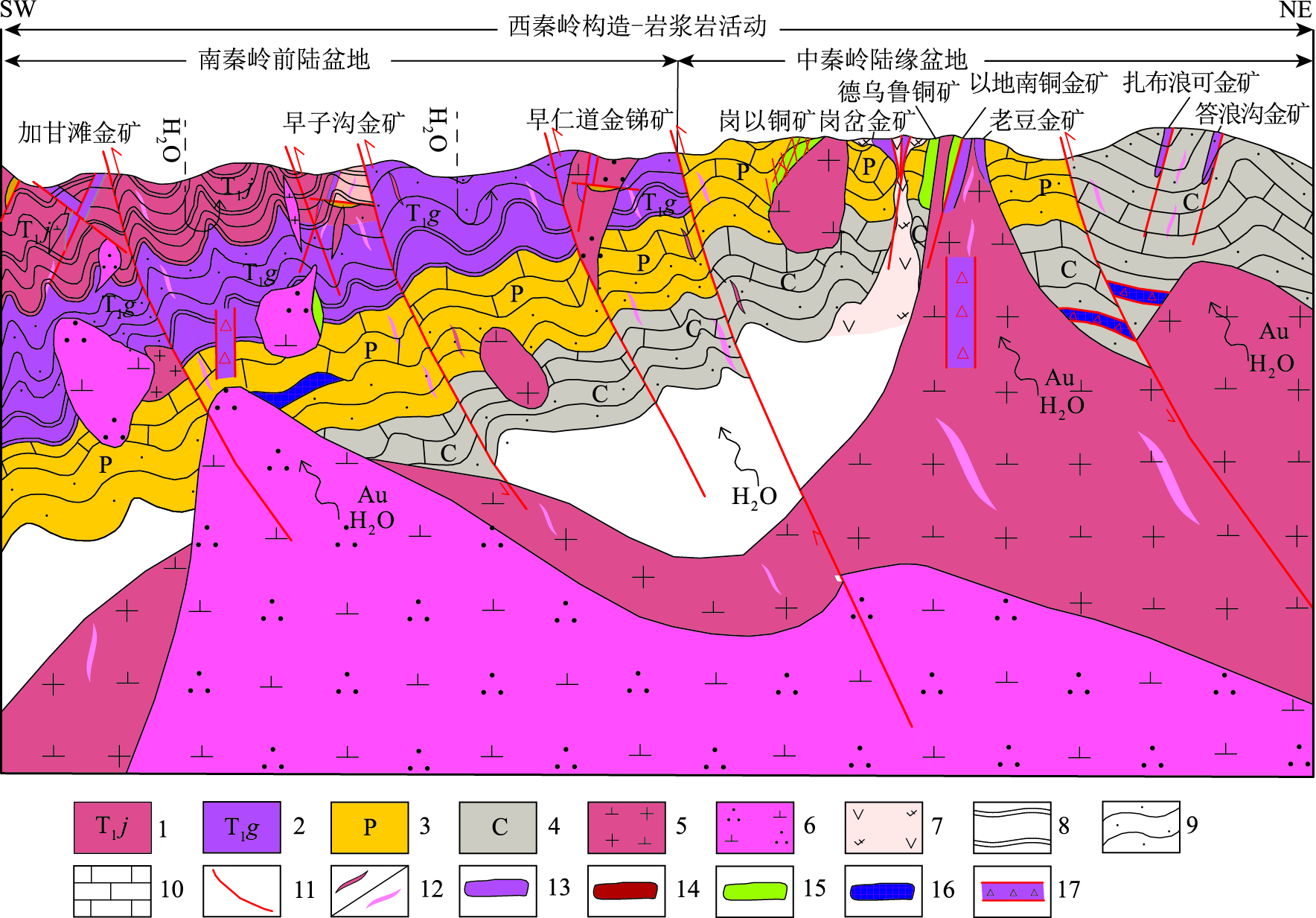
The Au-Cu polymetallic mineralization system related to intermediate to felsic intrusive rocks and the prospecting prediction in Xiahe-Hezuo area of Gansu, West Qinling orogenic belt
-
摘要:
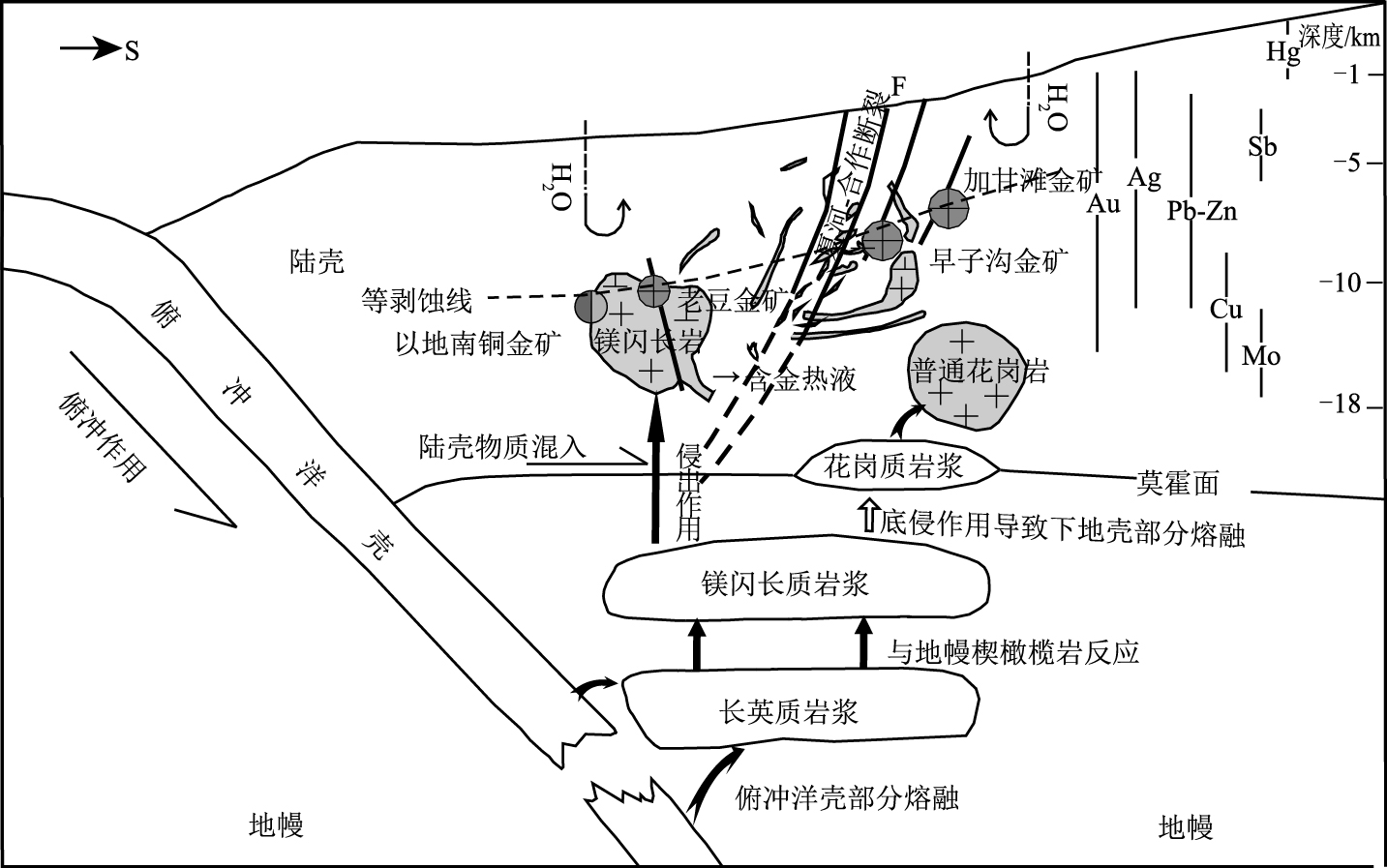
甘肃夏河—合作地区岩浆岩与矿产分布具有分带性:夏河-合作断裂以北侵入岩规模较大,以岩基、岩株为主,发育Cu、Au、W、Mo、Pb、Zn等以中高温元素为主的矿化,受岩体边缘接触带及断裂双重控制;夏河-合作断裂以南侵入岩规模较小,多以小岩株、脉岩出现,发育Au、Hg、Sb等中低温矿化,受断裂破碎带控制。地球化学组成显示,该区侵入岩具有镁闪长岩、TTG岩套的双重特点,为"热壳"+"热幔"的壳幔结构,成矿条件极为有利。硫、氢、氧稳定同位素特征指示,成矿物质主要来自地幔岩浆析出的热液,后期有大气降水的参与。夏河—合作地区为与中酸性侵入岩有关的金铜等多金属矿成矿系统,在夏河-合作断裂以南,剥蚀较浅,可寻找远成低温热液型金、锑矿等,在其深部还应注意寻找斑岩型或矽卡岩型铜金矿床。而在剥蚀程度较高的北带,应以斑岩型和矽卡岩型矿床为主。
Abstract:The distribution of magmatic rocks and mineral deposits in Xiahe-Hezuo area has a zoning characteristics:The intrusive rocks in northern Xiahe-Hezuo fault have larger scales and are mainly batholiths and stocks.The mineralization in intrusive rocks is dominated by medium and high temperature elements, such as Cu, Au, W, Mo, Pb and Zn, and is controlled jointly by the contact zone at the edge of rock mass and the fracture.The intrusive rocks to the south of Xiahe-Hezuo fault are smaller and are mainly small stocks and dikes.The mineralization in intrusive rocks is dominated by medium and low temperature elements and is controlled by the fracture.Geochemical characteristics in this area show that the intrusive rocks have the dual characteristics of magnesium diorite and TTG rock suite, and structurally belong to crust-mantle structure that is "thermal shell" + "thermal mantle"; therefore, the metallogenic condition in this area is extremely favorable. S, H, O and other stable isotope characteristics show that the ore-forming material was mainly derived from the hydrothermal fluid in the mantle magma and, in the later period, there occurred the participation of atmospheric precipitation.The Au-Cu polymetallic ore-forming system in Xiahe-Hezuo area was associated with medium-acid intrusive rocks.Therefore, exploration should be focused on searching for remote low temperature hydrothermal gold and antimony deposits in the shallow part and searching for porphyry and skarn deposits in the depth to the south of Xiahe-Hezuo fault, due to the shallow denudation degree.However, the prospecting should be based on porphyry and skarn deposits to the north of Xiahe-Hezuo fault characterized by a high denudation.
-
致谢: 感谢中国地质调查局发展研究中心程志中研究员及其团队在工作中给予的帮助,感谢中国地质大学(北京)邱坤峰副教授及审稿专家提出的宝贵修改意见。
-
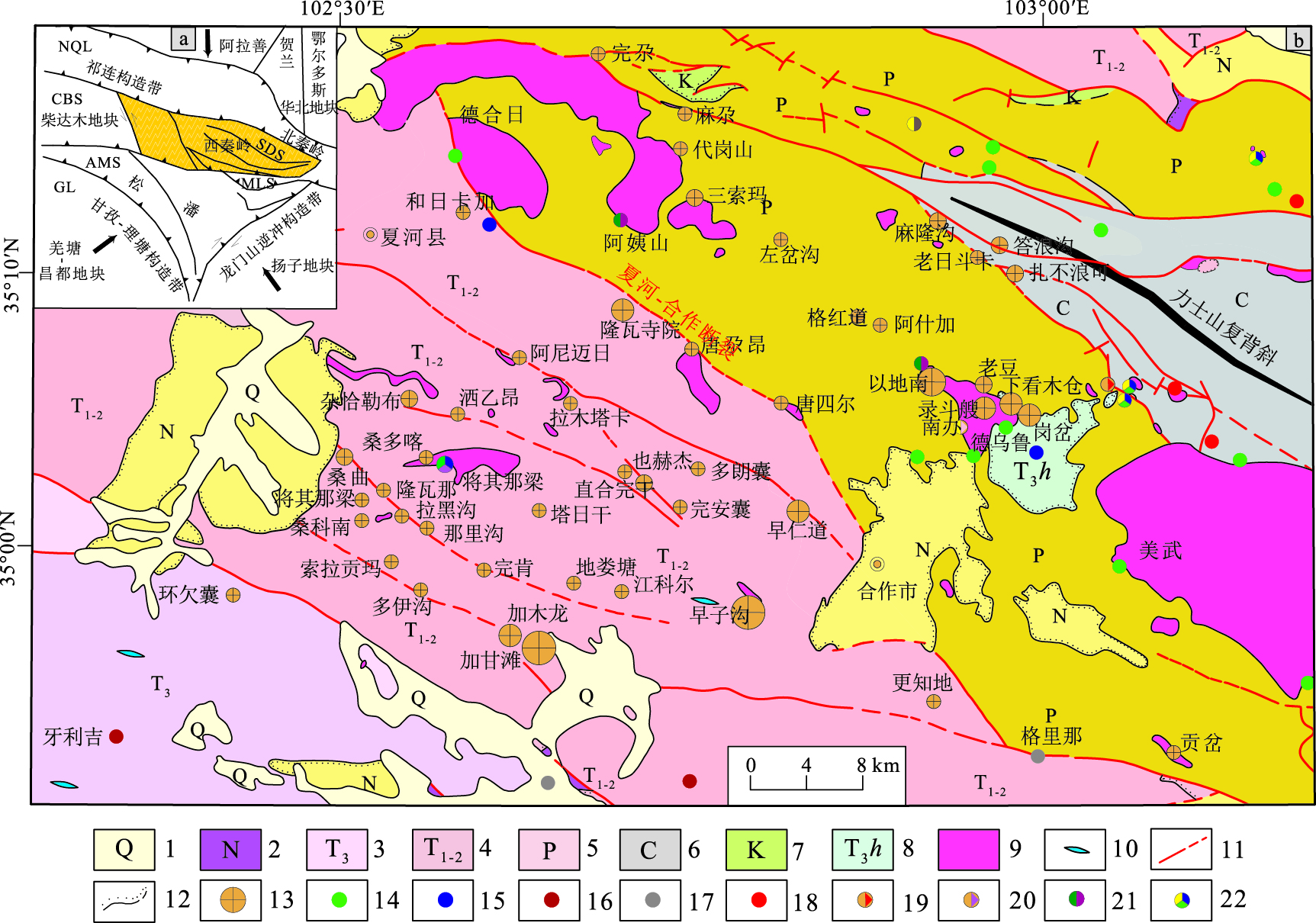
图 1 夏河—合作地区地质简图(a据参考文献[4];b据参考文献[5])
1-第四系; 2-新近系; 3-上三叠统; 4-中下三叠统; 5-二叠系; 6-石炭系; 7-白垩纪玄武岩; 8-三叠纪火山岩; 9-印支期花岗岩; 10-中酸性脉岩; 11-断裂; 12-角度不整合界线; 13-金矿; 14-铜矿; 15-铅矿; 16-锑矿; 17-汞矿; 18-铁矿; 19-铁铜矿; 20-铜钼矿; 21-铜钨矿; 22-多金属矿; CBS-柴北缘古缝合带; SDS-商丹古缝合带; KLS-东昆仑古缝合带; AMS-阿尼玛卿古缝合带; NQL-北祁连缝合带; MLS-勉略古缝合带; GL-甘孜-理塘缝合带
Figure 1. Geological map of Xiahe-Hezuo area
图 2 以地南铜金矿地质图及13勘查线剖面图(据参考文献②修改)
1—石英闪长岩;2—矽卡岩;3—大理岩;4—矿体及编号;5—地质界线;6—断层破碎蚀变带及编号;Q—第四系;P1dg4—下二叠统大关山组四段;P1dg3—下二叠统大关山组三段;P1dg2—下二叠统大关山组二段
Figure 2. Geological map of the Yidinan Cu-Au deposit and geological section along No.13 exploration line
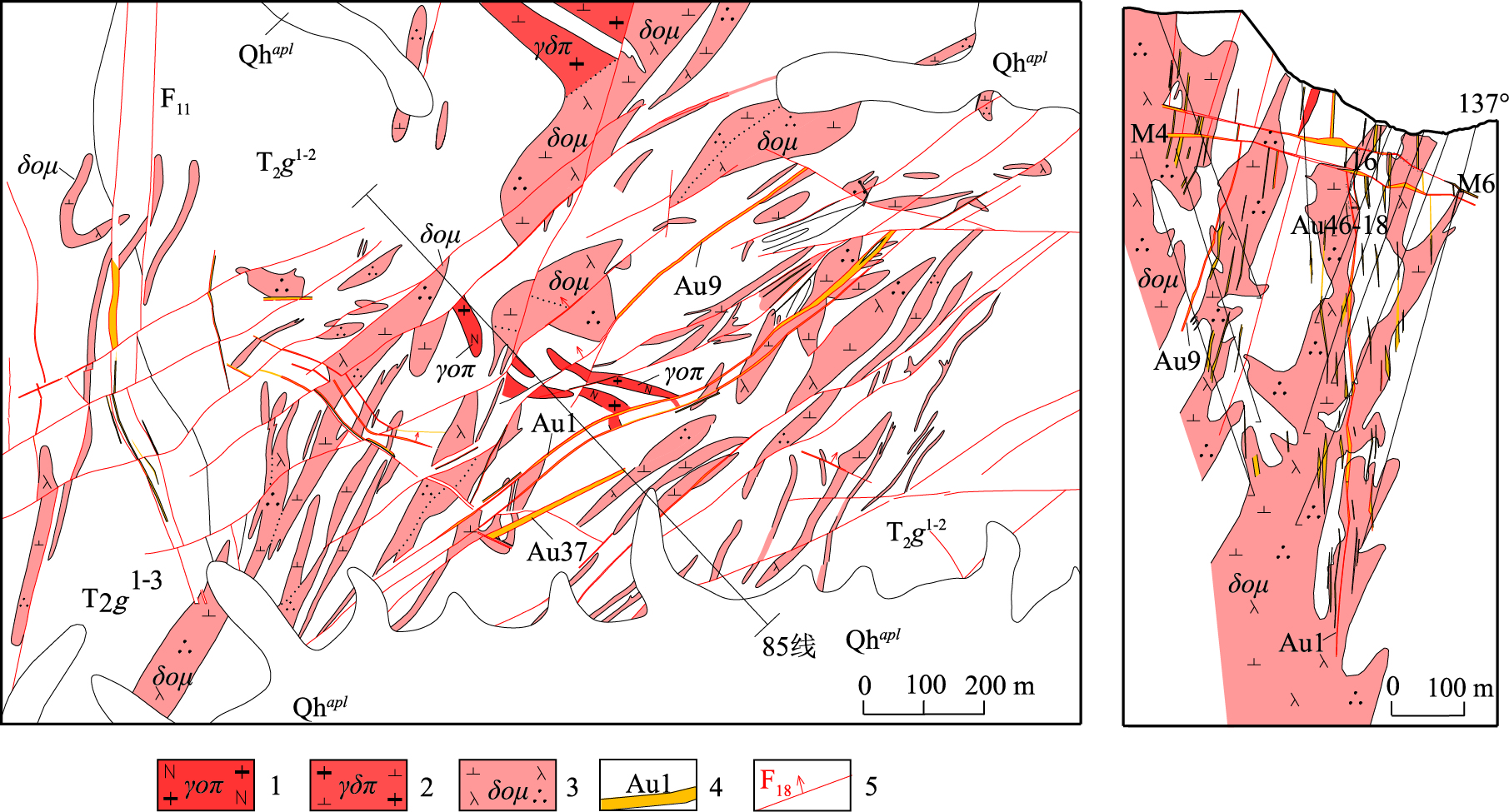
图 3 早子沟金矿地质图及85勘查线剖面图(据参考文献③修改)
1—斜长花岗斑岩;2—花岗闪长斑岩;3—石英闪长玢岩;4—金矿体及编号;5—断裂及编号;Qhapl—第四系冲洪积物;T2g1-3—中三叠世古浪堤组一段第三岩性段;T2g1-2—中三叠世古浪堤组一段第二岩性段
Figure 3. Geological map of the Zaozigou gold deposit and geological section along No.85 exploration line
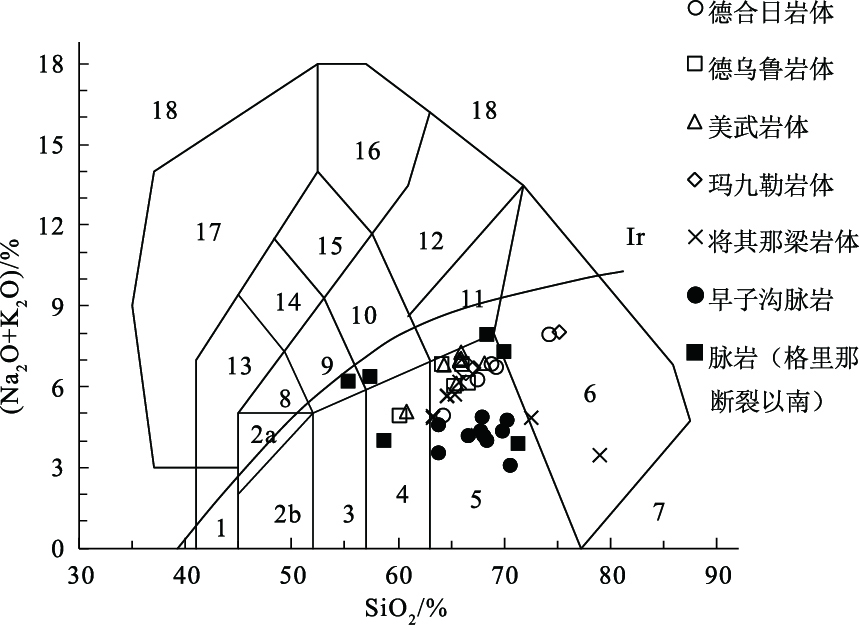
图 4 侵入岩TAS分类图解[17]
1-橄榄辉长岩; 2a-碱性辉长岩; 2b-亚碱性辉长岩; 3-辉长闪长岩; 4-闪长岩; 5-花岗闪长岩; 6-花岗岩; 7-硅英岩; 8-二长辉长岩; 9-二长闪长岩; 10-二长岩; 11-石英二长岩; 12-正长岩; 13-副长石辉长岩; 14-副长石二长闪长岩; 15-副长石二长正长岩; 16-副长正长岩; 17-副长深成岩; 18-霓方钠岩/磷霞岩/粗白榴岩; Ir为分界线, 上方为碱性, 下方为亚碱性
Figure 4. TAS classification diagram of intrusions
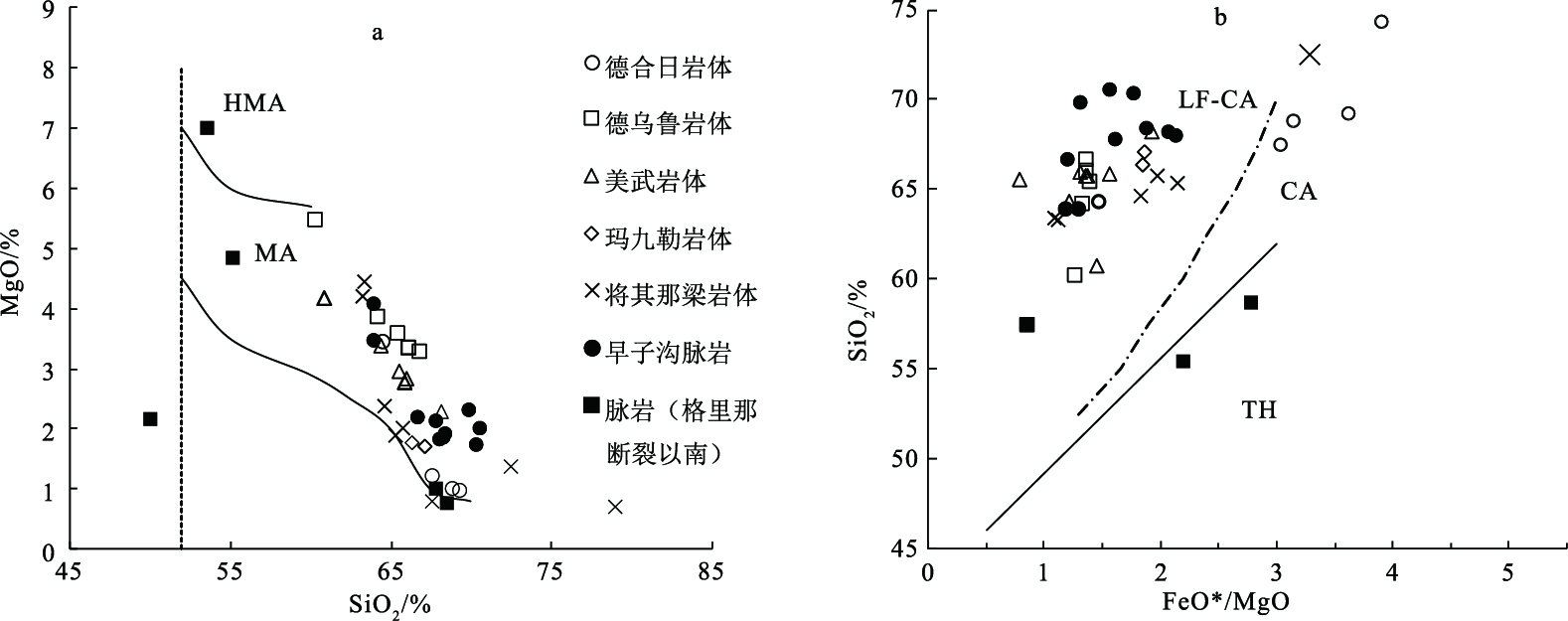
图 5 岩浆系列SiO2-K2O判别图解[18]
Figure 5. SiO2-K2O diagram of magma series
图 7 TTG岩套An-Ab-Or判别图解[21]
Figure 7. An-Ab-Or classification diagram of TTG
表 1 夏河—合作地区主要侵入岩主量元素及相关参数
Table 1 The content of major elements and main parameters of intrusions in Xiahe-Hezuo area
% 地点 样号 岩性 SiO2 TiO2 Al2O3 Fe2O3 FeO MnO MgO CaO Na2O K2O P2O5 总计 Na2O+K2O FeO*/MgO 数据来源 德合日岩体 PM048-1-1 花岗闪长岩 62.71 0.66 15.75 0.69 4.33 0.09 3.38 4.95 2.5 2.28 0.12 97.46 4.78 1.46 ④ PM048-3-1 花岗闪长岩 67.74 0.53 15.72 0.2 3 0.04 1.01 3.24 2.8 3.9 0.19 98.37 6.70 3.15 PM048-6-1 花岗闪长岩 66.32 0.6 16.42 0.49 3.2 0.06 1.2 3.6 2.7 3.44 0.19 98.22 6.14 3.03 PM048-10-1 花岗闪长岩 73.42 0.18 14.49 0.09 1.05 0.02 0.29 1.35 3.3 4.5 0.1 98.79 7.80 3.90 PM048-12-1 似斑状花岗闪长岩 68.37 0.6 15.34 0.39 3.12 0.04 0.96 3.09 2.52 4.12 0.19 98.74 6.64 3.62 德乌鲁岩体 DW-1 石英闪长岩 58.6 0.74 14.86 0.44 6.29 0.11 5.31 5.94 2.98 1.8 0.15 97.22 4.78 1.26 ⑤ DW-2 石英闪长岩 63.16 0.61 14.48 0.55 4.55 0.08 3.81 4.32 3.86 2.84 0.14 98.40 6.70 1.32 DW-3 石英二长闪长岩 64.6 0.57 14.72 0.56 4.39 0.08 3.54 4.25 2.69 3.24 0.12 98.76 5.93 1.38 DW-4 石英二长闪长岩 65.15 0.52 14.23 0.63 3.89 0.08 3.3 3.96 3.86 2.88 0.12 98.62 6.74 1.35 DW-5 花岗闪长岩 65.96 0.5 14.51 0.59 3.87 0.07 3.24 3.99 2.78 3.25 0.1 98.86 6.03 1.36 美武岩体 MW-1 石英闪长岩 64.87 0.55 14.85 0.86 3.51 0.07 2.74 3.7 3.86 3.31 0.14 98.46 7.17 1.56 ⑤ MW-2 二长花岗岩 67.02 0.52 14 1.1 3.35 0.08 2.26 3.06 2.95 3.79 0.17 98.30 6.74 1.92 MW-3 花岗闪长岩 64.37 0.6 14.99 0.26 2.05 0.06 2.9 6.81 4.66 1.36 0.16 98.22 6.02 0.79 MW-4 花岗闪长岩 66.46 1.05 18.9 2.46 4.37 0.22 4.56 5.65 2.89 2.64 0.12 109.32 5.53 1.44 MW-5 石英闪长岩 65.26 0.37 15.84 0.4 3.38 0.09 2.74 4.04 3.56 3.36 0.13 99.17 6.92 1.36 MW-6 石英闪长岩 65.14 0.33 15.91 0.73 3.04 0.09 2.73 4 3.67 3.22 0.13 98.99 6.89 1.35 MW-7 石英闪长岩 65.12 0.32 15.84 0.58 3.15 0.08 2.8 3.74 3.66 3.31 0.13 98.73 6.97 1.31 MW-8 石英闪长岩 63.58 0.36 16.03 0.11 3.97 0.09 3.35 4.51 3.58 3.13 0.12 98.83 6.71 1.21 玛久勒岩体 MJ-1 黑云母花岗闪长岩 65.31 0.62 16.76 0.07 3.18 0.05 1.75 4.01 2.84 3.73 0.14 98.46 6.57 1.85 ⑤ MJ-2 蚀变花岗斑岩 74.58 0.05 14.7 0.2 0.56 0.03 0.09 1.02 3.61 4.33 0.03 99.20 7.94 8.22 MJ-3 二长花岗岩 65.68 0.56 16.48 0.16 2.98 0.05 1.68 3.59 2.93 3.65 0.13 97.89 6.58 1.86 将其那梁岩体 JQ-1 石英闪长玢岩 62.99 0.6 16.14 4.06 0.08 0.75 4.58 0.49 3.46 0.109 93.26 3.95 4.87 ⑥ JQ-2 石英闪长玢岩 59.94 0.57 15.72 5.07 0.1 4.2 4.28 2.38 2.24 0.099 94.60 4.62 1.09 JQ-3 花岗斑岩 76.08 0.16 12.01 2.27 0.07 0.67 1.73 0.24 3.08 0.029 96.34 3.32 3.05 JQ-4 石英闪长玢岩 60.4 0.62 16.08 4.99 0.09 4 4.53 2.41 2.24 0.108 95.47 4.65 1.12 JQ-5 花岗斑岩 71.29 0.61 13.2 4.9 0.15 1.34 1.95 3.51 1.28 0.137 98.37 4.79 3.29 JQ-6 闪长玢岩 60.17 0.54 15.75 4.14 0.12 1.73 4.29 2.26 3.03 0.106 92.14 5.29 2.15 JQ-7 黑云石英闪长玢岩 63.02 0.57 16.69 4.75 0.1 2.33 4.45 2.63 2.89 0.105 97.54 5.52 1.83 JQ-8 闪长玢岩 64.29 0.54 16.74 4.3 0.09 1.96 3.68 3.18 2.87 0.104 97.75 6.05 1.97 早子沟脉岩 2011Ⅱ1QH-6 闪长玢岩型矿石 63.26 0.513 16.19 2.80 0.83 0.046 1.78 3.29 0.112 3.57 0.11 92.50 3.68 1.88 [16] 2011Ⅱ1QH-7 闪长玢岩型矿石 57.82 0.552 14.55 2.72 1.63 0.058 3.14 5.74 0.125 4.02 0.099 90.45 4.15 1.30 2011Ⅱ1QH-8 闪长玢岩 57.65 0.553 15.17 3.36 1.31 0.064 3.67 5.21 0.318 2.83 0.095 90.23 3.15 1.18 2011Ⅱ1QH-9 闪长玢岩 64.41 0.465 14.84 2.12 0.97 0.038 1.85 3.71 0.195 2.57 0.111 91.28 2.77 1.56 2011Ⅱ1QH-10 闪长玢岩型矿石 65.55 0.454 14.62 1.84 1.22 0.036 1.62 3.34 0.936 3.47 0.103 93.19 4.41 1.78 11ⅥYQ-6 石英闪长玢岩 62.68 0.57 15.81 1 2.65 0.05 1.72 3.52 0.096 3.72 0.11 91.93 3.82 2.06 11ⅥYQ-9 石英闪长玢岩 63.29 0.46 13.96 1.05 1.82 0.05 2.1 3.88 0.11 3.78 0.08 90.58 3.89 1.32 11ⅥYQ-10 石英闪长玢岩 60.7 0.5 14.7 0.96 2.18 0.05 1.9 4.57 0.093 3.76 0.08 89.49 3.85 1.60 11ⅥYQ-7 闪长岩 60.09 0.58 16.43 1.63 0.91 0.05 1.98 4.66 0.13 3.59 0.1 90.15 3.72 1.20 11ⅥYQ-8 闪长岩 63.24 0.6 16.65 0.67 3.01 0.05 1.7 2.43 0.13 4.39 0.1 92.97 4.52 2.13 脉岩(格里那
断裂以南)2017XⅥYQ-1 闪长玢岩 55.14 0.806 17.22 6.01 5.19 0.082 4.84 3.78 4.56 1.56 0.266 99.45 6.12 2.19 本文 2017XⅥYQ-2 闪长玢岩 68.42 0.475 15.28 3.44 0.45 0.042 0.772 1.66 4.38 2.72 0.129 97.77 7.10 4.59 2017XⅥYQ-3 闪长玢岩 67.8 0.462 15.08 3.3 1.73 0.036 1.02 1.62 4.1 3.76 0.12 99.03 7.86 4.61 2017XⅥYQ-4 石英闪长玢岩 65.17 0.52 12.38 3.05 0.71 0.107 0.107 5.50 1.37 2.18 0.151 91.24 3.55 32.28 S98-2 闪长玢岩 50.08 0.53 9.39 4.93 1.62 0.15 2.18 12.87 1.36 2.04 0.1 85.25 3.40 2.78 Ⅲ-10-1 闪长玢岩 53.56 0.75 14.55 2.23 3.89 0.09 6.99 4.75 4.26 1.65 0.52 93.24 5.91 0.84 表 2 夏河—合作地区典型矿床硫稳定同位素δ34S值
Table 2 The sulfur stable isotope δ34S values of typical deposits in Xiahe-Hezuo area
测试对象 黄铁矿/‰ 毒砂/‰ 辉锑矿/‰ 数据来源 老豆金矿 -5.9~2.9 平均-2.48 -5.9~3.2 平均-4.87 2.9~5.0 平均4.81 [15] 以地南铜金矿 2.2~4.9 平均3.86 -3.8~7.1 平均2.33 2.8~4.6 平均3.7 早子沟金矿 -9.3~-5 平均-7.4 -10.1~-5.72 平均-8.89 -12.3~-7 平均-10.1 [24-25] 早子沟金矿含金黄铁矿 -1.5~-2.9 平均-2.2 本文 加甘滩金矿 -12.5~-7.5 平均-10 -13.4 平均-13.4 注:测试单位为核工业北京地质研究院分析测试研究中心;测试仪器为Delta v plus气体同位素质谱计;精度优于0.2‰ 表 3 夏河—合作地区典型矿床H-O稳定同位素组成
Table 3 The sulfur stable isotope H-O values of typical deposits in Xiahe-Hezuo area
测试对象 δ18OH2O/‰ δD/‰ 数据来源 老豆金矿 绢云母 3.5~7.3 平均4.8 -88.4~-65.1 平均-75.8 [26] 电气石 -1.45~0.85 平均-0.33 -70.1~-55.3 平均-66.2 以地南铜金矿 石英 15.5~15.4 平均15.4 -87.6~-85.8 平均-86.7 本文 早子沟金矿 石英 6.1~12.1 平均9.16 -103.4~-67.4 平均-94.5 [27-29] 加甘滩金矿 石英 9~11.4 平均9.8 -99.9~-93.7 平均-96.7 本文 注:测试单位为中国地质大学(武汉)地质过程与矿产资源国家重点实验室;测试仪器为Delta V Advantage;精度:H为2‰、O为0.2‰ -
任纪舜, 张正坤, 牛宝贵, 等.论秦岭造山带一中朝与扬子陆块的拼合过程[C]//叶连俊, 钱祥麟, 张国伟.秦岭造山带学术讨论会论文选集.西安: 西北大学出版社, 1991: 99-110. 闫臻.西秦岭晚古生代弧前盆地沉积与成矿作用[D].中国科学院研究生院地质与地球物理研究所博士学位论文, 2002: 20-50. 张国伟, 郭安林, 姚安平.中国大陆构造中的西秦岭-松潘大陆构造结[J].地学前缘, 2004, 11(3):23-32. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dxqy200403004 张国伟, 张宗清, 董云鹏, 等.秦岭造山带主要构造岩石地层单元的构造性质及其大地构造意义[J].岩石学报, 1995, 11(2):101-113. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-YSXB199502000.htm 李康宁, 李鸿睿, 贾儒雅, 等, 甘肃早子沟金矿"三位一体"找矿预测地质模型的构建[J].矿产勘查, 2019, 10(6):1397-1408. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ytgcj201906016 Qiu K F, Yu H C, Deng J, et al, The giant Zaozigou Au-Sb deposit in West Qinling, China:magmatic- or metamorphic-hydrothermal origin?[J].Mineralium Deposita, 2020, 55:345-362. doi: 10.1007/s00126-019-00937-w
李建威, 隋吉祥, 靳晓野, 等, 西秦岭夏河—合作地区与还原性侵入岩有关的金成矿系统及其动力学背景和勘查意义[J].地学前缘, 2019, 26(5):17-32. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dxqy201905003 李康宁, 金鼎国, 蔡龙, 等.早子沟金矿黄铁矿标型特征及其地质意义[J].甘肃地质, 2014, 23(2):33-40, http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gsdzxb201402004 刘伯崇, 李康宁, 史海龙, 等.西秦岭甘青交界一带晚三叠世火山岩岩石成因及构造指示意义[J].现代地质, 2018, 32(4):704-717. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=xddz201804008 张克信, 朱云海, 林启祥, 等.青海同仁县隆务峡地区首次发现镁铁质-超镁铁质岩带[J].地质通报, 2007, 26(6):661-667. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=200706116&flag=1 邓晋福, 冯艳芳, 狄永军, 等.中国侵入岩大地构造图(1:2500000)[M].北京:地质出版社, 2016:1-100. 秦江锋.秦岭造山带晚三叠世花岗岩类成因机制及深部动力学背景[D].西北大学博士学位论文, 2010: 1-173. 高婷.西秦岭西段北部重要侵入体年代学、地质地球化学、形成构造环境及与成矿作用关系[D].长安大学硕士学位论文, 2011: 1-82. 张宏飞, 靳兰兰, 张利.等.西秦岭花岗岩岩类地球化学和Pb-Sr-Nd同位素组成对基底性质及其构造属性的限制[J].中国科学(D辑), 2005, 35:914-926. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgkx-cd200510002 陈明辉, 郭素雄, 徐军伟, 等.德乌鲁岩体内外接触带金多金属成矿区成岩成矿地质地球化学特征及成因探讨[J].矿产与地质, 2016, 30(4):518-530. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kcydz201604001 陈国忠, 梁志录, 王建龙, 等.早子沟金矿岩石地球化学特征及其地质意义[J].甘肃地质, 2012, 21(4):23-31. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK201206096440 Le Maitre R W.A Classification of Igneous Rocks and Glossary of Terms[M].Blackwell, Oxford, 1989: 1-193.
Peccerillo A, Taylor S R.Geochemistry of Eocene calcalkaline volcanic rocks from the Kastamonu area, northern Turkey[J].Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1976, 58(1):63-81. doi: 10.1007/BF00384745
邓晋福, 刘翠, 冯艳芳, 等.高镁安山岩/闪长岩类(HMA)和镁安山岩/闪长岩类(MA):与洋俯冲作用相关的两类典型的火成岩类[J].中国地质, 2010, 37(4):1112-1118. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201004027.htm 邓晋福, 冯艳芳, 狄永军, 等.岩浆弧火成岩构造组合与洋陆转换[J].地质论评, 2015, 61(3):473-484. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzlp201503001 O'Connor J T, classification for quartz-rich igneous rocks based on feldspar ratios[J].United States Geological Survey Professional Paper, 1965, 525B:79-84. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/245542124_A_classification_of_quartz-rich_igneous_rocks_based_on_feldspar_ratio
李康宁, 刘伯崇, 狄永军.三叠纪西秦岭西北部洋俯冲的记录:来自镁安山岩/高镁安山岩的证据[J].中国地质, 2020, 47(3):350-365. Wyllie P J.Constraints imposed by experimental petrology on possible and impossible magma sources and products[J].Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A Mathematical Physical & Engineering Sciences, 1984, A310(1514):439-453. doi: 10.1098/rsta.1984.0003
李康宁, 金鼎国, 蔡龙, 等.早子沟金矿黄铁矿标型特征及其地质意义[J].甘肃地质, 2014, 23(2):33-40. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gsdzxb201402004 姜琪, 王荣超, 甘肃枣子沟金矿床形成环境及矿床成因[J].黄金科学技术, 2010, 18(4):37-40. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hjkxjs201004008 靳晓野.西秦岭夏河-合作地区老豆金矿矿床成因的地球化学和同位素年代学制约[D].中国地质大学(武汉)硕士学位论文, 2013: 1-144. 刘勇.甘肃省枣子沟金矿中酸性脉岩与金成矿关系研究[D].长安大学硕士学位论文, 2012: 1-72. 曹晓峰, Mohamed Lamine Salifou Sanogo, 吕新彪, 等, 甘肃枣子沟金矿床成矿过程分析——来自矿床地质特征、金的赋存状态及稳定同位素证据[J].吉林大学学报, 2012, 42(4):1039-1054. 陈国忠, 张愿宁, 梁志录, 等, 利用包裹体测温资料估算早子沟金矿成岩成矿压力及pH、Eh值[J].甘肃地质, 2014, 23(4):23-32. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gsdzxb201404004 Taylor H P.The application of oxygen and hydrogen isotope studies to problems of hydrothermal alteration and ore deposit[J].Econ.Geol., 1974, 69:843-883. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.69.6.843
Zhang H F, Jin L L, Zhang L, et al.Geochemical and Pb-Sr-Nd isotopic compositions of granitoids from western Qinling belt:Constraints on basement nature and tectonic affinity[J].Science in China:Earth Sciences, 2007, 50(2):184-196. doi: 10.1007/s11430-007-2015-3
Meng Q R, Wang E, Hu J M.Mesozoic sedimentary evolution of the northwest Sichuan basin:Implication for continued clockwise rotation of the South China block[J].Geological Society of America Bulletin, 2005, 117(3/4):396-410. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/215614456_Mesozoic_sedimentary_evolution_of_the_northwest_Sichuan_Basin_implication_for_continued_clockwise_rotation_of_the_South_China_Block
Li X W, Mo X X, Yu X H, et al.U-Pb zircon geochronology, geochemical and Sr-Nd-Hf isotopic compositions of the Early Indosinian Tongren Pluton in West Qinling:Petrogenesis and geodynamic implications?[J].Lithos, 2013, 172:158-174. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S136791201400474X
Groves D I, Goldfarb R J, Gebre-Mariam M, et al.Orogenic gold deposits:a proposed classification in the context of their crustal distribution and relationship to other gold deposit types[J].Ore Geology Reviews, 1998, 13:7-27. doi: 10.1016/S0169-1368(97)00012-7
张旗, 殷先明, 殷勇, 等.西秦岭与埃达克岩和喜马拉雅型花岗岩有关的金铜成矿及找矿问题[J].岩石学报, 2009, 25(12):3103-3122. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98200912001 殷勇, 赵彦庆.甘肃西秦岭金矿富集区花岗岩与金成矿作用的关系[J].甘肃地质, 2006, 15(1):36-41. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gsdzxb200601006 殷勇, 殷先明.西秦岭北缘与埃达克岩和喜马拉雅型花岗岩有关的斑岩型铜-钼-金成矿作用[J].岩石学报, 2009, 25(5):1239-1252. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98200905016 徐学义, 李婷, 陈隽璐, 等.西秦岭西段花岗岩浆作用与成矿[J].西北地质, 2012, 45(4):76-82. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=xbdz201204008 甘肃省地矿局第三地质矿产勘查院.甘肃省夏河县加甘滩金矿资源储量核实暨扩大区详查报告.2015. 湖南省有色地质勘查局二四五队.甘肃省合作市以地南铜金矿补充详查报告(2012-2014).2015. 甘肃省地矿局第三地质矿产勘查院.甘肃省合作市早子沟金矿接替资源勘查报告.2016. 中国地质大学(武汉)地质调查研究院.1: 25万《临夏幅》报告.2006. 甘肃省地矿局第三地质矿产勘查院.甘肃省合作—美武一带1: 5万矿产远景调查报告.2013. 陈正乐, 韩凤彬, 王功文, 等.甘肃省合作市早子沟金矿找矿预测研究.中国地质科学院地质力学研究所, 2015.



 下载:
下载: