A discussion on the genetic model of the copper deposit in Lala copper orefied, Sichuan Province
-
摘要:
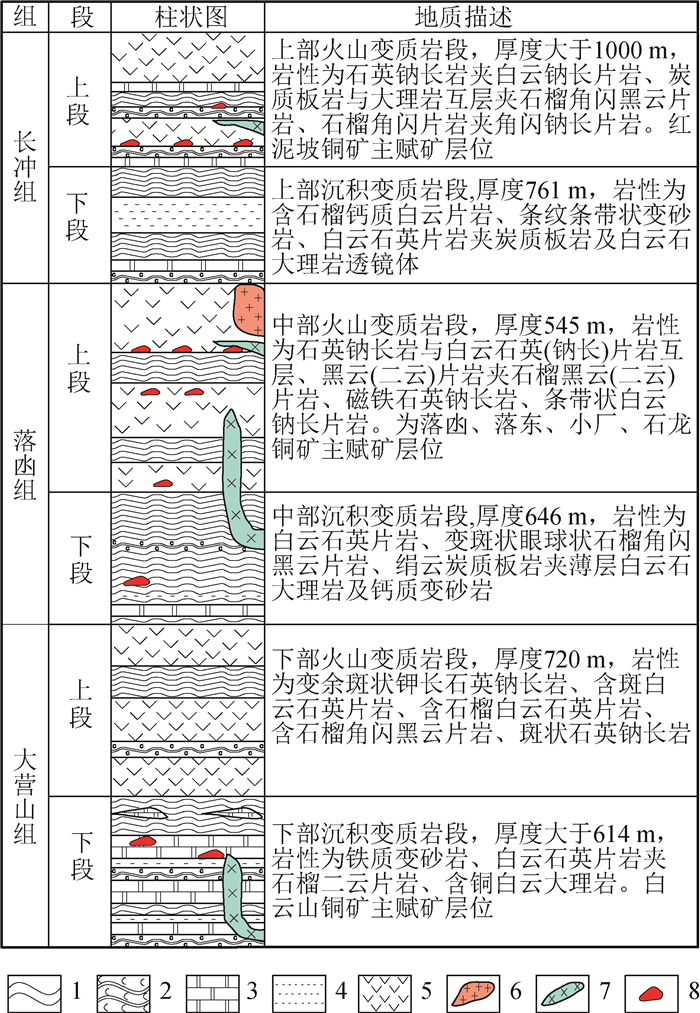
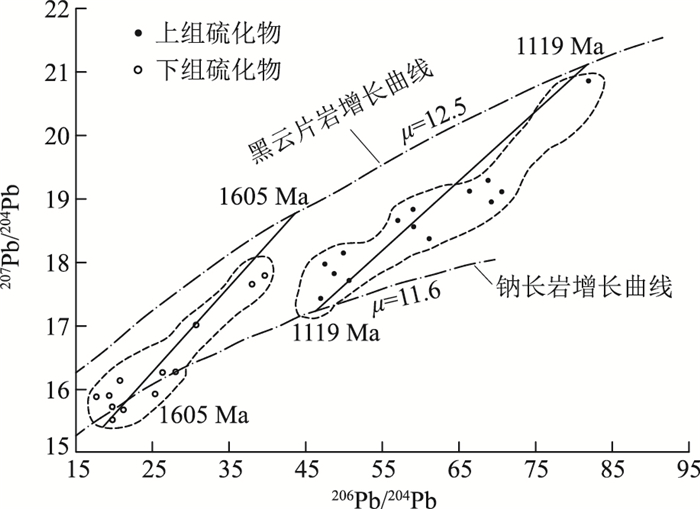
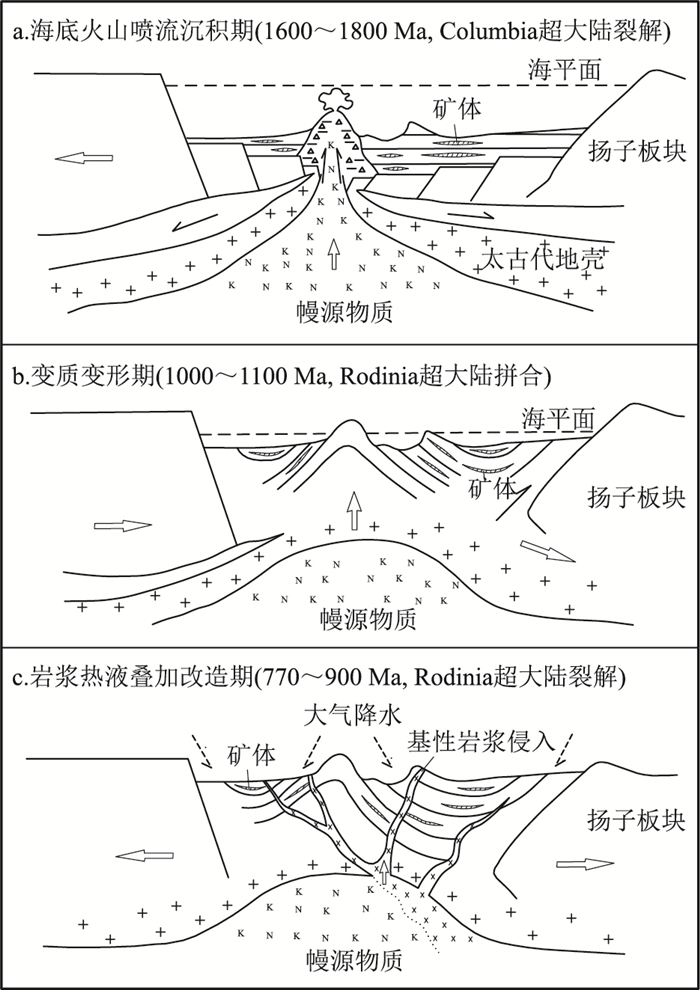
四川省会理县拉拉铜矿田处于川滇被动大陆边缘裂谷系的构造环境,成矿作用受会理-东川裂陷槽构造-岩浆演化控制。矿体产于古元古界河口群富钠质的细碧-角斑岩系中。矿石中金属硫化物的δ34S值集中分布在-1‰~4‰之间,均接近0,具塔式分布特征,表明硫主要来自火山喷发作用。矿床与火山喷流沉积型矿床的流体类型相似,其包裹体基本为早期石英硫化物中的Ⅰ型包裹体及后期方解石、石英硫化物中的Ⅱ和Ⅲ型包裹体,Ⅰ型包裹体反映为火山喷发沉积期的主成矿阶段;而Ⅱ型和部分Ⅲ型包裹体反映了晚期流体混溶现象,显示矿床经历了后期改造。根据同位素测年数据,将矿床的成矿过程大致分为火山喷流作用(1600~1800 Ma)、变质变形作用(1000~1100 Ma)和热液叠加改造作用(770~900 Ma)3个阶段。初步认为拉拉铜矿田矿床成因类型属海相火山岩型铜矿床,但河口群不同的火山喷发旋回具有不同的矿化样式。
Abstract:The tectonic environment of the Lala copper orefield is located in the Sichuan-Yunnan passive continental margin rift system of Huili County, Sichuan Province, and its mineralization is controlled by the tectonic-magmatic evolution of the Huili-Dongchuan rift trough.The orebody is located in the Na-rich spilite-keratophyre series of the Paleoproterozoic Hekou Group.The values of the δ34S of metal sulfide in the ore are distributed in the range of -1‰~4‰, and are close to zero, which have characteristics of tower distribution, indicating that sulfur mainly came from volcanic eruption.The fluid type of the deposit is similar to that of the volcanic effusive sedimentary deposit, the inclusions are basically Ⅰ-type inclusions in early quartz sulfide and Ⅱ-type and Ⅲ-type inclusions in late calcite quartz sulfide; I-type inclusions reflect the main metallogenic stage of volcanic eruptive-sedimentary period, while Ⅱ-type and Partial Ⅲ-type inclusions reflect terminal fluid miscibility, which indicates that the deposit has undergone late reformation.According to isotopic dating data, the metallogenic process of the deposit can be roughly divided into three stages:volcanic spouting(1600~1800 Ma), metamorphism and deformation(1000~1100 Ma), and hydrothermal superposition modification(770~900 Ma).It is preliminarily considered that the genetic type of deposits about the Lala copper orefield belongs to marine volcanic rock type copper deposit, but different volcanic eruption cycles of Estuary Group have different mineralization patterns.
-
长期以来,伊宁盆地的油气勘探工作主要针对中生界及上二叠统[1-3],未取得明显进展。近年准噶尔盆地和三塘湖盆地石炭系油气勘探取得重大突破,是天然气产量的主要增长区,使中国北方石炭系成为重要的油气资源新层系。伊宁盆地与准噶尔盆地、三塘湖盆地在石炭纪具有相同的构造背景,因此需要对伊宁盆地石炭系烃源岩进行评价,明确其是否具有较好的生烃条件。
李玉文等[1]、郝继鹏等[4]对下石炭统阿克沙克组烃源岩进行了初步评价。本文通过对阿克沙克剖面和琼阿希剖面阿克沙克组烃源岩分布及油气地球化学特征的系统分析,明确了该套烃源岩具有良好的生烃条件,指示伊宁盆地石炭系具有良好的油气资源前景。
1. 地质背景
伊宁盆地位于新疆维吾尔自治区西部,盆地西部与哈萨克斯坦及吉尔吉斯坦接壤,东部收敛于南、北天山接合部,呈西宽东窄、向西开口的三角形,石炭系地层在区内广泛分布(图 1)。
伊宁盆地属于古生代和中生代叠合盆地,对西天山伊犁地区石炭纪火山-沉积岩系形成构造环境的认识目前还存在很大争议,其中一种主要观点认为,古天山洋的闭合时间在晚泥盆世之前,早石炭世开始进入新的造山后裂谷拉伸阶段,火山-沉积岩系具有板内裂谷火山岩系岩石地球化学特征,形成于碰撞后裂谷拉伸环境[5-6]。这些火山-沉积岩系的形成可能与碰撞后裂谷拉张环境的古地幔柱活动有关[7]。西天山伊犁地区石炭纪火山-沉积盆地充填序列反映了裂谷盆地充填演化过程[8]。笔者所在的研究团队通过野外调查,利用火山岩地球化学和沉积建造综合分析,结合前人资料,认为伊宁盆地石炭纪为大陆裂谷环境,与前人认识一致。
伊宁盆地石炭系自下而上可划分为4套岩石组合:大哈拉军山组(C1d)→阿克沙克组(C1a)→伊什基里克组(C2y)→东图津河组(C2d)。大哈拉军山组岩石组合为玄武岩、安山岩、流纹岩、粗面岩、火山碎屑岩、碎屑岩及少量灰岩;阿克沙克组岩石组合为含砾粗砂岩、砂岩、生物碎屑灰岩和泥岩;伊什基里克组岩石组合为玄武岩、流纹岩及火山碎屑岩;东图津河组岩石组合为砂岩、细砂岩夹砂砾岩及泥灰岩。阿克沙克组沉积时期,海水范围最大,各地层之间为火山喷发不整合或整合接触关系,总体反映了石炭纪盆地火山喷发-正常沉积的充填过程和海侵到海退的沉积环境变化。
2. 烃源岩展布特征
2.1 阿克沙克组岩石组合特征
研究剖面主要为阿克沙克剖面,该剖面是下石炭统阿克沙克组的建组剖面,位于昭苏县城西北方向的阿克沙克沟地区。阿克沙克组与下伏下石炭统大哈拉军山组整合接触,与上覆二叠系铁木里克组呈角度不整合接触,自下而上可划分为a、b两段,a段下部以灰色中厚层长石杂砂岩、细砂岩为主,上部粒度变细,以粉砂岩和泥质粉砂岩为主,含植物碎片化石;b段下部以灰色中层状泥晶生屑灰岩、介壳灰岩、生屑灰岩为主,偶夹少量薄层砂岩,上部以粉砂质泥岩和泥岩为主。伊宁市东北的琼阿希剖面,地层出露不全,未见顶底,发育一套暗色泥岩。
2.2 烃源岩纵向分布
阿克沙克剖面实测结果表明,暗色泥岩集中分布在b段中上部,主要集中分布在三段(图 2),厚度较大,自下而上,厚度依次为65.9m(一段)、75m(二段)、56m(三段),在一段下部有一套5.2m厚的薄层暗色泥岩,累计厚度可达202.1m;琼阿希剖面可见一套28m厚的暗色泥岩。
3. 烃源岩地球化学特征
烃源岩的有效评价直接决定了油气勘探的方向与前景。对于中国古生界海相烃源岩的评价标准目前争论仍较大[9-10],参考前人研究成果,并结合伊宁盆地实际特点,本次研究采用SY/T5735—1995国家标准对阿克沙克组烃源岩进行评价。
3.1 有机质丰度
有机质丰度评价通常采用总有机碳含量(TOC)、生烃潜量(S1+S2)、氯仿沥青“A”等指标。对于地表剖面采集的样品或演化程度较高的样品,生烃潜量(S1+S2)和氯仿沥青“A”作为丰度指标评价烃源岩受影响较大,与钻井岩心样品的测试结果相比,这2个参数的值往往低许多,难以反映真实的有机质丰度特征,仅可作为参考指标[11-13]。
3.1.1 总有机碳(TOC)含量
阿克沙克剖面采集18个样品进行了总有机碳含量及热解分析。结果表明,TOC含量主体分布在0.6%~2%之间,平均为1.19%,达到中等-好标准(图 3),TOC大于1%的泥岩累计厚度达144.18m。纵向上自下而上TOC含量逐渐增大,平均值分别为0.79%、1.17%、1.19%,二段、三段全部样品TOC均大于1%,达到好标准。在琼阿希剖面采集了8个烃源岩样品进行分析,TOC均大于1%,部分样品TOC大于2%,平均值为1.73%,达到好-最好标准(图 4)。
3.1.2 生烃潜量和氯仿沥青“A”
阿克沙克剖面烃源岩生烃潜量(S1+S2)仅为0.04~0.43mg/g,平均值为0.19mg/g,氯仿沥青“A”仅为0.005%~0.015%,平均值为0.011%,指示非-差标准。琼阿希剖面烃源岩S1+S2较高,为0.55~1.80mg/g,平均值为1.13mg/g,为差标准;氯仿沥青“A”主体为0.020%~0.057%,平均值为0.034,显示差-中等标准,低于TOC评价结果(图 5)。
综上所述,由于地表样品风化影响严重,研究区露头样品的S1+S2及氯仿沥青“A”均低于TOC判别结果,不适宜作为烃源岩丰度的评价指标。TOC结果显示,阿克沙克组暗色泥岩有机质丰度可达中等-好标准。
3.2 有机质类型
有机质类型的评价指标较多,但对于地表露头样品或高-过成熟样品,部分指标不宜采用,如风化作用往往引起C、H元素流失,O元素相对富集,使有机质类型向Ⅲ型偏移,导致与之相关的IH-IO和H/CO/C判别方法可信度降低;风化作用同样会引起S2降低,使对应的Tmax峰值不准确,导致IH-Tmax(最高热解峰温)判别方法可信度降低;此外,随着热演化程度增加,干酪根碳同位素(δ 13CPDB)逐渐变重,H/C-O/C向碳极收敛,正构烷烃碳优势逐渐消失[13-18]①,相关参数的使用均须慎重。相比之下,甾烷等生物标志化合物稳定,能够有效地保留原始有机质来源信息,与之相关的类型参数为目前能够有效划分露头或高成熟样品有机质类型的重要指标。
3.2.1 正构烷烃
不同来源的正构烷烃,其组成特征差异较大。一般认为,具有奇偶优势的高碳数(>C23)正构烷烃的分布指示陆源有机质的输入,以C15、C17为主,奇偶优势不明显的中等相对分子质量(nC15~nC21)的正构烷烃指示藻类等低等水生生物来源[11]。
根据阿克沙克剖面一、三段烃源岩代表样品的饱和烃色谱图(图 6),受到生物降解作用影响,色谱基线均有一定的漂移,且高碳数缺失较多,由于CPI考察C24~C34段的奇偶性,所以该参数会有一定程度的失真,如阿克沙克剖面样品的CPI高值可达2.10,低值为1.22。而OEP仅考察主峰碳及前后4个碳数的正构烷烃,因此影响较小,如同一剖面对应样品的OEP仅为0.83~1.02,结合Ro结果表明,基本为成熟偏高导致的奇偶优势比消失,但从正构烷烃的峰型特征看,整体均呈双峰态分布,且前锋较高,表明有机质来源为低等水生生物及高等植物混合贡献,且前者贡献较高。此外,Ph/nC18-Pr/nC17特征也指示Ⅰ型有机质贡献较高(图 7)。
3.2.2 甾烷化合物
尽管许多缺乏陆生植物的前泥盆纪沉积物中富含C29甾烷,但一般仍认为,水生生物富含C27和C28甾烷,而高等植物富含C29甾烷,故可通过有机质的甾烷谱图特征及C27-C28-C29相对含量百分图来判断干酪根的有机质类型。
根据阿克沙克剖面一段、三段烃源岩代表样品的饱和烃色质图,C27αααR、C28αααR、C29αααR甾烷系列的相对组成分布大多具有混源特征,以C27占优势,显示Ⅱ1型有机质特征。从样品的ααα 20R构型C27-C28-C29甾烷三角图同样可以看出(图 8),该剖面阿克沙克组烃源岩有机质类型以Ⅱ1为主。
3.2.3 其他参数
由于风化作用及高成熟度影响,部分常用判别参数所得出的研究剖面目的层烃源岩有机质类型差别较大,如7个δ13CPDB分布范围为-23.8‰ ~ -20.1‰,均指示Ⅲ型特征,δ13CPDB偏重可能与热演化程度较高有关;8个样品饱/芳值分布在0.4~1.6之间,其中阿克沙克剖面中1个样品(S8)的饱/芳值为1.6,指示Ⅱ1型,另外3个样品(S5,S13,S16)的饱/芳值均小于1.0,指示Ⅲ型。琼阿希剖面的4个样品均小于1.0,指示Ⅲ型,饱和烃含量偏低可能与其主要组成—正构烷烃对生物降解和热力作用最敏感有关;H/C-O/C结果指示有机质为Ⅱ2~Ⅲ型,其中阿克沙克剖面的4个样品均指示Ⅲ型,琼阿希剖面的1个样品(S3)为Ⅱ2型,其余3个样品(S1,S6,S8)均为Ⅲ型,H、O元素的差异亏损可能与差异风化有关。上述3种参数判别效果较差,本次主要利用生物标志化合物进行判别。
综合分析,生物标志化合物受风化、热演化作用等影响较小,可作为有机质类型判别的主要依据。根据阿克沙克组烃源岩甾烷组合特征分析,有机质类型主要为Ⅱ1型,部分样品为Ⅱ2型,与浅海陆棚沉积环境一致。
3.3 有机质成熟度
镜质体反射率(Ro)是有机质成熟度的有效指标,随热演化程度的升高而增大,并具有相对广泛、稳定的可比性。Tmax为烃源岩中有机质热解烃S2峰的峰顶温度,其数值的高低与有机质热演化程度密切相关,在一定程度上也可以反映有机质成熟度,但由于地表露头样品S2往往较低,仅作为有机质成熟度评价的参考指标。此外,特征生物标志化合物也能够指示一定的热演化程度。
根据4件样品的统计结果(表 1),阿克沙克组烃源岩的Ro介于1.38% ~1.75%之间,平均值为1.56%,处于高成熟阶段。根据22件样品的统计结果(图 9),阿克沙克组烃源岩的Tmax为468~572℃,平均值为518℃,亦处于高成熟阶段。同时,αααC29S/(S+R)-C29ββ/(αα+ββ)甾烷的分布特征同样指示所有样品均经历过成熟阶段。综合研究认为,阿克沙克组烃源岩整体处在高成熟阶段,利于生气。
表 1 伊宁盆地典型剖面阿克沙克组烃源岩Ro统计Table 1. Ro of Akeshake Formation for representative sections in Yi'ning basin剖面名称 样品编号 岩性 Ro/% 测点数 琼阿希 14QAX-S3 灰黑色薄层泥岩 1.45 15 14QAX-S6 灰黑色薄层泥岩 1.38 18 阿克 14AKSK-S5 粉砂质泥岩 1.67 20 沙克 14AKSK-S16 粉砂质泥岩 1.75 20 4. 有机质沉积环境
Pr/Ph(姥鲛烷/植烷)为指示有机质沉积环境的重要指标,Pr富集代表氧化环境,Ph富集则代表还原环境。总体上,Pr/Ph>1指示氧化环境,值越大,反映氧化程度越大,水体越浅,如沼泽、湿地、海陆交互环境等。Pr/Ph < 1指示还原环境,值越小,反映还原程度越大,水体越深,如淡水、咸湖、海相等。具体可细分为:Pr/Ph < 0.5,为强还原性膏盐沉积环境;0.5~1.0为还原性环境;1.0~2.0为弱还原-弱氧化环境;Pr/Ph>2.0为偏氧化环境;Pr/Ph>2.5为煤系地层。根据阿克沙克剖面4个样品的统计结果可得,Pr/Ph值为0.47%~0.67%,指示强还原-还原环境,有利于有机质的保存。
5. 结论
(1)伊宁盆地石炭纪为海相裂谷盆地,以浅海陆棚相沉积为主,有利于暗色泥岩的发育,阿克沙克组发育多套厚度较大的暗色泥页岩,分布范围广。
(2)该套暗色泥岩有机质丰度高、以Ⅱ1~Ⅱ2型为主,处于高成熟阶段,以生气为主,指示石炭系可作为油气调查的新层系,具有良好的资源前景。
-
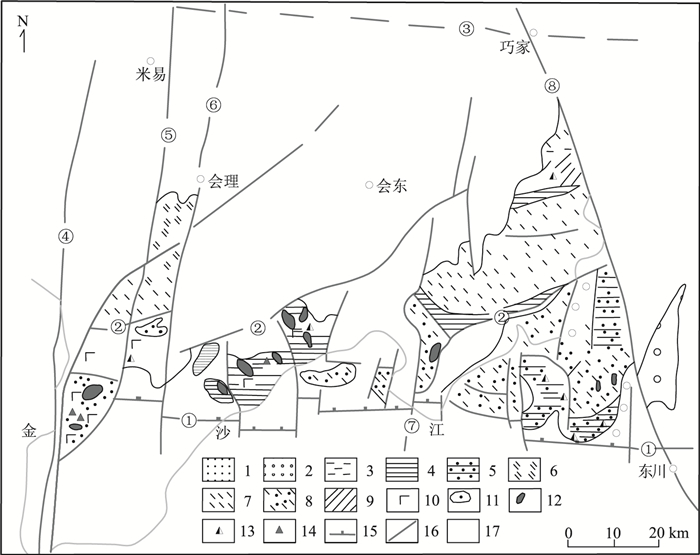
图 1 会理-东川裂陷槽地质矿产略图[11]
1、2—河口群:1—深盆相火山-细屑岩;2—浅海相碎屑-碳酸盐岩;3~8—会理群:3—深盆相;4—斜-台地相;5—潮坪-湖相;6—斜坡槽盆相浊积碳酸盐岩;7—斜坡槽盆相浊积碎屑岩夹碳酸盐岩;8—潮坪—湖相碎屑岩-碳酸盐岩;9—天宝山组;10—基性火山岩;11—变质橄榄岩;12—晋宁期辉长岩;13—沉积型铜矿;14—火山型铜矿;15—裂陷槽边界断层;16—断裂;17—显生宙盖层;①—宝台厂-九龙断裂;②—菜子园-麻塘断裂;③—天宝山-巧家断裂;④—磨盘山断裂;⑤—小关河断裂;⑥—益门-鹿厂断裂;⑦—普渡河断裂;⑧—小江断裂
Figure 1. Geological and mineral sketch map of Huili-Dongchuan rift trough
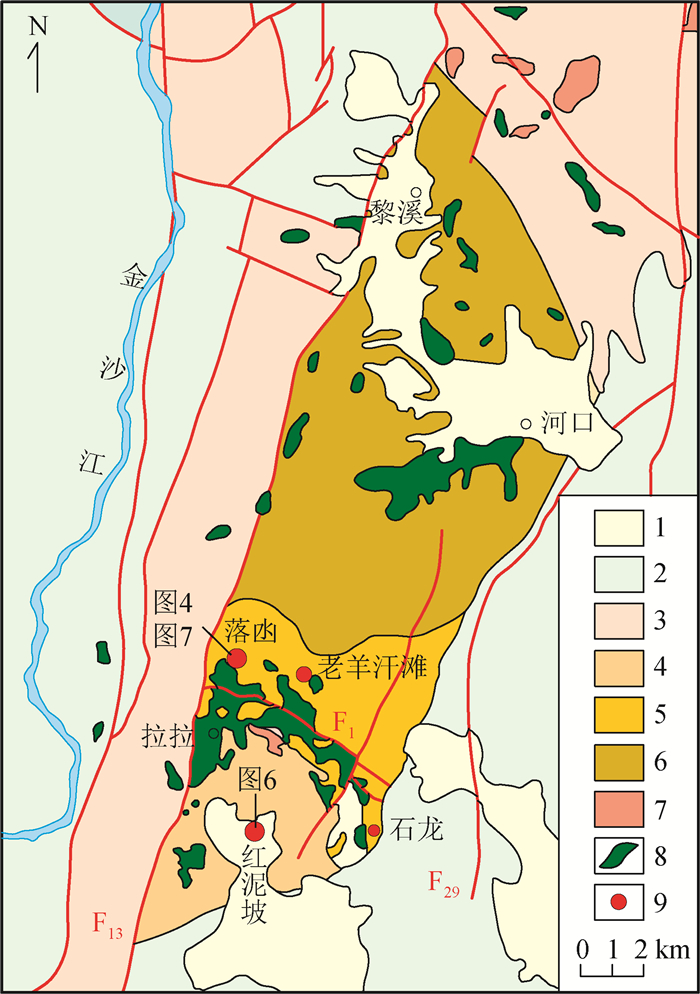
图 2 拉拉铜矿田地质简图[12]
1—第四系;2—震旦系-新近系;3—会理群;4—河口群长冲组;5—河口群落水组;6—河口群大营山组;7—斑岩;8—辉长石;9—铜矿床
Figure 2. Geological sketch map of the Lala copper orefield
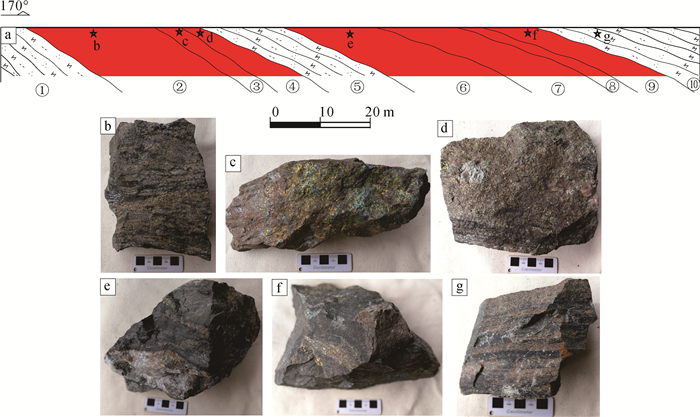
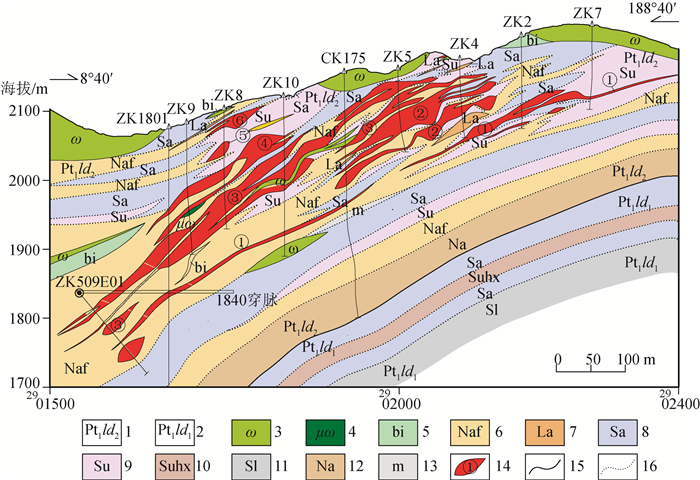
图 7 落凼矿床露天采场1974 m平台剖面示意图(a)及典型矿石照片(b~g)
①—黑云石英钠长岩;②—纹层状矿石;③—块状矿石;④—角砾状矿石;⑤—黑云石英钠长片岩;⑥—脉状矿石;⑦—纹层状矿石;⑧—块状矿石;⑨—角砾状矿石;⑩—黑云石英钠长片岩;b—层纹状黄铜黄铁矿石;c—块状黄铜黄铁矿石;d—角砾状黄铜黄铁矿石;e—脉状黄铜黄铁矿石;f—角砾状黄铜黄铁矿石;g—黑云石英钠长片岩
Figure 7. Diagrammatic cross-section(a)and typical ore photograph(b~g)of 1974 m platform in open-pit stope of the Luodang deposit
表 1 落凼矿床与别子型矿床主要成矿要素对比
Table 1 Comparison of major metallogenic factors between the Luodang deposit and the Biezi type deposit
成矿要素 别子型矿床 落凼矿床 大地构造环境 板块交界处(陆缘裂谷或弧前盆地),尤其是弧前海沟 扬子陆块的西缘川滇被动大陆边缘裂谷 成矿时代 元古宙、古生代及中生代 元古宙 含矿建造 三波川群基性火山岩-近源陆源碎屑沉积岩建造 河口群富钠质的细碧角斑岩-沉积岩建造 容矿岩石 拉斑玄武岩-安山质凝灰岩和角砾岩、杂砂岩, 局部为黑色页岩 石英钠长岩、黑云片岩 矿体特征 矿体呈板状,与围岩产状一致;矿体长1700 m,延深3500 m,单层矿体厚度不大,一般厚3~10 m,最厚10~20 m 矿体呈层状、似层状,与围岩产状基本一致;矿体长720~1960 m,延深100~525 m,平均厚度12.27~26.47 m 矿石特征 矿石构造主要为块状、条带状矿石,次为角砾状、细脉状矿石;矿石矿物以黄铜矿、闪锌矿、黄铁矿为主,有较多磁铁矿、磁黄铁矿,少量斑铜矿、毒砂、辉砷钴矿等 矿石构造以浸染状、纹层状和条带状构造为主,次有角砾状、网脉状、块状构造;矿石矿物主要为黄铜矿、斑铜矿、黄铁矿,少量辉钴矿、方硫镍钴矿、辉钼矿、磁铁矿 有用元素组合 铜-锌型/Cu-Zn(Au) 铜型/Cu 变质作用 绿片岩相-角闪岩相 高绿片岩相 围岩蚀变 微弱的硅化、碳酸盐化 黑云母化、硅化和碳酸盐化 -
孙燕, 李承德.四川拉拉铜矿床成矿机制研究[J].成都地质学院学报, 1990, 17:1-9. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CJFD&filename=CDLG199004000 申屠保涌.四川会理拉拉厂铜矿床地质地球化学特征及成矿模式[J].特提斯地质, 1997, 21:112-126. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-TTSD721.008.htm 李泽琴, 王奖臻, 刘家军, 等.拉拉铁氧化物-铜-金-钼-稀土矿床Re-Os同位素年龄及其地质意义[J].地质找矿论丛, 2003, 18:39-42. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzzklc200301007 陈根文, 夏斌.四川拉拉铜矿床成因研究[J].矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2001, 20:42-44. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kwysdqhxtb200101009 黄崇珂, 白治, 朱裕生, 等.中国铜矿床[M].北京:地质出版社, 2001:1-705. 何德锋.四川省拉拉铜矿床岩石学及地球化学研究[D].中国科学院地球化学研究所博士学位论文, 2009. 朱志敏, 曾令熙, 周家云, 等.四川拉拉铁氧化物铜金矿床(IOCG)形成的矿相学证据[J].高校地质学报, 2009, 15(4):485-495. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gxdzxb200904007 Zhao X F, Zhou M F.Fe-Cu deposits in the Kangdian region, SW China:A Proterozoic IOCG(iron-oxide-copper-gold)metallogenic province [J].Mineralium Deposita, 2011, 46:731-747. doi: 10.1007/s00126-011-0342-y
方维萱.论扬子地块西缘元古宙铁氧化物铜金型矿床与大地构造演化[J].大地构造与成矿学, 2014, 4:733-757. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ddgzyckx201404002 陈好寿.同位素地球化学研究[M].杭州:浙江大学出版社, 1994:1-340. 刘肇昌.元古代会理-东川坳拉槽与川滇铜铁成矿带[J].矿床地质, 1994, (S1):23-25. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/93610X/1994S1/4001440730.html Chen W T, Zhou M F.Paragenesis, stable isotopes, and molybdenite Re-Os isotope age of the Lala Iron-Copper deposit, Southwest China[J].Economic Geology, 2012, 107(3):459-480. doi: 10.2113/econgeo.107.3.459
李复汉, 覃嘉铭, 申玉莲.康滇地区的前震旦系[M].重庆:重庆出版社, 1988:1-426. 周家云, 郑荣才, 朱志敏, 等.拉拉铜矿含矿岩系地球化学特征及其构造意义[J].矿产与地质, 2009, 23(2):163-170. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kcydz200902013 骆耀南.康滇构造带的古板块历史演化[J].四川地质学报, 1982, 2:1006-0995. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-SCDB198202030.htm Ohmoto H.Firnatuib if volcanic-associated massive sulfide deposits:The Kuroko perspective[J].Ore Geologica Review, 1996, 10:135-177. doi: 10.1016/0169-1368(95)00021-6
黄从俊, 李泽琴, 王奖臻.扬子西南缘拉拉IOCG矿床Pb同位素特征及意义[J].地质通报, 2015, 34(2/3):501-507. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=2015020325&flag=1 周家云, 毛景文, 刘飞燕, 等.扬子地台西缘河口群钠长岩锆石SHRIMP年龄及岩石地球化学特征[J].矿物岩石, 2011, 31(3):66-73. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kwys201103010 Chen W.Origin and tectonic environment of theLala Fe-Cu-(Mo, REE)deposit, Sichuan Province, SW China [D].PhD Thesis of The University of Hong Kong, 2013.
朱志敏.拉拉铁氧化物铜金矿: 成矿时代和金属来源[D].成都理工大学博士学位论文, 2011. 王冬兵, 孙志明, 尹福光, 等, 扬子地块西缘河口群的时代:来自火山岩锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb年龄的证据[J].地层学杂志, 2012, 36(3):630-635. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DCXZ201203014.htm 关俊雷, 郑来林, 刘建辉, 等.四川省会理县河口地区辉绿岩体的锆石SHRIMP U-Pb年龄及其地质意义[J].地质学报, 2011, 85(4):482-490. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dizhixb201104004 陈好寿, 冉崇英.康滇地轴铜矿床同位素地球化学[M].北京:地质出版社, 1992:1-100. 孙燕, 舒晓兰, 肖渊甫.四川省拉拉铜矿床同位素地球化学特征及成矿意义[J].地球化学, 2006, 35(5):553-559. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqhx200605011 Zhu Z M, Tan H Q, Liu Y D, et al.Multiple episodes of mineralization revealed by Re-Os molybdenite geochronology in the Lala Fe-Cu deposit, SW China[J].Mineralium Deposita, 2018, 53(3):311-322. doi: 10.1007/s00126-017-0740-x
刘肇昌, 李凡友, 钟康惠, 等.扬子地台西缘构造演化与成矿[M].成都:电子科技大学出版社, 1996:48-100. 刘德华, 王和道, 陈震荣, 等.四川省会理县拉拉铜矿落凼矿区详细勘探地质报告.四川省地质局攀西地质大队, 1982. 张洪刚, 李承炎.四川的前震旦系.四川省地质矿产局地质矿产科研所, 1984. 路远发, 吴越, 王亚东.四川省会理县拉拉铜矿接替资源勘查项目综合研究课题研究报告.长江大学, 2015. 黄智龙, 范宏鹏.四川省会理县拉拉铜矿接替资源勘查项目综合研究课题结题报告.中国科学院地球化学研究所, 2015.




 下载:
下载: