Lithofacies characteristics of the Longtan Formation and its control of gold mineralization in the Shuiyindong gold deposit, Southwestern Guizhou Province
-
摘要:
黔西南地区水银洞超大型金矿床产于上二叠统龙潭组,金异常富集的高品位层状-似层状矿体受特定的不纯碳酸盐岩和有利岩性组合控制。对龙潭组赋矿层及围岩开展系统岩石学对比分析,总结制约龙潭组沉积作用及岩石类型的控制因素,分析龙潭组中高品位金矿体产出特征及其对岩性岩相的选择性规律。结果表明,龙潭组整体为一套浅水三角洲泥炭沼泽与滨岸潮坪泻湖相沉积,以富含有机质为特征,灰岩夹层可能代表不同时期的海侵事件;峨眉山玄武岩浆的喷溢改变吴家坪期沉积古地理格局和龙潭组中陆源碎屑岩的成分,发育与火山活动有关的沉积,矿石中铁白云石可能是火山碎屑物质热蚀变产物;富有机质和玄武质火山碎屑的不纯生物碎屑灰岩是金异常富集形成高品位矿体的重要控制因素。在黔西南地区找寻该类型矿床时应重点评价特定的岩石类型及组合特征。
Abstract:The Shuiyindong superlarge gold deposit, located in southwestern Guizhou Provence, has a high-grade layered orebody in the Upper Permian Longtan Formation(P3l).It is controlled by specific impure carbonate rocks and favorable lithology.In this paper, the authors summarized constraints on the sedimentary facies and rock characteristics of the Longtan Formation.Based on a detailed and systematic petrographic comparative analysis of the host rocks and wall rock, the authors hold that the Longtan Formation consists of a set of shallow-water delta peat bogs and coastal tidal flat lagoon sediments characterized by rich organic matter.Limestone interlayers in Longtan Formation may represent transgressive events of different periods.The Emeishan basalt magma eruption changed Wujiapingian epoch sedimentary paleogeographic pattern and composition of terrigenous clastic rocks in the formation of the Longtan Formation and developed sediments related to volcanic activity; iron dolomite in the ore might have been a thermal alteration product of volcanic clastic material; organic matter and basaltic volcanic fragments in impure bioclastic limestone was an important controlling factor for the abnormal enrichment of gold to form high-grade orebodies.When looking for this type of gold deposits in southwestern Guizhou Provence, researchers should focus on the evaluation of the favorable lithological unit.
-
致谢: 中国地质大学(北京)刘家军、邱昆峰教授及审稿专家提出了宝贵的修改意见,在此一并表示衷心感谢。
-
图 1 黔西南地区区域地质矿产图(据参考文献[18]修改)
Figure 1. Simplified geological map of southwestern Guizhou Province
图 2 黔西南台地相区地层综合柱状图(据参考文献[20]修改)
Figure 2. Stratigraphic comprehensive columnar section of platform facies in southwestern Guizhou Province
图版Ⅰ
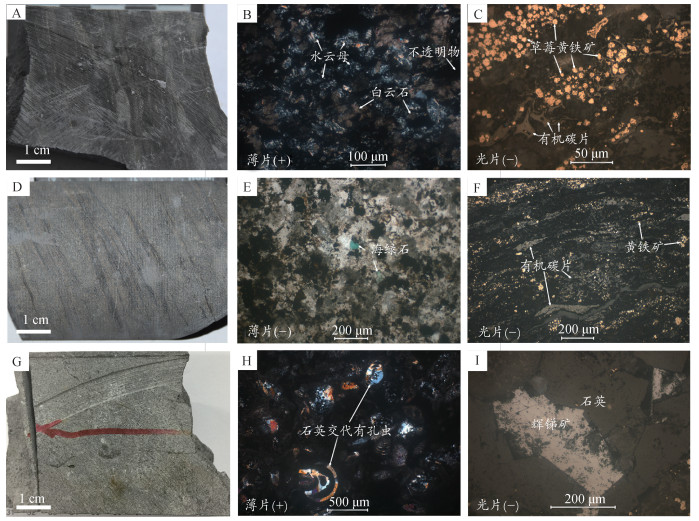
A.采自龙潭组二段(P3l2)Ⅲc矿体顶板,为白云石化水云母化玄武质粘土岩,见小型交错层理;B.图版Ⅰ-A标本薄片透射光显微照片,矿物主要由水云母、白云石、有机碳质、草莓黄铁矿组成。水云母主要形成于热变质作用影响的玄武质火山凝灰物及更细的火山尘,见白云石交代水云母;C.图版Ⅰ-A标本光片反射光显微照片,有机碳质较发育,成弯曲条带状、鸡骨状、片状、无定形状等形态,常见其包裹草莓状黄铁矿生长,长条状有机碳显示长轴定向分布特征;D.采自龙潭组二段(P3l2)Ⅲc矿体底板,为白云石化玄武质粘土质粉砂岩, 见交错层理、波状层理、脉状层理;E.图版Ⅰ-D标本薄片透射光显微照片,主要由0.01~0.05 mm粒级岩屑、晶屑(少见石英晶屑)、火山灰等火山凝灰物与白云石为主的碳酸盐矿物组成。白云石矿物可能为后期热液交代富含Fe、Mg元素的玄武质火山碎屑物的白云石化蚀变形成;F.图版Ⅰ-D标本光片反射光显微照片, 光片中见微层理构造。有机碳片长轴定向或无定形有机碳质定向分布叠加了与其密切共生的草莓状黄铁矿;G.采自龙潭组二段(P3l2)Ⅲc矿体,硅化生物碎屑灰岩,具生物碎屑结构;H.图版Ⅰ-G标本薄片透射光显微照片,见泥微晶方解石为主的碳酸盐矿物胶结生物碎屑,生物碎屑主要有海绵骨针、藻类、海胆、有孔虫、海百合、三叶虫碎片等。胶结物以泥微晶方解石为主,富含有机质,透光性稍差。浸染状分布的石英不同程度交代生物碎屑与胶结物碳酸盐矿物,石英交代易发生在孔洞发育、结构疏松的生物屑部位,见方解石细脉中包裹石英颗粒或切割石英细脉;I.图版Ⅰ-G标本光片反射光显微照片,石英强烈交代的生物碎屑中黄铁矿密集分布,且多颗粒聚集生长。在硅化强烈的部位,偶见粗大辉锑矿分布石英粒间
-
Hu R, Fu S, Huang Y, et al.The giant South China Mesozoic low-temperature metallogenic domain:Reviews and a new geodynamic model[J].Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2017, 137(SI):9-34. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2016.10.016
Gu X X, Zhang Y M, Li B H, et al.Hydrocarbon- and ore-bearing basinal fluids:a possible link between gold mineralization and hydrocarbon accumulation in the Youjiang basin, South China[J].Mineralium Deposita, 2012, 47(6):663-682. doi: 10.1007/s00126-011-0388-x
顾雪祥, 章永梅, 吴程赟, 等.黔西南卡林型金矿床与古油藏的成因联系:有机岩相学证据[J].地学前缘, 2013, 20(1):92-106. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DXQY201301011.htm Zhu J, Zhang Z, Santosh M, et al.Carlin-style gold province linked to the extinct Emeishan plume[J].Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2020, 530:1-12. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=5356c648013e2ad5d57840da25a1e4b0&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Su W, Heinrich C A, Pettke T, et al.Sediment-hosted gold deposits in Guizhou, China:products of wall-rock sulfidation by deep crustal fluids[J].Economic Geology, 2009, 104(1):73-93. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=30b342aca3fe6b12b7bc04facdede592&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Xie Z, Xia Y, Cline J S, et al.Magmatic origin for sediment-hosted au deposits, Guizhou province, China:in situ chemistry and sulfur isotope composition of pyrites, Shuiyindong and Jinfeng deposits[J].Economic Geology, 2018, 113(7):1627-1652. doi: 10.5382/econgeo.2018.4607
谢卓君, 夏勇, Cline Jean, 等.中国贵州与美国内华达卡林型金矿对比及对找矿勘查的指示作用[J].矿床地质, 2019, 38(5):1077-1093. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kcdz201905009 Goldfarb R J, Qiu K, Deng J, et al.Orogenic gold deposits of China[J].Society of Economic Geologists Special Publication, 2019, 22:263-324.
刘建中, 夏勇, 邓一明, 等.贵州水银洞超大型金矿床金的赋存状态再研究[J].贵州地质, 2007, 24(3):165-169. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gzdz200703001 杨成富, 刘建中.贵州灰家堡背斜构造蚀变体岩石地球化学特征[J].贵州地质, 2017, 34(1):18-25. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gzdz201701003 刘建中, 邓一明, 刘川勤, 等.贵州省贞丰县水银洞层控特大型金矿成矿条件与成矿模式[J].中国地质, 2006, 33(1):169-177. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgdizhi200601019 He B, Xu Y, Huang X, et al.Age and duration of the Emeishan flood volcanism, SW China:Geochemistry and SHRIMP zircon U-Pb dating of silicic ignimbrites, post-volcanic Xuanwei Formation and clay tuff at the Chaotian section[J].Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2007, 255(3/4):306-323. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=be16052d88f755855c3c65bc7f9792e6&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Zhao L, Dai S, Graham I T, et al.New insights into the lowest Xuanwei Formation in eastern Yunnan Province, SW China:Implications for Emeishan large igneous province felsic tuff deposition and the cause of the end-Guadalupian mass[J].Lithos, 2016, 264:375-391. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2016.08.037
于鑫, 杨江海, 刘建中, 等.黔西南晚二叠世龙潭组物源分析及区域沉积古地理重建[J].地质学报, 2017, 91(6):1374-1385. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dizhixb201706015 Deng X, Yang J, Cawood P A, et al.Detrital record of late-stage silicic volcanism in the Emeishan large igneous province[J].Gondwana Research, 2020, 79:197-208. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2019.09.015
Yang J, Cawood P A, Du Y, et al.Large Igneous Province and magmatic arc sourced Permian-Triassic volcanogenic sediments in China[J].Sedimentary Geology, 2012, 261:120-131. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=0010cac1eec0c501143a932ed015de57
Yang J, Cawood P A, Du Y.Voluminous silicic eruptions during late Permian Emeishan igneous province and link to climate cooling[J].Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2015, 432:166-175. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2015.09.050
王砚耕.试论黔西南卡林型金矿区域成矿模式[J].贵州地质, 1994, (1):1-7. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-GZDZ401.000.htm 王砚耕.中国西南地区沉积地质特征与沉积盆地分类[J].贵州地质, 1993, (4):265-271. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-GZDZ199304000.htm 王砚耕.黔西南及邻区两类赋金层序与沉积环境[J].岩相古地理, 1990, (6):8-13. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TTSD199006001.htm Cail T L, Cline J S.Alteration associated with gold deposition at the Getchell Carlin-type gold deposit, north-central Nevada[J].Economic Geology and the Bulletin of the Society of Economic Geologists, 2001, 96(6):1343-1359. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.96.6.1343
Xu Y G, Chung S L, Jahn B M, et al.Petrologic and geochemical constraints on the petrogenesis of Permian-Triassic Emeishan flood basalts in southwestern China[J].Lithos, 2001, 58(3/4):145-168. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=ee4949e0ae9bfc05051d101c75c25176&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Xiao L, Xu Y G, Mei H J, et al.Distinct mantle sources of low-Ti and high-Ti basalts from the western Emeishan large igneous province, SW China:implications for plume-lithosphere interaction[J].Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2004, 228(3/4):525-546. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=89d19375b8bea90d96ffde3e47ffa82b&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Lai S, Qin J, Li Y, et al.Permian high Ti/Y basalts from the eastern part of the Emeishan Large Igneous Province, southwestern China:Petrogenesis and tectonic implications[J].Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2012, 47(SI):216-230. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=fcf627aef388ab576cf255d266716d6e&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
He B, Xu Y, Zhong Y, et al.The Guadalupian-Lopingian boundary mudstones at Chaotian(SW China)are clastic rocks rather than acidic tuffs:Implication for a temporal coincidence between the end-Guadalupian mass extinction and the Emeishan volcanism[J].Lithos, 2010, 119(1/2):10-19. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2010.06.001
He B, Xu Y, Huang X, et al.Age and duration of the Emeishan flood volcanism, SW China:Geochemistry and SHRIMP zircon U-Pb dating of silicic ignimbrites, post-volcanic Xuanwei Formation and clay tuff at the Chaotian section[J].Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2007, 255(3/4):306-323. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=be16052d88f755855c3c65bc7f9792e6&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
White R S, Mckenzie D.Mantle plumes and flood basalts[J].Journal of Geophysical Research-Solid Earth, 1995, 100(B9):17543-17585. doi: 10.1029/95JB01585
Cox K G.The role of mantle plumes in the development of continental drainage patterns[J].Nature, 1989, 342(6252):873-877. doi: 10.1038/342873a0
Campbell I H, Griffiths R W.Implications of mantle plume structure for the evolution of flood basalts[J].Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1990, 99(1/2):79-93. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=a4a09f41fb8730f534bd81e1b345adc1&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
何斌, 徐义刚, 肖龙, 等.峨眉山地幔柱上升的沉积响应及其地质意义[J].地质论评, 2006, 52(1):30-37. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzlp200601005 何斌, 徐义刚, 王雅玫, 等.东吴运动性质的厘定及其时空演变规律[J].地球科学, 2005, (1):89-96. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqkx200501012 何斌, 徐义刚, 王雅玫, 等.用沉积记录来估计峨眉山玄武岩喷发前的地壳抬升幅度[J].大地构造与成矿学, 2005, 29(3):316-320. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ddgzyckx200503004 何斌, 王雅玫, 姜晓玮.上扬子西部茅口组灰岩顶部古喀斯特地貌的厘定及地质意义[J].中国地质, 2004, (1):46-50. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgdizhi200401006 贵州省地质矿产局.贵州省区域地质志[M].北京:地质出版社, 1987:404-493. 徐彬彬, 何明德.贵州煤田地质[M].徐州:中国矿业大学出版社, 2003:163-207.




 下载:
下载: