Characteristics of gravity and magnetic fields and deep prospecting implications in Changtuxili area, Inner Mongolia
-
摘要:
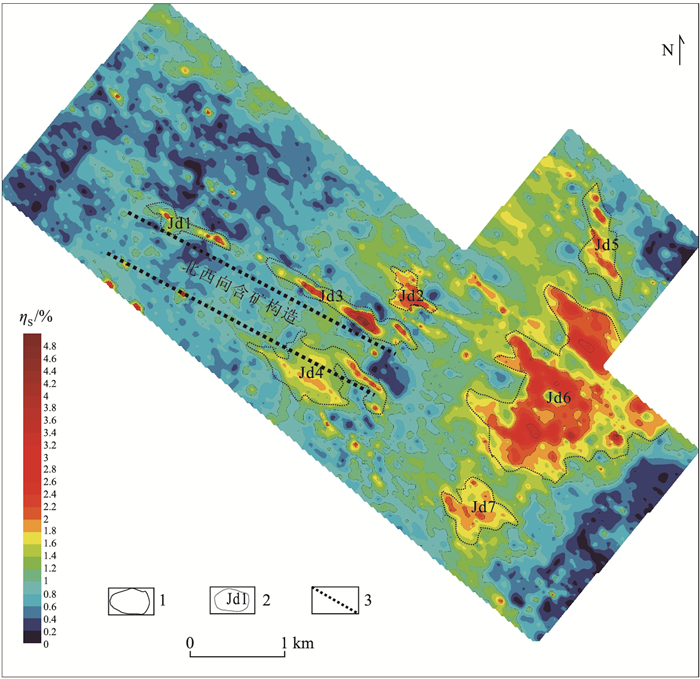
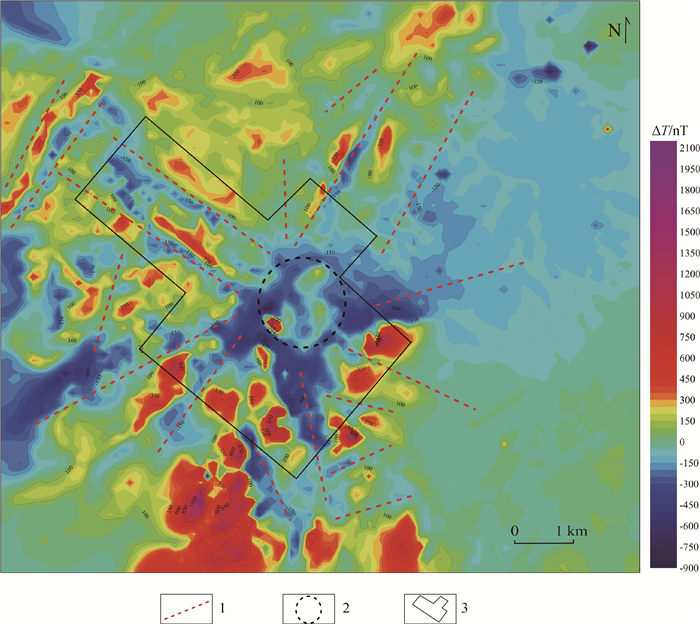
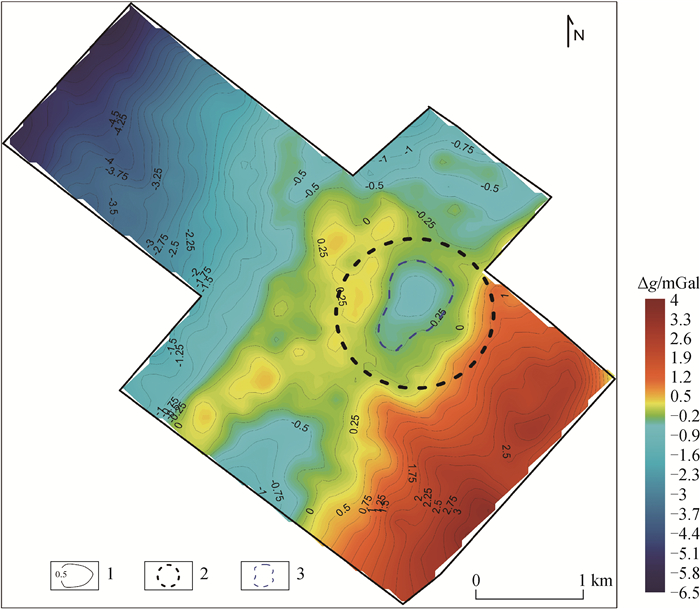
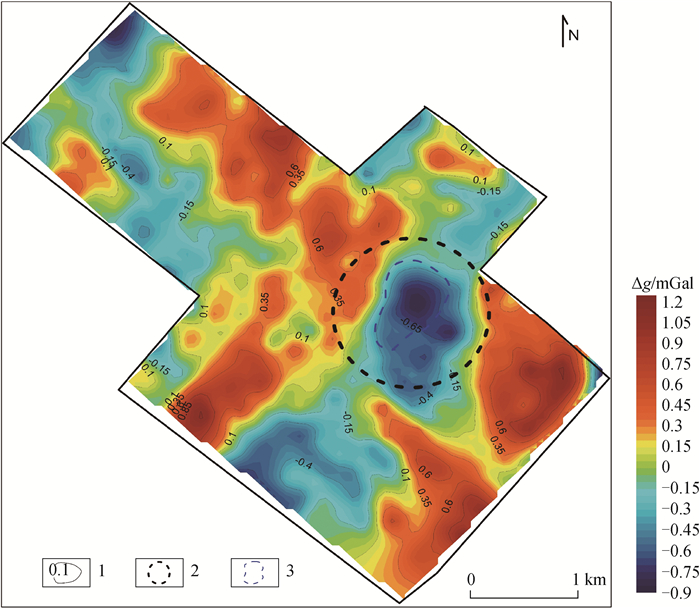
内蒙古昌图锡力地区位于大兴安岭成矿带南段西坡,成矿条件优越。前期研究发现,区内的银铅锌多金属矿产与中生代火山机构和中酸性岩浆的侵入有关,由于覆盖较厚,勘查程度不高,只依靠地表地质工作难以确定火山机构分布和侵入岩体的空间位置,不利于区内实现深部找矿突破。通过对磁测数据进行构造分析,揭示其可能为火山机构的放射状构造特征,推测构造18条,通过开展1:20000重力测量,并对重力场进行剩余异常提取、功率谱分析等处理,发现1处可能为隐伏侵入岩体引起的局部低重力异常,经计算其场源近似深度约1002.5 m。研究结果指示了区内可能的隐伏火山机构分布和侵入岩体空间位置,为该地区下一步开展深部找矿和钻探验证工作提供了重要参考。
Abstract:The Changtuxili area in Inner Mongolia is located on the west slope of the southern section of the Da Hinggan Mountains metallogenic belt.Its metallogenic conditions are superior.It is found that the Ag-Pb-Zn polymetallic deposits in this area are related to the invasion of Mesozoic volcanic apparatus and intermediate acid magma.However, due to the thick coverage and low exploration level, it is difficult to determine the distribution of volcanic apparatus and the spatial location of intrusive rock mass only relying on the surface geological work, which is not conducive to the deep exploration breakthrough in the area.Through the fracture analysis of the magnetic survey data, the authors revealed the radial structure characteristics that may be volcanic apparatus, and inferred 18 structures.Through the 1:20000 gravity survey, residual anomaly extraction and power spectrum analysis of the gravity field, a low gravity anomaly that may be caused by the concealed intrusive rock mass was found, and the approximate depth of the field source was calculated to be about 1002.5 m.The results indicate the distribution of the potential hidden volcanic apparatus and the spatial location of the intrusive rock mass, which provides an important reference for the further exploration and drilling verification work in this area.
-
致谢: 本次工作得到自然资源部矿产勘查技术指导中心刘士毅、程志中、庞振山教授级高工的悉心指导和帮助,在此表示感谢。
-
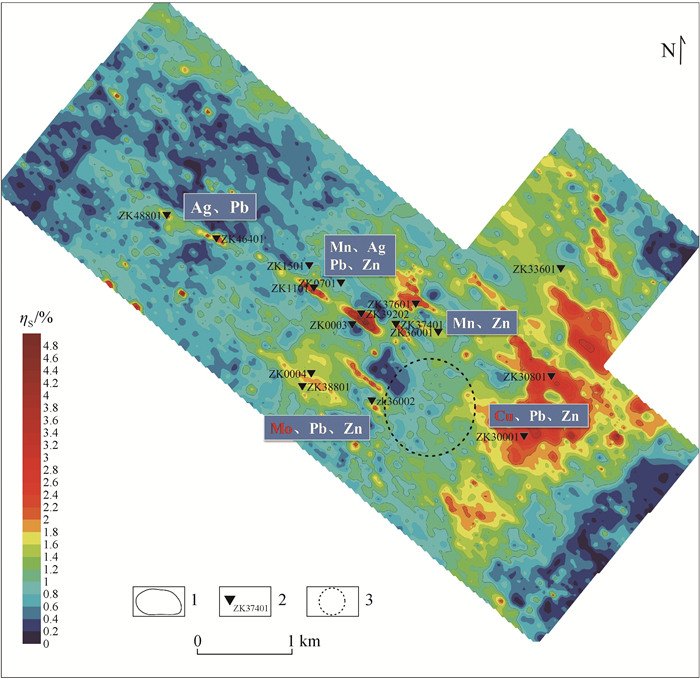
图 2 昌图锡力地区视极化率平面图[3]
1—视极化率等值线;2—激电异常及编号;3—已验证的含矿构造
Figure 2. Apparent polarizability of the Changtuxili area
表 1 岩(矿)石物性参数
Table 1 Statistical results of rocks(ores)physical parameters
岩(矿)石名称 样品数 极化率平均值
/%电阻率平均值
/(Ω·m)密度平均值/
(g·cm-3)磁化率平均值
/10-5SI剩余磁化强度平均值
/10-3A/M构造角砾岩 6 4.57 816.69 2.51 10.50 - 硅化角砾岩 1 7.74 45.63 2.58 8.81 - 硅化凝灰熔岩 1 0.36 41.77 2.61 21.35 - 角砾凝灰岩 30 3.62 58.19 2.50 62.51 - 凝灰岩 47 1.38 243.04 2.43 13.79 流纹斑岩 3 4.24 322.54 2.57 101.30 - 矿化硅化岩石 12 12.02 29.62 2.67 73.75 - 安山玢岩 5 0.96 279.23 2.63 241.82 - 安山岩 17 1.70 212.36 2.66 588.97 - 火山角砾岩 20 9.98 316.91 2.60 496.67 138.05 英安岩 36 3.43 197.37 2.56 79.71 - 富锰矿体
(氧化矿)15 21.67 348.72 3.00 56.90 1.89 蚀变英安岩 6 6.49 961.08 2.50 19.65 - 银铅锌矿石 26 13.33 6.16 3.00 - - 菱锰矿 4 1.30 5586.90 3.46 357.20 15.13 脉岩 9 10.32 417.48 - 94.22 - -



 下载:
下载: