Determination of Middle Triassic rhyolite in Caojian area, Yunlong County of western Yunnan, and its constraints on the Paleo-Tethys tectonic system transition
-
摘要:
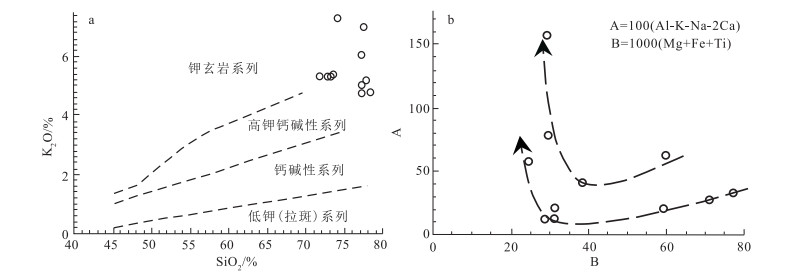
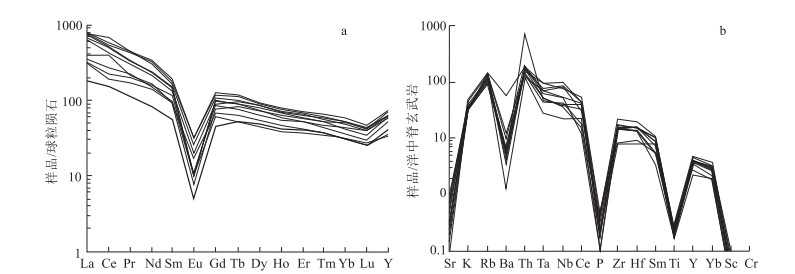
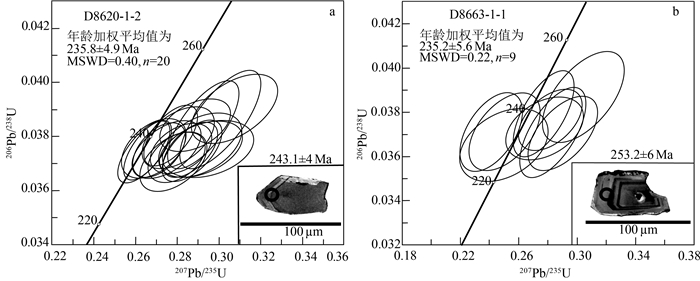
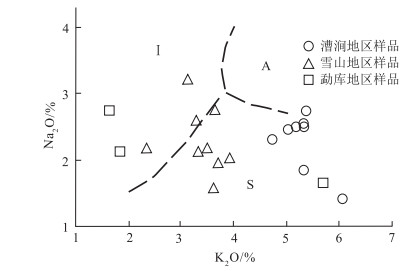
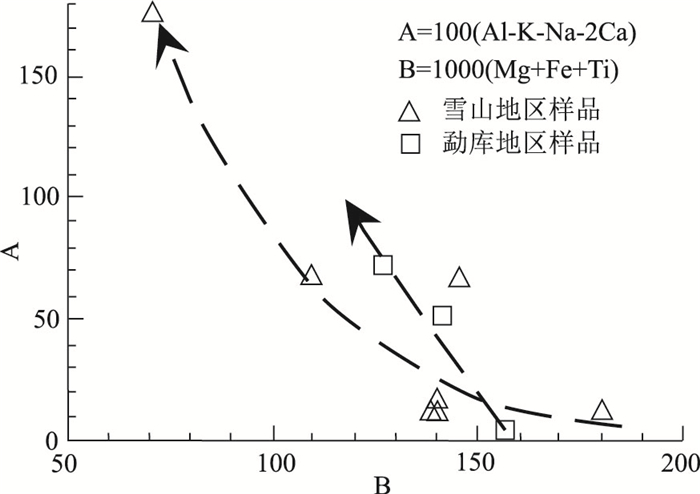
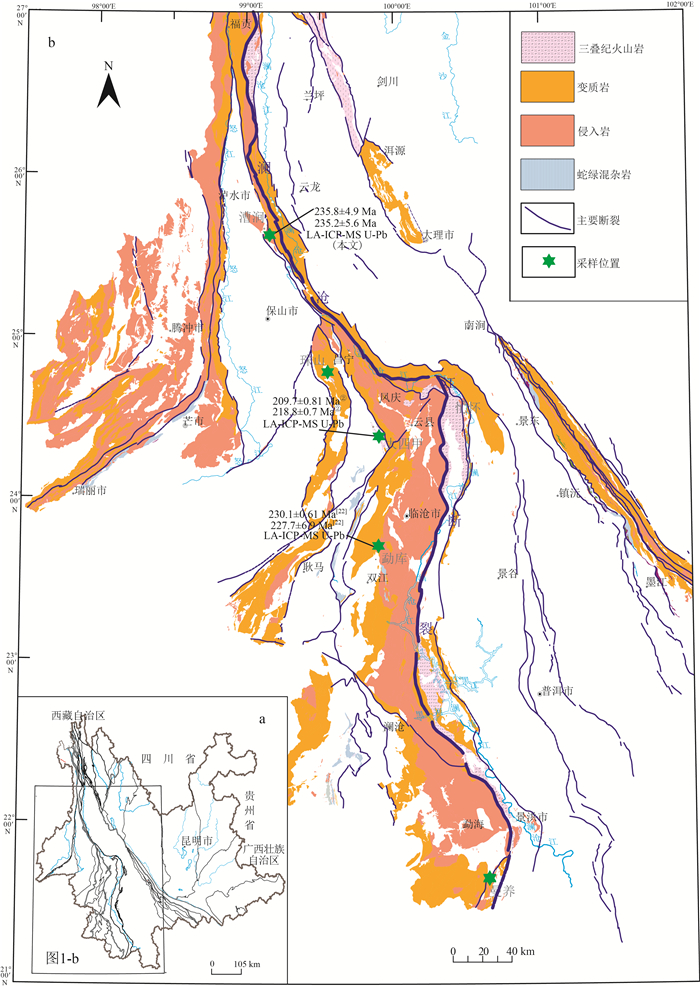
1:5万区域地质调查表明,在滇西澜沧江断裂带与保山地块之间断续出露一套中—晚三叠世中酸性-酸性火山岩、火山碎屑岩、火山-沉积岩,主要出露于云南云龙县漕涧、昌宁县珠山、凤庆县大四甲、双江县勐库、勐海县曼养等地,属弧间盆地内的火山-沉积岩系。对云龙县漕涧一带出露的流纹岩进行了地球化学和锆石U-Pb测年。结果表明,其A/CNK=1.05~2.44,为一套过铝质的高钾钙碱性-钾玄岩系列,LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄为235.8±4.9 Ma、235.2±5.6 Ma,属中三叠世。在地球化学特征上,该套火山岩以显著富集Nb、Ta、Th、Zr、Hf、Y等高场强元素(HFSE),亏损Sr、Ba等大离子亲石元素及P、Ti等高场强元素为特征,属中-上部地壳变质沉积岩低压角闪岩相条件下的低程度部分熔融物,是碰撞造山作用结束后,区域性地壳松弛过程中,深部地幔物质上涌引起的加热增温与隆升减压熔融联合作用的结果。往南至凤庆县、双江县等地,该套火山岩逐渐向准铝质-过铝质的高钾钙碱性-钙碱性系列过渡;微量元素蛛网图显示明显的"T-N-T"的负异常,指示在隆升减压条件下,受俯冲流体交代的中-下地壳物质在高压角闪岩相-麻粒岩相条件下发生了较高程度的部分熔融作用。这套三叠纪火山岩虽然在岩浆源区、部分熔融程度、岩浆形成的温-压条件等方面存在差异,但都是古特提斯洋关闭后,大洋构造体制向大陆构造体制转化的深部过程在地表的反映。
Abstract:In recent years, 1:50 000 regional geological survey reveals that a set of intermediate-acid and acid volcanic rocks, pyroclastic rocks and volcanic-sedimentary rocks of the Middle-Late Triassic are intermittently outcropped between the Lancang River fault in western Yunnan and Baoshan block. They are mainly outcropped in Caojian, Yunlong County, Zhushan, Changning County, Dasijia, Fengqing County, Mengku, Shuangjiang County, Manyan, Menghai County and other places, belonging to the volcanic-sedimentary rock series in the interarc basin. The study focuses on the rhyolite outcropped in Caojian of Yunlong County. Its A/CNK value of 1.05-2.44 indicates a peraluminous high-potassium calc-alkaline-potassic series. The zircon LA-ICP-MS U-Pb ages of 235.8±4.9 Ma and 235.2±5.6 Ma implies Middle Triassic. This set of volcanic rocks is chemically characterized by significant enrichment of high field strength elements such as Nb, Ta, Th, Zr, Hf and Y, depletion of large ionic elements such as Sr and Ba, and high field strength elements such as P and Ti. It is a low-grade partial melt under the condition of low-pressure amphibolite facies of metamorphic sedimentary rocks in the middle-upper crust. It is the result of the combined heating, warming, uplifting, decompression and melting caused by upwelling of deep mantle materials in the process of regional crustal relaxation after collision orogeny. Southward to Fengqing County, Shuangjiang County and other places, this set of volcanic rocks gradually transit to a quasi-aluminum-peraluminous series of high potassium calc-alkaline-calc-alkaline. The cobweb diagram of trace element ratio shows obvious negative anomaly of "T-N-T", which indicates a high degree of partial melting under the conditions of high-pressure amphibolite facies-granulite facies of the middle-lower crust metasomatized by subduction fluid under the conditions of uplift and decompression. Although there are some differences in magma source, partial melting degree and temperature-pressure conditions for magma formation, these Triassic volcanic rocks are all the reflection of the deep process of transition from oceanic tectonic system to continental tectonic system on the surface after the closure of the Paleo-Tethys Ocean.
-
致谢: 云南省地质调查院李静、张虎教授级高工及刘桂春、孙载波、刘军平、田素梅高级工程师认真审阅本文并提出了许多宝贵的修改意见,在研究及论文编写过程中云南1:5万归州等4幅区域地质调查项目组成员给与了帮助和支持,审稿专家对论文进行了详细审阅并提出宝贵的修改意见,在此一并表示衷心的感谢。
-
表 1 漕涧地区三叠纪流纹岩主量、微量和稀土元素测试数据
Table 1 Assay data of major, trace and rare earth elements of Triassic rhyolite in the Caojian area
元素 D8620 -1-2 D8621 -1-1-1 D8621 -1-1-2 PM022 -24-1 PM022 -28-1 PM022 -31-2 PM022-34-2 PM021 -15-1 PM021 -17-1 PM021 -17-2 PM021 -19-1 流纹岩 流纹岩 流纹岩 流纹岩 浅变质流纹岩 浅变质流纹岩 浅变质流纹岩 浅变质流纹岩 浅变质流纹岩 浅变质流纹岩 浅变质流纹岩 SiO2 76.41 71.79 70.81 75.76 76.08 71.71 72.34 76.38 76.54 73.25 76.84 TiO2 0.25 0.41 0.43 0.31 0.31 0.41 0.40 0.31 0.28 0.31 0.30 Al2O3 13.28 11.98 12.07 11.76 10.95 12.35 11.70 12.14 11.01 12.62 10.60 Fe2O3 2.36 1.61 1.87 2.62 3.33 2.17 1.98 1.79 2.80 2.50 1.92 FeO 0.28 4.12 4.55 0.15 0.75 3.28 3.32 0.32 0.52 0.37 1.18 MnO 0.02 0.21 0.35 0.005 0.003 0.29 0.24 0.01 0.05 0.11 0.11 MgO 0.15 0.30 0.30 0.18 0.11 0.32 0.29 0.18 0.12 0.21 0.15 CaO 0.07 0.43 0.42 0.05 0.04 0.38 0.28 0.25 0.28 0.40 0.20 Na2O 0.17 2.52 2.45 0.21 2.27 1.80 2.70 1.40 2.44 2.07 2.46 K2O 4.66 5.24 5.24 6.85 4.66 5.20 5.30 5.98 4.98 7.25 5.12 P2O5 0.01 0.05 0.04 0.02 0.01 0.05 0.05 0.04 0.01 0.03 0.01 CO2 0.043 0.043 0.043 0.10 0.05 0.07 0.07 0.032 0.032 0.043 0.28 烧失量 1.99 0.48 0.53 1.72 1.12 1.34 0.66 0.94 0.49 0.48 0.57 总计 99.66 99.13 99.07 99.65 99.62 99.30 99.25 99.73 99.51 99.59 99.45 La 57.24 247.30 237.70 95.17 95.41 121.61 226.48 111.17 219.24 197.20 207.79 Ce 125.45 452.99 435.18 177.17 154.22 317.12 547.74 221.60 415.27 337.91 399.22 Pr 13.46 53.74 51.44 23.79 20.73 26.42 55.28 27.18 41.62 37.14 39.37 Nd 48.67 200.13 192.36 96.20 82.73 98.50 180.99 93.67 142.99 129.28 137.93 Sm 10.96 36.30 34.70 23.06 18.28 17.61 32.47 18.69 29.25 25.58 28.14 Eu 0.36 2.33 2.21 0.79 0.55 1.21 1.90 0.74 0.68 1.42 0.81 Gd 11.82 32.21 31.03 23.50 19.98 17.19 27.30 15.61 25.98 21.68 25.17 Tb 2.53 5.48 5.26 4.59 3.92 2.96 4.77 2.53 4.28 3.57 4.13 Dy 15.61 30.18 29.16 27.70 23.65 17.81 27.10 14.59 25.23 20.37 23.78 Ho 3.06 5.77 5.53 5.11 4.25 3.32 4.87 2.75 4.79 3.88 4.49 Er 8.42 15.10 14.22 13.59 10.73 8.84 12.42 7.64 13.18 10.70 12.33 Tm 1.20 2.09 1.95 1.86 1.40 1.18 1.65 1.10 1.88 1.52 1.73 Yb 6.76 12.21 10.72 9.87 7.33 6.34 8.76 6.65 10.98 9.10 10.40 Lu 0.81 1.48 1.33 1.25 0.94 0.83 1.10 0.89 1.42 1.29 1.38 Y 69.37 146.50 140.50 124.34 102.20 81.07 118.63 66.31 120.93 113.40 113.30 δEu 0.10 0.20 0.20 0.10 0.09 0.21 0.19 0.13 0.07 0.18 0.09 δCe 1.05 0.91 0.91 0.87 0.80 1.29 1.15 0.94 0.98 0.89 1.00 (La/Sm)N 3.29 4.29 4.31 2.60 3.28 4.34 4.39 3.74 4.72 4.85 4.65 (Gd/Yb)N 1.41 2.13 2.34 1.92 2.20 2.19 2.52 1.89 1.91 1.92 1.95 Zr 1298.5 1948.1 1943.6 1508.9 1338.2 1353.6 1563.9 753.5 1381.8 714.1 1290.0 Zn 53.45 251.69 334.32 34.18 81.03 144.61 351.23 66.30 127.30 121.25 233.76 V 1.7 2.75 2.77 3.69 1.56 3.59 4.11 6.81 5.79 5.00 2.61 Th 36.81 31.92 36.72 27.99 29.43 25.39 31.20 23.98 35.10 33.62 32.27 Sc 0.92 1.62 1.47 3.48 3.13 3.53 3.78 2.55 0.86 2.26 1.36 Sr 9.1 87 84 18.2 17.2 74.2 53.3 14.97 34.80 21.48 11.09 Rb 250.90 211.36 190.06 282.85 236.00 211.95 218.25 231.61 294.69 279.21 228.38 Ni 1.35 0.4 0.3 1.23 1.42 0.63 1.01 3.76 2.36 2.01 1.29 Nb 192.00 310.20 355.80 147.16 126.66 300.46 273.65 79.72 185.33 131.58 140.87 Cu 8.76 3.44 3.45 2.18 1.92 3.06 2.80 3.37 7.07 2.91 2.72 Cr 8.6 18.4 21.5 6.09 9.74 10.29 11.52 7.03 11.16 9.25 9.67 Co 0.47 1.24 0.62 0.31 0.73 0.39 0.51 1.04 0.83 0.70 0.26 Ba 95.0 143.1 140.6 190.93 25.68 123.17 90.16 87.82 1123.79 244.22 74.15 Hf 33.9 47.3 46.4 37.0 33.1 32.1 36.6 21.30 39.50 18.70 37.10 Ta 12.13 13.83 17.32 7.97 9.29 13.11 16.97 5.17 10.91 9.39 8.28 U 9.90 3.62 3.95 2.12 2.53 3.98 3.99 2.03 5.02 5.85 4.45 Pb 27.96 33.35 37.78 39.80 17.88 27.34 27.54 19.68 27.00 32.62 26.08 注:主量元素分析结果首先按11项氧化物进行标准化,再按里特曼法进行全铁调整。标准矿物计算、作图均使用经过全铁调整后的数据进行。主量元素含量单位为%,微量和稀土元素含量单位为10-6 表 2 样品D8620-1-2和D8663-1-1锆石U-Th-Pb同位素分析结果
Table 2 U-Th-Pb isotopic analysis results of zircon D8620-1-2 and D8663-1-1 Samples
测点编号 元素/10-6 Th/U 同位素比值 同位素年龄/Ma Pb Th U 207Pb/206Pb ±1σ 207Pb/235U ±1σ 206Pb/238U ±1σ 207Pb/206Pb ±1σ 207Pb/235U ±1σ 206Pb/238U ±1σ D8620-1-2 01 11 104 169 0.61 0.0536 0.0022 0.2749 0.0111 0.0375 0.0007 354 97 247 9 237 4 02 12 125 201 0.62 0.0565 0.0025 0.2918 0.0130 0.0375 0.0007 472 96 260 10 238 4 03 12 121 216 0.56 0.0516 0.0015 0.2657 0.0076 0.0375 0.0007 333 60 239 6 238 4 04 11 111 203 0.55 0.0514 0.0016 0.2638 0.0083 0.0374 0.0008 261 69 238 7 237 5 05 9 75 140 0.54 0.0544 0.0025 0.2803 0.0119 0.0380 0.0008 387 104 251 9 240 5 06 11 114 187 0.61 0.0531 0.0017 0.2770 0.0086 0.0380 0.0007 345 72 248 7 241 5 07 12 112 186 0.60 0.0520 0.0020 0.2684 0.0106 0.0375 0.0007 287 89 241 8 238 4 08 11 104 194 0.53 0.0547 0.0022 0.2781 0.0107 0.0371 0.0007 467 89 249 9 235 4 09 24 239 377 0.64 0.0544 0.0017 0.2794 0.0091 0.0372 0.0006 387 68 250 7 236 4 10 12 109 208 0.52 0.0558 0.0023 0.2934 0.0153 0.0375 0.0007 456 125 261 12 237 4 11 12 106 211 0.50 0.0546 0.0021 0.2886 0.0110 0.0384 0.0006 398 85 257 9 243 4 12 12 114 209 0.55 0.0577 0.0026 0.3078 0.0137 0.0390 0.0008 517 102 272 11 247 5 13 15 139 240 0.58 0.0547 0.0020 0.2820 0.0100 0.0376 0.0006 398 79 252 8 238 4 14 11 88 166 0.53 0.0574 0.0018 0.3205 0.0111 0.0406 0.0009 509 70 282 9 256 5 15 8 76 157 0.49 0.0559 0.0023 0.2909 0.0132 0.0377 0.0008 450 117 259 10 239 5 16 9 70 208 0.34 0.0559 0.0022 0.2926 0.0116 0.0384 0.0010 456 82 261 9 243 6 17 11 114 209 0.55 0.0500 0.0018 0.2487 0.0088 0.0363 0.0006 195 81 226 7 230 4 18 9 72 159 0.45 0.0582 0.0030 0.3008 0.0132 0.0386 0.0012 600 111 267 10 244 7 19 14 154 210 0.73 0.0558 0.0018 0.2859 0.0087 0.0374 0.0007 443 75 255 7 237 4 20 9 80 161 0.50 0.0557 0.0017 0.2870 0.0095 0.0375 0.0007 443 69 256 7 237 5 D8663-1-1 01 15 125 231 0.54 0.0505 0.0039 0.2497 0.0196 0.0365 0.0011 220 178 226 16 231 7 02 20 203 295 0.69 0.0544 0.0035 0.2775 0.0178 0.0373 0.0009 387 143 249 14 236 6 03 20 163 264 0.62 0.0544 0.0026 0.2769 0.0141 0.0379 0.0013 387 109 248 11 240 8 04 26 234 425 0.55 0.0483 0.0021 0.2682 0.0125 0.0401 0.0010 122 100 241 10 253 6 05 14 130 248 0.52 0.0543 0.0028 0.2815 0.0147 0.0377 0.0009 389 117 252 12 238 6 06 79 176 596 0.29 0.0647 0.0018 1.0503 0.0349 0.1181 0.0030 765 64 729 17 720 18 07 41 202 198 1.02 0.0580 0.0027 0.6498 0.0334 0.0826 0.0024 528 104 508 21 512 14 08 16 164 269 0.61 0.0474 0.0029 0.2110 0.0122 0.0326 0.0009 78 131 194 10 207 6 09 14 109 194 0.56 0.0579 0.0030 0.3039 0.0184 0.0387 0.0014 528 115 269 14 245 9 10 132 151 266 0.57 0.1046 0.0020 4.1142 0.1054 0.2857 0.0063 1706 36 1657 21 1620 32 11 14 113 209 0.54 0.0570 0.0030 0.2829 0.0155 0.0370 0.0014 500 117 253 12 235 8 12 28 260 234 1.11 0.0545 0.0034 0.2981 0.0184 0.0401 0.0011 391 141 265 14 254 7 13 50 170 152 1.12 0.0750 0.0031 1.1216 0.0542 0.1102 0.0040 1133 83 764 26 674 23 14 14 137 240 0.57 0.0575 0.0031 0.2901 0.0160 0.0370 0.0011 522 121 259 13 234 7 15 293 305 752 0.41 0.1047 0.0023 4.0403 0.1177 0.2808 0.0076 1709 36 1642 24 1596 38 16 10 87 191 0.46 0.0532 0.0048 0.2510 0.0228 0.0341 0.0011 345 206 227 19 216 7 17 17 148 257 0.57 0.0483 0.0029 0.2412 0.0137 0.0371 0.0012 122 128 219 11 235 8 18 12 109 278 0.39 0.0487 0.0025 0.2501 0.0160 0.0371 0.0012 132 -73 227 13 235 7 -
钟大赉. 川滇西部古特提斯造山带[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1998: 1-231. 莫宣学, 沈上越, 朱勤文, 等. 三江中南段火山岩-蛇绿岩与成矿[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1998: 1-128. 潘桂棠, 陈智梁, 李兴振, 等. 东特提斯地质构造形成演化[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1997: 1-218. 刘本培, 冯庆来, 方念乔, 等. 滇西昌宁-孟连带和澜沧江带古特提斯多岛洋构造演化[J]. 地球科学, 1993, 18(5): 529-539. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX199305000.htm 刘本培, 冯庆来, Chonglakmani C, 等. 滇西古特提斯多岛洋的结构及其南北延伸[J]. 地学前缘2002, 9(3): 67-76. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200203027.htm 潘桂棠, 李兴振, 王立全, 等. 青藏高原及邻区大地构造单元初步划分[J]. 地质通报, 2002, 21(11): 701-707. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2002.11.002 李静. 云南省双江县石炭纪牛井山蛇绿混杂岩的岩石学研究[D]. 昆明理工大学硕士学位论文, 2004. 从柏林, 吴根耀, 张旗, 等. 中国滇西古特提斯构造带岩石大地构造演化[J]. 中国科学(B辑), 1993, 23(11): 1201-1207. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JBXK199311012.htm 李兴振, 刘文均, 王义昭, 等. 西南三江地区特提斯构造演化与成矿(总论)[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1999: 23-167. 张旗, 周德进, 赵大升. 滇西古特提斯造山带的威尔逊旋回: 岩浆活动记录和深部过程讨论[J]. 岩石学报, 1996, 12(1): 17-28. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0569.1996.01.002 段向东. 滇西南耿马地区昌宁-孟连带盆地演化[D]. 中国地质大学(武汉)博士学位论文, 2008. 莫宣学, 潘桂棠. 从特提斯到青藏高原形成: 构造-岩浆事件的约束[J]. 地学前缘, 2006, 13(6): 43-51. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2006.06.007 李静, 孙载波, 黄亮, 等. 滇西勐库退变质榴辉岩的P-T-t轨迹及地质意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2017, 33(7): 2285-2291. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201707022.htm 《矿产资源工业要求手册》编委会. 矿产资源工业要求手册[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1998: 217-225. 沈上越, 冯庆来, 魏启荣, 等. 南澜沧江带北段上二叠统陆源弧火山岩的厘定[J]. 矿物岩石, 2006, 26(2): 35-39. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6872.2006.02.006 朱勤文. 滇西南澜沧江带三叠纪火山岩大地构造环境[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 1999, 12(2): 134-143. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.1999.02.005 朱勤文, 莫宣学, 张双全. 南澜沧江古特提斯演化的岩浆岩证据[J]. 特提斯地质, 1999, 23: 16-30. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TTSD199900001.htm 沈上越, 冯庆来, 刘本培. 三江地区南澜沧江带火山岩构造岩浆类型[J]. 矿物岩石, 2002, (3): 66-71. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6872.2002.03.015 张彩华, 刘继顺, 刘德利. 滇西南澜沧江带官房地区三叠纪火山岩地质地球化学特征及其构造环境[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2006, 25(5): 377-386. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2006.05.002 王硕, 董国臣, 莫宣学, 等. 澜沧江南带三叠纪火山岩岩石学、地球化学特征、Ar-Ar年代学研究及其构造意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2012, 28(4): 1148-1162. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201204013.htm 彭头平, 王岳军, 范蔚茗, 等. 澜沧江南段早中生代酸性火成岩SHRIMP锆石U-Pb定年及构造意义[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 2006, 36(2): 123-132. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK200602001.htm 吴嘉林, 孙载波, 周坤, 等. 云南双江县勐库地区三叠纪火山岩的发现及其意义[J]. 云南地质, 2018, 37(3): 261-268. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1885.2018.03.002 李国昌, 王巍, 杨立刚, 等. 滇西凤庆三岔河晚三叠世火山岩年代学、地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2018, 32(6): 1263-1271. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ201806014.htm 廖忠礼, 莫宣学, 潘桂棠, 等. 过铝花岗岩的研究动向和进展——兼论西藏过铝花岗岩[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 2004, 24(2): 22-29. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-3850.2004.02.004 林广春, 马昌前. 过铝花岗岩的成因类型与构造环境研究综述[J]. 华南地质与矿产, 2003, (1): 65-70. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-3701.2003.01.013 张旗, 王焰, 李承东, 等. 花岗岩的Sr-Yb分类及其地质意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2006, 22(9): 2249-2269. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200609000.htm 张旗, 金惟俊, 李承东, 等. 再论花岗岩按照Sr-Yb的分类: 标志[J]. 岩石学报, 2010, 26(4): 985-1015. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201004002.htm 张旗, 金惟俊, 李承东, 等. 三论花岗岩按照Sr-Yb的分类: 应用[J]. 岩石学报, 2010, 26(12): 3431-3455. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201012002.htm 丁烁, 黄慧, 牛耀龄, 等. 东昆仑高Nb-Ta流纹岩的年代学、地球化学及成因[J]. 岩石学报, 2011, 27(12): 3603-3614. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201112009.htm 张新远, 李五福, 欧阳光文, 等. 东昆仑东段青海战红山地区早三叠世火山岩的发现及其地质意义[J]. 地质通报, 2020, 39(5): 631-641. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20200504&flag=1 云南省地质调查院. 1: 5万归州幅、宝丰幅、漕涧幅、功果街幅区域地质矿产调查报告. 2018. 云南省地质矿产勘查院. 1: 5万营盘幅、雪华幅区域地质调查报告. 2017. 云南省地质矿产勘查开发局. 1: 5万孟定街幅、色树坝幅(国内部分)区域地质调查报告. 2000. 云南省地质调查院. 1: 25万临沧县幅、滚龙幅(国内部分)区域地质调查报告. 2003. 云南省地质调查院. 1: 5万香竹林幅、勐勇幅、勐撒幅、懂过幅、安雅幅、勐库幅、耿马幅区域地质矿产调查报告. 2017. 云南省地质局区域地质调查队. 1: 20万勐海幅、孟马幅区域地质调查报告. 1980. 云南省地质调查院. 1: 25万景洪市幅、勐腊县幅区域地质调查报告. 2013. 云南省地质调查院. 1: 5万曼各幅、小街幅、曼班幅、大勐龙幅、万纳兰幅、勐宋坝幅区域地质调查报告. 2019. 云南省地质调查院. 1: 25万凤庆县幅区域地质调查报告. 2008.



 下载:
下载: