Geochemical characteristics, zircon U-Pb age and Hf isotope of the gabbro in the Huanghuatan Cu-Ni deposit, Darhan Muminggan Joint Banner, Inner Mongolia
-
摘要:
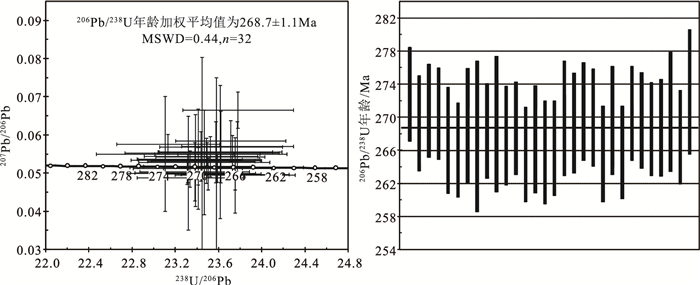
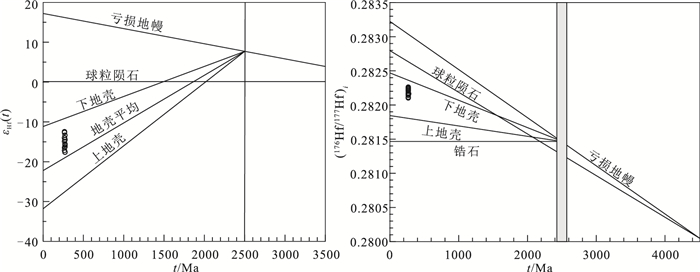
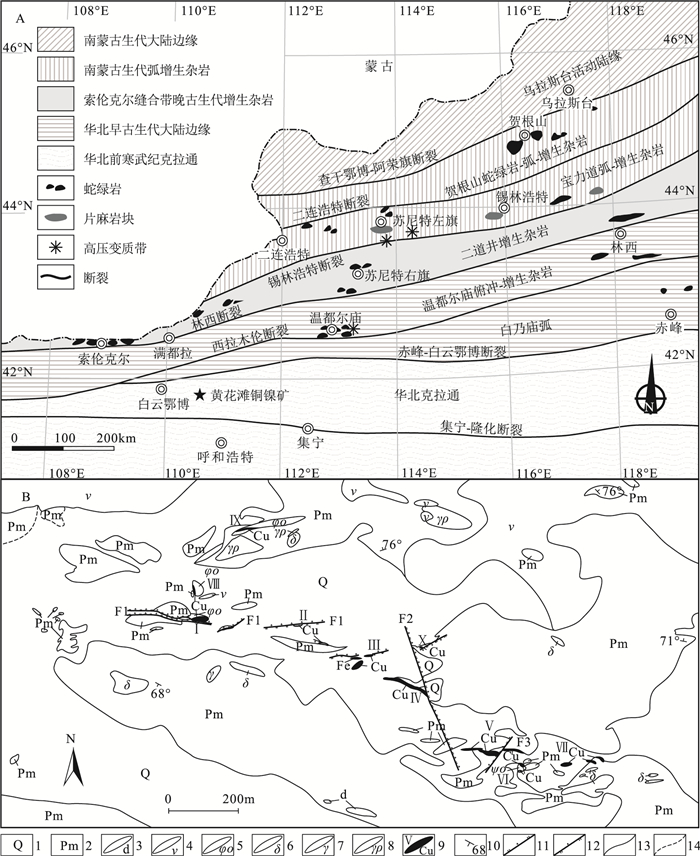
内蒙古达茂旗黄花滩铜镍矿位于华北克拉通北缘白云鄂博裂谷系,铜镍矿体产出于辉长岩体边缘与片麻岩的接触部位。利用LA-ICP-MS技术测得黄花滩铜镍矿辉长岩锆石206Pb/238U年龄为268.7±1.1 Ma(MSWD=0.44,n=32),限定黄花滩铜镍矿是中二叠世岩浆活动的产物。黄花滩矿区辉长岩具有高Al2O3(17.72%~19.81%)、偏碱性(K2O+Na2O=4.37%~5.09%)、低P2O5(0.28%~0.42%)、低Ti2O(0.83%~1.21%)的特征,属钙碱性系列。岩石稀土元素总量为144×10-6~167×10-6,富集轻稀土元素,(La/Yb)N介于7.43~8.85之间,显弱负Eu异常(δEu=0.84~0.88),微量元素富集大离子亲石元素(Rb、Ba、K、Sr),亏损高场强元素(Nb、Ta、Ti)。锆石εHf(t)变化范围为-17.69~-12.53(平均值为-15.21),二阶段"地壳"Hf模式年龄(tHf2)介于2082~2411 Ma之间。地球化学特征表明,辉长岩源区为大量遭受地壳混染的岩石圈地幔,地壳物质很可能由色尔腾山群岩石部分熔融形成。结合区域构造演化,认为黄花滩辉长岩形成于造山后构造背景,为晚古生代伸展体制下幔源岩浆活动的产物。
Abstract:Located in Darhan Muminggan Joint Banner of Inner Mongolia, the Huanghuatan Cu-Ni deposit is hosted in the contact zone of the gabbro and gneiss which lies in the Bayan Obo rift system on the northern margin of the North China Craton.LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb dating of Huanghuatan gabbro yielded a weighted average age of 268.7±1.1 Ma (MSWD=0.44, n=32), which suggests that the Huanghuatan Cu-Ni deposit is a product of Middle Permian magmatic activity.The Huanghuatan gabbro, belonging to calc-alkaline series, is characterized by high Al2O3 (17.72%~19.81%), rich alkali (K2O+Na2O=4.37%~5.09%), low P2O5 (0.28%~0.42%) and low Ti2O (0.83%~1.21%).The REE content ranges from 144×10-6 to 167×10-6, showing strong fractionation between LREE and HREE (LaN/YbN=7.43~8.85), with slightly negative Eu anomalies (δEu=0.84~0.88).The gabbro is distinctively enriched in LILE (Rb, Ba, K, Sr)but depleted in HFSE (Nb, Ta, Ti).The zircons have concentrated negative εHf(t) values (-17.69~-12.53) and two-stage Hf isotopic crust model ages (tHf2=2082~2411 Ma).The geochemical characteristics reveal that the parental magma of Huanghuatan gabbro was derived probably from the mantle, which was subjected to abundant crustal contamination.The crustal materials were probably formed by the partial melting of Sertengshan Group.Combined with the regional tectonic setting, the authors propose that the Huanghuatan gabbro was mantle origin and formed in an extensional regime of the Late Paleozoic.
-
Keywords:
- Cu-Ni deposit /
- LA-ICP-MS /
- Hf isotope /
- zircon U-Pb age /
- lithogeochemistry /
- Huanghuatan /
- Inner Mongolia
-
致谢: 研究过程中得到了中国地质调查局天津地质调查中心周红英教授、李俊建研究员、中国地质大学(北京)薛春纪教授的帮助和指导,审稿专家对本文提出了建设性意见,在此一并致谢。
-
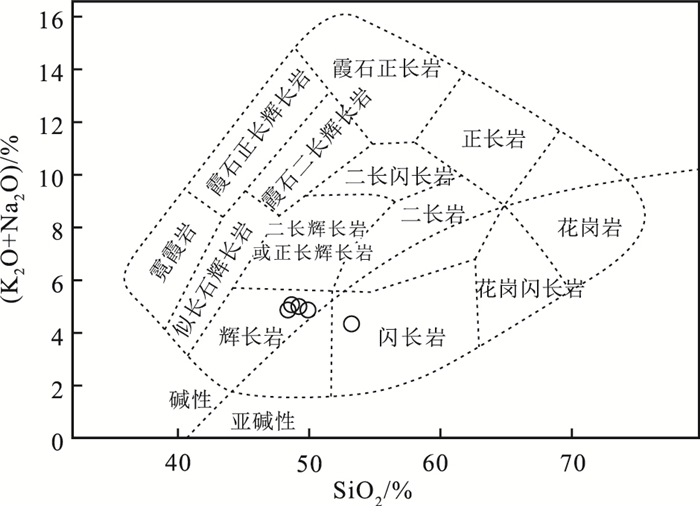
图 5 黄花滩铜镍矿辉长岩TAS图解(底图据参考文献[23])
Figure 5. TAS diagram for the gabbro from the Huanghuatan Cu-Ni deposit
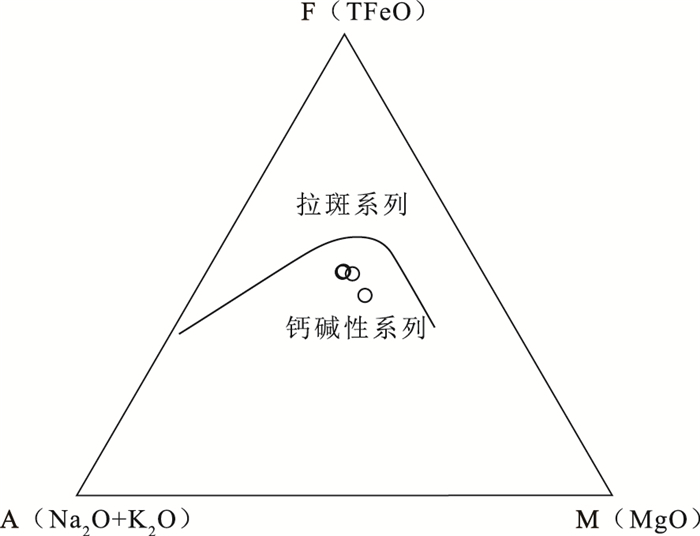
图 6 黄花滩铜镍矿辉长岩AFM图解(底图据参考文献[22])
Figure 6. AFM diagram for the gabbro from the Huanghuatan Cu-Ni deposit
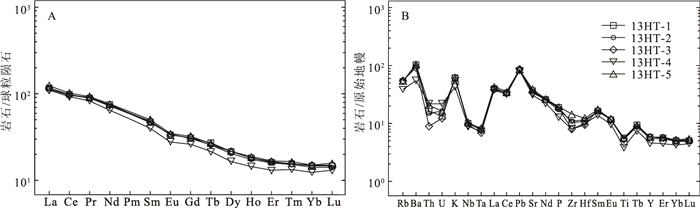
图 7 黄花滩铜镍矿辉长岩稀土元素配分图(A)和微量元素蛛网图(B)(标准化数据据参考文献[24])
Figure 7. Chondrite-normalized REE patterns (A) and primitive mantle-normalized trace element patterns (B) for gabbro in the Huanghuatan Cu-Ni deposit
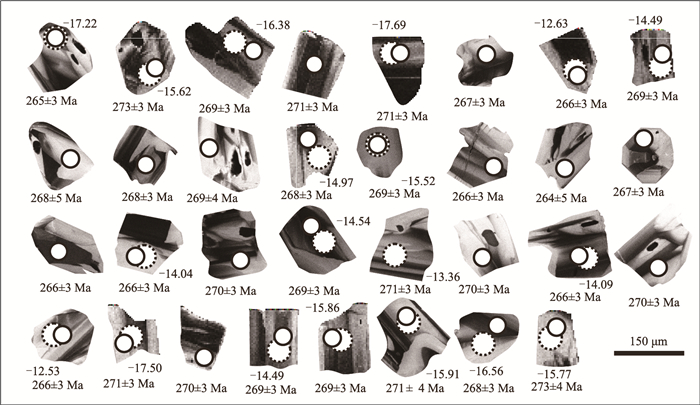
表 1 黄花滩铜镍矿辉长岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Th-Pb同位素数据
Table 1 LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Th-Pb data for the gabbro from the Huanghuatan Cu-Ni deposit
测点号 含量/10-6 同位素比值 年龄/Ma Pb Th U 232Th/238U 1σ 207Pb/206Pb 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ 207Pb/206Pb 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ 1 6 92 118 0.78 0.0028 0.06 0.0042 0.35 0.0243 0.04 0.0005 607 151 303 21 265 3 2 38 804 702 1.14 0.0018 0.06 0.0013 0.34 0.0081 0.04 0.0004 516 49 300 7 273 3 3 20 335 400 0.84 0.0024 0.05 0.0022 0.31 0.0134 0.04 0.0005 339 94 277 12 269 3 4 30 650 580 1.12 0.0045 0.05 0.0015 0.30 0.0094 0.04 0.0004 205 71 264 8 271 3 5 49 1237 905 1.37 0.0021 0.05 0.0012 0.32 0.0073 0.04 0.0004 357 49 280 6 271 3 6 6 81 125 0.65 0.0006 0.06 0.0047 0.33 0.0275 0.04 0.0005 491 181 292 24 267 3 7 17 394 322 1.22 0.0061 0.06 0.0025 0.32 0.0153 0.04 0.0004 413 100 282 13 266 3 8 5 70 109 0.65 0.0008 0.05 0.0068 0.31 0.0394 0.04 0.0005 325 293 275 35 269 3 9 3 24 55 0.44 0.0017 0.05 0.0118 0.30 0.0579 0.04 0.0007 268 522 268 51 268 5 10 20 446 400 1.12 0.0027 0.05 0.0026 0.32 0.0155 0.04 0.0005 388 108 281 14 268 3 11 3 28 55 0.52 0.0028 0.06 0.0126 0.33 0.066 0.04 0.0006 425 508 286 58 269 4 12 7 122 161 0.76 0.0027 0.06 0.004 0.33 0.0239 0.04 0.0005 436 161 286 21 268 3 13 25 532 522 1.02 0.0035 0.06 0.0015 0.32 0.0092 0.04 0.0004 417 61 285 8 269 3 14 13 263 268 0.98 0.0032 0.07 0.0024 0.39 0.0144 0.04 0.0005 825 75 332 12 266 3 15 2 19 50 0.38 0.0007 0.08 0.0128 0.48 0.0679 0.04 0.0008 1291 297 401 56 264 5 16 8 146 165 0.89 0.0034 0.06 0.0087 0.32 0.0506 0.04 0.0005 438 349 286 44 267 3 17 6 76 133 0.57 0.0021 0.05 0.005 0.29 0.0284 0.04 0.0005 173 233 257 25 266 3 18 12 245 262 0.94 0.0019 0.06 0.0027 0.34 0.016 0.04 0.0005 549 100 297 14 266 3 19 5 76 122 0.62 0.0017 0.05 0.006 0.32 0.0346 0.04 0.0005 347 254 278 31 270 3 20 8 132 187 0.71 0.0028 0.05 0.0032 0.32 0.0193 0.04 0.0005 392 133 282 17 269 3 21 15 299 313 0.96 0.0042 0.05 0.0018 0.30 0.0113 0.04 0.0005 256 83 269 10 271 3 22 10 155 214 0.72 0.003 0.05 0.0038 0.30 0.0228 0.04 0.0005 219 175 265 20 270 3 23 10 168 215 0.78 0.0056 0.06 0.0032 0.33 0.0193 0.04 0.0005 495 125 290 17 266 3 24 5 61 113 0.54 0.0024 0.05 0.0065 0.32 0.0376 0.04 0.0005 361 275 279 33 270 3 25 15 62 363 0.17 0.0007 0.05 0.002 0.29 0.0117 0.04 0.0004 181 93 257 10 266 3 26 30 733 578 1.27 0.032 0.05 0.0013 0.29 0.0077 0.04 0.0005 143 60 258 7 271 3 27 13 265 260 1.02 0.0035 0.05 0.0024 0.31 0.0148 0.04 0.0005 282 108 271 13 270 3 28 19 384 386 0.99 0.0031 0.05 0.0021 0.29 0.0127 0.04 0.0004 189 99 261 11 269 3 29 10 180 206 0.87 0.0028 0.05 0.0029 0.31 0.0173 0.04 0.0005 343 125 277 15 269 3 30 4 26 83 0.32 0.0031 0.05 0.0075 0.30 0.0424 0.04 0.0006 199 346 263 38 271 4 31 19 332 368 0.90 0.0128 0.05 0.0018 0.30 0.011 0.04 0.0004 259 81 267 10 268 3 32 4 47 81 0.58 0.0027 0.06 0.0075 0.33 0.0429 0.04 0.0006 416 305 289 38 273 4 表 2 黄花滩铜镍矿辉长岩锆石Lu-Hf同位素数据
Table 2 Zircon Lu-Hf isotope compositions of the gabbro from the Huanghuatan Cu-Ni deposit
测点号 t/Ma 176Yb/177Hf 2σ 176Lu/177Hf 2σ 176Hf/177Hf 2σ εHf(0) εHf(t) tHf1/Ma tHf2/Ma fLu/Hf 1 265 0.009247 0.000044 0.000254 0.000001 0.282122 0.000020 -20.79 -17.22 1561 2378 -0.99 2 273 0.069069 0.000798 0.001775 0.000025 0.282170 0.000027 -21.36 -15.62 1557 2282 -0.95 3 269 0.089309 0.000338 0.002179 0.000013 0.282153 0.000026 -19.34 -16.38 1598 2326 -0.93 4 271 0.025011 0.000307 0.000629 0.000007 0.282107 0.000023 -20.23 -17.69 1597 2411 -0.98 5 266 0.036620 0.000350 0.000861 0.000008 0.282254 0.000025 -18.81 -12.63 1403 2089 -0.97 6 269 0.083191 0.001569 0.001919 0.000029 0.282205 0.000033 -19.80 -14.49 1513 2208 -0.94 7 268 0.013847 0.000116 0.000332 0.000002 0.282184 0.000027 -17.97 -14.97 1479 2239 -0.99 8 269 0.015206 0.000229 0.000333 0.000005 0.282168 0.000035 -23.20 -15.52 1501 2274 -0.99 9 266 0.140477 0.001273 0.003006 0.000019 0.282225 0.000045 -20.30 -14.04 1529 2177 -0.91 10 269 0.052841 0.000849 0.001232 0.000022 0.282200 0.000023 -21.64 -14.54 1492 2212 -0.96 11 271 0.124662 0.000959 0.002756 0.000015 0.282240 0.000032 -21.78 -13.36 1497 2138 -0.92 12 266 0.026205 0.000400 0.000713 0.000004 0.282212 0.000021 -22.35 -14.09 1455 2181 -0.98 13 266 0.094690 0.000876 0.002276 0.000016 0.282264 0.000029 -21.61 -12.53 1442 2082 -0.93 14 271 0.056553 0.001984 0.001391 0.000049 0.282116 0.000024 -20.79 -17.50 1617 2399 -0.96 15 269 0.020958 0.000219 0.000518 0.000006 0.282198 0.000019 -21.36 -14.49 1467 2209 -0.98 16 269 0.023321 0.000119 0.000647 0.000003 0.282160 0.000020 -19.34 -15.86 1525 2295 -0.98 17 271 0.013458 0.000123 0.000418 0.000004 0.282156 0.000020 -20.23 -15.91 1521 2300 -0.99 18 268 0.015530 0.000116 0.000496 0.000003 0.282140 0.000018 -18.81 -16.56 1546 2338 -0.99 19 273 0.027577 0.000967 0.000869 0.000030 0.282161 0.000018 -19.80 -15.77 1532 2292 -0.97 注:εHf(0)=[(176Hf/177Hf)S/(176Hf/177Hf)CHUR, 0-1]×10000; εHf(t)={[(176Hf/177Hf)S-(176Lu/177Hf)S×(eλt-1)]/[(176Hf/177Hf)CHUR, 0-(176Lu/177Hf)CHUR×(eλt-1)]-1}×10000; tHf1=1/λ×ln{1+[(176Hf/177Hf)S-(176Hf/177Hf)DM]/[(176Lu/177Hf)S-(176Hf/177Hf)DM]}; tHf2= tHf1-(tHf1- t)(fCC- fS)/(fCC- fDM); fLu/Hf=(176Lu/177Hf)S/(176Lu/177Hf)CHUR-1;其中(176Hf/177Hf)S和(176Hf/177Hf)S为测定值,(176Lu/177Hf)CHUR和(176Hf/177Hf)CHUR, 0分别为0.0332和0.282772 [19]; (176Lu/177Hf)DM和(176Hf/177Hf)DM值分别为0.0384和0.28325 [20], fCC、fS、fDM分别为大陆地壳、样品和亏损地幔的的fLu/Hf。λ=1.867×10-11 a-1[21], t为锆石的形成时间 表 3 黄花滩铜镍矿辉长岩主量、微量和稀土元素分析结果
Table 3 Major, trace and rare earth element data of the gabbro from the Huanghuatan Cu-Ni deposit
样号 13HT01 13HT02 13HT03 13HT04 13HT05 SiO2 48.66 49.84 48.26 53.25 49.21 Al2O3 19.81 19.56 19.24 17.72 19.55 Fe2O3 2.70 2.40 2.31 2.14 2.55 FeO 7.12 7.02 7.51 5.78 6.98 FeOT 9.55 9.18 9.59 7.71 9.27 CaO 8.23 8.21 8.58 8.19 8.09 MgO 5.04 4.81 5.50 5.73 4.89 K2O 1.83 1.72 1.82 1.28 1.78 Na2O 3.26 3.18 3.09 3.09 3.25 TiO2 1.21 1.15 1.15 0.83 1.19 P2O5 0.41 0.38 0.40 0.28 0.42 MnO 0.15 0.14 0.15 0.14 0.14 烧失量 0.5 0.51 0.85 0.62 0.84 总量 98.92 98.92 98.86 99.05 98.89 Mg# 48.46 48.28 50.54 56.97 48.45 Na2O+ K2O 5.09 4.90 4.91 4.37 5.03 K2O/ Na2O 0.56 0.54 0.59 0.41 0.55 La 27.7 27.8 26.5 25.9 29.4 Ce 60.1 59.2 59.1 56.4 62.6 Pr 8.53 8.41 8.58 7.89 8.86 Nd 34.8 33.7 34.6 30.1 35.7 Sm 7.29 7.11 7.42 6.1 7.74 Eu 1.96 1.97 1.94 1.61 2.02 Gd 6.39 6.27 6.34 5.35 6.68 Tb 1.02 0.95 0.96 0.8 1 Dy 5.44 5.17 5.45 4.21 5.48 Ho 1.03 0.99 1.02 0.82 1.06 Er 2.67 2.60 2.71 2.15 2.78 Tm 0.4 0.39 0.4 0.34 0.42 Yb 2.5 2.38 2.56 2.10 2.52 Lu 0.37 0.36 0.38 0.33 0.40 Y 26.6 25.1 26 20.7 26.6 ∑REE 160.20 157.30 157.96 144.10 166.66 LREE 140.38 138.19 138.14 128.00 146.32 HREE 19.82 19.11 19.82 16.10 20.34 LREE/HREE 7.08 7.23 6.97 7.95 7.19 LaN/YbN 7.95 8.38 7.43 8.85 8.37 δEu 0.86 0.88 0.84 0.84 0.84 δCe 0.95 0.94 0.96 0.96 0.94 Li 10.2 9.82 8.91 8.17 10.4 Rb 33.3 33.3 34.6 24.5 33.90 Cs 0.66 0.59 0.62 0.4 0.58 Sr 778 745 708 656 827 Ba 725 707 648 384 734 V 232 224 234 193 234 Sc 28.3 27.7 29.7 28.7 28.4 Nb 7.17 6.9 6.79 6.3 7.38 Ta 0.32 0.33 0.28 0.3 0.34 Zr 116 121 89.2 89.9 162 Hf 3.34 3.52 2.94 3.05 3.8 Be 0.95 1.01 0.96 1.01 0.94 Ga 23 22.4 22.7 20.1 23.1 Ge 3.55 3.31 3.56 3 3.66 U 0.28 0.34 0.26 0.46 0.34 Th 1.39 1.26 0.75 1.87 1.76 F 855 816 818 813 822 注:Mg#=100×Mg2+/(Mg2++TFe2+);TFeO=FeO+0.8998×Fe2O3;主量元素含量单位为%,微量和稀土元素含量单位为10-6 -
刘国军, 王建平.内蒙古镁铁质-超镁铁质岩型铜镍矿床成矿条件与找矿远景分析[J].地质与勘探, 2004, 40(1):17-20. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzykt200401004 Peng R M, Zhai Y S, Li C S, et al.The Erbutu Ni-Cu Deposit in the Central Asian Orogenic Belt:A Permian Magmatic Sulfide Deposit Related to Boninitic Magmatism in An Arc Setting[J].Economic Geology, 2013, 108:1879-1888. doi: 10.2113/econgeo.108.8.1879
江思宏, 聂凤军, 刘妍, 等.内蒙古小南山-铂-铜-镍矿区辉长岩地球化学特征及成因[J].地球学报, 2003, 24(2):121-126. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-3021.2003.02.005 党智财, 李俊建, 赵泽霖, 等.内蒙古四子王旗地区小南山辉长岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄及其地质意义[J].地质通报, 2016, 35(4):583-592. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2016.04.014 梁有彬.黄花滩铂矿地质特征及其找矿方向[J].地质与勘探, 1981, 12:17-21. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DZKT198112004.htm 朱建兴, 贾文艳, 李福占.内蒙古黄花滩铜、镍矿矿床地质特征及矿床成因[J].西部资源, 2014, 6:128-130. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/xbzy201401074 李尚林, 袁华钵, 杨文瑞, 等.内蒙古乌拉特中旗克布钴镍矿地质特征[J].矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2011, 30(增刊):68-69. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Conference/7680045 李鹏, 任陪林, 白启星, 等.乌拉特中旗克布矿区镍矿床岩石学特征及成因浅析[J].现代矿业, 2013, 530(6):65-66. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-6082.2013.06.021 李志丹, 王佳营, 文思博, 等.内蒙古乌拉特中旗克布镍矿地质特征及超基性-基性岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄[J].矿物学报, 2015, S1:130-131. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Conference/9132928 马娟, 彭斌.内蒙古特颇格日图超基性岩体特征及成矿潜力研究[J].地质调查与研究, 2009, 33(3):175-180. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4135.2009.03.002 王楫, 李双庆, 王保良, 等.狼山-白云鄂博裂谷系[M].北京:北京大学出版社, 1992:1-132. Xiao W, Windley B F, Hao J, et al.Accretion leading to collision and the Permian Solonker suture, Inner Mongolia, China:Termination of the Central Asian Orogenic Belt[J].Tectonics, 2003, 22(6):1069-1089.
李怀坤, 耿建珍, 郝爽, 等.用激光烧蚀多接收器等离子体质谱仪测定锆石U-Pb同位素年龄的研究[J].矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2009, 28(增刊):77. 李国占, 郝爽, 王家松, 等.浅谈多接收器电感耦合等离子体质谱仪的日常维护[J].地质调查与研究, 2019, 42(4):271-277. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4135.2019.04.007 Liu Y S, Gao S, Hu Z C, et al.Continental and oceanic crust recycling-induced melt-peridotite interactions in the Trans-North China Orogen:U-Pb dating, Hf isotopes and trace elements in zircons from mantle xenoliths[J].J.Petrol., 2010, 51(1/2):537-571. doi: 10.1093-petrology-egp082/
Ludwig K R.Users manual for isoplot/Ex (rsv.3.0):A Geochronologica Toolkit for Microsoft excel:Berkrley Geochronology Center[J].Special Publication, 2003, 1a:1-55.
耿建珍, 李怀坤, 张健, 等.锆石Hf同位素组成的LA-MC-ICP-MS测定[J].地质通报, 2011, 30(10):1508-1513. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2011.10.004 Morel M L A, Nebel O, Nebel-Jacobsen Y J, et al.Hafnium isotope characterization of the GJ-1 zircon reference material by solution and laser-ablation MC-ICPMS[J].Chemical Geology, 2008, 255(1/2):231-235. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=1c7ffc35c732ec0b528043cdec4a2a69
Blichert T J, Albarede F.The Lu-Hf geochemistry of the chondrites and the evolution of the mantle-crust system[J].Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1997, 148:243-258. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(97)00040-X
Griffin W L, Pearson N J, Belousova E A, et al.The Hf isotope composition of cratonic mantle:LA-MC-ICP-MS analysis of zircon megacrysts in kimberlites[J].Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2000, 64:133-147. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(99)00343-9
Söderlund U, Patchett J P, Vervoort J D, et al.The Lu-176 decay constant determined by Lu-Hf and U-Pb isotope systematic of Precambrian mafic intrusions[J].Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2004, 219:311-324. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(04)00012-3
Wilson M.Igneous Petrogenesis[M].London:Unwin Hyman, 1989:1-464.
Middlemost E A K.Magmas and Magmatic Rocks[M].London:Longman, 1985:1-266.
Sun S S, McDonough W F.Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts:Implications for mantle composition and processes[J].Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 1989, 42(1):313-345. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.1989.042.01.19
赵磊, 吴泰然, 罗红玲.内蒙古乌拉特中旗北七哥陶辉长岩SHRIMP锆石U-Pb年龄、地球化学特征及其地质意义[J].岩石学报, 2011, 27(10):3071-3082. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201110022 Peng R M, Li C S, Zhai Y S, et al.Geochronology, petrology and geochemistry of the Beiligaimiao magmatic sulfide deposit in a Paleozoic active continental margin, North China[J].Ore Geology Reviews, 2017, 90:607-617. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2017.05.004
Sklyarov E V, Gladkochub D P, Mazukabzov A M, et al.Neoproterozoic mafic dike swarms of the Sharyzhalgai metamorphic massif, southern Siberian craton[J].Precambrian Research, 2003, 122(1):359-376.
孔会磊, 李金超, 栗亚芝, 等.青海东昆仑东段加当辉长岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb测年及其地质意义[J].地质与勘探, 2017, 53(5):889-902. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzykt201705006 Condie K C.Geochemical changes in baslts and andesites across the Archean-Proterozoic boundary:Identification and significance[J].Lithos, 1989, 23(1):1-18.
Davidson J P.Deciphering mantle and crustal signatures in subduction zone magmatism[J].Washington Dc American Geophysical Union Geophysical Monograph, 1996, 96:251-262.
Anderson D L.Komatiites and picrites:evidence that the 'plume' source is depleted[J].Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1994, 128(3/4):303-311. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0012821X9490152X
Taylor S R, McLennan S M.The Continental Crust:Its composition and Evolution[M].London:Blackwell, 1985:57-72.
McCulloch M T, Gamble J A.Geochemical and geodynamical constraints on subduction zone magmatism[J].Earth and Plenetary Science Letters, 1991, 102(3):358-374. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/0012821X9190029H
Hawkesworth C J, Gallagher K, Hergt J M, et al.Mantle and Slab Contribution in Arc Magmas[J].Annual Review of Earth & Planetary Sciences, 1993, 21:175-204. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dxqy-e201806016
Amelin Y, Lee D C, Halliday A N.Early-middle Archaean crustal evolution deduced from Lu-Hf and U-Pb isotopic studies of single zircon grains[J].Geochimica Et Cosmochimica Acta, 2000, 64(24):4205-4225. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(00)00493-2
Vervoort J D, Patchett P J, Gehrels G E, et al.Constraints on early Earth differentiation from hafnium and neodymium isotopes[J].Nature, 1996, 379(65/66):624-627. https://ui.adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/1996Natur.379..624V
王荃, 刘雪亚, 李锦轶.中国华夏与安加拉古陆间的板块构造[M].北京:北京大学出版社, 1991:50-60. Sengör A M C, Natal'in B A, Burtman V S.Evolution of the Altaid tectonic collage and Palaeozoic crustal growth in Eurasia[J].Nature, 1993, 364(6435):299-307. doi: 10.1038/364299a0
Windley B F, Alexeiev D, Xiao W, et al.Tectonic models for accretion of the Central Asian Orogenic Belt[J].Journal of the Geological Society, 2007, 164(12):31-48. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=407c8a0b623113b1dd6b69ee8fde6a21
李锦轶, 张进, 杨天南, 等.北亚造山区南部及其毗邻地区地壳构造分区与构造演化[J].吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2009, 39(4):584-605. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/cckjdxxb200904002 Tang K.Tectonic development of Paleozoic foldbelts at the north margin of the Sino-Korean Craton[J].Tectonics, 1990, 9(2):249-260. doi: 10.1029-TC009i002p00249/
邵济安.中朝板块北缘中段地壳演化[M].北京:北京大学出版社, 1991:1-135. 洪大卫, 黄怀曾, 肖宜君, 等.内蒙古中部二叠纪碱性花岗岩及其地球动力学意义[J].地质学报, 1994, 68(3):219-230. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.1994.03.001 徐备, 陈斌.内蒙古北部华北板块与西伯利亚板块之间中古生代造山带的结构及演化[J].中国科学(D辑), 1997, 27(3):227-232. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-JDXK199703005.htm 张晋瑞, 初航, 魏春景, 等.内蒙古中部构造混杂带晚古生代-早中生代变质基性岩的地球化学特征及其大地构造意义[J].岩石学报, 2014, 30(7):1935-1947. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201407009 施光海, 苗来成, 张福勤, 等.内蒙古锡林浩特A型花岗岩的时代及区域构造意义[J].科学通报, 2004, 49(4):384-389. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2004.04.015 Zhu Y F.Permian volcanism in the Mongolian orogenic zone, northeast China:Geochemistry, magma sources and petrogenesis[J].Geological Magazine, 2001, 138(2):101-115. doi: 10.1017/S0016756801005210
Zhang X H, Zhang H F, Tang Y J, et al.Geochemistry of Permian bimodal volcanic rocks from central Inner Mongolia, North China:implication for tectonic setting and Phanerozoic continental growth in Central Asian Orogenic Belt[J].Chemical Geology, 2008, 249(3/4):262-281. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0009254108000053
Miao L C, Fan W M, Liu D Y, et al.Geochronology and geochemistry of the Hegenshan ophiolitic complex:implications for late-stage tectonic evolution of the Inner Mongolia-Daxinganling Orogenic Belt, China[J].Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2008, 32(5/6):348-370. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1367912007002222
晨辰, 张志诚, 郭召杰, 等.内蒙古达茂旗满都拉地区早二叠世基性岩的年代学、地球化学及其地质意义[J].中国科学(地球科学), 2012, 42(3):343-358. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgkx-cd201203004 中国建筑材料工业地质勘查中心内蒙古总队.内蒙古自治区达茂联合旗黄花滩铜镍铂矿区V号矿体资源储量核实报告.2005.



 下载:
下载: