Geochemical anomaly characteristics and mineral potential mapping in Milashan area of Tibet
-
摘要:
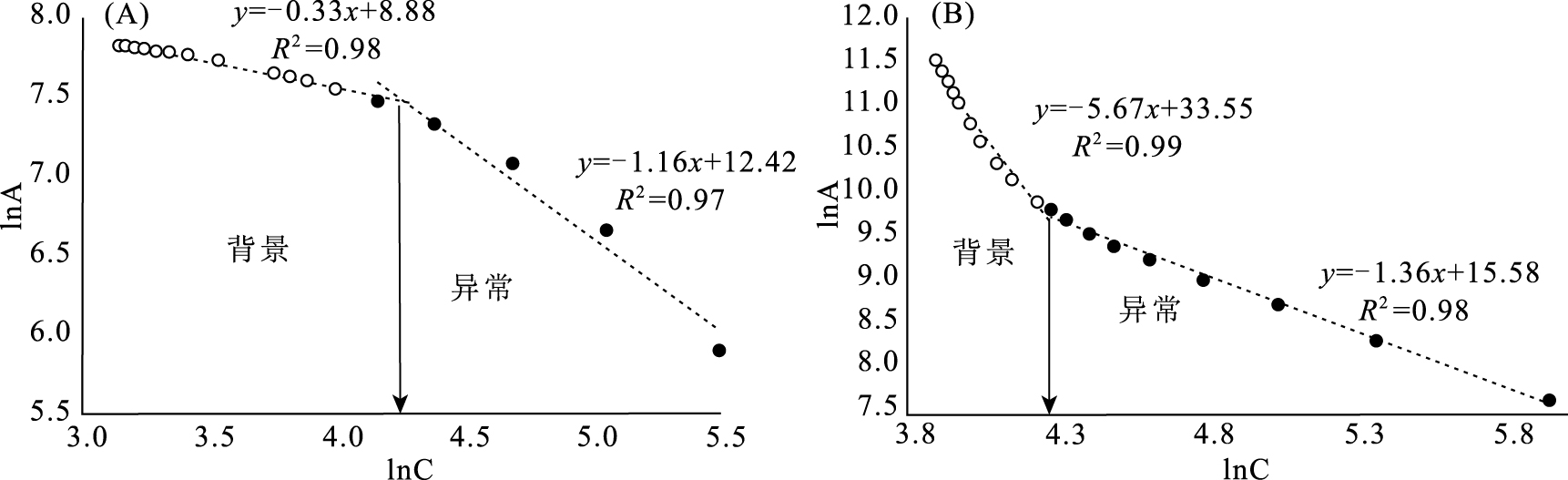
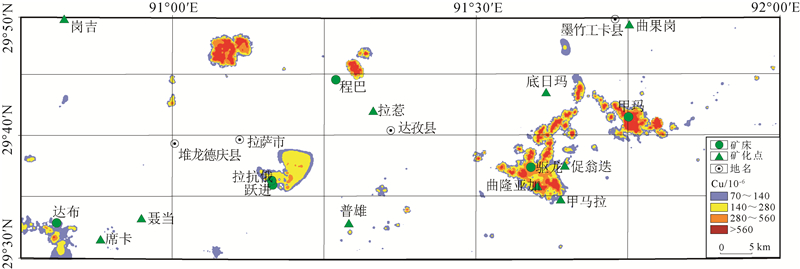
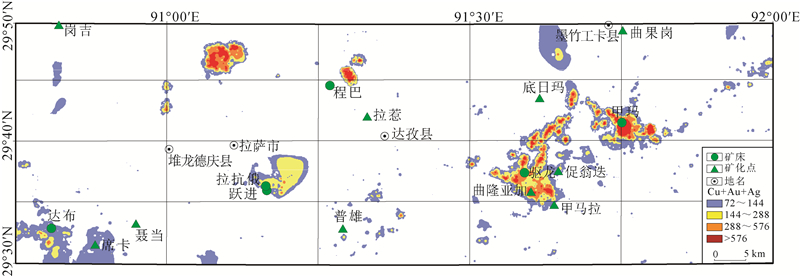
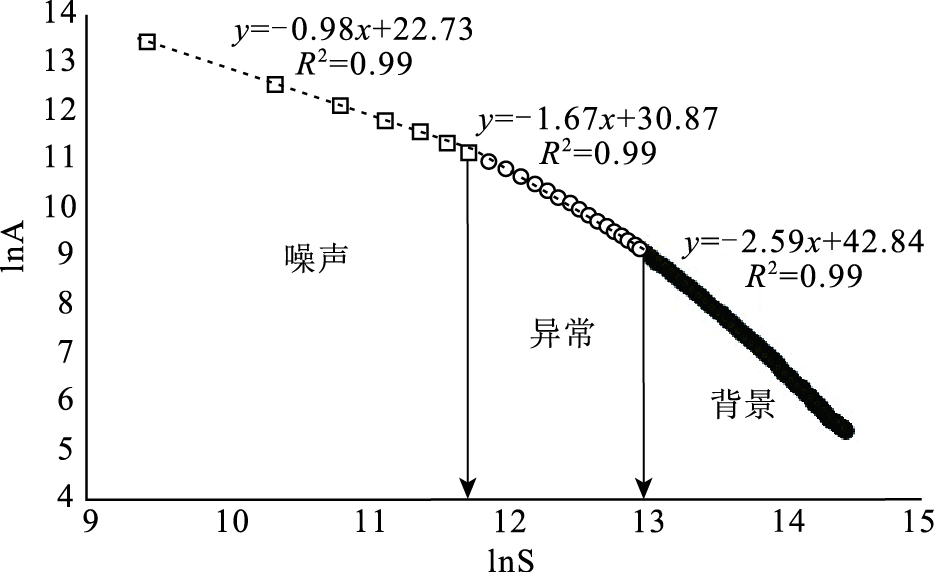
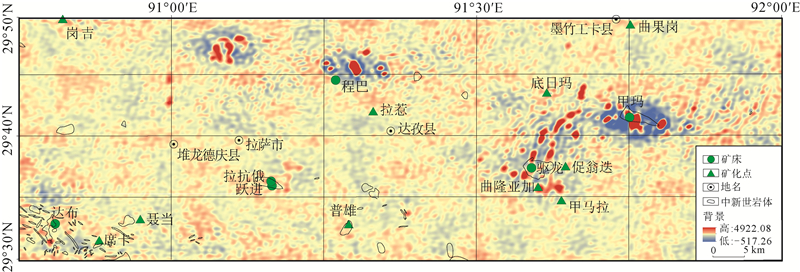
水系沉积物地球化学异常分析在勘查找矿方面一直发挥着重要作用。采用中位数+2倍绝对中位差和C-A分形法,对米拉山地区1:5万水系沉积物Cu元素及由R型因子分析确定的Cu+Au+Ag组合元素进行了异常分析,确定了阈值。结果显示C-A分形法能更好地识别异常下限,且C-A分形模型确定的Cu元素异常比Cu+Au+Ag组合元素能更有效地反映米拉山地区与铜矿相关的化学异常特征。进而对Cu元素进行了S-A多重分形滤波处理,筛选出背景场和异常场,为圈定异常区提供更精准的依据。借助S-A分形模型和中位数方法划分了甲类异常2处(驱龙、甲玛)、乙类异常3处(达布、拉抗俄、程巴)、丙类异常2处(普雄、甲布纳)。甲类异常区包含冈底斯最大的2个斑岩铜矿,异常强,具有四级浓度分带,异常面积最大,外围找矿潜力巨大。乙类异常区包含3个大中型铜矿,都具有四级浓度分带,具有很好的找矿潜力。丙类异常区目前尚未发现铜矿,但值得进一步开展地质工作,查明成矿潜力。
Abstract:The analysis of geochemical anomalies derived from stream sediment geochemical data is a fundamental task in mineral prospecting.In this study, median+2 median absolute deviations(median+2MAD)and concentration-area(C-A)were applied to analyze geochemical anomaly delineation of Cu and Cu+Au+Ag association from factor analysis of stream sediment geochemical data in Milashan area of Tibet.The results show that the C-A fractal method is a favorable means for identifying the anomaly.Cu anomaly provides more information than Cu+Au+Ag associated anomaly.Furthermore, the S-A analysis was used to decompose the Cu element and distinguish the background from anomaly components, which provides a more accurate basis for delineating the anomalous area.Six anomalous areas have been classified into classes A(Qulong and Jiama), B(Dabu, Lakange and Chengba)and C(Puxiong and Jiabuna).Class A anomalous areas containing two largest porphyry copper deposits in the Gangdise belt are characterized by great anomalous intensity and largest anomalous area, and have great potential for periphery prospecting.Class B prospective areas contain three large and medium-sized copper deposits.Particularly, the Chengba anomalous area has similar anomalous intensity to Qulong and Jiama anomalous areas and thus has good prospecting potential.Copper deposits have not been discovered in Class C anomalous areas, but it deserves exploration work for identifying the mineral potential.
-
Keywords:
- stream sediment data /
- anomaly /
- factor analysis /
- ore prospecting /
- Milashan area
-
区域地质调查和填图是地质工作的基础,也是衡量一个国家基础地质调查和研究程度及水平的重要指标,具有重要的战略意义。中国地质调查局高度重视基础地质调查与填图方式、方法的改革,树立“地质填图的过程就是科学研究的过程”的理念,确定“需求决定工作部署”、“问题决定调查方式”的工作思路,提升解决制约重大资源环境的基础地质问题和地球系统科学问题的能力。在中国地质调查局总工室和基础部的协调、领导下,由中国地质科学院地质研究所、地质力学所联合地调局六大区域地质调查中心开展了国际分幅和非国际分幅的中大比例尺专题试点填图,取得了重要进展。这是中国第一次较系统地构建填图方法体系。2019年11月6—7日,中国地质调查局召开了第三次全国区域地质调查工作会议。同时,成立了全国区域地质调查专家委员会,并组织了全国区调填图方法研讨会,来自全国地质行业近100人参加了培训和研讨,有30人在会议上交流发言,展现了区调改革在技术方法上的创新及取得的一批新进展、新发现,收效良好。
本专辑是本次会议成果的一次体现。本专辑共收录15篇论文,内容涉及短周期密集台阵方法在专题填图中的运用、遥感技术的使用等,以及地层、岩浆岩(侵入岩和火山岩)、变质岩、蛇绿混杂岩、构造、古生物、矿床等基础学科填图成果;还有论文,包括岩溶地区填图方法和地貌演变、造山带构造变形、侵入岩、蛇绿混杂岩、年轻变质事件及热泉的填图成果介绍,将在下一辑发表。这些论文集中展示了填图的成果。
(1)地球物理方法在填图中的运用。新填图方法和理念的运用是现代填图的重要内容,卢占武等介绍了利用短周期密集台阵进行近地表结构调查的应用实例,提出了该技术在专题地质填图中的应用前景,丰富和完善了专题填图的技术方法体系。李娜等介绍了高光谱遥感技术在中国西部基岩区填图中的应用,高光谱遥感数据对不同岩性段和岩相带、细小构造等区分能力突出,提高了地质调查填图的效率和质量。
(2)蛇绿混杂岩填图。蛇绿混杂岩的填图历经数十年的探索,也是造山带研究的基础数据来源,王国强等系统介绍了近十余年来北山造山带关键地段1:5万区域地质调查和综合研究成果,突出了造山带蛇绿混杂岩带填图方法在北山地区的实践和应用。付长垒等在大比例尺填图的基础上,在拉脊山识别出连续的洋岛海山火山-沉积组合序列,为造山带古洋盆构造演化研究提供了新思路。
(3)侵入岩区填图。侵入岩是造山带的重要组成部分,对它们的刻画和研究一直是造山带研究的基础性工作。苑新晨等对滇西澜沧江地区南段复式岩基进行研究,确定其是古特提斯封闭及保山-思茅地块碰撞的响应。卢鹏等在前期开展同位素填图的基础上,在东准噶尔乌伦古河地区识别出一套晚古生代富碱细晶花岗质岩墙,这期岩墙在整个中亚造山带中普遍发育,具有重要的构造环境指示意义。车亚文等在1:5万填图的基础上,对大兴安岭南段林西地区辉长闪长岩开展系统工作,确定其与蒙古-鄂霍茨克洋闭合引起的碰撞后伸展背景有关。王帅等报道了1:5万填图发现的迪彦庙SSZ型蛇绿岩北部晚石炭世马尼塔埃达克岩,确定其为洋内俯冲岩石组合的重要组成部分,表明古亚洲洋东段在晚石炭世处于洋内俯冲消减过程中。
(4)沉积岩区填图。沉积岩区填图是建立地层系统与格架、恢复区域和生命演化的重要手段。向忠金等通过对中越边界富宁—那坡地区的1:5万填图,查明早—中三叠世火山岩及其相关沉积序列,确定了扬子南缘地区印支期岛弧火山-沉积环境。石秋圆等报道了新建立的中—上三叠统卡尼阶岩石地层单位——嘎热扎地组,该工作填补了措勤中—上三叠统卡尼阶岩石地层单位的空白。安显银等报道了在西藏察雅地区侏罗纪红层中发现的恐龙化石,丰富了侏罗系恐龙的地理分布,有助于了解亚洲地区蜥脚类和兽脚类恐龙的早期演化和分异。
(5)变质岩区填图。变质岩填图是填图的难点,也是获得突破和新发现的主要基础。李猛等对东昆仑西段金水口岩群白沙河岩组的碎屑锆石进行研究,指出东昆仑早古生代可能存在一条近千千米的高压变质岩带。张连祥等通过莱阳地区1:5万变质基底填图,限定了胶北荆山群禄格庄组的原岩为古元古代,推测粉子山群小宋组与祝家夼组沉积时可能靠近被动大陆边缘的一侧,而禄格庄组更靠近岩浆岛弧的一侧,二者可能属于同时异相沉积的产物。
(6)复杂构造区填图。构造地质是中国填图中最薄弱的环节,复杂现象和关系的识别及构造过程的建立得益于详细地地质填图。张北航等在1:5万填图的基础上,厘定出狼山地区自晚侏罗世以来发育6期陆内变形,并认为先存构造和欧亚板块边缘自晚侏罗世以来不同方向的增生是控制狼山地区陆内变形的主要因素。柯昌辉等通过对白云鄂博矿田内褶皱及断层构造特征的剖析,确定了中元古代—晚古生代4期构造活动,对矿区深部及外围找矿工作具有重要的指导意义。
本专辑的文章是填图试点的部分成果及方法探索,希望能够为今后进一步开展中大比例尺(1:5万和1:2.5万)区域地质填图和专题填图起到推广和借鉴作用,成功的经验和失败的教训都是未来继续工作不可多得的财富。希望专辑中介绍的新方法、新理念能够逐步为广大一线工作认可,并运用到新时期地质调查工作中。
张 进 王 涛
中国地质科学院地质研究所
2020年12月20日
-
表 1 米拉山水系沉积物数据特征统计
Table 1 Statistics of stream sediment geochemical data from Milashan area
参数 Au Ag Cu Pb Zn Ba Mo Sn Sb Bi W 采样点个数 15622 15622 15622 15622 15622 15622 15622 15622 15622 15622 15622 平均值 3.29 0.14 47.57 54.58 94.2 435.96 1.71 3.22 2.13 1.1 4.19 中位数 1.86 0.09 22.5 30 71.8 431 0.78 3.04 1.18 0.48 3.37 标准偏差 17 0.49 277 1391 972 94 14 3 27 10 9 方差 278 0.25 77133 193526 944468 8831 188 8 741 103 74 偏度 58 31 35 93 75 2 60 19 71 31 33 峰度 3887 1267 1779 9658 6109 10 4523 487 5439 1182 1584 最小值 0.01 0.01 2.10 4.90 10.40 3.00 0.10 0.44 0.04 0.04 0.23 最大值 1236 26 18600 153000 89200 1852 1206 103 2384 501 528 25%累计频率 1.24 0.07 18.30 25.90 61.00 398.00 0.59 2.39 0.90 0.35 2.61 50%累积频率 1.86 0.09 22.50 30.00 71.80 431.00 0.78 3.04 1.18 0.48 3.37 75%累积频率 2.82 0.13 28.10 34.40 83.40 467.00 1.10 3.71 1.52 0.61 4.10 95%累积频率 7.4 0.25 62.1 53.79 119 577 3.16 4.77 3.75 1.18 7.84 98%累积频率 16.2 0.45 266.54 88.35 184.54 658 9.08 5.32 7.01 2.69 15.5 注:元素含量Au的单位为10-9,其他元素均为10-6 表 2 米拉山地区正交旋转因子(F1-F3)载荷矩阵
Table 2 Orthometric rotating factor(F1-F3)loading matrix in Milashan area
因子 F1 F2 F3 Au 0.007 0.856 -0.035 Ag 0.259 0.739 0.403 Cu 0.480 0.686 0.186 Pb 0.960 0.041 0.001 Zn 0.975 0.079 0.020 Ba -0.078 0.052 -0.39 Mo 0.929 0.230 0.033 Sn -0.017 0.203 0.807 Sb 0.957 0.192 0.015 Bi -0.02 0.204 0.839 W 0.794 0.121 0.174 累计方差贡献率/% 46 66 75 表 3 Cu元素及Cu+Au+Ag组合元素异常下限值确定
Table 3 Anomaly threshold values calculated for Cu and Cu+Au+Ag
元素 异常下
限方法异常
下限总矿
床数覆盖
矿床
个数异常面积
出现矿床
概率(n)/%异常面积
占比(s)
/%n/s Cu C-A分形法 70 16 7 43.8 5.2 8.4 中位数方法 32 16 10 62.5 15.4 4.1 Cu+Au+Ag C-A分形法 72 16 8 50.0 7.8 6.4 中位数方法 59 16 9 56.3 13.7 4.1 -
Xie X J, Wang X Q, Zhang Q, et al.Multi-scale geochemical mapping in China[J].Geochemistry:Exploration, Environment, Analysis, 2008, 8(3/4):333-341. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/249545254_Multi-scale_geochemical_mapping_in_China?ev=auth_pub
王瑞廷, 毛景文, 任小华, 等.区域地球化学异常评价的现状及其存在的问题[J].中国地质, 2005, (1):168-175. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgdizhi200501023 曾曼平, 毛晓冬.西藏米拉山地区铜钼矿化特征及找矿前景浅析[J].矿物学报, 2015, 35(S1):180-181. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=9132890 武进.基于模糊证据权的找矿远景区预测方法研究与应用[D].成都理工大学硕士学位论文, 2016. Zuo R G.Identifying geochemical anomalies associated with Cu and Pb-Zn skarn mineralization using principal component analysis and spectrum-area fractal modeling in the Gangdese Belt, Tibet(China)[J].Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2011, 111(1/2):1-22. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=694199cf37b52ab4a41e9c49b4e6e091
Sun X, Zheng Y Y, Wangle C M, et al.Identifying geochemical anomalies associated with Sb-Au-Pb-Zn-Ag mineralization in North Himalaya, southern Tibet[J].Ore Geology Reviews, 2016, 73:1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2015.10.020
潘桂棠, 莫宣学, 侯增谦, 等.冈底斯造山带的时空结构及演化[J].岩石学报, 2006, (3):521-533. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98200603001 孙祥, 郑有业, 吴松, 等.冈底斯明则-程巴斑岩-夕卡岩型Mo-Cu矿床成矿时代与含矿岩石成因[J].岩石学报, 2013, 29(4):1392-1406. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98201304023 曾忠诚, 刘德民, 王明志, 等.西藏冈底斯东段驱龙—甲马地区构造-岩浆演化与成矿[J].地质论评, 2016, 62(3):663-678. http://qikan.cqvip.com/Qikan/Article/Detail?id=668885716 李世杰, 魏启荣, 次琼, 等.西藏达布矿区含矿岩体的时代、岩石地球化学特征及岩石成因[J].地球科学, 2018, 43(9):3218-3233. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqkx201809021 周洪伟.正态性检验的几种常用的方法[J].南京晓庄学院学报, 2012, (3):13-18 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=njxzxyxb201203004 朱裕生.矿产资源评价方法学导论[M].北京:地质出版社, 1984. 刘平.浅谈主成分分析与因子分析的异同[J].辽宁师专学报(自然科学版), 2004, (3):4-6. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=lnszxb200403003 林海明, 张文霖.主成分分析与因子分析的异同和SPSS软件——兼与刘玉玫、卢纹岱等同志商榷[J].统计研究, 2005, (3):65-69. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=15282088 林鑫, 周军, 张兵.基于主成分分析的化探异常圈定新方法——以新疆西准噶尔地区1:50000岩屑数据为例[J].地质找矿论丛, 2012, 27(4):516-521. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/90755X/201204/44316632.html 叶红刚, 叶红锋.SPSS软件数理统计应用及异常下限确定不同方法对比研究——以鹰咀山岩屑测量为例[J].甘肃地质, 2018, 27(2):83-92. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/96503X/20182/675653403.html 丛源, 陈建平, 肖克炎, 等."三江"地区北段区域地球化学元素组合异常提取及其找矿意义[J].地质通报, 2012, 31(7):1164-1169. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20120716&flag=1 李雪菲.吉林省和龙地区化探数据处理方法对比研究[D].吉林大学硕士学位论文, 2012. 宗序平, 姚玉兰.利用Q-Q图与P-P图快速检验数据的统计分布[J].统计与决策, 2010, (20):151-152. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=tjyjc201020047 Reimann C, Filzmoser P, Garrett R G.Background and threshold:critical comparison of methods of determination[J].Sci.Total Environ., 2005, 346(1/3):1-16. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0048969704007983
Cheng Q M, Agterberg F, Ballantyne S.The separation of geochemical anomalies from background by fractal methods[J].Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 1994, 51(2):109-130. doi: 10.1016/0375-6742(94)90013-2
成秋明.空间模式的广义自相似性分析与矿产资源评价[J].地球科学, 2004, (6):733-743. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqkx200406013 成秋明, 张生元, 左仁广, 等.多重分形滤波方法和地球化学信息提取技术研究与进展[J].地学前缘, 2009, 16(2):185-198. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DXQY200902018.htm Chen X, Zheng Y Y, Xu R K, et al.Application of classical statistics and multifractals to delineate Au mineralization-related geochemical anomalies from stream sediment data:a case study in Xinghai-Zeku, Qinghai, China[J].Geochemistry:Exploration, Environment, Analysis, 2016, 16:153-264.
Zuo R G, Xia Q L, Zhang D J.A comparison study of the C-A and S-A models with singularity analysis to identify geochemical anomalies in covered areas[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2013, 33(6):165-172. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dda5f6bdfd9d458017d36a7dc0a56776
向运川, 牟绪赞, 任天祥, 等.全国矿产资源潜力评价化探资料应用研究[M].北京:地质出版社.2018. Li Y, Selby D, Feely M, et al.Fluid inclusion characteristics and molybdenite Re-Os geochronology of the Qulong porphyry copper-molybdenum deposit, Tibet[J].Miner Deposita, 2017, 52(2):137-158. doi: 10.1007/s00126-016-0654-z
Zheng W B, Tang J X, Zhong K H, et al.Geology of the Jiama porphyry copper-polymetallic system, Lhasa Region, China[J].Ore Geology Reviews, 2016, 74:151-169. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2015.11.024
唐菊兴, 王勤, 杨欢欢, 等.西藏斑岩-矽卡岩-浅成低温热液铜多金属矿成矿作用、勘查方向与资源潜力[J].地球学报, 2017, 38(5):571-613. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqxb201705002 刘鹏辉.西藏林周县程巴铜多金属矿床地质特征及成矿条件研究[J].河南科技, 2015, (15):80-82. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hnkj201515032 雷波.西藏拉萨幅1:25万Cu、Pb、Zn地球化学异常特征及找矿远景圈定[J].矿物学报, 2013, 33(S2):780-781. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-KWXB2013S2435.htm 德西央宗, 多吉, 张金树, 等.西藏米拉山整装勘查区专项填图与技术应用示范报告.西藏自治区地质调查院, 2017. 泽仁扎西, 刘德民, 杨明生.西藏驱龙地区矿产远景调查报告.西藏自治区地质调查院, 2012. 陆宗德, 张圣, 何勇军, 等.西藏自治区林周县程巴矿区铜多金属矿详查报告.重庆市地质矿产勘查开发局川东南地质大队, 2008.




 下载:
下载: