Genetic types and source characteristics of hydrocarbon gases adsorbed by Mesozoic-Paleozoic marine strata in well CSDP-2, Laoshan uplift, South Yellow Sea Basin
-
摘要:
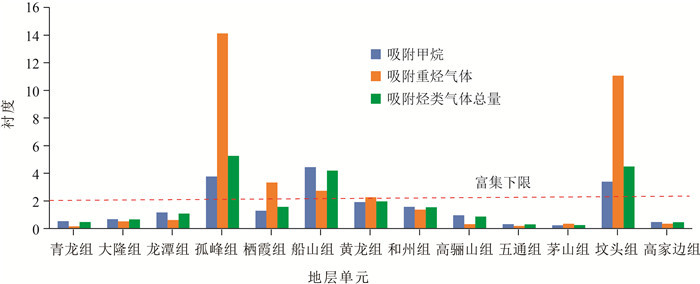
通过对南黄海盆地崂山隆起CSDP-2井不同时期地层吸附烃类气体分子及碳、氢同位素组成分析,探讨了吸附烃类气体成因类型和源区特征。崂山隆起不同时期地层的吸附烃类气体含量具有明显差异,主要富集层位依次是坟头组、孤峰组、船山组、栖霞组和黄龙组。吸附烃类气体富集受地层岩性、有机质含量、烃类气体运移等多种因素控制。孤峰组主要显示烃源岩特征,而坟头组、船山组、栖霞组和黄龙组主要显示储层特征。各时期地层吸附烃类气体主要为热成因类型,其中孤峰组、坟头组和栖霞组由于受同型不同源气或同源不同时期气的混合而部分偏离热成因区。吸附烃类气体的源区有机质类型属于Ⅱ型干酪根(海相源岩),其中,有些层位有Ⅲ型干酪根(陆相源岩)的混入。吸附烃类气体热成熟度Ro在0.6%~1.6%之间,处于成熟到过成熟范围。研究成果为南黄海盆地崂山隆起区中—古生界海相油气勘探提供了地球化学依据。
Abstract:Based on the analysis of molecular and carbon and hydrogen isotopic composition of adsorbed hydrocarbon gases within different period's strata in well CSDP-2 of Laoshan uplift in the South Yellow Sea Basin, the genetic types and source characteristics of adsorbed hydrocarbon gases were discussed.Different period's strata exhibit different contents of adsorbed hydrocarbon gas and the main enrichment horizons are the Fentou Formation, Gufeng Formation, Chuanshan Formation, Qixia Formation and Huanglong Formation in turn.Adsorbed hydrocarbon gas enriched in strata is controlled by many factors, including lithology, organic contents and hydrocarbon gas migration etc.Gufeng Formation mainly shows source rock characteristics, while Fentou Formation, Chuanshan Formation, Qixia Formation and Huanglong Formation mainly show reservoir characteristics.The hydrocarbon gases adsorbed in the strata of each period are mainly thermogenic types, among which the Gufeng Formation, Fentou Formation and Qixia Formation are partially deviated from the thermogenic areas due to the mixing of the same type with different source gases or the same gas in different periods.The source organic matter type of adsorbed hydrocarbon gases belongs to type Ⅱ kerogen (marine source rock), in which some horizons have type Ⅲ kerogen (terrestrial source rock) mixed.The thermal maturity (Ro) of adsorbed hydrocarbon gas is between 0.6% and 1.6%, which is in the range of maturity to over-maturity.The results provide geochemical basis for the exploration of Mesozoic-Paleozoic oil and gas in Laoshan uplift, South Yellow Sea Basin.
-
Keywords:
- South Yellow Sea Basin /
- well CSDP-2 /
- adsorbed hydrocarbon gas /
- genetic types /
- thermal maturity
-
致谢: 感谢项目组人员的付出和大陆架科学钻探项目组提供样品支持,同时感谢审稿专家提出的宝贵意见。
-
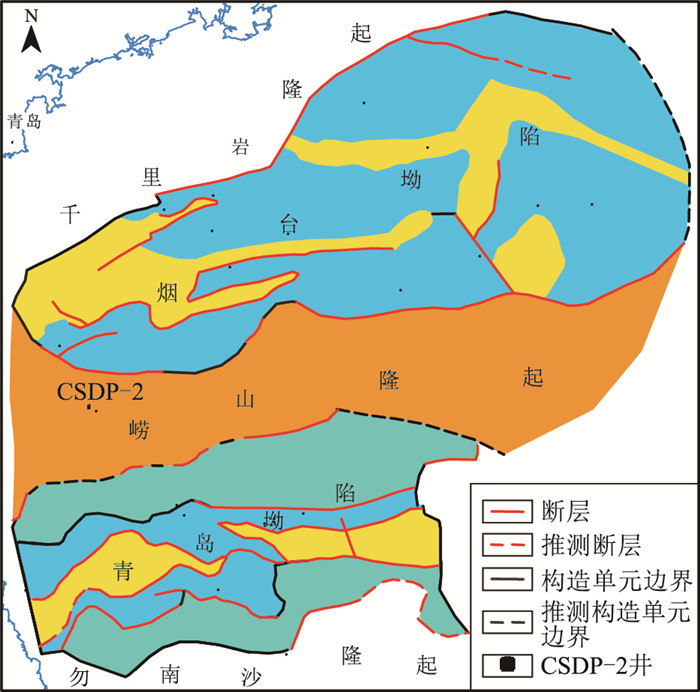
图 1 南黄海盆地构造单元及CSDP-2井位置图
(据参考文献[1]修改)
Figure 1. Tectonic units of South Yellow Sea and location of well CSDP-2
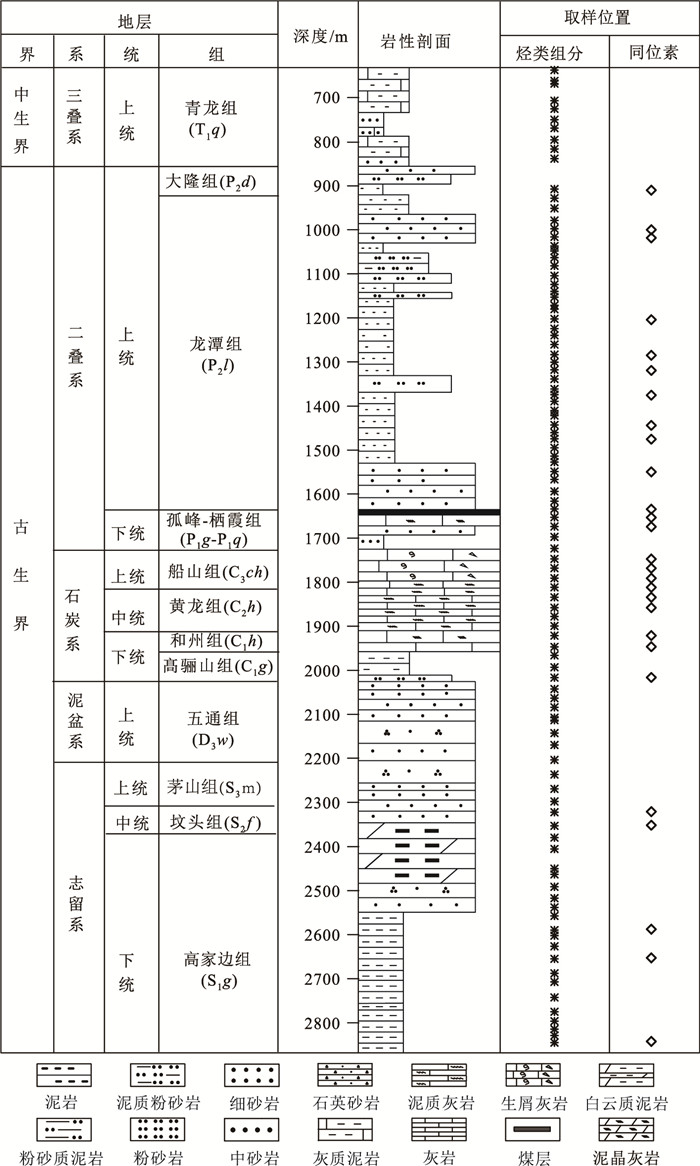
图 2 CSDP-2井地层岩性柱状图及采样位置图
(据参考文献[8]修改)
Figure 2. Stratigraphic column and sampling locations in well CSDP-2
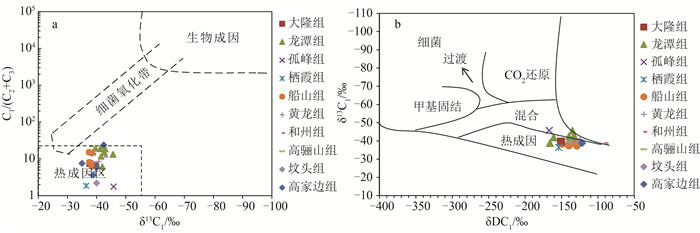
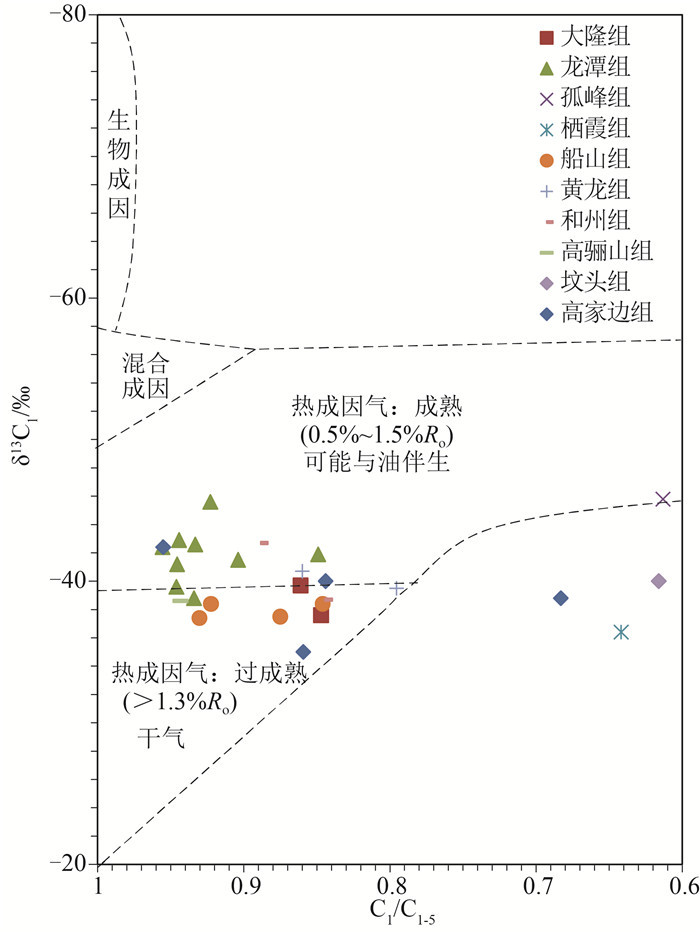
图 5 CSDP-2井不同时期地层吸附烃类气体C1/C1-5-δ13C1关系图
(据参考文献[3]修改)
Figure 5. C1/C1-5-δ13C1 diagram of adsorbed hydrocarbon gases from the strata of different periods in well CSDP-2
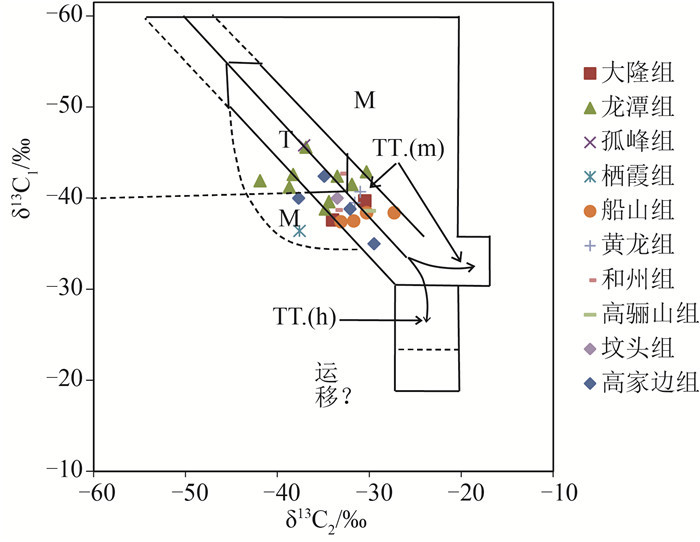
图 6 CSDP-2井不同时期地层岩心吸附烃类气体δ13C1-δ13C2相关图(据参考文献[17]修改)
TT.(m)—腐泥型有机质来源的非伴生气;M—混合来源气;TT.(h)—腐殖型有机质来源的非伴生气;T—伴生气
Figure 6. δ13C1-δ13C2 diagram of adsorbed hydrocarbon gases from the strate of different periods in well CSDP-2
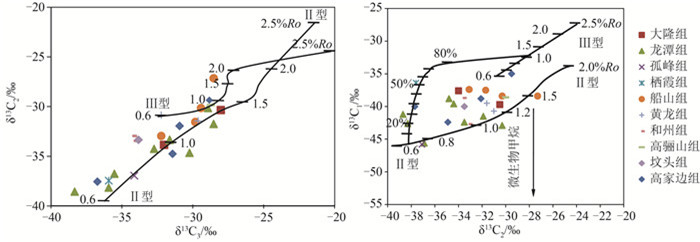
图 7 CSDP-2井不同时期地层吸附烃类气体δ13C3-δ13C2和δ13C2-δ13C1相关图
(据参考文献[22]修改)
Figure 7. δ13C3-δ13C2 and δ13C2-δ13C1 diagrams of adsorbed hydrocarbon gases from the strata of different periods in well CSDP-2
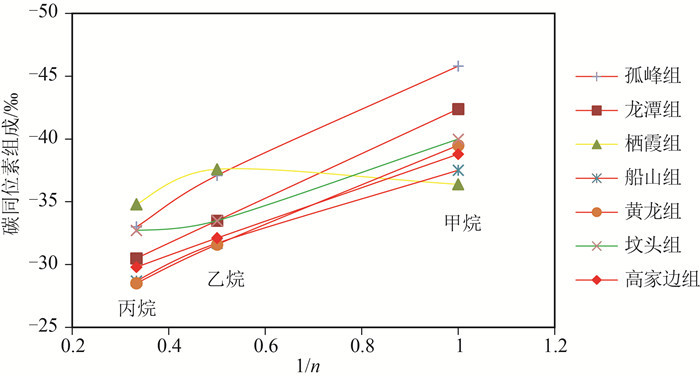
图 8 CSDP-2井不同时期吸附烃类气体碳同位素组成与1/n关系图
(据参考文献[25]修改)
Figure 8. Carbon isotopic composition and 1/n diagram of adsorbed hydrocarbon gases from the strata of different periods in well CSDP-2
表 1 CSDP-2井不同时期地层吸附烃类气体含量和平均值
Table 1 Contents and means of adsorbed hydrocarbon gas of different period's strata in well CSDP-2
地层 吸附甲烷/(μL· kg-1) 吸附乙烷/(μL·kg-1) 吸附丙烷/(μL·kg-1) 吸附异丁烷/(μL·kg-1) 吸附正丁烷/(μL·kg-1) 吸附异戊烷/(μL·kg-1) 吸附正戊烷/(μL·kg-1) 湿度比/% 青龙组 506.56~1503.62/ 1063.74 18.64~56.07/ 37.86 4.86~12.89/8.92 0.79~4.58/ 2.10 1.48~3.37/ 2.44 0.47~1.82/ 1.01 0.47~1.39 /0.97 3~6/ 5 大隆组 21.95~4883.00/ 1371.00 2.14~636.50/ 139.06 0.48~108.90/ 25.39 0.13~19.39/ 5.15 0.20~14.61/ 4.08 0.01~5.95/ 1.60 0.07~2.10/0.91 5~14/ 10 龙潭组 127.67~6528.00/ 2341.41 8.56~884.40/ 151.31 0.95~185.60/ 35.69 0.17~23.35/ 6.19 0.20~41.41/ 8.29 0.13~14.05/ 3.33 0.02~13.66/2.66 1~15/ 7 孤峰组 7573.65 3279.87 1005.71 126.85 230.01 62.34 70.45 39 栖霞组 352.37~4635.07/ 2580.44 43.62~2101.92/ 892.20 4.86~388.19/ 172.09 1.26~33.20/ 17.77 1.94~44.27/ 23.74 0.61~16.40/ 9.34 0.70~17.89/ 8.62 10~36/ 21 船山组 6318.49~13601.70/8920.04 404.51~848.40/648.76 78.79~205.52/ 146.00 16.16~47.66 /32.52 26.03~74.86/50.41 10.88~32.07/20.40 12.04~43.47/27.17 7~15/ 11 黄龙组 457.38~7367.87/3842.09 12.85~1053.13/464.79 4.06~273.66/ 141.91 1.01~70.29 /34.58 1.46~116.94/55.69 1.25~60.47/27.11 2.60~91.32/39.69 5~20/ 12 和州组 286.43~5411.05/3144.01 8.48~346.68/204.34 3.77~181.55/ 105.75 3.69~53.93 /31.41 1.60~87.64/51.41 0.66~52.27/28.22 2.65~74.72/41.82 7~16/11 高骊山组 739.42~3090.81/1915.11 16.94~104.84/ 60.89 5.32 ~36.05 / 20.69 1.91~8.75 / 5.33 2.15 ~14.02/ 8.08 0.73 ~14.33/ 7.53 3.54~7.98/ 5.76 4~6/5 五通组 80.57~1789.00/ 630.68 6.54 ~84.43/ 36.90 3.49 ~29.73/ 13.73 0.49 ~4.76/ 2.19 1.56~10.99 / 4.98 0.46~10.11/ 3.17 0.47~5.32/ 2.33 8~23/ 14 茅山组 277.62~673.83/ 464.59 29.29~108.84/ 60.14 10.62~56.61 28.61 2.14~11.63/ 5.76 3.36~23.29/ 11.08 1.44~9.15/ 4.86 1.81~12.43/ 5.97 12~25/ 18 坟头组 6276.34~7330.82/ 6803.58 1072.63~2238.36/ 1655.50 662.06~1072.52/ 867.29 308.83~367.10/ 337.97 334.81~446.88/ 390.85 217.80~253.73/ 235.77 221.33~283.96/ 252.65 32~38/ 35 高家边组 307.02~3526.59/ 947.45 20.64~275.73/ 66.52 7.51~69.47/ 23.64 0.86~11.08/ 4.11 1.60~29.66/ 8.50 0.46~86.50/ 10.61 0.61~14.07/ 4.13 5~25/ 12 表 2 CSDP-2井不同时期地层吸附烃类气体碳同位素及甲烷氢同位素组成
Table 2 Carbon and hydrogen isotopic composition of adsorbed hydrocarbon gases of different period's strata in well CSDP-2
‰ 样号 深度/m 层位 δ13C1 δ13C2 δ13C3 δDC1 DP11 907.4 大隆组 -37.6 -34.0 -30.9 DP15 997.3 龙潭组 -39.7 -30.5 -26.9 -151 DP16 1015.9 龙潭组 -42.9 -30.3 -27.8 -133 DP27 1201.95 龙潭组 -45.6 -36.9 -34.4 -135 DP31 1282.9 龙潭组 -42.4 -33.5 -30.5 -140 DP33 1317.28 龙潭组 -41.2 -38.7 -37.2 -132 DP36 1373.58 龙潭组 -42.6 -38.3 -34.8 -133 DP40 1442.28 龙潭组 -39.6 -34.4 -31.6 -140 DP42 1473.7 龙潭组 -38.8 -34.8 -29.1 -166 DP46 1547.99 龙潭组 -41.5 -31.9 -27.4 DP50 1632.8 龙潭组 -41.9 -41.9 -38.2 -161 DP51 1651.78 孤峰组 -45.8 -37.1 -33.0 -167 DP52 1672.8 栖霞组 -36.4 -37.6 -34.8 -154 DP55 1746.08 船山组 -38.4 -27.3 -27.4 -149 DP56 1767.08 船山组 -37.4 -33.1 -31.1 -129 DP57 1789.78 船山组 -37.5 -31.7 -28.7 -140 DP58 1810.68 船山组 -38.4 -30.3 -28.3 -130 DP59 1833.18 黄龙组 -40.7 -31.0 -31.1 DP60 1856.88 黄龙组 -39.5 -31.6 -28.5 -139 DP63 1920.28 和州组 -42.7 -33.1 -33.1 DP64 1945.58 和州组 -38.7 -33.6 -33.0 -91 DP67 2015.48 高骊山组 -38.6 -30.0 -27.6 DP78 2320.68 坟头组 -40.0 -33.5 -32.7 -125 DP79 2351.5 高家边组 -38.8 -32.1 -29.8 -122 DP87 2587.98 高家边组 -35.0 -29.5 -27.7 DP90 2653.18 高家边组 -42.4 -34.9 -30.3 DP100 2843.18 高家边组 -40.0 -37.7 -35.6 -
陈建文, 雷宝华, 梁杰, 等. 南黄海盆地油气资源调查新进展[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2018, 38(3): 1-23. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ201803001.htm 张海启, 陈建文, 李刚, 等. 地震调查在南黄海崂山隆起的发现及其石油地质意义[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2009, 29(3): 107-113. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ200903019.htm 王丰, 李慧君, 张银国. 南黄海崂山隆起地层属性及油气地质[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2010, 30(2): 95-102. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ201002020.htm 陈建文, 龚建明, 李刚, 等. 南黄海盆地海相中-古生界油气资源潜力巨大[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2016, 32(1): 1-7. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDT201601001.htm 陈建文. 南黄海海相中生界-古生界具有形成大型油气田的物质基础[J]. 中国地质调查成果快讯, 2016, 2(12): 6-10. 郭兴伟, 朱晓青, 宋世杰. 大陆架科钻CSDP-2井在南黄海海相地层中首次钻遇油气显示[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2015, 35(5): 124. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ201505019.htm 蔡来星, 肖国林, 郭兴伟等. 南黄海盆地科学钻探CSDP-2井上古生界-中生界烃源岩评价及海相油气勘探前景[J]. 石油学报, 2018, 39(6): 660-673 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201806005.htm 蔡来星, 王蛟, 郭兴伟, 等. 南黄海中部隆起中-古生界沉积相及烃源岩特征: 以CSDP-2井为例[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2017, 47(4): 1030-1046. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ201704006.htm 张晓华, 张训华, 吴志强, 等. 南黄海中部隆起中-古生代地层发育新认识——基于大陆架科学钻探CSDP-02井钻探成果[J]. 地球物理学报, 2018, 61(6): 2369-2379. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX201806018.htm 陈建文, 施剑, 刘俊, 等. 南黄海海相中-古生界地震地质条件[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2016, 32(10): 1-9. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDT201610001.htm Bernard B B, Brooks J M, Sackett W M. Light hydrocarbons in recent Texas continental shelf and slope sediments[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1978, 83: 4053-4061. doi: 10.1029/JC083iC08p04053
Whiticar M J. Correlation of natural gases with their sources[C]//Magoon L B, Dow W G. The Petroleum System-From Source To Trap, AAPG Memoir, 1994, 60: 261-283.
Tissot B P, Welte D H. Petroleum Formation and Occurrence[M]. Springer, Berlin, 1984: 207-224.
夏新宇, 李春圆, 赵林. 天然气混源作用对同位素判源的影响[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 1998, 25(3): 89-90 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK803.024.htm Stahl W J, Carey B D J. Source-rock identification by isotope analyses of natural gases from fields in the Val Verde and Delaware basins, West Texas[J]. Chemical Geology, 1975, 16: 257-267. doi: 10.1016/0009-2541(75)90065-0
Schoell M. Genetic characterization of natural gases. American Association of Petroleum Geologists Bulletin, 1983, 67(12): 2225-2238. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0165037883901249
Schoell M. Isotope studies in petroleum research[C]//Brooks J M, Welte D H. Advances in Petroleum Geochemistry, Vol. 1. Academic Press, London, 1984: 215-245.
James A T. Correlation of natural gas by use of carbon isotopic distribution between hydrocarbon components[J]. Am. Assoc. Pet. Geol. Bull., 1983, 67(7): 1176-1191. http://aapgbull.geoscienceworld.org/content/67/7/1176
戴金星. 天然气碳氢同位素特征和各类天然气鉴别[J]. 天然气地球科学, 1993, 4(23): 1-40. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX1993Z1000.htm Berner U, Faber E. Maturity related mixing model for methane, ethane and propane, based on carbon isotopes[J]. Adv. Org. Geochem., 1988, 13: 67-72. doi: 10.1016/0146-6380(88)90026-5
Berner U, Faber E. Light hydrocarbons in sediments of the Nankai Accretionary Prism(LEG 131, SITE 808)[C]//Hill I A, Taira A, Firth J V. et al. Ocean Drilling Program: Scientific Results, 1993, 131: 185-195.
Whiticar M J, Faber E. Methane oxidation in sediment and water column environments-isotope evidence. Advances in Organic Chemistry 1985(12th EAOG meeting)[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 1986, 10: 759-768 doi: 10.1016/S0146-6380(86)80013-4
Berner U, Faber E. Empirical carbon isotope/maturity relationships for gases from algal kerogens and terrigenous organic matter, based on dry, open-system pyrolysis[J]. Org. Geochem, 1996, 24: 947-955. doi: 10.1016/S0146-6380(96)00090-3
Hakan H Y M, NamV YV, Bernhard C, et al. Molecular and isotopic composition of gas occurrences in the Thrace basin(Turkey): origin of the gases and characteristics of possible source rocks[J]. Chemical Geology, 2005, 214: 179-191. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2004.09.004
Chung H M, Gormly J R, Squires R M. Origin of gaseous hydrocarbons in subsurface environments: theoretical considerations of carbon isotope distribution[J]. Chemical Geology, 1988, 71: 97-103. doi: 10.1016/0009-2541(88)90108-8



 下载:
下载: