Hydrogeochemistry and origin of groundwater in the south coast of Hainan
-
摘要:
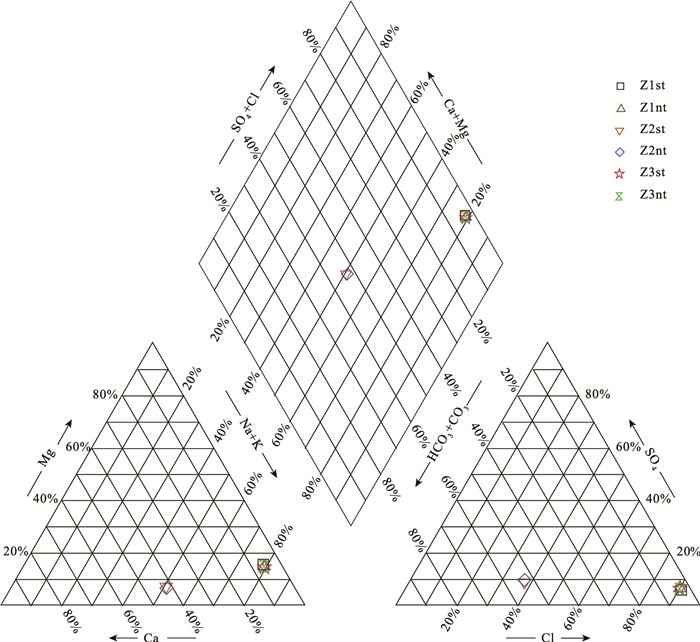
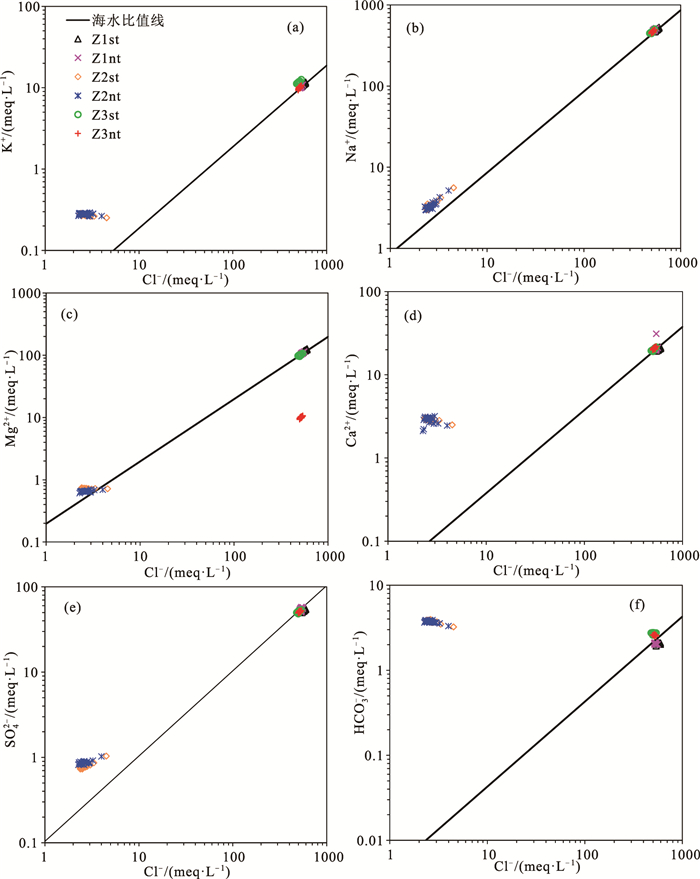
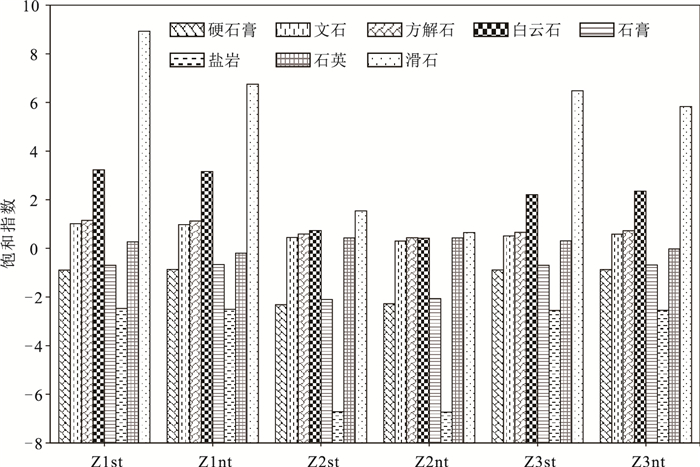
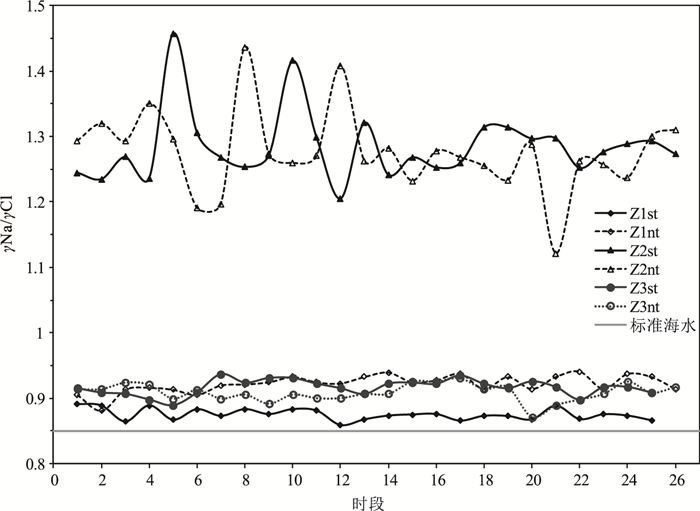
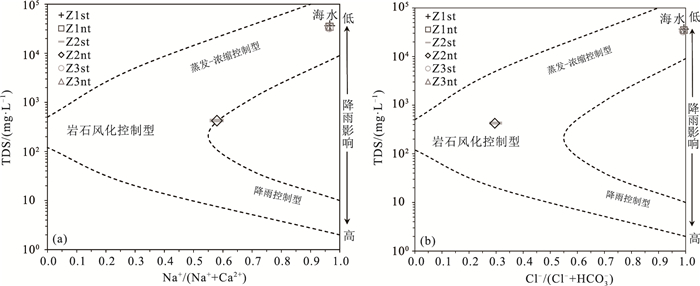
海岸带地下水的水文地球化学特征及其成因研究对海岸带地区地下水合理利用、保护和污染防治等具有重大意义。利用Piper图、矿物相平衡分析、离子比例系数和Gibbs分析,揭示了海南南部沿海黎安港Z1、三亚湾Z2和板桥Z3监测井在大、小潮时段地下水的水文地球化学过程、水岩交互作用、成矿趋势和地下水的成因。结果表明,Z1、Z2和Z3的地下水分别为盐水、淡水和极度咸水。水化学类型分别为Cl-Na型、HCO3·Cl-Na·Ca型和Cl-Na型。硬石膏、石膏和岩盐溶解是该区地下水中的主要离子来源。Z1和Z3的地下水来源与受蒸发浓缩控制型的高矿化度的海水紧密相关,Z2的水化学环境主要受含钠硅酸盐矿物的岩石风化溶解作用影响。研究结果为进一步开展海岸带地下水环境监测和污染防治提供基础资料。
Abstract:The study of hydrogeochemical characteristics and genesis of groundwater is of great significance for rational utilization, protection and pollution control of coastal groundwater.Piper map, mineral phase equilibrium analysis, ion proportion coefficient and Gibbs analysis were applied to reveal the hydrogeochemical process, water-rock interaction, mineralization trend and origin of groundwater during spring tide and neap tide through the monitoring of Wells Z1 in Li'an Port, Z2 in Sanya Bay and Z3 in Banqiao in the south coast of Hainan.The results indicate that groundwater in Z1, Z2 and Z3 are saline water, fresh water and extremely salty water respectively, their hydrochemical types belong to Cl-Na, HCO3·Cl-Na·Ca and Cl-Na respectively, and ions in the groundwater result from the dissolution of anhydrite, gypsum and halite.It is suggested that the groundwater sources of Z1 and Z3 are closely related to high-salinity seawater controlled by evaporation and concentration, while the hydrochemical environment of Z2 is mainly affected by weathering and dissolution of rocks with sodium silicate minerals.The above research results can provide basic data for the further monitoring of coastal groundwater environment and pollution control.
-
花岗岩型铀矿床是中国重要的铀矿床类型,主要分布于华南地区,目前占中国已探明铀资源量的22.9%[1-6]。华南地区花岗岩型铀矿床主要产于花岗岩体内部或外接触带附近,受断裂构造控制[7-8]。鉴于其成因类型属于热液型铀矿床[9],因此成矿流体始终是探讨该地区铀成矿作用过程最重要和最直接的手段[10-13]。
桃山-诸广山铀成矿带位于南岭地区,是中国最大的花岗岩型铀成矿带[14],其预测资源量占整个花岗岩型铀矿床预测资源量的50%[6],长期以来一直是学者们关注的焦点[15-17]。长排矿区位于诸广山岩体南缘长江铀矿田中部,毗邻著名的棉花坑(302)铀矿床,被认为是桃山-诸广山铀成矿带最具找矿潜力的地区之一。前人对该矿区开展了大量的岩石学、年代学、找矿勘查等方面的研究工作[18-20],但关于成矿作用和成矿机制方面的研究则较少。众所周知,流体包裹体研究可以查明成矿流体性质和成矿物质沉积机制,是研究成矿作用和成矿机制的重要手段[21-24]。因此,本文选择长排矿区开展流体包裹体及同位素研究,通过查明成矿流体的性质并探讨其成矿机制,为总结区域成矿规律和找矿提供依据。
1. 区域及矿区地质特征
诸广山地区位于广东、湖南和江西三省交界处,以出露巨型诸广山花岗岩岩基为特点。诸广山花岗岩位于该区中部,产状受南岭东西向构造和诸广山南北向构造的联合控制[25]。诸广山花岗岩体主要为过铝质花岗岩,岩性有二云母花岗岩、黑云母花岗岩、二长花岗岩等。区内地层多分布于诸广山岩体边部,主要包括:震旦系、寒武系、奥陶系变质砂岩、泥岩;泥盆系、石炭系灰岩和砂岩;白垩系—新近系碎屑岩[26]。长江矿田位于诸广山地区中部,是中国重要的铀矿田之一。该矿田以出露白垩纪、侏罗纪和三叠纪花岗岩为主,几乎未见地层露头。区内构造由NE—SW向、NW—SE向、N—S向和E—W向断裂构造组成,由北向南还分布有NE— SW向的里周、棉花坑和黄溪水断裂及NW—SE向的油洞断裂4条区域性断裂(图 1)。
![]() 图 1 长江铀矿田及长排矿区地质图(据参考文献[26]修改)Figure 1. Geological map of the Changjiang Uranium ore district and Changpai area
图 1 长江铀矿田及长排矿区地质图(据参考文献[26]修改)Figure 1. Geological map of the Changjiang Uranium ore district and Changpai area长排矿区位于长江铀矿田中部,其北接棉花坑铀矿床,受油洞断裂控制(图 1)。区内出露的侵入岩体主要为油洞岩体和长江岩体,其次为中基性岩脉等。油洞岩体形成于印支期,岩性主要为中粒小斑状二云母花岗岩。长江岩体形成于燕山期,呈岩基状产出,岩性主要为中粒黑云母花岗岩,局部出露细粒不等粒黑云母花岗岩,与毗邻油洞岩体呈侵入接触。长排矿区铀矿化严格受断裂控制,矿体产于NW向油洞断裂及NNW向断裂中。矿区硅化、赤铁矿化、黄铁矿化、紫黑色萤石化等蚀变与矿化关系密切,且具有水平分带特征,即由构造带中心向外侧依次为硅化→赤铁矿化→绢云母化→粘土化。矿石矿物主要为沥青铀矿,多呈脉状、浸染状构造。根据矿物组合可将长排矿区矿化期次划分为成矿前期、成矿期和成矿后期。其中,成矿前期以形成白色石英脉为主要特点;成矿期主要形成灰色微晶石英沥青铀矿、红色微晶石英沥青铀矿、萤石、黄铁矿等;成矿后期主要为白色石英及少量萤石。
2. 样品采集及分析方法
2.1 样品特征
进行流体包裹体测温的10件样品分别采自长排矿区7号(ZK304- 3)、61号(ZK41- 1)和9号(ZK11-2,ZK223-1,ZK4-3)富矿带中,其中成矿期样品来自钻孔ZK11-2,ZK4-3,ZK41-1,是发育于蚀变花岗岩中的灰色-红色石英脉、紫黑色萤石脉;成矿后期样品来自钻孔ZK11- 2,ZK304- 3,ZK223-1,主要为淡绿(紫)色和白色方解石脉。硫同位素样品均采于长排矿区9号带南段的钻孔ZK11-2中。样品为产于不同深度含矿花岗岩中的成矿期黄铁矿,多为细粒结构、团块状构造。
2.2 流体包裹体显微测温和激光拉曼分析
流体包裹体显微测温工作在中国地质大学(北京)地球化学教研室流体包裹体实验室完成。测试仪器为LINK THMSGS 600型冷热台,显微测温采用标准物质(KNO3、K2CrO3、CCl4)及人工配制的NaCl标准溶液对仪器进行温度标定,测定温度范围为-196~600℃,测试环境始终保持在25℃左右。包裹体测定时选用的显微镜倍数为500倍,首先利用液氮对包裹体进行降温,并观察包裹体的变化,包裹体被冷冻后,缓慢升温,当接近相变点时,减慢升温速率至0.1℃/min,记录冰点温度;继续升温,观察相态变化,当接近相变点时,减慢升温速率至0.5℃/ min或1℃/min,记录笼形物消失温度、部分均一温度和完全均一温度。均一温度误差为1℃,冰点温度误差为0.1℃。NaCl-H2O体系盐度根据NaClH2O型流体包裹体在冰点与盐度关系表中查得[27],密度值根据经验公式计算求得[28]。
流体包裹体激光拉曼分析在核工业北京地质研究院分析测试所实验室进行,测试仪器为LABHR-VISLabRAM HR800型显微激光拉曼光谱仪,扫描范围为100~4200cm-1,波长为532nm,湿度为50%,测试环境为25℃。
2.3 硫同位素分析
硫同位素分析在核工业北京地质研究院分析测试中心完成。以Cu2O做氧化剂制备测试样品,仪器型号为Finnigan MAT-251型质谱仪,分析结果采用国际标准CDT表达,分析精度优于0.2‰。
3. 分析结果
3.1 流体包裹体岩相学特征
本次重点对成矿期和成矿后期的石英、萤石及方解石中的流体包裹体进行了岩相学观察和显微测温实验。根据室温下流体包裹体岩相学特征,可将原生包裹体分为2种类型:含CO2三相包裹体(Ⅰ型:VCO2 + LCO2 +LH2O)和气液两相包裹体(Ⅱ型:V+L)(图 2)。
Ⅰ型:含CO2三相包裹体(VCO2 + LCO2 +LH2O),室温下(25℃)可见到液相CO2围绕气泡呈环状分布,此类包裹体气相组分占15%~85%,主要形态为椭圆状、长条状,少数为不规则状,长轴为4~12μm,主要赋存在成矿期石英中,加热多数均一到气相。
Ⅱ型:气液两相包裹体(V+L),此类包裹体最发育,与其他类型包裹体共存。根据包裹体气液比,又可分为2个亚类型:Ⅱ-1型和Ⅱ-2型。Ⅱ-1型包裹体为富液相流体包裹体,气相组分占3%~30%,多为5%~15%,形态主要有椭圆形、长条形和不规则形,长轴为3~18μm,成群分布,均一化过程中多均一为液相。Ⅱ-2型包裹体为富气相流体包裹体,气相组分占50%~90%,形态多为椭圆形和多边形,长轴为3~10μm,呈孤立分布,均一化过程中多均一为气相。镜下观察显示,Ⅱ-1型包裹体比Ⅱ-2型包裹体更发育。
成矿后期包裹体主要以富液相流体包裹体(Ⅱ-1型)为主,气相组分占3%~30%,多为5%~10%,形态主要有椭圆形、近四边形和不规则形,长轴为4~19μm,个别可达40~50μm,属原生包裹体,在均一化过程中均一为液相。
3.2 流体包裹体显微测温和激光拉曼分析结果
在流体包裹体岩相学特征的基础上,对各类型流体包裹体进行显微测温工作。实验结果(表 1;图 3、图 4)显示,成矿期流体包裹体均一温度和盐度变化范围较大,分别为120~388℃和1.74% ~10.24% NaCleqv。其中,Ⅰ型流体包裹体初熔温度范围为-61.9~-58.9℃,其笼形物消失温度为5.5~8.2℃,部分均一温度为19.7~29.4℃,完全均一温度范围为291~388℃,盐度为3.52%~7.87% NaCleqv;Ⅱ-1型包裹体均一温度范围为113~356℃,主要集中在120~280℃范围,盐度为1.74% ~10.24% NaCleqv;Ⅱ-2型包裹体均一温度范围为222~378℃,盐度为3.23%~7.02% NaCleqv。成矿后期的原生Ⅱ-1型富液相流体包裹体均一温度范围为80~179℃,主要集中在120~170℃,盐度为0.35%~6.3% NaCleqv。
表 1 长排矿区流体包裹体显微测温结果Table 1. The temperature determination of fluid inclusions at Changpai成矿期次 包裹体类型 测试
数目CO2包裹体 均一温度/℃ 冰点/℃ 盐度/%NaCleqv 初溶温度/℃ 笼形物消失温度/℃ 部分均一温度/℃ 范围 平均 范围 平均 成矿期 I 17 -61.9~-58.9 5.5~8.2 19.7~29.4 291~388 338 - 3.52~7.87 5.40 Ⅱ-1 149 - - - 113~356 199 -6.8~-1 1.74~10.24 5.52 Ⅱ-2 12 - - - 222~378 314 -4.4~-1.9 3.23~7.02 4.63 成矿后期 Ⅱ-1 56 - - - 80~179 134 -3.9~-0.2 0.35~6.3 3.8 本文对成矿期流体包裹体的气相组分进行了激光拉曼分析。分析结果显示(图 5),成矿期Ⅱ-1型富液相两相水溶液包裹体气相组分主要为CO2、CH4和H2,Ⅱ-2型富气相两相水溶液包裹体气相组分主要为CO2。
3.3 硫同位素组成
本次共测定了成矿期4件黄铁矿的硫同位素组成(表 2),4件样品均采于长排矿区9号带南段的钻孔ZK11-2中。结果显示,黄铁矿的硫同位素组成变化范围不大,δ34S值在-10.2‰~-3.2‰之间。
表 2 长排矿区黄铁矿硫同位素组成Table 2. S isotopic compositions of the pyrite from the Changpai area序号 样号 矿物 δ34s/‰ 岩石名称 1 GZN201-3 黄铁矿 -9.1 产于灰色微晶石英脉屮 2 GZN201-1 黄铁矿 -3.2 产于灰色微晶石英脉屮 3 GZN201-11 黄铁矿 -9.7 产于猪肝色赤铁矿化蚀变花岗岩屮 4 ZK11-2-2 黄铁矿 -10.7 产于肉红色微晶硅质脉屮 4. 讨论
4.1 成矿流体性质
根据包裹体显微测温结果(表 1;图 3),可将长排矿区成矿期流体包裹体划分为2组。第1组为含CO2三相(Ⅰ型)和富气相包裹体(Ⅱ-2型),均一温度主要集中在300~400℃,盐度为3.2% ~7.9% NaCleqv。第2组主要为富液相包裹体(Ⅱ-1型),均一温度范围主要集中在140~260℃,盐度为1.74%~ 10.24% NaCleqv。由此可知,根据流体包裹体岩相学特征和显微测温结果,长排矿区的成矿期流体可分为2组,第1组具有中高温、中高盐度的特点,以含CO2三相和富气相包裹体为主,表现出岩浆水的特征,而第2组为中低温、中高盐度流体,以富液相流体包裹体为主,表现出大气水的特征。激光拉曼分析结果显示(图 5),长排矿区成矿流体含有CO2、CH4、H2等气相成分。其中,第1组包裹体中的Ⅱ-2型包裹体气相组分主要为CO2;第2组包裹体中的Ⅱ-1型包裹体气相组分主要为CO2、CH4和H2。此外,测温实验结果显示(表 1),第1组包裹体中的Ⅰ型流体包裹体初熔温度范围为-61.9~-58.9℃,低于其三相点温度-56.6℃,说明流体包裹体中应该存在CH4等气体。关于CO2气体的来源问题,华南花岗岩型铀矿床成矿流体中的CO2属地幔来源,是白垩纪—新近纪地壳拉张期间,由地幔去气作用或幔源基性岩浆侵入提供而不是来自于产铀花岗岩体[10]。综上所述,长排矿区的成矿流体可能主要为岩浆水和大气水,以含有CO2、CH4、H2等气相成分为特征。
本次研究对与成矿有关的石英和萤石进行了流体包裹体测温,所测温度代表了成矿期流体的温度范围。这一温度范围(120~400℃)与铀氧化物溶解的最大温度区间[29-31]基本一致。由上文可知,长排矿区成矿流体分为中高温(300~400℃)和中低温(140~260℃)2组。然而,中高温流体温度范围明显高于华南地区花岗岩型铀矿床的铀成矿温度范围(120~260℃)[32],但是与角砾状沥青铀矿成矿流体的温度范围基本一致(290~345℃)[31]。由此,考虑到长排矿区绝大部分成矿期流体包裹体均一温度范围(140~294℃;图 3)与华南地区花岗岩型铀矿床的铀成矿温度范围(120~260℃)[32]一致,以及华南地区铀矿床普遍发育角砾状沥青铀矿[31],笔者建议将长排矿区成矿流体划分为成矿期早阶段流体(300~ 400℃)和成矿期晚阶段流体(140~260℃)。其中,成矿期晚阶段流体最重要。这种成矿流体具有中高温和中低温2种情况的现象在华南地区其他矿床也有报道,如棉花坑矿床成矿流体划分为中高温(290~310℃)流体和中低温(140~270℃)流体,并指出这2种流体分别代表了早、晚2次成矿作用[31]。另外,根据粤北下庄铀矿田包裹体研究结果,指出该矿床成矿期存在2种不同来源流体[33],一种为高温(270~320℃)中等盐度岩浆流体;另一种为中低温(120~160℃)低盐度壳源流体。这一现象很可能说明长排矿区成矿期存在不同流体的混合。
4.2 成矿机制初探
根据成矿期黄铁矿的硫同位素分析结果(表 2)可知,δ34S值范围在-10.2‰~-3.2‰之间,含铀花岗岩的硫同位素范围[34],亦与华南地区其他铀矿床,如湖南340、380和广西376等铀矿床的硫同位素范围基本一致(δ34S=-9.36‰~-3.35‰)[35],反映了长排矿区硫化物的硫同位素组成受围岩制约的特点。强过铝质富铀花岗岩常被认为是华南地区重要的铀源岩[5, 12, 36-37],其形成与古元古代晚期—中元古代早期富铀基底部分熔融关系密切[5, 38-39]。最近研究显示,华南地区的富铀基底可能是在古元古代晚期之后(约2.2Ga)含铀矿物在浅海中沉积形成[12],而后期的构造-岩浆活动使这些古老沉积岩中的U在花岗岩中不断富集,进而导致花岗岩成为重要的铀源岩[34, 39-40]。长排矿区的铀矿化主要产于区内的长江岩体和油洞岩体中。元素地球化学特征和Sr-Nd同位素组成显示,长江岩体和油洞岩体的原岩分别为砂质岩和泥岩,是古元古代晚期基底(2.0~1.8Ga)部分熔融的产物[18-19],与南岭地区产铀花岗岩的特征[38, 41]基本一致。因此,结合成矿期黄铁矿硫同位素组成特征,本文认为长排矿区成矿流体中的U应主要来源于区内古老含铀地层部分熔融形成的花岗岩。
实验研究表明,U常与O结合成UO22+,进而和OH-、CO32-、SO42-、Cl-、F-等组成络合物在流体中运移[42]。长排矿区的铀矿化主要与硅化、赤铁矿化、黄铁矿化及紫黑色萤石化等蚀变密切相关,而且成矿流体具有中高盐度及富CO2、CH4、H2等气相成分的特点(图 4、图 5)。这说明,该区成矿流体中的U很可能与CO32-、F-、Cl-等结合成络合物进行运移和富集。在温度-盐度图解(图 4)中,第2组流体相对于第1组流体具有较低的均一温度及较大的盐度变化范围,说明成矿期晚期流体很可能发生了流体的混合作用。众所周知,降温、减压及流体的混合会导致U的CO32-、F-及Cl-络合物水解,进而使U发生沉淀[43]。因此,长排矿区U的沉淀很可能与流体温度的降低和流体的混合作用有关。此外,成矿后期流体包裹体均一温度和盐度明显低于成矿期流体(图 4),说明成矿物质卸载沉淀之后,流体温度继续降低,并形成淡(紫)绿色萤石、方解石等矿物。
大量证据表明,华南地区富铀花岗岩主要为印支期花岗岩,而且印支期花岗岩的成矿部位常见到燕山期岩浆作用的叠加[12, 37]。研究表明,华南地区燕山期大规模的铀矿化与华南和华北地块后碰撞及太平洋板块俯冲引起的岩石圈伸展有关[1]。岩石圈的伸展形成了大规模的断裂构造,不仅有利于花岗质岩浆的侵入和CO2等气体的上升[3],还为大气水的下渗提供了有利条件。长排矿区在印支期和燕山期发生了2期岩浆作用,分别形成了油洞岩体(232±4Ma)[18]和长江岩体(161.6±2.1Ma)[19],矿体即赋存于这些花岗岩岩体的断裂破碎带中。因此,结合区域地质背景可将长排矿区铀成矿作用机制初步概括为,①在印支期后碰撞和燕山期板块俯冲导致的伸展背景下,古元古代基底部分熔融形成岩浆,并沿深大断裂上侵,先后形成富铀的油洞岩体和长江岩体;②富含CO2、CH4、H2等的岩浆水与大气水可能沿油洞岩体和长江岩体内的断裂及裂隙淋滤出大量的U;③U以UO22+的形式与OH-、CO32-等组成络合物在成矿流体运移;④随着成矿流体温度的降低及流体混合作用的发生,U的络合物发生水解并沉淀,形成灰色微晶石英沥青铀矿、红色微晶石英沥青铀矿、萤石和黄铁矿等矿物。
5. 结论
(1)长排矿区成矿期流体包裹体可分为2组,气相成分主要为CO2、CH4和H2等。第1组均一温度主要在291~388℃之间,盐度为3.2%~7.9%NaCleqv,属Ⅰ型含CO2三相和Ⅱ-2型富气相包裹体。第2组均一温度为140~260℃,盐度为1.74% ~10.24% NaCleqv,属Ⅱ-1型富液相包裹体。
(2)长排矿区成矿流体中的U应主要来源于古老含铀地层部分熔融形成的富铀花岗岩。
(3)结合区域地质及地球化学特征可知,长排矿区铀成矿作用很可能形成于岩石圈伸展的背景下,温度的降低和流体的混合作用可能是导致U质沉淀的重要因素。
致谢: 衷心感谢海南省地质调查研究院对野外数据采集提供的帮助,海南省地质测试研究中心提供良好的实验条件使文稿获得了精确的实验数据,及审稿专家在文稿修改过程中提出的宝贵意见。 -
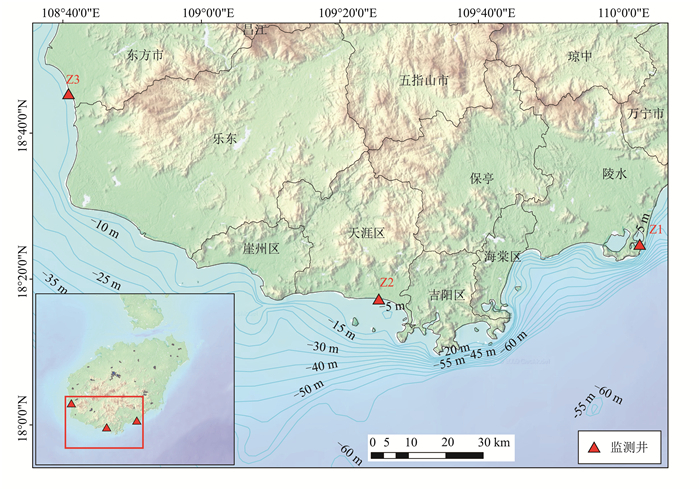
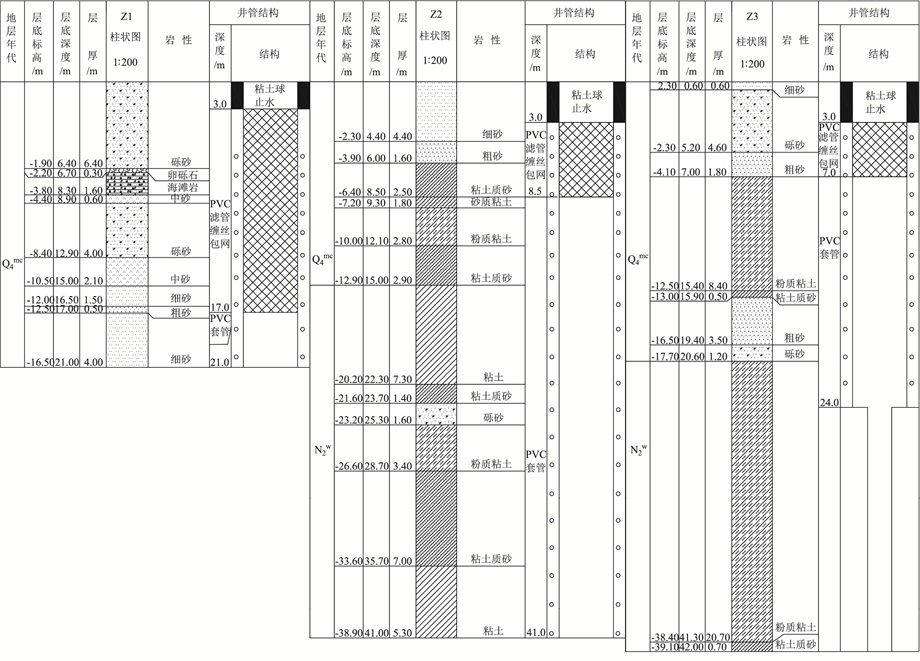
表 1 监测井地理位置和井深信息
Table 1 Location and depth information of the monitoring wells
监测井编号 东经 北纬 点位 井深/m Z1 110°03′59.51″ 18°24′39.87″ 陵水县黎安港 21.0 Z2 109°26′30.02″ 18°17′14.07″ 三亚市三亚湾 41.0 Z3 108°41′10.94″ 18°45′05.46″ 东方市板桥镇 42.0 表 2 大、小潮时段地下水化学参数统计
Table 2 Chemical parameters of groundwater during spring tide and neap tide
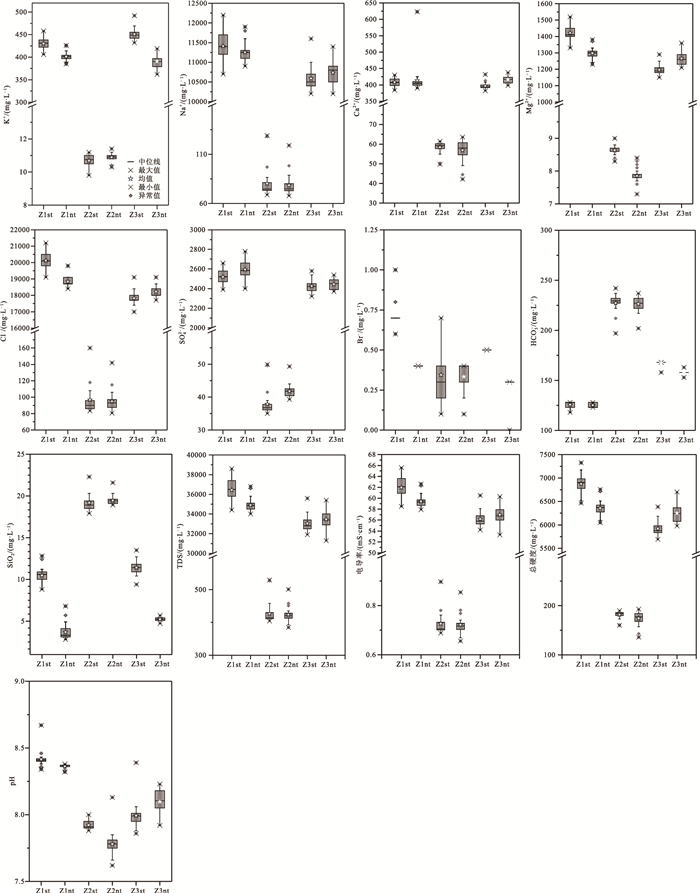
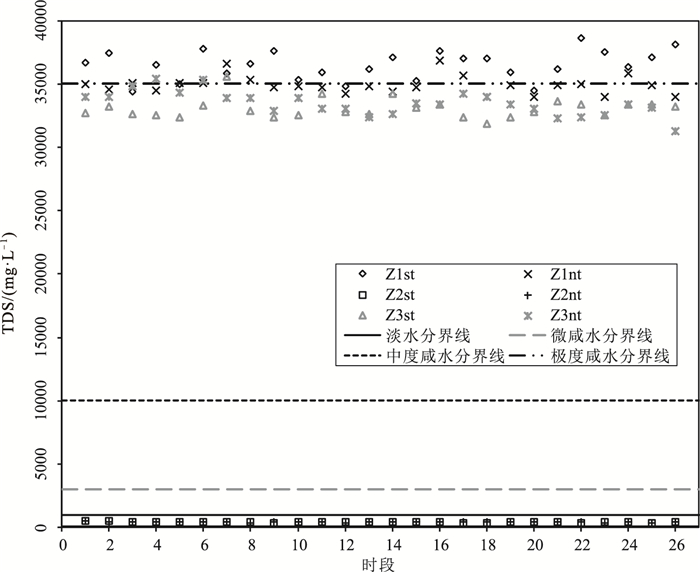
编号 样品数 统计项 化学成分/(mg·L-1) 化学参数 Na+ K+ Mg2+ Ca2+ Cl- SO42- HCO3- Br- 可溶性SiO2 TDS/(mg·L-1) 总硬度/(mg·L-1) 电导率/(mS·cm-1) pH Z1st 25 平均值 11412 430 1422 408 20124 2518 125.8 0.72 10.47 36444 6876 61.96 8.41 最小值 10700 406 1330 384 19100 2390 118 0.6 8.8 34400 6469 58.5 8.34 最大值 12200 458 1520 430 21200 2660 128 1.0 12.8 38600 7327 65.6 8.67 标准差 390.85 14.64 47.41 13.2 623.35 76.03 2.92 0.07 0.89 1153.65 219.89 1.96 0.06 变异系数 0.03 0.03 0.03 0.03 0.03 0.03 0.02 0.1 0.08 0.03 0.03 0.03 0.01 偏态系数 -0.1 -0.08 -0.06 0.08 0.03 -0.07 -0.94 3.12 0.72 -0.13 -0.03 -0.11 3.08 峰态系数 -0.6 -0.79 -0.45 -0.89 -0.96 -0.9 0 12.8 1.44 -0.80 -0.49 -0.84 13.36 Z1nt 26 平均值 11254 401 1298 413 18839 2594 125.1 0.4 3.69 34908 6357 59.42 8.36 最小值 10900 385 1230 390 18400 2400 123 0.4 2.8 34000 6050 57.9 8.32 最大值 11900 426 1380 623 19800 2780 128 0.4 6.8 36800 6756 62.6 8.38 标准差 264.17 10.5 34.33 43.59 386.86 88.82 2.52 0 0.94 710.45 165.44 1.20 0.02 变异系数 0.02 0.03 0.03 0.11 0.02 0.03 0.02 0 0.26 0.02 0.03 0.02 0 偏态系数 0.66 0.69 0.34 4.8 1.04 0.15 0.33 -1.06 1.96 1.13 0.46 1.14 -1.18 峰态系数 0.53 0.74 0.87 23.88 1.08 0.18 -2.06 -2.17 4.08 1.63 0.78 1.63 0.61 Z2st 26 平均值 80.32 10.69 8.63 58.38 96.78 37.88 227.2 0.34 19.19 426.85 181.81 0.726 7.92 最小值 68.7 9.8 8.3 49.8 83.3 35 197 L 17.9 404 160 0.688 7.88 最大值 129 11.2 9 61.5 160 49.9 242 0.7 22.3 527 190 0.897 8.00 标准差 15.41 0.36 0.14 2.93 20.17 3.74 10.63 0.22 1.07 32.61 7.46 0.05 0.03 变异系数 0.19 0.03 0.02 0.05 0.21 0.1 0.05 0.63 0.06 0.08 0.04 0.08 0 偏态系数 2.61 -0.92 0.12 -1.88 2.64 2.71 -1.87 1.02 1.98 2.55 -1.89 2.52 0.97 峰态系数 6.48 0.46 1.07 3.66 6.55 7.03 3.77 -0.25 4.22 6.15 3.73 6.03 0.34 Z2nt 26 平均值 78.4 10.89 7.85 56.85 94.97 41.78 226.4 0.33 19.46 423.65 174.31 0.722 7.78 最小值 67.8 10.3 7.3 42.2 80.5 39.3 202 L 18.9 385 136 0.656 7.62 最大值 119 11.4 8.4 63.6 142 49.3 237 0.4 21.6 501 193 0.854 8.13 标准差 10.59 0.27 0.22 5.42 12.71 1.97 7.26 0.11 0.55 21.84 13.73 0.04 0.09 变异系数 0.14 0.03 0.03 0.1 0.13 0.05 0.03 0.34 0.03 0.05 0.08 0.05 0.01 偏态系数 2.63 -0.84 0.33 -1.28 2.18 2.2 -1.31 -1.53 2.49 1.76 -1.31 1.78 2.24 峰态系数 8.42 0.66 1.66 1.33 6.81 7.95 4.1 1.26 8.46 5.80 1.66 5.87 9.56 Z3st 25 平均值 10588 451 1196 397 17820 2427 167.6 0.5 11.42 33040 5920 56.18 7.99 最小值 10200 432 1150 382 17000 2320 158 0.5 9.4 31900 5690 54.2 7.86 最大值 11600 492 1290 432 19100 2580 168 0.5 13.5 35600 6386 60.5 8.39 标准差 290.57 12.7 32.13 10.09 411.3 66.63 2 0 0.84 777.82 156.18 1.30 0.10 变异系数 0.03 0.03 0.03 0.03 0.02 0.03 0.01 0 0.07 0.02 0.03 0.02 0.01 偏态系数 1.9 1.49 1.12 1.88 1.08 0.58 -5 - 0.20 1.64 1.17 1.64 3.06 峰态系数 5.28 3.42 1.72 5.25 3.13 -0.07 25 - 1.20 3.81 2.07 3.97 13.18 Z3nt 26 平均值 10735 391 1266 416 18223 2445 157.6 0.29 5.22 33458 6249 56.97 8.10 最小值 10200 362 1210 398 17700 2370 153 L 4.7 31300 5975 53.3 7.92 最大值 11400 419 1360 438 19100 2540 163 0.3 5.7 35400 6701 60.3 8.23 标准差 308.47 12.8 39.82 11.29 417.91 53.46 1.96 0.06 0.22 952.12 191.76 1.65 0.09 变异系数 0.03 0.03 0.03 0.03 0.02 0.02 0.01 0.2 0.04 0.03 0.03 0.03 0.01 偏态系数 0.33 0.07 0.64 0.23 0.56 0.2 -0.79 -5.1 -0.26 0.09 0.51 0.08 -0.50 峰态系数 -0.34 0.09 -0.07 -0.62 -0.46 -1.09 4.18 26 0.42 0.18 -0.17 0.02 -0.29 标准海水[9] 10800 392 1290 410 19400 2700 142 67.3 注:“L”表示低于检测限;“-”表示不存在;“st”和“nt”分别代表大潮、小潮 表 3 水质分类
Table 3 Water quality classification
分类 淡水 微咸水 中度咸水 极度咸水 盐水 TDS范围/(mg·L-1) 0~1000 1000~3000 3000~10000 10000~35000 >35000 表 4 大、小潮时段地下水水化学类型
Table 4 Hydrochemical types of the groundwater during spring tide and neap tide
样品编号 水化学类型 样品编号 水化学类型 Z1st Cl-Na Z1nt Cl-Na Z2st HCO3·Cl-Na·Ca Z2nt HCO3·Cl-Na·Ca Z3st Cl-Na Z3nt Cl-Na 表 5 大、小潮时段地下水的矿物饱和指数统计结果
Table 5 Statistics of mineral saturation index of groundwater during spring tide and neap tide
编号 统计项 硬石膏 文石 方解石 白云石 石膏 岩盐 石英 滑石 Z1st 平均值 -0.89 1.01 1.16 3.23 -0.69 -2.47 0.27 8.93 最小值 -0.92 0.96 1.10 2.42 -0.73 -2.52 0.20 5.78 最大值 -0.77 1.13 1.27 3.51 -0.57 -2.42 0.36 10.71 标准差 0.03 0.04 0.04 0.18 0.03 0.03 0.03 0.77 反应状态 溶解态 饱和态 饱和态 饱和态 溶解态 溶解态 平衡态 饱和态 Z1nt 平均值 -0.86 0.98 1.13 3.17 -0.67 -2.50 -0.19 6.75 最小值 -0.91 0.93 1.07 3.07 -0.72 -2.53 -0.30 6.32 最大值 -0.67 1.15 1.29 3.33 -0.47 -2.46 0.08 7.83 标准差 0.04 0.04 0.04 0.05 0.04 0.02 0.10 0.40 反应状态 溶解态 饱和态 饱和态 饱和态 溶解态 溶解态 平衡态 饱和态 Z2st 平均值 -2.31 0.45 0.59 0.74 -2.10 -6.71 0.43 1.54 最小值 -2.34 0.31 0.45 0.52 -2.13 -6.82 0.40 1.26 最大值 -2.27 0.55 0.69 0.91 -2.06 -6.28 0.50 2.11 标准差 0.02 0.05 0.05 0.08 0.02 0.14 0.02 0.21 反应状态 溶解态 平衡态 饱和态 饱和态 溶解态 溶解态 平衡态 饱和态 Z2nt 平均值 -2.27 0.30 0.45 0.42 -2.07 -6.72 0.43 0.66 最小值 -2.40 0.16 0.30 0.10 -2.19 -6.84 0.42 -0.31 最大值 -2.23 0.54 0.68 0.98 -2.03 -6.37 0.47 2.64 标准差 0.04 0.07 0.07 0.15 0.04 0.10 0.01 0.53 反应状态 溶解态 平衡态 平衡态 平衡态 溶解态 溶解态 平衡态 饱和态 Z3st 平均值 -0.89 0.52 0.66 2.21 -0.69 -2.55 0.32 6.48 最小值 -0.91 0.40 0.54 1.97 -0.71 -2.58 0.23 5.86 最大值 -0.85 1.10 1.24 3.37 -0.65 -2.48 0.39 8.83 标准差 0.01 0.13 0.13 0.26 0.01 0.02 0.03 0.55 反应状态 溶解态 饱和态 饱和态 饱和态 溶解态 溶解态 平衡态 饱和态 Z3nt 平均值 -0.87 0.59 0.73 2.35 -0.68 -2.54 -0.03 5.83 最小值 -0.89 0.45 0.59 2.08 -0.69 -2.57 -0.08 4.88 最大值 -0.85 0.69 0.83 2.56 -0.65 -2.49 0.02 6.55 标准差 0.01 0.07 0.07 0.13 0.01 0.02 0.02 0.45 反应状态 溶解态 饱和态 饱和态 饱和态 溶解态 溶解态 平衡态 饱和态 -
沈照理, 朱宛华, 钟佐燊. 水文地球化学基础[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1993. 钱会, 马致远. 水文地球化学[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2005. Kebede S, Travi Y, Alemayehu T, et al. Groundwater Recharge, Circulation and Geochemical Evolution in the Source Region of the Blue Nile River, Ethiopia[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2005, 20(9): 1658-1676. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2005.04.016
刘瑞平, 徐友宁, 张江华, 等. 宁东煤炭基地梅花井矿区地下水三氮特征及成因[J]. 地质通报, 2018, 37(12): 2192-2198. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20181209&flag=1 李华, 文章, 谢先军, 等. 贵阳市三桥地区岩溶地下水水化学特征及其演化规律[J]. 地球科学, 2017, 42(5): 804-812. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201705015.htm 袁晓婕, 黄向青, 甘华阳, 等. 海南岛南部沿岸地下水水化学要素变化及海水入侵特征[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2017, 33(8): 32-40. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDT201708005.htm 周祖光. 海南岛地下水资源特征与开发利用[J]. 水资源保护, 2005, (3): 51-54. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SZYB200503016.htm 唐金平, 张强, 胡漾, 等. 湔江冲洪积扇地下水化学特征及控制因素分析[J]. 环境科学, 2019, 40(7): 3089-3098. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ201907015.htm Hem J D. Study and Interpretation of the Chemical Characteristics of Natural Water[M]. Alexandria: United States Government Printing Office, 1985.
Robinove C L, Langford R H, Brookhart J W. Saline water resources of North Dakota[M]. Washington: United States Government Printing Office, 1958.
Ma F, Wei A, Deng Q, et al. Hydrochemical Characteristics and the Suitability of Groundwater in the Coastal Region of Tangshan, China[J]. Journal of Earth Science, 2014, 25(6): 1067-1075. doi: 10.1007/s12583-014-0492-9
Hamed Y. The Hydrogeochemical Characterization of Groundwater in Gafsa-Sidi Boubaker Region(Southwestern Tunisia)[J]. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 2013, 6(3): 697-710. doi: 10.1007/s12517-011-0393-5
宋献方, 李发东, 于静洁, 等. 基于氢氧同位素与水化学的潮白河流域地下水水循环特征[J]. 地理研究, 2007, (1): 11-21. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0585.2007.01.002 Vengosh A, Ben-Zvi A. Formationof A Salt Plume in the Coastal Plain Aquifer of Israel: the Be'er Toviyya Region[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 1994, 160(1/4): 21-52. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0022169494900329
肖凯. 滨海湿地潮间带氮循环及大孔隙优先流机制研究[D]. 中国地质大学(北京)博士学位论文, 2018. 唐辉, 陈洁, 钱会. 饱和指数在水-岩作用研究中的应用及其灵敏度分析[J]. 水资源与水工程学报, 2012, 23(6): 180-183. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBSZ201206042.htm 孙英, 周金龙, 魏兴, 等. 巴楚县平原区地下水水化学特征及成因分析[J]. 环境化学, 2019, 38(11): 1-9. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJHX201911022.htm Nath B, Jean J S, Lee M K, et al. Geochemistry of High Arsenic Groundwater in Chia-Nan Plain, Southwestern Taiwan: Possible Sources and Reactive Transport of Arsenic[J]. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 2008, 99(1/4): 85-96. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18572272
许万才. 饱和指数法在地下热水化学研究中的应用[J]. 长安大学学报(自然科学版), 1992, (3): 66-70. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XAGX199203011.htm 王凤波, 郭应征, 曹朝雷. 基于SI模型评价新安江库水水质特征[J]. 工程与试验, 2011, (4): 59-61. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SNSN201104016.htm Vengosh A, Helvaci C, Karamanderesi, I H. Geochemical Constraintsfor the Origin of Thermal Waters from Western Turkey[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2002, 17(3): 163-183 doi: 10.1016/S0883-2927(01)00062-2
张文杰, 谭红兵, 陈喜, 等. 广东硇洲岛地下水化学演化及成因机理[J]. 水文, 2012, 32(3): 51-59. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWZZ201203011.htm 李学礼, 孙占学, 刘金辉. 水文地球化学[M]. 北京: 原子能出版社, 1982. 汪啸. 广东沿海典型深大断裂带地热水系统形成条件及水文地球化学特征[D]. 中国地质大学博士学位论文, 2018. Jalali M. Application of Multivariate Analysis to Study Water Chemistry of Groundwater in A Semi-Arid Aquifer, Malayer, Western Iran[J]. Desalination and Water Treatment, 2010, 19(1/3): 307-317. doi: 10.5004/dwt.2010.1077
Reddy A G S, Saibaba B, Sudarshan G. Hydrogeochemical Characterization of Contaminated Groundwater in Patancheru Industrial Area, Southern India[J]. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 2012, 184(6): 3557-3576. doi: 10.1007/s10661-011-2208-2
Moujabber, M E, Samra B B, Darwish T, et al. Comparison of Different Indicators for Groundwater Contamination by Seawater Intrusion on the Lebanese Coast[J]. Water Resources Management, 2006, 20(2): 161-180. doi: 10.1007/s11269-006-7376-4
Kura N U, Ramli M F, Ibrahim S, et al. An Integrated Assessment of Seawater Intrusion in A Small Tropical Island Using Geophysical, Geochemical, and Geostatistical Techniques[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2014, 21(11): 7047-7064. doi: 10.1007/s11356-014-2598-0
章光新, 邓伟, 何岩, 等. 中国东北松嫩平原地下水水化学特征与演变规律[J]. 水科学进展, 2006, (1): 20-28. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKXJ200601003.htm 周慧芳, 谭红兵, 张西营, 等. 江苏南通地下水补给源、水化学特征及形成机理[J]. 地球化学, 2011, 40(6): 566-576. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX201106007.htm Gibbs R. Mechanisms Controlling World Water Chemistry[J]. Science(New York, N.Y. ), 1971, 170: 1088-1090. http://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/17777828
於昊天, 马腾, 邓娅敏, 等. 江汉平原东部地区浅层地下水水化学特征[J]. 地球科学, 2017, 42(5): 685-692. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201705003.htm 王亚平, 王岚, 许春雪, 等. 长江水系水文地球化学特征及主要离子的化学成因[J]. 地质通报, 2010, 29(2): 446-456. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=2010020332&flag=1




 下载:
下载: