LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb age of A-type granite from the Shibanjing area of middle Beishan orogenic belt, Inner Mongolia, and its constraint on closure time of Beishan Ocean
-
摘要:
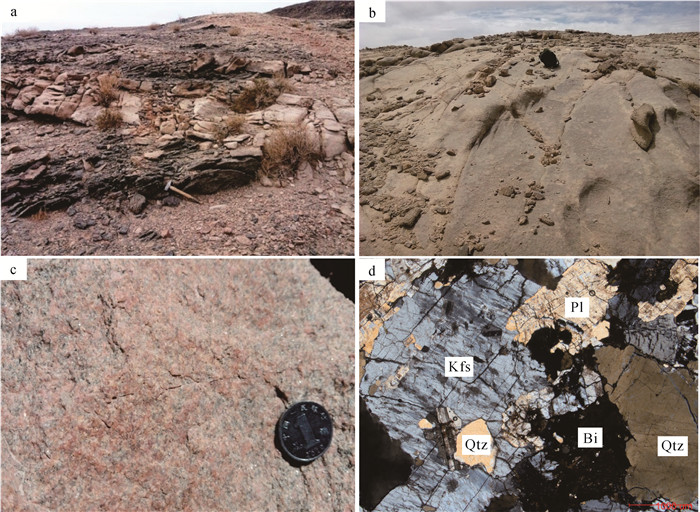
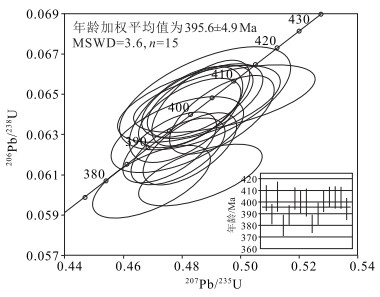
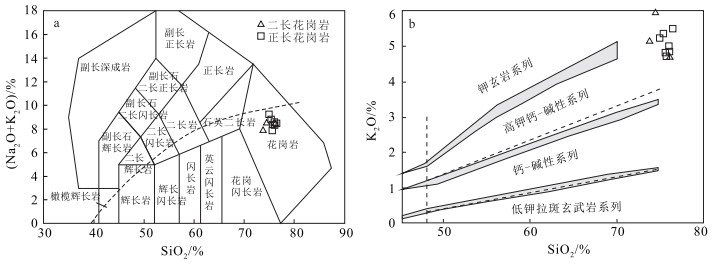
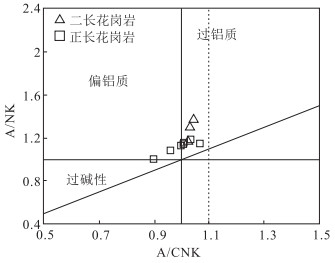
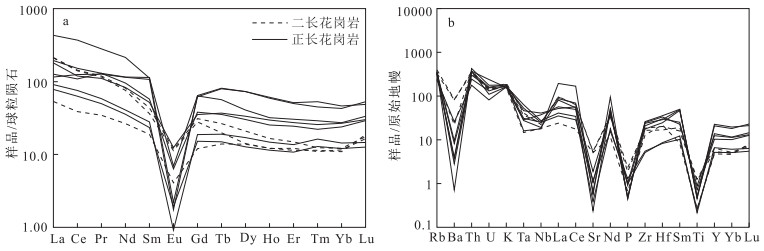
石板井A型花岗岩体位于内蒙古北山造山带中段,岩性组成以正长花岗岩为主,二长花岗岩次之。LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb测年获得该岩体的侵位年龄为395.6±4.9 Ma(MSWD=3.6,n=15),时代为早泥盆世。岩石属偏铝-弱过铝质高钾钙碱性系列,具有高硅(SiO2=72.71%~76.43%),富碱(K2O+Na2O=7.80%~9.23%),低铝(Al2O3=12.09%~13.73%),贫镁(MgO=0.06%~0.51%)和钙(CaO=0.44%~1.69%),K2O>Na2O的特点;稀土元素配分曲线呈轻稀土元素富集的右倾型,形态呈"海鸥式"分布,Eu强烈亏损(δEu=0.02~0.35,平均0.16);富集高场强元素Zr、Hf、U、Th和大离子亲石元素Rb、K等,而元素P、Ti、Ba、Sr明显亏损。上述地球化学特征指示该岩体属A型花岗岩,源于下地壳在高温条件下部分熔融及其后长石、磷灰石、榍石等的分离结晶。构造判别图解指示具有A2型花岗岩的特征,形成于后碰撞伸展构造环境,指示牛圈子-洗肠井蛇绿岩带所代表的北山洋闭合时限在早泥盆世之前,早泥盆世该区的构造已由挤压体制转变为伸展体制。
Abstract:The Shibanjing A-type granite intrusion is located in the middle section of the Beishan orogenic belt of Inner Mongolia.Its lithologic composition is dominated by syenogranites, followed by monzogranite.The age of the granite obtained by LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb dating is 395.6±4.9 Ma(MSWD=3.6, n=15), suggesting Early Devonian.The rocks belong to the meta-aluminium-weak peraluminous high potassium calc-alkaline series and are characterized by high silicon(SiO2=72.71%~76.43%), rich alkali(K2O+Na2O=7.80%~9.23%), low aluminum(Al2O3=12.09%~13.73%), poor magnesium(MgO=0.06%~0.51%), calcium(CaO=0.44%~1.69%)and K2O > Na2O.The chondrite-normalized REE patterns of the granite belong to the "seagull" pattern of the right-type, with significant negative Eu anomalies(δ Eu=0.02~0.35, averaging 0.16).The granitic rocks are enriched in high field strength elements(e.g., Zr, Hf, U and Th)and large ion lithophile elements(e.g., K and Rb)but depleted in P, Ti, Ba, Sr.All these characteristics resemble features of A-type granites which originated from the partial melting of lower crust under high temperature conditions and the subsequent fractional crystallization of feldspar, apatite, titanite and some other rocks.The tectonic discriminant diagram indicates that it has the characteristics of A2 granite, which was formed in the post-collision extension tectonic environment, indicating that the closure time of the Beishan Ocean represented by the Niuquanzi-Xichangjing ophiolite belt was prior to the Early Devonian, and that the structure of the area in the Early Devonian had changed from a compressional system to an extensional system.
-
Keywords:
- Beishan orogenic belt /
- A-type granite /
- zircon U-Pb dating /
- post-collision /
- Beishan Ocean
-
致谢: 中国地质调查局天津地质调查中心王惠初研究员、张永高级工程师等在工作过程中给予了大力支持;在野外工作中得到河北省区域地质调查院魏文通高级工程师的帮助;评审专家对文章提出了诸多宝贵意见,在此一并表示衷心感谢。
-
图 6 石板井地区正长花岗岩和二长花岗岩A/CNK-A/NK图解(底图据参考文献[24])
Figure 6. A/CNK-A/NK diagram of syenogranite and monzogranite in Shibanjing area
图 7 石板井地区正长花岗岩、二长花岗岩稀土元素球粒陨石标准化配分图(a)和微量元素原始地幔标准化蛛网图(b)(标准化值据参考文献[25])
Figure 7. Chondrite-normalized REE patterns(a)and primitive-mantle normalized spider diagrams(b)of syenogranite and monzogranite in Shibanjing area
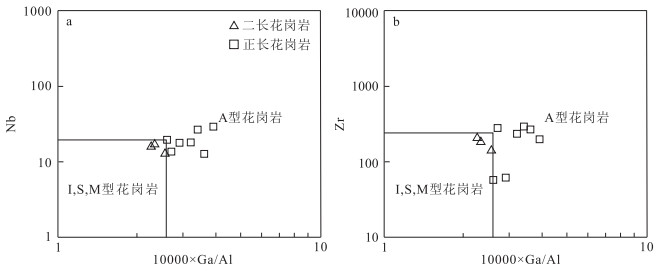
图 8 石板井二长花岗岩、正长花岗岩10000×Ga/Al-Nb(a)和10000×Ga/Al-Zr图解(b)(底图据参考文献[31])
Figure 8. 10000×Ga/Al-Nb(a) and 10000×Ga/Al-Zr(b) diagram of syenogranite and monzogranite in Shibanjing area
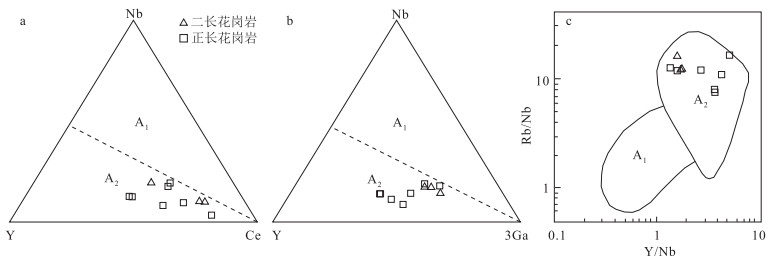
图 9 石板井二长花岗岩、正长花岗岩Nb-Y-Ce(a)、Nb-Y-Ce(b)和Y/Nb-Rb/Nb(c)图解(底图据参考文献[36])
Figure 9. Nb-Y-Ce(a), Nb-Y-Ce(b) and Y/Nb-Rb/Nb(c) diagrams of syenogranite and monzogranite in Shibanjing area
表 1 石板井地区二长花岗岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Th-Pb同位素分析结果
Table 1 LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Th-Pb data for the monzogranite in Shibanjing area
样品号 含量/10-6 同位素比值 年龄/Ma Pb U 206Pb/
238U1σ 207Pb/
235U1σ 207Pb/
206Pb1σ 208Pb/
232Th1σ 232Th/
238U1σ 206Pb/
238U1σ 207Pb/
235U1σ 207Pb/
206Pb1σ 1 424 6666 0.0646 0.0009 0.4864 0.0068 0.0546 0.0008 0.0235 0.0009 0.222 0.001 403 6 402 6 397 31 2 83 976 0.0623 0.0007 0.4828 0.0066 0.0562 0.0008 0.0369 0.0013 0.856 0.006 390 4 400 5 460 32 3 33 403 0.0648 0.0010 0.4878 0.0120 0.0546 0.0019 0.0231 0.0011 1.101 0.008 405 6 403 10 396 77 4 191 2523 0.0607 0.0007 0.4696 0.0081 0.0561 0.0007 0.0592 0.0017 0.395 0.010 380 5 391 7 458 28 5 48 612 0.0622 0.0007 0.4788 0.0066 0.0558 0.0007 0.0417 0.0011 0.572 0.006 389 4 397 5 446 27 6 70 888 0.0646 0.0008 0.4857 0.0113 0.0546 0.0016 0.0216 0.0007 1.042 0.004 403 5 402 9 394 65 7 187 2968 0.0640 0.0008 0.4937 0.0072 0.0559 0.0007 0.0237 0.0006 0.215 0.002 400 5 407 6 450 26 8 67 931 0.0640 0.0010 0.4813 0.0079 0.0545 0.0012 0.0249 0.0007 0.613 0.003 400 6 399 7 394 51 9 60 754 0.0610 0.0006 0.4861 0.0086 0.0578 0.0009 0.0152 0.0003 1.788 0.014 382 4 402 7 523 34 10 62 823 0.0624 0.0007 0.4757 0.0066 0.0553 0.0008 0.0370 0.0008 0.560 0.001 390 5 395 5 425 33 11 77 981 0.0641 0.0007 0.4825 0.0072 0.0546 0.0007 0.0228 0.0006 1.010 0.001 400 4 400 6 397 31 12 157 2302 0.0648 0.0007 0.4945 0.0126 0.0554 0.0013 0.0260 0.0012 0.401 0.002 405 4 408 10 427 53 13 176 2285 0.0647 0.0007 0.4878 0.0081 0.0547 0.0008 0.0197 0.0005 1.050 0.016 404 5 403 7 400 32 14 154 2226 0.0646 0.0007 0.4850 0.0077 0.0544 0.0007 0.0176 0.0004 0.653 0.012 404 5 402 6 388 28 15 91 1171 0.0630 0.0007 0.4781 0.0093 0.0550 0.0008 0.0283 0.0008 0.829 0.005 394 5 397 8 413 33 表 2 石板井地区二长花岗岩、正长花岗岩主量、稀土和微量分析结果
Table 2 Analytical results of major, trace elements and REE concentrations of the syenogranite and monzogranite in Shibanjing area
岩性 正长花岗岩 正长花岗岩 正长花岗岩 正长花岗岩 正长花岗岩 正长花岗岩 正长花岗岩 二长花岗岩 二长花岗岩 二长花岗岩 样品编号 YQ0145-1 TL19YQ1 PM02-YQ2 PM27YQ1 PM27YQ2 PM06YQ1 PM06YQ2 SYQ3 PM02-YQ4 PM02-YQ6 SiO2 75.34 76.43 75.57 75.98 76.05 74.91 75.68 73.52 72.71 75.41 TiO2 0.10 0.11 0.19 0.05 0.05 0.15 0.10 0.25 0.27 0.06 Al2O3 12.40 12.41 12.09 12.72 12.64 12.25 12.67 13.73 13.62 13.01 Fe2O3 0.81 1.14 2.04 0.27 0.40 1.09 0.63 0.04 1.13 1.13 FeO 0.90 0.25 0.28 0.75 0.60 0.62 1.11 1.00 0.80 0.14 MnO 0.02 0.01 0.00 0.02 0.03 0.03 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.01 MgO 0.06 0.12 0.13 0.08 0.19 0.13 0.08 0.24 0.51 0.10 CaO 0.79 0.44 0.81 0.80 0.86 0.76 0.81 1.52 1.69 0.84 Na2O 3.45 2.98 3.05 3.58 3.47 4.00 3.66 2.53 2.72 3.75 K2O 5.35 5.49 4.81 5.00 4.84 5.22 4.71 5.89 5.08 4.64 P2O5 0.01 0.01 0.02 0.02 0.03 0.02 0.01 0.04 0.05 0.01 H2O+ 0.46 0.40 0.61 0.40 0.38 0.41 0.36 0.71 0.55 0.40 H2O- 0.16 0.18 0.24 0.12 0.26 0.13 0.11 0.21 0.23 0.12 烧失量 0.73 0.57 0.93 0.72 0.81 0.75 0.48 1.06 1.26 0.83 总计 99.96 99.96 99.93 99.99 99.98 99.96 99.96 99.84 99.87 99.94 TFeO 1.64 1.28 2.14 1.00 0.96 1.61 1.69 1.05 1.85 1.17 Mg# 5.69 14.04 9.63 11.87 26.12 12.81 7.69 29.53 33.10 13.34 K2O/Na2O 1.55 1.84 1.58 1.40 1.39 1.30 1.29 2.33 1.87 1.24 A/CNK 0.96 1.07 1.03 1.00 1.01 0.90 1.01 1.03 1.04 1.02 TZr/℃ 800.23 840.94 841.53 703.63 710.32 806.59 841.58 809.72 800.42 778.85 La 35.70 133.26 55.74 28.11 24.15 60.06 39.08 65.33 66.08 16.50 Ce 100.67 298.72 96.04 60.88 50.77 122.54 87.68 113.19 115.50 31.24 Pr 15.40 34.20 13.46 7.10 6.06 15.84 15.80 14.08 14.52 4.20 Nd 68.54 128.33 49.73 24.41 21.33 57.17 69.12 45.34 48.74 15.88 Sm 20.83 21.75 10.09 5.44 4.55 11.18 22.13 7.05 8.47 3.68 Eu 0.13 0.51 0.91 0.07 0.14 0.46 0.16 0.83 0.87 0.30 Gd 16.63 16.43 9.12 4.85 3.92 9.83 16.00 7.22 8.02 3.10 Tb 3.84 2.67 1.75 0.90 0.71 1.68 3.77 0.94 1.25 0.66 Dy 23.41 13.08 10.75 5.48 4.09 9.70 23.44 4.54 6.73 4.45 Ho 4.36 2.29 2.13 1.06 0.82 1.82 4.24 0.87 1.19 0.88 Er 10.77 6.38 5.74 2.86 2.26 5.13 10.48 2.55 3.12 2.39 Tm 1.71 0.94 0.83 0.53 0.42 0.72 1.45 0.35 0.40 0.37 Yb 9.66 5.69 5.58 3.00 2.52 4.98 8.93 2.41 2.53 2.28 Lu 1.56 1.07 0.97 0.47 0.41 0.94 1.70 0.53 0.56 0.60 ∑REE 313.21 665.30 262.84 145.13 122.15 302.04 303.97 265.23 277.99 86.52 LREE/HREE 3.35 12.70 6.13 6.59 7.07 7.68 3.34 12.67 10.67 4.88 δEu 0.02 0.08 0.28 0.04 0.10 0.13 0.03 0.35 0.32 0.26 (La/Yb)N 2.65 16.79 7.16 6.73 6.88 8.65 3.14 19.44 18.70 5.19 Y 102.95 62.79 56.46 30.07 23.51 46.94 94.82 24.58 29.38 21.76 Rb 231.28 206.40 147.68 228.96 222.24 213.71 199.11 253.05 210.55 158.66 Sr 5.06 11.82 39.86 8.16 24.94 22.07 14.12 110.58 114.20 107.23 Ba 5.00 25.68 180.08 19.74 66.65 57.41 27.72 584.65 568.09 153.40 Ta 1.90 0.66 1.13 2.60 2.17 1.27 1.18 1.68 1.50 0.60 Nb 29.12 12.71 13.64 19.49 17.81 17.96 26.58 15.94 17.17 13.06 Hf 7.57 8.91 10.28 2.66 2.55 9.29 10.97 6.25 5.18 6.78 Zr 197.72 267.29 279.08 57.26 61.51 233.99 291.70 206.05 184.82 143.82 V 19.06 24.11 3.09 20.35 22.40 5.03 3.30 11.31 15.38 4.69 Ni 0.32 0.19 0.59 0.06 0.54 0.50 0.99 0.99 1.86 0.78 Co 0.04 0.01 0.85 0.21 0.38 0.68 0.43 1.63 2.72 0.62 Cs 3.56 1.19 2.10 5.48 4.36 3.64 3.15 5.18 3.64 1.42 Pb 35.09 26.80 10.71 41.92 44.02 28.05 22.63 22.31 16.79 15.46 Th 36.17 29.98 15.02 25.60 31.75 20.78 31.38 28.22 30.88 32.14 U 3.71 3.35 1.71 3.24 2.30 2.75 5.02 2.82 2.95 2.99 Cr 5.12 4.97 3.83 4.26 4.57 4.04 3.93 5.05 7.87 4.85 Ga 25.34 23.48 17.10 17.79 19.39 20.44 22.93 16.62 17.06 17.70 10000*Ga/Al 3.83 3.55 2.64 2.62 2.87 3.13 3.40 2.26 2.33 2.55 注:Mg#=n(Mg)/(n(Mg)+n(Fe));A/CNK=Al2O3/(Na2O+CaO+K2O);TZr为计算的锆石饱和温度;δEu= EuN/((SmN+GdN)/2);主量元素含量单位为%,微量和稀土元素含量单位为10-6 -
左国朝, 何国琦.北山板块构造及成矿规律[M].北京:北京大学出版社, 1990:1-226. 李锦轶, 张进, 杨天南, 等.北亚造山区南部及其毗邻地区地壳构造分区与构造演化[J].吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2009, 39(4):584-605. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=cckjdxxb200904002 杜玉良, 殷先明, 冯治汉, 等.北山地区中生代构造-岩浆活动与成矿[J].西北地质, 2009, 42(2):48-54. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=xbdz200902003 Xiao W J, Mao Q G, Windley B F, et al.Paleozoic multiple accretionary and collisional processes of the Beishan orogenic collage[J].American Journal of Science, 2010, 310(10):1553-1594. doi: 10.2475/10.2010.12
刘雪亚, 王荃.中国西部北山造山带的大地构造及其演化[J].地学研究, 1995, 28(1):37-48. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=HY000002240926 何世平, 任秉琛, 姚文光, 等.甘肃内蒙古北山地区构造单元划分[J].西北地质, 2002, 35(4):30-40. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=xbdz200204004 聂凤军, 江思宏, 白大明, 等.北山地区金属矿床成矿规律及找矿方向[M].北京:地质出版社, 2002:1-408. 龚全胜, 刘明强, 李海林, 等.甘肃北山造山带类型及基本特征[J].西北地质, 2002, 35(3):28-34. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=xbdz200203004 杨合群, 李英, 李文明, 等.北山成矿构造背景概论[J].西北地质, 2008, 41(1):22-28. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=xbdz200801002 贺振宇, 宗克清, 姜洪颖, 等.北山造山带南部早古生代构造演化:来自花岗岩的约束[J].岩石学报, 2014, 30(8):2324-2338. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/94579X/201408/661925033.html 郑荣国, 吴泰然, 张文, 等.北山地区月牙山-洗肠井蛇绿岩的地球化学特征及形成环境[J].地质学报, 2012, 86(6):961-971. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dizhixb201206010 余吉远, 李向民, 王国强, 等.甘肃北山地区辉铜山和帐房山蛇绿岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄及地质意义[J].地质通报, 2012, 31(12):2038-2045. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgqydz201212013 李向民, 余吉远, 王国强, 等.甘肃北山地区芨芨台子蛇绿岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb测年及其地质意义[J].地质通报, 2012, 31(12):2025-2031. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgqydz201212011 王国强, 李向民, 徐学义, 等.甘肃北山红石山蛇绿岩锆石U-Pb年代学研究及构造意义[J].岩石学报, 2014, 30(6):1685-1694. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98201406011 周国庆, 陈小明, 赵建新, 等.内蒙古石板井-小黄山与蛇绿岩相伴的变质岩及其演化[J].高校地质学报, 2001, 7(3):229-344. 杨合群, 李英, 赵国斌, 等.北山蛇绿岩特征及构造属性[J].西北地质, 2010, 43(1):26-36. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=xbdz201001002 徐学义, 何世平, 王洪亮, 等.中国西北部地质概论—秦岭、祁连、天山地区[M].北京:科学出版社, 2008:1-347. 孟贵祥, 吕庆田, 严加永, 等.北山内蒙古地区铁矿成矿特征及其找矿前景[J].矿床地质, 2009, 28(6):815-829. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kcdz200906010 廖云峰, 胡新茁, 程海峰, 等.内蒙古月牙山蛇绿岩的岩石学、地球化学特征及其地质意义[J].地质通报, 2016, 35(8):1243-1254. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20160805&flag=1 Liu Y S, Gao S, Hu Z C, et al.Continental and oceanic crust recycling-induced melt-peridotite interactions in the Trans North China Orogen:U-Pb dating, Hf isotopes and trace elements in zircons from mantle xenoliths[J].Journal of Petrology, 2009, 51:537-571. https://academic.oup.com/petrology/article/51/1-2/537/1463381
Ludwig K R.Isoplot/EX version 2.49.A geochronological toolkit for Microsoft Excel[M].Berkeley:Berkeley Geochronology Center Special Publication No.1a, 2003:1-56.
Middlemost E A K.Naming materials in the magma/igneous rock system[J].Earth Science Research, 1994, 37:215-224. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0012825294900299
Maniar P D, Piccoli P M.Tectonic discrimination of granitoids[J].Geological Society of American Bulletin, 1989, 101:635-643. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1989)101<0635:TDOG>2.3.CO;2
Thompson R T.British Tertiary volcanic province[J].Scottish Journal of Geology, 1982, 18:49-107. doi: 10.1144/sjg18010049
Sun S S, Mc Donough W F.Chemical and isotopic system atics of oceanic basalts:implications for mantle compositi on and processes[J].London:Geological Society Special Publication, 1989, 42:313-345. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.1989.042.01.19
贾小辉, 王强, 唐功建.A型花岗岩的研究进展及意义[J].大地构造与成矿, 2009, 33(3):465-480. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ddgzyckx200903017 吴锁平, 王梅英, 戚开静.A型花岗岩研究现状及其述评[J].岩石矿物学杂志, 2007, 26(1):57-66. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=yskwxzz200701009 King P L, White A J R, Chappell B W, et al.Characterization and origin aluminous A Type granites from Lachlan Fold Belt.Southeastern Australia[J].J.Petrol., 1997, 38(3):371-391. doi: 10.1093/petroj/38.3.371
王强, 赵振华, 熊小林.桐柏-大别造山带燕山晚期A型花岗岩的厘定[J].岩石矿物学杂志, 2000, 19(4):297-306. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=yskwxzz200004002 李小伟, 莫宣学, 赵志丹, 等.关于A型花岗岩判别过程中若干问题的讨论[J].地质通报, 2010, 29(2/3):278-285. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=2010020312&flag=1 Whalen J B, Currie K L, Chappell B W.A-type granites:Geochemical characteristics, discrimination and petrogenesis[J].Contrib.Mineral.Petrol., 1987, 95:407-419. doi: 10.1007/BF00402202
Watson E B, Harrison T M.Zircon saturation revisited:Temperature and composition effects in a variety of crustal magma types[J].Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1983, 64(2):295-304. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(83)90211-X
Loiselle M C, Wones D R.Characteristics of anorogenic granites[J].Geological Society of America(Abstracts with Programs), 1979, 11:468. http://ci.nii.ac.jp/naid/10019593683
Pearce J A, Harris N B W, Tindle A G.Trace element discrimination diagrams for the tectonic interpretation of granitic rocks[J].Journal of Petrology, 1984, 25(4):956-983. doi: 10.1093/petrology/25.4.956
Eby G N.The A-type granitoids:A review of their occurrence and chemical characteristics and speculations on their petrogenesis[J].Lithos, 1990, 26(1/2):115-134. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/002449379090043Z
Eby G N.Chemical subdivision of the A-type granitoids:Petrogenetic and tectonic implications[J].Geology, 1992, 20(7):641-644. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1992)020<0641:CSOTAT>2.3.CO;2
Turner S P, Foden J D, Morrison R S.Derivation of some A-type magmas by fractionation of basaltic magma:An example from the Padthaway Ridge, South Australia[J].Lithos, 1992, 28(2):151-179. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/002449379290029X
韩宝福, 王式洗, 江博明.新疆乌伦古河碱性花岗岩Nd同位素特征及其对显生宙地壳生长的意义[J].科学通报, 1997, 42(17):1829-1832. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kxtb199717011 Harris C, Marsh J S, Milner S C.Petrology of the alkaline core of the Messum igneous complex, Namibia:Evidence for the progressively decreasing effect of crustal contamination[J].Journal of Petrology, 1999, 40:1377-1397. doi: 10.1093/petroj/40.9.1377
Mingram B, Trumbull R B, Littman S, et al.A petrogenetic study of anorogenic felsic magmatism in the Cretaceous Paresis ring complex, Namibia:Evidence for mixing of crust and mantle-derived components[J].Lithos, 2000, 54:1-22. doi: 10.1016/S0024-4937(00)00033-5
Yang J H, Wu F Y, Chung S L, et al.A hybrid origin for the Qianshan A-type granite, northeast China:Geochemical and Sr-Nd-Hf isotopic evidence[J].Lithos, 2006, 89:89-106. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2005.10.002
CollinsW J, Beams S D, White A J R, et al.Nature and origin of A-type granites with particular reference to south eastern Australia[J].Contrib.Mineral.Petrol., 1982, 80:189-200. doi: 10.1007/BF00374895
Clemens J D, Holloway J R, White A J R.Origin of A-type granites:Experimental constraints[J].American Minerologist, 1986, 71:317-324. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/279898234_Origin_of_an_A-type_granite_experimental_constraints
Anderson J L, Bender E E.Nature and origin of Proterozoic A-type granitic magmatism in the southwestern United States of America[J].Lithos, 1989, 23:19-52. doi: 10.1016/0024-4937(89)90021-2
Creaser R A, Price R C, Wormald R J.A-type granites revisited:Assessment of a residual source model[J].Geology, 1991, 19:163-166. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1991)019<0163:ATGRAO>2.3.CO;2
Frost C D, Frost B R.Reduced rapakivi-type granites:The tholeiite connection[J].Geology, 1997, 25:647-650. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1997)025<0647:RRTGTT>2.3.CO;2
Wu F Y, Sun D Y, Li X H, et al.A-type granites in Northeastern China:Age and geochemical constraints on their petrogenesis[J].Chemical Geology, 2002, 187:143-173. doi: 10.1016/S0009-2541(02)00018-9
Wilson B M.Igneous Petrogenesis:A Global Tectonic Approach[M].London:Unwin Hyman, 2007:1-466.
Creaser R A, Price R C, Wormald R J.A-type granites revisited:assessment of a residual-source model[J].Geology, 1991, 19(2):163-166. http://adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/1991Geo....19..163C
Green T H.Significance of Nb/Ta as an indicator of geochemical processes in the crust-mantle system[J].Chemical Geology, 1995.120:347-359. doi: 10.1016/0009-2541(94)00145-X
Hofmann A W.Chemical differentiation of the Earth:The relationship between mantle, continental crust, and oceanic crust Earth Planet[J].Sci.Lett., 1988, 90:297-314. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0012821X8890132X
Rapp R P, Watson E B.Dehydration melting of metabasalt at 8~32kbar:Implications for continental growth and crust-mantle recycling[J].Journal of Petrology, 1995, 36(4):891-931 doi: 10.1093/petrology/36.4.891
吴福元, 李献华, 杨进辉, 等.花岗岩成因研究的若干问题[J].岩石学报, 2007, 23(6):1217-1238. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98200706001 洪大卫, 王式洸, 韩宝福, 等.碱性花岗岩的构造环境分类及其鉴别标志[J].中国科学(B辑), 1995, 25(4):418-426. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199500247293 Batchelor R A, Bowden P.Petrogenetic interpretation of granitoid rock series using multicationic parameters[J].Chemical Geology, 1985, 48, (1):43-55. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0009254185900348
左国朝, 刘义科, 刘春燕.甘新蒙北山地区构造格局及演化[J].甘肃地质学报, 2003, 12(1):1-15. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gsdzxb200301001 陈超, 修迪, 潘志龙, 等.北山造山带中部早古生代伸展构造体制:来自石板井辉长岩的年代学及地球化学证据[J].地质学报, 2017, 91(8):1661-1673. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DZXE201708001.htm 何世平, 周会武, 任秉琛, 等.甘肃内蒙古北山地区古生代地壳演化[J].西北地质, 2005, 38(3):6-15. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=xbdz200503002 孙立新, 张家辉, 任邦方, 等.北山造山带白云山蛇绿混杂岩的地球化学特征、时代及地质意义[J].岩石矿物学杂志, 2017, 36(2):131-147. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=yskwxzz201702001 杨合群, 赵国斌, 李英, 等.新疆-甘肃-内蒙古衔接区古生代构造背景与成矿的关系[J].地质通报, 2012, 31(2/3):413-421. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=2012020326&flag=1 修迪, 陈超, 专少鹏, 等.北山石板井地区英云闪长岩-石英闪长岩体锆石U-Pb年龄、成因及对古洋盆俯冲作用时限的制约[J].地质通报, 2018, 37(6):975-986. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20180602&flag=1 专少鹏, 陈超, 申宗义, 等.北山地区早古生代洋盆俯冲记录—来自石板井高镁闪长岩的年代学、地球化学证据[J].岩石矿物学杂志, 2018, 37(4):533-546. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=yskwxzz201804002 程先钰, 任邦方, 田健, 等.内蒙古北山白云山蛇绿混杂岩带南部锡林柯博组碎屑岩地球化学特征、源区属性及构造意义[J].地质通报, 2020, 39(6):893-904. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20200609&flag=1 张元元, 郭召杰.甘新交界红柳河蛇绿岩形成和侵位年龄的准确限定及大地构造意义[J].岩石学报, 2008, 24(4):803-809. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98200804019 潘志龙, 张欢, 陈超, 等.内蒙古北山敖包呼图仁斑状正长花岗岩锆石U-Pb年龄、Lu-Hf同位素组成及其地质意义[J].地质科学, 2017, 52(1):301-316. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzkx201701021 程海峰, 廖云峰, 徐旭明, 等.内蒙古1: 5万1524.6高地、二龙包西、高地、炮台山西幅区域地质矿产调查报告.2015. 潘志龙, 魏文通, 刘增效, 等.内蒙古1: 5万基东、尖山、蒜井子、三道明水幅区域地质矿产调查报告.2016. 陈超, 赵华平, 张金龙, 等.内蒙古1: 5万西林陶勒、梧桐井、石桩子井、石板井幅区域地质矿产调查报告.2017. 陈超, 刘增校, 潘志龙, 张欢, 张金龙.1: 5万石板井等四幅区域地质图.2016. 潘志龙, 陈超, 刘增校, 张欢, 王硕.1: 5万基东等四幅区域地质图.2015.



 下载:
下载: