Measurement results of in-situ stress in Guyuan area of Ningxia on the southwest margin of Ordos block and its causation analysis
-
摘要:
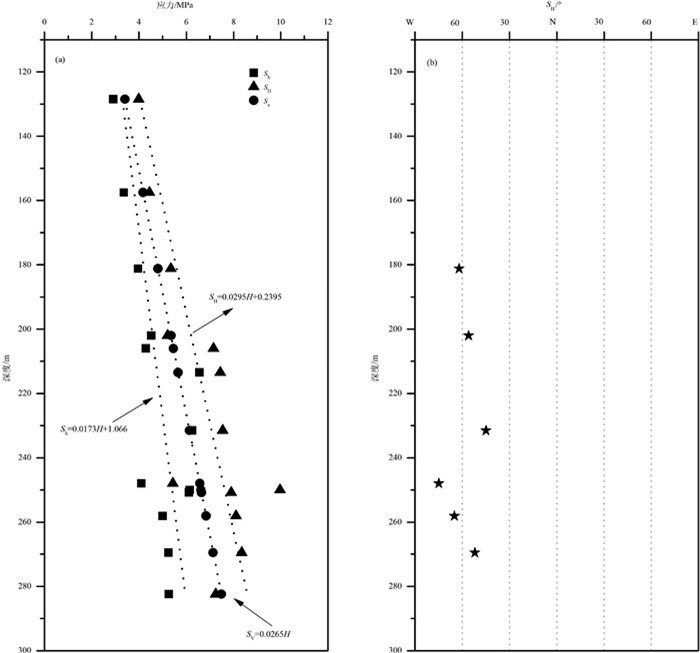
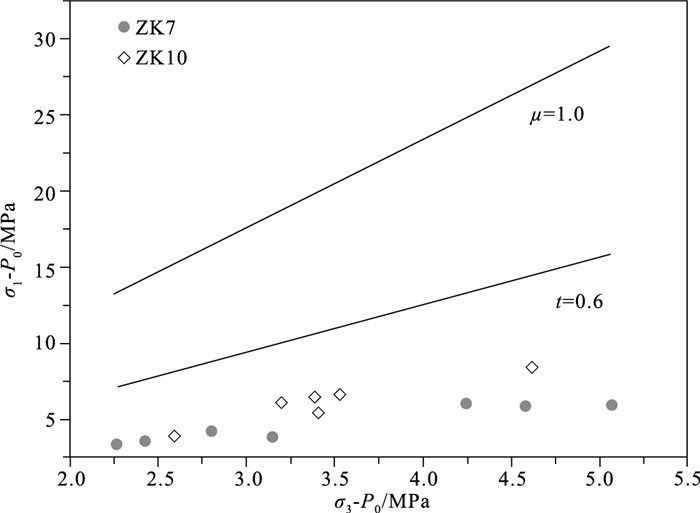
鄂尔多斯地块西南缘新构造活动强烈、地震频发,具有复杂多样的构造变形模式和活动特征。为了解鄂尔多斯地块西南缘地壳浅部地应力分布规律及断层稳定性,利用宁夏固原地区的水压致裂地应力测量数据,结合其他实测及震源机制解资料,分析了鄂尔多斯地块西南缘构造应力场特征。结果表明:①研究区2个钻孔的主应力关系整体表现为SH > Sv > Sh,水平应力起主导作用,属于走滑型应力状态,钻孔附近最大水平主应力方位平均为N59°W,与震源机制解获得的青藏高原东北缘主压应力方位有差异,推断鄂尔多斯地块西南缘现今NWW向走滑剪切应力环境的形成可能主要受到海原断裂带和六盘山断裂带的影响,应为局部构造和区域构造应力场共同作用的结果。②利用Mohr-Coulomb准则及Byerlee定律,摩擦系数取0.6~1.0,对研究区的现今地应力状态分析后发现,鄂尔多斯地块西南缘海原断裂带和六盘山断裂带的地应力大小未达到地壳浅部断层产生滑动失稳的临界条件,处于较稳定的应力状态。该研究成果为鄂尔多斯地块关键构造部位的断裂活动性分析和地质环境安全评价提供了参考依据。
Abstract:The southwestern margin of the Ordos block has experienced many great earthquakes with complicated tectonic deformation and tectonic activities.In order to understand in-situ stress environment of southwestern margin of the Ordos block and to evaluate the seismic risk, the authors carried out the in-situ stress measurement by hydraulic fracturing in two boreholes in the Guyuan area of Ningxia.Combined with other measured data and focal mechanism solutions, the authors discussed the tectonic stress field characteristics of the southwestern margin of the Ordos block.Some conclusions have been reached:(1) The results show that the relationship of principal stress of the two boreholes in the study area is SH > Sv > Sh, belonging to the strike-slip stress state.The azimuth of maximum horizontal principal stress near the borehole is N59°W; however, it is different from the P-axis orientation of focal mechanism solutions on the northeastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau.It is considered that the formation of the NWW strike-slip shear stress environment on the southwestern margin of the Ordos block is mainly affected by the Haiyuan fault and Liupanshan fault zone.The current stress environment may be the result of the combined effect of local structure and regional tectonic stress fields.(2) The crustal activity in the study area is discussed using the Mohr-Coulomb criterion and Byerlee's law under the premise that the friction coefficient is 0.6~1.0.The in-situ stress state of the southwestern margin of the Ordos block has not reached the sliding critical condition of the shallow fault and is in a relatively stable crustal stress state.The results have great significance for analysis of active faults as well as assessment of the regional geological environment and geological disasters prevention.
-
多龙矿集区位于青藏高原改则县西北约100km处,大地构造位置处于班公湖-怒江缝合带北缘、南羌塘地块最南缘、日土-多不杂岩浆弧东段,主要由多不杂、波龙、拿顿、拿若、铁格龙、尕尔勤、地堡那木岗等矿体组成,是新近探明具有超大型远景的、典型的富金斑岩型铜矿区,同时也是班公湖-怒江成矿带最大的斑岩型铜金矿区[1-2]。目前,关于多龙矿集区的成岩成矿地质背景依然存在争议:①曲晓明等[3]认为,其形成于大陆碰撞地壳隆升阶段;②佘宏全等[4]暗示,其成岩成矿作用与洋脊俯冲有关;③大多数学者均赞同,多龙矿集区是典型的岛弧型斑岩型铜金矿区,其成岩成矿作用与班公湖-怒江新特提斯洋的北向俯冲密切相关[5-13];④段志明等[14-15]和符家骏等[16]进一步强调,多龙斑岩型铜矿是发育在增生楔体系之上的岛弧型斑岩型铜金矿床。本文基于区域地质调查研究,在多龙矿集区新厘定出岩墙岭蛇绿岩残片,对揭示班公湖-怒江缝合带西段构造格架、班公湖-怒江洋的演化历史及多龙矿集区成岩成矿地质背景具有重要的地质意义。
1. 地质背景
班公湖-怒江缝合带横亘于青藏高原中部,向西延伸到克什米尔,向东南沿怒江河谷延伸出西藏,在中国境内延伸2500km 以上,是班公湖-怒江洋消亡闭合后的遗迹,是分割北拉萨地块和南羌塘地块的重要地质界线,同时也是青藏高原一条重要的多金属成矿带[2, 17]。班公湖-怒江洋的构造演化一直是地学界争论的焦点之一,主流观点认为其闭合时间为晚侏罗世—早白垩世[18-22],但越来越多的资料指示,班公湖-怒江洋在早白垩世仍具有一定规模[23-28]。
多龙矿集区位于班公湖-怒江缝合带西段,南羌塘地块最南缘日土-多不扎岩浆弧东段,受控于班公湖-怒江洋北向俯冲、消减、碰撞等动力学过程,构造地质特征极其复杂,同时具有良好的成矿条件(图 1-a)。矿集区出露的主体地层为下侏罗统曲色组和中侏罗统色哇组(图 1-b),岩性组成包括石英砂岩、长石岩屑杂砂岩、粉砂岩、页岩、泥岩、灰岩等,砂页岩韵律互层现象明显,砂岩的矿物成熟度和结构成熟度均较差,并发育底面印模构造和完整的鲍玛序列,是一套深水-半深水环境的复理石沉积①②(①吉林大学地质调查院.中华人民共和国1∶5 万多不扎幅区域地质调查报告.2015.②四川省地质调查院.中华人名共和国1∶25 万物玛幅区域地质调查报告.2004.)(待发表)。下白垩统美日切错组火山岩沉积地层角度不整合于下伏地层之上(图 1-b),岩石组合以杂色安山岩和安山质角砾岩为主,次为流纹岩、流纹质凝灰岩、玄武岩等,表现出多期次旋回性喷发的特点(待发表)。上白垩统阿布山组大面积分布于矿集区西北部,不整合于下伏地层之上(图 1-b),岩性主要为中厚-巨厚层状红褐色细砾岩、细-粗角砾岩与中厚层状含砾粗砂岩及中细砂岩,其中砾石成分包括橄榄岩、辉长岩、灰岩、砂岩、火山岩等,为班公湖-怒江洋闭合后的一套山间磨拉石沉积①(①吉林大学地质调查院.中华人民共和国1∶5 万多不扎幅区域地质调查报告.2015.)。
![]() 图 1 青藏高原构造简图(a)及班公湖-怒江缝合带西段多龙矿集区地质简图①(①吉林大学地质调查院.中华人民共和国1∶5 万多不扎幅区域地质调查报告.2015.)(b)KMKSZ—康西瓦-玛沁-昆仑山构造带;JSSZ—金沙江构造带;LSSZ—龙木错-双湖缝合带;BNSZ—班公湖-怒江缝合带;SNMZ—狮泉河-纳木错蛇绿混杂岩带;LMF—洛巴堆-米拉山断裂带;IYZSZ—印度河-雅鲁藏布缝合带;ATF—阿尔金断裂Figure 1. Tectonic framework of the Tibetan Plateau (a) and simplified geologicalmap of the Duolong ore concentration area in the westernsegment of Bangong-Nujiang River suture zone
图 1 青藏高原构造简图(a)及班公湖-怒江缝合带西段多龙矿集区地质简图①(①吉林大学地质调查院.中华人民共和国1∶5 万多不扎幅区域地质调查报告.2015.)(b)KMKSZ—康西瓦-玛沁-昆仑山构造带;JSSZ—金沙江构造带;LSSZ—龙木错-双湖缝合带;BNSZ—班公湖-怒江缝合带;SNMZ—狮泉河-纳木错蛇绿混杂岩带;LMF—洛巴堆-米拉山断裂带;IYZSZ—印度河-雅鲁藏布缝合带;ATF—阿尔金断裂Figure 1. Tectonic framework of the Tibetan Plateau (a) and simplified geologicalmap of the Duolong ore concentration area in the westernsegment of Bangong-Nujiang River suture zone岩浆岩在矿集区分布广泛,岩石类型复杂多样,包括中酸性侵入体、基性岩墙群等,均侵入于侏罗系内(图 1-b)。酸性岩浆活动最为强烈,主要岩性为花岗闪长斑岩、花岗斑岩、二长花岗岩、石英斑岩等;中性岩浆活动较弱,主要岩性为闪长岩、闪长玢岩等,侵入体规模较小,均为小型岩株及岩瘤,成群、成带分布,在横截面上多呈近圆形、椭圆形或纺锤状;基性岩浆活动较强,表现为近东西向展布的基性岩墙群,主要岩性为辉长岩。多项矿产普查和专题研究工作表明,区内优势矿种为铜和金,铜资源量超过1300×104t,金资源量超过400t[29],花岗闪长斑岩和花岗斑岩是区内斑岩型铜金矿主要的成矿岩体。大量的年代学资料表明,中酸性侵入体的形成时代集中在116~128Ma 之间[1, 3-13],矿体的成矿时代为118~119Ma[4, 6-7],侵入于侏罗纪增生楔体系内的基性岩墙群的形成时代为126~127Ma(图 1-b),表明多龙矿集区的成岩-成矿时代基本一致,同时指示多龙矿集区在早白垩世应处于伸展拉张的构造环境[30]。近年来的区域地质调查研究表明,多龙矿集区南侧出露一套岩石组合特征鲜明的岩墙岭蛇绿岩残片。
2. 蛇绿岩残片基本地质特征
蛇绿岩残片整体呈近东西向分布于矿集区岩墙岭地区(图 1-b),组成端元包括席状岩墙群、玄武岩及硅质岩,因后期构造肢解而缺失堆晶杂岩和地幔橄榄岩端元。岩墙岭蛇绿岩残片的各端元呈棱形或透镜体状断续分布于侏罗系,构成典型的网结状构造。糜棱岩普遍发育在岩墙岭蛇绿岩残片各端元和围岩的接触部位,为岩墙岭蛇绿岩属性的进一步确定提供了重要证据。各个岩性端元详细描述如下。
(1)席状岩墙群是岩墙岭蛇绿岩残片的重要组成端元,主体岩性为辉长岩,在一个露头上可见上百条岩墙呈平行的席状产出,部分岩墙呈直立状(图版Ⅰ-A),部分岩墙因后期构造作用呈斜坡状,单个岩墙的宽度一般在0.5~1m 之间,个体独立产出,且个体之间可见冷凝边和烘烤边。岩石风化面呈灰褐色、红褐色,新鲜面呈灰绿色、灰黑色,发育典型的辉长结构,由针柱状、板状斜长石和半自形辉石构成(图版Ⅰ-B),块状构造。
(2)玄武岩是岩墙岭蛇绿岩残片的另一组成端元,其中枕状玄武岩出露最为广泛,次为杏仁状玄武岩、气孔状玄武岩,枕状玄武岩的枕状构造保存完整(图版Ⅰ-C),单个岩枕呈椭圆形,长轴一般在0.2~0.5m 之间,部分不与岩墙群直接接触,部分直接覆盖于岩墙群之上(图版Ⅰ-D)。岩石风化面呈灰黑、红褐色,新鲜面为灰绿色、灰黑色。气孔状玄武岩构造破碎严重,多呈小岩块混杂在片理化砂岩内(图版Ⅰ-E)。杏仁状玄武岩发育斑状结构,由0.5~1.5mm 的椭圆状-圆状杏仁体和基质组成(图版Ⅰ-F)。
(3)硅质岩作为岩墙岭蛇绿岩残片的上覆岩系,代表着远洋深海沉积物,在矿集区内呈一系列构造块体分布于侏罗系内,天然露头较好,风化面呈黄白色、灰白色,新鲜面呈灰白色、灰色,条带状构造明显(图版Ⅰ-G)。
(4)糜棱岩主要发育在硅质岩、玄武岩与围岩的接触部位,由韧性基质(40%)和变斑晶(60%)组成,发育典型的眼球状构造(图版Ⅰ-H),这既明确了岩墙岭蛇绿岩与侏罗系间的构造接触关系,也为岩墙岭蛇绿岩构造属性的确定提供了重要依据。
3. 意义及结论
岩墙岭蛇绿岩残片主要由席状岩墙群、玄武岩及硅质岩组成,整体呈棱形或透镜体状断续分布于侏罗系中,两者共同组成多龙矿集区的增生楔体系。结合前人研究成果,笔者支持多龙矿集区是发育在增生楔体系之上的观点,早白垩世基性岩墙群的确定进一步指示,多龙矿集区早白垩世成岩成矿作用形成于增生楔之上伸展拉张的地质背景。岩墙岭蛇绿岩残片位于班公湖-怒江缝合带的北缘,应该是班公湖-怒江蛇绿岩带的重要组成部分,因此,它的发现为班公湖-怒江缝合带的延伸及其构造演化的研究提供了新的线索。
-
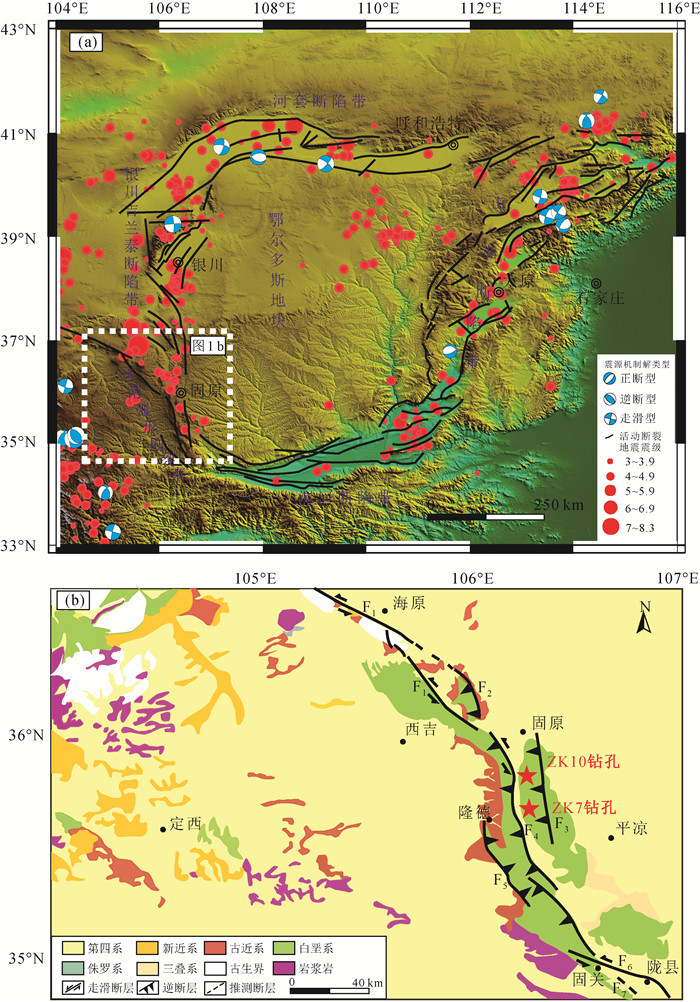
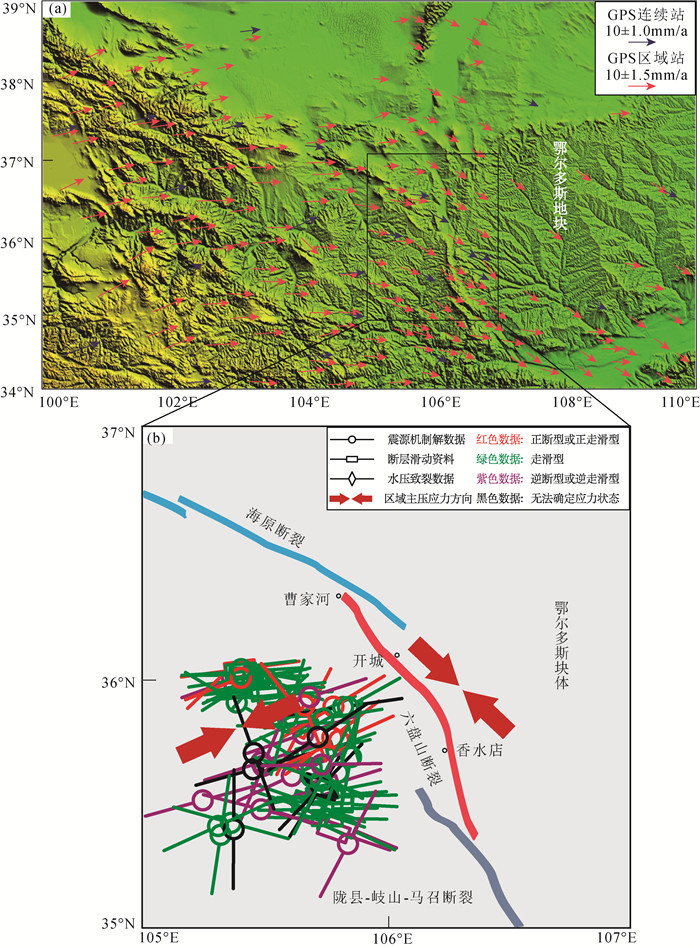
图 1 鄂尔多斯地块地形地貌、活动断裂、地震分布特征(a)和研究区地质构造简图[29](b)
F1—海原断裂带;F2—马东山褶皱逆冲带;F3—小关山断裂;F4—六盘山东麓断裂;F5—六盘山西麓断裂;F6—陇县-岐山-马召断裂;F7—固关-虢镇断裂。图中地震目录数据(MS≥3.0)来自USGS,震源机制解数据(MS≥4.5)来自GCMT
Figure 1. Landform, active tectonic characteristics and earthquake distribution of the Ordos block(a)and simplified geological map of the research region(b)
表 1 鄂尔多斯西南缘水压致裂地应力测量结果
Table 1 Results of in-situ stress measurement on the southwest margin of Ordos block
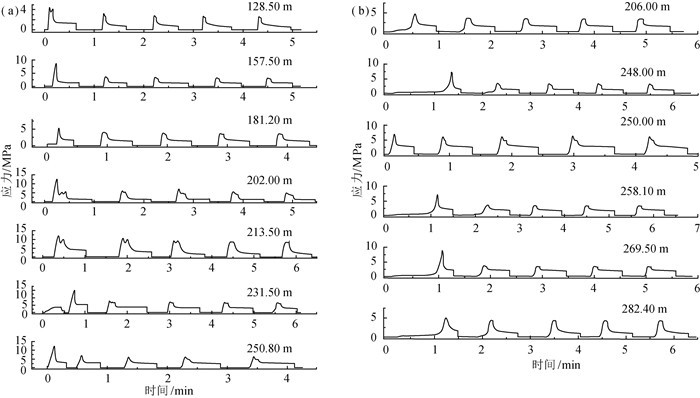
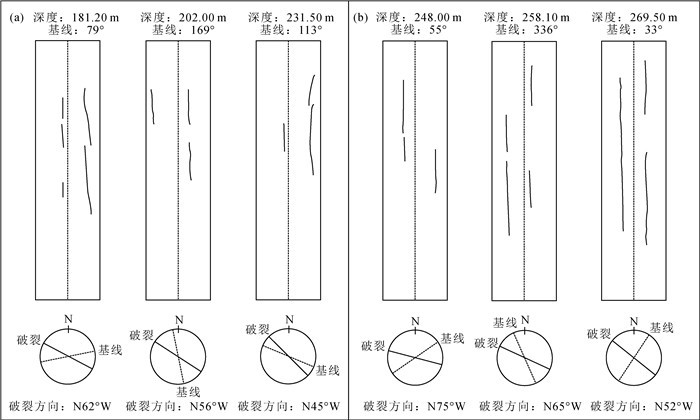
钻孔 深度/m 压裂参数/MPa 应力值/MPa 破裂方位 Pb Pr Ps PH P0 Sh SH Sv ZK7 128.50 5.77 4.09 2.91 1.29 0.64 2.91 3.99 3.41 157.50 10.44 4.70 3.36 1.58 0.93 3.36 4.44 4.17 181.20 7.11 5.37 3.96 1.81 1.16 3.96 5.35 4.80 N62°W 202.00 14.72 6.98 4.52 2.02 1.37 4.52 5.21 5.35 N56°W 213.50 13.97 10.74 6.56 2.14 1.49 6.56 7.44 5.66 231.50 17.70 9.53 6.25 2.32 1.67 6.25 7.54 6.13 N45°W 250.80 15.08 8.57 6.11 2.51 1.86 6.11 7.90 6.65 ZK10 206.00 6.77 4.63 4.29 2.06 1.09 4.29 7.15 5.46 248.00 9.91 5.36 4.10 2.48 1.51 4.10 5.43 6.57 N75°W 250.00 9.69 6.95 6.15 2.50 1.53 6.15 9.97 6.63 258.10 9.90 5.28 5.00 2.58 1.61 5.00 8.11 6.84 N65°W 269.50 11.94 5.67 5.25 2.70 1.72 5.25 8.35 7.14 N52°W 282.40 7.90 6.69 5.26 2.82 1.85 5.26 7.25 7.48 注:Pb为岩石原地破裂压力;Pr为破裂面重张压力;Ps为破裂面瞬时关闭压力;PH为静水压力;P0为孔隙压力;SH为最大水平主应力;Sh为最小水平主应力;Sv为根据上覆岩层重量计算的垂向主应力(岩石密度取2.65 g/cm3) 表 2 不同地区SH、Sh随深度变化情况
Table 2 Variation of SH and Sh with the depth in different regions
-
盛书中, 万永革, 黄骥超, 等.应用综合震源机制解法推断鄂尔多斯块体周缘现今地壳应力场的初步结果[J].地球物理学报, 2015, 58(2):436-452. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqwlxb201502008 郭祥云, 蒋长胜, 王晓山, 等.鄂尔多斯块体周缘中小地震震源机制及应力场特征[J].大地测量与地球动力学, 2017, 37(7):675-685. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dkxbydz201707003 薛宏运, 鄢家全.鄂尔多斯地块周围的现代地壳应力场[J].地球物理学报, 1984, 27(2):144-152. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5733.1984.02.004 张培震.中国大陆岩石圈最新构造变动与地震灾害[J].第四纪研究, 1999, 19(5):404-413. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.1999.05.003 邓起东, 尤惠川.鄂尔多斯周缘断陷盆地带的构造活动特征及其形成机制, 现代地壳运动研究[M].北京:地震出版社, 1985:58-78. 徐锡伟, 程国良, 马杏垣, 等.华北及其邻区块体转动模式和动力来源[J].地球科学, 1994, 19(2):129-138. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-2383.1994.02.005 陈强森, 鲍学伟, 徐树斌, 等.利用背景噪声反演鄂尔多斯块体及其南缘地区地壳速度结构[J].高校地质学报, 2013, 19(3):504-512. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2013.03.012 张培震, 邓起东, 张竹琪, 等.中国大陆的活动断裂、地震灾害及其动力过程[J].中国科学:地球科学, 2013, 43(10):1607-1620. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgkx-cd201310005 张培震, 张会平, 郑文俊, 等.东亚大陆新生代构造演化[J].地震地质, 2014, 36(3):574-585. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2014.03.003 Wang C Y, Sandvol E, Zhu L, et al.Lateral variation of crustal structure in the Ordos block and surrounding regions, North China, and its tectonic implications[J].Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2014, 387:198-211. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2013.11.033
丰成君, 陈群策, 李国歧, 等.青藏高原东南缘丽江-剑川地区地应力测量与地震危险性[J].地质通报, 2014, 33(4):524-534. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2014.04.009 李孟銮, 赵知军.宁夏地区现代构造应力场及其与地震活动的关系[J].地震研究, 1986, 9(3):33-48. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DZYJ198603003.htm 单修政, 徐世芳, 段峰.鄂尔多斯周缘地带未来强震发生地区初探[J].华北地震科学, 2002, 20(1):10-15. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-1375.2002.01.002 赵知军, 刘秀景, 康凌燕.宁夏及邻近地区震源机制解特征[J].西北地震学报, 2002, 24(2):162-166. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=xbdzxb200202011 范俊喜, 马瑾, 刁桂苓.由小震震源机制解得到的鄂尔多斯周边构造应力场[J].地震地质, 2003, 25(1):88-99. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2003.01.009 张辉, 刘小凤, 赵凌云.由多个震源机制解分析甘肃及边邻地区应力场特征[J].华南地震, 2007, 27(2):33-39. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8662.2007.02.005 刘芳, 王晓山, 杨雅琼.内蒙古中西部地区小震震源机制解分析[J].大地测量与地球动力学, 2010, 30(S1):7-11. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dkxbydz2010z1002 Zoback M D, Healy J H.Friction, faulting and in-situ stress[J].Annales Geophsicae, 1984, 2:689-698.
Byerlee J.Friction of rocks[J].Pure and Applied Geophysics, 1978, 116(4/5):615-626. doi: 10.1007/BF00876528
王锋, 赵红格.鄂尔多斯地块西部构造研究中几个值得注意的问题[J].中国地质, 2007, 34(3):392-399. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2007.03.004 邓起东, 程绍平, 闵伟, 等.鄂尔多斯块体新生代构造活动和动力学的讨论[J].地质力学学报, 1999, 5(3):13-21. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.1999.03.003 张岳桥, 廖昌珍, 施炜, 等.鄂尔多斯盆地周边地带新构造演化及其区域动力学背景[J].高校地质学报, 2006, 12(3):285-297. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2006.03.001 Tapponnier P, Peltzer G, Le Dain A Y, et al.Propagating extrusion tectonics in asia:new insights from simple experiments with plasticine[J].Geology, 1982, 10(12):611. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1982)10<611:PETIAN>2.0.CO;2
Peltzer G, Tapponnier P, Zhang Z T, et al.Neogene and quaternary faulting in and along the Qinling Shan[J].Nature, 1985, 317(6037):500-505. doi: 10.1038/317500a0
Zhang Y Q, Vergely P, Mercier J L.Pliocene-Quaternary faulting pattern and left-slip propagation tectonics in North China[J].Episodes, 1999, 22(2):84-88. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzlxxb199903007
Uyeda S, Kanamori H.Back-arc opening and the mode of subduction[J].Journal of Geophysical Research Solid Earth, 1979, 84(B3):1049-1061. doi: 10.1029/JB084iB03p01049
Northrup C J, Royden L H, Burchfiel B C.Motion of the Pacific plate relative to Eurasia and its potential relation to Cenozoic extension along the eastern margin of Eurasia[J].Geology, 1995, 23(8):719-722. https://ui.adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/1995Geo....23..719N/abstract
Tian X, Teng J, Zhang H, et al.Structure of crust and upper mantle beneath the ordos block and the yinshan mountains revealed by receiver function analysis[J].Physics of the Earth & Planetary Interiors, 2011, 184(3):186-193. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0031920110002475
刘兴旺, 袁道阳, 吴赵, 等.六盘山断裂带活动性差异及其对六盘山隆升的影响[J].第四纪研究, 2016, 36(4):898-906. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dsjyj201604010 李新男.鄂尔多斯西南缘活动构造几何图像、运动特征及构造变形模式[J].国际地震动态, 2018, 473(5):46-48. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gjdzdt201805009 徐锡伟, 于贵华, 陈桂华, 等.青藏高原北部大型走滑断裂带近地表地质变形带特征分析[J].地震地质, 2007, 29(2):201-207. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2007.02.002 李清河, 郭守年, 吕德徽.鄂尔多斯西缘与西南缘深部结构与构造[M].北京:地震出版社, 1999:1-257. 孟庆筱, 景鹏旭, 何申海, 等.GPS约束下陇西地区断裂带现今滑动速率的非连续接触模拟研究[J].大地测量与地球动力学, 2018, 38(12):1227-1231. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dkxbydz201812003 王海燕, 高锐, 尹安, 等.深地震反射剖面揭示的海原断裂带深部几何形态与地壳形变[J].地球物理学报, 2012, 55(12):3902-3909. doi: 10.6038/j.issn.0001-5733.2012.12.003 孙赫, 徐晶, 柳皓元.基于InSAR的广义海原断裂带中东段现今深部运动特征[J].大地测量与地球动力学, 2017, 37(11):1141-1145. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dkxbydz201711009 许英才, 高原, 石玉涛, 等.鄂尔多斯块体西缘地壳介质各向异性:从银川地堑到海原断裂带[J].地球物理学报, 2019, 62(11):4239-4258. doi: 10.6038/cjg2019M0309 杜方, 闻学泽, 冯建刚, 等.六盘山断裂带的地震构造特征与强震危险背景[J].地球物理学报, 2018, 61(2):545-559. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqwlxb201802014 邓起东, 张维岐.海原走滑断裂带及其尾端挤压构造[J].地震地质, 1989, 11(1):1-14. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DZDZ198901000.htm Haimson B C, Cornet F H.ISRM suggested methods for rockstress estimation-Part 3:hydraulic fracturing(HF)and/orhydraulic testing of pre-existing fractures(HTPF)[J].International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2003, 40(7/8):1011-1020.
Haimson B C, Rummel F.Hydrofracturing stress measurements in the Iceland research drilling project drill hole at Reydarfjordur, Iceland[J].Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth, 1982, 87(B8):6631-6649. doi: 10.1029/JB087iB08p06631
Zoback M D, Apel R, Baumgärtner J, et al.Upper-crustal strength inferred from stress measurements to 6 km depth in the KTB borehole[J].Nature 1993, 365:633-635. doi: 10.1038/365633a0
Zhao X G, Wang J, Qin X H, et al.In-situ stress measurements and regional stress field assessment in the Xinjiang candidate area for China's HLW disposal[J].Engineering geology, 2015, 197:42-56. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=bc90eb6ae03f1f459cb05dbf5fabc79d
陈群策, 丰成君, 孟文, 等.5·12汶川地震后龙门山断裂带东北段现今地应力测量结果分析[J].地球物理学报, 2012, 55(12):3923-3932. doi: 10.6038/j.issn.0001-5733.2012.12.005 Aamodt L, Kuriyagawa M.Measurement of instantaneous shut in pressure in crystalline rock[C]//Monterey C A.Presented at the Workshop on Hydraulic Fracturing Stress Measurements.1981, 218(4): 715-716.
Hayashi K, Haimson B C.Characteristics of shut-in curves in hydraulic fracturing stress measurements and determination of in situ minimum compressive stress[J].Journal of Geophysical Research, 1991, 96(B11):18311-18321. doi: 10.1029/91JB01867
Hayashi K, Sakurai I.Interpretation of hydraulic fracturing shut-in curves for tectonic stress measurements[J].International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences & Geomechanics Abstracts, 1989, 26(6):477-482. doi: 10.1016/0148-9062(89)91424-1
丰成君, 陈群策, 吴满路, 等.水压致裂应力测量数据分析——对瞬时关闭压力Ps的常用判读方法讨论[J].岩土力学, 2012, 33(7):2149-2159. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2012.07.035 Meng W, Chen Q C, Zhao Z, et al.Characteristics and implications of the stress state in the Longmen Shan fault zone, eastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau[J].Tectonophysics, 2015, 656:1-19. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=f45b5d5ec9bbdb7e940bf677268a190f
Tan C, Wang R, Sun Y, et al.Numerical modelling estimation of the'tectonic stress plane'(TSP)beneath topography with quasi-U-shaped valleys[J].International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2004, 2(41):303-310. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=bd3311626cfabbaeea908a4ef99baf9c
黄禄渊, 杨树新, 崔效锋, 等.华北地区实测应力特征与断层稳定性分析[J].岩土力学, 2013, 34(S1):204-213. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ytlx2013z1032 杨树新, 姚瑞, 崔效锋, 等.中国大陆与各活动地块、南北地震带实测应力特征分析[J].地球物理学报, 2012, 55(12):4207-4217. doi: 10.6038/j.issn.0001-5733.2012.12.032 王艳华, 崔效锋, 胡幸平, 等.基于原地应力测量数据的中国大陆地壳上部应力状态研究[J].地球物理学报, 2012, 55(9):3016-3027. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqwlxb201209020 景锋, 盛谦, 张勇慧, 等.中国大陆浅层地壳实测地应力分布规律研究[J].岩石力学与工程学报, 2007, 26(10):2057-2062. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=yslxygcxb200710014 Anderson E M.The dynamics of faulting[J].Transactions of the Edinburgh Geological Society, 1905, 8(3):387-402. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/238338902_The_Dynamics_of_Faulting
Wang Q.Present-Day Crustal Deformation in China Constrained by Global Positioning System Measurements[J].Science, 2001, 294(5542):574-577. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgkx-ed200210001
徐婉桢, 孟国杰, 苏小宁.基于GPS观测的六盘山断裂震间闭锁特征研究[J].地震, 2016, 36(3):14-24. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=diz201603002 谢富仁, 陈群策, 崔效锋, 等.中国大陆地壳应力环境基础数据库[J].地球物理学进展, 2007, 22(1):131-136. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2903.2007.01.018 牛琳琳, 丰成君, 张鹏, 等.鄂尔多斯地块南缘地应力测量研究[J].地质力学学报, 2018, 24(1):25-34. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzlxxb201801003 孟召平, 蓝强, 刘翠丽, 等.鄂尔多斯盆地东南缘地应力, 储层压力及其耦合关系[J].煤炭学报, 2013, (1):122-128. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-MTXB201301019.htm 陈小斌, 臧绍先, 刘永岗, 等.鄂尔多斯地块的现今水平运动状态及其与周缘地块的相互作用[J].中国科学院大学学报, 2005, 22(3):309-314. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgkxyyjsyxb200503008 Su S, Stephansson O.Effect of a fault on in situ stresses studied by the distinct element method[J].International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 1999, 8(36):1051-1056. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=c57c0d657e5062ed4a1ae2543a2c2197
Lin W, Yeh E C, Ito H, et al.Current stress state and principal stress rotations in the vicinity of the Chelungpu fault induced by the 1999 Chi-Chi, Taiwan, earthquake[J].Geophysical Research Letters, 2007, 34(16). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=74831bd2876d3862fdff632d3e3a6d8f
Hudson J A, Harrison J P.Engineering rock mechanics:an introduction to the principles[M].Netherlands:Elsevier Science and Technology, 2000:1-456.
Hickman S, Zoback M.Stress orientations and magnitudes in the SAFOD pilot hole[J].Geophysical Research Letters, 2004, 31(15):1-4. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=10.1029/2004GL020043
许英才, 曾宪伟, 许文俊, 等.基于台阵的青藏高原东北缘海原-六盘山断裂带及邻区地壳结构研究[J].中国地震, 2018, 34(3):101-114. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgdz201803010 秦向辉, 陈群策, 谭成轩, 等.龙门山断裂带西南段现今地应力状态与地震危险性分[J].岩石力学与工程学报, 2013, 32(1):2870-2876. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=yslxygcxb2013z1038 张鹏, 秦向辉, 丰成君, 等.郯庐断裂带山东段深孔地应力测量及其现今活动性分析[J].岩土力学, 2013, 34(8):2329-2335. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ytlx201308042 Zoback M D, Healy J H.In situ stress measurements to 3.5 km depth in the Cajon Pass Scientific Research Borehole:Implications for the mechanics of crustal faulting[J].Journal of Geophysical Research, 1992, 97(B4):5039-5057. doi: 10.1029/91JB02175
崔笃信, 郝明, 李煜航, 等.鄂尔多斯块体周缘地区现今地壳水平运动与应变[J].地球物理学报, 2016, 59(10):3646-3661. doi: 10.6038/cjg20161012 Liao C T.Stress change near the Kunlun fault before and after the Ms 8.1 Kunlun earthquake[J].Geophysical Research Letters, 2003, 30(20):2027. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=10.1029/2003GL018106




 下载:
下载: