Research on gliding distance estimation of loess landslide based on multiple regression: A case study of Tianshui region, Gansu Province
-
摘要:
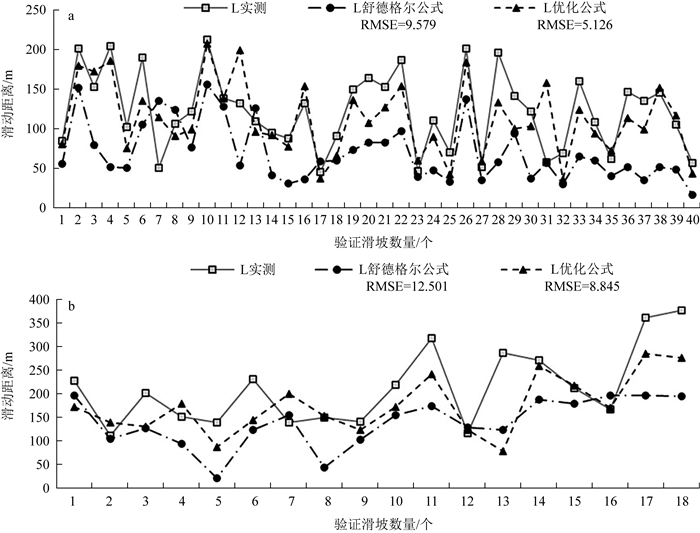
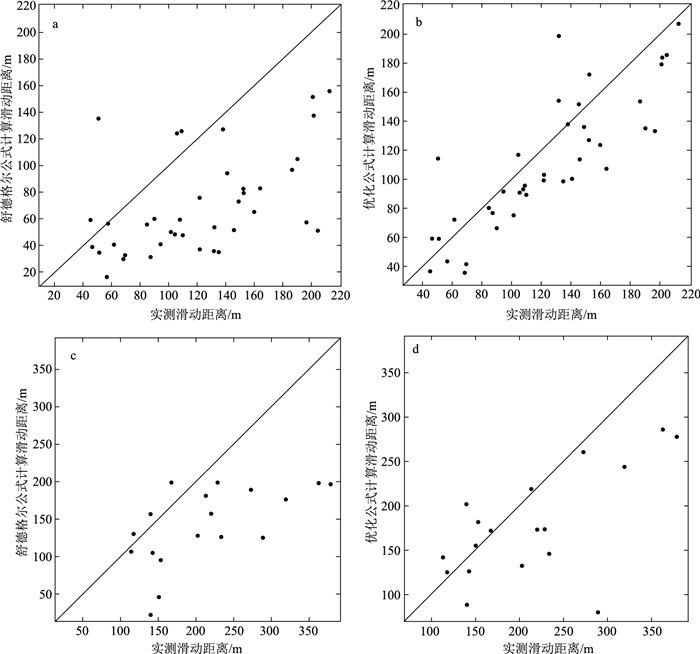
滑坡滑动距离的预测是实现大比例尺滑坡风险评估的关键瓶颈之一。为定量分析滑坡地形高差、滑坡体积、坡体长宽比、滑坡平面曲率、斜坡坡度、植被覆盖等因素对黄土滑坡滑动距离的影响,以天水地区多年滑坡数据为例,应用因子相关分析法对滑动距离影响因子进行了综合分析,基于舒德格尔公式,采用多元回归模型对降雨、地震诱发滑坡滑动距离估测方程进行了优化。结果表明,滑坡前后缘高差、滑坡体积、坡体长宽比和斜坡坡度可作为天水地区滑坡滑动距离预测模型的输入因子,其对滑坡滑动距离的影响程度可用偏回归系数定量描述。滑动距离预测模型优化后比舒德格尔公式增加了坡体长宽比和斜坡坡度2个指标,提高了模型在天水地区应用的准确度。
Abstract:The prediction of the gliding distance of landslide is one of the key problems in the risk assessment of large slip landslide.To quantitatively analyze the effects of landslide topography height difference, landslide volume, landslide length-width ratio, landslide plane curvature, slope and vegetation cover on the runout distance of loess landslide, the authors chose long-term landslide data in the Tianshui region as an example to analyze the significance of the factors affecting the gliding distance by the factor correlation analysis and revised the gliding distance induced by rainfall and earthquake estimation equation based on Schudger formula and multiple regression in this paper.The results show that elevation difference, landslide volume, landslide length-width ratio and slope can be used as the input of landslide gliding distance prediction model in Tianshui region, and the degree of influence of each factor on the gliding distance of landslide can be quantitatively described by partial regression coefficient.After the optimization of the gliding distance prediction model in this paper, two indexes of landslide length-width ratio and slope are increased by the Schudger formula, which improves the accuracy of the model applied in the Tianshui region.
-
阿根廷境内已发现金矿床(矿化点)337个,其中,内生金矿床(矿化点)273个,砂金矿床(矿化点)64个[1],储量/资源量2254t。阿根廷西部的安第斯地区是南美洲安第斯金成矿带的重要组成部分,因产出有世界级Bajo de la Alumbrera斑岩型铜金矿床、Far allón Negro、El Indio-Pascua和Deseado Massif浅成低温热液型金矿集区而闻名于世[2-3]。与中国金矿床类型以造山型、胶东型和斑岩型为主不同[4-5],阿根廷金矿床类型以浅成低温热液型和斑岩型为主[6],其中浅成低温热液型金矿床找矿潜力巨大[3]。
1. 区域成矿地质背景
在大地构造单元上,阿根廷位于安第斯造山带中南段(包括巴塔哥尼亚地台),以及中巴西地盾南部拉普拉达克拉通,横跨了安第斯造山带和南美地台区两大构造域。自前寒武纪开始,该区先后经历了新元古代—早寒武世潘比亚(Pampeano)旋回、古生代—中生代早期法玛蒂娜(Famatiniano)和冈瓦纳(Gondwánico)旋回、中生代侏罗纪—白垩纪巴塔哥尼亚(Patagonídico)旋回4期构造事件,使潘比亚(Pampia)地块、库亚尼亚(Cuyania)地块、智利尼亚(Chilenia)地体和巴塔哥尼亚(Patagonia)地台先后发生增生作用,拼合至冈瓦纳大陆西缘拉普拉达克拉通。中—新生代安第斯(Andico)造山运动使阿根廷西部开始整体隆升。上述5期构造事件形成了阿根廷现今的构造格架,也引发了区域多期火山-岩浆作用(图 1)。金成矿作用与上述构造事件形成的造山带和火山-岩浆岩带有密切的时空关系。
![]() 矿集区名称:1—Rinconada;2—Antofalla;3—Taca Taca;4—Farallon Negro;5—Casposo-Castaño-San Jorge;6—El Indio–Pascua;7—Nevados del Famatina;8—Pampeanas Ⅰ;9—Pampeanas Ⅱ;10—Pampeans Ⅲ;11—Deseado Massif;12—Cerro Vanguardia;13—El Dorado-Monserrat;14—Cerro Negro;15—ChubutFigure 1. Distribution of main gold deposits and belts in Argentina
矿集区名称:1—Rinconada;2—Antofalla;3—Taca Taca;4—Farallon Negro;5—Casposo-Castaño-San Jorge;6—El Indio–Pascua;7—Nevados del Famatina;8—Pampeanas Ⅰ;9—Pampeanas Ⅱ;10—Pampeans Ⅲ;11—Deseado Massif;12—Cerro Vanguardia;13—El Dorado-Monserrat;14—Cerro Negro;15—ChubutFigure 1. Distribution of main gold deposits and belts in Argentina2. 金成矿作用及主要矿床类型
阿根廷金矿床类型主要有浅成低温热液型金-银矿床(低硫型、高硫型)、斑岩型铜-金矿床、造山型金矿床和砂金矿床。
(1)浅成低温热液型金矿床:是阿根廷主要的金矿床类型,在安第斯造山带自北向南均有发育,其成矿作用与长英质-中性火山岩有关,矿床/矿体严格受控于区域各级断裂构造。北部以高硫浅成低温热液型为主,如Veladero矿床;南部以低硫浅成低温热液型为主,如Cerro Negro矿床。前者形成于中新世,后者主要形成于侏罗纪,少量金矿床形成于中新世。高硫浅成低温热液型金矿床可能与钙碱性岩浆去气化作用有关[7];低硫浅成低温热液型金矿床成矿机制与成矿流体的沸腾作用有关[8]。
(2)斑岩型铜-金矿床:是阿根廷重要的金矿床类型,主要分布于阿根廷西北部安第斯地区,以Ba jo de la Alumbrera斑岩型铜-金矿床最典型。含矿岩体主要为钙碱性斑岩,岩性有英安斑岩、石英闪长斑岩等。该类型矿床常与浅成低温热液型金矿床在成因和时空上密切相关,如Farallon Negro金矿集区与Bajo de la Alumbrera矿床。这与两者同处于统一的斑岩成矿系统有关,发育于板块汇聚边缘与俯冲作用相关的陆缘弧环境,与火山-次火山侵入岩成因关系密切[9-10]。
(3)造山型金矿床:也是阿根廷重要的金矿床类型之一,在阿根廷北部米纳毕格塔斯地区和中部拉里奥哈省均有发育,分别以Tormo矿床和Callana矿床为典型代表。成矿流体的运移和金的沉淀与潘比亚旋回期Tilcárica增生造山作用和法玛蒂娜旋回期Chánica增生造山作用关系密切,分别发育于潘比亚、智利尼亚等地块与冈瓦纳西缘的汇聚板块边缘。该类型金矿床严格受构造断裂控制,矿体以含金石英脉的形式赋存于区域二级断裂构造或更次级的断裂中[11]。
(4)砂金矿床:在阿根廷分布广泛,重要矿集区位于巴塔哥尼亚地区。其成矿作用受金的补给源和地质地貌条件控制。
3. 金成矿时代
南美洲各地质历史时期均产出金矿床,以新生代最重要,其次是古元古代、太古宙和新元古代,上述各时期金资源量占南美洲金总资源量的比例分别为51.52%、29.24%、9.90%和4.10%。在新生代矿床中,以中新世金矿床占绝对优势,且以产于安第斯造山带的浅成低温热液型金矿床和富金斑岩型矿床为主,其金资源量占南美洲金总资源量的42.98%。元古宙是南美洲金另一重要金成矿期,以产于南美地台区克拉通的造山型金矿床为主[12]。
阿根廷金成矿时代与南美洲既有相似之处,又有显著的地域特色。其金成矿时代与4期构造-岩浆事件密切相关(表 1、表 2),先后为:①法玛蒂娜旋回期Chánica造山运动形成的造山型金矿床,成矿时代主要为泥盆纪;②冈瓦纳旋回形成的低硫浅成低温热液型金矿床,成矿时代为三叠纪;③巴塔哥尼亚旋回形成的低硫浅成低温热液型金矿床,成矿时代为侏罗纪;④安第斯造山运动形成的浅成低温热液型金矿床(低硫型、高硫型)和富金斑岩型矿床,成矿时代主要为中新世和渐新世。
表 1 阿根廷金矿带主要矿床成矿时代Table 1. Metallogenic epochs of main gold deposits in various gold belts, Argentina金矿带 金矿集区 典型矿床 成矿期 成矿时代 成矿年龄/Ma 文献来源 编号 名称 编号 名称 Ⅰ 北部造山型金矿带 1 Rinconada EI Torno 法玛蒂娜 志留纪 430 [13] Minas Azules 430 2 Antofalla Incahuasi 泥盆纪 415±3.7 [1] Ⅱ 北部斑岩型、浅成低温热液型金矿带 3 TacaTaca TacaTaca Bajo 安第斯 古近纪 23.89±0.20 [1] Taca Taca Alto [1] 4 Farallon Negro Bajo de la Alumbrera 新近纪 7.12±0.13 [14] Farallon Negro-Alto de la Blenda 6.55±0.14 [1] Agua Rica 6.29±0.06 Ⅲ 西北部浅成低温热液型金矿带 5 Casposo-Castano -San Jorge San Jorge 冈瓦纳 二叠纪 263±6 [1] Casposo 三叠纪 6 El Indio-Pascua Pascua-Lama 安第斯 新近纪 Veladero 10.09±0.08~13.12±0.18 [15] 7 Nevados del Famatina La Mejicana 5±0.3~3.8±0.2 [3] Ⅳ 中部造山型金矿带 8 Sierras Pampeanas Ⅰ Cerro Blanco 法玛蒂娜 二叠纪 259±13 [1] 9 Sierras Pampeanas Ⅱ Callana VI 泥盆纪 390 10 Sierras Pampeanas Ⅲ Puigari-Monserrat 泥盆纪 376~378 Ⅴ 巴塔哥尼亚浅成低温热液型金矿带 11 Deseado Massif Manantial Espejo 巴塔哥尼亚 白垩纪 124.8±3~142.6±3.5 [1] 12 Cerro Vanguardia Cerro Vanguardia 侏罗纪-白垩纪 138.5±3.3~152.4±3.6 13 El Dorado-Monserrat El Dorado-Monserrat 侏罗纪 172(?) 14 Cerro Negro Cerro Negro 侏罗纪 172(?) 15 Chubut Esquel 侏罗纪 161±4 [16] 表 2 阿根廷各成矿期主要金矿床储量/资源量Table 2. The reserves/ resources of main gold deposits of various metallogenic periods, Argentina成矿期 储量/资源量/t 成矿时代 储量/资源量/t 安第斯 1691.29 上新世 73.69 中新世 1239.43 渐新世 280 古近纪一新近纪 98.17 巴塔哥尼亚 367.39 侏罗纪 367.39 冈瓦纳 44.47 二叠纪-三叠纪 44.47 法玛蒂娜 151.12 151.12 合计 2254.27 2254.27 3.1 法玛蒂娜成矿期(泥盆纪)
阿根廷古生代晚期的法玛蒂娜旋回形成2个重要的金成矿带:北部造山型金矿带和中部造山型金矿带。
阿根廷西北部Arequipa-Antofalla地块与Pam pia地块在460~470Ma发生碰撞,导致岩层变质和变形,发育胡胡伊-萨尔塔省Rinconada金矿集区。其成矿作用与早奥陶世浊积岩变质作用无关,而与区域褶皱和断裂作用有关,成因类型为造山型金矿床,典型矿床如EI Torno。
晚泥盆世,阿根廷西部Chilenia地块与Pam pia地块碰撞增生,形成Sierra Pampeanas山区重要的构造带,在南部逐渐发展出一系列剪切带,在Pampeanas地区形成与剪切带有关的金矿床,产出阿根廷大部分的造山型金矿床,典型矿床如Callana Ⅳ[1]。
3.2 冈瓦纳成矿期(三叠纪)
晚古生代—早中生代冈瓦纳旋回,在圣胡安省(San Juan)和门多萨省(Mendoza)形成以三叠纪火山岩和造山后花岗岩为代表的火山-岩浆活动,产出晚古生代—早侏罗世金矿床(表 1、表 2),成因类型主要有低硫浅成低温热液矿床和斑岩型铜-钼-金矿床。Casposo-Castaño-San Jorge金矿集区为其中的代表,矿床主要赋存于泥盆系—石炭系沉积岩中,上覆三叠系火山岩。该成矿期在圣胡安省主要发育低硫浅成低温热液矿床,在门多萨省发育斑岩型铜-钼-金斑岩矿床。
3.3 巴塔哥尼亚成矿期(侏罗纪)
中生代巴塔哥尼亚旋回,在巴塔哥尼亚地区发育重要的侏罗纪金成矿作用(表 1、表 2),形成多个重要的低硫浅成低温热液型金矿集区,如Desea do Massif金矿集区。矿床主要赋存于中侏罗统Bajo Pobre组安山岩和玄武岩(如El Dorado矿床)、上侏罗统Chon Aike组流纹岩中(如Cerro Vanguardia矿床)[2-3]。
3.4 安第斯成矿期(中新世)
新生代安第斯造山运动在Cordillera地区和Precordillera地区发育大规模金成矿作用,与古近纪和新近纪的2次造山运动密切相关。自第四纪开始的剥蚀作用生成了大量的砂金矿床。
古近纪造山运动在潘比亚地体Puna-Arizaro地区形成Taca Taca等金矿集区,以富金斑岩型矿床为主。新近纪Neogeno造山运动形成阿根廷最重要的金矿床(表 2),广泛分布于阿根廷西北部,如Far allon Negro矿集区(表 1)。
综上所述,安第斯成矿期是阿根廷最重要的金成矿时代,成矿集中于中新世,以浅成低温热液型和富金斑岩型为主,其次为巴塔哥尼亚成矿期,成矿集中于侏罗纪,以浅成低温热液型为主。同时,阿根廷又因自身独特的构造演化史,缺失南美地台元古宙造山型金矿床,而发育独特的泥盆纪造山型金矿床。
据不完全统计,阿根廷已探明金资源量为2254.27t,其中安第斯成矿期、巴塔哥尼亚成矿期和冈瓦纳成矿期金储量/资源量分别为1691.29t、367.39t、44.47t和151.12t(图 2)。总体而言,成矿时代越新,矿化强度越强。
![]() 图 2 阿根廷各成矿期金储量/资源量分布直方图(数据来源于表 2)Figure 2. The histogram of reserves/ resources of various metallogenic periods, Argentina
图 2 阿根廷各成矿期金储量/资源量分布直方图(数据来源于表 2)Figure 2. The histogram of reserves/ resources of various metallogenic periods, Argentina4. 金矿空间分布规律
阿根廷中南段主要分布有Farallon Negro金矿集区、智利-阿根廷EI Indio-Maricunga金矿集区及延伸至阿根廷的El Indio-Pascua(高硫型)金矿集区;南段主要分布有巴塔哥尼亚金矿带。根据阿根廷已发现金矿床的成矿时代、矿床类型、分布特征等,结合金成矿与区域构造事件和火山-次火山岩带的关系,将阿根廷金矿划分为5个金矿带(图 1)。
4.1 北部造山型金矿带(Ⅰ)
北部造山型金矿带主体位于潘比亚地体,金矿化主要与法玛蒂娜旋回期的Chánica造山运动有关,可进一步划分为胡胡伊-萨尔塔省Rinconada和卡塔马卡省Antofalla两个金矿集区(图 1)。
胡胡伊-萨尔塔省Rinconada金矿集区,位于阿根廷普纳高原的Sierra de Rinconada地区,由2套NNE向奥陶纪岩浆岩-沉积岩带组成,被上覆的古近纪—新近纪火山-碎屑岩分割为Faja Eruptiva Oc cidental和Faja Eruptiva Oriental[1]。2期奥陶纪岩浆作用分别发育奥陶纪早期低钾玄武岩,以及后期的安山岩、玄武质岩石[19]。该成矿区金矿床展布与区域性褶皱轴向近平行,矿床由位于褶皱轴部和逆断层中连续或断续的含金石英脉组成[1],以EI Torno和Minas Azules矿床最典型(表 3)。赋矿围岩主要为中奥陶统浊积岩,经历了绿片岩相变质作用。矿体以含金石英脉形式产出,呈NS走向。Minas Azules矿床多数矿脉产于褶皱东翼,而西翼石英脉矿化较差[20]。两矿床毒砂Re-Os定年指示,该区金成矿年龄可能为430Ma[3, 13],成矿作用可能持续到中生代。
表 3 阿根廷各金矿带典型矿床地质特征Table 3. Geological characteristics of typical gold deposits of various gold belts, Argentina金矿带 大地构造位置 成矿期 典型矿床 矿石矿物 脉石矿物 蚀变 矿体 围岩 矿区构造 矿床类型 成矿环境 成矿时代 编号 名称 Ⅰ 北部造山型金矿带 潘比业 法玛蒂娜 EITorno 自然金、自然银、黄铁矿、毒砂 石英、绢云母 绢云母化、粘土化、黄铁矿化和碳酸岩化 脉状 奥陶系砂岩、细屑岩、板岩 背斜和向斜 浊积岩中的脉型金矿 盆地边缘浊流沉积 志留纪 Ⅱ 北部斑岩型、浅成低温热液型金矿带 潘比亚 安第斯 Taca Taca Bajo 黄铜矿、自然金、铜蓝 石英 钾长石化、绢英岩化、硅化、粘土化 浸染、网脉状 石英斑岩、花岗岩 NW向断裂 斑岩型铜金矿 区域深大断裂 渐新世 FarallonNegro-Alto de laBlenda 闪锌矿、黄铁矿、方铅矿、黄铜矿、自然金 石英、方解石等 硅土化、青磐岩化 脉状 安山岩、二长岩 NW向区域断裂 浅成低温热液型金矿 岩浆弧 中新世 Bajo de la Alumbrera 黄铁矿、黄铜矿、自然金、方铅矿、辉铜矿、蓝辉铜矿、闪锌矿、磁铁矿 石英、石膏、硬石膏 钾长石化、绢云母化、青磐岩化 浸染状 英安斑岩、安山岩、二长岩 断裂 斑岩型铜金矿 岩浆弧 中新世 Agua Rica 黄铁矿、自然金、黄铜矿 石英 钾长石化、青磐岩化、粘土化 浸染、网脉状 斑岩'安山岩 N-NW向断裂 斑岩型铜金矿 造山带岩浆弧 中新世 Ⅲ 西北部浅成低温热型金矿带 智利尼亚、库亚尼亚、潘比亚 安第斯、冈瓦纳 San Jorge 自然金、黄铜矿、黄铁矿、斑铜矿、闪锌矿、方铅矿、铜蓝 钾化、粘土化、青磐岩化 浸染状 安山岩、斑岩 斑岩型铜金矿 岩浆弧 二叠纪 Casposo 石英 硅化、绢云母化、青磐岩化 脉状 安山岩、流纹岩 低硫浅成低温热液型金矿 岩浆弧 三叠纪 Veladero 黄铁矿、黄铜矿 石英、明矾石 硅化、粘土化 脉状 英安岩、流纹岩 SW向、SN向、NE向断裂 高硫浅成低温热液型金矿 岩浆弧 中新世 La Mejicana 黝铜矿、黄铜矿、黄铁矿、闪锌矿、斑铜矿、自然金、自然银、白铁矿 石英 脉状 F.Negro Peinado变质岩 高硫浅成低温热液型金矿 岩浆弧 上新世 Ⅳ 中部造山型 潘比亚、拉普拉达 法玛蒂娜 Cerro Blanco 方铅矿、闪锌矿、黄铜矿、褐铁矿 石英 脉状 片岩、流纹岩 造山型金矿 剪切带 二叠纪 Callana Ⅳ 自然金、孔雀石、蓝铜矿 石英 板状 花岗闪长岩、英云闪长岩、闪长岩 NW SE剪切带 造山型金矿 剪切带 中泥盆世 Puigari-Monserrat 黄铁矿、闪锌矿、方铅矿、黄铜矿、毒砂、赤铁矿、针铁矿 石英 绢云母化、青磐岩化 脉状 片麻岩、花岗岩 造山型金矿 剪切带 泥盆纪 Ⅴ 巴塔哥尼亚浅成低温热液型金矿带 巴塔哥尼亚 巴塔哥尼亚 Manantial Espejo 自然金、金银矿、自然银、黄铁矿、毒砂、方铅矿、闪锌矿、褐铁矿 石英、卫髓、冰长石、高岭土、方解石 硅化、绢云母化、高岭土化、绿泥石化 脉状、网脉状 碎屑岩、安山岩 低硫浅成低温热液型金矿 区域岩浆岩 晚侏罗世 Cerro Vanguardia 自然金、金银矿、自然银、辉银矿、黄铁矿、毒砂、方铅矿、闪锌矿 石英、冰长石1、重晶石1、方解石、菱铁矿 硅化、粘土化 脉状、网脉状 火山碎屑岩、流纹岩 断裂和次级断裂 低硫浅成低温热液型金矿 区域岩浆岩 晚侏罗世一曱-白垩世 El Dorado-Monserrat 银金矿(?)、黄铁矿、磁铁矿 石英、重晶石、冰长石 硅化、粘土化、青磐岩化、绢云母化 脉状 安山岩 NE10°断裂 低硫浅成低温热液型金矿 区域岩浆岩 侏罗纪 Cerro Negro 石英 高岭土化 脉状、网状状 灰岩、流纹岩 断裂 低硫浅成低温热液型金矿 区域岩浆岩 侏罗纪 Esquel 自然金、金银矿、黝铜矿、黄铁矿 石英 硅化、伊利石化、蒙脱石化、绿泥石化 脉状、网状状 安山岩、流纹岩 断裂 低硫浅成低温热液型金矿 区域岩浆岩 侏罗纪 卡塔马卡省Antofalla矿集区以Incahuasi矿床最典型。矿床受区域NS向韧脆性剪切带控制,为石英脉型矿化,赋矿围岩为中奥陶统低级变质岩[3],成矿年龄为415±3.7Ma[1]。
4.2 北部斑岩型、浅成低温热液型金矿带(Ⅱ)
北部斑岩型、浅成低温热液型金矿带在大地构造位置上位于潘比亚地体西北部。斑岩型、浅成低温热液型金矿化与渐新世—中新世火山-次火山岩浆岩带有关,金矿床主要分布于萨尔塔省和卡塔马卡省的西部,少量分布在土库曼省西部,主要矿床类型是斑岩型铜金矿床和浅成低温热液金矿床(图 1)。该带是阿根廷最重要的金矿带,同时也是阿根廷最重要的铜矿带,产有塔卡-塔卡(Taca Taca)、阿雷布鲁拉(Bajo de la Alumbrera)、阿瓜利卡(Agua Ri ca)等世界级斑岩铜金矿床与浅成低温热液型金矿床,以Farallon Negro和Taca Taca金矿集区最典型。
Farallon Negro火山杂岩带(FNVC)为最重要的金矿集区,以Bajo de la Alumbrera斑岩铜金矿床和Farallon Negro低硫浅成低温热液型金矿集区最典型(表 3)[21]。FNVC位于Sierras Pampeanas地体北缘大型盆地内,基底岩石为下寒武统泥质片岩和砂屑岩,被晚奥陶世—早志留世花岗质岩石侵入[22]。其由数个火山喷发中心组成,展布面积超过700km2[23]。同源斑岩体侵入到FNVC安山岩中,如Bajo de la Alumbrera和Alto de la Blenda。Bajo de la Alumbrera斑岩型铜金矿床受区域NE向至SN向区域断裂带控制,矿化斑岩体呈放射状分布,倾角较大[24]。该矿集区发育中新世浅成低温热液型金矿床,成矿年龄集中于5~8Ma(表 1)。其产出两大脉体系统,走向NNW,倾向NE60°~75°,分别为Farallon Negro矿床中的Farallon Negro、Farallón Negro Rama Norte等矿脉,以及Alto de la Blenda矿床中的Laboreo、Port ezuelo、Chica等矿脉。矿脉主要赋存于Alto de la Blenda二长岩内,局部在La Chilca安山岩内[3]。
Taca-Taca矿集区(S24°00′~25°15′、W65°50′~ 68°00′)位于萨尔塔省西北部与智利交界处,大地构造位置上属于Sierras Pampeanas地体。矿集区包括Taca Taca Bajo、Taca Taca Alta等斑岩型铜-金矿床(表 3),成矿作用与该区钙碱性火山-次火山岩有密切时空关系。赋矿围岩为渐新世石英斑岩和花岗岩,其受NW向断裂严格控制。金主要与绢英岩化蚀变有关,与石英、磁铁矿等共生[1]。
4.3 西北部浅成低温热液型金矿带(Ⅲ)
西北部浅成低温热液型金矿带位于智利尼亚北部、库亚尼亚北部和潘比亚西部的结合带。该区域发育2期金成矿作用,早期金成矿与冈瓦纳运动有关,形成圣胡安省-门多萨省(Mendoza)CasposoCastaño-San Jorge金矿集区(以低硫型为主,斑岩型次之);晚期金成矿与安第斯运动有关,形成圣胡安省El Indio-Pascua(高硫型)和拉里奥哈省Nevados del Famatina金矿集区(以高硫型为主,斑岩型次之)(图 1)。该带是阿根廷的主要金矿带之一,产有多个大型-超大型浅成低温热液型金矿床,如Velade ro、Pasua Lama等矿床。
Casposo-Castaño-San Jorge金矿集区在El Indio-Pascua金矿集区以南约150km处,与二叠纪—三叠纪火山-岩浆活动有关,在北部圣胡安省主要形成低硫浅成低温热型金矿床,以Casposo为代表;在南部门多萨省形成富金斑岩型铜钼矿床,以San Jorge矿床最典型。该区广泛出露二叠系—三叠系Choiyoi群流纹岩和安山质火山岩,上覆古生代基底沉积岩,两者呈不整合接触关系。该基底在法玛蒂娜和冈瓦纳造山期经历了强烈的变形作用[3]。古近纪—新近纪火山-沉积岩上覆于Choiyoi群之上,并被古近纪—新近纪花岗岩类侵入,随后在安第斯造山运动中发生变形[25]。
El Indio-Pascua金矿集区位于圣胡安省西部与智利交界处,是世界级金矿集区(图 1),发育Pas cua-Lama矿床(阿根廷/智利)、Veladero矿床(阿根廷)(表 3)、Sancarron矿床(智利)、Rio del Medio矿床(智利)、El Indio矿床(智利)和Tambo矿床(智利),受控于NS向和NW向断裂带。区域基底为晚古生代—早侏罗世长英质钙碱性火山-侵入岩,上覆中生代火山-沉积岩及渐新世—中新世火山-岩浆岩和火山碎屑岩[3]。其中,与区域金成矿有关的中新世火山-岩浆岩受NS向高角度逆断裂控制。该区金矿床成矿年龄集中于6.0~9.5Ma,与区域帕斯卡组英安岩和凝灰岩年龄一致[26]。
Nevados del Famatina金矿集区位于潘比亚地体。区域基底为寒武系—下奥陶统海相沉积岩,经历晚奥陶世低级变质作用和Nunorco花岗岩侵入,其上覆晚古生界陆相沉积岩。矿区英安斑岩-流纹岩侵位年代为5.0±0.3Ma。区域基底断裂形成于法纳蒂娜造山期,呈NE向和NW走向,其后随安第斯造山活化,进一步发育NS向断裂和褶皱。英安斑岩-流纹岩沿上述NS向断裂侵入,其内赋存富金斑岩型铜钼矿床,矿化呈细脉浸染状、脉状和网脉状,以黄铁矿、黄铜矿和闪锌矿为主。矿区也发育个别EW向断裂,控制La Mejicana浅成低温热液型铜、金矿床的产出[3, 27]。
4.4 中部造山型金矿带(Ⅳ)
中部造山型金矿带在大地构造位置上位于安第斯前科迪勒拉东部的潘比亚地体,该区域为潘比亚地体与拉普拉达克拉通、库亚尼亚地体的缝合带(图 1)。基底主要由下—中古生界变质岩和火成岩组成。该地体在新元古代—寒武纪潘比亚远动期间经历广泛的变形-变质作用,达到角闪岩相-麻粒岩相,并发育长英质岩浆作用。随后,法玛蒂娜造山运动在该区发育碰撞背景下的镁铁质-超镁铁质岩浆作用。在古生代中期Achalian造山运动期间,冈瓦纳边缘重新汇聚导致挤压变形,并发育泥盆纪早期岩浆弧,影响了潘比亚大部分区域。泥盆纪—石炭纪花岗岩持续活动侵入到变质基底中。地体基底在安第斯造山运动期间持续抬升形成了一系列盆地[2, 28]。
泥盆纪为该带最重要的金成矿期,发育造山型金矿床,主要分布在科尔多瓦省(Córdoba)、圣路易斯省(San Luis)和拉里奥哈省(La Rioja),少量分布在圣胡安省(图 1)。此类矿床多为石英脉型矿体,矿脉严格受断裂控制,走向呈NE—NW向,与区域断裂产状一致。赋矿围岩多样,如片麻岩、糜棱岩、花岗岩、花岗闪长岩等。该带造山型金矿床规模均较小,如Rio Candelaria(Au资源量60000 Oz, )、San Ignacio(Au资源量40000 Oz),尚未发现大型-超大型矿床,目前以小规模民采矿床为主。依据赋矿围岩不同,可进一步分为3个金矿集区:Pampeanas Ⅰ、Pampeanas Ⅱ和Pampeans Ⅲ。Pampeanas Ⅰ金矿集区位于圣胡安省La Huerta山区,发育Cerro Blanco、El Morado和Martha Ⅰ、Ⅱ等金矿床。矿体呈脉状或透镜体状产出,走向NW,赋存于Fertil valley群变质岩内[1]。Pampeanas Ⅱ金矿集区位于拉里奥哈省Chepes、Las Minas和Ulapes地区及San Luis省山区,成矿时代为泥盆纪—石炭纪,以Callana Ⅵ最典型(表 3)。矿床赋存于前寒武系变质岩和古生代火成岩中,为石英脉型矿化,矿体呈脉状和透镜状,走向NW—NE,呈线形和“S”形断续延伸。Pampeans Ⅲ金矿集区位于科尔多瓦省Pampia地区Grande de Cordoba山脉东侧,由Puigari-Monserrat等60多个矿床(体)组成。矿床产于NS向元古宙片麻岩岩群中,为石英脉型矿化,矿体走向NW30°—NE30°,呈透镜体状和“S”形。绢云母Ar-Ar年龄为376~ 378Ma[1]。
4.5 巴塔哥尼亚浅成低温热液型金矿带(Ⅴ)
大地构造位置上,巴塔哥尼亚浅成低温热液型金矿带位于巴塔哥尼亚地台区,金矿化与白垩纪—侏罗纪火山-次火山岩浆岩有关。金矿床主要分布在巴塔哥尼亚地区,集中于圣克鲁斯省(Santa Cruz)、丘布特省(Chubut)、内格罗河省(Río Ne gro)和内乌肯省(Neuquén),尤以圣克鲁斯省Deseado Massif、Cerro Vanguardia、El Dorado-Monserrat、Cerro Negro及丘布特省Chubut五个金矿集区最发育(图 1;表 3)。
圣克鲁斯省金矿集区多位于巴塔哥尼亚南部Deseado Massif地区,含矿地层是该区变质基底的多个小范围露头,其上覆弧后伸展作用形成的二叠系—三叠系沉积岩,两者呈不整合接触关系。由于大西洋打开,南美洲和非洲大陆分离,该区在经历断块作用和半地堑作用后形成裂谷和断陷盆地。中—晚侏罗世双峰式火山作用形成了Bajo Pobre组,岩性为玄武岩和安山岩,以及Bahía Laura群,岩性为熔结凝灰岩和凝灰岩,相对偏酸性。白垩系和新生界玄武岩和海相沉积岩上覆于侏罗系火山岩。侏罗纪伸展构造作用形成了巨大的NNW-N向半地堑,以陡峭铲式正断层为界,多为二叠纪—三叠纪裂谷作用的再活化[3, 29]。金矿床主要赋存于裂谷地区,受裂谷和断裂带控制,其成因与侏罗纪火山作用有关。Deseado Massif矿集区矿床形成于晚侏罗世,多赋存于Bahía Laura群熔结凝灰岩(Chon Aike Complex)内,主要为La Matilda凝灰岩层。Cerro Vanguardia矿集区发育超大型金矿床,金储量3.5Moz,成矿年龄范围为138.5±3.3~152.4± 3.6Ma。矿体赋存于Chon Aike组长英质凝灰岩中,为石英脉型矿化,矿区北部矿脉走向WNW向,南部矿脉走向N—NW,倾角较大。El Dorado-Mon serrat矿集区毗邻Cerro Vanguardia矿集区,矿体赋存于Bajo Pobre组安山岩中,呈雁行脉形式产出。El Dorado矿床中含金石英脉沿E向剪切带发育,而Monserrat矿区含金石英脉沿N向剪切带发育[30]。Cerro Negro矿集区位于Deseado Massif西北部,为新近发现的金矿集区,区内圈定的金、银资源量分别为2.54Moz和23.2Moz[3]。矿床赋存于上侏罗统火山岩中,矿体沿EW向、NW向断层,以及上述断层交会处产出[31]。
丘布特省Chubut金矿集区位于巴塔哥尼亚南部Cordillera Patagónica Septentrional地区。该区中侏罗世双峰式火山作用形成了Lago La Plata组,岩性为安山岩和流纹岩,其下伏地层为下侏罗统黑色页岩、砂岩、砾岩和灰岩,两者呈不整合接触关系[32]。Lago La Plata组是该矿集区主要的赋矿围岩。Esquel金矿床金、银储量分别为3.8Moz和7Moz,为石英脉型矿化,赋存于Lago La Plata组中性-镁铁质火山岩中。其成矿年龄不晚于161± 4Ma。N—NE向含金石英脉沿NS向构造产出,南部以WNW向断裂为界[16]。
综上所述,阿根廷以北部的斑岩型、浅成低温热液型金矿带(Ⅱ)最重要,其次为西北部浅成低温热液型金矿带(Ⅲ)和巴塔哥尼亚浅成低温热液型金矿带(Ⅴ)。北部斑岩型、浅成低温热液型金矿带(Ⅱ)Farallon Negro矿集区阿雷布鲁拉和阿瓜利卡斑岩型铜金矿床金资源量分别高达489t[9]和263t[17];塔卡-塔卡矿集区塔卡-塔卡斑岩型铜金矿床金资源量高达280t[17]。Farallon Negro矿集区中新世Bajo de la Alumbrera、Alto de la Blenda岩体和塔卡-塔卡矿集区渐新世石英斑岩具有很大的找矿潜力。西北部浅成低温热液型金矿带(Ⅲ)El Indio– Pascua金矿集区与智利EI Indio-Maricunga金矿带毗邻,两者处于同一构造-岩浆岩带,在智利一侧已发现数个超大型金矿床,而阿根廷一侧目前仅发现Veladero矿床。该带帕斯卡组英安岩和凝灰岩具有很大的找矿潜力。巴塔哥尼亚浅成低温热液型金矿带(Ⅴ)是阿根廷重要的浅成低温热液型金矿带[33],该带Deseado Massif矿集区的Bahía Laura群熔结凝灰岩、Chon Aike组长英质凝灰岩和Bajo Pobre组安山岩,以及丘布特矿集区的Lago La Plata组安山岩和流纹岩,均有很大的找矿潜力。
5. 结论
(1)阿根廷经历了潘比亚旋回、法玛蒂娜旋回、冈瓦纳旋回、巴塔哥尼亚旋回和安第斯造山运动5期构造事件,形成一系列造山带和火山-岩浆岩带。构造事件引发的区域造山作用、火山-岩浆作用与金成矿作用关系密切。金矿床成因类型主要为浅成低温热液型(低硫型、高硫型)、斑岩型、造山型等。前2种金矿床类型在阿根廷占据主导地位。
(2)阿根廷金成矿作用主要发生在4个时期:①泥盆纪造山型金矿床,形成于法玛蒂娜旋回期Chánica造山运动;②三叠纪低硫浅成低温热液型金矿床,形成于冈瓦纳旋回期;③侏罗纪低硫浅成低温热液型金矿床,形成于巴塔哥尼亚旋回期;④古近纪—新近纪高硫浅成低温热液型金矿床,形成于安第斯造山期。侏罗纪和新近纪是阿根廷最重要的金成矿期。
(3)阿根廷金矿集中分布在5个金矿带:①北部造山型金矿带(Ⅰ);②北部斑岩型、浅成低温热液型金矿带(Ⅱ);③西北部浅成低温热液型金矿带(Ⅲ);④中部造山型金矿带(Ⅳ);⑤巴塔哥尼亚浅成低温热液型金矿带(Ⅴ)。
(4)阿根廷5个金矿集区的特定岩层(体)具有较大的找矿潜力,分别是:北部斑岩型、浅成低温热液型金矿带(Ⅱ)的Farallon Negro矿集区中新世Ba jo de la Alumbrera、Alto de la Blenda岩体和塔卡-塔卡矿集区渐新世石英斑岩体;西北部浅成低温热液型金矿带(Ⅲ)的El Indio–Pascua矿集区帕斯卡组英安岩和凝灰岩;巴塔哥尼亚浅成低温热液型金矿带(Ⅴ)的Deseado Massif矿集区Bahía Laura群熔结凝灰岩、Chon Aike组长英质凝灰岩、Bajo Pobre组安山岩和丘布特矿集区Lago La Plata组安山岩和流纹岩。
致谢: 本文滑坡数据由中国地质科学院地质力学所提供,审稿专家对本文提出了宝贵的修改意见和建议,在此一并表示感谢。 -
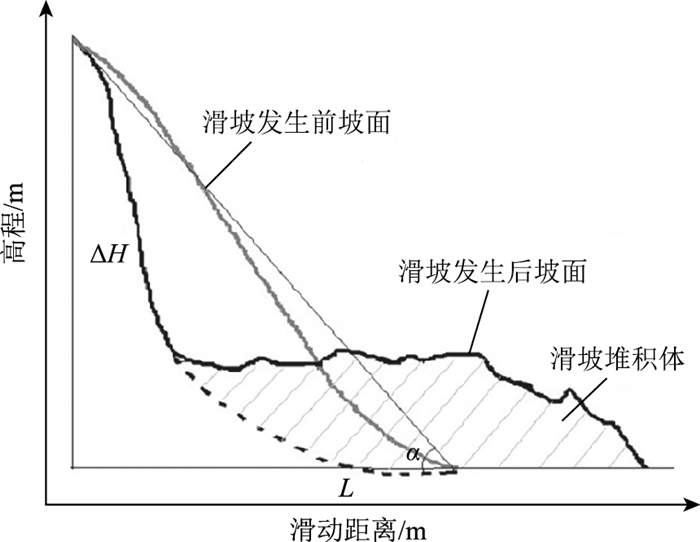
图 2 滑坡要素关系图[22]
Figure 2. The relationship of key elements of landslide
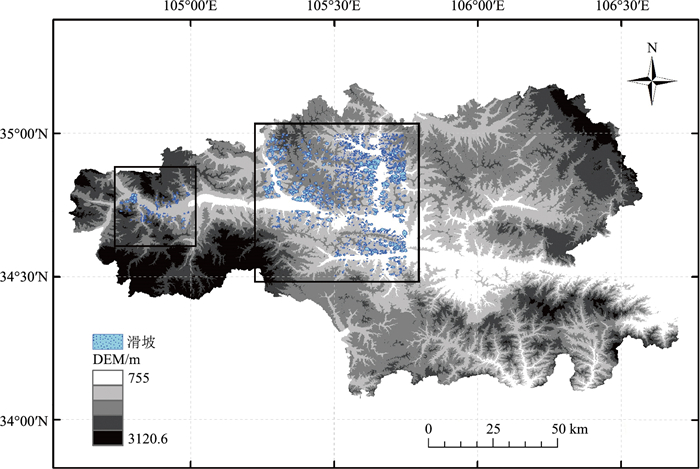
表 1 基础数据类型及来源
Table 1 Basic data types and sources
数据名称 数据类型 空间分辨率 数据来源 数字高程(DEM) 栅格(.tif) 25 m*25 m 中国地质科学院
地质力学研究所天水市历史滑坡灾害点 矢量(.shp) - 中国地质科学院
地质力学研究所归一化植被指数(NDVI) 栅格(.tif) 1 km 中国科学院资源环境信息中心 表 2 天水市滑坡参数统计
Table 2 Statistics of landslide parameters in Tianshui region
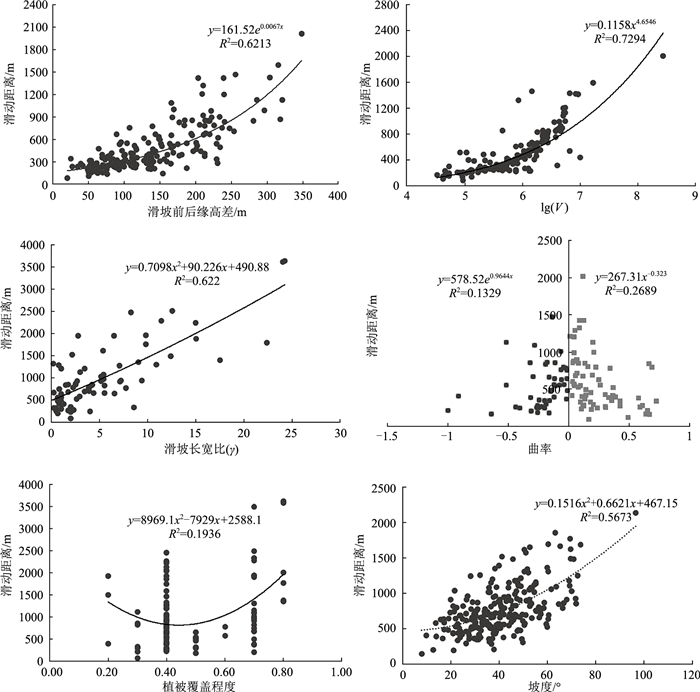
序号 诱因 剖面形态 规模 滑坡体积/m3 前后缘高差/m 植被覆盖度 坡度/° 滑动距离/m 1 地震 凹形 大 5181684 254.23 0.80 1.17 713.45 2 降雨 直线 小 2811160 112.34 0.80 1.67 412.84 3 降雨 直线 小 3554304 89.94 0.70 4.15 324.91 4 降雨 复合 大 557351 87.10 0.70 4.44 262.28 5 降雨 复合 大 557351 71.33 0.40 5.86 256.02 6 降雨 直线 小 600471.6 55.75 0.70 5.86 182.97 7 降雨 直线 小 600471.6 42.30 0.70 5.87 255.14 8 地震 直线 大 1330968 169.17 0.70 7.66 425.62 9 降雨 凹形 小 49581.6 180.84 0.40 9.58 401.49 10 地震 凹形 小 49581.6 201.24 0.40 9.96 470.21 11 降雨 直线 小 878660 134.56 0.40 10.28 407.53 12 地震 凹形 中 4342725 139.28 0.40 10.37 421.08 13 降雨 凹形 大 787000 78.82 0.40 11.06 258.25 14 降雨 直线 大 5547253 85.57 0.80 11.77 245.12 15 降雨 直线 大 5547253 130.44 0.70 12.01 346.69 … … … … … … … … … 192 降雨 直线 中 84419.2 137.75 0.40 12.45 273.26 表 3 影响因子间的相关系数矩阵
Table 3 Correlation coefficient matrix between impact factors
因子 ΔH lg(V) α γ ΔH 1.000 -0.005 0.038 -0.262 lg(V) -0.005 1.000 0.010 -0.073 α 0.038 0.010 1.000 -0.021 γ -0.262 -0.073 -0.021 1.000 表 4 多元回归分析输出
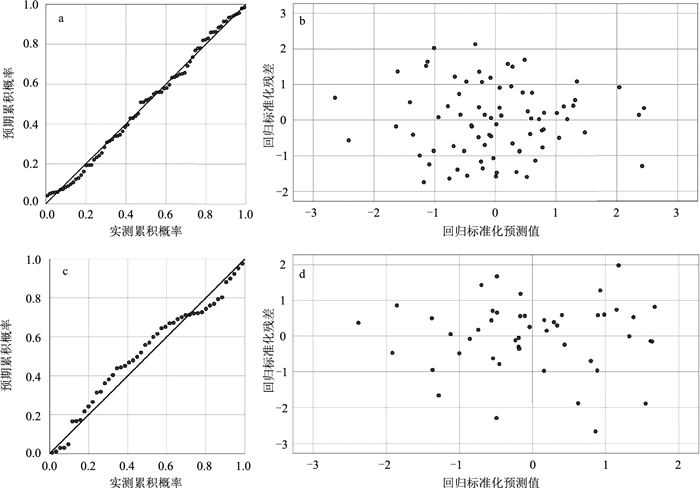
Table 4 Multiple regression analysis output
滑坡类型 模型参数 系数 标准差 显著性(P值) 降雨诱发 (常量) 0.286 0.286 0.000 a -0.128 0.047 0.008 b -0.006 0.002 0.005 c -0.016 0.005 0.004 地震诱发 (常量) 0.900 0.179 0.001 a -0.074 0.031 0.030 c -0.013 0.021 0.002 -
王家鼎, 张倬元.地震诱发高速黄土滑坡的机理研究[J].岩土工程学报, 1999, 21(6):670-674. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.1999.06.008 彭达, 杨顺, 李孝波.甘肃通渭县黄土地震滑坡分布特征及发育机理[J].中国地质灾害与防治学报, 2017, 28(3):31-38. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGDH201703005.htm 田尤, 杨为民, 黄晓, 等.天水市麦积区幅黄土滑坡发育分布特征及其孕灾因素分析[J].地质力学学报, 2016, 22(1):25-38. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2016.01.003 孟华君, 姜元俊, 张向营, 等.地震扰动区碎石土滑坡滑动能力分析及预测[J].人民长江, 2017, 48(14):45-49, 54. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-RIVE201714011.htm Budetta P, De Riso R.The mobility of some debris flows in pyroclastic deposits of the northwestern Campanian region(southern Italy)[J].Bull.Eng.Geol.Environ., 2004, 63:293-302. doi: 10.1007/s10064-004-0244-7
李秀珍, 孔纪名."5·12"汶川地震诱发滑坡的滑动距离预测[J].四川大学学报(工程科学版), 2010, 42(5):243-249. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SCLH201005037.htm Guo D, Masanori H, He C, et al.An empirical model for landslide travel distance prediction in Wenchuan earthquake area[J].Landslides, 2014, 11(2):281-291. doi: 10.1007/s10346-013-0444-y
Heim A.Bergsturz und Menschenleben[M].Zütich:Naturforschenden Gesellschaft, 1932.
Scheidegger A E.On the prediction of the reach and velocity of catastrophic landslides[J].Rock Mechanics, 1973, 5(4):231-236. doi: 10.1007/BF01301796
张克亮.贵州江口县土司城滑坡成因分析及滑距预测[J].中国地质灾害与防治学报, 2016, 27(3):29-33. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGDH201603005.htm 孙即超, 王光谦, 董希斌, 等.膨胀土膨胀模型及其反演[J].岩土力学, 2007, 28(10):2055-2059. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2007.10.009 吴钟腾.基于运动学原理的滑坡运动距离预测方法研究[C]//中国地质学会工程地质专业委员会.2016年全国工程地质学术年会论文集, 2016: 690-697. Sassa K, Fukuoka H, Wang G H, Naohide Ishikawa.Undrained dynamic-loading ring-shear apparatus and its application to landslide dynamics[J].Landslides, 2004, 1(1):7-19. doi: 10.1007/s10346-003-0004-y
江晓禹, 乔建平.典型滑坡危险性的接触力学预测模型[J].工程力学, 2006, 23(8):106-109. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4750.2006.08.020 Hungr O.A model for the runout analysis of rapid flow slides, debris flows, and Avalanches[J].Canadian Geotechnical Journal, 1995, 32:610-623. doi: 10.1139/t95-063
Yoichi O, Hikaru K, Toshiaki S.The effects of rock fall volume on run out distance[J].Engineering Geology, 2000, 58:109-124. doi: 10.1016/S0013-7952(00)00049-1
刘悦, 黄强兵.一种黄土滑坡滑距预测模型[J].灾害学, 2001, (3):7-12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4574.2001.03.002 王鼐, 王兰民, 王谦, 等.黄土高原地震作用下黄土滑坡滑距预测方法[J].地震工程学报, 2016, 38(4):533-540. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0844.2016.04.0533 殷坤龙, 晏同珍.滑坡预测及相关模型[J].岩石力学与工程学报, 1996, (1):1-8. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.1996.01.001 Wang L, Wang N, Wang Q.Prediction of sliding distance of seismic landslides in Loess Plateau, China[J].Japanese Geotechnical Society, 2016, 32(2):1177-1182. http://ci.nii.ac.jp/naid/130005124016
翟张辉.天水市大沟滑坡-泥石流运动过程模拟分析[C]//中国地质学会、中国地质学会工程地质专业委员会.2017年全国工程地质学术年会论文集, 2017: 408-414. 王念秦, 张倬元, 王家鼎.一种典型黄土滑坡的滑距预测方法[J].西北大学学报(自然科学版), 2003, (1):111-114. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-274X.2003.01.030 孟华君, 姜元俊, 张树轩, 等.汶川地震前后都江堰山区滑坡滑动距离影响因素变化分析[J].地质力学学报, 2017, 23(6):904-913. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLX201706011.htm 黄发明, 殷坤龙, 蒋水华, 等.基于聚类分析和支持向量机的滑坡易发性评价[J].岩石力学与工程学报, 2018, 37(1):156-176. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX201801016.htm 樊晓一, 乔建平, 韩萌, 等.灾难性地震和降雨滑坡的体积与运动距离研究[J].岩土力学, 2012, 33(10):3051-3058. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX201210030.htm 樊晓一, 冷晓玉, 段晓冬.坡脚型与偏转型地震滑坡运动距离及地形因素作用[J].岩土力学, 2015, 36(5):1380-1388. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX201505022.htm 彭建兵, 吴迪, 段钊, 等.典型人类工程活动诱发黄土滑坡灾害特征与致灾机理[J].西南交通大学学报, 2016, 51(5):971-980. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2016.05.021 黄恒伟.云南昌宁"9·16"群发性浅层滑坡与植被关系研究[D].昆明理工大学硕士学位论文, 2017. 谭龙, 陈冠, 曾润强, 等.人工神经网络在滑坡敏感性评价中的应用[J].兰州大学学报(自然科学版), 2014, 50(1):15-20. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LDZK201401003.htm 张茂省, 校培喜, 魏兴丽, 等.延安宝塔区滑坡崩塌地质灾害[M].北京:地质出版社, 2008:1-187. 谭楚琰.多元线性回归模型分析[J].现代商业, 2019, (2):161-162. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5889.2019.02.078 桑非凡, 宋孝玉.黄土高原沟壑区土壤水分入渗模型适用性探讨[J].灌溉排水学报, 2014, 33(S1):183-185. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GGPS2014S1054.htm




 下载:
下载: