3D geological modeling and deep visualization application of Xiongcun No. Ⅰ orebody Tibet
-
摘要:
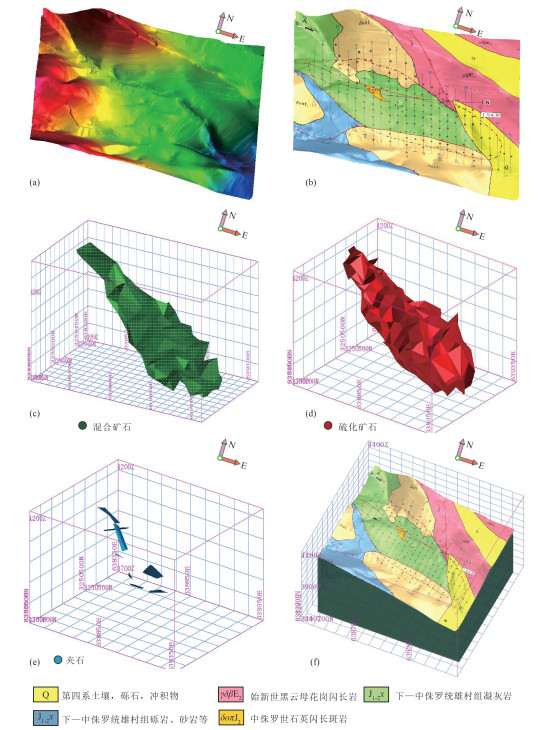
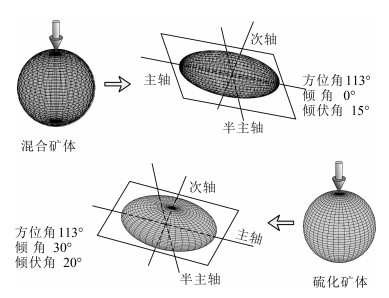
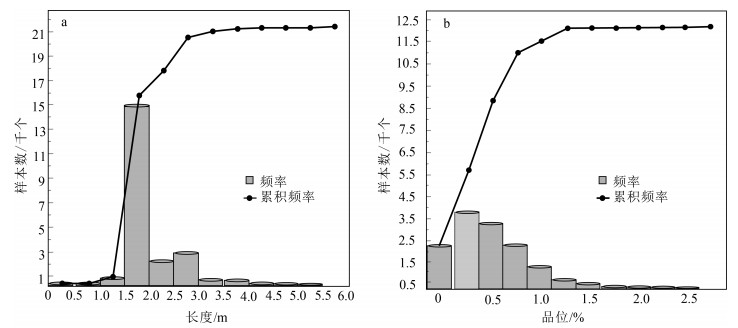
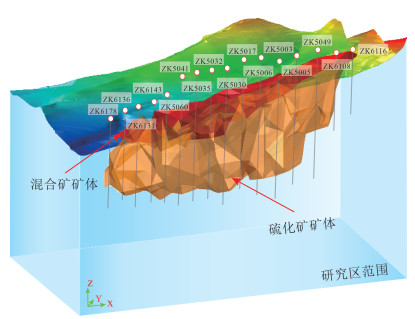
21世纪以来随着地球科学的发展,深部三维建模技术逐渐进入地学领域,数学地质与计算机科学的结合为地学领域开辟了新的认知空间,也给地球科学工作者带来了新的挑战与机遇。通过三维建模SURPAC软件对西藏雄村铜-金矿床Ⅰ号矿体162个钻孔数据预处理、分析及矿体解译,针对雄村Ⅰ号矿体深部数字化资源/储量估算及深部成矿元素分布问题,采用地质统计学法对Ⅰ号矿体钻井数据进行矿体模型、实体模型建立及数字化自动资源/储量估算,以深部实体模型二维切片模型为指导,探讨了深部成矿元素的空间分布形态及相互关系。研究表明,采用距离幂次反比法进行资源/储量估算,结果均大于96%,有效揭示了区内资源/储量定量评估。在矿体模型、实体模型的指导下,以深部二维精细化切片模型展布了矿体深部三维空间成矿元素分布特征及相互关系,有效减少了雄村Ⅰ号矿体深部成矿单一信息多解性问题,为西藏雄村斑岩型铜-金矿床Ⅰ号矿体深部精确定量找矿提供了参考依据。
Abstract:With the development of Earth Science since the 21st century, the age of 3D has gradually come into the geosciences.The combination of mathematical geology and computer science has opened up a new cognitive space for the field of geoscience, and also brought new challenges and opportunities to geoscientists.Through 3D modeling and SURPAC software, 162 borehole data of No.Ⅰorebody of the Xiongcun Cu-Au deposit in Tibet were preprocessed and analyzed to interprete the orebody.According to the deep digital resource/reserve estimation of No.Ⅰorebody and the distribution of deep ore-forming elements in Xiongcun, the solid model and digital automatic resource/reserve estimation system were established by the method of geological statistics based on the drilling data.Based on the two-dimensional slice model of deep solid model, the spatial distribution and interrelationship of deep ore-forming elements were discussed.Research shows that the results of resource/reserve estimation by means of the inverse power of distance method are all greater than 96%, and effectively reveal the quantitative assessment of resources/reserves in the region.Under the guidance of ore body model and entity model and using the deep 2D fine slicing technology, the distribution characteristics and interrelationship of mineralization elements in the deep 3D space of the ore body are clearly displayed.That effectively reduces the ambiguity of single information of deep orebody and provides a reference basis for accurate deep prospecting.
-
Keywords:
- 3D geological modeling /
- SURPAC software /
- visualization /
- model slicing /
- Xiongcun /
- Tibet
-
党的十九大报告指出,“要以‘一带一路’为重点,坚持引进来和走出去并重,遵循共商共建共享原则,加强创新能力开放合作,形成陆海内外联动、东西双向互济的开放格局”。在国家实施“一带一路”建设及拉美战略的契机下,提升中国在拉丁美洲地区地学领域的话语权,提高服务水平和质量,从粗放型服务向精准型服务转变,依靠科技创新解决全球重大资源环境问题和地球系统科学问题的能力,是新形势下对境外地质工作的新需求。因此,“两种资源、两个市场”、实施“走出去”是中国长期的资源战略任务,而拉丁美洲地区是中国实施“走出去”战略最重要的优选地区之一。
拉丁美洲是指从墨西哥起的西半球南部的整个地区,也就是地处北纬32°42′和南纬56°54′之间的大陆,东濒加勒比海和大西洋,与非洲大陆的最短距离约为2494.4km;西临太平洋;南隔德雷克海峡与南极洲相望;北界墨西哥与美国界河布拉沃河(即格兰德河),与美国为邻。拉丁美洲包括北美洲的墨西哥、中美洲和南美洲大陆,共有34个国家和地区,2008年人口约5.77亿,主要是印欧混血和黑白混血人种,其次为黑人、印第安人和白种人。由于本区都隶属拉丁语族,因此这些国家被称为拉丁美洲国家,这个地区被称为拉丁美洲。
早在20世纪20年代,澳大利亚学者安德鲁斯E就已指出统一的环太平洋成矿带的存在。40年代原苏联学者斯米尔诺夫C C将环太平洋成矿带划分为以铜为主的内带和以锡钨为主的外带,尔后西里托(1976)、米切尔(1976)、拉德科维奇(1983)均做出了巨大贡献,包括拉丁美洲在内的环太平洋地区的构造与矿产受到普遍重视,发表了大量的论文和专著。中国学者从西太平洋和东太平洋分析对比的角度出发做了许多研究,如张炳熹、李文达、裴荣富、戚建中、陆志刚、陶奎元等。近年来,随着境外地质矿产工作的开展,年轻一代的学者又做了许多有益的工作。特别是中国地质调查局南京地质调查中心境外地质室,他们的工作成果正陆续推向社会。《拉丁美洲地区重要矿产成矿规律研究》专辑的发表正是其集中体现。
该专辑系国内首次总结拉丁美洲地区的成矿地质条件,划分成矿区带,研究成矿系列,将对该地区进一步规划和开发起到指导作用。其主要特色在于:
(1)全面清晰地讨论了拉丁美洲地区重要成矿带的区域地质背景和成矿地质环境,通过对代表性的成矿带、成矿作用和典型矿床的研究,以点带面地阐明了拉丁美洲地区的优势矿产资源。
(2)利用大量的第一手资料,涉及原创、方法及技术,进行系统性、集成性、综合性分析整理,为拉丁美洲地区优势矿产资源成矿规律研究的真实性、准确性提供了依据,并能够使读者顺藤摸瓜,进一步查找所需资料。
(3)文章涵盖面广泛,论文编写单位以中国地质调查局南京地质调查中心为主,中国地质调查局发展研究中心、中国地质科学院地质研究所、吉林大学地球科学学院、福州大学紫金学院,以及秘鲁地质矿产冶金研究院、中国中资企业等多家单位参与;从学科领域看,从典型矿床解剖、重要成矿带成矿规律到投资环境均有涉及,并进行了国际、国内的对比研究,提升了文章的学术水平。可以服务不同层面,满足不同层次的需求。
总之,加强境外地质矿产研究工作十分重要,不仅要收集境外地质矿产资料,开展实地考察,更要加强综合研究,使境外地质矿产编图、成矿区带划分、成矿规律总结等得到深化,才能集成为有影响的大成果。《拉丁美洲地区重要矿产成矿规律研究》专辑的出版,为进一步开展境外地质成矿规律综合研究提供了有借鉴意义的工作思路、方法和实例。
在此,我热诚祝贺这一系列研究成果的取得,并向具有创新意识和国际化视野的地学人才、为境外地质矿床研究作出贡献的专家学者们表示由衷的祝贺!
 致谢: 衷心感谢项目组成员对本文给予的无私帮助,感谢两位审稿专家对本文的审阅及提出的建设性修改意见。
致谢: 衷心感谢项目组成员对本文给予的无私帮助,感谢两位审稿专家对本文的审阅及提出的建设性修改意见。 -
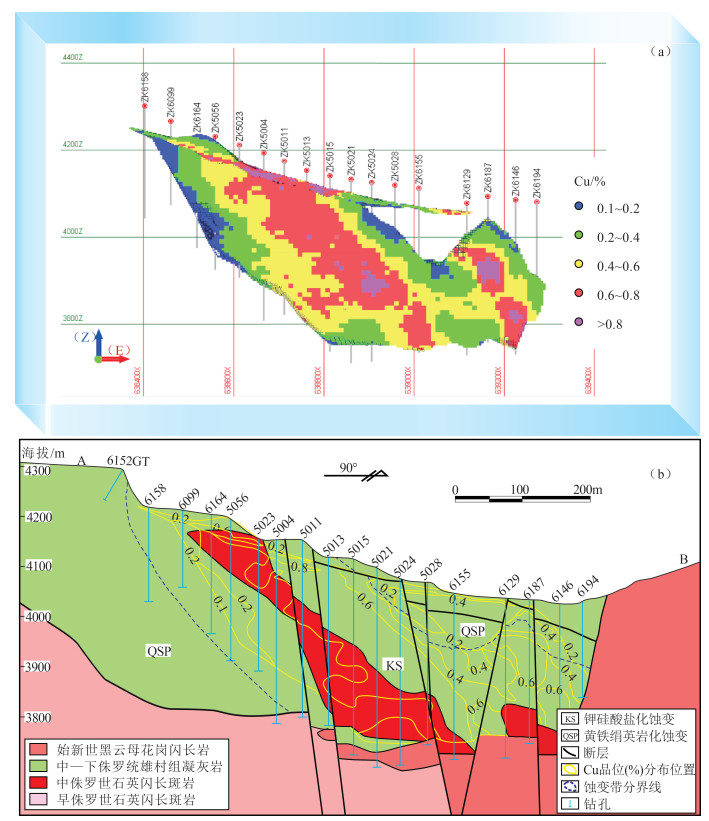
图 6 西藏雄村Ⅰ号矿体三维Cu品位空间分布位置(a)与A-B剖面图(b)[56]
Figure 6. Spatial distribution of Cu element grade(a)and cross section of A-B in the transverse section of the sulfide orebody(b)of No.Ⅰ orebody in Xiongcun, Tibet
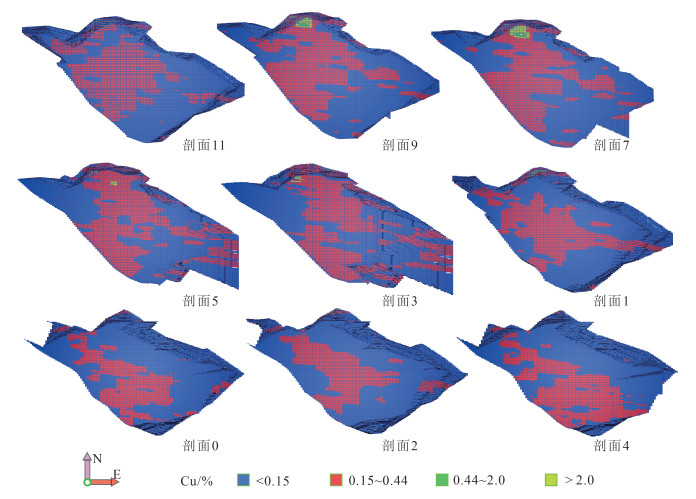
图 7 西藏雄村Ⅰ号矿体二维切片Cu品位空间分布位置(剖面位置见图 1勘探线剖面位置)
Figure 7. Spatial distribution of Cu grade in the transverse section of 2D model of No.Ⅰ orebody, Tibet
表 1 SURPAC数据库数据结构
Table 1 Structure of SURPAC database data
孔口表数据结构(部分数据) 条目 类型 是否空值 字段长度 小数位 下限 上限 真实值/虚拟 孔号 字符型 N 10 Null Null Null 真实值 北坐标 实数 Y 10 2 -99 99 真实值 东坐标 实数 Y 10 2 -99 99 真实值 自 实数 Y 10 2 -99 99 真实值 至 实数 Y 10 2 -99 99 真实值 测斜表数据结构(部分数据) 条目 类型 是否 空值 字段 长度 小数位 下限 上限 真实值/ 虚拟 孔号 字符型 N 10 Null Null Null 真实值 方位角 实数 Y 10 2 -999 999 真实值 倾角 实数 Y 10 2 -999 999 真实值 化验表数据结构(部分数据) 条目 类型 是否 空值 字段 长度 小数位 下限 上限 真实值/虚拟 孔号 字符型 N 10 Null Null Null 真实值 自 实数 Y 10 2 -99 99 真实值 至 实数 Y 10 2 -99 99 真实值 au 实数 Y 10 2 -99 99 真实值 ag 实数 Y 10 2 -99 99 真实值 cu 实数 Y 10 2 -99 99 真实值 岩性表数据结构(部分数据) 条目 类型 是否空值 字段长度 小数位 下限 上限 真实值/虚拟 Hold_id 字符型 N 10 Null Null Null 真实值 Lithology 字符型 N 20 Null Null Null 真实值 Sample_id 实数型 Y 10 2 0 999999 真实值 表 2 SURPAC数据库信息
Table 2 SURPAC database information
孔口坐标Collar(部分数据) 测斜数据 Survey 孔号 北坐标 东坐标 高程 孔深/m 勘探线号 ZK5001 3250373 638661.1 4202.959 390.3 N1 孔号 孔深 ZK5002 3250374 638712.3 4182.1 330.1 N3 ZK5001 0 ZK5003 3250322 638711.8 4181.66 273.7 N5 ZK5002 0 岩性数据Geology(部分数据) 孔号 样品编号 自 至 长度 岩性 方位角 倾角 ZK5001 195001 0 2 2 OB1 0 -90 ZK5002 196001 0 3 3 OB1 0 -90 ZK5003 197001 0 2.5 2.5 OB1 0 -90 化验数据 Sample(部分数据) 孔号 样品编号 自 至 长度/m Au Cu Ag ZK5001 195001 0 2 2 0.41 0.137 4.6 ZK5002 196001 0 3 3 0.032 0.0272 0.3 ZK5003 197001 0 2.5 2.5 0.168 0.0159 0.7 注:OB1表示岩性代码 表 3 西藏雄村Ⅰ号矿体资源/储量估算结果
Table 3 Resources/Reserves estimation result of No.Ⅰ orebody in Xiongcun, Tibet
矿石类型 储量/t 传统地质断面法 距离幂次反比法 Ⅰ号矿体混合矿 Cu矿石量 22140183 21495324 Cu金属量 123977 167635 Ⅰ号矿体硫化矿 Cu矿石量 177519081 183957596 Cu金属量 923575 938019 -
Lang X H, Deng Y L, Wang X H, et al. Geochronology and geochemistry of volcanic rocks of the Bima Formation, southern Lhasa subterrane, Tibet: Implications for early Neo-Tethyan subduction[J]. Gondwana Research, 2020, 80: 335-349. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2019.11.005
郎兴海, 唐菊兴, 谢富伟, 等. 西藏雄村矿区地面磁测异常特征及其对找矿方向的指示[J]. 地质与勘探, 2014, 50(3): 411-418. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT201403002.htm 郎兴海. 西藏雄村斑岩型铜金矿集区成矿作用与成矿预测[D]. 成都理工大学博士学位论文, 2012. 谢富伟, 唐菊兴, 郎兴海, 等. 西藏雄村矿区Ⅰ号矿体斑岩含矿性研究——来自热液蚀变矿物和副矿物的证据[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2015, 34(1): 51-64. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2015.01.004 郎兴海, 陈毓川, 唐菊兴, 等. 西藏谢通门县雄村斑岩型铜金矿集区Ⅰ号矿体的岩石地球化学特征: 对成矿构造背景的约束[J]. 地质与勘探, 2010, 46(5): 887-898. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT201005014.htm 唐菊兴, 黄勇, 李志军, 等. 西藏谢通门县雄村铜金矿床元素地球化学特征[J]. 矿床地质, 2009, (1): 18-31. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ200901003.htm 丁枫, 郎兴海, 胡正华, 等. 西藏雄村铜金矿Ⅰ号矿体赋矿凝灰岩成因探讨: 来自岩石地球化学、Sr-Nd-Pb同位素地球化学特征的证据[J]. 地球学报, 2012, 33(4): 546-558. doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2012.04.15 郎兴海, 唐菊兴, 陈毓川, 等. 西藏谢通门县雄村斑岩型铜金矿集区Ⅱ号矿体中辉钼矿Re-Os年代学及地质意义[J]. 矿物岩石, 2010, (4): 55-61. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6872.2010.04.011 Ord A, Hobbs B E, Zhao C. Fundamentals of Computational Geoscience[M]. Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg, 2009, 122(3): 1-257.
赵鹏大, 陈建平, 张寿庭. "三联式"成矿预测新进展[J]. 地学前缘, 2003, 10(2): 455-463. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2003.02.025 陈建平, 于萍萍, 史蕊, 等. 区域隐伏矿体三维定量预测评价方法研究[J]. 地学前缘, 2014, 21(5): 211-220. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201405020.htm 陈建平, 王功文, 侯昌波, 等. 基于GIS技术的西南三江北段矿产资源定量预测与评价[J]. 矿床地质, 2005, 24(1): 15-24. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2005.01.002 Hill R I. Starting plumes and continental break-up[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1991, 104(2/4): 1-416. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0012821X91902187
陈建平, 陈勇, 曾敏, 等. 基于数字矿床模型的新疆可可托海3号脉三维定位定量研究[J]. 地质通报, 2008, 27(4): 124-131. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20080412&flag=1 唐攀, 唐菊兴, 林彬等. 传统几何法与地质统计学法在矿产资源储量估算中的对比分析[J]. 地质科技情报, 2016, 35(1): 156-160. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201601024.htm Tang J X, Song Y, Wang Q, et al. Geological characteristics and exploration model of the Tiegelongnan Cu(Au-Ag) deposit: the first ten million tons metal resources of a porphyry-epithermal deposit in Tibet[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2016, 37(6): 663-690. http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-DQXB201606003.htm
Tang J X, Lang X H, Xie F W, et al. Geologicalcharacteristics and genesis of the Jurassic No. Ⅰ porphyry Cu-Au deposit in the Xiongcun district, Gangdese porphyry copper belt, Tibet[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2015, 70(4): 438-456. http://search.ebscohost.com/login.aspx?direct=true&db=aph&AN=103157905&site=ehost-live
Lang X H, Tang J X, Li Z J, et al. U-Pb and Re-Os geochronological evidence for the jurassic porphyry metallogenic event of the xiongcun district in the gangdese porphyry copper belt, southern Tibet, PRC[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2014, 79(2): 608-622. http://smartsearch.nstl.gov.cn/paper_detail.html?id=d202b6c68da714010408f5a78b6d91ce
Lang X H, Tang J X, Li Z J, et al., Geological characteristics of the No. Ⅰ deposit in theXiongcun district, southern Gangdese belt, Tibet[J]. Advances in Earth and Environmental Sciences, 2013, 189: 229-235. http://www.geojournals.cn/dzxben/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=dzxben2003z10376&flag=1
黄勇, 唐菊兴, 张丽, 等. 西藏雄村斑岩铜金矿集区火山-岩浆岩锆石Hf同位素组成[J]. 地质学报, 2014, 88(8): 1528-1538. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201408014.htm Lang X H, Tang J X, Xie F W, et al. CH4-Rich Fluid of the No. Ⅰ Porphyry Copper-Gold Deposit in the Xiongcun District, Gangdese Porphyry Copper Belt, Tibet, PRC[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2014, 88(S2): 547-548. doi: 10.1111/1755-6724.12374_24
Zhu D C, Zhao Z D, Niu Y, et al. The Lhasa terrane: record of a microcontinent and its histories of drift and growth[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2011, 301(1/2): 241-255. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0012821X10007004
Lang X H, Tang J X, Xie F W, et al. Geological Characteristics and Exploration Potential of the NO. Ⅲ Deposit in the Xiongcun District, Tibet, China[J]. Advanced Materials Research, 2014, 868: 217-223. http://www.scientific.net/AMR.868.217
Lang X H, Tang J X, Li Z J, et al. Geological characteristics and exploration potential of the No. Ⅱ deposit in the Xiongcun district, South Gangdese belt, Tibet[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2013, 87: 709-712. http://www.geojournals.cn/dzxben/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=dzxben2003z10376&flag=1
郎兴海, 邓煜霖, 王旭辉, 等. 西藏雄村矿区Ⅲ号矿体硫、铅同位素特征及成矿物质来源[J]. 地质科技情报, 2018, 37(4): 7-15. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201804002.htm 郎兴海, 郭文铂, 王旭辉, 等. 西藏雄村矿集区含矿斑岩成因及构造意义: 来自年代学及地球化学的约束[J]. 岩石学报, 2019, 35(7): 2105-2123. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201907010.htm 郎兴海, 唐菊兴, 李志军, 等. 西藏谢通门县雄村斑岩型铜金矿集区Ⅰ号矿体的蚀变与矿化特征[J]. 矿床地质, 2011, 30(2): 327-338. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2011.02.013 尹青, 郎兴海, 唐菊兴, 等. 西藏雄村矿区Ⅱ号矿体硫、铅同位素地球化学特征[J]. 矿床地质, 2015, 34(5): 1016-1029. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ201505010.htm 黄勇, 丁俊, 唐菊兴, 等. 西藏雄村铜金矿床Ⅰ号矿体成矿构造背景与成矿物质来源探讨[J]. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2011, 30(2): 361-373. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CDLG201103011.htm Lang X H, Tang J X, Yin Q, et al. Geochemistry and genesis of Eocene Lamprophyres in theXiongcun porphyry copper-gold district, southern margin of the Lhasa terrane, Tibet, China[J]. Geochemical Journal, 2017, 51(2): 123-142. doi: 10.2343/geochemj.2.0442
Xie F W, Tang J X, Chen Y C, et al. Apatite and zircon geochemistry of Jurassic porphyries in the Xiongcun district, southern Gangdese porphyry copper belt: Implications for petrogenesis and mineralization[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2018, 96: 98-114. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2018.04.013
王旭辉, 郎兴海, 邓煜霖, 等. 西藏冈底斯南缘汤白斑状花岗岩锆石U-Pb年代学、地球化学及地质意义[J]. 高校地质学报, 2018, 24(1): 41-55. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXDX201801004.htm 郎兴海, 崔志伟, 王旭辉, 等. 西藏谢通门县雄村矿集区综合信息找矿模型及靶区预测[J]. 地球学报, 2017, 38(5): 790-802. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB201705018.htm 郎兴海, 唐菊兴, 李志军, 等. 化探在西藏雄村矿区Ⅱ、Ⅲ号矿体发现中的作用[J]. 物探与化探, 2014, 38(4): 667-672. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTYH201404007.htm 郎兴海, 唐菊兴, 李志军, 等. 西藏雄村斑岩型铜金矿集区Ⅰ号矿体的硫、铅同位素特征及其对成矿物质来源的指示[J]. 地球学报, 2012, 33(4): 459-470. doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2012.04.07 李志军, 黄勇, 唐菊兴, 等. 西藏雄村铜金矿矿集区Ⅰ号矿体磁黄铁矿矿物特征及指示意义[J]. 矿物学报, 2012, 32(2): 205-210. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWXB201202006.htm Wang X H, Lang X H, Tang J X, et al. Early-Middle Jurassic(182-170 Ma) Ruocuo adakitic porphyries, southern margin of the Lhasa terrane, Tibet: Implications for geodynamic setting and porphyry Cu-Au mineralization[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2019, 173: 336-351. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2019.01.042
邓煜霖, 郎兴海, 杨宗耀, 等. 西藏拉孜县彭措林石英闪长斑岩的年代学及地球化学特征[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2018, 37(5): 953-966. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYDH201805020.htm 维克托·迈尔-舍恩伯格, 肯尼思·库克耶. 大数据时代[M]. 杭州: 浙江人民出版社, 2013: 1-78. 陈建平, 李婧, 崔宁, 等. 大数据背景下地质云的构建与应用[J]. 地质通报, 2015, 34(7): 1260-1265. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2015.07.002 Rehman Ghori S G. Spatial estimation of global solar radiation using geostatistics[J]. Renewable Energy, 2000, 21(3): 583-605. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0960148100000781
Luo Z Q, Liu X M, Su J H, et al. Deposit 3D modeling and application[J]. Journal of Central South University of Technology, 2007, 2(14): 225-229. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-ZNGY200702016.htm
罗周全, 鹿浩, 刘晓明, 等. 矿山三维实体建模[J]. 南华大学学报(自然科学版), 2007, 21(4): 12-18. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZNGB200704004.htm 赵鹏大, 池顺都. 初论地质异常[J]. 地球科学, 1991, 16(3): 241-248. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-2383.1991.03.001 赵鹏大. 矿产勘查理论与方法[M]. 武汉: 中国地质大学出版社, 2006: 1-452. 赵军芳. 基于矿山地质三维建模及深部矿产预测[D]. 成都理工大学博士学位论文, 2014. 张德会, 周圣华, 万天丰等. 矿床形成深度与深部成矿预测[J]. 地质通报, 2007, 26(12): 1509-1518. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2007.12.002 翟裕生, 王建平, 邓军等. 成矿系统时空演化及其找矿意义[J]. 现代地质, 2008, 22(2): 144-150. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ200802001.htm Han J, Kamber M, Pei J. Data Mining: Concepts and Techniques[M]. Burlington: Morgan Kaufmann, 2012.
Fayyad U M. Advances in Knowledge Discovery and DataMining[J]. Menlo Park CA: AAAI/MIT Press, 1996: 1-231.
王登红, 刘新星, 刘丽君. 地质大数据的特点及其在成矿规律、成矿系列研究中的应用[J]. 矿床地质, 2015, 34(6): 1143-1154. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ201506005.htm 娄渝明, 郎兴海, 祁婧, 等. 西藏雄村斑岩型铜金矿区Ⅱ号矿体资源储量估算方法对比[J]. 有色金属工程, 2018, 8(6): 79-85. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YOUS201806015.htm 于萍萍, 陈建平, 王勤. 西藏铁格隆南铜(金)矿床三维模型分析与深部预测[J]. 岩石学报, 2018, 35(3): 897-912. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201903017.htm 陈念, 毛景文, 范成龙等. 秘鲁DonJavier斑岩型铜钼矿床矿化蚀变特征及矿床三维勘查模型[J]. 矿床地质, 2017, 36(3): 705-718. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ201703011.htm 唐菊兴, 宋扬, 王勤, 等. 西藏铁格隆南铜(金银)矿床地质特征及勘查模型——西藏首例千万吨级斑岩-浅成低温热液型矿床[J]. 地球学报, 2016, 37(6): 663-690. doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2016.06.03 薛建玲, 庞振山, 程志中, 等. 深部找矿基本问题及方法[J]. 地质通报, 2020, 39(8): 1125-1136. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20200801&flag=1 蒲万峰, 李鸿睿, 袁臻, 等. 甘肃省玛曲县大水金矿"三位一体"找矿预测地质模型[J]. 地质通报, 2020, 39(8): 1163-1172. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20200804&flag=1



 下载:
下载: