Geochemical characteristics, source area properties and tectonic significance of clastic rocks of Xilinkobo Formation in the south of Baiyunshan ophiolite melange belt, Beishan, Inner Mongolia
-
摘要:
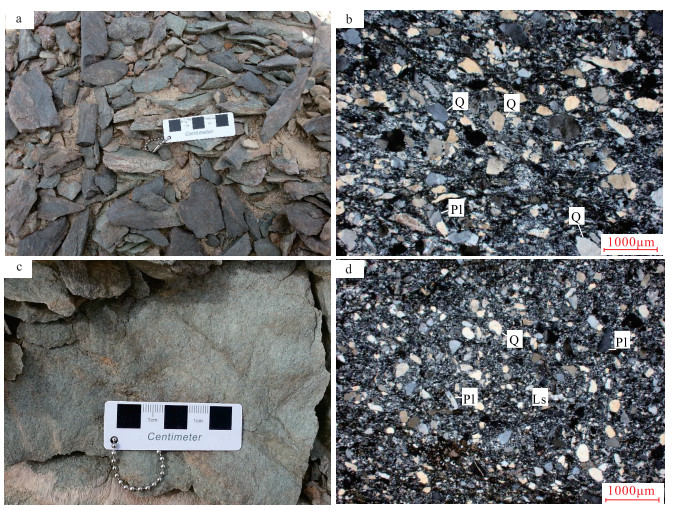
为揭示北山洋俯冲极性问题,对内蒙古北山造山带白云山地区的锡林柯博组砂岩进行了地球化学分析。结果表明,砂岩主要为长石石英砂岩和长石岩屑砂岩,少量为岩屑石英砂岩,且均表现为弱变质;矿物成分主要为石英、斜长石、钾长石等;主量元素平均含量SiO2为80.70%,Al2O3为8.07%,MgO为1.08%,CaO为1.48%,TFe2O3为1.86%,K2O为1.12%,Na2O为1.75%;稀土元素配分模式曲线一致,LREE/HREE=11.32~16.54,平均为13.83,(La/Yb)N=7.38~12.39,平均10.43,负Eu异常,轻稀土元素相对重稀土元素明显富集,稀土元素分馏明显。锡林柯博组碎屑沉积岩CIA值反映研究区物源碎屑岩遭受了温暖、湿润条件下中等的化学风化作用,其母岩可能来源于酸性火山岩或花岗岩。结合锡林柯博组岩石组合特征、构造组合特征及地球化学特征,认为其源岩形成于被动陆缘构造环境,揭示了物源可能来自于塔里木地块,从侧面反映了北山洋向北俯冲的极性。
Abstract:To reveal the polarity of the subduction of the Beishan ocean, the authors made a geochemical analysis of the sandstone of Xilinkebo Formation in Baiyunshan area of Beishan orogenic belt, Inner Mongolia.The results show that the rocks are mainly composed of feldspar quartz sandstone and feldspar lithic sandstone, with a small amount of lithic quartz sandstone, and all of them show weak metamorphism.The main mineral components are mainly quartz, plagioclase and K-feldspar.Average percentage content of major element oxides are SiO2 80.70%, Al2O3 8.07%, MgO 1.08%, CaO 1.48%, TFe2O3 1.86%, K2O 1.12% and Na2O 1.75%.The REE patterns of curves are consistent, with LREE/HREE being 11.32~16.54, 13.83 on average, and (La/Yb)N being 7.38~12.39, 10.43 on average.Eu anomaly value is 0.57, LREE are obviously enriched relative to HREE, and REEs fractionate evidently.The CIA value of clastic sedimentary rocks in Xilinkebo Formation suggests that the clastic rocks of provenance in the study area were subjected to moderate chemical weathering under warm and wet conditions.Their parent rocks probably originated from acidic volcanic rocks or granites.Combined with the rock assemblage characteristics, tectonic combined characteristics and geochemical characteristics of Xilinkebo Formation, it is considered that the source rocks were formed in a tectonic environment of passive continental margin.It is revealed that the provenance might have come from the Tarim block, indirectly reflecting the polarity of northward subduction of Beishan Ocean.
-
Keywords:
- Inner Mongolia /
- Baiyunshan /
- Xilinkebo Formation /
- clastic rock /
- provenance /
- passive continental margin
-
致谢: 审稿专家和中国地质调查局天津地质调查中心李承东教授级高工对本文提出了建设性修改意见;内蒙古1 5万月牙山、儿驼山幅区域地质调查项目组为本文提供了丰富的第一手资料,在此一并表示感谢。
-
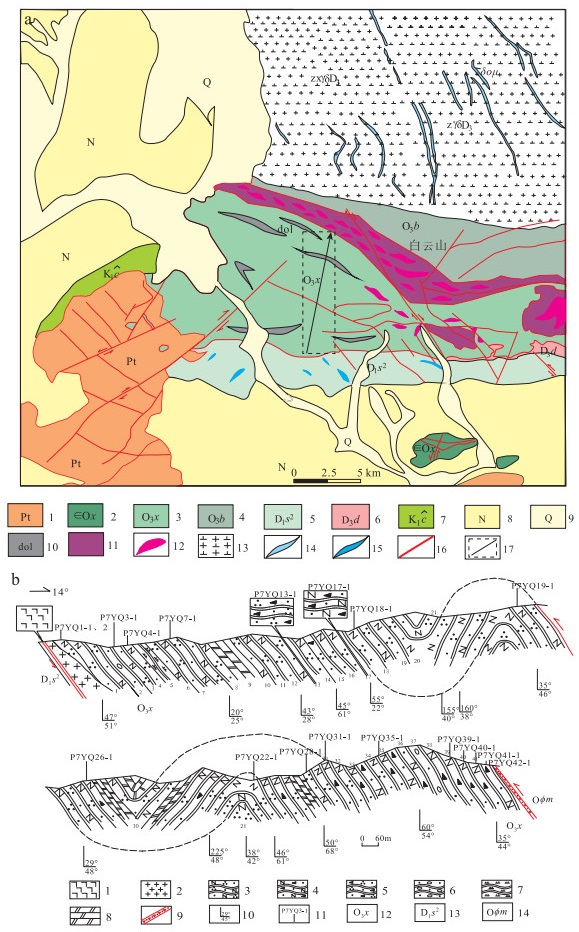
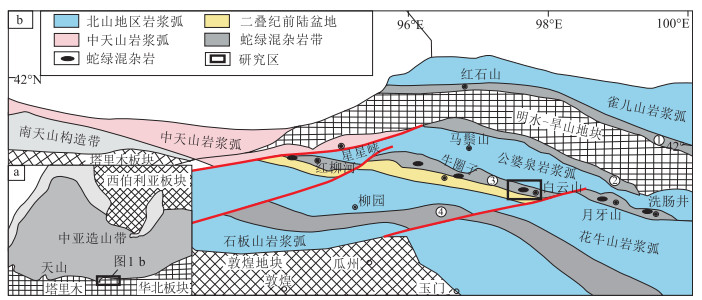
图 1 北山造山带蛇绿岩时空分布(a)和亚造山带构造简图(b)(据参考文献[25]修改)
①—红石山:②—小黄山:③—红柳河-牛圈子白云山-月牙山-洗肠井:④—柳园
Figure 1. Temporal and spatial distribution of ophiolites in the Beishan orogenic belt(a)and structural sketch map of the Central Asian orogenic belt(b)
图 2 月牙山幅地质简图(a)和锡林柯博组PM7实测剖面(b)
a图:1—中、新元古代碳酸岩组合;2—寒武纪-奥陶纪西双鹰山组;3—晚奥陶世锡林克博组;4—晚奥陶世白云山组;5—早泥盆世三个井组二段;6—晚泥盆世墩墩山组;7—早白垩世赤金堡组;8—新近系;9—第四系;10—白云岩透镜体;11—蛇绿岩带;12—超基性岩块;13—花岗闪长岩;14—石英闪长岩脉;15—闪长岩脉;16—断层;17—PM07剖面位置;b图:1—玄武岩;2—花岗斑岩脉;3—变质长石石英砂岩;4—变质长石岩屑砂岩;5—变质岩屑石英砂岩;6—变质含砾砂岩;7—变质粉砂岩;8—白云岩;9—断层破碎带;10—产状;11—采样位置;12—锡林柯博组;13—三个井组二段;14—蛇绿岩
Figure 2. Geological map of Yueyashan Sheet(a)and measured profile PM07 of Xilinkebo Formation(b)
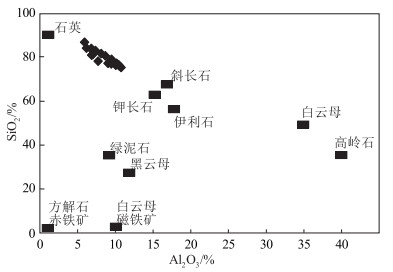
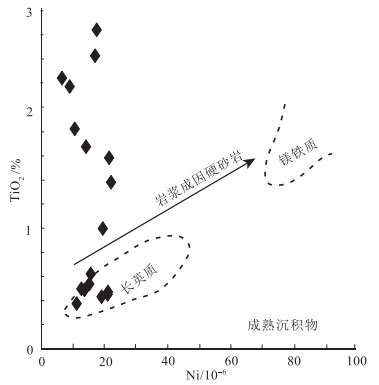
图 5 白云山地区锡林柯博组砂岩Al2O3-SiO2图解[30]
Figure 5. Al2O3-SiO2 diagram of sandstones from Xinlinkebo Formation in Baiyunshan area
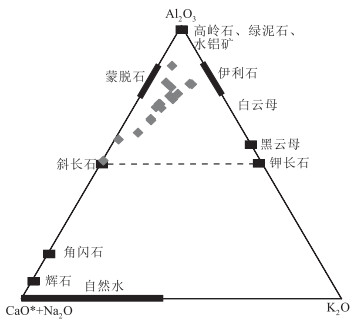
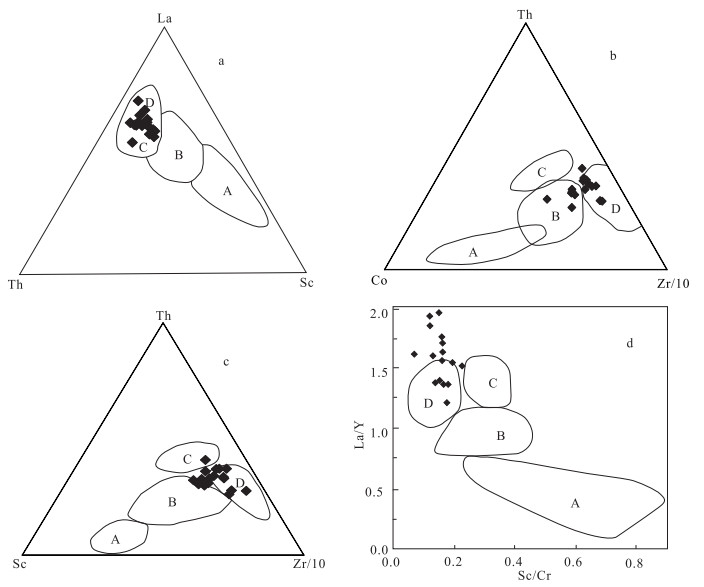
图 6 白云山地区锡林柯博组砂岩A-CN-K判别图解[32]
Figure 6. A-CN-K diagram of the Xilinkebo Formation sandstones in Baiyunshan area
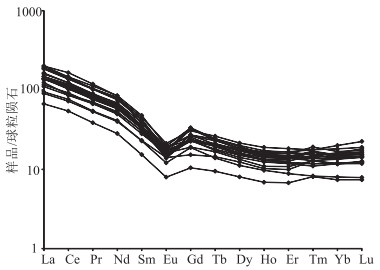
图 8 白云山地区锡林柯博组砂岩稀土元素模式配分曲线(球粒陨石数据据参考文献[40])
Figure 8. Chondrite-normalized REE patterns of the Xilinkebo Formation sandstones in Baiyunshan area
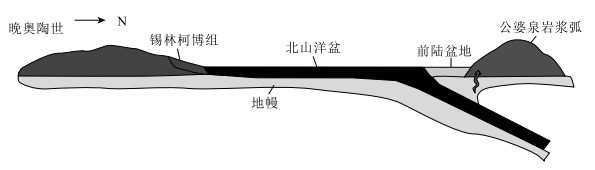
图 10 北山洋盆晚奥陶世演化模式图①
Figure 10. Late Ordovician evolution model of Beishan Ocean basin
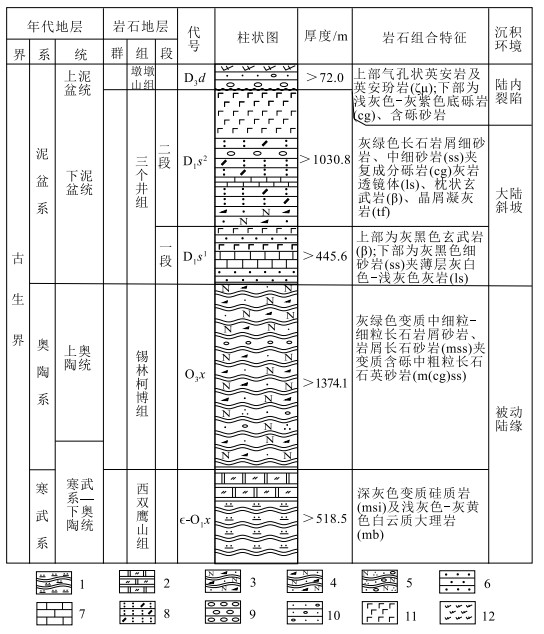
表 1 白云山锡林柯博组砂岩主量、微量和稀土元素分析数据
Table 1 Major, trace and rare earth element content of sandstone from Xilinkebo Formation in Baiyunshan area
送样号 P7YQ
1-1P7YQ1-2 P7YQ3-1 P7YQ4-1 P7YQ7-1 P7YQ
39-1P7YQ
41-1P7YQ
42-1P7YQ
13-1P7YQ
18-1P7YQ
19-1P7YQ
26-1P7YQ
22-1P7YQ
28-1P7YQ
31-1P7YQ
35-1P7YQ
40-1SiO2 77.53 76.89 80.86 81.90 76.61 83.04 82.82 84.25 83.30 81.43 79.28 75.59 81.25 78.49 84.42 87.07 77.19 Al2O3 9.05 9.47 8.69 8.15 10.08 7.06 7.33 6.84 7.38 7.02 9.52 10.78 6.87 7.73 6.19 5.95 9.18 Fe2O3 2.56 3.49 1.27 1.29 1.56 1.00 0.92 0.79 0.51 0.72 0.50 0.56 0.34 0.38 0.44 0.23 0.44 MgO 0.22 0.20 1.22 1.12 1.40 0.96 0.99 0.84 0.34 1.02 0.41 0.92 2.58 2.39 1.03 0.85 1.81 CaO 2.03 1.42 0.27 0.30 1.04 0.89 0.69 0.73 2.05 2.62 2.38 2.81 1.24 2.27 1.70 0.75 1.93 Na2O 5.00 5.04 1.22 1.27 2.72 1.44 1.45 1.68 1.10 1.08 1.08 2.18 0.84 1.36 0.52 0.57 1.27 K2O 0.26 0.40 1.90 1.69 1.64 1.32 1.39 1.18 0.97 1.12 1.28 1.48 0.65 1.17 0.83 0.41 1.30 MnO 0.04 0.05 0.03 0.04 0.05 0.04 0.03 0.03 0.10 0.14 0.11 0.12 0.08 0.09 0.08 0.05 0.12 TiO2 0.57 0.66 0.50 0.48 0.46 0.53 0.52 0.40 1.78 1.06 2.81 1.68 2.31 1.47 1.94 2.38 2.58 P2O5 0.08 0.21 0.11 0.10 0.13 0.10 0.10 0.09 0.03 0.03 0.04 0.04 0.09 0.08 0.03 0.02 0.06 烧失量 2.12 1.78 1.52 1.45 2.07 1.65 1.56 1.45 1.48 2.32 1.73 2.72 3.00 3.51 1.87 1.22 2.81 总量 99.95 99.97 99.76 99.78 99.76 99.81 99.77 99.83 99.93 99.93 99.93 99.90 99.92 99.91 99.95 99.95 99.91 CIA 55.39 57.99 71.94 71.43 65.12 65.92 67.50 65.58 64.18 59.24 66.70 62.48 71.59 61.70 66.96 77.39 67.10 La 35.00 47.50 26.20 22.40 29.40 44.40 43.60 32.80 35.08 47.52 32.10 33.28 27.47 21.42 37.76 15.84 26.19 Ce 70.40 89.70 52.50 46.80 53.60 84.80 84.10 62.80 72.27 101.21 67.26 68.95 56.30 44.25 75.87 33.22 53.37 Pr 8.05 10.70 6.38 5.17 6.70 9.76 9.73 7.38 8.27 11.30 7.66 7.89 6.38 5.07 8.57 3.68 5.89 Nd 30.20 39.70 24.30 19.20 24.90 36.00 35.20 27.10 29.63 39.22 27.92 28.62 23.23 18.72 31.18 13.21 21.61 Sm 5.47 7.30 4.68 3.49 4.63 6.52 6.41 4.96 5.33 5.84 5.30 5.31 4.29 3.54 5.46 2.35 4.02 Eu 0.86 1.14 0.92 0.70 0.84 1.01 0.95 0.80 0.91 1.09 0.98 1.11 0.93 0.82 0.85 0.46 0.81 Gd 5.58 6.85 4.72 3.86 4.75 6.85 6.57 5.24 4.64 5.57 4.72 4.80 3.91 3.13 4.91 2.15 3.58 Tb 0.77 0.88 0.67 0.52 0.65 0.91 0.88 0.72 0.75 0.90 0.79 0.78 0.62 0.54 0.76 0.35 0.55 Dy 4.55 4.53 3.82 2.84 3.59 5.08 4.66 3.89 3.99 4.93 4.46 4.35 3.40 3.14 4.08 2.04 2.82 Ho 0.94 0.87 0.74 0.55 0.70 0.97 0.88 0.74 0.76 0.89 0.82 0.82 0.62 0.58 0.73 0.39 0.50 Er 2.76 2.41 2.02 1.46 1.95 2.73 2.45 2.00 2.23 2.60 2.33 2.40 1.79 1.65 2.10 1.12 1.50 Tm 0.45 0.37 0.30 0.21 0.28 0.39 0.36 0.30 0.42 0.49 0.43 0.43 0.33 0.33 0.38 0.21 0.27 Yb 3.40 2.75 2.00 1.36 2.00 2.72 2.54 2.04 2.45 2.85 2.42 2.58 1.98 2.01 2.33 1.26 1.72 Lu 0.57 0.46 0.31 0.20 0.30 0.42 0.39 0.31 0.37 0.44 0.37 0.39 0.32 0.32 0.36 0.19 0.29 LREE/
HREE11.57 16.54 12.14 14.23 13.18 14.32 15.34 14.11 14.23 16.18 12.56 12.76 13.53 11.32 15.32 12.78 15.07 ∑REE 169.00 215.16 129.56 108.76 134.29 202.56 198.72 151.08 167.10 224.85 157.56 161.72 131.56 105.51 175.33 76.45 123.14 (La/Yb)N 7.38 12.39 9.40 11.81 10.54 11.71 12.31 11.53 10.28 11.96 9.52 9.25 9.96 7.63 11.62 9.05 10.91 δEu 0.48 0.49 0.60 0.58 0.55 0.46 0.45 0.48 0.56 0.58 0.60 0.67 0.69 0.75 0.50 0.63 0.65 Li 0.17 0.07 9.43 8.06 12.00 9.23 8.08 7.87 10.76 14.57 13.14 13.92 7.42 12.98 7.61 3.37 11.88 Be 0.91 1.35 1.67 1.87 1.50 1.11 1.14 1.03 1.15 1.13 1.29 2.11 0.93 1.43 0.70 0.60 1.36 Sc 7.21 3.99 8.18 3.43 6.44 6.96 5.41 5.60 7.22 7.96 8.39 9.70 5.70 7.27 5.54 3.69 7.74 Nb 10.50 12.20 8.94 8.11 8.45 9.53 9.33 7.33 12.11 12.99 12.43 14.28 8.17 9.58 10.97 5.86 10.96 Ta 1.01 1.15 0.86 0.79 0.77 0.95 0.92 0.74 0.90 1.16 0.93 1.07 0.62 0.69 0.88 0.49 0.74 Zr 322.00 394.00 175.00 176.00 187.00 312.00 328.00 224.00 246.59 368.87 229.70 237.06 158.35 140.33 256.26 113.67 183.44 V 28.70 34.40 53.00 47.30 47.40 40.30 42.20 31.50 43.22 63.30 45.54 60.81 27.37 43.05 30.63 16.02 41.51 Cr 51.40 56.00 52.80 48.10 48.50 42.30 44.00 34.00 44.56 65.31 45.94 57.89 28.87 40.66 36.32 16.14 47.78 Co 5.73 6.36 8.09 8.69 8.40 7.39 7.74 6.26 5.68 6.10 6.53 9.98 4.12 12.60 5.20 2.75 8.13 Ni 15.30 15.80 21.30 21.20 19.20 12.80 13.80 11.30 14.29 19.65 17.68 21.63 9.11 22.24 10.70 6.63 17.15 Cu 12.60 13.00 58.30 45.60 14.30 9.01 8.44 6.96 9.03 6.85 11.03 13.42 7.35 14.86 7.40 12.55 8.98 Zn 24.80 27.50 44.80 41.20 44.10 34.30 32.70 29.40 37.29 48.66 44.68 51.68 23.12 47.82 27.30 13.59 41.61 Ga 12.20 11.30 11.60 9.93 11.90 8.79 9.18 8.06 9.84 9.70 11.40 15.10 7.44 10.42 7.18 5.23 10.74 Rb 7.65 14.10 81.00 72.20 60.10 56.90 57.20 51.60 59.56 57.26 59.21 124.31 42.87 76.09 27.72 29.72 64.59 Sr 92.30 110.00 16.60 15.50 26.20 26.10 26.00 25.30 27.74 18.03 36.10 51.76 109.57 74.10 52.87 48.08 87.36 Y 24.90 21.90 18.40 13.60 18.00 25.50 23.10 19.60 21.96 24.14 23.08 23.92 17.29 17.32 18.90 10.24 14.61 Cs 0.33 0.45 2.82 2.66 2.66 2.10 2.24 1.87 1.82 1.81 1.96 3.60 1.50 2.35 0.89 1.12 2.25 Ba 69.60 83.50 302.00 240.00 302.00 341.00 382.00 298.00 284.65 187.69 246.38 497.68 241.92 366.71 117.72 201.56 372.97 Pb 7.15 6.32 6.85 7.43 8.51 5.59 4.90 6.41 5.97 4.43 7.02 6.17 16.56 12.24 6.15 4.28 4.94 Th 13.90 16.50 11.20 8.07 12.30 22.50 22.50 16.40 16.39 22.03 14.00 14.19 12.11 10.09 15.68 10.41 12.61 U 3.14 4.08 2.11 2.08 2.59 1.79 1.98 1.40 2.31 2.77 2.52 2.51 1.46 1.77 1.81 1.18 1.52 Th/U 4.43 4.04 5.31 3.88 4.75 12.57 11.36 11.71 7.10 7.94 5.56 5.66 8.28 5.70 8.65 8.81 8.31 Th/Sc 1.93 4.14 1.37 2.35 1.91 3.23 4.16 2.93 2.27 2.77 1.67 1.46 2.13 1.39 2.83 2.82 1.63 La/Sc 4.85 11.90 3.20 6.53 4.57 6.38 8.06 5.86 4.86 5.97 3.83 3.43 4.82 2.95 6.82 4.29 3.39 注:CIA=100×Al2O3/(Al2O3+CaO*+Na2O+K2O), 其中CaO*为硅酸盐矿物中的CaO矫正后的摩尔量[29];主量元素含量单位为%, 微量和稀土元素含量单位为10-6 -
Jahn B M, Wu F Y, Chen B.Granitoids of the Central Asian Orogenic Belt and continental growth in the Phanerozoic.Transactions of the Royal Society of Edinburgh[J].Earth Sciences, 2000, 91:181-193. doi: 10.1017-S0263593300007367/
Kovalenko V I, Yarmolyuk V V, Kovach V P, et al.Isotopic provinces, mechanism of generation and sources of the continental curst in the Central Asian mobile belt:geological and isotopic evidence[J].Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2004, 23:605-627. doi: 10.1016/S1367-9120(03)00130-5
Sengör A M C, Natal'in B A, Burtman V S.Evolution of the Altaid tectonic collage and Paleozoic crustal growth in Eurasia[J].Nature, 1993, 364:299-307. doi: 10.1038/364299a0
Windley B F, Alexeiev D, Xiao W J, et al.Tectonic models for accretion of the Central Asian Orogenic Belt[J].Journal of the Geological Society, London, 2007, 164:31-47. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=7e84c1934fe7653e8eaaa83860d82e0a&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
杨合群, 李英, 赵国斌, 等.北山蛇绿岩特征及构造属性[J].西北地质, 2010, 43(1):26-36. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/xbdz201001002 Jack Gillespie, Stijn Glorie, Wenjiao Xiao, et al.Mesozoic reactivation of the Beishan, southern Central Asian Orogenic Belt:Insights from low-temperature thermochronology[J].Gondwana Research, 2017, 43(2017):107-122. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=435751d4ba2c5ca2023359125c61a13f&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Jahn B M.The Central Asian Orogenic Belt and growth of the continental crust in the Phanerozoic[C]//Malpas J, Fletcher C J N, Ali J R, et al.Aspects of the Tectonic Evolution of China.Geological Society, London, 2004: 3-100.
Xiao W, Mao Q G, Windley B F, et al.Paleozoic multiple accretionary and collisional processes of the Beishan orogenic collage[J].American Journal of Science, 2010, 310:1553-1594. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=6beaa6427ed0ce6dd480714eac0984d2
Song D F, Xiao W J, Han C M, et al.Progressive accretionary tectonics of the Beishan orogenic collage, Southern Altaids:insights from zircon U-Pb and Hf isotopic data of high-grade complexes[J].Precambrian Research, 2013, 227:368-388. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2012.06.011
Ding J X, Han C M, Xiao W J, et al.Geochronology, geochemistry and Sr-Nd isotopes of the granitic rocks associated with tungsten deposits in Beishan district, NW China, Central Asian Orogenic Belt:Petrogenesis, metallogenic and tectonic implications[J].Ore Geology Reviews, 2017, 89(2017):441-462. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2ae17433a4316b857978f17631d7e134&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Song D F, Xiao W J, Brian F, et al.Metamorphic complexes in accretionary orogens:Insights from the Beishan collage, southern Central Asian Orogenic Belt[J].Tectonophysics, 2016, 688(2016):135-147. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0040195116303730
胡新茁, 赵国春, 胡新悦, 等.内蒙古北山地区月牙山蛇绿质构造混杂岩带地质特征、形成时代及大地构造意义[J].地质通报, 2015, 34(2/3):425-436. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=2015020318&flag=1 左国朝, 何国琦.北山板块构造及成矿规律[M].北京:北京大学出版社, 1990:1-226. 龚全胜, 刘明强, 梁明宏, 等.北山造山带大地构造相及构造演化[J].西北地质, 2003, 36(1):11-17. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/xbdz200301002 龚全胜, 刘明强, 李海林, 等.甘肃北山造山带类型及基本特征[J].西北地质, 2002, 35(3):28-34. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/xbdz200203004 何世平, 任秉琛, 姚文光, 等.甘肃内蒙古北山地区构造单元划分[J].西北地质, 2002, 4:30-39 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/xbdz200204004 Ao S J, Xiao W J, Han C M, et al.Cambrian to early Silurian ophiolite and accretionary processes in the Beishan collage, NW China:implications for the architecture of the Southern Altaids[J].Cambridge University Press, 2012, 149(4):606-625. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=ae3c711e701a2f414160f0d6fb0895d7&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Liu Q, Zhao G C, Sun M, et al.Ages and tectonic implications of Neoproterozoic ortho- and paragneisses in the Beishan Orogenic Belt, China[J].Precambrian Research, 2015, 266:551-578. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=691d1f3271582a0feb27377058dc274d&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Guo Q Q, Xiao W J, Hou Q L, et al.Construction of Late Devonian Dundunshan arc in the Beishan orogen and its implication for tectonics of southern Central Asian Orogenic Belt[J].Lithos, 2014, 184:361-378. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=12623046eb693c8acdf0846752adffb9
Guo Q Q, Chun S L, Xiao W J, et al.Petrogenesis and tectonic implications of Late Devonian arc volcanic rocks in southern Beishan orogen, NW China:Geochemical and Nd-Sr-Hf isotopic constraints[J].Lithos, 2017, 278/281:84-96. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=24ae4c66ef95f8a7185878f32ec0182c&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Zhu J, Lv X B, Peng S G.U-Pb zircon geochronology, geochemistry and tectonic implications of the early Devonian granitoids in the Liuyuan area, Beishan, NW China[J].Geosciences Journal, 2016, 20(5):609-625. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=4331e9243d6153bb0eab9fa27c1e3bc5
田健, 辛后田, 滕学建, 等.内蒙古北山造山带白云山地区上泥盆统墩墩山组火山岩的厘定及其构造意义[J].岩石学报, 2019, 36(2):509-525. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98202002011 Shi Y R, Zhang W, Alfred Kröner, et al.Cambrian ophiolite complexes in the Beishan area, China, southern margin of the Central Asian Orogenic Belt[J].Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2018, 153(2018):193-205. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=90ed1193dec57282a4da9d2adc8295b9
侯青叶, 王忠, 刘金宝, 等.北山月牙山蛇绿岩地球化学特征及SHRIMP定年[J].现代地质, 2012, 26(5):1008-1017. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/xddz201205022 Wang S D, Zhang K X, Song B W, et al.Geochronology and geochemistry of the Niujuanzi ophiolitic mélange, Gansu Province, NW China:implications for tectonic evolution of the Beishan Orogenic Collage[J].International Journal of Earth Sciences, 2017, 107(1):269-289. doi: 10.1007/s00531-017-1489-2
Chen F K, Hegner E, Todt W.Zircon ages, Nd isotopic and chemical compositions of orthogneisses from the Black Forest, Germany:Evidence for a Cambrian magmatic arc[J].Internatianal Journal of Earth Sciences, 2000, 88:791-802. doi: 10.1007-s005310050306/
Chen F K, Siebel W, Satir M, et al.Geochronology of the Karadere basement(NW Turkey)and implications for the geological evolution of the Istanbul zone[J].International Journal of Earth Sciences, 2002, 91:469-481. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=a2248203d15c7bd8c670599d548a5084&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
陈刚.中生代鄂尔多斯盆地陆缘碎屑成分及其构造属性[J].岩石学报, 1999, 17(3):409-413. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.1999.03.012 Nesbitt H W, Young G M.Early Proterozoic climates and plate motions inferred from major element chemistry of lutites[J].Nature, 1982, 299(5885):715-717. doi: 10.1038-299715a0/
张金亮, 张鑫.塔中地区志留系砂岩元素地球化学特征与物源判别意义[J].岩石学报, 2007, 23(11):2990-3002. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200711029 冯连君, 储雪蕾, 张启锐, 等.化学蚀变指数(CIA)及其在新元古代碎屑岩中的应用[J].地学前缘, 2003, 10(4):539-544. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dxqy200304019 Sensarma S, Rajamani V, Tripathi J K.Petrography and geochemical characteristics of the sediments of the small River Hemavati, Southern India:Implications for provenance and weathering processes[J].Sedimentary Geology, 2008, 205(3):111-125. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=a75c33abdbb8e56fc95171b60e903c05&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Bhatia M R.Plate Tectonics and Geochemical Composition of Sandstones[J].The Journal of Geology, 1983, 91(6):611-627. doi: 10.1086-628815/
Bhatia M R, Crook K A W.Trace element characteristics of graywackes and tectonic setting discrimination of sedimentary basins[J].Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1986, 92(2):181-193. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=726d14abef54a68355ab0a529dadc6c0&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
Taylor S R, McLennan S M.The Continental Crust:Its Composition and Evolution[J].Ocford:Blackwell Scientific Publications, 1985:312. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/OAPaper/oai_doaj-articles_7b034b121c08912757b660fdefe8747e
Wronkiewicz D J, Condie K C.Geochemistry of Archean shales from the Witwatersrand Superground, South Africa:Source-area weathering and provenance[J].Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1987, 51(9):2401-2416. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(87)90293-6
沈渭洲, 舒良树, 向磊, 等.江西井冈山地区早古生代沉积岩的地球化学特征及其对沉积环境的制约[J].岩石学报, 2009, 25(10):2442-2458. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200910013 陈斌, 李勇, 王伟明, 等.晚三叠世龙门山前陆盆地须家河组物源及构造背景分析[J].地质学报, 2016, 90(5):857-872. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dizhixb201605003 Bhatia M R.Morphological strcture of bismuth-droped n-type amorphous germanium sulphidesemiconductors[J].Journal of Materials Geology, 1986, 5:1281-1284. doi: 10.1007/BF01729393
Sun S S, McDonough W F.Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts:implications for mantle composition and processes[J].Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 1989, 42:313-345. doi: 10.1144-GSL.SP.1989.042.01.19/
包汉勇, 杨凤丽, 王丹萍, 等.苏南地区中、古生界沉积岩地球化学特征——以圣科1井为例[J].吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2011, 41(1):29-38. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=cckjdxxb201101004 张建军, 牟传龙, 周恳恳, 等.滇西户撒盆地芒棒组砂岩地球化学特征及物源区和构造背景分析[J].地质学报, 2017, 5:1083-1096. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dizhixb201705009 王丛山, 陈文西, 单福龙.西藏雄巴地区中新世雄巴组砂岩地球化学特征及物源区、构造背景的指示[J].地质通报, 2016, 35(6):1195-1207. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dizhixb201606010 程先钰, 李以科, 董满华, 等.阿拉善右旗特拜金矿赋矿地层时代厘定及其地质意义[J].吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2019, 49(6):1565-1577. http://xuebao.jlu.edu.cn/dxb/CN/abstract/abstract11057.shtml 王树庆, 胡晓佳, 赵华雷.内蒙古苏左旗洪格尔地区新发现晚石炭世碱性花岗岩[J].地质调查与研究, 2019, 42(2):81-85. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/qhwjyjjz201902001 高伊航, 沈军辉, 苏永军, 等.重力调查在潍坊滨海区划分断裂和构造单元中的应用[J].地质调查与研究, 2019, 42(1):72-76. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/qhwjyjjz201901010 田健, 段霄龙.内蒙古1: 5万月牙山(K47E015010)、儿驼山(K47E016010)幅区域地质矿产调查报告.2018.



 下载:
下载: