Assessment of agricultural production suitability in Nantong City based on ArcGIS technology
-
摘要:
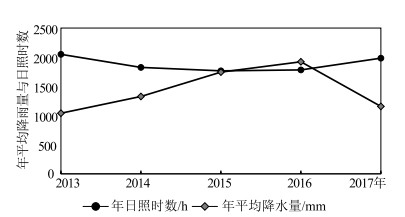
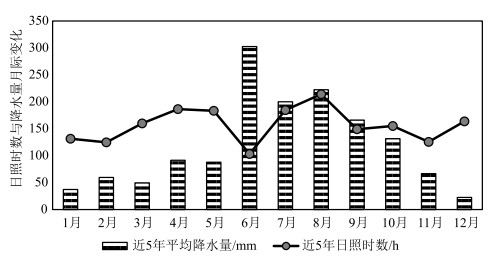
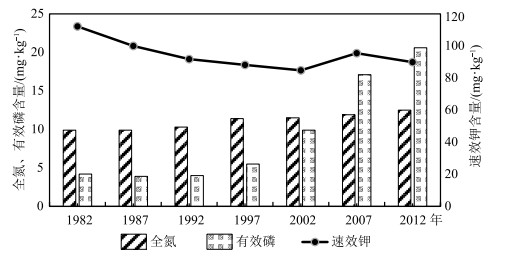
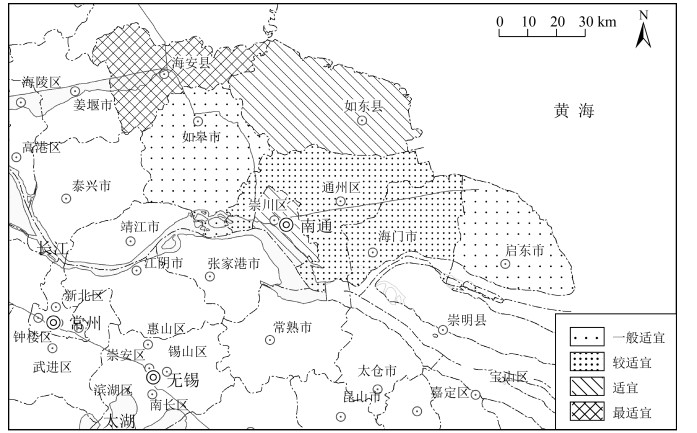
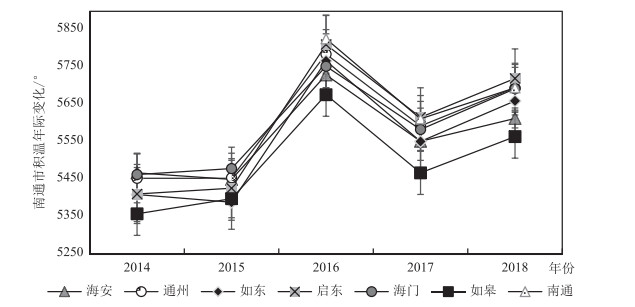
针对环境变化引起的区域农业生产适应性变化、农作物种植结构改变、产业布局调整,以南通市为研究对象,以积温、年降水量、土壤肥力、土壤重金属共同构建农业生产因素评价体系,探究南通市的农业生产适应性情况。结果显示,南通市积温值较高且年际变化大体呈递增趋势。降水量年际变化浮动大,随年份增加呈现先增后减的趋势,日照时数与降水量的变化特征呈负相关。土壤全氮与有效磷含量均满足土壤养分标准二级要求,速效钾含量仅达到四级标准要求。土壤重金属内梅罗综合污染指数在0.26~0.4之间,说明土壤环境质量安全。基于ArcGIS技术采用空间分析等技术手段,将南通地区的农业适宜区分为4级,海安为一级适宜区(最适宜),南通市辖区与如东为二级适宜区,通州、海门为三级适宜区,启东、如皋为四级适宜区。通过南通市农业生产适宜性评价,为今后南通地区科学的农作物生产布局、国土空间规划提供参考依据。
Abstract:Based on the regional adaptation of agricultural production, the change of crop planting structure and the industrial layout adjustment, as a result of environmental change, Nantong City was selected to build an evaluation system of agricultural production factors with accumulated temperature, annual precipitation, soil fertility, soil heavy metals and slope advantages.The results show the accumulated temperature of Nantong City is high and the interannual variation is generally increasing.The interannual variation of precipitation fluctuates greatly with a trend of firstly increasing and then decreasing over the years.There is a negative correlation between the sunshine duration and the variation of precipitation.Both total nitrogen and the available phosphorus content in soil meet the secondary requirements of soil nutrient standard, while the content of available potassium only meets the requirements of the fourth standard level.The Nemero index of heavy metals in soil is between 0.26 and 0.4, indicating that the environmental quality of soil is safe.Based on ArcGIS technology, spatial analysis and other technical methods are used to classify agricultural areas of Nantong into 4 levels.As a result, Haian is rated as the first-tier suitable area (the most suitable), municipal district of Nantong City and Rudong as the secondary one, Tongzhou and Haimen as the third one, and Qidong and Rugao are rated as the fourth one.The evaluation of agricultural production suitability in Nantong City is expected to provide a reference for layout of crop production and territorial space planning scientifically and rationally.
-
致谢: 审稿专家在成文过程中给予了宝贵的意见和建议,在此表示衷心感谢。
-
表 1 数据来源
Table 1 Data sources
数据名称 数据来源 数据类型 积温 天气网历史天气数据的日平均温度 统计数据 年降水量 《南通市统计年鉴》(2013—2017) 统计数据 日照时数 《南通市统计年鉴》(2013—2017) 统计数据 土壤养分数据 全国第二次土壤普查数据 统计数据 土壤重金属数据 全国第二次土壤普查数据、巩万合等[8, 10]关于南通市土壤肥力及重金属 统计数据 南通市行政区划图 地理信息共享平台(https://www.tianditu.gov.cn) 空间数据 南通市基础地理图 地理信息共享平台(https://www.tianditu.gov.cn) 空间数据 表 2 农业生产适应性评价体系
Table 2 Evaluation system of agricultural production adaptability
评价指标 指标因子 权重 分值 分类 评价指标 指标因子 权重 分值 分类 气候 积温/℃ 0.15 1 < 5000 土壤 土壤磷含量/(mg·kg-1) 0.1 2 50~70 2 5000~5500 3 70~90 3 5500~5700 4 ≥90 4 ≥5700 Cd/(mg·kg-1) 0.05 1 ≥0.2 年降水量/mm 0.1 1 < 1000 2 0.1~0.2 2 1000~1500 3 < 0.1 3 ≥1500 Cr/(mg·kg-1) 0.05 1 ≥60 日照时数/h 0.1 1 1000~1400 2 50~60 2 1400~2200 3 < 50 3 2200~3000 Hg/(mg·kg-1) 0.05 1 ≥0.12 土壤 土壤有机质/% 0.1 1 < 0.6 2 0.1~0.12 2 0.6~1 3 < 0.1 3 1~2 Pb/(mg·kg-1) 0.05 1 ≥25 4 2~3 2 20~25 土壤钾含量/(mg·kg-1) 0.1 1 < 10 3 15~20 2 10~20 4 < 15 3 20~30 As/(mg·kg-1) 0.05 1 ≥8 4 ≥30 2 6~8 土壤钾含量/(mg·kg-1) 0.1 1 < 50 3 < 6 表 3 南通市土壤重金属含量分析
Table 3 Analysis of heavy metal content in soil of Nantong
mg/kg 表 4 南通市各地区单因子指数与内梅罗综合污染指数
Table 4 Index of single factor and comprehensive pollution index in different areas of Nantong
区域 单因子指数 内梅罗综合指数 Cd Cr Pb As Hg 如皋 0.10 0.13 0.05 0.29 0.09 0.26 海安 0.11 0.13 0.04 0.28 0.09 0.26 启东 0.18 0.17 0.08 0.51 0.09 0.40 如东 0.18 0.15 0.05 0.30 0.09 0.27 通州 0.10 0.14 0.06 0.39 0.14 0.32 海门 0.17 0.16 0.05 0.34 0.10 0.30 南通 0.15 0.14 0.06 0.37 0.12 0.31 表 5 土壤重金属之间的相关系数
Table 5 Correlation coefficient among different heavy metals in soil
项目 Cd Cr Pb As Hg Cd 1 Cr 0.792* 1 Pb 0.41 0.673 1 As 0.412 0.758* 0.966** 1 Hg -0.361 -0.163 0.214 0.143 1 注:*代表显著性相关(p < 0.05),**代表极显著相关(p < 0.01) -
郭佳, 张宝林, 高聚林, 等. 气候变化对中国农业气候资源及农业生产影响的研究进展[J]. 北方农业学报, 2019, 47(1): 105-113. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2096-1197.2019.01.18 Zhang L, Song W, Song W. Assessment of agricultural drought risk in the Lancang-Mekong Region, South East Asia[J]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2020, 17(17): 6153-6176. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17176153
Wielemaker R, Wilken C, Chen W S, et al. Resource Dynamo: A GIS model to match urban nutrient supply with agricultural demand[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2020, 258: 120789. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.120789
Stork M, Schulte A, Murach D. Large-scale fuelwood production on agricultural fields in mesoscale river catchments-GIS-based determination of potentials in the Dahme river catchment(Brandenburg, NE Germany)[J]. Biomass and Bioenergy, 2014, 64: 42-49. doi: 10.1016/j.biombioe.2014.03.029
AK A, MPb C, SC A, et al. Land evaluation for sustainable development of Himalayan agriculture using RS-GIS in conjunction with analytic hierarchy process and frequency ratio[J]. Journal of the Saudi Society of Agricultural Sciences, 2021, 20(1): 1-17. doi: 10.1016/j.jssas.2020.10.001
Seyedmohammadi J, Sarmadian F, Jafarzadeh A A, et al. Development of a model using matter element, AHP and GIS techniques to assess the suitability of land for agriculture[J]. Geoderma, 2019, 352: 80-95. doi: 10.1016/j.geoderma.2019.05.046
吕建树. 江苏典型海岸带土壤及沉积物重金属环境地球化学研究[D]. 南京大学博士学位论文, 2015. 巩万合, 王志强, 郁伟, 等. 南通市农田土壤重金属含量及评价[J]. 黑龙江农业科学, 2014, (10): 34-39. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HLJN201410010.htm 巩万合, 王志强, 阚建鸾. 长三角典型农业区耕地土壤重金属污染与潜在生态风险评价[J]. 湖北农业科学, 2017, 56(23): 4493-4496. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HBNY201723018.htm 巩万合, 郁伟, 王志强, 等. 南通市耕地土壤肥力演变趋势及培肥对策[J]. 现代农业科技, 2014, (8): 189-191. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-5739.2014.08.119 巩万合, 杨连飞, 刘蓉蓉, 等. 江苏南通地区耕层土壤微量元素含量与有效性评价[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2014, 42(11): 378-380. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSNY201411134.htm 金成伟, 闫德智, 贾凤薇. 南通市不同农业土地利用方式对土壤理化性质的影响[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2013, 41(6): 336-339. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1302.2013.06.121 于淼, 吕晓, 廉丽姝, 等. 江苏省沿海地区土地利用变化及其生态效应[J]. 水土保持通报, 2017, 37(3): 131-139. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STTB201703023.htm 宁立新, 周云凯, 张启斌, 等. 近19年江苏海岸带地区土地利用变化特征[J]. 水土保持研究, 2017, 24(4): 227-233. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STBY201704038.htm 王雪薇, 董增川, 韩锐. 江苏省东台市近65年气温和降水量特征分析[J]. 水电能源科学, 2017, 35(11): 6-9, 21. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDNY201711002.htm 王涛, 陶辉, 杨强. 南通地区1960年-2007年气温与降水的年际和季节变化特征[J]. 资源科学, 2011, 33(11): 2080-2089. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZRZY201111011.htm 仇娟娟, 宋正逵, 周荣, 等. 南通市洪涝灾害案例分析与对策探讨[J]. 中国西部科技, 2014, 13(9): 57-59. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6396.2014.09.025 陈烨丽. 气象灾害对南通市通州区蔬菜生产的影响及防御措施[J]. 上海农业科技, 2016, (5): 27-28. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0106.2016.05.014 黄燕如, 郑玉萍, 廖楠. 基于国土空间规划背景的双评价应用研究——以广州市番禺区生态适宜性评价为例[J]. 现代信息科技, 2020, 4(11): 121-125. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDXK202011041.htm 严圣华, 黄跃飞, 熊娟, 等. 基于"双评价"的市县土地资源评价——以大冶市为例[J]. 国土与自然资源研究, 2020, 000(001): 43-47. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GTZY202001010.htm 杜海娥, 李正, 郑煜. 资源环境承载能力评价和国土空间开发适宜性评价研究进展[J]. 中国矿业, 2019, 28(S2): 159-165. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGKA2019S2036.htm 李瑞敏, 殷志强, 李小磊, 等. 资源环境承载协调理论与评价方法[J]. 地质通报, 2020, 39(1): 80-87. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20200108&flag=1 王忠蕾, 张训华, 许淑梅, 等. 海岸带地区环境承载能力评价研究综述[J]. 海洋地质动态, 2010, 26(8): 28-34. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDT201008007.htm 陈武, 李瑞敏, 殷志强, 等. 贵州乌蒙山毕节市七星关区资源环境承载能力评价[J]. 地质通报, 2020, 39(1): 114-123. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20200113&flag=1 曾毅, 项广鑫, 蒋星祥, 等. 基于国土空间自然适宜性的三类空间划分方法——以湖南省为例[J]. 地质通报, 2020, 39(1): 138-145. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20200116&flag=1 丰继林, 刘帅, 黄猛. Excel数据与GIS空间数据转换技术研究[J]. 中国新通信, 2013, 15(10): 90-91. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-4866.2013.10.070 董敏, 孙宝生, 陈川. 基于ArcGIS的地质图图例绘制及意义——以《西准噶尔地区地质图》为例[J]. 新疆地质, 2010, 28(1): 116-118. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8845.2010.01.023 葛全胜, 陈泮勤, 方修琦, 等. 全球变化的区域适应研究: 挑战与研究对策[J]. 地球科学进展, 2004(4): 516-524. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2004.04.005 钱凤魁, 王文涛, 刘燕华. 农业领域应对气候变化的适应措施与对策[J]. 中国人口资源与环境, 2014, 24(5): 19-24. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGRZ201405004.htm 廖启林, 刘聪, 金洋, 等. 江苏土壤地球化学分区[J]. 地质学刊, 2011, 35(3): 225-235. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-3636.2011.03.225 Lv J, Liu Y, Zhang Z, et al. Distinguishing anthropogenic and natural sources of trace elements in soils undergoing recent 10-year rapid urbanization: a case of Donggang, Eastern China[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2015, 22(14): 10539-10550. doi: 10.1007/s11356-015-4213-4
马志军. 江苏省盐城市沿海滩涂资源可持续开发利用研究[D]. 南京农业大学硕士学位论文, 2006. 毛桂囡, 龚政, 赵立梅, 等. 江苏入海河道河口治导线研究[J]. 河海大学学报(自然科学版), 2010, 38(4): 462-466. doi: 10.3876/j.issn.1000-1980.2010.04.021 杨宏忠. 关于海岸滩涂资源投资开发模式的探讨[J]. 中国农垦, 2012, (12): 55-57. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0529-6382.2012.12.022 张蛟, 冯芝祥, 崔世友, 等. 滩涂垦区不同盐分水平土壤的盐分动态及土壤因子变化[J]. 江苏农业报, 2017, 33(4): 836-842. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSNB201704018.htm



 下载:
下载: