheets: A summary[C]//Halls H C, Fahrig W F. Mafic Dyke Swarms, Special Publication-Geological Association of Canada, 1987: 75-80.
Wilson M. Igneous petrogenesis[M]. London: Unwin Hyman, 1989.
Bacon C R, Druitt T H. Compositional evolution of the zoned calcalkaline magma chamber of Mount Mazama, Crater Lake, Oregon[J]. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol., 1988, 98: 224-256. doi: 10.1007/BF00402114
Guffanti M, Clynne M, Muffler L, et al. Thermal and mass implications of magmatic evolution in the Lassen volcanic region, California, and constraints on basalt influx to the lower crust[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1996, 101: 3003-3013. doi: 10.1029/95JB03463
Roberts M P, Clemens J D. Origin of high-potassium, calc-alkaline, Ⅰ-type granitoids[J]. Geology, 1993, 21: 825. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1993)021<0825:OOHPTA>2.3.CO;2
张立雪, 王青, 朱弟成, 等. 拉萨地体锆石Hf同位素填图: 对地壳性质和成矿潜力的约束[J]. 岩石学报, 2013, 29(11): 3681-3688. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201311003.htm 朱弟成, 赵志丹, 牛耀龄, 等. 拉萨地体的起源和古生代构造演化[J]. 高校地质学报, 2012, 18(1): 1-15. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2012.01.001 Ding L, Kapp P, Wan X Q, et al. Paleocene-Eocene record of ophiolite obduction and initial India-Asia collision, south central Tibet[J]. Tectonics, 2005, 24(3): TC3001.
Yin A, Harrison T M. Geological evolution of the Himalayan-Tibetan Orogen[J]. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 2003, 28(1): 211-280.
Chen J S, Huang B C, Sun L S, et al. New constraints to the onset of the India-Asia collision: paleomagnetic reconnaissance on the Linzizong Group in the Lhasa Block, China[J]. Tectonophysics, 2010, 489: 189-209. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2010.04.024
李皓扬, 钟孙霖, 王彦斌, 等. 藏南林周盆地林子宗火山岩的时代、成因及其地质意义: 锆石U-Pb年龄和Hf同位素证据[J]. 岩石学报, 2007, 23(2): 493-500. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200702026.htm 周斌,韩奎,潘亮,等.西藏日多地区1:5万区域地质调查成果报告.陕西省地质调查中心,2019. 吉林大学地质调查院.中华人民共和国1:25万申扎幅区域地质调查报告.吉林大学档案馆,2002. 四川省地质调查院.中华人民共和国1:25万措勤县幅区域地质调查报告.成都理工大学档案馆,2002. 成都理工大学地质调查院.中华人民共和国1:5万措勤县南嘎仁错东部地区区域地质矿产调查报告.成都理工大学档案馆,2010. -
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 洛桑朗杰,尼玛次仁,格桑次仁,尼玛扎西,江白,次旺巴扎. 达若-状拉火山构造洼地林子宗群典中组火山岩地质特征. 西藏科技. 2023(06): 27-35 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)




 下载:
下载: