Research on the characteristics of basement fold structure and SN-trending mineralization zone in the Yinkeng lead-zinc-silver orefield in Jiangxi
-
摘要:
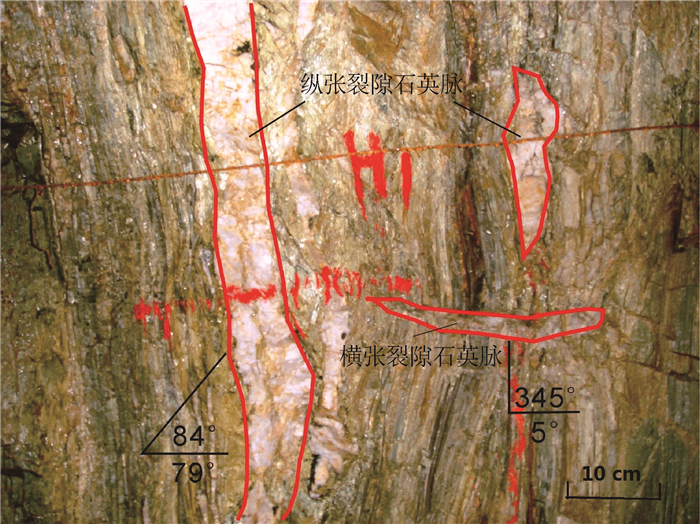
为了探究银坑铅锌银多金属矿田的构造特征和找矿潜力,选取区内基底复式褶皱作为研究区,开展野外调查和室内分析。揭示基底褶皱几何学和应力场特征并探讨对成矿的控制作用,重点研究褶皱作用晚期纵张断裂中的SN向交代充填石英矿脉的成矿特征。通过实测褶皱轴迹与两翼产状,分析其几何形态特征为:枢纽走向由北至南为NE→NNE→SN→NNW,翼间角范围为33°~52°,褶皱类型为紧闭陡立尖棱状褶皱。通过褶皱分析法与节理统计法,求得基底褶皱自加里东期至燕山期主应力方向变化为EW→NWW→NNW→NEE。基底地层早期受EW向挤压而形成SN向构造带与大量的SN向褶劈理带。应力场转换期间地层受到的应力由挤压向拉张转换,促进褶劈理带内形成SN向纵张裂隙,为后期NE向矿化提供空间。通过实测与观察,基底褶皱首次发现近SN向矿化石英矿脉充填于褶皱作用晚期的切层纵张和次级横张裂隙。含矿性分析显示,脉中铅、锌平均含量为0.133%和0.190%,金、银的平均含量0.127 g/t和15.33 g/t,具有较高的矿化特征。在桥子坑矿区地表和牛形坝矿区60、104和140中段新发现12条SN向矿脉,表明该区有巨大的成矿潜力。
Abstract:In order to explore the structural characteristics and prospecting potential of the Yinkeng lead-zinc-silver polymetallic orefield, the authors selected the basement folds in this area as the research area to conduct field investigation and indoor analysis and reveal the basement fold geometry and stress field characteristics. The focus was on the mineralization characteristics of SN-trending metasomatic filling quartz veins, which are developed in the longitudinal tension faults formed in the late stage of folding. Through the actual measurement of the fold axis trace and the attitudes of the two wings, the geometric characteristics were summarized as follows: the direction of the hub is NE→NNE→SN→NNW from north to south, the angle between wings ranges from 33°to 52°, and the fold type is the closed, steep and sharp prismatic fold. Through the fold analysis method and the joint statistical method, the principal stress directions of the basement folds from the Caledonian to the Yanshanian were EW→NWW→NNW→NEE. The basement strata were squeezed in the EW direction in the early stage to form an SN-trending structural belt and a large number of SN-trending fold cleavage belts. During the transition of the stress field, the stress on the formation changed from compression to tension, which promoted the formation of SN-trending longitudinal fractures in the fold cleavage zone, and provided space for later NS-trending mineralization.Through actual measurement and observation, it is the first time to discover mineralized quartz veins in nearly SN direction in the basement fold. This quartz vein filled the longitudinal and secondary transverse tension fractures in the section at the late stage of folding. Mineralization analysis shows that the quartz vein has high mineralization characteristics. The average values of lead and zinc in mineralized quartz veins are 0.133% and 0.190%, and the average values of gold and silver are 0.127 g/t and 15.33 g/t. Twelve new SN-trending veins were discovered on the surface of the Qiaozikeng mining area and the 60, 104, and 140 level of the Niuxingba mining area, indicating that this area has huge metallogenic potential.
-
安徽滁州地区探明的铜、金矿床(点)较多,典型的有上成金矿、郭大洼金矿、马厂金矿、大庙山金矿、铜苟城金矿、琅琊山铜矿等,地质学和年代学研究表明,这些矿床在空间和时间上与早白垩世岩体有关[1-2],地球化学研究进一步显示这些岩体具有埃达克质岩石的特征,并与长江中下游含矿埃达克岩特征类似[2]。目前国内学者对埃达克质岩成因的认识仍存在分歧[3-27]。比如,埃达克质岩的形成可能来自地壳混染的玄武岩浆结晶分异作用[5, 16-17, 20];或是幔源岩浆和壳源岩浆的混合,并可能有来自古太平洋板块俯冲带来的混入端元成分的参与[25-26];再或者是俯冲洋壳的部分熔融[18-22, 27];依据比俯冲洋壳高的87Sr/86Sr值和低的143Nd/144Nd值,一些学者认为,埃达克质岩由拆沉或加厚古老下陆壳部分熔融而成[3-4, 6-15]。尽管关于埃达克质岩的成因存在不同认识,但是世界上大部分著名的铜-金矿床都与埃达克(质)岩有关[28-33],且埃达克岩或埃达克质岩对陆壳的演化、地幔橄榄岩的交代作用[28]也有潜在的重要性,因此,本文通对安徽滁州张八岭地区闪长质岩锆石U-Pb年代学和岩石地球化学特征的详细研究,提供研究区闪长质岩的准确年龄数据,分析其岩石成因,初步讨论动力学背景及其与铜、金等的成矿关系,更好地为该区铜、金多金属矿提供找矿依据。
1. 区域地质背景
研究区大地构造位置处于张八岭隆起构造带与扬子前陆褶冲带结合部位,经过多次构造变形,断裂构造发育,主要断裂为近南北向管店-马厂断裂和北东向黄栗树-庙集断裂,北部张八岭隆起构造带出露的主要地层为新元古代北将军组和西冷岩组,北将军组主要为千枚岩为主的副变质岩系;西冷岩组主要为变细碧-角斑岩夹变粉砂岩,岩石类型包括绢云千枚岩、石英绢云千枚岩、绢云石英片岩、含云母石英片岩等。东南部扬子前陆褶冲带主要出露震旦系—奥陶系。下震旦统岩性主要为砂岩、粉砂岩、粉砂质千枚岩,上震旦统岩性主要为灰岩夹砂岩、砂质千枚岩;寒武系主要岩性为碳酸盐岩,下部见炭质页岩、硅质页岩夹石煤层;奥陶系主要岩性为灰岩、大理岩。研究区岩浆活动较强烈,有管店岩体、瓦屋刘岩体、瓦屋薛岩体、马厂岩体及广泛分布的中酸性脉岩(图 1)。
2. 岩相学特征和样品描述
本次采集了安徽滁州地区张八岭隆起区和扬子前陆带出露的管店岩体、马厂岩体及马厂地区出露的脉岩。马厂岩体及马厂地区出露的脉岩(图版Ⅰ-a)呈北东向展布,本次以马厂闪长玢岩为定年及岩石地球化学研究对象。岩石主要矿物成分为斜长石和角闪石,同成分组成斑晶和基质,基质具显微晶质结构。斜长石斑晶呈板柱状,均径为1.00~2.00mm,最大2.50mm,常见环带结构,为更-中长石,有绢云母化。角闪石斑晶为柱状,横切面为菱形,见解理,均径为1.00~1.50mm,有绿泥石化、绿帘石化,一般为普通角闪石。基质为同成分显微晶质结构,分布较均匀(图版Ⅰ-c、d)。
管店岩体呈北北东向展布,主要岩性包括石英二长岩、二长岩、黑云母花岗岩、花岗闪长岩、闪长玢岩及细晶闪长岩,采集了管店岩体北部的闪长玢岩脉及细晶闪长岩(图版Ⅰ-b)作为岩石地球化学研究对象,闪长玢岩主要矿物成分为斜长石和角闪石,其次为黑云母、钾长石,含少量石英。斜长石为板柱状,斑晶最大9mm,基质斜长石一般为1.50~2.00mm,双晶纹较对称,偶见环带结构,为中长石。钾长石为他形粒状,有高岭土化,为正长石。石英呈填隙状,含量很少。角闪石呈浅绿色,半自形,为普通角闪石,有绿泥石化,析出磁铁矿和榍石。细晶闪长岩主要矿物成分为斜长石和角闪石,含少量磁铁矿。斜长石为柱状,聚片双晶较对称,偶见环带结构,以中长石为主,有绢云母化、钠长石化。角闪石为浅黄绿色,绿泥石化、绿帘石化明显,析出的磁铁矿分布于表面(图版Ⅰ-e、f)。
3. 分析方法
3.1 LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Th-Pb同位素
原岩样品破碎成粉末,经淘洗和磁选分离出锆石重砂样,在双目镜下挑选出锆石晶体,将待测锆石颗粒制成环氧树脂样品靶,打磨至大部分颗粒的中心暴露出来,用于拍摄透射光和反射光、阴极发光(CL)图像及U-Th-Pb同位素测试。LA-MCICP-MS锆石U-Th-Pb同位素测试在中国地质科学院矿产资源研究所MC-ICP-MS实验室完成,所用仪器为Finnigan Neptune型MC-ICP-MS及与之配套的Newwave UP 213激光剥蚀系统。激光剥蚀斑束直径为25μm,频率为10Hz,能量密度约为2.5J/cm2,以氦为载气。LA-MC-ICP-MS激光剥蚀采样采用单点剥蚀的方式,数据分析前用锆石GJ-1进行调试仪器,使之达到最优状态,锆石U-Pb定年以锆石GJ1为外标,U、Th含量以锆石M257为外标进行校正。测试过程中每测定10个样品前后重复测定2个锆石标准,对样品进行校正,并测量1个锆石标准Plesovice,观察仪器的状态以保证测试的精确度。数据处理采用ICPMSData⁃ Cal程序[34],测量过程中绝大多数分析点206Pb/204Pb>1000,未进行普通铅校正,204Pb由离子计数器检测,剔除可能受包体等普通Pb的影响204Pb含量异常高的分析点,锆石U-Pb谐和图用Isoplot 3.0程序获得。
3.2 岩石地球化学
本次工作全岩主量和微量元素分析在广州澳实矿物实验室完成。主量元素分析采用X-射线荧光光谱分析法(XRF法),首先称取0.6g干燥粉末样品,在高温条件下加热,除去挥发分并计算烧失量(LOI),然后加入适量的硼酸将样品高温熔融成玻璃片,然后在X-射线荧光光谱仪上测定氧化物的含量,分析精度优于5%。微量元素采用ICPMS(电感耦合等离子体质谱)分析方法。将约40mg样品酸溶(对中酸性岩)或碱溶(对基性岩)后测定微量元素的浓度,大部分元素的分析精度优于2%。
4. 分析结果
4.1 锆石U-Th-Pb同位素
安徽滁州地区闪长质岩中2个闪长玢岩定年样品的LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄数据列于表 1,锆石CL图像见图 2。大部分锆石是无色、透明的,半自形到自形,具有典型的岩浆成因锆石生长环带。Th和U含量变化范围较大(Th为2×10-6~719×10-6,U为46×10-6~531×10-6),Th/U值变化范围为0.24~ 2.42,绝大多数大于0.1,与岩浆成因锆石一致。样品160309-1共获得23个点的年龄,其中14个点的206Pb/238U年龄集中在124~129Ma之间,其年龄加权平均值为126.2±0.44Ma(MSWD=6.9),代表岩体的形成年龄(图 3);另外7个点的207Pb/206Pb年龄介于1976~2657Ma之间,锆石具有岩浆环带,且Th/U值大于0.1,也属于岩浆成因锆石,代表古元古代—太古宙继承锆石年龄。160309-2共测得19个点的年龄,年龄可分为2组,其中7个点的206Pb/238U年龄介于126~130Ma之间,给出的206Pb/238U年龄加权平均值为126.4±0.7Ma(MSWD=8.8),代表岩体的形成年龄;其余12个点的207Pb/206Pb年龄集中在2013~ 2569Ma之间,是继承锆石的年龄,其中2480~ 2569Ma之间8个点的207Pb/206Pb年龄加权平均值为2505±19Ma(图 3)。
表 1 LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Th-Pb同位素测定结果Table 1. Results of the LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Th-Pb dating样品 含量/10-6 Th/U 207Pb/206Pb 206Pb/238U 207Pb/206Pb 206Pb/238U Pb 232Th 238U 比值 1σ 比值 1σ 年龄/Ma 1σ 年龄/Ma 1σ 160309-1-1 13 350 576 0.61 0.0517 0.0019 0.0194 0.0002 272 92 124 2 160309-1-2 190 14 459 0.03 0.1638 0.0013 0.3711 0.0037 2415 186 2035 18 160309-1-3 7 180 273 0.66 0.0524 0.0021 0.0201 0.0002 128 103 128 2 160309-1-5 8 293 313 0.94 0.0514 0.0022 0.0212 0.0003 209 90 128 2 160309-1-6 115 96 228 0.42 0.1594 0.0015 0.4145 0.0029 2368 16 2234 13 160309-1-7 11 377 367 1.03 0.0545 0.0028 0.0224 0.0003 276 122 141 2 160309-1-8 33 75 47 1.60 0.1636 0.0019 0.4575 0.0046 2503 20 2414 20 160309-1-9 24 527 1060 0.50 0.0526 0.0009 0.0212 0.0002 172 44 125 1 160309-1-10 6 210 257 0.82 0.0514 0.0025 0.0292 0.0003 332 101 124 2 160309-1-12 11 185 485 0.38 0.0575 0.0017 0.0214 0.0003 169 84 128 2 160309-1-13 151 248 258 0.96 0.1636 0.0018 0.4242 0.0035 2454 19 2283 16 160309-1-14 52 613 254 2.42 0.0754 0.0011 0.1251 0.0011 787 36 730 6 160309-1-15 14 719 531 1.35 0.0578 0.0013 0.0213 0.0002 102 65 126 1 160309-1-16 13 344 546 0.63 0.0507 0.0016 0.0245 0.0002 232 68 126 1 160309-1-17 126 337 276 1.22 0.1202 0.0013 0.3125 0.0034 1976 14 1755 17 160309-1-18 186 183 306 0.60 0.1812 0.0023 0.4645 0.0045 2657 22 2444 20 160309-1-19 3 105 137 0.76 0.0528 0.0027 0.0234 0.0002 272 120 126 1 160309-1-20 44 72 133 0.54 0.1515 0.0019 0.2775 0.0059 2396 21 1541 3 160309-1-21 4 126 155 0.82 0.0543 0.0041 0.0214 0.0004 217 179 125 2 160309-1-22 5 170 181 0.94 0.0531 0.0038 0.0236 0.0003 183 167 125 2 160309-1-23 11 281 469 0.60 0.0502 0.0015 0.0218 0.0003 161 72 129 2 160309-1-24 3 82 153 0.53 0.0537 0.0038 0.0248 0.0003 376 156 124 2 160309-1-25 5 150 191 0.79 0.0524 0.0035 0.0256 0.0003 195 137 129 2 160309-2-1 373 178 735 0.24 0.1625 0.0014 0.4475 0.0045 2480 15 2345 20 160309-2-2 73 95 130 0.73 0.1643 0.0016 0.4328 0.0033 2486 16 2321 15 160309-2-3 21 24 61 0.40 0.1216 0.0032 0.2946 0.0027 2013 45 1660 13 160309-2-4 40 49 73 0.68 0.1528 0.0016 0.4428 0.0039 2367 17 2344 18 160309-2-5 3 71 124 0.57 0.0575 0.0036 0.0201 0.0004 233 168 128 2 160309-2-6 98 121 175 0.69 0.1656 0.0014 0.4426 0.0046 2502 14 2340 21 160309-2-7 2 46 78 0.59 0.0585 0.0062 0.0209 0.0006 309 277 130 4 160309-2-8 167 174 307 0.57 0.1736 0.0014 0.4345 0.0046 2532 13 2321 21 160309-2-9 242 274 398 0.69 0.1715 0.0015 0.4805 0.0049 2569 15 2522 21 160309-2-10 27 1329 986 1.35 0.0515 0.0015 0.0207 0.0002 217 48 126 1 160309-2-11 76 72 193 0.37 0.1225 0.0013 0.3445 0.0034 2014 18 1886 16 160309-2-13 98 102 182 0.56 0.1775 0.0017 0.4316 0.0043 2517 51 2324 20 160309-2-14 45 69 79 0.87 0.1636 0.0017 0.4318 0.0044 2505 18 2323 20 160309-2-15 9 323 359 0.90 0.0545 0.0039 0.0218 0.0004 187 174 127 2. 160309-2-16 97 66 244 0.27 0.1425 0.0018 0.3438 0.0052 2333 21 1902 25 160309-2-17 7 151 276 0.55 0.0558 0.0022 0.0236 0.0002 354 93 126 1 160309-2-18 3 97 103 0.94 0.0563 0.0044 0.0279 0.0004 317 189 128 2 160309-2-19 113 157 192 0.82 0.1779 0.0019 0.4346 0.0051 2514 20 2318 23 160309-2-20 2 61 91 0.68 0.0548 0.0045 0.0228 0.0006 250 202 127 4 4.2 岩石地球化学特征
安徽滁州地区闪长质岩主量、微量测试结果列于表 2。SiO2含量变化范围为56.75%~60.90%,均大于56%,符合洋壳来源埃达克质岩的特征[28],在TAS图解中,样品点基本全部落入二长岩区域内(图 4),属于高钾钙碱性系列(图 5)。CaO含量变化范围为2.97% ~5.85%,Al2O3含量变化范围为14.82% ~15.77%,Na2O含量变化范围为3.69% ~4.68%;K2O含量变化范围为2.64%~3.55%,Mg#值变化范围为39~45。在Harker图解中,Al2O3、CaO、Fe2O3及K2O表现出随SiO2含量增加而减少的趋势,这与岩浆演化过程中一些矿物的结晶分异作用有关,而Na2O与SiO2无明显的线性关系(图 6)。
表 2 岩石主量、微量和稀土元素组成Table 2. Composition of major, trace and rare earth elements in rocks样号 160309-2-1 160309-2-2 160309-2-3 160309-2-4 160309-2-5 160703-1 160703-2 160703-3 160729-5 160729-6 160729-7 160729-8 160729-1 160729-2 160729-3 160729-4 SiO2 59.46 59.23 58.71 58.48 58.95 56.98 56.75 56.91 60.38 60.68 60.66 60.90 59.14 59.35 59.58 59.69 Al2O3 15.44 15.40 15.22 15.06 15.32 15.77 15.66 15.70 14.82 14.88 14.88 14.87 14.98 14.99 14.94 14.86 CaO 2.97 3.27 4.37 4.40 3.23 5.85 5.76 5.44 4.04 3.85 3.69 3.84 5.68 5.36 5.34 5.09 TFe2O3 5.71 5.69 5.80 5.81 5.95 7.19 6.98 7.12 5.30 5.56 5.52 5.38 6.49 6.22 6.18 6.12 K2O 3.22 2.82 3.01 3.09 3.17 3.20 3.31 3.55 2.82 2.39 2.80 2.64 3.12 3.33 3.30 3.45 MgO 4.62 4.20 4.58 3.69 4.98 4.87 4.90 4.93 4.16 4.15 4.30 4.03 4.97 4.78 4.67 4.67 MnO 0.07 0.08 0.08 0.07 0.08 0.12 0.11 0.11 0.06 0.06 0.06 0.06 0.11 0.10 0.10 0.10 Na2O 3.88 4.68 3.75 3.92 4.10 3.86 3.93 3.69 4.09 4.21 4.11 4.26 3.76 3.77 3.77 3.74 P2O5 0.29 0.28 0.28 0.27 0.28 0.44 0.46 0.46 0.28 0.27 0.28 0.28 0.41 0.39 0.38 0.37 TiO2 0.58 0.58 0.55 0.56 0.57 0.81 0.82 0.79 0.68 0.68 0.69 0.68 0.74 0.73 0.73 0.73 烧失量 3.72 4.07 3.77 4.54 3.31 0.70 0.86 1.00 3.62 3.33 3.13 3.01 0.93 0.94 0.86 0.75 总计 99.96 99.98 99.98 99.89 99.94 99.79 99.54 99.70 99.98 99.97 99.96 99.95 99.89 99.96 99.85 99.57 Mg# 45 42 44 39 46 40 41 41 44 43 44 43 43 43 43 43 Rb 69.2 58.8 64.9 69.4 67.6 58.4 66.2 62.7 72.6 77.0 84.0 77.6 58.9 63.0 65.7 68.1 Ba 1320 1455 1455 2710 1315 2140 1915 2000 1535 1255 1425 1410 1995 2040 2010 2030 Th 4.85 4.60 4.73 4.85 4.73 4.83 5.44 4.47 7.54 7.59 7.82 7.84 6.20 7.20 8.20 7.20 U 2.91 1.90 1.53 1.52 2.57 1.35 1.92 1.29 1.74 1.99 1.84 1.80 1.80 2.00 2.10 1.90 Nb 6.0 5.8 5.8 5.7 5.8 6.8 7.1 6.7 8.0 8.1 8.3 8.2 8.2 8.4 9.0 9.10 Ta 0.5 0.5 0.5 0.4 0.4 0.5 0.5 0.5 0.5 0.5 0.5 0.5 0.6 0.6 0.7 0.70 Pb 17 15 13 11 16 20 25 18 8 9 8 7 21 25 20 26 Sr 871 831 1030 1050 864 1320 1270 1230 767 800 786 816 1045 967 977 968 Nd 18.6 17.9 21.9 20.7 20.5 27.7 27.8 27.0 28.8 29.4 27.1 30.0 29.5 29.5 29.4 29.8 Zr 146 135 140 137 137 191 177 178 189 195 201 195 165 199 201 218 Hf 3.60 3.3 3.6 3.4 3.5 4.8 4.4 4.4 4.6 4.7 4.9 4.8 4.2 5.1 4.8 5.6 Tb 0.32 0.31 0.38 0.36 0.35 0.51 0.51 0.50 0.46 0.46 0.46 0.48 0.60 0.50 0.50 0.60 Er 0.96 0.93 1.05 1.01 1.11 1.61 1.54 1.50 1.20 1.08 1.19 1.19 1.50 1.60 1.60 1.60 La 27.1 22.8 30.5 28.8 28.8 34.6 35.1 33.7 43.5 41.6 32.5 42.9 38.8 38.8 39.3 39.6 Ce 49.9 44.2 56.5 53.5 53.4 67.2 66.4 64.5 77.8 75.7 62.8 78.0 74.4 73.3 75.3 75.5 Pr 5.13 4.79 5.84 5.65 5.49 7.23 7.17 7.11 7.93 8.02 6.97 8.2 7.97 7.91 7.88 7.95 Nd 18.6 17.9 21.9 20.7 20.5 27.7 27.8 27 28.8 29.4 27.1 30 29.5 29.5 29.4 29.8 Sm 3.26 3.2 3.8 3.5 3.51 5.07 5 4.83 5 4.86 4.83 5.25 5.26 5.43 5.01 5.42 Eu 0.97 0.93 1.21 1.1 1.12 1.61 1.54 1.56 1.46 1.47 1.51 1.48 1.59 1.47 1.52 1.56 Gd 2.48 2.38 2.93 2.82 2.9 4.08 4.01 4.05 3.82 3.77 3.97 3.94 4.09 4.04 4.08 4.09 Tb 0.32 0.31 0.38 0.36 0.35 0.51 0.51 0.5 0.46 0.46 0.46 0.48 0.58 0.53 0.51 0.55 Dy 1.62 1.62 1.86 1.85 1.82 2.78 2.64 2.74 2.4 2.24 2.41 2.37 2.9 2.85 2.81 2.87 Ho 0.34 0.34 0.37 0.36 0.38 0.54 0.56 0.53 0.45 0.42 0.44 0.45 0.56 0.55 0.56 0.57 Er 0.96 0.93 1.05 1.01 1.11 1.61 1.54 1.5 1.2 1.08 1.19 1.19 1.51 1.55 1.59 1.61 Tm 0.15 0.15 0.16 0.15 0.15 0.21 0.21 0.21 0.16 0.15 0.16 0.16 0.21 0.23 0.22 0.23 Yb 0.81 0.79 0.99 0.9 0.95 1.25 1.24 1.33 0.85 0.83 0.91 0.94 1.33 1.32 1.26 1.39 Lu 0.13 0.13 0.14 0.13 0.13 0.19 0.18 0.18 0.13 0.12 0.13 0.12 0.2 0.21 0.2 0.21 Y 8.7 8.6 10.1 9.5 9.9 14.8 14.3 14.2 11.7 11.4 11.9 11.7 15.5 15.2 15.7 15.4 Sr/Y 100.1 96.6 102.0 110.5 87.3 89.2 88.8 86.6 65.6 70.2 66.1 69.7 67.4 63.6 62.2 62.9 δEu 1.00 0.99 1.07 1.04 1.04 1.05 1.02 1.05 0.98 1.01 1.02 0.95 1.01 0.92 1.00 0.97 注:Mg#=100×Mg2+/(Mg2++TFe2+); 主量元素含量单位为%,微量和稀土元素为10-6 稀土元素总量(ΣREE)为100.47×10-6~175.48×10-6,平均值为145.47×10-6。在稀土元素配分模式图上,各稀土元素配分曲线近一致,显示同源岩浆演化的特点(图 7)。(La/Yb)N值为18.18~36.71,变化范围较大,表明后期岩浆分异较强烈。稀土元素配分曲线明显右倾,强烈富集轻稀土元素,轻、重稀土元素分馏明显。轻稀土元素(LREE)的总量与ΣREE呈同消长,而重稀土元素总量变化小,表明岩体ΣREE的差别主要由LREE引起。δEu为0.95~1.11,几乎全部接近于1,说明Eu异常不明显,表明该岩体源区几乎没有斜长石的分离,暗示源区为榴辉岩或角闪榴辉岩,熔融的残留矿物为石榴子石和金红石,没有或很少有斜长石。在MORB标准化微量元素蛛网图上,富集Ba、U、Pb、Sr,亏损Nb、Ta和Ti(图 7)。
![]() 图 7 稀土元素配分曲线及微量元素蛛网图(标准化值据参考文献[35])Figure 7. Chondrite-normalized REE patterns and primitive mantle-normalized trace element spider diagram
图 7 稀土元素配分曲线及微量元素蛛网图(标准化值据参考文献[35])Figure 7. Chondrite-normalized REE patterns and primitive mantle-normalized trace element spider diagram5. 讨论
5.1 形成时代
本次研究获得的锆石U-Pb年龄为126Ma。李学明等[36]用U-Pb法获得张八岭隆起北段管店岩体的年龄为128Ma,牛漫兰[37]测得瓦屋刘、瓦屋薛岩体的黑云母40Ar/39Ar年龄分别为128.2Ma和120.1Ma,资峰等[38]测得管店岩体的U-Pb年龄为131.5 ± 1.6Ma;胡子龙[2]利用锆石U-Pb测得滁县岩体的年龄为121.8±1.9Ma和124.0±1.4Ma,马厂岩体的年龄为123.1±2.0Ma,上腰铺岩体的年龄为126.6±1.8Ma和123.4±1.9Ma。基于以上的定年数据,安徽滁州地区闪长质岩的侵位时代应为120~130Ma,为早白垩世。
5.2 岩石成因
安徽滁州地区闪长质岩地球化学特征显示,其具有高Al2O3、Sr、Sr/Y、La/Yb,低Y、Yb,Sr正异常的特征,富集轻稀土元素和大离子亲石元素(LILE),亏损高场强元素Nb、Ta、Ti,Eu异常不明显,与典型的埃达克质岩一致[28]。在Y-Sr/Y图解和Yb-La/Yb图解中,大部分样品点落入埃达克岩区域(图 8)。
埃达克岩最初指由俯冲洋壳熔融形成的一套具有特殊地球化学性质的中酸性岩石,如Eu弱负异常至正异常。随着对埃达克岩的深入研究,发现除俯冲洋壳模式外,一些其他的形成机制也可以产生具有埃达克岩地球化学特征的岩石(埃达克质岩),如增厚下地壳熔融、拆沉下地壳熔融、玄武质岩浆的地壳混染和低压分离结晶过程,以及岩浆混合作用等。安徽滁州地区埃达克质岩具有高Mg(3.69%~4.98%)的特征,在SiO2-MgO图解上落入俯冲洋壳熔融和拆沉下地壳熔融形成的埃达克岩的共同区域,但与长江下游埃达克质岩相比,具有较高的MgO含量(图 9)。
![]() 图 9 安徽滁州地区埃达克质岩的成因分类图解(长江中下游埃达克质岩数据参考文献[27])Figure 9. Petrogenetic diagrams of the adakitic rocks in Chuzhou area of Anhui
图 9 安徽滁州地区埃达克质岩的成因分类图解(长江中下游埃达克质岩数据参考文献[27])Figure 9. Petrogenetic diagrams of the adakitic rocks in Chuzhou area of Anhui另外,安徽滁州地区埃达克质岩K2O/Na2O值变化于0.57~0.96之间,平均值为0.75,明显低于大别造山带加厚下地壳埃达克岩[13, 39-40],安徽滁州地区埃达克质岩无论SiO2含量高还是低,均具有较高的Mg#值,变化范围为39~45,几乎全部大于40,高于玄武岩的实验熔体值[41],有效地排除了加厚下地壳部分熔融形成的埃达克质岩成因;安徽滁州地区埃达克质岩具有高Sr、Sr/Y及低Y的特点,但是Sr含量最高不过1270×10-6,Sr/Y值最高达110,属于高硅埃达克质岩,因此不属于与长英质板片熔体反应交代过橄榄岩地幔楔熔融形成的埃达克岩。此外,安徽滁州地区埃达克质岩具有不高的Cr和Ni含量, 也不支持橄榄岩与熔体相互作用成因的埃达克质岩。一般来说,陆壳Ce /Pb值为4~5[42-43],比洋壳(约24[35])低,安徽滁州地区埃达克质岩Ce /Pb值集中在3~5之间,少数较高,最高不超过10,明显低于洋壳。此外,受海水蚀变的洋壳更富集Sr,导致Sr/La值升高,安徽滁州地区埃达克质岩Sr/La值也明显低于洋壳,排除了俯冲洋壳部分熔融形成的埃达克质岩成因。区域上缺失与埃达克岩同期的基性岩及从基性岩、中基性岩到埃达克岩的一系列岩石组合,排除了玄武质岩浆分离结晶成因的埃达克质岩。由此认为,安徽滁州埃达克质侵入岩很可能由拆沉下地壳部分熔融形成,产生的埃达克质岩浆在上升过程中与地幔橄榄岩发生反应,导致熔体的MgO、Cr、Ni等含量增高。
5.3 动力学背景
现有研究认为,从早侏罗世开始,中国东部已逐渐变成与古太平洋俯冲有关的活动大陆边缘[44-45]。太平洋板块向欧亚大陆俯冲,大陆岩石圈地壳受挤压增厚,地壳玄武岩向榴辉岩转变,密度增大,为后期下地壳的拆沉提供了必要的先决条件。直到早白垩世中期,太平洋板块向欧亚大陆俯冲方向发生急剧变化,由北向南西俯冲,中国东部地壳构造背景经历了重大转变,开始伸展减薄,区域内重要断裂重新活化,下地壳发生拆沉,岩石圈地幔和拆沉下地壳进入下伏软流圈参与地幔循环,并发生部分熔融产生埃达克质岩浆,这些岩浆在上升过程中受到地幔物质不同程度的混染,使岩浆的MgO含量、Mg#值及相容元素含量明显升高,最终沿伸展激活的断裂带侵位形成安徽滁州地区的高镁埃达克质岩,从而形成与断裂走向一致的平面展布特征。
5.4 铜、金成矿指示意义
世界范围内,铜、金矿床与埃达克质岩有密切关系,埃达克质岩可作为铜、金的找矿标志[28-33]。安徽滁州地区埃达克质岩与成矿也有密切的联系,管店岩体内部的郭大洼金矿、岩体外接触带的上成金矿及南部马厂大庙山、龙王尖金矿均与埃达克质岩密切相关。
长江中下游是目前中国最重要的铜、金成矿区之一,从鄂东—九瑞到安庆—铜陵地区,埃达克质岩形成于140~145Ma,是由俯冲洋壳部分熔融形成的[27],洋壳部分熔融来源的岩浆具有偏高的Cu含量[22]。俯冲进入地幔的洋壳,由于本身携带大量水、物质和具有较高的氧逸度,形成高氧逸度和富水的溶体,富含Cu、Au等成矿物质的溶体在快速上升到地壳浅处时,由于温度的降低和压力的释放有利于成矿[12-13]。此外,由于氧逸度降低,上升至地表浅处的岩浆也可能导致Cu、Au等成矿物质从溶体中释放而成矿[43]。与之不同的是,安徽滁州地区埃达克质岩是由拆沉下地壳部分熔融形成的,也有地幔物质的参与,地幔物质带来部分Cu、Au等成矿元素,从成矿规模看,远小于长江中下游地区,但是,埃达克质岩依然可作为该地区Cu、Au矿床的找矿标志。
6. 结论
(1)安徽滁州地区闪长质岩形成年龄为120~130Ma。具有高Al2O3、MgO、Sr、Sr/Y、La/Yb,低Y、Yb的特征,同时富集轻稀土元素和大离子亲石元素,亏损高场强元素Nb、Ta、Ti,Eu异常不明显,与典型的埃达克质岩一致。岩石地球化学研究结果表明,该地区埃达克质岩是由拆沉下地壳部分熔融形成的,并在上升过程中与地幔橄榄岩发生了反应。
(2)早白垩世中期太平洋板块俯冲转向,中国东部的地壳伸展减薄导致下地壳拆沉,使研究区埃达克质岩沿断裂上升侵位,平面展布与区域上断裂走向一致。
(3)安徽滁州地区埃达克质岩区别于长江中下游俯冲洋壳成因的埃达克质岩,但也有地幔物质的参与,带来Cu、Au等成矿元素,成矿规模小于长江中下游地区,但依然可作为该地区铜、金矿床的找矿标志。
致谢: 在此祝贺尊敬的吕古贤研究员70华诞,感谢老师多年的教诲,衷心祝愿老师身体健康,向您为地质事业做出的卓越贡献致敬;感谢同门王殿良、韩璐、罗毅甜和袁月蕾在银坑期间的指导与帮助;感谢审稿专家提出的建设性意见和建议。 -
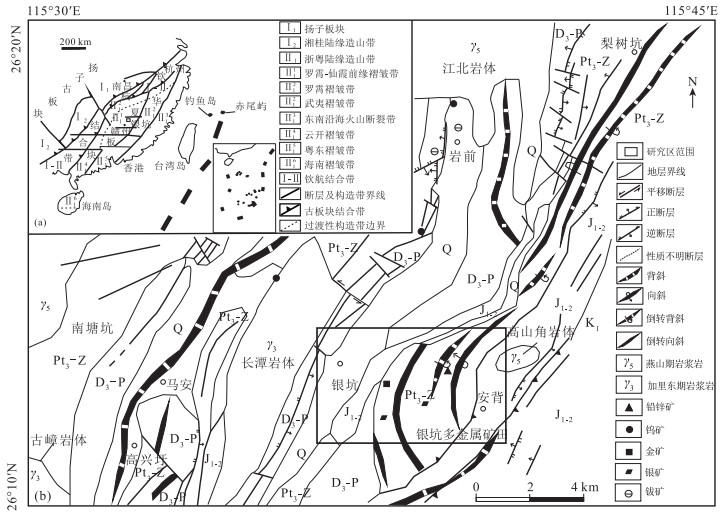
图 1 江西银坑矿田构造位置图(a)及研究区地质简图(b)(底图据参考文献[9])
Q—第四系;K1—下白垩统;J1-2—中-下侏罗统;D3-P—上泥盆统-二叠系;Pt3-Z—青白口系-震旦系;γ5—燕山期岩浆岩;γ3—加里东期岩浆岩
Figure 1. Regional geological map of Yinkeng area, Jiangxi
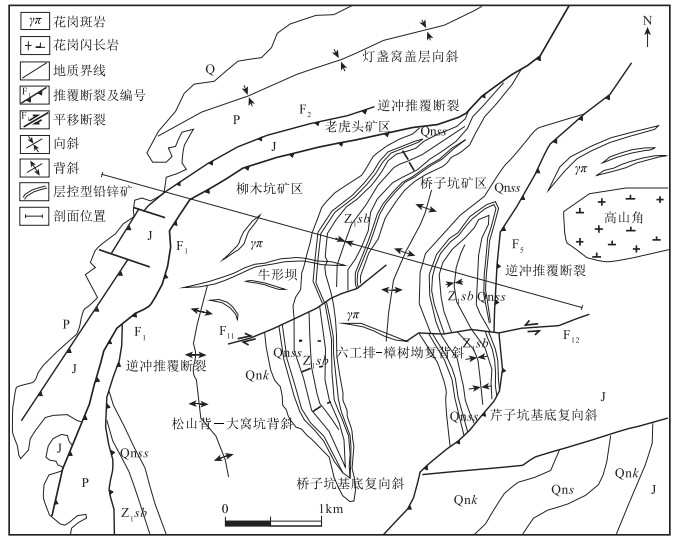
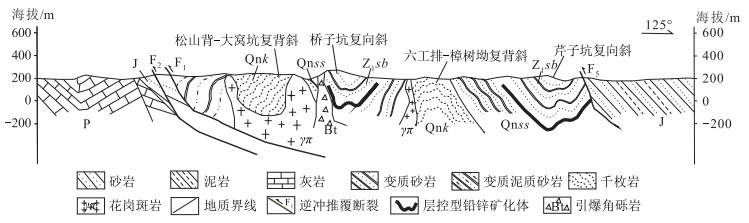
图 2 江西银坑铅锌银矿田构造简图(底图据参考文献[9])
Q—第四系;J—侏罗系;P—二叠系;Z1sb—下震旦统沙坝黄组;Qnss—青白口系上施组;Qnk—青白口系库里组
Figure 2. Structural map of the Yinkeng lead-zinc-silver orefield in Jiangxi
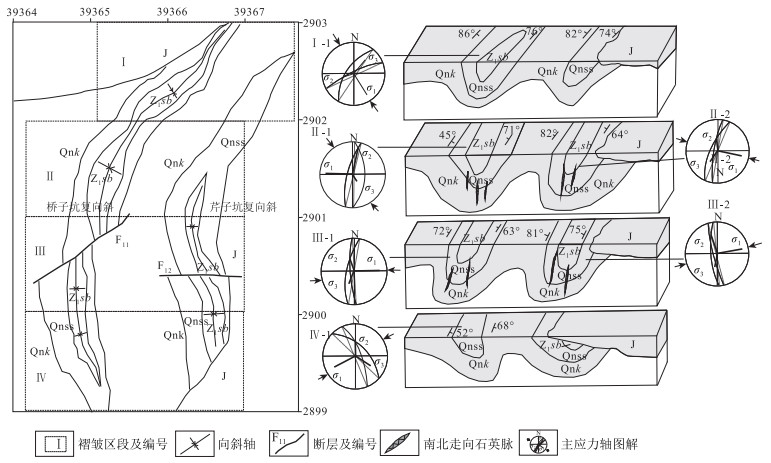
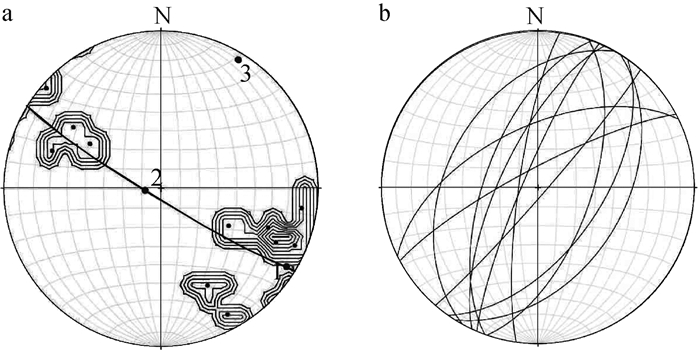
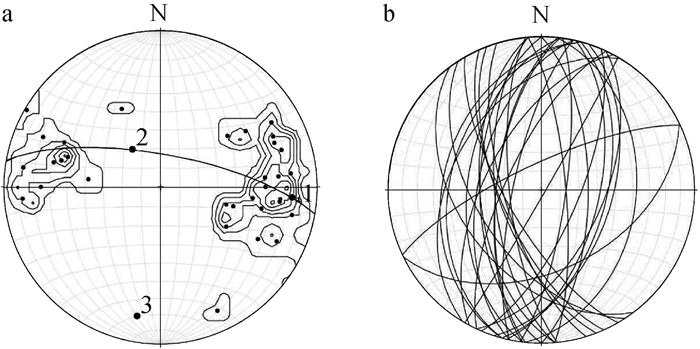
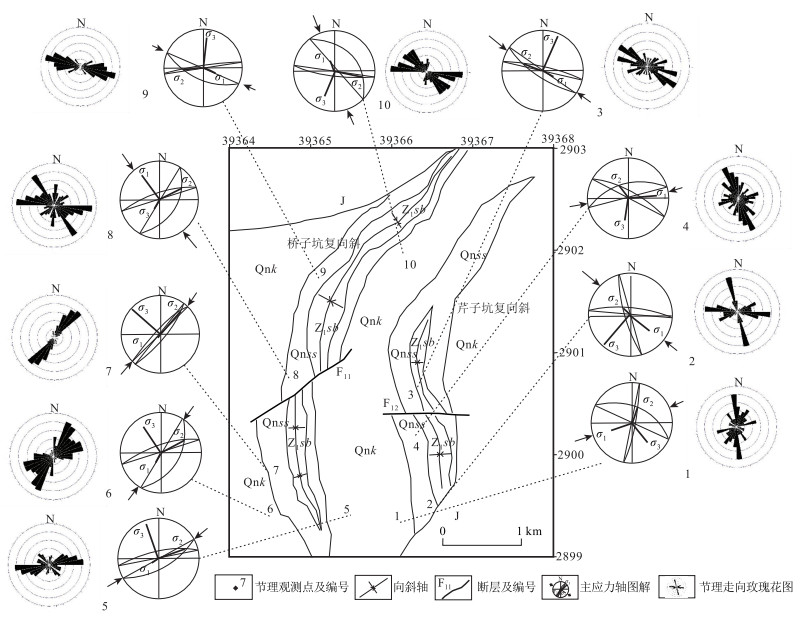
图 4 银坑矿田基底褶皱几何形态及应力场分布图(地层代号注释同图 2)
Figure 4. The fold geometry and stress field distribution of the basement of the Yinkeng orefield
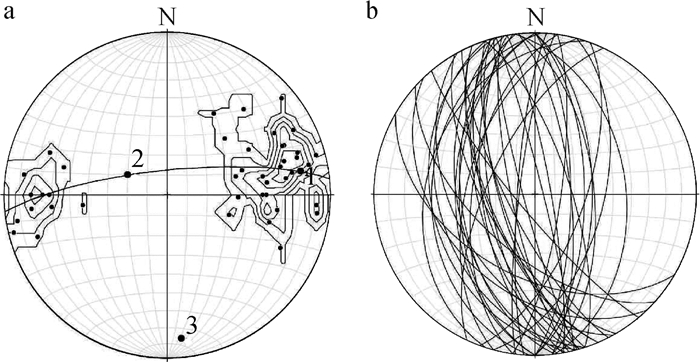
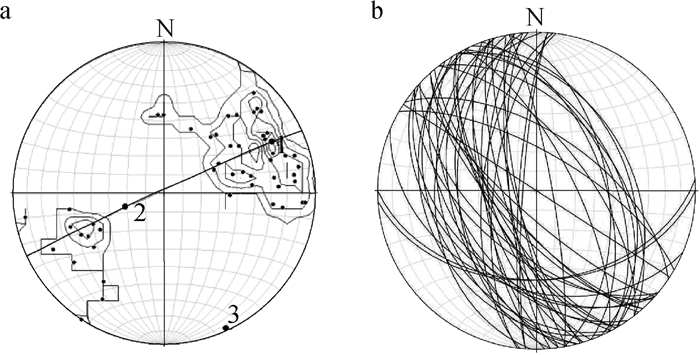
图 10 银坑矿田基底褶皱应力场分布图(地层代号注释同图 2)
Figure 10. Distribution of stress field of basement folds in the Yinkeng orefield
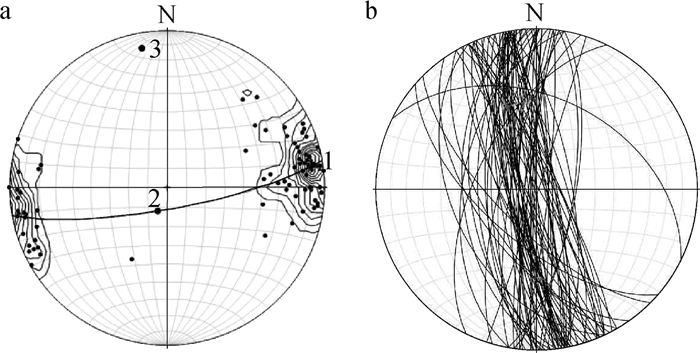
表 1 桥子坑-芹子坑复式向斜构造产状及应力方向数据
Table 1 Data of attitude and stress direction of Qiaozikeng-Qinzikeng compound syncline structure
区段
编号位置 产状
数量两翼岩层的优选产状 枢纽产状 轴面产状 点应力状态 东翼 西翼 σ1 σ2 σ3 Ⅰ-1 桥子坑复向斜 13 151°∠44° 313°∠51° 32°∠6° 326°∠82° 147°∠17 ° 256°∠54 ° 39°∠37° Ⅱ-1 桥子坑复向斜 32 287°∠45° 96°∠55° 183°∠11° 104°∠84° 279°∠8°、 12°∠6 °、 135°∠74° Ⅱ-2 芹子坑复向斜 11 272°∠52° 83°∠57° 182°∠11° 271°∠85°。 101°∠12 ° 4°∠31° 216°∠41° Ⅲ-1 桥子坑复向斜 43 266°∠41° 75°∠53° 174°∠12° 261°∠86°。 92°∠18 ° 351°∠36° 208°∠44° Ⅲ-2 芹子坑复向斜 88 233°∠74° 95°∠76° 345°∠12° 252°∠86° 85°∠10 ° 337°∠36° 182°∠51° Ⅳ-1 桥子坑复向斜 50 244°∠45° 66°∠52° 155°∠6° 66°∠78° 244°∠27 ° 351°∠36 ° 117°∠38° 注:测试精度为1°,误差为5° 表 2 银坑矿田基底褶皱节理统计数据
Table 2 Statistical data of basement fold joints in the Yinkeng orefield
点号 位置 构造归属 地层及岩性 节理
条数共轭剪节理产状 主应力轴方向 S1 S2 σ1 σ3 1 八公排南 芹子坑复向斜南部西翼 Qnk变质凝灰质砂岩 66 101°∠79° 25°∠46° 141°∠24° 253°∠31° 2 五公坑南 芹子坑复向斜南部中部 Qnk变质砂岩 191 252°∠74° 6°∠74° 129°∠25° 220°∠1° 3 樟树坳东 芹子坑复向斜南部中部 Qnss变质沉凝灰岩 178 11°∠79° 214°∠71° 120°∠55° 21°∠6° 4 樟树坳东 芹子坑复向斜南部西翼 Qnss变质凝灰质砂岩 172 343°∠52° 28°∠71° 84°∠21° 186°∠29° 5 秀坑北东 桥子坑复向斜南部西翼 Qnk粉砂岩 163 347°∠71° 150°∠61° 233°∠69° 342°∠7° 6 茶背东 桥子坑复向斜南部西翼 Qnk砂质、粉砂质板岩 177 340°∠69° 121°∠40° 206°∠60° 324°∠14° 7 大山排东南 桥子坑复向斜南部西翼 Qnss板岩 168 313°∠77° 127°∠71° 210°∠76° 311°∠2° 8 大山西 桥子坑复向斜南部西翼 Qnss板岩 158 92°∠72° 139°∠75° 205°∠4° 295°∠16° 9 松山背东 桥子坑复向斜北部西翼 Qnk变质凝灰质粉砂岩 170 350°∠83° 203°∠54° 115°∠51° 8°∠14° 10 桥子坑东 桥子坑复向斜北部东翼 Qnk凝灰质板岩 158 186°∠76° 48°∠30° 338°∠57° 201°∠24° 注:测试精度为1°,误差为5°;表中地层代号注释同图 2 表 3 银坑矿田桥子坑矿区SN向矿化石英脉主要成矿元素含量
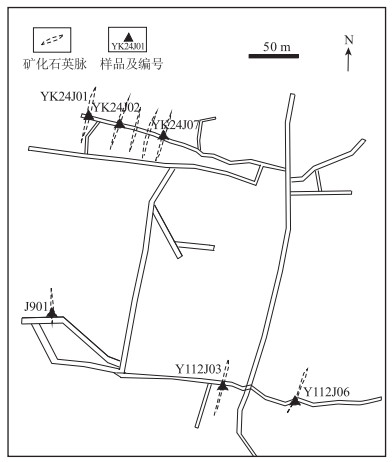
Table 3 Content of main metallogenic elements in the Qiaozikeng mining area, Yinkeng orefield
10-6 元素 YK24J01 YK24J02 YK24J07 J901 Y112J03 Y112J06 地壳
丰度[30]Pb 93.60 6890.00 25.60 40.00 842.00 46.60 12.50 Zn 788.00 >10000 169.00 142.00 115.00 39.00 70.00 Ag 2.77 7.33 0.29 2.53 78.40 0.54 0.07 Au 0.02 0.28 0.02 0.05 0.41 <0.005 0.00 Cu 231.00 226.00 109.50 55.50 448.00 6.10 60.00 W 37.80 2.20 5.50 1.80 0.80 1.10 1.25 Mn 1800.00 425.00 2070.00 2930.00 4850.00 850.00 950.00 Mo 1.56 1.62 1.34 11.60 1.60 2.84 1.20 Sb 1.43 4.21 0.83 1.19 2.59 0.35 0.20 注:样品由澳实分析检测(广州)有限公司测定,Au分析方法为火试金法,其他为质谱/光谱仪 -
张家菁.赣南东部银坑矿田控矿因素及找矿方向浅析[J].江西地质, 1997, (4):23-29. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CJFD&filename=JXDZ704.003 梅勇文.江西南部推(滑)覆构造系统研究[J].江西地质, 1997, (3):52-60. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-JXDZ703.008.htm 高贵荣, 林长仔.于都县银坑矿田F_1断裂特征及其控矿作用[J].江西地质, 2000, (1):49-53. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical_jxdz200001009.aspx 陈毓川, 裴荣富, 王登红.三论矿床的成矿系列问题[J].地质学报, 2006, (10):1501-1508. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/periodical/dizhixb200610003 陈毓川, 王登红, 徐志刚, 等.对中国成矿体系的初步探讨[J].矿床地质, 2006, (2):155-163. http://www.cqvip.com/Main/Detail.aspx?id=21785749 吕古贤, 曹钟清, 郭涛, 等.长江中下游中生代构造岩相体系分布与成矿规律——新华夏构造体系的"长江式"构造研究[J].大地构造与成矿学, 2011, 35, (4):495-501. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DGYK201104005.htm 吕古贤.构造物理化学基本问题与金矿成矿预测[J].地球学报, 1998, (2):3-5. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DQXB802.001.htm 吕古贤.关于矿田地质学的初步探讨[J].地质通报, 2011, 30(04):478-486. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20110403&flag=1 施明兴, 高贵荣.江西于都银坑矿田银金铅锌矿床地质特征[J].资源调查与环境, 2006, (2):164-172. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hsdzykc200602014 Carter, Andrew, Roques, et al.Understanding Mesozoic accretion in Southeast Asia:Significance of Triassic thermotectonism[J].Geology, 2001, 29:211-214. doi: 10.1021/jo00039a051
Mao J R, Li Z L, Zhao X L, et al.Geochemical characteristics, cooling history and mineralization significance ofZhangtiantang pluton in South Jiangxi Province, P.R.China[J].Chinese Journal of Geochemistry, 2010, 29:53-64. http://search.ebscohost.com/login.aspx?direct=true&db=aph&AN=47374442&site=ehost-live
Wang Y J, Fan W M, Guo F, et al.U-Pb dating of Mesozoic granodioritic intrusions in southeastern Hunan Province and its petrogenetic implication[J].Science in China, 2001, 45:271-280. http://ci.nii.ac.jp/naid/10011476749
Zeng Q T, Mao J R, Chen R, et al.Chronology and cooling history of the Tianmenshan pluton in South Jiangxi Province and their geological significance[J].Chinese Journal of Geochemistry, 2008, 27:276-284. doi: 10.1007/s11631-008-0276-y
毛景文, 陈懋弘, 袁顺达, 等.华南地区钦杭成矿带地质特征和矿床时空分布规律[J].地质学报, 2011, 85(5):636-658. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DZXE201105006.htm 毛景文, 谢桂青, 郭春丽, 等.南岭地区大规模钨锡多金属成矿作用:成矿时限及地球动力学背景[J].岩石学报, 2007, (10):2329-2338. http://www.oalib.com/paper/1472704 舒良树, 周新民, 邓平, 等.南岭构造带的基本地质特征[J].地质论评, 2006, (2):251-265. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DZLP200602017.htm 赵正, 陈毓川, 陈郑辉, 等.赣南银坑矿田高山角花岗闪长岩SHRIMP U-Pb定年及其与成矿的关系[J].岩矿测试, 2012, 31(3):536-542. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ykcs201203029 翟裕生.成矿构造研究的回顾和展望[J].地质论评, 2002, (2):140-146. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/91067X/200202/6165205.html 刘如琦, 张宝华, 蔡一廷.圆锥状褶皱的几何分析[J].地质科学, 1985, (2):113-124. http://www.cnki.com.cn/article/cjfdtotal-dzkx198502001.htm 苗培森.五台山西部变质岩系中圆锥状褶皱的分析[J].中国区域地质, 1991, (1):17-24. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-ZQYD199101002.htm 钱光谟.褶皱构造几何学研究[J].中国矿业学院学报, 1988, (2):72-79. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-ZGKD198802008.htm 翟裕生, 林新多.矿田构造学[M].北京:地质出版社, 1993:2-54. 万天丰.构造应力场研究及其在区域地质调查工作中的意义[J].中国区域地质, 1984, (2):83-88. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-ZQYD198402009.htm 陈正乐, 杨农, 王平安, 等.江西临川地区相山铀矿田构造应力场分析[J].地质通报, 2011, 30(4):514-531. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20110407&flag=1 张长厚, 吴淦国, 徐德斌, 等.燕山板内造山带中段中生代构造格局与构造演化[J].地质通报, 2004, 23(2/3):864-875. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=200409157&flag=1 吴淦国, 吕承训.矿田构造的研究历史、现状与发展[J].地质通报, 2011, 30(4):461-468. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20110401&flag=1 吴淦国.矿田构造与成矿预测[J].地质力学学报, 1998, (2):3-5. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DZLX802.000.htm 杨开庆.动力成岩成矿理论的研究内容和方向[J].中国地质科学院地质力学研究所文集, 1986, (1):1-15. http://search.cnki.net/down/default.aspx?filename=DZLY198601003&dbcode=CJFD&year=1986&dflag=pdfdown 杨兴科, 晁会霞, 吕古贤, 等.金属矿田构造类型划分与找矿预测思路分析[J].矿物学报, 2011, 31(S1):897-898. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/95783X/2011S1/1003573637.html Taylor S R. Abundance of chemical elements in the continental crust:a new table[J].Geochimica Et Cosmochimica Acta, 1964, 28(8):1273-1285. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0016703764901292




 下载:
下载: