Petrogenesis of the Neoarchean diorite and hornblendite in the Taishan area, western Shandong: Constraints on crustal evolution
-
摘要:
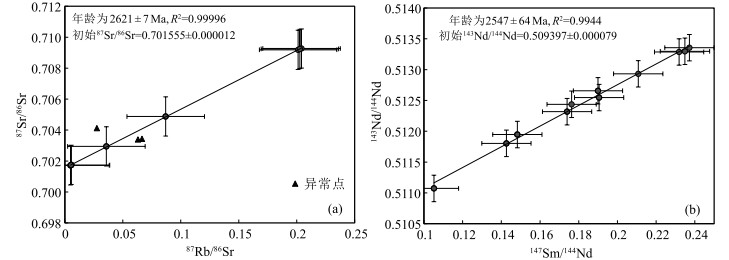
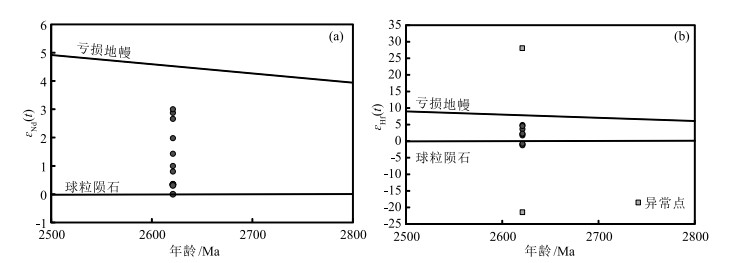
泰山地区的闪长岩及角闪石岩与TTG片麻岩在空间上密切共生,是太古宙地体的重要组成部分,探究其母岩浆性质和岩石成因,对认识华北克拉通鲁西早期大陆地壳形成与演化具有重要意义。以泰山闪长岩和角闪石岩为研究对象,开展了详细的锆石U-Pb年龄、矿物化学和全岩-矿物Sr-Nd-Hf同位素研究。LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年结果显示,1件闪长岩和2件角闪石岩样品的207Pb/206Pb年龄加权平均值分别为2615 ±8 Ma、2627 ±14 Ma和2616 ±10 Ma,与全岩-矿物(角闪石和斜长石)Rb-Sr等时线定年得到的年龄结果(2621 ±7 Ma)一致,表明二者均属于新太古代约2.6 Ga岩浆作用的产物。2个岩体形成时代及矿物地球化学特征的相似性,表明它们应为同源岩浆不同演化阶段的产物,其母岩浆在后期上升侵位过程中受到分离结晶作用的影响,而率先形成的角闪石岩受分离结晶作用影响较小。利用角闪石的成分和已知的角闪石-熔体的分配系数计算得到的与闪长岩和角闪石岩中角闪石平衡的熔体表现为低Mg#值(平均值分别为31.9和43.4),富集Ba、Pb等大离子亲石元素,亏损Nb、Ta、Zr、Ti等高场强元素,以及具有平坦的重稀土元素配分型式。此外,岩石具有低的87Sr/86Sr初始值和接近亏损地幔的εNd(t)(-0.01~2.87)、εHf(t)(-0.76~4.89),且两阶段Nd模式年龄TDM2为2.97~2.73 Ga。综合来看,研究区闪长岩和角闪石岩的母岩浆可能来自于幔源岩浆底侵引起新生基性下地壳在角闪岩相条件下熔融形成的安山质母岩浆;该母岩浆经历了以斜长石、角闪石等矿物为主的结晶分异。鲁西地区在2.9~2.7 Ga经历了大规模的大陆地壳生长,新太古代晚期2.6~2.5 Ga经历了广泛的大陆地壳重熔再造,幔源岩浆的幕式底侵作用可能是华北克拉通新太古代早期(2.8~2.6 Ga)大陆地壳生长和分异的主要动力学原因之一。
Abstract:The diorite and hornblendite associated with TTG gneisses constitute the important components of Precambrian metamorphic terranes in the Taishan area and their petrogenesis can provide significant insights into understanding the crustal growth and reworking events involving in the evolution of the North China Craton. The lithological, geochronological and geochemical analyses were carried out for the study of the representative diorite and hornblendite in the Taishan area. Zircon U-Pb dating of 1 diorite and 2 hornblendite samples yields 2615 ±8 Ma, 2627 ±14 M and 2616 ±10 Ma respectively, which are consistent with the emplacement age of 2621 ±7 Ma yielded from bulk rock-mineral Rb-Sr isochron dating. They are all magmatic products of the Neoarchean ~2.6 Ga. The similarity of the formation ages and mineral geochemical characteristics of the two intrusives indicates that they are the products of different evolution stages of the homologous magma. The parent magma experienced the influence of separation crystallization in the process of uplift and emplacement in the late stage, while the first hornblende was less affected by separation crystallization. Based on the composition of amphibole and the known amphibole melt partition coefficient, the melt in equilibrium with amphibole in diorite and amphibole is characterized by low Mg# value(mean value is 31.9 and 43.4, respectively), enrichment of large ion lithophile elements such as Ba and Pb, and depletion of high field strength elements such as Nb, Ta, Zr and Ti, and a flat distribution pattern of heavy rare earth elements. In addition, the rocks have a low initial 87Sr/86Sr value close to the εNd(t) value(-0.01~2.87) and εHf(t) value(-0.76~4.89) of the depleted mantle, and the two-stage Nd model age TDM2 ranges from 2.97 Ga to 2.73 Ga. On the basis of these data and in the context of the regional geology, it is inferred that the diorite and hornblendite were probably derived from the partial melting of juvenile mafic lower crust under the amphibolite facies conditions. The initial magma underwent crystallization differentiation of minerals such as plagioclase and hornblende. The west Shandong underwent extensive continental crustal growth at 2.9~2.7 Ga and extensive continental crustal remelting at 2.6~2.5 Ga in the late Neoarchean. The episodic diapirism of mantle derived magma might be one of the main dynamic causes for the growth and differentiation of the continental crust in the Early Neoarchean(2.8~2.6 Ga) of the North China Craton.
-
Keywords:
- Taishan /
- Neoarchean /
- cumulates /
- petrogenesis /
- crustal evolution
-
柴达木盆地为青藏高原北缘最大的山间盆地[1-2],随着高原的隆升,自新生代以来沉积了周缘造山带剥落的巨厚碎屑沉积物。长期以来,学者们对青藏高原的研究多围绕东部、南部和高原内部区域进行,关于其隆升历史的认识主要来自地层沉积速率变化和Ar-Ar定年、裂变径迹低温热年代学方法,对盆地尤其是柴达木盆地新生代沉积物与高原和毗邻山脉的制约关系涉及较少[3-5]。沉积物作为连接盆地和剥蚀源区的纽带,准确记录了印度和欧亚板块碰撞过程中周缘造山带的构造活动及隆升过程[6-9]。另一方面,沉积物在搬运、堆积过程中,成分受环境和气候影响小,且不受地域构造热事件的约束,可以作为洞悉盆山耦合过程及相互作用的理想载体。对柴达木盆地沉积物源追踪及特征的研究,是反演和认识高原北缘构造隆升历程的有效途径,有助于解决整个青藏高原的隆升问题。
本文以柴达木盆地北缘露头较好、年代精确、新生代地层连续的路乐河地区沉积剖面为研究对象,应用阴极发光技术,通过标志性碎屑组分变化的对比和系统的物源分析,识别路乐河地区对周缘造山带的响应沉积,有效界定青藏高原北缘构造运动和隆升事件的时限,为进一步科学认识高原演化、隆升历史及板块碰撞远程效应提供重要线索。
1. 地质概况
路乐河地区位于柴达木盆地的北缘,在大地构造位置上,东北毗邻祁连山-南山,西北靠近赛北逆冲断裂[10]和略远的阿尔金左行走滑断裂带[11-12],南端远离东昆仑山脉(图 1-a)。受南特提斯洋盆的俯冲消减及印度-欧亚碰撞远程效应的影响,柴达木盆地及邻接造山带经历了多期次的重大构造地质事件[13-17]。路乐河地区也沉积了巨厚的新生代岩层,记录着盆地接纳沉积物填充过程中山脉隆升与环境变化的演化信息,能够为研究青藏高原北缘造山带的隆升增添佐证。路乐河地区地层从底到顶依次为白垩系犬牙沟组(K1q)、古新统—始新统路乐河组(E1+2l)、始新统下干柴沟组(E2g)、渐新统上干柴沟组(E3g)、中新统下油砂山组(N1y1)和上油砂山组(N1y2),以及中新统—上新统狮子沟组(N1+2s)共7套地层(图 1-b)[18]。其中路乐河组与犬牙沟组呈角度不整合接触,下、上油砂山组界线不明显,文中并称为油砂山组。
据马海幅1:20万区域地质调查报告①,赛什腾山主要岩性有浅变质千枚岩和绢云母片岩、碎屑岩及大量花岗岩类,并含少量安山岩、玄武岩等中基性喷出岩。南祁连山以古元古界片麻岩和大理岩深变质岩系、石炭系和三叠系碎屑岩、碳酸盐岩及达肯大坂地区达肯大坂群的斜长片麻岩和变质石英岩为主,出露岩浆岩主要为加里东期和海西期花岗岩、奥陶纪和志留纪中酸性火山岩。阿尔金山脉主要出露中、新元古界及少量奥陶系[19-20],中元古界岩性为变质碎屑岩、碳酸盐岩,发育少量玄武岩-安山岩-流纹岩组合,蓟县系出露些许闪长岩、花岗岩等侵入岩;新元古界和奥陶系均由碎屑岩和碳酸盐岩组成,火山岩不发育;新元古界变质岩系分布较多,由变质砂岩、斜长变粒岩、角闪片岩及结晶灰岩构成。
2. 碎屑矿物阴极发光特征
2.1 阴极发光原理
在外部能量的激发下,多数绝缘矿物会发生光子辐射。当激发源为高能电子束时,矿物发射可见光波段的光子,即为阴极发光(Cathodolumines-cence)[21]。矿物阴极发光根本上是由晶格中的微量元素或固有缺陷激发引起的,这些元素和晶格缺陷统称为发光中心(Luminescence centers)[22]。晶格中发光中心含量越高、越密集,矿物阴极发光的强度越强[23]。碎屑岩中不同类型的矿物颗粒,像石英、长石等,以及不同成因的矿物晶体,如喷出型石英和侵入型石英,由于其内部结构、元素组成各不相同,其阴极发光的颜色和强度也有所差别,因此阴极发光可以很好地指示沉积岩碎屑成分,这已为多数学者认同[24-29]。
2.2 阴极发光特征
石英是碎屑岩中含量最高的造岩矿物,传统的碎屑组分统计方法将其简单地划分为单晶石英和多晶石英,忽略了石英不同成因及来源的深层次信息。一般而言,蓝紫色、深蓝色-蓝色为岩浆岩石英,棕色、深棕褐色阴极光为变质型来源(图版Ⅰ-A、B)。由于石英重结晶过程中微量元素和晶格缺陷重新调整,或变形强烈造成高密度的发光中心,能量激发时声子发射(能量热)代替光子发射,从而降低了发光强度[30-31]。长石也是碎屑岩中常见的造岩矿物,在长距离搬运过程中易发生破裂、溶解,故长石含量的高低可以作为岩石风化强度和搬运距离的量化指标。如图版Ⅰ-B、C所示,斜长石阴极发光显示天蓝色、灰蓝色、黄绿色和少量黄色,微斜长石发黄灰色阴极光,其中亮蓝色为碱性长石(钙长石、钾长石),钙长石因Fe2+的存在呈芥末黄色、灰蓝色,酸性更长石以黄绿色居多[24, 32-33]。
![]() 图版ⅠA.岩浆型石英(Q1)、变质型石英(Q2)阴极发光特征;B.碳酸盐岩(Lsc)阴极发光特征;C.不同类型长石(K为微斜长石,P为长石)阴极发光特征;D.泥岩(Ls)阴极发光特征;E.变质石英岩(Lm)及碳酸盐胶结世代(C1、2)阴极发光特征;F.千枚岩-片岩(Lm)、花岗岩(Lg)阴极发光特征;G.喷出岩(Lv)阴极发光特征(图片据参考文献[36]);H.路乐河砂岩砾石组分特征图版Ⅰ.
图版ⅠA.岩浆型石英(Q1)、变质型石英(Q2)阴极发光特征;B.碳酸盐岩(Lsc)阴极发光特征;C.不同类型长石(K为微斜长石,P为长石)阴极发光特征;D.泥岩(Ls)阴极发光特征;E.变质石英岩(Lm)及碳酸盐胶结世代(C1、2)阴极发光特征;F.千枚岩-片岩(Lm)、花岗岩(Lg)阴极发光特征;G.喷出岩(Lv)阴极发光特征(图片据参考文献[36]);H.路乐河砂岩砾石组分特征图版Ⅰ.岩屑是母岩机械破碎的产物,继承了母岩岩性和岩石的结构特征,可直接反映物源区的岩石类型及岩性组合[34-35]。常见的岩屑类型有沉积岩、变质岩和岩浆岩。沉积岩岩屑含泥岩、碳酸盐岩等;泥岩岩屑不具阴极发光,但内部显示大量无规则的蓝色石英斑点(图版Ⅰ-D),识别标志独特,碳酸盐岩阴极发光颜色主要为亮黄色和橙红色色调,且可观察到碎屑颗粒至少经历了2期世代的碳酸盐胶结作用(图版Ⅰ-B、E)。路乐河碎屑组分变质岩岩屑含量较高,主要为千枚岩-片岩和石英岩。千枚岩-片岩岩屑与泥岩相似,表面含蓝色和棕色阴极光斑点,但其微定向排列的特点及规则外形易于被甄别(图版Ⅰ-A、F)。石英岩由砂岩和硅质岩经区域变质或接触变质作用形成,由多个亚石英晶粒构成,颗粒之间呈镶嵌接触,阴极发光呈棕色和部分蓝色(图版Ⅰ-E),前者表示其经历了高级变质重结晶作用[26]。侵入岩岩屑以花岗岩岩屑最常见,阴极发光下,花岗岩岩屑亦可见典型的花岗结构(图版Ⅰ-A、F),矿物颗粒明显;酸性喷出岩基质阴极发光呈血红色,石英斑晶不发光,两者界线截然(图版Ⅰ-G)。
3. 分析结果及物源指示
盆地沉积物主要由周缘造山带基岩经抬升剥蚀、搬运堆积形成,碎屑成分变化可以间接反映母岩或物源区的改变[37]。另外,沉积序列中特征岩石组分的出现标志着毗邻造山带隆升活动的启动[38-39]。依据上述不同矿物及岩屑类型的阴极发光特征,共完成了50件碎屑岩薄片组分的统计。统计工作在中国石油华北油田勘探开发研究院生油实验室完成,样品分布于各个层组,并对特征矿物和岩屑含量垂向序列变化进行了比较。
3.1 碎屑组分变化
沉积碎屑组分变化是反映盆地物源演化历程的重要物质表现。值得注意的是,单种碎屑成分的突然出现或消失,可以解释为构造运动造成源区物质组成的改变,再者出露地层被剥蚀殆尽所致。通过对比发现(图 2),新生代53.5~2.9Ma期间,路乐河沉积碎屑组分垂向上有3次明显的阶段性波动。第一次急剧变化发生在路乐河组中部,时间为50.1~46.6Ma,石英、长石及火山岩岩屑含量均保持在最低水平,石英岩岩屑达到峰值。盆地沉积物的高速率堆积与高原造山带的隆升相对应[41],暗示路乐河源区山脉经历了相对短暂的快速隆升剥蚀事件。在路乐河组与下干柴沟组交界(约44.5Ma),以云母和黄绿色长石首次大量出现及火山岩岩屑消失为标志,为路乐河地区沉积物源的第二次转换事件,碳酸盐岩和变质岩岩屑含量也急剧降低。云母主要赋存于花岗岩类或低级变质岩中,故云母的出现表征了物源区上述岩石的大面积暴露。第三次显著变化位于上干柴沟组顶部,时间为22.6Ma左右,黄绿色长石、碳酸盐岩和变质岩岩屑突增,变质型石英也呈增加趋势。概略地说,在50.1~46.6Ma、44.5Ma和22.6Ma前后,路乐河物源区可能爆发了剧烈的构造活动,致使路乐河地区沉积物组分发生阶段性变化。
![]() 图 2 路乐河地区物源转换事件与全球气候变化图(δ18O据参考文献[40])Figure 2. Transformation events in Lulehe and global climatic changes during the Cenezoic period
图 2 路乐河地区物源转换事件与全球气候变化图(δ18O据参考文献[40])Figure 2. Transformation events in Lulehe and global climatic changes during the Cenezoic period3.2 物源分析
河流是沉积物搬运的主要载体,古水流流向或优势流向的识别,有助于判别物源方位、追溯源区[42]。自古新世以来,柴达木盆地一直是一个内流汇水盆地[43-44],古水系[10]和物源恢复显示(图 3),路乐河地区新生代水流方向变化稳定,主体方位为SW向。此外,在路乐河地区除50.1~46.6Ma整个新生代沉积期外,碎屑矿物长石含量较高,平均为24.3%,其母岩类型应以含长石丰富的花岗岩或花岗片麻岩类为主[45-46],这同野外见到大量花岗岩及片麻岩砾石成分的事实一致(图版Ⅰ-H)。高长石含量的特征反映碎屑岩成分成熟度低,地层为干旱气候条件近物源快速搬运堆积形成。结合古水流方向和沉积物源方向可知(图 3),路乐河沉积体系主要受NE向南祁连和赛什腾造山带的供给制约,其沉积碎屑组分的3次变化分别表征物源的3次转变事件。
![]() 图 3 柴达木盆地新生代物源及古水流变化②Figure 3. The change of provenance and paleocurrent in Qaidam basin during the Cenozoic period
图 3 柴达木盆地新生代物源及古水流变化②Figure 3. The change of provenance and paleocurrent in Qaidam basin during the Cenozoic period(1)从犬牙沟组顶部到50.1Ma,各造岩矿物(长石、石英)及岩屑组分(石英岩、火山岩等)稳定沉积。通过对比赛什腾和南祁连山的岩性发现,变质石英岩、酸性火山岩和碳酸盐岩仅在南祁连山发育,因此路乐河此阶段物源区主要为南祁连山。50.1~46.6Ma,石英岩含量急增,表明南祁连可能经历过加速隆升事件[41],隆升引起变质岩基高速剥蚀,进而石英岩岩屑含量增大,其余组分则大幅减少。46.6Ma之后,碎屑组分恢复至50.1Ma之前的状态,南祁连山构造趋于稳定。
(2)44.5Ma,云母的发育表征了花岗岩类或含云母低级变质岩的大面积暴露,这与赛什腾山岩性一致,表明南祁连山不再是路乐河物源的主要供给者;另一方面,酸性火山岩岩屑的消失也指示路乐河的主要物源区由南祁连山向赛什腾山转变,石英岩和碳酸盐岩岩屑含量逐渐减少至消失亦印证了这一观点。
(3)22.6Ma前后,路乐河物源区再次发生转变。云母的稳定沉积及千枚岩-片岩的出现,反映赛什腾山持续为路乐河供给物源,而石英岩和碳酸盐岩岩屑的重新发育,表明南祁连山也开始为路乐河地区提供大量碎屑物质。变质岩贡献比例的加强,使岩浆型和变质型石英分别呈缩减和增加趋势。
4. 物源转换对构造隆升的响应
造山带的隆升和盆地的沉积是一个耦合过程,气候变化和构造运动对青藏高原隆升均具有一定的影响,如构造隆升促进化学风化作用的增加[47-48],造成大量基岩的脱落和搬运堆积;气候异常引起的快速侵蚀卸载作用造成山体总质量的亏缺,进而发生重力均衡效应[49],迫使山体抬升。但在长时间和大空间尺度上,构造运动对地体抬升的制约更甚于气候变化的影响[50-53],且构造活动的强弱程度能够由山脉剥蚀量或物源区岩性的变化直接体现[54]。与此同时,始新世早—中期和中新世早期全球气候变化趋于稳定(图 2),因此气候条件对路乐河地区新生代物源变化的影响可不予考虑。
(1)50.1~46.6Ma构造隆升响应
早在65~55Ma,印度和欧亚板块就已发生拼贴碰撞[12, 55-57],并在55~45Ma达到高峰[58],陆内拉萨、羌塘等刚性块体远程传递两大板块汇聚的强劲应力,隆升活动也同步传达到了高原北部地区[59-61]。现有柴达木和河西走廊地层学资料显示,阿尔金断裂起始于古新世49Ma[12],柴盆北缘的赛北断裂带及柴北缘断裂带在54.8~49Ma开始形成[10]。Jo-livet等[62]通过片麻岩磷灰石热模拟研究发现,祁连山在50Ma左右发生了快速的剥露事件,在路乐河剖面也曾报道51Ma存在一期高速率沉积[63]。从更大空间尺度看,青藏高原早期阶段的隆升在其他地区也有响应,如距高原较远的西南天山托云盆地新生代48.1±1.6Ma的幔源岩浆活动[64-65]和白垩纪—古近纪期间的托云块体旋转运动[66],可见青藏高原北缘构造变形活动相比印度-欧亚板块碰撞,滞后了约10±5Ma。以上研究均与南祁连山开始为路乐河地区提供大量剥蚀物的时限一致,揭示南祁连山50.1~46.6Ma的急剧抬升是对印度-欧亚板块碰撞的远程响应,也是碰撞应力在高原北部远程传递的有力证据。
(2)44.5Ma构造隆升响应
此时,印度与欧亚板块已完成全面碰撞,汇聚产生的应力推挤陆内已拼合的块体,使之横向缩短并相互叠置,引起陆内严重形变和逆冲推覆构造[67-68]。经热年代学研究[69],在当雄地区新厘定的纳木错逆冲推覆构造于古近纪44Ma经历过一次变形抬升事件,在高原腹地不同位置还发现大规模挤压型钾质-超钾质火山岩的踪迹[70-73],且在45~40Ma岩浆活动异常活跃。岩浆是板块碰撞挤压最直观的表现,区域性的岩浆侵位必将造成岩石圈增厚,高原整体性抬升[68, 74-75],在羌塘多格错仁地区新发现的埃达克岩表明,地壳在45~38Ma经历了缩短加厚[76]。然而,古地磁数据揭示[77],中始新世—早渐新世阿尔金主断裂和柴北缘断裂带山前沉积未发生明显的旋转变形,换言之,青藏高原新生代第二阶段的隆升以地壳垂向增生为主,具体表现为陆内块体南北向缩短、岩浆侵位和块体边界逆冲构造的发育。从44.5Ma开始,路乐河物源区由南祁连山向赛什腾山快速转变,表明赛北逆冲断裂伴随显著的隆升卸载作用,对应于高原内部的构造隆升事件。
(3)22.6Ma构造隆升响应
印度板块在中新世持续向大陆俯冲,逆冲构造以前展式推覆方式向前陆迁移、消减,形成一系列走滑-逆冲断裂和地层形变[67, 78]。来自五道梁雅西措组的古地磁结果显示,可可西里盆地在渐新世末期有29.1°±8.5°的顺时针垂轴旋转[79],赛北断裂山前地层有14°左右的移位[78]。George等[80]基于酒西盆地磷灰石裂变径迹分析,揭示出祁连山23Ma的快速隆升事件,Wang等[81]也获得了相同的冷却年龄。同时,西秦岭发生与高原隆升响应的构造-热事件,剥蚀速率急增[82],此次运动得到岩浆活动(22~23Ma)的证实[83-84],在高原内部也广泛存在相近年龄的火山喷发活动[85-89]。另一方面,在东昆仑山和阿尔金山前盆地也保留了中新世22Ma前后的岩浆活动、磨拉石沉积、断层平移、物源转型等隆升事件的地质记录[43, 62, 90-92],遥远的喀拉昆仑和西天山地区[93]亦发生与印度-欧亚板块碰撞相关的山体快速剥露事件。不言而喻,青藏高原在渐新世—中新世之交发生了大规模的构造运动,几乎波及整个高原。青藏高原整体性准同时隆升,进一步肯定了22.6Ma南祁连山与赛什腾山协同为路乐河供应沉积物的合理性。路乐河地区物源3次阶段性变化的认识也间接反映了青藏高原为阶段式隆升的观点[13, 67, 94-95]。
5. 结论
(1)沉积碎屑组分变化是反映盆地物源演化过程的重要物质表现。路乐河地区新生代碎屑组分高长石含量的特点,指示其为近物源搬运沉积形成。同时沉积物来源方向和周缘山系岩性对比揭示,路乐河物源主要受南祁连山和赛什腾山供给的控制。
(2)路乐河地区物源在新生代53.5~2.9Ma期间至少存在3次转换,发生时间同印度-欧亚板块碰撞及高原构造隆升事件吻合,间接反映了青藏高原为阶段式隆升的观点,时间依次为50.1~46.6Ma、44.5Ma和22.6Ma,深入认识青藏高原隆升历史及板块碰撞远程效应具有重要意义。
(3)44.5Ma之前,路乐河物源区主要为南祁连山,而50.1~46.6Ma南祁连山的快速抬升是对印度-欧亚板块初始碰撞应力的传递响应;青藏高原第二阶段的隆升以地壳垂向增厚为主,逆冲推覆构造发育,赛北断裂于44.5Ma发生显著的剥露作用,路乐河物源区由南祁连向赛什腾山转变;渐新世—中新世之交(22.6Ma),青藏高原准同时整体性隆升,赛什腾山和南祁连山协同为路乐河地区供应沉积物。
致谢: 感谢中国科学院海洋研究所大洋岩石圈与地幔动力学实验室王晓红老师在样品分析测试工作中提供的帮助。 -
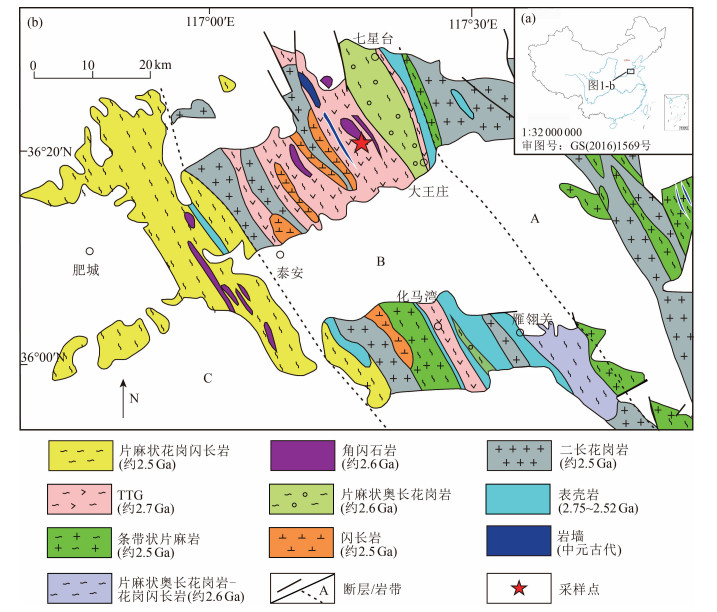
图 1 中国大陆简化构造图(a)和泰山地区区域地质简图及采样点位置(b, 据参考文献[8]修改)(A、B、C含义见正文)
Figure 1. Simplified tectonic map of continents in China(a)and geological map of the Taishan region showing sampling localtion(b)
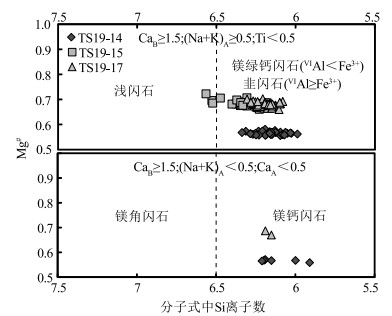
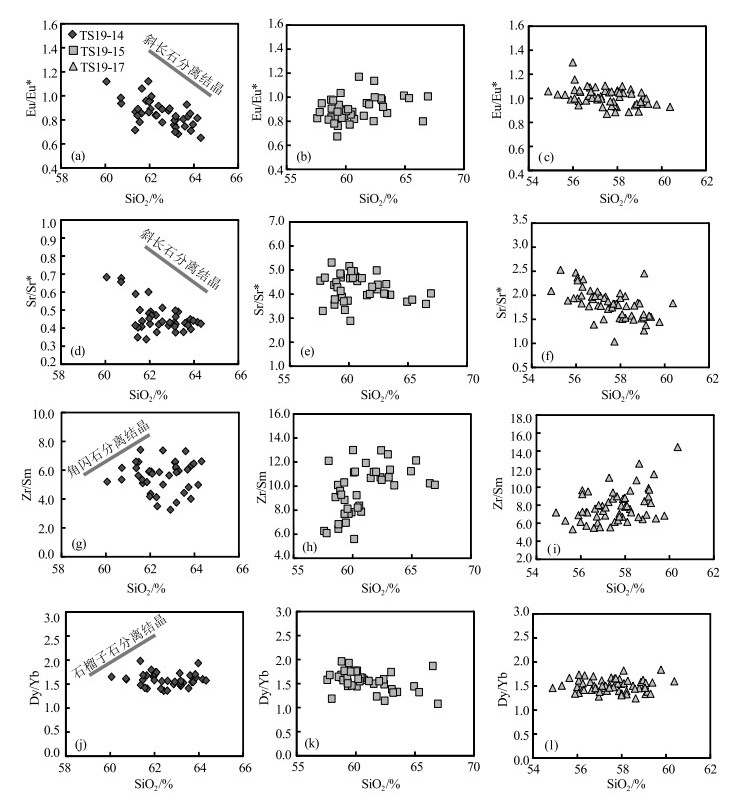
图 3 泰山闪长岩和角闪石岩的钙质角闪石分类图解[18]
Figure 3. Classification of the calcic amphiboles from the diorite and hornblendites in Taishan area
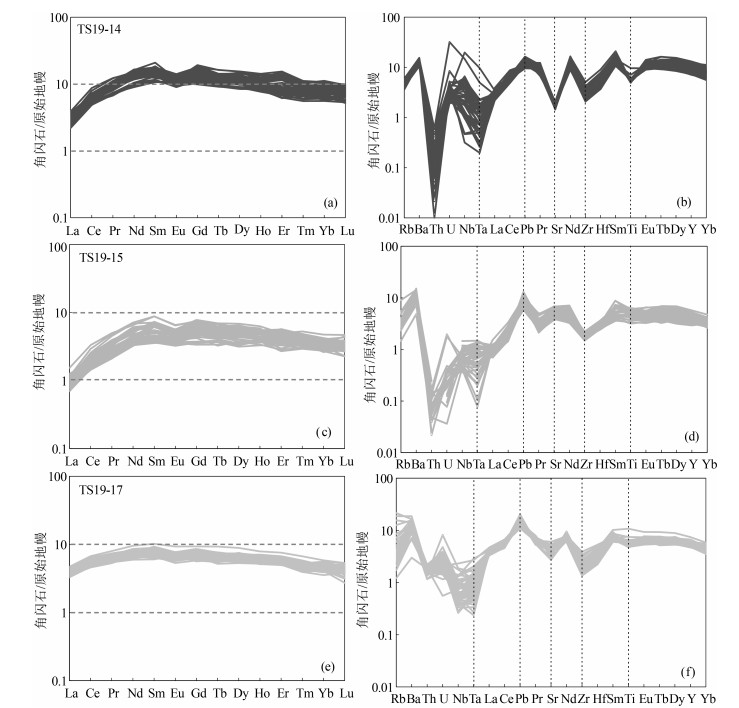
图 5 泰山闪长岩和角闪石岩中角闪石原始地幔标准化稀土元素配分图(a、c、e)和微量元素蛛网图(b、d、f)
(原始地幔标准化数据据参考文献[19])
Figure 5. Primitive mantle normalized REE patterns(a, c, e)and trace element spider diagrams (b, d, f)of amphibole from diorite and hornblendites in Taishan
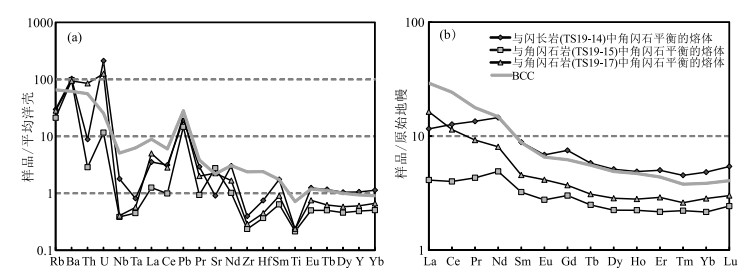
图 8 与泰山闪长岩和角闪石岩中角闪石平衡熔体(平均值)的平均洋壳标准化微量元素蛛网图(a)和原始地幔标准化稀土元素配分图(b)(平均洋壳据参考文献[45];平均大陆地壳(BCC)据参考文献[46])
Figure 8. The average ocean crust(OC)normalized incompatible element spidergrams(a) and PM normalized REE patterns(b) for calculated compositions of melt in equilibrium with amphibole from diorite and hornblendites in Taishan
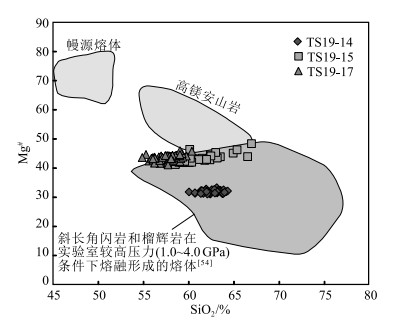
图 10 与泰山闪长岩和角闪石岩中角闪石平衡的熔体
SiO2-Mg#图解(底图据参考文献[56])
Figure 10. Mg# vs.SiO2 diagram for the calculated parental magma in equilibrium with amphibole in diorite and hornblendites
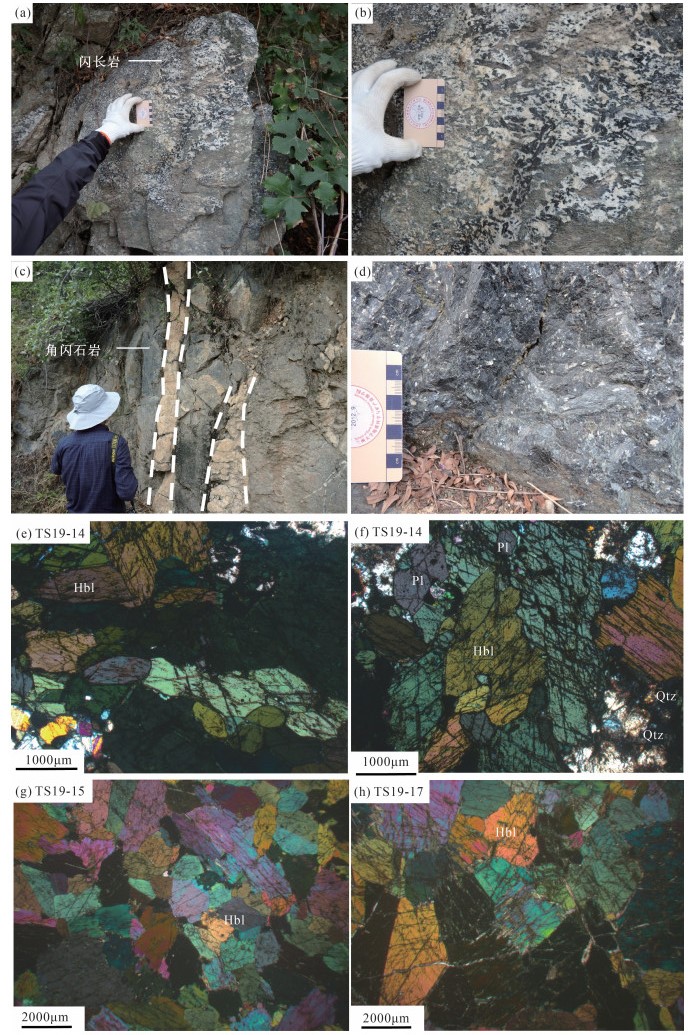
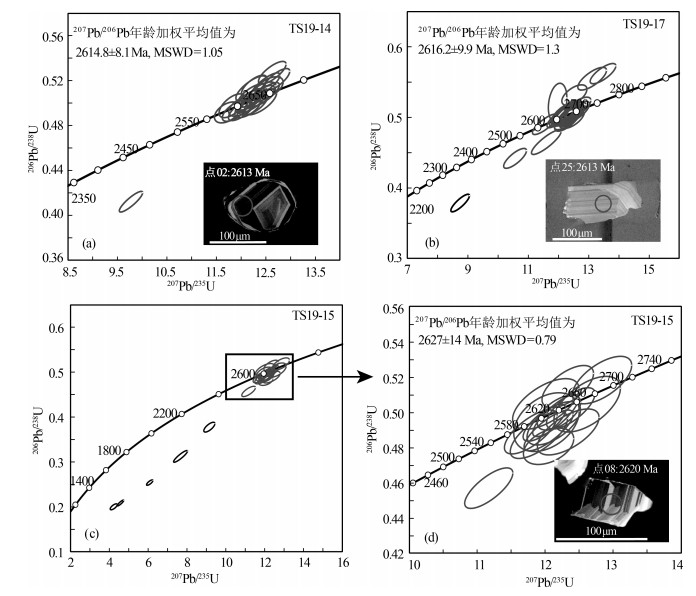
表 1 泰山地区闪长岩和角闪石岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Th-Pb定年数据
Table 1 LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Th-Pb dating of the diorite and hornblendites from the Taishan area
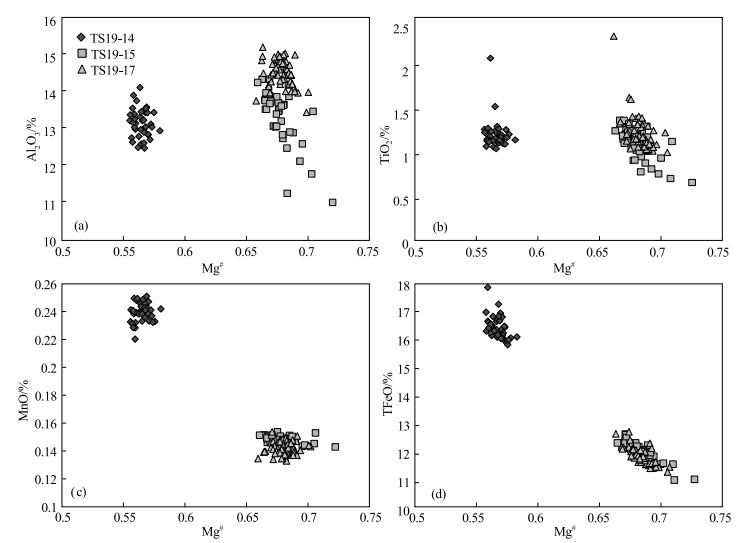
分析点位 元素/10-6 Th/U 同位素比值 年龄/Ma 谐和度 Pb Th U 207Pb/206Pb 1 σ 207Pb/235U 1 σ 206Pb/238U 1 σ 207Pb/206Pb 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ TS19-14-1 41 39 64 0.61 0.1782 0.0023 12.4926 0.1956 0.5073 0.0070 2637 21 2642 15 2645 30 99% TS19-14-2 75 72 120 0.60 0.1756 0.0019 12.1651 0.1762 0.5006 0.0063 2613 17 2617 14 2616 27 99% TS19-14-3 52 44 81 0.55 0.1737 0.0021 12.6462 0.1843 0.5268 0.0067 2594 20 2654 14 2728 28 97% TS19-14-4 55 57 85 0.67 0.1754 0.0022 12.5106 0.1934 0.5160 0.0070 2610 20 2644 15 2682 30 98% TS19-14-5 31 24 52 0.46 0.1798 0.0029 12.4072 0.2166 0.5008 0.0077 2651 26 2636 17 2617 33 99% TS19-14-6 52 48 82 0.59 0.1766 0.0024 12.4320 0.1892 0.5092 0.0061 2621 23 2638 14 2653 26 99% TS19-14-7 39 47 60 0.79 0.1754 0.0024 12.0289 0.1743 0.4968 0.0059 2610 23 2607 14 2600 25 99% TS19-14-8 26 20 41 0.49 0.1766 0.0025 12.2260 0.1950 0.5021 0.0070 2621 29 2622 15 2623 30 99% TS19-14-9 40 29 66 0.44 0.1773 0.0021 12.1528 0.1743 0.4959 0.0060 2628 19 2616 14 2596 26 99% TS19-14-10 48 39 78 0.50 0.1781 0.0025 12.2668 0.1955 0.4996 0.0071 2635 22 2625 15 2612 31 99% TS19-14-11 50 47 81 0.58 0.1748 0.0023 11.8959 0.1724 0.4928 0.0062 2606 21 2596 14 2583 27 99% TS19-14-12 36 29 59 0.48 0.1753 0.0021 12.1863 0.1745 0.5024 0.0059 2609 19 2619 14 2624 25 99% TS19-14-13 46 42 75 0.56 0.1721 0.0021 12.2216 0.2061 0.5127 0.0074 2589 20 2622 16 2668 32 98% TS19-14-14 30 24 49 0.49 0.1726 0.0024 11.8331 0.1741 0.4973 0.0070 2583 22 2591 14 2602 30 99% TS19-14-15 131 92 273 0.34 0.1718 0.0022 9.7879 0.1561 0.4117 0.0061 2576 22 2415 15 2222 28 91% TS19-14-16 29 29 46 0.63 0.1728 0.0026 11.7373 0.1725 0.4913 0.0062 2585 24 2584 14 2576 27 99% TS19-14-17 37 31 59 0.53 0.1746 0.0023 12.2348 0.1921 0.5064 0.0068 2602 23 2623 15 2641 29 99% TS19-14-18 44 39 68 0.57 0.1722 0.0021 12.2790 0.1694 0.5150 0.0063 2579 20 2626 13 2678 27 98% TS19-14-19 50 69 76 0.91 0.1761 0.0023 12.0268 0.1772 0.4936 0.0063 2616 22 2606 14 2586 27 99% TS19-14-20 23 20 36 0.56 0.1773 0.0025 12.5834 0.1863 0.5137 0.0062 2627 24 2649 14 2672 27 99% TS19-14-21 119 35 204 0.17 0.1767 0.0020 12.7348 0.1748 0.5205 0.0066 2633 20 2660 13 2702 28 98% TS19-14-22 98 74 160 0.46 0.1776 0.0021 12.4378 0.1650 0.5061 0.0062 2631 19 2638 13 2640 27 99% TS19-15-01 28 26 44 0.60 0.1814 0.0037 12.0500 0.2444 0.4810 0.0068 2665 33 2608 19 2531 30 97% TS19-15-02 28 12 49 0.24 0.1776 0.0033 12.1263 0.2596 0.4940 0.0081 2631 31 2614 20 2588 35 98% TS19-15-04 121 113 190 0.59 0.1752 0.0026 11.9907 0.2082 0.4943 0.0069 2609 25 2604 16 2589 30 99% TS19-15-05 76 52 118 0.44 0.1731 0.0030 12.3320 0.2502 0.5149 0.0079 2587 29 2630 19 2677 34 98% TS19-15-08 52 5 90 0.06 0.1764 0.0028 12.2025 0.2110 0.5000 0.0065 2620 31 2620 16 2614 28 99% TS19-15-09 149 77 244 0.32 0.1763 0.0026 12.1545 0.2230 0.4984 0.0079 2618 24 2616 17 2607 34 99% TS19-15-10 15 7 26 0.26 0.1784 0.0046 12.0195 0.3180 0.4947 0.0110 2639 43 2606 25 2591 47 99% TS19-15-12 61 25 103 0.24 0.1780 0.0029 12.3760 0.2357 0.5025 0.0077 2635 27 2633 18 2624 33 99% TS19-15-14 45 36 75 0.48 0.1736 0.0030 11.7890 0.2567 0.4891 0.0082 2594 28 2588 20 2567 36 99% TS19-15-15 50 74 69 1.08 0.1787 0.0035 12.8363 0.2878 0.5186 0.0089 2640 32 2668 21 2693 38 99% TS19-15-16 24 23 37 0.62 0.1814 0.0042 12.6172 0.3230 0.5048 0.0104 2666 38 2652 24 2635 45 99% TS19-15-17 28 44 39 1.12 0.1758 0.0034 11.9073 0.2776 0.4874 0.0088 2614 31 2597 22 2559 38 98% TS19-15-18 66 33 121 0.27 0.1757 0.0029 11.1700 0.2338 0.4572 0.0076 2612 27 2537 20 2427 34 95% TS19-15-19 14 14 21 0.67 0.1714 0.0039 12.0086 0.3220 0.5050 0.0095 2572 38 2605 25 2635 41 98% TS19-15-20 25 1 44 0.03 0.1816 0.0037 12.3387 0.2992 0.4891 0.0086 2733 33 2631 23 2567 37 97% TS19-15-21 112 15 198 0.08 0.1767 0.0028 12.0504 0.2386 0.4900 0.0076 2622 27 2608 19 2570 33 98% TS19-15-03 192 421 686 0.61 0.1578 0.0023 4.5783 0.1110 0.2087 0.0043 2432 25 1745 20 1222 23 64% TS19-15-06 206 402 782 0.51 0.1525 0.0034 4.2278 0.1197 0.2002 0.0044 2376 39 1679 23 1176 23 64% TS19-15-07 169 668 432 1.55 0.1731 0.0025 6.0816 0.1092 0.2541 0.0040 2587 24 1988 16 1460 20 69% TS19-15-11 194 845 258 3.27 0.1754 0.0032 9.1488 0.1885 0.3776 0.0072 2610 30 2353 19 2065 34 86% TS19-15-13 154 254 417 0.61 0.1764 0.0027 7.6680 0.2379 0.3125 0.0086 2620 31 2193 28 1753 42 77% TS19-17-1 55 34 89 0.38 0.1749 0.0028 12.1655 0.2524 0.5029 0.0082 2605 22 2617 20 2626 35 99% TS19-17-2 86 59 136 0.43 0.1706 0.0029 11.9727 0.2026 0.5205 0.0183 2565 28 2602 16 2702 78 96% TS19-17-3 127 53 213 0.25 0.1741 0.0027 11.9717 0.2303 0.4986 0.0088 2598 26 2602 18 2608 38 99% TS19-17-4 48 24 71 0.33 0.1736 0.0028 13.4761 0.2809 0.5620 0.0095 2592 27 2714 20 2875 39 94% TS19-17-5 54 20 88 0.23 0.1715 0.0033 13.1168 0.3139 0.5548 0.0106 2572 33 2688 23 2845 44 94% TS19-17-6 59 33 101 0.32 0.1705 0.0031 11.5521 0.2724 0.4900 0.0096 2563 30 2569 22 2571 41 99% TS19-17-7 36 23 56 0.41 0.1712 0.0033 12.5277 0.2742 0.5315 0.0096 2569 32 2645 21 2748 41 96% TS19-17-8 72 32 120 0.27 0.1749 0.0028 12.1207 0.2329 0.5007 0.0081 2605 21 2614 18 2617 35 99% TS19-17-10 31 20 51 0.39 0.1751 0.0034 12.1889 0.2764 0.5043 0.0105 2606 32 2619 21 2632 45 99% TS19-17-11 48 23 78 0.30 0.1766 0.0033 12.6287 0.2931 0.5136 0.0099 2621 31 2652 22 2672 42 99% TS19-17-12 94 42 151 0.28 0.1739 0.0027 12.2894 0.2273 0.5087 0.0085 2595 26 2627 17 2651 37 99% TS19-17-13 49 25 79 0.32 0.1772 0.0030 12.4982 0.2701 0.5069 0.0095 2628 28 2643 20 2644 41 99% TS19-17-14 25 15 41 0.37 0.1802 0.0037 12.4427 0.2789 0.4993 0.0100 2655 34 2638 21 2611 43 98% TS19-17-15 59 45 93 0.48 0.1736 0.0032 12.1133 0.2709 0.5016 0.0097 2594 36 2613 21 2621 42 99% TS19-17-16 77 32 148 0.22 0.1790 0.0034 11.5974 0.3239 0.4647 0.0115 2644 31 2572 26 2460 51 95% TS19-17-17 42 28 65 0.44 0.1787 0.0033 12.6095 0.2760 0.5081 0.0097 2643 31 2651 21 2649 42 99% TS19-17-18 62 30 101 0.30 0.1771 0.0030 12.3572 0.2641 0.5026 0.0098 2626 28 2632 20 2625 42 99% TS19-17-19 86 29 163 0.18 0.1720 0.0030 10.5643 0.2498 0.4417 0.0093 2577 28 2486 22 2358 42 94% TS19-17-20 25 18 40 0.44 0.1753 0.0036 12.3060 0.3112 0.5071 0.0113 2609 35 2628 24 2644 48 99% TS19-17-21 55 42 86 0.49 0.1785 0.0034 12.4304 0.2883 0.5025 0.0102 2639 31 2637 22 2625 44 99% TS19-17-22 46 21 76 0.28 0.1793 0.0031 12.3214 0.2950 0.4980 0.0117 2646 30 2629 23 2605 50 99% TS19-17-23 27 13 44 0.30 0.1780 0.0031 12.3179 0.3004 0.4989 0.0109 2635 29 2629 23 2609 47 99% TS19-17-24 43 23 68 0.34 0.1760 0.0032 12.3472 0.3031 0.5055 0.0105 2617 35 2631 23 2638 45 99% TS19-17-25 35 17 57 0.31 0.1757 0.0033 12.2159 0.2793 0.5025 0.0099 2613 32 2621 22 2625 43 99% TS19-17-9 103 39 252 0.15 0.1669 0.0026 8.7463 0.2034 0.3783 0.0082 2528 26 2312 21 2068 38 88% 表 2 泰山闪长岩和角闪石岩中角闪石激光原位主量元素数据
Table 2 Major elements compositions of amphibole in diorite and hornblendites from Taishan
% 点位 Na2O MgO Al2O3 SiO2 K2O CaO TiO2 MnO TFeO 总计 Mg# Si AlⅣ AlⅥ Ti Fe3+ Mg Fe2+ Fe2+ Mn2+ Ca Na Na K P/kbar TP16/℃ 深度/km SiO2/% Mg# TS19-14(闪长岩) 1 1.51 11.1 12.9 41.9 0.71 11.8 1.12 0.23 16.5 97.63 0.57 6.19 1.81 0.44 0.13 0.70 2.44 1.30 0.03 0.03 1.87 0.07 0.36 0.14 7.69 877 28 63.5 32.39 2 1.64 11.3 13.0 42.0 0.67 11.6 1.17 0.24 16.1 97.63 0.58 6.19 1.81 0.45 0.13 0.68 2.48 1.26 0.05 0.03 1.83 0.09 0.38 0.13 7.75 884 29 63.1 33.26 3 1.54 10.7 13.3 41.1 0.78 11.7 1.28 0.23 17.0 97.63 0.56 6.10 1.90 0.42 0.14 0.76 2.37 1.31 0.04 0.03 1.86 0.08 0.37 0.15 8.03 887 30 62.4 31.06 4 1.62 10.8 13.5 41.5 0.70 11.7 1.21 0.24 16.3 97.63 0.57 6.15 1.85 0.50 0.14 0.64 2.39 1.33 0.04 0.03 1.85 0.08 0.39 0.13 8.19 888 30 62.1 32.17 5 1.52 10.9 13.1 41.9 0.70 11.7 1.23 0.24 16.4 97.63 0.57 6.20 1.80 0.48 0.14 0.63 2.40 1.36 0.04 0.03 1.86 0.08 0.36 0.13 7.84 878 29 63.2 32.13 6 1.69 10.5 14.0 41.0 0.75 11.7 1.30 0.25 16.4 97.63 0.56 6.08 1.92 0.52 0.15 0.63 2.33 1.38 0.03 0.03 1.86 0.07 0.41 0.14 8.61 898 32 60.7 31.32 7 1.65 10.7 14.2 40.7 0.77 11.8 1.26 0.25 16.4 97.63 0.56 6.03 1.97 0.50 0.14 0.71 2.36 1.28 0.03 0.03 1.87 0.07 0.40 0.15 8.77 905 32 60.1 31.79 8 1.53 10.9 13.4 40.9 0.75 11.8 1.54 0.24 16.7 97.63 0.56 6.05 1.95 0.39 0.17 0.78 2.41 1.26 0.03 0.03 1.87 0.07 0.37 0.14 8.10 899 30 61.7 31.81 9 1.66 10.9 13.6 41.1 0.79 11.8 1.22 0.24 16.2 97.63 0.57 6.10 1.90 0.48 0.14 0.66 2.40 1.33 0.03 0.03 1.88 0.07 0.41 0.15 8.33 897 31 61.4 32.27 10 1.57 11.0 13.5 41.5 0.77 11.8 1.23 0.23 16.1 97.63 0.58 6.13 1.87 0.48 0.14 0.66 2.43 1.30 0.03 0.03 1.87 0.07 0.38 0.15 8.18 891 30 62.0 32.81 11 1.58 10.6 13.2 41.0 0.75 11.6 2.08 0.25 16.5 97.63 0.56 6.08 1.92 0.40 0.23 0.61 2.36 1.40 0.04 0.03 1.85 0.08 0.38 0.14 7.99 905 30 61.6 31.49 12 1.57 11.1 12.9 41.7 0.69 11.8 1.18 0.25 16.5 97.63 0.57 6.17 1.83 0.42 0.13 0.71 2.44 1.31 0.03 0.03 1.88 0.07 0.38 0.13 7.70 882 28 63.3 32.35 13 1.43 11.0 12.6 42.0 0.71 11.8 1.18 0.23 16.7 97.63 0.57 6.21 1.79 0.41 0.13 0.72 2.42 1.32 0.04 0.03 1.86 0.07 0.34 0.13 7.48 870 28 64.2 31.89 14 1.53 11.0 13.0 41.6 0.73 11.7 1.13 0.24 16.7 97.63 0.57 6.15 1.85 0.42 0.13 0.76 2.43 1.27 0.04 0.03 1.85 0.08 0.36 0.14 7.79 881 29 63.2 32.02 15 1.53 11.2 12.7 41.4 0.70 11.8 1.13 0.25 16.9 97.63 0.57 6.13 1.87 0.33 0.13 0.86 2.48 1.21 0.03 0.03 1.87 0.07 0.37 0.13 7.50 882 28 63.7 32.08 16 1.57 10.9 13.8 40.5 0.74 11.8 1.26 0.25 16.8 97.63 0.56 5.99 2.01 0.40 0.14 0.87 2.40 1.19 0.03 0.03 1.88 0.07 0.39 0.14 8.47 903 31 60.7 31.55 17 1.50 11.2 13.1 41.0 0.72 11.9 1.17 0.24 16.8 97.63 0.57 6.06 1.94 0.35 0.13 0.89 2.47 1.17 0.03 0.03 1.88 0.06 0.37 0.14 7.86 891 29 62.6 32.19 18 1.51 11.1 13.3 40.8 0.72 11.9 1.32 0.25 16.8 97.63 0.57 6.03 1.97 0.35 0.15 0.89 2.45 1.17 0.03 0.03 1.88 0.07 0.37 0.14 8.01 897 30 62.0 31.96 19 1.49 11.3 13.3 40.6 0.71 11.7 1.17 0.24 17.1 97.63 0.57 6.00 2.00 0.31 0.13 1.04 2.49 1.03 0.04 0.03 1.85 0.08 0.34 0.13 7.99 897 30 62.0 32.06 20 1.51 11.3 13.2 40.0 0.70 11.8 1.22 0.24 17.7 97.63 0.56 5.91 2.09 0.21 0.14 1.18 2.49 0.97 0.03 0.03 1.86 0.07 0.36 0.13 7.95 904 29 61.6 31.29 21 1.78 10.8 13.6 41.3 0.69 11.9 1.14 0.24 16.2 97.63 0.57 6.13 1.87 0.51 0.13 0.59 2.38 1.40 0.02 0.03 1.89 0.06 0.45 0.13 8.31 895 31 61.5 32.22 22 1.77 10.7 13.5 41.5 0.70 12.0 1.13 0.24 16.0 97.63 0.57 6.16 1.84 0.52 0.13 0.52 2.38 1.46 0.01 0.03 1.91 0.05 0.46 0.13 8.22 891 30 61.9 32.33 23 1.74 10.7 12.8 42.6 0.69 11.9 1.12 0.24 15.9 97.63 0.57 6.32 1.69 0.55 0.13 0.37 2.38 1.58 0.02 0.03 1.89 0.06 0.44 0.13 7.61 871 28 63.9 32.52 24 1.79 10.6 12.8 42.2 0.73 11.9 1.09 0.24 16.2 97.63 0.56 6.29 1.72 0.54 0.12 0.38 2.34 1.62 0.02 0.03 1.90 0.05 0.46 0.14 7.71 873 29 63.6 31.71 25 1.71 10.7 13.0 42.0 0.74 12.0 1.29 0.24 16.1 97.63 0.57 6.23 1.77 0.50 0.14 0.44 2.36 1.55 0.01 0.03 1.91 0.05 0.44 0.14 7.80 881 29 63.1 32.07 26 1.68 10.6 13.3 41.4 0.78 12.1 1.15 0.23 16.5 97.63 0.56 6.15 1.85 0.49 0.13 0.56 2.35 1.48 0.01 0.03 1.92 0.04 0.44 0.15 8.11 887 30 62.3 31.41 27 1.76 10.4 13.0 42.1 0.75 12.0 1.20 0.24 16.2 97.63 0.56 6.27 1.73 0.56 0.14 0.35 2.31 1.65 0.01 0.03 1.91 0.05 0.46 0.14 7.88 876 29 63.2 31.45 28 1.81 10.7 13.2 42.0 0.71 11.8 1.28 0.24 15.8 97.63 0.57 6.23 1.77 0.54 0.14 0.41 2.38 1.53 0.02 0.03 1.88 0.06 0.46 0.14 7.96 887 29 62.6 32.59 29 1.69 10.9 13.1 41.9 0.74 11.9 1.19 0.23 16.0 97.63 0.57 6.21 1.79 0.50 0.13 0.52 2.41 1.44 0.02 0.03 1.89 0.06 0.43 0.14 7.89 884 29 62.9 32.66 30 1.83 10.7 13.6 41.5 0.64 11.9 1.19 0.25 16.0 97.63 0.57 6.15 1.85 0.53 0.13 0.52 2.36 1.45 0.02 0.03 1.89 0.06 0.47 0.12 8.31 895 31 61.5 32.22 31 1.60 10.4 13.5 41.6 0.76 12.1 1.16 0.23 16.3 97.63 0.56 6.19 1.82 0.54 0.13 0.49 2.31 1.53 0.01 0.03 1.93 0.04 0.42 0.15 8.20 882 30 62.3 31.39 32 1.78 10.3 13.4 41.6 0.74 12.0 1.25 0.24 16.3 97.63 0.56 6.19 1.81 0.55 0.14 0.42 2.29 1.60 0.01 0.03 1.91 0.05 0.47 0.14 8.21 887 30 62.1 31.09 33 1.69 10.5 13.0 42.1 0.74 12.0 1.18 0.24 16.1 97.63 0.56 6.25 1.75 0.54 0.13 0.41 2.34 1.59 0.01 0.03 1.92 0.04 0.44 0.14 7.86 877 29 63.2 31.84 34 1.62 10.6 12.8 41.9 0.78 11.9 1.09 0.23 16.7 97.63 0.56 6.23 1.77 0.48 0.12 0.54 2.35 1.52 0.02 0.03 1.90 0.05 0.42 0.15 7.67 872 28 63.7 31.19 35 1.64 10.5 12.7 41.9 0.76 12.3 1.17 0.23 16.4 97.63 0.56 6.25 1.75 0.48 0.13 0.42 2.33 1.63 0.00 0.02 1.97 0.02 0.46 0.15 7.60 873 28 63.8 31.26 36 1.77 10.7 12.5 42.6 0.69 11.9 1.16 0.24 16.1 97.63 0.57 6.34 1.66 0.53 0.13 0.34 2.36 1.64 0.02 0.03 1.90 0.06 0.45 0.13 7.43 868 28 64.3 32.12 37 1.87 10.6 12.5 42.2 0.70 12.0 1.16 0.24 16.3 97.63 0.56 6.29 1.72 0.49 0.13 0.38 2.36 1.64 0.01 0.03 1.92 0.04 0.50 0.13 7.48 876 28 64.0 31.65 38 1.68 10.6 13.6 40.8 0.73 12.1 1.15 0.24 16.6 97.63 0.56 6.07 1.93 0.46 0.13 0.66 2.35 1.41 0.00 0.03 1.94 0.04 0.45 0.14 8.35 896 31 61.4 31.25 39 1.56 10.6 13.1 41.4 0.75 12.3 1.14 0.22 16.6 97.63 0.56 6.16 1.84 0.45 0.13 0.59 2.36 1.47 0.00 0.02 1.95 0.02 0.43 0.14 7.91 881 29 62.9 31.39 40 1.71 10.6 13.5 41.5 0.76 12.0 1.07 0.24 16.2 97.63 0.57 6.16 1.84 0.53 0.12 0.52 2.35 1.48 0.01 0.03 1.92 0.05 0.45 0.14 8.25 887 31 62.0 31.88 TS19-15(角闪石岩) 1 1.83 13.4 12.2 44.9 0.41 12.3 0.78 0.14 11.6 97.63 0.70 6.53 1.47 0.62 0.09 0.17 2.90 1.22 0.02 0.02 1.92 0.04 0.48 0.08 6.92 879 26 64.9 45.12 2 2.02 12.7 13.5 43.3 0.46 12.3 1.27 0.15 11.9 97.63 0.68 6.32 1.68 0.66 0.14 0.16 2.77 1.28 0.02 0.02 1.93 0.04 0.53 0.09 8.09 915 30 60.7 43.15 3 2.10 12.8 13.5 43.2 0.46 12.2 1.20 0.15 12.0 97.63 0.68 6.31 1.69 0.64 0.13 0.21 2.79 1.23 0.03 0.02 1.91 0.05 0.55 0.09 8.08 917 30 60.6 43.11 4 2.10 12.9 13.7 42.7 0.46 12.5 1.26 0.15 11.9 97.63 0.68 6.24 1.76 0.60 0.14 0.26 2.81 1.19 0.01 0.02 1.95 0.03 0.57 0.09 8.23 929 30 59.4 43.60 5 2.11 12.3 14.4 42.0 0.49 12.5 1.39 0.15 12.3 97.63 0.66 6.17 1.84 0.66 0.15 0.22 2.68 1.29 0.00 0.02 1.97 0.02 0.58 0.09 8.84 937 33 57.6 41.62 6 1.94 13.4 12.9 43.6 0.43 12.5 0.84 0.15 11.9 97.63 0.69 6.35 1.65 0.57 0.09 0.33 2.90 1.11 0.01 0.02 1.95 0.03 0.52 0.08 7.56 904 28 62.4 44.46 7 2.01 12.9 13.3 43.4 0.45 12.3 1.10 0.15 12.0 97.63 0.68 6.34 1.66 0.62 0.12 0.21 2.80 1.24 0.01 0.02 1.93 0.04 0.53 0.09 7.85 910 29 61.5 43.35 8 1.82 13.4 12.5 43.7 0.43 12.5 0.90 0.15 12.2 97.63 0.68 6.37 1.63 0.52 0.10 0.38 2.90 1.11 0.01 0.02 1.95 0.03 0.49 0.08 7.22 896 27 63.5 43.89 9 2.09 13.4 13.5 43.4 0.46 12.4 1.15 0.15 11.1 97.63 0.71 6.31 1.69 0.63 0.13 0.21 2.91 1.13 0.01 0.02 1.94 0.03 0.56 0.08 8.03 925 30 60.1 46.39 10 2.00 12.8 13.6 42.4 0.50 12.3 1.17 0.15 12.7 97.63 0.67 6.20 1.80 0.54 0.13 0.42 2.80 1.11 0.02 0.02 1.92 0.04 0.53 0.09 8.13 923 30 60.1 41.91 11 2.03 13.1 13.9 42.4 0.45 12.6 1.20 0.15 11.8 97.63 0.69 6.19 1.81 0.59 0.13 0.34 2.84 1.10 0.00 0.02 1.96 0.02 0.56 0.08 8.39 933 31 58.8 44.08 12 1.67 13.5 11.3 44.8 0.40 12.5 1.04 0.15 12.3 97.63 0.69 6.52 1.48 0.46 0.11 0.29 2.93 1.20 0.00 0.02 1.95 0.03 0.45 0.07 6.22 872 23 66.5 43.91 13 1.94 12.9 13.1 43.2 0.47 12.5 1.08 0.14 12.3 97.63 0.67 6.31 1.69 0.57 0.12 0.29 2.80 1.22 0.00 0.02 1.96 0.02 0.53 0.09 7.76 909 29 61.8 42.63 14 1.75 14.0 11.8 44.7 0.37 12.5 0.73 0.15 11.6 97.63 0.71 6.48 1.53 0.50 0.08 0.38 3.03 1.02 0.01 0.02 1.94 0.03 0.46 0.07 6.61 883 24 65.4 46.26 15 2.02 12.6 14.0 42.5 0.47 12.4 1.18 0.15 12.3 97.63 0.67 6.22 1.78 0.63 0.13 0.29 2.75 1.21 0.01 0.02 1.95 0.03 0.55 0.09 8.45 925 31 59.3 42.27 16 1.95 12.6 13.8 42.7 0.52 12.3 1.21 0.15 12.4 97.63 0.67 6.24 1.76 0.62 0.13 0.30 2.74 1.20 0.02 0.02 1.93 0.04 0.51 0.10 8.35 919 31 59.9 41.87 17 2.08 12.7 14.0 42.2 0.50 12.4 1.23 0.15 12.4 97.63 0.67 6.18 1.82 0.60 0.14 0.34 2.76 1.17 0.01 0.02 1.94 0.03 0.56 0.09 8.49 931 31 58.8 42.09 18 2.07 12.5 14.0 42.7 0.49 12.3 1.30 0.15 12.2 97.63 0.67 6.25 1.75 0.67 0.14 0.20 2.72 1.28 0.02 0.02 1.93 0.04 0.55 0.09 8.48 924 31 59.3 42.16 19 1.92 12.8 13.6 43.0 0.52 12.3 1.26 0.15 12.1 97.63 0.68 6.27 1.73 0.62 0.14 0.28 2.79 1.17 0.02 0.02 1.92 0.04 0.50 0.10 8.15 917 30 60.4 43.15 20 1.84 13.1 12.8 43.8 0.46 12.4 0.98 0.15 12.1 97.63 0.68 6.38 1.62 0.58 0.11 0.29 2.85 1.18 0.01 0.02 1.94 0.03 0.49 0.09 7.45 897 28 63.1 43.52 21 2.14 12.2 14.3 42.5 0.49 12.2 1.27 0.15 12.4 97.63 0.66 6.23 1.77 0.70 0.14 0.17 2.66 1.33 0.02 0.02 1.92 0.04 0.57 0.09 8.76 927 32 58.5 41.22 22 1.92 13.0 13.1 43.6 0.44 12.2 0.93 0.15 12.4 97.63 0.68 6.35 1.65 0.60 0.10 0.34 2.82 1.14 0.03 0.02 1.90 0.06 0.49 0.08 7.70 901 28 62.4 42.81 23 1.91 13.0 13.8 42.7 0.45 12.4 1.05 0.15 12.2 97.63 0.68 6.22 1.78 0.58 0.12 0.41 2.82 1.07 0.01 0.02 1.94 0.03 0.51 0.08 8.24 921 30 60.0 43.10 24 1.85 13.1 12.9 44.0 0.42 12.4 0.81 0.15 12.1 97.63 0.68 6.40 1.60 0.62 0.09 0.28 2.84 1.19 0.01 0.02 1.93 0.04 0.49 0.08 7.52 892 28 63.2 43.48 25 2.18 12.7 13.7 43.0 0.47 12.4 1.34 0.15 11.7 97.63 0.68 6.30 1.70 0.66 0.15 0.09 2.76 1.34 0.01 0.02 1.95 0.03 0.59 0.09 8.24 926 30 59.7 43.57 26 2.17 12.8 13.8 42.3 0.46 12.6 1.29 0.15 12.1 97.63 0.68 6.19 1.81 0.57 0.14 0.29 2.80 1.20 0.00 0.01 1.97 0.02 0.60 0.09 8.29 935 31 58.8 43.08 27 2.10 12.9 14.2 42.4 0.45 12.4 1.32 0.15 11.7 97.63 0.69 6.18 1.82 0.63 0.15 0.29 2.81 1.13 0.01 0.02 1.94 0.03 0.56 0.08 8.65 939 32 57.8 44.02 28 2.03 12.6 14.4 42.1 0.48 12.4 1.14 0.15 12.3 97.63 0.67 6.15 1.85 0.63 0.13 0.36 2.75 1.13 0.01 0.02 1.94 0.03 0.55 0.09 8.79 933 33 58.0 42.29 29 1.92 12.8 14.0 42.3 0.50 11.9 1.39 0.15 12.7 97.63 0.67 6.16 1.84 0.57 0.15 0.49 2.79 1.00 0.05 0.02 1.86 0.08 0.47 0.09 8.46 930 31 58.9 41.97 30 2.16 12.7 13.9 42.6 0.47 12.4 1.20 0.15 12.0 97.63 0.68 6.23 1.77 0.63 0.13 0.23 2.77 1.24 0.01 0.02 1.95 0.03 0.58 0.09 8.42 929 31 59.0 42.95 31 1.74 14.6 11.1 45.4 0.33 12.6 0.69 0.14 11.1 97.63 0.72 6.57 1.43 0.45 0.08 0.33 3.14 1.00 0.00 0.02 1.96 0.02 0.47 0.06 5.95 875 22 67.0 48.36 32 1.88 13.6 12.6 43.8 0.42 12.5 0.96 0.14 11.7 97.63 0.70 6.37 1.63 0.54 0.11 0.32 2.94 1.10 0.00 0.02 1.96 0.02 0.51 0.08 7.31 903 27 63.0 45.35 33 2.07 12.7 13.5 43.3 0.47 12.4 1.07 0.14 12.0 97.63 0.68 6.34 1.66 0.66 0.12 0.15 2.76 1.32 0.01 0.02 1.95 0.03 0.56 0.09 8.03 911 30 61.1 42.91 34 2.03 12.8 13.6 42.7 0.50 12.2 1.13 0.15 12.6 97.63 0.67 6.24 1.76 0.58 0.12 0.35 2.78 1.16 0.02 0.02 1.92 0.05 0.53 0.09 8.13 919 30 60.3 42.01 35 2.01 13.0 13.7 42.9 0.45 12.4 1.03 0.15 12.1 97.63 0.68 6.25 1.75 0.61 0.11 0.32 2.82 1.14 0.01 0.02 1.95 0.03 0.54 0.08 8.18 920 30 60.2 43.36 36 2.11 12.5 13.8 42.4 0.47 12.7 1.21 0.15 12.4 97.63 0.67 6.22 1.79 0.60 0.13 0.24 2.73 1.28 0.00 0.01 1.99 0.01 0.60 0.09 8.36 927 31 59.3 41.87 37 1.87 13.3 13.0 43.7 0.43 12.1 1.04 0.15 12.0 97.63 0.69 6.35 1.65 0.57 0.11 0.37 2.89 1.06 0.03 0.02 1.89 0.06 0.47 0.08 7.56 904 28 62.5 44.16 38 2.00 12.9 13.1 43.4 0.45 12.4 0.94 0.15 12.3 97.63 0.68 6.33 1.67 0.59 0.10 0.28 2.82 1.21 0.01 0.02 1.95 0.03 0.54 0.08 7.74 906 29 62.0 42.94 39 2.10 12.5 13.8 42.6 0.48 12.5 1.35 0.15 12.1 97.63 0.67 6.24 1.76 0.62 0.15 0.19 2.74 1.30 0.00 0.01 1.97 0.02 0.58 0.09 8.34 928 31 59.3 42.41 40 2.01 12.7 13.7 42.4 0.49 12.5 1.25 0.15 12.4 97.63 0.67 6.21 1.79 0.58 0.14 0.33 2.77 1.19 0.00 0.02 1.96 0.02 0.55 0.09 8.27 926 31 59.6 42.32 TS19-17(角闪石岩) 1 2.09 12.5 14.3 42.6 0.57 12.1 1.15 0.15 12.2 97.63 0.67 6.23 1.77 0.68 0.13 0.26 2.73 1.21 0.03 0.02 1.89 0.06 0.54 0.11 8.68 926 32 58.8 42.22 2 2.15 12.6 15.1 42.0 0.56 12.0 1.24 0.15 11.9 97.63 0.68 6.13 1.87 0.72 0.14 0.31 2.74 1.10 0.04 0.02 1.87 0.07 0.54 0.10 9.33 945 35 56.0 43.07 3 2.12 12.7 14.7 42.3 0.59 12.1 1.15 0.15 11.8 97.63 0.68 6.18 1.83 0.71 0.13 0.28 2.76 1.13 0.03 0.02 1.89 0.06 0.54 0.11 9.03 937 33 57.3 43.30 4 2.07 12.7 14.9 42.0 0.79 11.7 1.21 0.15 12.1 97.63 0.68 6.13 1.87 0.69 0.13 0.36 2.76 1.05 0.06 0.02 1.83 0.09 0.50 0.15 9.20 941 34 56.6 42.88 5 2.20 12.7 14.9 42.4 0.56 12.0 1.08 0.15 11.7 97.63 0.68 6.18 1.82 0.74 0.12 0.25 2.75 1.14 0.04 0.02 1.87 0.07 0.55 0.10 9.19 939 34 56.8 43.59 6 2.01 12.8 14.0 42.0 0.63 12.2 1.25 0.15 12.5 97.63 0.67 6.14 1.86 0.56 0.14 0.43 2.80 1.08 0.02 0.02 1.92 0.04 0.53 0.12 8.50 934 31 58.5 42.32 7 2.14 12.9 14.8 41.9 0.53 12.0 1.34 0.14 11.9 97.63 0.68 6.10 1.90 0.64 0.15 0.40 2.81 1.01 0.04 0.02 1.87 0.07 0.54 0.10 9.08 949 34 56.1 43.59 8 2.14 12.7 15.1 42.3 0.55 11.9 1.21 0.14 11.6 97.63 0.68 6.16 1.84 0.75 0.13 0.26 2.75 1.10 0.05 0.02 1.86 0.08 0.53 0.10 9.33 942 35 56.3 43.73 9 2.04 13.1 14.4 42.4 0.52 11.8 1.14 0.15 12.1 97.63 0.68 6.16 1.84 0.62 0.13 0.47 2.84 0.94 0.06 0.02 1.84 0.08 0.49 0.10 8.73 935 32 58.0 43.68 10 2.12 12.8 14.5 42.6 0.54 12.1 1.12 0.14 11.8 97.63 0.68 6.20 1.80 0.70 0.12 0.28 2.78 1.12 0.04 0.02 1.88 0.06 0.54 0.10 8.87 933 33 57.9 43.60 11 2.14 12.3 15.3 42.0 0.58 12.0 1.34 0.15 11.9 97.63 0.67 6.13 1.87 0.76 0.15 0.22 2.68 1.19 0.04 0.02 1.88 0.06 0.54 0.11 9.51 945 35 55.6 42.43 12 1.97 12.8 14.4 42.6 0.89 11.7 1.13 0.14 11.9 97.63 0.68 6.22 1.78 0.69 0.13 0.29 2.79 1.10 0.06 0.02 1.84 0.09 0.47 0.17 8.77 926 32 58.6 43.51 13 2.07 12.6 14.8 42.2 0.63 11.9 1.06 0.14 12.2 97.63 0.67 6.16 1.85 0.70 0.12 0.36 2.75 1.07 0.05 0.02 1.86 0.08 0.51 0.12 9.10 934 34 57.3 42.54 14 2.13 12.7 14.6 42.3 0.52 12.0 1.17 0.14 12.1 97.63 0.68 6.17 1.84 0.67 0.13 0.35 2.77 1.09 0.04 0.02 1.87 0.07 0.53 0.10 8.90 936 33 57.5 42.84 15 1.85 13.1 14.2 42.4 0.49 11.4 1.23 0.14 12.8 97.63 0.67 6.15 1.85 0.58 0.13 0.63 2.83 0.83 0.09 0.02 1.78 0.12 0.40 0.09 8.54 926 32 59.1 42.23 16 2.13 13.0 14.2 42.9 0.53 12.1 1.04 0.15 11.6 97.63 0.69 6.25 1.75 0.69 0.11 0.26 2.83 1.12 0.04 0.02 1.89 0.06 0.54 0.10 8.57 928 32 58.9 44.57 17 2.02 12.8 14.3 43.0 0.52 11.9 1.14 0.14 11.9 97.63 0.68 6.26 1.74 0.71 0.13 0.28 2.77 1.13 0.05 0.02 1.85 0.08 0.49 0.10 8.64 922 32 59.2 43.26 18 2.16 12.6 14.8 42.7 0.54 11.8 1.21 0.14 11.7 97.63 0.68 6.22 1.78 0.75 0.13 0.22 2.74 1.16 0.05 0.02 1.85 0.08 0.53 0.10 9.06 934 34 57.5 43.34 19 1.67 13.7 14.3 43.0 0.70 10.8 1.05 0.15 12.4 97.63 0.69 6.19 1.81 0.61 0.11 0.74 2.93 0.60 0.14 0.02 1.66 0.18 0.29 0.13 8.51 917 32 59.8 44.09 20 2.10 12.8 14.6 42.9 0.57 11.6 1.17 0.14 11.7 97.63 0.69 6.24 1.76 0.74 0.13 0.26 2.78 1.09 0.07 0.02 1.81 0.10 0.49 0.11 8.90 929 33 58.1 43.95 21 2.03 12.9 14.3 43.1 0.55 11.9 1.06 0.15 11.6 97.63 0.69 6.27 1.73 0.73 0.12 0.26 2.80 1.10 0.05 0.02 1.85 0.08 0.49 0.10 8.69 923 32 59.0 44.21 22 2.15 12.4 14.9 42.4 0.60 11.9 1.41 0.15 11.7 97.63 0.68 6.20 1.80 0.77 0.16 0.16 2.70 1.22 0.05 0.02 1.86 0.08 0.53 0.11 9.24 939 34 56.6 43.04 23 2.07 12.9 14.1 43.0 0.58 11.9 1.10 0.14 11.8 97.63 0.68 6.27 1.73 0.68 0.12 0.26 2.80 1.13 0.05 0.02 1.86 0.07 0.51 0.11 8.49 923 31 59.4 43.76 24 2.25 12.5 15.0 42.2 0.56 11.9 1.38 0.14 11.7 97.63 0.68 6.16 1.84 0.74 0.15 0.20 2.73 1.18 0.05 0.02 1.86 0.07 0.56 0.11 9.29 947 34 55.9 43.31 25 2.11 12.5 14.9 42.4 0.58 12.0 1.17 0.14 11.8 97.63 0.68 6.19 1.81 0.75 0.13 0.23 2.73 1.16 0.04 0.02 1.88 0.07 0.53 0.11 9.17 935 34 57.1 43.19 26 2.11 12.8 14.7 42.7 0.59 11.9 1.14 0.14 11.6 97.63 0.68 6.22 1.78 0.74 0.13 0.24 2.77 1.13 0.05 0.02 1.86 0.08 0.52 0.11 8.98 932 33 57.7 43.90 27 2.07 13.2 14.0 43.1 0.53 12.0 1.11 0.14 11.5 97.63 0.69 6.27 1.73 0.67 0.12 0.28 2.86 1.07 0.05 0.02 1.86 0.07 0.51 0.10 8.43 925 31 59.3 44.93 28 2.23 12.9 14.3 43.1 0.54 11.8 1.16 0.14 11.5 97.63 0.69 6.29 1.72 0.74 0.13 0.16 2.80 1.18 0.06 0.02 1.84 0.09 0.55 0.10 8.66 928 32 58.6 44.41 29 2.02 12.8 14.5 42.7 0.53 12.3 1.06 0.14 11.6 97.63 0.69 6.22 1.78 0.72 0.12 0.24 2.77 1.15 0.02 0.02 1.92 0.04 0.53 0.10 8.86 929 33 58.2 44.01 30 2.14 12.7 14.9 42.3 0.53 12.2 1.09 0.14 11.6 97.63 0.68 6.16 1.84 0.72 0.12 0.27 2.77 1.13 0.02 0.02 1.91 0.05 0.56 0.10 9.17 940 34 56.7 43.81 31 2.17 12.7 14.8 42.6 0.55 11.9 1.32 0.14 11.5 97.63 0.69 6.21 1.79 0.75 0.15 0.20 2.76 1.15 0.05 0.02 1.85 0.08 0.53 0.10 9.07 939 34 57.0 44.14 32 2.07 12.9 14.5 42.5 0.54 12.2 1.11 0.14 11.6 97.63 0.69 6.19 1.81 0.68 0.12 0.30 2.81 1.08 0.03 0.02 1.90 0.06 0.53 0.10 8.84 934 33 57.8 44.24 33 2.15 13.0 14.5 42.5 0.53 12.1 1.10 0.14 11.6 97.63 0.69 6.20 1.81 0.69 0.12 0.30 2.82 1.08 0.04 0.02 1.88 0.06 0.54 0.10 8.85 936 33 57.6 44.31 34 2.11 13.0 15.1 41.8 0.51 12.1 1.27 0.15 11.5 97.63 0.69 6.08 1.92 0.66 0.14 0.40 2.83 0.97 0.03 0.02 1.89 0.06 0.54 0.10 9.28 953 34 55.3 44.65 35 2.09 12.9 14.6 42.7 0.54 11.9 1.14 0.15 11.7 97.63 0.69 6.22 1.79 0.71 0.13 0.29 2.79 1.08 0.05 0.02 1.86 0.08 0.51 0.10 8.89 932 33 57.9 44.05 36 1.99 13.7 14.0 42.9 0.51 11.7 1.02 0.14 11.5 97.63 0.70 6.21 1.79 0.60 0.11 0.51 2.96 0.82 0.07 0.02 1.82 0.10 0.46 0.09 8.39 930 31 59.1 45.94 37 2.06 13.1 14.3 42.6 0.50 12.2 1.17 0.14 11.7 97.63 0.69 6.19 1.81 0.64 0.13 0.34 2.84 1.05 0.03 0.02 1.90 0.06 0.53 0.09 8.64 934 32 58.2 44.39 38 2.03 13.4 13.5 43.4 0.51 12.0 1.25 0.14 11.3 97.63 0.70 6.31 1.69 0.62 0.14 0.27 2.91 1.07 0.04 0.02 1.88 0.07 0.51 0.10 8.00 922 30 60.4 45.75 39 2.15 12.3 14.6 42.4 0.55 12.0 1.35 0.14 12.2 97.63 0.67 6.20 1.80 0.71 0.15 0.20 2.68 1.26 0.04 0.02 1.89 0.06 0.55 0.10 8.95 933 33 57.7 41.73 40 2.19 12.7 14.7 42.5 0.52 11.8 1.29 0.14 11.9 97.63 0.68 6.20 1.80 0.72 0.14 0.25 2.75 1.14 0.06 0.02 1.84 0.08 0.54 0.10 8.98 938 33 57.3 43.20 41 2.11 12.5 14.5 42.6 0.54 11.8 1.36 0.14 12.1 97.63 0.67 6.22 1.78 0.72 0.15 0.23 2.71 1.19 0.06 0.02 1.84 0.08 0.52 0.10 8.88 931 33 58.0 42.42 42 2.17 12.2 14.9 42.3 0.55 11.8 1.35 0.14 12.2 97.63 0.66 6.18 1.82 0.75 0.15 0.22 2.66 1.23 0.05 0.02 1.85 0.08 0.54 0.10 9.22 937 34 56.9 41.59 43 2.25 12.4 15.0 42.2 0.54 11.8 1.43 0.14 11.8 97.63 0.67 6.17 1.83 0.75 0.16 0.19 2.70 1.21 0.05 0.02 1.85 0.08 0.56 0.10 9.29 945 34 56.1 42.72 44 2.18 12.2 15.0 42.0 0.57 12.0 1.37 0.14 12.2 97.63 0.66 6.15 1.85 0.74 0.15 0.21 2.66 1.24 0.04 0.02 1.88 0.06 0.56 0.11 9.33 942 35 56.3 41.65 45 2.17 12.6 14.7 42.3 0.53 12.0 1.27 0.14 12.0 97.63 0.68 6.17 1.83 0.70 0.14 0.28 2.74 1.14 0.04 0.02 1.87 0.07 0.55 0.10 9.03 940 33 57.0 42.88 46 2.04 12.3 14.3 42.7 0.68 11.9 1.64 0.13 11.9 97.63 0.67 6.25 1.75 0.72 0.18 0.11 2.69 1.30 0.05 0.02 1.86 0.07 0.51 0.13 8.76 931 32 58.3 42.44 47 2.23 12.6 14.5 42.8 0.51 11.7 1.18 0.14 11.9 97.63 0.68 6.24 1.77 0.73 0.13 0.23 2.75 1.17 0.06 0.02 1.84 0.09 0.54 0.10 8.86 932 33 58.0 43.05 48 2.25 13.0 14.1 43.2 0.47 11.8 1.11 0.14 11.7 97.63 0.69 6.28 1.72 0.70 0.12 0.23 2.82 1.13 0.06 0.02 1.84 0.09 0.55 0.09 8.48 927 31 59.1 44.30 49 1.86 12.4 13.8 41.6 0.48 12.3 2.33 0.13 12.7 97.63 0.66 6.11 1.90 0.49 0.26 0.35 2.71 1.19 0.02 0.02 1.93 0.04 0.49 0.09 8.35 946 31 57.7 41.08 50 2.13 12.6 14.6 42.1 0.50 11.8 1.62 0.14 12.1 97.63 0.67 6.15 1.85 0.65 0.18 0.32 2.75 1.10 0.06 0.02 1.84 0.09 0.52 0.09 8.92 944 33 56.8 42.60 51 2.22 12.7 14.9 42.3 0.55 11.6 1.43 0.14 11.8 97.63 0.68 6.17 1.83 0.72 0.16 0.27 2.75 1.10 0.07 0.02 1.81 0.10 0.53 0.10 9.16 945 34 56.3 43.30 52 2.18 12.8 14.8 42.6 0.53 11.7 1.19 0.13 11.8 97.63 0.68 6.20 1.81 0.74 0.13 0.29 2.77 1.08 0.07 0.02 1.82 0.09 0.52 0.10 9.08 937 34 57.1 43.66 53 2.34 12.8 15.1 41.8 0.53 11.7 1.41 0.14 11.8 97.63 0.68 6.10 1.90 0.69 0.16 0.34 2.79 1.03 0.07 0.02 1.82 0.10 0.57 0.10 9.31 957 34 54.9 43.59 54 2.10 13.2 14.1 42.9 0.49 11.9 1.08 0.14 11.7 97.63 0.69 6.24 1.76 0.65 0.12 0.35 2.86 1.02 0.05 0.02 1.85 0.08 0.51 0.09 8.46 928 31 59.1 44.62 55 2.01 13.6 14.5 42.2 0.50 11.4 1.12 0.14 12.2 97.63 0.69 6.10 1.90 0.58 0.12 0.68 2.92 0.70 0.09 0.02 1.76 0.13 0.44 0.09 8.77 940 32 57.4 44.27 56 2.11 12.9 14.4 42.4 0.52 12.0 1.09 0.13 12.1 97.63 0.68 6.17 1.83 0.64 0.12 0.40 2.81 1.04 0.04 0.02 1.88 0.07 0.53 0.10 8.72 934 32 58.1 43.25 57 2.25 12.8 14.8 42.2 0.54 11.6 1.31 0.14 11.9 97.63 0.68 6.15 1.85 0.69 0.14 0.34 2.79 1.04 0.07 0.02 1.82 0.10 0.54 0.10 9.11 946 34 56.3 43.49 58 2.24 12.6 15.0 42.2 0.55 11.7 1.34 0.13 11.8 97.63 0.68 6.16 1.84 0.74 0.15 0.26 2.74 1.12 0.07 0.02 1.83 0.09 0.54 0.10 9.27 945 34 56.1 43.19 注:以23个氧原子为基准计算的阳离子数;Mg# = molar Mg / (Mg + Fe); 最右侧SiO2含量和Mg#值指通过左侧对应角闪石成分和已知角闪石-熔体的分配系计算得到的样品角闪石平衡熔体的SiO2含量和Mg#值 表 3 泰山闪长岩和角闪石岩中角闪石激光原位微量和稀土元素数据
Table 3 Trace and rare earth element compositions of amphibole in diorite and hornblendites from Taishan
10-6 测点号 Rb Ba Th U Nb Ta Pb Sr Zr Hf Y Ti La Ce Pr Nd Sm Eu Gd Tb Dy Ho Er Tm Yb Lu ∑REE TS19-14(闪长岩) 1 3.24 84.8 0.01 0.06 2.40 0.06 0.82 30.4 26.4 1.48 41.0 6742 1.86 11.1 2.54 17.4 6.45 1.73 8.16 1.19 8.16 1.52 4.31 0.57 4.22 0.51 69.69 2 2.60 73.9 0.01 0.07 0.34 0.02 0.77 32.8 40.5 2.12 40.5 6987 1.81 10.2 2.33 17.1 6.70 1.60 7.66 1.30 7.76 1.56 4.12 0.57 3.68 0.51 66.96 3 3.60 95.2 0.02 0.07 2.02 0.04 1.01 31.4 32.8 1.43 35.3 7699 1.71 10.3 2.42 15.9 6.05 1.75 6.88 1.04 6.68 1.44 3.47 0.54 3.59 0.49 62.21 4 2.29 88.0 0.02 0.11 0.23 0.01 0.95 37.1 35.3 1.49 37.9 7258 2.07 11.1 2.47 15.9 6.45 1.79 7.16 1.14 8.01 1.59 3.69 0.49 3.35 0.44 65.58 5 3.07 83.9 0.01 0.05 0.76 0.03 0.86 33.7 45.5 2.10 44.4 7365 1.94 10.7 2.82 19.6 8.04 1.90 9.39 1.34 8.72 1.74 4.35 0.61 4.35 0.50 76.02 6 3.58 105.6 0.01 0.06 0.33 0.02 0.99 42.6 28.1 1.39 33.6 7765 1.64 9.17 2.06 13.2 4.94 1.61 6.86 0.99 6.42 1.29 3.23 0.52 2.93 0.52 55.37 7 3.07 102.1 0.01 0.08 0.74 0.02 1.15 40.6 23.3 1.14 33.2 7556 1.63 8.68 1.92 12.6 4.84 1.83 6.33 1.00 6.22 1.38 3.01 0.41 2.75 0.39 53.01 8 3.45 103.2 0.05 0.18 2.24 0.05 0.98 37.7 25.7 1.32 35.7 9232 2.56 12.3 2.69 18.8 5.46 1.90 6.70 1.08 7.29 1.48 3.41 0.49 3.78 0.48 68.41 9 2.75 100.6 0.02 0.07 0.70 0.01 0.79 38.4 29.4 1.20 32.8 7321 1.51 8.62 2.04 14.2 5.16 1.51 6.75 1.04 6.34 1.32 2.99 0.54 3.13 0.41 55.63 10 3.34 97.6 0.04 0.08 0.68 0.01 0.89 36.1 25.9 1.24 33.0 7359 2.07 9.70 2.04 12.2 4.75 1.75 5.90 0.99 6.47 1.36 2.95 0.48 2.87 0.44 53.96 11 3.23 96.4 0.05 0.67 10.49 0.20 0.87 38.4 44.4 2.17 40.7 12490 1.95 10.7 2.48 16.3 6.47 1.61 7.50 1.24 7.53 1.60 3.71 0.57 3.87 0.56 66.12 12 2.54 82.7 0.01 0.07 0.84 0.02 0.92 38.3 36.8 2.13 41.0 7076 1.70 9.12 2.41 17.4 6.69 1.53 8.54 1.28 7.73 1.55 3.65 0.59 3.70 0.53 66.38 13 2.62 86.1 0.02 0.11 3.68 0.08 1.13 34.8 32.4 2.03 41.4 7083 2.01 11.0 2.47 17.9 7.03 1.78 7.77 1.21 8.17 1.62 3.86 0.57 3.73 0.58 69.73 14 3.51 89.0 0.01 0.05 4.72 0.07 0.68 34.0 24.6 1.71 40.6 6781 1.70 10.4 2.58 17.2 7.09 1.76 7.76 1.31 7.95 1.62 3.92 0.56 3.95 0.51 68.30 15 2.81 84.3 0.02 0.06 2.93 0.04 0.78 33.9 33.8 2.18 40.2 6787 1.79 10.5 2.44 17.3 6.04 1.78 7.03 1.13 8.06 1.68 3.78 0.57 3.82 0.54 66.46 16 2.52 95.7 0.01 0.07 1.37 0.04 1.03 40.0 24.4 1.14 32.4 7540 1.83 9.52 1.86 13.7 4.94 1.59 6.07 1.01 6.57 1.26 3.24 0.44 2.98 0.43 55.40 17 2.97 89.6 0.00 0.05 1.57 0.03 0.85 32.4 27.7 1.51 38.1 6984 2.01 9.61 1.98 13.9 5.98 1.60 8.07 1.18 7.71 1.47 3.69 0.54 3.60 0.49 61.80 18 2.62 86.7 0.00 0.09 1.31 0.03 0.99 31.1 31.7 1.43 35.8 7889 1.90 9.27 2.02 14.2 5.78 1.61 6.91 1.09 7.31 1.42 3.26 0.45 3.18 0.47 58.87 19 2.63 92.1 0.00 0.06 1.78 0.04 0.85 31.0 24.4 1.34 35.9 7016 1.82 10.2 2.22 16.6 6.05 1.78 6.54 1.23 7.42 1.33 3.50 0.54 3.18 0.42 62.80 20 3.23 94.4 0.01 0.06 1.92 0.05 0.80 32.6 30.7 1.50 35.2 7307 1.79 10.2 2.53 17.3 6.20 1.75 7.78 1.22 7.42 1.31 3.67 0.48 3.23 0.38 65.29 21 3.30 99.4 0.00 0.09 0.85 0.03 0.91 34.1 35.1 1.63 38.3 6856 2.05 12.5 3.03 21.6 6.74 1.91 8.91 1.25 7.17 1.60 5.00 0.53 3.30 0.55 76.13 22 2.65 96.4 0.05 0.10 0.95 0.02 0.80 33.6 31.0 1.42 40.2 6780 2.67 15.5 3.40 20.0 6.47 1.97 7.45 1.11 7.55 1.55 5.02 0.64 3.07 0.52 76.91 23 2.65 77.5 0.02 0.07 0.77 0.02 0.84 36.4 45.1 2.30 48.4 6710 2.14 12.3 2.79 21.0 7.70 1.88 10.43 1.51 9.39 1.92 6.23 0.66 4.19 0.62 82.79 24 3.22 88.6 0.02 0.06 1.40 0.05 0.85 36.2 44.2 2.19 47.2 6510 1.87 11.3 2.66 18.5 6.52 1.76 9.81 1.39 9.19 1.93 5.78 0.70 4.00 0.58 75.94 25 3.48 84.9 0.02 0.07 1.51 0.03 0.99 36.1 41.7 2.14 44.4 7732 2.03 11.9 2.72 19.6 6.84 1.86 9.13 1.36 9.24 1.72 5.53 0.60 3.91 0.62 77.02 26 3.17 99.0 0.02 0.05 3.51 0.07 0.98 41.0 26.4 1.84 52.2 6889 1.60 10.5 2.81 18.4 6.90 2.01 9.55 1.39 9.18 1.95 6.30 0.75 4.78 0.69 76.86 27 3.04 82.8 0.01 0.06 2.91 0.05 0.74 41.6 47.2 2.42 56.2 7212 1.77 10.1 2.58 18.6 8.19 1.97 11.07 1.54 10.53 2.23 6.74 0.81 5.08 0.74 81.98 28 2.46 95.9 0.01 0.05 1.25 0.02 0.94 39.1 49.2 1.77 45.1 7673 1.72 11.0 2.81 19.6 7.22 2.10 8.88 1.40 8.38 1.74 5.48 0.64 4.49 0.64 76.13 29 3.55 92.0 0.02 0.09 2.85 0.05 1.16 40.7 41.1 2.28 55.7 7137 1.82 12.0 3.07 21.5 7.88 2.37 10.60 1.76 11.30 2.06 7.21 0.77 5.51 0.72 88.61 30 3.00 91.0 0.03 0.10 0.83 0.01 0.91 40.5 37.1 1.53 41.9 7156 2.23 14.1 3.36 20.6 6.08 1.88 8.43 1.36 7.76 1.68 4.81 0.57 3.36 0.62 76.84 31 3.46 94.4 0.02 0.06 4.02 0.09 0.92 35.8 24.8 1.27 48.2 6966 2.06 11.6 2.97 20.8 7.66 2.18 10.18 1.49 9.30 1.86 5.67 0.76 4.36 0.65 81.59 32 3.76 108.0 0.02 0.05 0.77 0.03 0.93 42.6 32.6 1.41 38.9 7481 2.18 10.5 2.81 20.1 6.12 2.11 8.44 1.14 8.52 1.48 4.70 0.56 3.56 0.53 72.73 33 3.24 87.2 0.01 0.04 1.51 0.03 0.83 37.6 36.0 2.19 49.0 7097 2.07 10.6 2.63 17.2 6.66 1.99 9.90 1.41 10.22 1.78 5.86 0.66 4.78 0.65 76.46 34 3.68 83.9 0.02 0.05 4.10 0.09 0.85 35.0 27.3 1.56 46.0 6545 2.05 11.5 2.68 18.0 6.12 1.81 8.94 1.38 8.81 1.75 5.54 0.58 4.17 0.66 74.02 35 3.44 87.7 0.00 0.09 4.39 0.08 0.88 41.9 28.1 1.68 49.3 7030 2.37 12.9 2.90 20.6 7.56 2.15 9.63 1.49 9.59 2.02 5.58 0.62 4.11 0.56 82.15 36 3.18 77.2 0.01 0.06 1.48 0.07 0.80 40.8 56.8 2.80 59.9 6959 1.76 10.2 2.88 22.0 9.28 1.98 11.45 1.75 11.39 2.34 7.40 0.82 5.28 0.70 89.22 37 2.90 76.9 0.02 0.07 1.78 0.06 0.78 43.2 47.1 2.43 53.9 6930 1.99 10.2 2.94 22.4 7.87 1.98 9.81 1.51 10.57 2.21 6.22 0.79 3.99 0.72 83.16 38 3.57 89.9 0.00 0.07 2.65 0.09 0.92 38.7 45.8 2.43 52.0 6923 2.03 11.5 2.88 20.7 7.51 1.86 10.31 1.50 10.86 1.97 6.47 0.72 4.00 0.60 82.96 39 3.23 88.3 0.00 0.07 14.06 0.40 0.91 41.7 23.8 1.41 50.4 6839 2.35 12.9 3.04 21.1 7.90 2.35 10.04 1.42 9.73 1.97 6.33 0.64 4.59 0.58 84.94 40 3.48 92.9 0.00 0.05 3.22 0.06 1.01 39.4 26.5 1.64 47.8 6388 1.88 10.6 2.75 18.8 6.86 2.24 9.23 1.36 8.98 1.96 5.93 0.69 4.15 0.59 76.06 TS19-15(角闪石岩) 1 1.74 63.5 0.00 0.01 0.29 0.01 0.51 84.6 20.1 0.86 16.4 4688 0.64 3.14 0.72 5.0 1.93 0.66 2.52 0.35 2.77 0.60 1.72 0.26 1.40 0.24 21.94 2 1.74 79.8 0.00 0.00 0.45 0.03 0.71 122.7 20.9 1.01 21.9 7586 0.60 2.85 0.81 6.2 2.87 0.84 4.22 0.64 4.47 0.92 2.26 0.35 2.07 0.26 29.37 3 3.24 85.3 0.00 0.01 0.70 0.05 0.54 118.7 21.7 0.95 22.0 7163 0.59 3.05 0.77 5.6 2.81 0.78 3.25 0.61 4.22 0.81 2.24 0.31 1.90 0.23 27.20 4 2.12 89.7 0.01 0.00 0.37 0.03 0.74 137.6 18.8 0.79 23.9 7566 0.68 3.99 1.04 8.3 2.93 0.95 4.07 0.64 4.62 0.88 2.60 0.36 1.75 0.33 33.12 5 2.10 91.4 0.01 0.00 0.85 0.05 0.93 145.4 18.8 0.84 26.0 8306 0.61 3.49 1.02 6.9 3.24 0.95 4.65 0.75 5.06 1.03 2.39 0.39 2.34 0.35 33.13 6 1.71 68.2 0.00 0.00 0.29 0.00 0.61 88.7 19.0 0.77 14.9 5025 0.82 3.35 0.68 4.5 1.58 0.60 2.01 0.36 2.72 0.56 1.36 0.23 1.34 0.17 20.25 7 2.36 81.8 0.02 0.00 0.78 0.06 0.64 119.2 24.2 1.05 19.9 6580 0.83 4.01 0.95 6.6 2.45 0.80 4.13 0.56 3.55 0.78 1.93 0.28 1.73 0.27 28.84 8 1.84 76.5 0.01 0.00 0.34 0.00 0.54 83.6 18.6 0.78 15.8 5421 0.77 3.16 0.68 4.5 2.00 0.63 2.99 0.47 2.78 0.64 1.43 0.25 1.53 0.25 22.05 9 1.84 70.4 0.01 0.01 0.26 0.02 0.70 121.6 20.2 0.97 23.6 6868 1.06 5.92 1.38 8.8 3.91 1.10 4.39 0.68 4.77 0.92 1.87 0.36 1.97 0.27 37.42 10 2.19 97.9 0.00 0.01 0.45 0.01 0.72 107.2 23.5 0.79 20.1 7017 0.73 3.06 0.75 4.9 2.28 0.70 3.29 0.53 3.70 0.80 1.57 0.30 1.87 0.25 24.69 11 1.94 85.2 0.01 0.00 0.46 0.02 0.75 121.7 19.4 0.76 23.9 7177 0.70 4.35 1.09 7.3 3.25 0.93 4.40 0.68 4.61 0.96 1.84 0.35 2.07 0.28 32.84 12 1.49 60.6 0.01 0.00 0.54 0.02 0.57 78.9 19.5 0.85 17.2 6216 0.68 3.03 0.62 5.4 2.06 0.67 3.85 0.49 3.31 0.72 1.41 0.26 1.30 0.21 23.97 13 1.73 93.4 0.00 0.00 0.41 0.01 0.68 94.1 20.6 0.81 18.5 6487 0.87 3.32 0.75 5.0 1.99 0.68 2.95 0.48 3.22 0.68 1.62 0.28 1.90 0.23 23.97 14 1.53 50.9 0.01 0.01 0.36 0.01 0.42 85.5 18.1 0.81 14.4 4378 0.79 3.55 0.70 5.1 1.61 0.55 2.14 0.40 2.45 0.62 1.30 0.22 1.35 0.20 20.94 15 1.94 85.9 0.01 0.00 0.58 0.04 0.78 123.6 20.4 0.88 20.6 7045 0.78 3.71 0.85 5.6 2.87 0.73 3.70 0.62 3.65 0.80 1.83 0.27 1.84 0.26 27.52 16 5.74 99.4 0.00 0.00 0.79 0.05 0.75 117.6 21.4 0.96 22.2 7270 0.84 3.72 0.94 7.2 2.96 0.85 3.87 0.61 4.16 0.84 2.05 0.33 1.72 0.26 30.39 17 2.14 95.4 0.00 0.00 0.49 0.03 0.81 119.5 20.6 0.79 21.1 7360 0.74 3.48 0.85 6.0 2.20 0.79 3.35 0.56 3.71 0.82 1.95 0.30 1.61 0.27 26.67 18 1.76 85.6 0.00 0.01 0.71 0.06 0.87 129.6 19.8 0.81 22.3 7800 0.71 3.39 0.83 6.0 2.43 0.76 4.01 0.62 3.89 0.86 2.17 0.33 1.86 0.28 28.08 19 3.13 101.9 0.00 0.00 0.57 0.03 0.74 117.1 20.8 0.83 19.7 7522 0.76 3.33 0.76 5.1 2.74 0.77 3.38 0.55 3.85 0.71 2.16 0.28 1.73 0.23 26.31 20 2.49 86.6 0.01 0.04 0.37 0.02 0.61 92.0 18.7 0.81 16.5 5855 0.65 3.10 0.75 4.8 1.88 0.67 2.84 0.49 2.98 0.62 1.72 0.28 1.58 0.21 22.57 21 2.43 102.7 0.01 0.01 0.60 0.03 0.77 139.5 20.3 0.78 21.8 7596 0.48 2.84 0.75 6.3 2.42 0.75 4.06 0.59 3.98 0.86 2.59 0.30 1.77 0.27 27.97 22 2.22 88.0 0.00 0.00 0.38 0.04 0.52 104.7 20.3 0.90 17.0 5595 0.48 2.64 0.63 4.8 2.04 0.58 2.92 0.45 3.42 0.65 1.98 0.26 1.57 0.23 22.65 23 2.31 105.8 0.00 0.00 0.34 0.02 0.66 113.6 20.1 0.84 16.9 6291 0.57 2.75 0.67 4.9 1.67 0.57 2.84 0.45 3.19 0.67 1.92 0.25 1.33 0.23 22.05 24 1.96 86.1 0.00 0.00 0.32 0.01 0.68 91.6 19.8 0.86 15.6 4833 0.56 2.60 0.58 5.1 1.88 0.60 2.62 0.44 2.59 0.60 1.67 0.24 1.44 0.20 21.09 25 2.15 84.8 0.01 0.00 0.71 0.05 0.78 137.6 22.6 0.95 21.7 8055 0.74 4.55 1.25 9.3 3.17 0.88 4.10 0.73 4.16 0.84 2.49 0.36 2.08 0.28 34.97 26 1.94 85.7 0.01 0.00 0.42 0.02 0.79 127.9 19.0 0.78 23.8 7717 0.67 3.76 1.04 7.5 3.00 0.93 4.06 0.65 4.35 0.82 2.75 0.36 1.62 0.28 31.83 27 2.21 84.2 0.00 0.00 0.64 0.04 0.77 142.9 22.0 0.93 22.2 7910 0.79 5.20 1.34 9.6 3.90 1.08 4.48 0.73 4.45 0.88 2.46 0.31 1.94 0.26 37.45 28 1.96 92.6 0.01 0.00 0.39 0.02 0.92 117.7 18.7 0.75 19.0 6828 0.62 3.06 0.69 6.3 1.67 0.63 3.05 0.52 3.25 0.72 2.22 0.27 2.00 0.21 25.19 29 3.45 103.3 0.01 0.04 0.51 0.04 0.82 110.1 21.3 0.80 20.9 8303 0.82 3.35 0.74 5.6 2.40 0.77 2.99 0.55 4.30 0.91 2.46 0.35 2.00 0.32 27.51 30 2.02 95.0 0.01 0.00 1.04 0.06 0.86 131.9 24.9 1.11 22.1 7202 0.72 3.56 0.90 7.3 2.90 0.83 4.47 0.64 4.30 0.90 2.71 0.30 1.78 0.25 31.53 31 0.94 33.9 0.00 0.00 0.29 0.01 0.47 81.9 16.6 0.77 13.3 4111 0.66 2.99 0.64 4.4 1.78 0.58 2.11 0.40 2.32 0.54 1.59 0.22 1.57 0.17 20.01 32 2.48 93.0 0.00 0.00 0.67 0.05 0.59 107.5 23.7 1.01 18.5 5761 0.79 3.65 0.86 5.7 2.02 0.75 3.21 0.51 3.59 0.73 2.17 0.29 1.51 0.22 26.04 33 2.15 92.1 0.01 0.00 0.47 0.03 0.68 111.5 19.7 0.89 17.5 6442 0.72 3.48 0.77 5.1 1.78 0.76 2.72 0.52 3.38 0.66 2.16 0.27 1.59 0.25 24.15 34 3.18 99.9 0.00 0.01 0.41 0.02 0.64 109.8 20.0 0.82 20.8 6753 0.54 2.70 0.68 5.6 2.34 0.64 3.37 0.56 3.98 0.82 2.37 0.31 1.87 0.29 26.05 35 1.82 96.7 0.00 0.00 0.43 0.04 0.55 114.6 20.9 0.79 18.5 6192 0.52 2.89 0.71 5.2 2.02 0.65 2.97 0.54 3.41 0.70 2.15 0.30 1.56 0.22 23.84 36 2.00 93.1 0.00 0.00 0.66 0.05 0.78 119.0 22.2 0.99 22.2 7258 0.56 2.85 0.67 6.1 2.33 0.58 3.65 0.58 3.83 0.84 2.50 0.32 1.74 0.26 26.85 37 2.10 70.1 0.01 0.01 0.41 0.02 0.60 85.0 19.1 0.85 15.7 6247 0.54 2.56 0.59 4.4 1.96 0.62 2.23 0.42 2.57 0.66 1.75 0.25 1.65 0.23 20.40 38 1.76 77.3 0.00 0.01 0.39 0.03 0.55 102.8 20.3 1.00 17.7 5624 0.65 2.98 0.73 5.4 1.96 0.66 2.87 0.48 3.23 0.66 1.86 0.24 1.52 0.26 23.46 39 2.01 84.9 0.00 0.00 0.74 0.04 0.76 138.2 19.3 0.83 21.9 8070 0.65 4.04 1.04 7.4 2.71 0.83 3.80 0.64 4.06 0.81 2.33 0.35 1.98 0.26 30.89 40 2.49 97.5 0.00 0.00 0.76 0.05 0.71 129.3 21.1 0.89 21.3 7515 0.75 4.11 1.06 8.0 2.81 0.95 3.43 0.67 4.15 0.88 2.34 0.29 1.73 0.26 31.39 TS19-17(角闪石岩) 1 2.25 90.2 0.17 0.06 0.47 0.03 1.16 92.9 21.1 0.89 27.3 6906 2.90 10.3 1.77 9.8 3.53 1.14 4.71 0.71 5.46 1.13 3.13 0.39 2.75 0.39 48.06 2 2.35 91.7 0.19 0.07 0.37 0.02 1.23 104.2 15.2 0.69 21.5 7430 2.54 8.87 1.51 8.1 2.68 1.15 3.36 0.64 4.01 0.87 2.45 0.35 1.98 0.29 38.79 3 4.54 115.3 0.13 0.06 0.35 0.03 0.98 81.9 27.4 0.97 23.3 6892 2.87 10.7 1.85 11.1 3.55 1.16 4.17 0.63 4.50 0.91 2.64 0.35 2.26 0.32 46.96 4 8.03 109.6 0.14 0.05 0.44 0.02 1.09 86.2 18.8 0.77 23.2 7260 2.66 9.37 1.78 9.1 3.70 1.12 4.06 0.60 4.42 0.92 2.54 0.32 2.04 0.30 42.97 5 2.32 95.0 0.17 0.05 0.19 0.02 0.98 98.4 19.4 0.81 22.9 6498 2.71 9.71 1.74 10.4 3.46 1.21 4.06 0.62 4.26 0.84 2.58 0.31 2.07 0.28 44.22 6 5.48 85.3 0.16 0.06 0.58 0.03 1.11 82.0 34.0 1.62 24.0 7467 2.99 10.4 1.86 10.0 3.41 1.02 4.41 0.70 4.60 0.96 2.65 0.40 2.24 0.33 45.99 7 2.24 99.6 0.13 0.04 1.00 0.08 1.13 102.7 30.5 1.43 23.6 8024 2.73 10.1 1.88 10.2 3.42 1.20 4.21 0.70 4.59 0.85 2.58 0.35 2.47 0.30 45.57 8 1.68 77.4 0.14 0.06 0.33 0.03 1.17 91.3 17.8 0.85 23.7 7250 2.79 9.77 1.76 9.7 3.37 1.08 4.17 0.65 4.69 0.90 2.71 0.35 2.37 0.23 44.53 9 1.85 81.7 0.15 0.06 0.64 0.06 0.97 85.5 29.8 1.34 25.1 6825 2.79 10.1 1.98 10.9 3.66 1.10 4.38 0.69 4.59 0.95 2.68 0.36 2.17 0.36 46.74 10 1.83 82.1 0.14 0.05 0.30 0.03 1.00 88.7 21.1 0.96 25.7 6690 2.66 9.30 1.74 9.7 3.40 1.09 4.55 0.70 4.80 0.99 2.80 0.34 2.51 0.36 44.90 11 2.16 84.5 0.15 0.08 0.59 0.04 1.13 94.1 17.2 0.74 23.3 8021 2.83 9.83 1.65 10.3 3.49 1.19 4.34 0.68 4.44 0.93 2.68 0.35 1.95 0.29 44.97 12 11.91 130.7 0.16 0.05 0.41 0.01 0.96 81.0 21.1 0.87 25.0 6801 2.88 10.4 1.85 10.9 3.42 1.21 4.27 0.70 4.56 0.92 2.92 0.36 2.31 0.32 47.11 13 4.66 92.5 0.14 0.06 0.24 0.01 1.10 87.4 17.0 0.73 23.8 6380 2.39 8.16 1.46 9.2 3.32 1.08 4.69 0.71 4.53 1.01 2.65 0.31 2.36 0.30 42.20 14 1.68 74.4 0.15 0.05 0.43 0.02 1.07 86.7 19.2 0.85 25.0 7032 2.66 9.01 1.69 10.2 3.37 0.97 4.20 0.75 4.65 1.07 2.81 0.32 2.03 0.29 43.97 15 3.79 60.1 0.19 0.08 0.71 0.03 1.00 57.6 29.6 1.06 23.8 7359 2.26 8.35 1.52 9.3 3.77 1.10 4.00 0.70 4.59 0.93 2.94 0.39 2.51 0.34 42.74 16 0.77 20.9 0.16 0.04 0.53 0.05 0.78 91.0 29.5 1.42 27.8 6232 2.71 9.99 1.71 9.9 3.77 1.22 4.95 0.83 5.18 1.09 3.14 0.41 2.39 0.32 47.61 17 1.76 63.3 0.13 0.04 0.32 0.02 1.11 74.1 29.4 1.25 24.7 6851 2.63 9.68 1.87 10.6 3.86 1.23 4.43 0.72 4.62 1.01 2.79 0.35 2.44 0.30 46.59 18 1.30 63.7 0.15 0.03 0.51 0.06 1.06 88.9 28.6 1.21 23.9 7250 2.75 10.57 1.88 9.8 3.55 1.15 3.79 0.65 4.56 0.99 2.65 0.37 2.19 0.32 45.19 19 9.91 99.1 0.14 0.04 0.45 0.02 0.94 64.0 18.7 0.76 22.0 6274 2.38 8.44 1.59 8.5 2.96 0.90 3.46 0.59 4.40 0.90 2.60 0.29 1.75 0.28 39.04 20 1.29 63.6 0.14 0.03 0.43 0.03 1.14 86.2 22.6 0.97 27.2 7003 3.02 10.5 1.93 11.6 3.97 1.30 4.76 0.75 5.52 1.06 3.20 0.41 2.59 0.34 50.98 21 2.15 88.0 0.16 0.04 0.36 0.03 0.88 82.6 22.1 1.06 27.7 6355 2.98 10.0 1.85 11.0 3.44 1.05 4.66 0.80 5.44 1.11 3.19 0.37 2.45 0.32 48.65 22 2.48 90.2 0.18 0.04 0.79 0.04 1.25 105.0 20.7 0.79 23.0 8441 2.82 9.84 1.75 9.8 2.94 1.10 3.85 0.64 4.59 0.93 2.48 0.34 2.36 0.29 43.75 23 2.03 87.8 0.18 0.05 0.56 0.03 0.87 84.3 24.8 1.08 30.5 6594 3.15 11.0 1.96 10.3 4.11 1.29 5.11 0.82 5.21 1.16 3.22 0.43 2.42 0.35 50.55 24 1.88 80.5 0.13 0.07 0.57 0.04 1.26 98.7 21.2 0.89 24.3 8243 2.69 9.64 1.89 9.4 3.32 1.14 4.54 0.60 4.63 1.03 2.90 0.34 2.52 0.30 44.96 25 2.35 81.7 0.17 0.04 0.20 0.02 1.38 98.3 20.6 0.93 23.9 7013 2.64 9.54 1.72 9.8 3.25 1.07 4.08 0.67 4.76 0.96 3.08 0.37 2.16 0.31 44.39 26 2.01 83.7 0.16 0.04 0.25 0.02 1.11 92.6 24.2 1.19 24.6 6846 2.59 9.64 1.83 9.7 3.71 1.12 4.41 0.66 4.88 1.02 2.84 0.33 2.28 0.36 45.38 27 1.38 47.3 0.14 0.04 0.36 0.03 0.92 87.1 36.4 1.52 24.9 6663 2.77 10.4 1.90 11.0 3.44 1.09 3.98 0.79 4.58 1.04 2.87 0.36 2.50 0.32 47.00 28 1.31 70.5 0.14 0.04 0.67 0.06 0.90 96.0 38.7 1.53 23.3 6961 2.77 10.1 1.83 10.8 3.32 1.13 4.10 0.66 4.28 0.91 2.76 0.32 2.52 0.26 45.77 29 1.55 49.3 0.16 0.05 0.37 0.03 1.43 96.1 23.8 1.25 24.7 6346 2.58 9.82 1.64 9.8 3.40 1.16 3.75 0.69 4.36 1.01 2.86 0.36 2.29 0.32 44.06 30 2.12 81.9 0.15 0.05 0.25 0.02 1.07 95.5 20.6 0.88 23.4 6521 2.53 9.53 1.72 9.4 3.30 1.06 3.72 0.68 4.65 0.98 2.90 0.38 2.00 0.33 43.16 31 2.58 88.1 0.13 0.05 0.70 0.05 1.04 102.8 24.9 0.94 22.9 7917 2.61 9.60 1.82 9.2 3.40 1.09 3.92 0.56 3.92 0.85 2.59 0.30 2.24 0.28 42.39 32 4.05 81.7 0.14 0.06 0.38 0.05 1.12 89.7 26.6 1.13 23.4 6681 2.60 9.83 1.68 9.8 3.62 1.11 4.11 0.62 4.32 0.85 2.59 0.31 2.03 0.29 43.80 33 2.56 79.5 0.15 0.04 0.30 0.02 1.02 93.8 29.2 1.17 22.9 6617 2.62 10.3 1.88 10.5 3.51 1.12 3.73 0.61 4.14 0.93 2.72 0.30 2.05 0.27 44.67 34 1.76 74.6 0.16 0.04 0.35 0.02 1.09 113.1 18.7 0.81 22.6 7605 2.80 8.72 1.60 8.6 3.22 1.06 3.76 0.62 4.23 0.88 2.54 0.31 2.05 0.23 40.59 35 2.50 83.0 0.11 0.06 0.29 0.01 0.96 94.9 31.1 1.22 24.4 6830 2.71 10.2 1.84 10.4 3.86 1.01 3.84 0.68 4.91 0.94 2.83 0.34 2.18 0.38 46.14 36 2.23 63.2 0.10 0.05 0.43 0.04 1.03 76.6 29.6 1.22 23.2 6136 2.64 9.95 1.72 9.8 3.23 0.99 3.65 0.66 4.38 0.96 2.63 0.35 2.11 0.34 43.46 37 1.37 49.8 0.14 0.04 0.25 0.02 0.91 75.2 28.8 1.03 23.1 7013 2.81 9.88 1.87 8.8 3.24 1.07 3.68 0.63 4.15 0.93 2.60 0.31 2.28 0.28 42.56 38 1.76 80.5 0.13 0.04 0.96 0.12 0.82 99.8 43.6 1.64 23.9 7471 2.85 10.4 1.89 10.7 3.26 0.97 3.84 0.71 4.65 0.84 2.39 0.32 2.12 0.25 45.22 39 2.75 92.8 0.18 0.05 0.60 0.04 1.22 95.6 21.5 0.95 26.4 8080 2.71 10.0 1.94 9.7 3.68 1.23 4.94 0.67 5.54 1.02 2.96 0.36 2.44 0.38 47.54 40 3.25 95.7 0.15 0.04 1.66 0.11 1.03 111.8 36.0 1.57 24.8 7743 3.20 11.3 2.04 11.1 3.52 1.20 4.72 0.72 4.95 1.06 2.79 0.36 2.41 0.34 49.70 41 4.61 96.5 0.14 0.07 0.81 0.05 1.05 91.8 20.8 0.80 22.2 8154 2.66 8.96 1.74 8.8 2.88 1.04 3.77 0.70 4.13 0.86 2.38 0.36 2.25 0.27 40.78 42 2.70 95.1 0.14 0.03 0.41 0.04 1.25 101.8 18.1 0.79 22.9 8075 2.63 9.32 1.81 10.0 3.53 1.08 3.77 0.65 4.56 0.93 2.51 0.31 2.29 0.29 43.67 43 2.56 99.0 0.12 0.03 1.00 0.05 1.05 111.3 24.0 0.95 22.4 8554 2.89 9.49 1.71 8.9 2.82 0.96 3.73 0.63 4.42 0.90 2.42 0.31 2.00 0.30 41.44 44 2.48 94.7 0.14 0.06 0.42 0.03 1.11 104.0 22.3 0.94 22.2 8203 3.10 10.6 1.83 10.2 3.33 1.02 4.00 0.64 4.28 0.86 2.40 0.38 2.01 0.20 44.81 45 2.93 108.9 0.15 0.04 0.55 0.05 1.13 93.4 23.7 0.91 25.9 7631 2.93 10.4 1.73 10.8 3.48 1.23 4.15 0.76 5.18 0.99 2.86 0.30 2.74 0.34 47.88 46 13.62 114.6 0.14 0.10 0.78 0.06 1.18 91.5 21.5 1.02 27.1 9833 2.73 10.1 1.88 9.7 3.22 1.18 4.54 0.77 5.07 1.06 2.77 0.41 2.30 0.31 46.08 47 2.61 100.1 0.12 0.06 0.55 0.05 0.96 104.0 26.0 0.93 24.5 7053 2.86 9.85 1.87 9.5 3.19 1.16 4.34 0.73 4.62 0.95 2.64 0.31 2.58 0.36 44.98 48 1.10 50.0 0.16 0.01 0.53 0.04 1.02 127.5 27.5 1.12 23.7 6638 2.96 9.58 1.77 10.5 3.06 1.03 3.59 0.63 4.40 0.90 2.42 0.29 2.06 0.28 43.42 49 4.05 83.1 0.18 0.06 1.26 0.05 1.00 66.8 28.3 1.35 33.9 13974 3.22 11.9 2.20 12.9 4.53 1.57 5.57 1.00 6.55 1.29 3.63 0.49 2.88 0.39 58.16 50 1.33 63.4 0.12 0.17 1.34 0.07 1.18 74.5 28.5 1.08 24.7 9712 2.71 9.98 1.86 10.6 3.84 1.24 4.12 0.75 4.98 0.96 2.78 0.31 2.50 0.29 46.91 51 2.64 89.7 0.13 0.02 0.94 0.08 1.02 110.5 28.0 1.24 23.3 8582 2.65 9.46 1.67 9.3 3.18 1.12 4.08 0.66 4.53 0.93 2.46 0.34 1.92 0.29 42.56 52 1.99 83.1 0.13 0.05 0.26 0.02 1.17 89.6 22.2 0.93 24.5 7158 2.87 9.96 1.73 10.1 3.10 1.13 4.65 0.72 4.84 0.97 2.68 0.36 2.35 0.29 45.73 53 2.36 87.3 0.13 0.05 0.55 0.04 1.08 101.0 20.9 0.78 23.3 8463 2.72 9.75 1.66 9.7 3.15 1.12 4.07 0.69 4.53 0.89 2.64 0.35 2.27 0.32 43.81 54 1.59 64.2 0.12 0.05 0.35 0.02 0.95 81.7 26.5 1.18 25.2 6480 2.67 9.77 1.75 10.2 3.20 1.10 4.57 0.68 4.86 0.99 2.68 0.32 2.43 0.31 45.48 55 1.86 90.4 0.10 0.03 0.42 0.04 1.10 86.8 26.7 1.04 22.7 6694 2.50 8.85 1.67 8.8 3.07 1.13 3.91 0.64 4.28 0.88 2.54 0.31 2.13 0.30 41.03 56 2.46 100.3 0.13 0.06 0.39 0.03 0.88 84.8 26.4 1.20 26.5 6506 2.73 9.98 1.78 10.8 3.61 1.27 4.63 0.72 5.18 1.09 2.98 0.42 2.08 0.31 47.55 57 2.24 89.8 0.13 0.03 0.68 0.04 0.97 101.5 21.2 0.87 24.1 7831 2.70 9.19 1.62 9.2 3.18 1.06 3.55 0.69 4.16 0.92 2.59 0.30 2.14 0.24 41.56 58 2.60 95.8 0.14 0.04 0.58 0.04 1.43 109.2 21.0 0.76 24.1 8020 2.68 9.36 1.54 9.9 3.12 1.21 4.03 0.67 4.55 0.89 2.69 0.31 1.92 0.31 43.22 表 4 泰山闪长岩全岩-矿物Sr-Nd-Hf同位素成分
Table 4 Bulk rock-mineral Sr-Nd-Hf isotopic composition for the diorite from Taishan area
样品号 Rb/10-6 Sr/10-6 87Sr/86Sr 2 σ (87Sr/86Sr)i Sm/10-6 Nd/10-6 143Nd/144Nd 2 σ (143Nd/144Nd)i εNd(t) TDM/Ga TDM2/Ga Lu/10-6 Hf/10-6 176Hf/177Hf 2 σ (176Hf/177Hf)i εHf(t) TS19-14 (角闪石-1) 3.7 52.4 0.709271 10 0.701529 6.6 16.7 0.513356 4 0.509255 0.34 1.33 2.94 0.52 1.50 0.283740 6 0.281244 4.89 TS19-14 (角闪石-2) 3.7 52.9 0.709189 6 0.701559 6.7 17.4 0.513287 4 0.509278 0.80 1.15 2.90 0.53 1.47 0.283768 6 0.281209 3.63 TS19-14 (角闪石-3) 3.8 53.9 0.709245 6 0.701559 7.0 20.0 0.512932 2 0.509288 1.00 10.96 2.89 0.54 1.47 0.283712 4 0.281081 -0.93 TS19-14 (斜长石) 19.2 10862 0.701724 10 0.701531 1.0 5.8 0.511073 4 0.509255 0.35 2.90 2.94 0.03 1.02 0.281475 8 0.281235 4.57 TS19-14 (角闪石+斜长石-1) 3.6 119 0.704878 8 0.701580 6.3 16.3 0.513298 4 0.509237 -0.01 1.06 2.97 0.51 1.36 0.283736 6 0.281072 -1.25 TS19-14 (角闪石+斜长石-2) 2.0 1014 0.701757 8 0.701544 0.5 1.7 0.512657 12 0.509373 2.66 3.14 2.75 0.04 0.14 0.283008 30 0.281156 1.73 TS19-14 (角闪石+斜长石-3) 2.0 1070 0.701736 10 0.701534 0.2 1.0 0.511947 10 0.509384 2.87 2.79 2.74 0.01 0.09 0.283029 6 0.281904 28.36 TS19-14 (全岩-1) 13.6 620 0.703398 10 0.701006 3.8 13.0 0.512318 6 0.509310 1.43 3.17 2.85 0.26 0.96 0.282410 38 0.280497 -21.71 TS19-14 (全岩-2) 9.2 397 0.703432 10 0.700907 4.9 16.9 0.512438 6 0.509390 3.00 2.88 2.73 0.35 1.04 0.283573 8 0.281166 2.11 TS19-14 (全岩-3) 7.1 573 0.702949 8 0.701590 6.1 25.7 0.511804 8 0.509338 1.98 2.87 2.81 0.35 1.11 0.283337 6 0.281086 -0.76 TS19-14 (全岩-4) 5.3 548 0.704124 8 0.703077 5.2 16.4 0.512547 6 0.509253 0.31 3.93 2.94 0.35 1.17 0.283330 8 0.281171 2.28 注:87Sr/86Sr(i) =[(87Sr/86Sr)-(87Rb/86Sr)(eλt-1)], 其中λ(87Rb)=1.42 × 10-11年-1[20]; 143Nd/144Nd(i) =[(143Nd/144Nd)-(143Sm/144Nd)(eλt-1)], εNd(t) =[(143Nd/144Nd)/(143Nd/144NdCHUR)-1]× 104, 其中λ(147Sm)=6.54 × 10-12 a-1[21], 147Sm/144NdCHUR = 0.1967, 143Nd/144NdCHUR = 0.512638, 147Sm/144NdDM = 0.2137, 143Nd/144NdDM = 0.51315, 147Sm/144NdCC = 0.12.176Hf/177Hf(i) =[(176Hf/177Hf)-(176Lu/177Hf)(eλt-1)], εHf(t) =[(176Hf/177Hf)/(176Hf/177HfCHUR)-1]× 104, 其中λ(176Lu)=1.867 × 10-11 a-1 [22], 176Lu/177HfCHUR = 0.0332, 176Hf/177HfCHUR = 0.282772[23],176Lu/177HfDM = 0.0384, 176Hf/177HfDM = 0.283251[24], 176Lu/177HfCC =0.015[25] 表 5 计算过程中使用的角闪石分配系数
Table 5 Amphibole partition coefficients used in computation process
元素 分配系数 Rb 0.14 Ba 0.12 Th 0.017 U 0.008 Nb 0.853 Ta 0.609 Pb 0.12 Sr 0.28 Zr 1.564 Hf 1.534 Y 2 Ti 5.175 La 0.245 Ce 0.485 Pr 0.70 Nd 0.92 Sm 1.69 Eu 1.62 Gd 1.90 Tb 2.06 Dy 2.23 Ho 2.10 Er 1.97 Tm 1.798 Yb 1.625 Lu 1.385 注:角闪石的分配系数据参考文献[44] -
Liu D Y, Nutman A P, Compston W, et al. Remnants of > 3800 Ma crust in the Chinese part of the Sino-Korean craton[J]. Geology, 1992, 20: 339-342. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1992)020<0339:ROMCIT>2.3.CO;2
Song B, Allen P N, Liu D Y, et al. 3800 to 2500 Ma crustal evolution in the Anshan area of Liaoning province, northeastern China[J]. Precambrian Research, 1996, 78: 79-94. doi: 10.1016/0301-9268(95)00070-4
温德娟. 华北地台北缘鞍山白家坟奥长花岗岩地球化学特征、锆石U-Pb年龄及意义[J]. 地质通报, 2019, 38(10): 1711-1717. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20191011&flag=1 Condie K C, Belousova E, Griffin W L, et al. Granidoid events in space and time: Constraints from igneous and detrital zircon age spectra[J]. Gondwana Research, 2009, 15(3/4): 228-242. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1342937X08001019
Nutman A P, Wan Y S, Du L L, et al. Multistage Late Neoarchaean crustal evolution of the North China Craton, eastern Hebei[J]. Precambrian Research, 2011, 189(1/2): 43-65. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0301926811001008
Wan Y S, Wang S J, Liu D Y, et al. Redefinition of depositional ages of Neoarchean supracrustal rocks in western Shandong Province, China: SHRIMP U-Pb zircon dating[J]. Gondwana Research, 2012, 21(4): 768-784. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2011.05.017
彭游博. 辽北开原地区新太古代变质深成岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄及地球化学特征[J]. 地质通报, 2020, 39(5): 670-680. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20200508&flag=1 Wan Y S, Xie S W, Yang C H, et al. Early Neoarchean (~2.7 Ga) tectonothermal events in the North China Craton: A synthesis[J]. Precambrian Research, 2014, 247: 45-63. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2014.03.019
Wan Y S, Liu D Y, Wang S J, et al. Juvenile magmatism and crustal recycling at the end of the Neoarchean in western Shandong Province, North China Craton: evidence from SHRIMP zircon dating[J]. American Journal of Science, 2010, 310: 1503-1552. doi: 10.2475/10.2010.11
Wan Y S, Liu D Y, Wang S J, et al. 2.7 Ga juvenile crust formation in the North China Craton (Taishan-Xintai area, western Shandong Province): further evidence of an understated event from zircon U-Pb dating and Hf isotope composition[J]. Precambrian Research, 2011, 186: 169-180. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2011.01.015
Chen Y, Zhang J, Liu J, et al. Crustal growth and reworking of the eastern North China Craton: Constraints from the age and geochemistry of the Neoarchean Taishan TTG gneisses[J]. Precambrian Research, 2020, 343: 105706. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2020.105706
Xiao Y Y, Chen S, Niu Y L, et al. Mineral compositions of syn-collisional granitoids and their implications for the formation of juvenile continental crust and adakitic magmatism[J]. Journal of Petrology, 2020, 61(3): egaa038. doi: 10.1093/petrology/egaa038
Liu Y S, Gao S, Hu Z C, et al. Continental and oceanic crust recycling-induced melt-peridotite interactions in the Trans-North China Orogen: U-Pb dating, Hf isotopes and trace elements in zircons from mantle xenoliths[J]. Journal of Petrology, 2010, 51: 537-571. doi: 10.1093/petrology/egp082
Ludwig K R. ISOPLOT 3.0: A Geochronological Toolkit for Microsoft Excel[M]. Berkeley: Berkeley Geochronology Center, 2003: 1-71.
Su Y P, Zheng J P, Griffin W L, et al. Geochronology and geochemistry of deep-seated crustal xenoliths in the northern North China Craton: Implications for the evolution and structure of the lower crust[J]. Lithos, 2017, 292/293: 1-14. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2017.08.017
Sun P, Niu Y L, Guo P Y, et al. Elemental and Sr-Nd-Pb isotope geochemistry of the Cenozoic basalts in Southeast China: Insights into their mantle sources and melting processes[J]. Lithos, 2017, 272/273: 16-30. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2016.12.005
Chen S, Wang X H, Niu Y L, et al. Simple and cost-effective methods for precise analysis of trace element abundances in geological materials with ICP-MS[J]. Science Bulletin, 2017, 62: 277-289. doi: 10.1016/j.scib.2017.01.004
Leake B E, Woolley A R, Arps C E S, et al. Nomenclature of amphiboles: report of the subcommittee on amphiboles of the International Mineralogical Association, commission on new minerals and mineral names[J]. The Canadian Mineralogist, 1997, 35: 219-246. doi: 10.1180/minmag.1997.061.405.13
Sun S S, McDonough W F. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: implications for mantle composition and processes[J]. Geological Society London Special Publications, 1989, 42: 313-345. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.1989.042.01.19
Steiger R H, E Jäger. Subcommission on geochronology: Convention on the use of decay constants in geo- and cosmochronology[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1977, 36(3): 359-362. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(77)90060-7
Lugmair G W, Marti K. Lunar initial 143Nd/144Nd: Differential evolution of the lunar crust and mantle[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1978, 39(3): 349-357. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(78)90021-3
Soderlund U, Patchett P J, Vervoort J D, et al. The 176Lu decay constant determined by Lu-Hf and U-Pb isotope systematics of Precambrian mafic intrusions[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2004, 219(3/4): 0-324. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0012821X04000123
Blichert-Toft J, Albarède F. The Lu-Hf geochemistry of chondrites and the evolution of the mantle-crust system[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1997, 148: 243-258. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(97)00040-X
Vervoort J D, Blicherttoft J. Evolution of the depleted mantle: hafnium isotope evidence from juvenile rocks through time[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1999, 63(3/4): 533-556.
Griffin W L, Wang X, Jackson S E, et al. Zircon chemistry and magma mixing, SE china: In-situ analysis of Hf isotopes, tonglu and pingtan igneous complexes[J]. Lithos, 2002, 61(3/4): 237-269. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0024493702000828
Holland T, Blundy J. Non-ideal interactions in calcic amphiboles and their bearing on amphibole-plagioclase thermometry[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1994, 116: 433-447. doi: 10.1007/BF00310910
Anderson J L, Barth A P, Wooden J L, et al. Thermometers and Thermobarometers in Granitic Systems[J]. Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry, 2008, 69: 121-142. doi: 10.2138/rmg.2008.69.4
Schmidt M W. Amphibole composition in tonalite as a function of pressure: An experimental calibration of the Al-in-hornblende barometer[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1992, 110: 304-310. doi: 10.1007/BF00310745
Putirka K. Amphibole thermometers and barometers for igneous systems and some implications for eruption mechanisms of felsic magmas at arc volcanoes[J]. American Mineralogist, 2016, 101: 841-858. doi: 10.2138/am-2016-5506
King P L, Hervig R L, Holloway J R, et al. Partitioning of Fe3+/Fetotal between amphibole and basanitic melt as a function of oxygen fugacity[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2000, 178(1/2): 97-112. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0012821X00000716
Zhang L, Han B F, Wei C J, et al. Cumulate hornblendite enclaves in diorite-porphyrite intrusions from the Shuangyashan, Northeast China, and implications for the transition from lower crust to upper mantle in subduction setting[J]. Int. J. Earth Sci. (Geol. Rundsch), 2011, 100: 63-79. doi: 10.1007/s00531-009-0502-9
Cui X H, Zhai M G, Guo J H, et al. Field occurrences and Nd isotopic characteristics of the meta-maficultramafic rocks from the Caozhuang Complex, eastern Hebei: Implications for early Archean crustal evolution of the North China Craton[J]. Precambrian Research, 2018, 310: 425-442. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2018.03.006
Niu Y L. Generation and evolution of basaltic magmas: some basic concepts and a hypothesis for the origin of the Mesozoic-Cenozoic volcanism in eastern China[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 2005, 11: 9-46. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-GXDX200501001.htm
王伟, 翟明国, M Santosh. 鲁西太古宙表壳岩的成因及其对地壳演化的制约[J]. 地球科学, 2016, 46(7): 949-962. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK201607007.htm 陈艳红, 杨经绥, 张岚, 等. 西藏泽当蛇绿岩中角闪辉长岩矿物学特征及其成因启示[J]. 中国地质, 2015, 42(5): 1421-1442. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2015.05.016 Bindeman I N, Davis A M, Drake M J. Ion microprobe study of plagioclase-basalt partition experiments at natural concentration levels of trace elements[J]. Geochim Cosmochim Acta, 1998, 62(7): 1175-1193. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(98)00047-7
Berno D, Tribuzio R, Zanetti A, et al. Evolution of mantle melts intruding the lowermost continental crust: constraints from the Monte Capio-Alpe Cevia mafc-ultramafc sequences (Ivrea-Verbano Zone, northern Italy)[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 2020, 175: 2. doi: 10.1007/s00410-019-1637-8
Nandedkar R H, Ulmer P, Müntener O. Fractional crystallization of primitive, hydrous arc magmas: an experimental study at 0.7 GPa[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 2014, 167(6): 1015. doi: 10.1007/s00410-014-1015-5
Chen S, Niu Y L, Sun W L, et al. On the origin of mafic magmatic enclaves (MMEs) in syn-collisional granitoids: evidence from the Baojishan pluton in the North Qilian Orogen, China[J]. Mineralogy and Petrology, 2015, 109: 577-596. doi: 10.1007/s00710-015-0383-5
Shao F L, Niu Y L, Liu Y, et al. Petrogenesis of Triassic granitoids in the East Kunlun Orogenic Belt, northern Tibetain Plateau and their tectonic implications[J]. Lithos, 2017, 282/283: 33-44. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2017.03.002
Niu Y L, Zhao Z D, Zhu D C, et al. Continental collision zones are primary sites for net continental crust growth-a testable hypothesis[J]. Earth Science Reviews, 2013, 127: 96-110. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2013.09.004
Tiepolo M, Langone A, Morishita T, et al. On the recycling of amphibole-rich ultramafic intrusive rocks in the arc crust: evidence from Shikanoshima Island (Kyushu, Japan)[J]. Journal of Petrology, 2012, 53: 1255-1285. doi: 10.1093/petrology/egs016
Tang G J, Wang Q, Wyman D A, et al. Genesis of pristine adakitic magmas by lower crustal melting: a perspective from amphibole composition[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 2017, 122: 1934-1948. doi: 10.1002/2016JB013678
Niu Y L, O'Hara M J. MORB mantle hosts the missing Eu (Sr, Nb, Ta and Ti) in the continental crust: New perspectives on crustal growth, crust-mantle differentiation and chemical structure of oceanic upper mantle[J]. Lithos, 2009, 112: 1-17. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0024493708002934
Niu Y L, O'Hara M J. Origin of ocean island basalts: a new perspective from petrology, geochemistry, and mineral physics considerations[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 2003, 108: 1-19. doi: 10.1029/2002JB002048/abstract
Rudnick R L, Gao S. Composition of the continental crust[J]. Treatise on geochemistry, 2003, 3: 1-64. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780080959757003016
Zeng L S, Gao L E, Xie K, et al. Mid-Eocene high Sr/Y granites in the Northern Himalayan Gneiss Domes: Melting thickened lower continental crust[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2011, 303(3/4): 251-266. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0012821X11000173
Shaw A, Downes H, Thirlwall M F. The quartz-diorites of Limousin: elemental and isotopic evidence for Devono-Carboniferous subduction in the Hercynian Belt of the French Massif-Central[J]. Chemical Geology, 1993, 107: 1-18. doi: 10.1016/0009-2541(93)90098-4
Martin H, Smithies R H, Rapp R, et al. An overview of adakite, tonalite-trondhjemite-granodiorite (TTG), and sanukitoid: Relationships and some implications for crustal evolution[J]. Lithos, 2005, 79: 1-24. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2004.04.048
Jung S, Hoernes S, Mezger K. Synorogenic melting of mafic lower crust: constraints from geochronology, petrology and Sr, Nd, Pb and O isotope geochemistry of quartz diorites (Damara orogen, Namibia)[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 2002, 143: 551-566. doi: 10.1007/s00410-002-0366-5
Grove T L, Elkins-Tanton L T, Parman S W, et al. Fractional crystallization and mantle-melting controls on calcalkaline differentiation trends[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 2003, 145: 515-533. doi: 10.1007/s00410-003-0448-z
Moyen J F. High Sr/Y and La/Yb ratios: The meaning of the "adakitic signature"[J]. Lithos, 2009, 112(3/4): 556-574. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0024493709001285
Rollinson H R. Using Geochemical Data: Evaluation, Presentation, Interpretation[M]. Singapore: Longman Singapore Publishers (Pte) Ltd., 1993: 352.
Rapp R P, Watson E B. Dehydration melting of metabasalt at 8~32 kbar: Implication for continental growth and crust-mantle recycling[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1995, 36: 891-931. doi: 10.1093/petrology/36.4.891
Rapp R P, Shimizu N, Norman M D, et al. Reaction between slab-derived melts and peridotite in the mantle wedge: Experimental constraints at 3.8 GPa[J]. Chemical Geology, 1999, 160(4): 335-356. doi: 10.1016/S0009-2541(99)00106-0
Cai Y F, Wang Y J, Cawood P A, et al. Neoproterozoic crustal growth of the Southern Yangtze Block: Geochemical and zircon U-Pb geochronological and Lu-Hf isotopic evidence of Neoproterozoic diorite from the Ailaoshan zone[J]. Precambrian Research, 2015, 266: 137-149. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2015.05.008
Wan Y S, Dong C Y, Wang S J, et al. Middle Neoarchean magmatism in western Shandong, North China Craton: SHRIMP zircon dating and LA-ICP-MS Hf isotope analysis[J]. Precambrian Research, 2014, 255: 865-884. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2014.07.016
Ren P, Xie H, Wang S, et al. A Ca. 2.60 Ga Tectono-Thermal Event in Western Shandong Province, North China Craton from Zircon U-Pb-O Isotopic Evidence: Plume or Convergent Plate Boundary Process[J]. Precambrian Research, 2016, 281: 236-252. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2016.05.016
马铭株, 万渝生, 颉颃强, 等. 鲁西七星台地区新太古代基性岩浆作用: 变质辉长岩的时代和组成[J]. 地球科学, 2020, 45(7): 2610-2628. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX202007031.htm Condie K C, Kröner A. The building blocks of continental crust: evidence for a major change in the tectonic setting of continental growth at the end of the Archean[J]. Gondwana Research, 2013, 23: 394-402. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2011.09.011
Moyen J F, Martin H. Forty years of TTG research[J]. Lithos, 2012, 148: 312-336. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2012.06.010
Green T H. Significance of Nb/Ta as an Indicator of Geochemical Processes in the Crust-Mantle System[J]. Chemical Geology, 1995, 120(3/4): 347-359. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/000925419400145X
万渝生, 董春艳, 任鹏, 等. 华北克拉通太古宙TTG岩石的时空分布、组成特征及形成演化: 综述[J]. 岩石学报, 2017, 33(5): 1405-1419. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201705003.htm Polat A, Li J, Fryer B, et al. Geochemical characteristics of the Neoarchean(2800~2700 Ma) Taishan greenstone belt, North China Craton: evidence for plume-craton interaction[J]. Chemical Geology, 2006, 230: 60-87. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2005.11.012
Jahn B M, Liu D Y, Wan Y S, et al. Archean crustal evolution of the Jiaodong Peninsula, China, as revealed by zircon SHRIMP geochronology, elemental and Nd-isotope geochemistry[J]. American Journal of Science, 2008, 308: 232-269. doi: 10.2475/03.2008.03
Wang W, Zhang X, Wang S, et al. Geochronology and geochemistry of Neoarchean granitoids from the western Shandong province, north china craton, implications for crustal evolution and cratonization[J]. Precambrian Research, 2017, 303: 749-763. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2017.10.007
Wang Y J, Zhang Y Z, Zhao G C, et al. Zircon U-Pb geochronological and geochemical constraints on the petrogenesis of the Taishan sanukitoids(Shandong): Implications for Neoarchean subduction in the Eastern Block, North China Craton[J]. Precambrian Research, 2009, 174: 273-286. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2009.08.005
Wang W, Zhai M G, Wang S J, et al. Crustal reworking in the North China Craton at~2.5 Ga: Evidence from zircon U-Pb age, Hf isotope and whole rock geochemistry of the felsic volcano-sedimenttary rocks from the western Shandong Province[J]. Geological Journal, 2013, 48: 406-428. doi: 10.1002/gj.2493




 下载:
下载: