Petrogenesis of anorthosite in the Laguoco ophiolite western part of the Bangong-Nujiang suture zone and its constraint to the evolution of the Meso-Tethys Ocean
-
摘要:
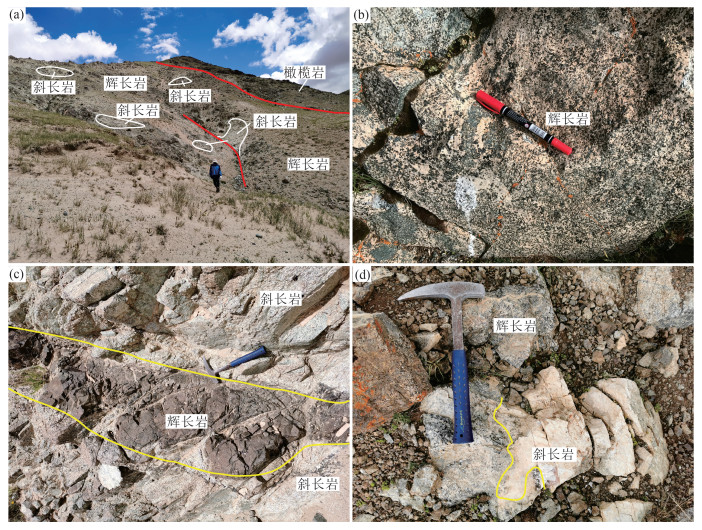
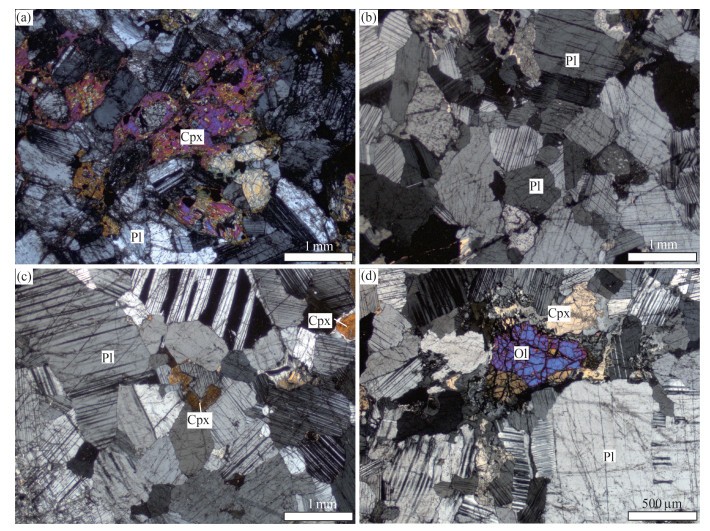
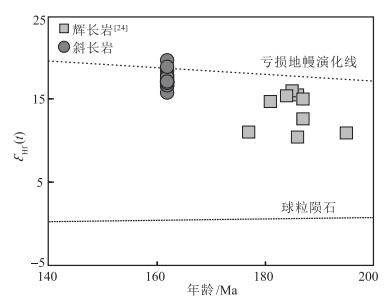
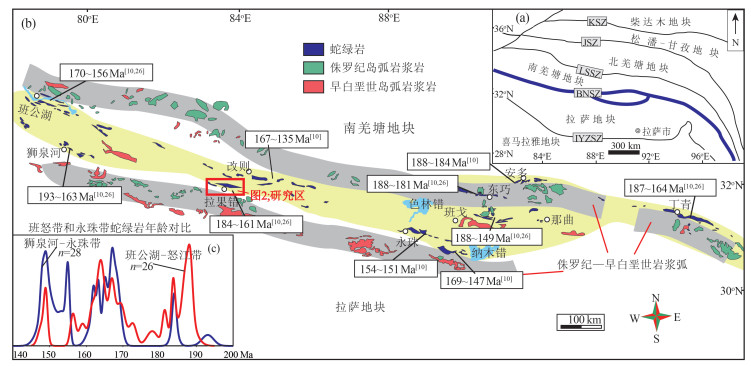
拉果错蛇绿岩位于青藏高原北部的改则地区,是狮泉河-永珠带内保存最好、岩石组合最完整的蛇绿岩之一。为进一步约束拉果错蛇绿岩成因及其构造属性,对其中斜长岩开展了详细的岩石学、锆石U-Pb年代学和地球化学研究。结果显示,斜长岩主要呈不规则脉体或透镜体侵入到辉长岩中,锆石U-Pb定年结果表明斜长岩形成于162 Ma,略晚于蛇绿岩中基性岩形成时代。这些锆石均具有明显正的εHf(t)值(+15.8~+19.7),暗示其岩浆源自亏损的地幔源区。斜长岩具有明显低SiO2、TiO2和高CaO的特征,具有与正常型大洋中脊玄武岩(N-MORB)类似的稀土元素配分形式和低的微量元素含量,富集Rb、Ba、Th和Sr,亏损Nb、Ta、Zr等微量元素。此外,斜长岩显示出高的Nb/La值和低的Th/Nb、Ba/Nb值,暗示其源自富集地幔源区高程度的部分熔融,形成过程还受到俯冲组分的影响。综合上述特征,推测拉果错斜长岩是地幔柱影响下再富集的亏损地幔源区高程度部分熔融的产物。俯冲过程中,再富集地幔源区(地幔楔)产生的原始岩浆快速上涌过程,并伴随着富Mg-Fe矿物的结晶分异,残余富Ca、Al岩浆。残余岩浆侵入到俯冲带上盘洋壳中(辉长岩),由于快速减压而形成斜长岩。结合区域研究成果,表明拉果错蛇绿岩形成于与早侏罗世—晚侏罗世早期俯冲相关的构造背景。
Abstract:The Laguoco ophiolite is distributed in the Gaize area, north Tibetan plateau, and is one of the most complete and well-preserved ophiolites in the Shiquanhe-Yongzhu belt. The petrological, zircon U-Pb geochronology and geochemistry of anorthosite intruding gabbros are studied to manifest the genesis and tectonic affinities of the Laguoco ophiolite. The anorthosite was emplaced within gabbros mainly as irregular dikes or lenses, with zircon U-Pb ages of 162±1 Ma, slightly later than mafic rocks of the ophiolite. All zircons yield remarkable positive εHf(t) values (+15.8~+19.7), indicating that the magma was derived from a long-term depleted mantle source. All anorthosites are characterized by low SiO2, TiO2 and high CaO contents, MORB-like REE patterns with low trace element concentrations, enrichment of Rb, Ba, Th and Sr, and depletion of Nb, Ta and Zr. Moreover, these samples show high Nb/La but low Th/Nb and Ba/Nb ratios, which suggests their magma was affected by enriched mantle with variable inputting of subduction materials. The comprehensive analysis suggests that the Laguoco anorthosite was derived from high degree partial melting of depleted mantle source with re-enrichment of plume. The primary magma deriving from (enriched) mantle wedge rapidly ascended into oceanic crust in company with the crystallization differentiation of Mg-Fe oxides. Then, residual Ca, Al-bearing magma injected into the gabbros and formed anorthosite with the decrease of pressure. Combining with regional geology, it is suggested that the Laguoco ophiolite was formed in a subduction-related setting during the Jurassic.
-
Keywords:
- Bangong-Nujiang suture zone /
- Shiquanhe-Yongzhu belt /
- ophiolite /
- anorthosite /
- zircon U-Pb age
-
致谢: 野外工作得到了青藏高原二次科考项目办和西藏自治区科技厅的大力协助,审稿专家提出了建设性的修改意见,在此一并表示感谢。
-
图 8 拉果错斜长岩球粒陨石标准化稀土元素配分图(a)和原始地幔标准化微量元素蛛网图(b) (标准化值据参考文献[44])
Figure 8. Chondrite-normalized REE patterns(a) and primitive-normalized trace element spider diagrams(b) of the Laguoco anorthosite
表 1 拉果错斜长岩锆石U-Th-Pb分析结果
Table 1 Zircon U-Th-Pb age data of the Laguoco anorthosite
样品点 Pb /10-6 Th /10-6 U /10-6 Th/U 207Pb/206Pb 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ 206Pb/238U年龄/Ma 1σ 谐和度 20T133-01 2.8 36 80 0.45 0.0505 0.0035 0.1771 0.0116 0.0258 0.0004 164.1 2.8 99% 20T133-02 1.6 17 49 0.35 0.0534 0.0047 0.1764 0.0152 0.0247 0.0005 157.2 2.9 95% 20T133-03 2.0 33 60 0.55 0.0492 0.0045 0.1646 0.0147 0.0248 0.0005 158.2 3.0 97% 20T133-04 1.3 11 39 0.28 0.0527 0.0065 0.1799 0.0208 0.0263 0.0006 167.5 3.6 99% 20T133-05 1.0 14 31 0.44 0.0528 0.0092 0.1628 0.0269 0.0243 0.0006 154.5 3.8 99% 20T133-06 3.4 34 108 0.31 0.0491 0.0027 0.1712 0.0098 0.0256 0.0005 162.7 2.9 98% 20T133-07 4.6 28 141 0.20 0.0516 0.0028 0.1752 0.0094 0.0250 0.0004 159.5 2.3 97% 20T133-08 2.5 23 78 0.29 0.0497 0.0042 0.1690 0.0146 0.0247 0.0004 157.6 2.6 99% 20T133-09 2.2 16 70 0.22 0.0503 0.0069 0.1669 0.0233 0.0259 0.0006 165.0 3.7 94% 20T133-10 2.5 32 72 0.45 0.0506 0.0037 0.1781 0.0130 0.0259 0.0005 165.0 3.0 99% 20T133-11 1.8 17 54 0.32 0.0532 0.0044 0.1809 0.0139 0.0254 0.0005 161.7 3.1 95% 20T133-12 3.2 27 98 0.27 0.0504 0.0032 0.1715 0.0115 0.0252 0.0004 160.7 2.7 99% 20T133-13 1.3 15 39 0.38 0.0498 0.0060 0.1792 0.0224 0.0262 0.0005 166.8 3.4 99% 20T133-14 1.4 14 41 0.35 0.0580 0.0066 0.1938 0.0201 0.0261 0.0006 165.8 3.8 91% 20T133-15 2.0 19 63 0.31 0.0505 0.0043 0.1635 0.0139 0.0244 0.0005 155.2 3.0 99% 20T133-16 1.8 18 55 0.32 0.0545 0.0048 0.1801 0.0153 0.0255 0.0006 162.5 3.6 96% 20T133-17 2.2 32 62 0.51 0.0463 0.0037 0.1613 0.0133 0.0254 0.0005 161.4 3.2 93% 20T133-18 2.1 21 64 0.32 0.0502 0.0038 0.1704 0.0124 0.0255 0.0004 162.4 2.8 98% 20T133-19 2.1 29 58 0.50 0.0507 0.0042 0.1785 0.0143 0.0261 0.0004 166.0 2.6 99% 20T133-20 1.4 18 40 0.44 0.0574 0.0063 0.1901 0.0190 0.0259 0.0005 164.5 3.4 92% 20T133-21 2.7 22 83 0.26 0.0537 0.0046 0.1726 0.0132 0.0247 0.0004 157.6 2.7 97% 20T133-22 1.6 14 46 0.31 0.0501 0.0049 0.1694 0.0153 0.0265 0.0006 168.5 3.7 94% 20T133-23 1.3 12 38 0.31 0.0493 0.0059 0.1641 0.0199 0.0258 0.0007 164.5 4.5 93% 20T133-24 3.2 45 91 0.50 0.0540 0.0036 0.1845 0.0124 0.0255 0.0005 162.2 2.9 94% 20T133-25 2.5 18 75 0.24 0.0540 0.0038 0.1905 0.0128 0.0263 0.0005 167.3 3.1 94% 表 2 拉果错斜长岩锆石Hf同位素分析结果
Table 2 Zircon Hf isotope of the Laguoco anorthosite
样品点 176Yb/177Hf 2σ 176Lu/177Hf 2σ 176Hf/177Hf 2σ (176Hf/177Hf)i εHf(t) 2σ TDM /Ma fLu/Hf 20T133-1 0.0157 0.0001 0.0006 0.0000 0.283143 0.000018 0.283142 16.6 0.6 151 -0.98 20T133-2 0.0417 0.0007 0.0014 0.0000 0.283234 0.000019 0.283230 19.7 0.7 23 -0.96 20T133-3 0.0358 0.0021 0.0011 0.0001 0.283123 0.000019 0.283119 15.8 0.7 183 -0.97 20T133-4 0.0565 0.0011 0.0020 0.0000 0.283201 0.000020 0.283195 18.5 0.7 72 -0.94 20T133-5 0.0604 0.0003 0.0022 0.0000 0.283185 0.000019 0.283179 17.9 0.7 95 -0.93 20T133-6 0.0311 0.0011 0.0011 0.0000 0.283158 0.000020 0.283155 17.1 0.7 132 -0.97 20T133-7 0.0355 0.0003 0.0013 0.0000 0.283164 0.000020 0.283161 17.3 0.7 123 -0.96 20T133-8 0.0345 0.0002 0.0012 0.0000 0.283159 0.000021 0.283155 17.1 0.7 132 -0.96 20T133-9 0.0426 0.0006 0.0014 0.0000 0.283157 0.000018 0.283153 17.0 0.6 134 -0.96 20T133-10 0.0349 0.0014 0.0011 0.0000 0.283170 0.000019 0.283166 17.5 0.7 115 -0.97 20T133-11 0.0345 0.0009 0.0011 0.0000 0.283176 0.000020 0.283172 17.7 0.7 107 -0.97 20T133-12 0.0372 0.0004 0.0013 0.0000 0.283148 0.000019 0.283144 16.7 0.7 148 -0.96 20T133-13 0.0524 0.0005 0.0019 0.0000 0.283213 0.000020 0.283208 19.0 0.7 54 -0.94 20T133-14 0.0417 0.0006 0.0014 0.0000 0.283157 0.000020 0.283152 17.0 0.7 135 -0.96 20T133-15 0.0409 0.0012 0.0014 0.0000 0.283162 0.000019 0.283157 17.2 0.7 128 -0.96 表 3 拉果错斜长岩全岩主量、微量和稀土元素组成
Table 3 Whole-rock major, trace and rare earth element compositions of the Laguoco anorthosite
样品编号 20T132 20T133 20T134 20T135 20T136 20T137 20T138 SiO2 43.93 43.35 45.90 43.53 42.81 44.05 43.85 Al2O3 29.18 29.33 26.04 29.17 27.36 26.92 26.39 MgO 5.05 4.76 5.71 4.89 5.91 4.55 5.18 Na2O 0.63 0.68 0.50 0.65 0.62 0.78 0.62 K2O 0.05 0.08 0.03 0.06 0.11 0.07 0.04 P2O5 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01 TiO2 0.13 0.13 0.13 0.13 0.14 0.15 0.14 CaO 15.47 15.04 16.33 16.40 16.04 17.02 16.38 TFe2O3 3.92 4.16 4.41 3.22 3.65 4.42 5.30 MnO 0.05 0.05 0.06 0.05 0.06 0.05 0.05 烧失量 1.58 2.10 1.43 1.87 2.01 1.86 1.54 总计 100.00 99.70 100.57 100.00 99.73 99.88 99.49 Mg# 0.72 0.69 0.72 0.75 0.76 0.67 0.66 Li 3.59 2.89 3.19 3.51 16.50 3.91 1.45 Be 0.04 0.05 0.03 0.03 0.05 0.05 0.04 Sc 21.6 20.0 25.3 20.0 26.3 23.7 20.5 Ti 318 313 332 306 358 387 335 V 51.8 49.6 59.3 49.7 61.3 59.4 51.4 Cr 95.1 83.1 94.9 82.2 95.3 73.0 81.4 Co 20.30 19.70 22.80 20.20 23.70 22.10 21.60 Ni 30.50 30.90 32.90 31.50 33.20 29.70 32.80 Ga 12.10 12.20 11.70 12.20 11.80 11.70 12.00 Rb 3.47 3.69 2.43 6.62 4.31 3.36 2.58 Sr 123 148 99 145 124 133 121 Y 1.23 1.01 1.05 1.08 1.14 1.23 1.05 Zr 4.82 1.08 0.86 1.32 0.97 1.22 1.28 Nb 0.40 0.45 0.59 0.11 0.77 0.18 0.61 Cs 0.40 0.99 0.14 0.43 1.53 0.99 0.20 Ba 12.10 15.60 12.60 16.60 27.40 22.40 9.95 La 0.17 0.13 0.10 0.24 0.11 0.13 0.11 Ce 0.53 0.44 0.38 0.55 0.39 0.44 0.40 Pr 0.04 0.03 0.02 0.05 0.03 0.03 0.03 Bd 0.22 0.18 0.15 0.21 0.18 0.21 0.18 Sm 0.09 0.09 0.09 0.12 0.10 0.12 0.10 Eu 0.13 0.12 0.12 0.08 0.09 0.11 0.11 Gd 0.18 0.18 0.21 0.20 0.22 0.19 0.21 Tb 0.03 0.02 0.02 0.03 0.03 0.03 0.03 Dt 0.21 0.19 0.19 0.20 0.21 0.25 0.20 Ho 0.04 0.04 0.04 0.04 0.05 0.05 0.05 Er 0.10 0.10 0.10 0.10 0.12 0.12 0.09 Tm 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 Yb 0.11 0.10 0.11 0.09 0.11 0.13 0.11 Lu 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 Hf 0.12 0.04 0.03 0.12 0.04 0.05 0.04 Ta 0.03 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.01 0.01 Pb 0.15 0.24 0.21 0.30 0.35 0.24 0.88 Th 0.14 0.07 0.05 0.13 0.05 0.05 0.05 U 0.04 0.04 0.04 0.04 0.04 0.03 0.03 注:主量元素含量单位为%,微量和稀土元素含量单位为10-6 -
Coleman R G. Ophiolite[M]. New York: Springer Verlag, 1977: 1-220.
Pearce J A, Lippard S J, Roberts S. Characteristics and tectonic significance of supra-subduction zone ophiolites[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 1984, 16(1): 77-94. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.1984.016.01.06
Dilek Y, Furnes H. Ophiolite genesis and global tectonics: Geochemical and tectonic fingerprinting of ancient oceanic lithosphere[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 2011, 123(3/4): 387-411. http://search.ebscohost.com/login.aspx?direct=true&db=aph&AN=58150964&site=ehost-live
Yang J S, Wu W W, Lian D Y, et al. Peridotites, chromitites and diamonds in ophiolites[J]. Nature Reviews Earth & Environment, 2021, 16: 1-5. http://www.nature.com/articles/s43017-020-00138-4?utm_source=other&utm_medium=other&utm_content=null
Yin A, Harrison T M. Geologic evolution of the Himalayan-Tibetan orogen[J]. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 2000, 28: 211-280. doi: 10.1146/annurev.earth.28.1.211
Kapp P, Yin A, Manning C E, et al. Tectonic evolution of the early Mesozoic blueschist-bearing Qiangtang metamorphic belt, central Tibet[J]. Tectonics, 2003, 22(4): 1043.
Zhu D C, Li S M, Cawood P A, et al. Assembly of the Lhasa and Qiangtang terranes in central Tibet by divergent double subduction[J]. Lithos, 2016, 245: 7-17. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2015.06.023
Guynn J H, Kapp P, Pullen A, et al. Tibetan basement rocks near Amdo reveal "missing" Mesozoic tectonism along the Bangong suture, central Tibet[J]. Geology, 2006, 34(6): 505-508. doi: 10.1130/G22453.1
Li S M, Wang Q, Zhu D C, et al. Reconciling orogenic drivers for the evolution of the Bangong-Nujiang Tethys during Middle-Late Jurassic[J]. Tectonics, 2020, 39(2): e2019TC005951. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/338768096_Reconciling_Orogenic_Drivers_for_the_Evolution_of_the_Bangong-Nujiang_Tethys_During_Middle-Late_Jurassic
Tang Y, Zhai Q G, Chung S L, et al. First mid-ocean ridge-type ophiolite from the Meso-Tethys suture zone in the north-central Tibetan plateau[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 2020, 132(9/10): 2202-2220.
Fan J J, Niu Y, Liu Y M, et al. Timing of closure of the Meso-Tethys Ocean: Constraints from remnants of a 141-135 Ma ocean island within the Bangong-Nujiang Suture Zone, Tibetan Plateau[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 2021, https://doi.org/10.1130/B35896.1.
刘海永, 曾庆高, 旺姆, 等. 班公湖-怒江缝合带西段聂尔错-拉果错地区火山岩锆石U-Pb年龄及其地球化学特征[J]. 地质通报, 2019, 38(7): 1136-1145. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20190707&flag=1 潘桂棠, 莫宣学, 侯增谦, 等. 冈底斯造山带的时空结构及演化[J]. 岩石学报, 2006, 22(3): 521-533. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200603001.htm 王保弟, 许继峰, 曾庆高, 等. 西藏改则地区拉果错蛇绿岩地球化学特征及成因[J]. 岩石学报, 2007, 23(6): 1521-1530. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0569.2007.06.026 Pan G T, Wang L Q, Li R S, et al. Tectonic evolution of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2012, 53: 3-14. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2011.12.018
Girardeau J, Marcoux J, Alleger C J, et al. Tectonic environment and geodynamic significance of the Neo-Cimmerian Donqiao ophiolite, Bangong-Nujiang suture zone, Tibet[J]. Nature, 1984, 307(5): 27-31. http://www.nature.com/articles/307027a0
Kapp P, DeCelles P G, Gehrels G E, et al. Geological records of the Lhasa-Qiangtang and Indo-Asian collisions in the Nima area of central Tibet[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 2007, 119(7/8): 917-933.
Xu M J, Li C, Zhang X Z, et al. Nature and evolution of the Neo-Tethys in central Tibet: synthesis of ophiolitic petrology, geochemistry, and geochronology[J]. International Geology Review, 2014, 56(9): 1072-1096. doi: 10.1080/00206814.2014.919616
Zeng Y C, Xu J F, Chen J L, et al. Geochronological and geochemical constraints on the origin of the Yunzhug ophiolite in the Shiquanhe-Yunzhug-Namu Tso ophiolite belt, Lhasa Terrane, Tibetan Plateau[J]. Lithos, 2018, 300: 250-260.
张玉修, 张开均, 黎兵, 等. 西藏改则南拉果错蛇绿岩中斜长花岗岩锆石SHRIMP U-Pb年代学及其成因研究[J]. 科学通报, 2007, 52(5): 100-106. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB200701017.htm Wang W L, Aitchison J C, Lo C H, et al. Geochemistry and geochronology of the amphibolite blocks in ophiolitic mélanges along Bangong-Nujiang suture, central Tibet[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2008, 33: 122-138. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2007.10.022
Zeng X W, Wang M, Li C, et al. Lower Cretaceous turbidites in the Shiquanhe-Namco Ophiolite Mélange Zone, Asa area, Tibet: Constraints on the evolution of the Meso-Tethys Ocean[J]. Geoscience Frontiers, 2021, 12(4): 101127. doi: 10.1016/j.gsf.2020.12.008
Yuan Y J, Yin Z X, Liu W L, et al. Tectonic Evolution of the Meso-Tethys in the Western Segment of Bangonghu-Nujiang Suture Zone: Insights from Geochemistry and Geochronology of the Lagkor Tso Ophiolite[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2015, 89(2): 369-388. doi: 10.1111/1755-6724.12436
徐建鑫, 李才, 范建军, 等. 西藏改则县拉果错蛇绿岩构造属性: 来自岩石学, 地球化学, 年代学及Lu-Hf同位素的制约[J]. 地质通报, 2018, 37(8): 1541-1553. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20180818&flag=1 刘海永, 曾庆高, 王雨, 等. 西藏拉果错蛇绿混杂岩岩石学, 锆石U-Pb年龄及地球化学特征[J]. 地质通报, 2020, 39(2/3): 164-76. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=2020020302&flag=1 Qian Q, Hermann J, Dong F, et al. Episodic formation of Neotethyan ophiolites(Tibetan plateau): Snapshots of abrupt global plate reorganizations during major episodes of supercontinent breakup?[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2020, 203: 103144. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2020.103144
王希斌, 鲍佩声, 邓万明, 等. 西藏蛇绿岩[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1987: 138-214. 李观龙, 杨经绥, 薄容众, 等. 西藏班公湖-怒江缝合带东段丁青蛇绿岩中的铬铁矿: 产出特征与类型[J]. 中国地质, 2019, 46(1): 1-20. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201901002.htm Li S, Yin C Q, Guilmette C, et al. Birth and demise of the Bangong-Nujiang Tethyan Ocean: A review from the Gerze area of central Tibet[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2019, 198: 102907. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2019.102907
Ma A L, Hu X M, Kapp P, et al. The disappearance of a Late Jurassic remnant sea in the southern Qiangtang Block(Shamuluo Formation, Najiangco area): Implications for the tectonic uplift of central Tibet[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2018, 506: 30-47. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2018.06.005
Yan L L, Zhang K J. Infant intra-oceanic arc magmatism due to initial subduction induced by oceanic plateau accretion: A case study of the Bangong Meso-Tethys, central Tibet, western China[J]. Gondwana Research, 2020, 79: 110-124. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2019.08.008
Chen S S, Fan W M, Shi R D, et al. Early Cretaceous volcanic rocks in Yunzhug area, central Tibet, China, associated with arc-continent collision in the Tibetan Plateau?[J]. Lithos, 2021, 80: 105827.
Zhu D C, Zhao Z D, Niu Y L, et al. The Lhasa Terrane: record of a microcontinent and its histories of drift and growth[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2011, 301: 241-255. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2010.11.005
Hou Z Q, Duan L F, Lu Y J, et al. Lithospheric architecture of the Lhasa terrane and its control on ore deposits in the Himalayan-Tibetan orogen[J]. Economic Geology, 2015, 110: 1541-1575. doi: 10.2113/econgeo.110.6.1541
侯可军, 李延河, 田有荣. LA-MC-ICP-MS锆石微区原位U-Pb定年技术[J]. 矿床地质, 2009, 28(4): 481-492. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2009.04.010 Jackson S E, Pearson N J, Griffin W L, et al. The application of laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry to in situ U-Pb zircon geochronology[J]. Chemical Geology, 2004, 211: 47-69. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2004.06.017
Sláma J, Kosler J, Condon D J, et al. Plešovice zircon-A new natural reference material for U-Pb and Hf isotopic microanalysis[J]. Chemical Geology, 2008, 249: 1-35. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2007.11.005
Liu Y S, Gao S, Hu Z C, et al. Continental and oceanic crust recycling-induced mel-peridotite interactions in the Trans-North China Orogen: U-Pb dating, Hf isotopes and trace elements in zircons from mantle xenoliths[J]. Journal of Petrology, 2010, 51(1/2): 537-571. http://www.ingentaconnect.com/content/oup/petroj/2010/00000051/F0020001/art00023
Ludwig K R. Users Manual for Isoplot 3.00: A Geochronological Toolkit for Microsoft Excel[J]. Special Publication No. 4. Berkeley Geochronology Centre, 2003. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/245539605_Users_manual_for_IsoplotEx_a_geochronological_toolkit_for_Microsoft_Excel
Woodhead J D, Hergt J M. A preliminary appraisal of seven natural zircon reference materials for in situ Hf isotope determination[J]. Geostandards and Geoanalytical Research, 2005, 29(2): 183-195. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-908X.2005.tb00891.x
Morel M L A, Nebel O, Nebel-Jacobsen Y J, et al. Hafnium isotope characterization of the GJ-1 zircon reference material by solution and laser-ablation MC-ICPMS[J]. Chemical geology, 2008, 255(1/2): 231-235. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0009254108002647
Hoskin P W O, Schaltegger U. The composition of zircon and igneous and metamorphic petrogenesis[J]. Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry, 2003, 53: 27-62. doi: 10.2113/0530027
吴元保, 郑永飞. 锆石成因矿物学研究及其对U-Pb年龄解释的制约[J]. 科学通报, 2004, 49(16): 1589-1604. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2004.16.002 Sun S S, McDonough W F. Chemical and Isotopic Systematics of Oceanic Basalts: Implications for Mantle Composition and Processes[J]. Geological Society. Special Publications, London, 1989: 313-345. http://petrology.oxfordjournals.org/cgi/ijlink?linkType=ABST&journalCode=specpubgsl&resid=42/1/313
Baxter A T, Aitchison J C, Zyabrev S V. Radiolarian age constraints on Meso-Tethyan ocean evolution, and their implications for development of the Bangong-Nujiang suture, Tibet[J]. Journal of the Geological Society, 2009, 166: 689-694. doi: 10.1144/0016-76492008-128
Zhu D C, Zhao Z D, Niu Y L, et al. The origin and pre-Cenozoic evolution of the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Gondwana Research, 2013, 23: 1429-1454. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2012.02.002
王保弟, 刘函, 王立全, 等. 青藏高原狮泉河-拉果错-永珠-嘉黎蛇绿混杂岩带时空结构与构造演化[J]. 地球科学, 2020, 45(8): 2764-2784. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX202008002.htm Shi R D, Griffin W L, O'Reilly S Y, et al. Melt/mantle mixing produces podiform chromite deposits in ophiolites: implications of Re-Os systematics in the Dongqiao Neo-tethyan ophiolite, northern Tibet[J]. Gondwana Research, 2012, 21: 194-206. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2011.05.011
黄启帅, 史仁灯, 丁炳华, 等. 班公湖MOR型蛇绿岩Re-Os同位素特征对班公湖-怒江特提斯洋裂解时间的制约[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2012, 31(4): 465-478. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2012.04.001 Zhang Y X, Li Z W, Zhu L D, et al. Newly discovered eclogites from the Bangong Meso-Tethyan suture zone(Gaize, central Tibet, western China): mineralogy, geochemistry, geochronology, and tectonic implications[J]. International Geology Review, 2016, 58(5): 574-587. doi: 10.1080/00206814.2015.1096215
Boudier F, Nicolas A. Axial melt lenses at oceanic ridges-A case study in the Oman ophiolite[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2011, 304(3/4): 313-325. doi: 10.1029/2010JB007934
Sotiriou P, Polat A. Comparisons between Tethyan anorthosite-bearing ophiolites and Archean anorthosite-bearing layered intrusions: Implications for Archean geodynamic processes[J]. Tectonics, 2020, 39(8): e2020TC006096. doi: 10.1029/2020TC006096
Kelemen P B, Aharanov E. Periodic formation of magma fractures and generation of layered gabbros in the lower crust beneath oceanic spreading ridges[J]. Geophysical Monograph-American Geophysical Union, 1998, 106: 267-90. doi: 10.1029/GM106p0267
Fan J J, Li C, Xie C M, et al. Petrology, geochemistry, and geochronology of the Zhonggang ocean island, northern Tibet: implications for the evolution of the Banggongco-Nujiang oceanic arm of the Neo-Tethys[J]. International Geology Review, 2014, 56(12): 1504-1520. doi: 10.1080/00206814.2014.947639
Kapp P, DeCelles P G. Mesozoic-Cenozoic geological evolution of the Himalayan-Tibetan orogen and working tectonic hypotheses[J]. American Journal of Science, 2019, 319(3): 159-254. doi: 10.2475/03.2019.01
Liu W L, Huang Q T, Gu M, et al. Origin and tectonic implications of the Shiquanhe high-Mg andesite, western Bangong suture, Tibet[J]. Gondwana Research, 2018, 60: 1-14. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2018.03.017
Shi R D, Yang J S, Xu Z Q, et al. Discovery of the boninite series volcanic rocks in the Bangong Lake ophiolite mélange, western Tibet, and its tectonic implications[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2004, 49(12): 1272-1278. doi: 10.1360/04wd0006
周亚楠, 邵瑞琦, 姜南, 等. 拉萨地块保吉地区晚侏罗世-早白垩世地层磁组构特征[J]. 地质通报, 2019, 38(4): 522-535. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20190405&flag=1 尹涛, 李威, 尹显科, 等. 西藏阿翁错地区早白垩世花岗闪长岩——班公湖-怒江洋壳南向俯冲消减证据[J]. 中国地质, 2019, 46(5): 1105-1115. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201905012.htm Tang Y, Zhai Q G, Hu P Y, et al. Southward subduction of the Bangong-Nujiang Tethys Ocean: insights from ca. 161-129 Ma arc volcanic rocks in the north of Lhasa terrane, Tibet[J]. International Journal of Earth Sciences, 2020, 109(2): 631-647. doi: 10.1007/s00531-020-01823-x
和钟铧, 杨德明, 王天武, 等. 西藏嘉黎断裂带凯蒙蛇绿岩的地球化学特征及构造意义[J]. 矿物岩石, 2006, 26(1): 69-74. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6872.2006.01.013 和钟铧, 杨德明, 王天武. 西藏嘉黎断裂带凯蒙蛇绿岩的年代学、地球化学特征及大地构造意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2006, 22(3): 653-660. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200603014.htm 吴功建, 肖序常, 李廷栋. 青藏高原亚东-格尔木地学断面[J]. 地质学报, 1989, 63(4): 285-296. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.1989.04.003



 下载:
下载: