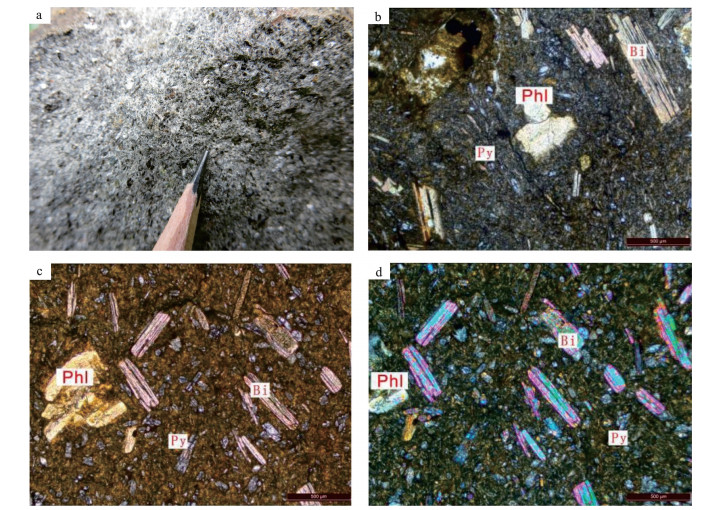
The petrogenesis of minette from Luocheng of Northern Guangxi: Geochemistry and U-Pb geochronology
-
摘要:
对桂北罗城地区云煌岩开展系统的地球化学研究及LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb测年,获得锆石U-Pb年龄为248 ±1 Ma。其富钾(K2O/Na2O=4.23~136.2),富碱(K2O+Na2O=6.86%~8.03%),钾的含量显著高于大陆地壳平均值,富集轻稀土元素及大离子亲石元素,亏损高场强元素,具有较低的La/Nb值,Nb/U值低于洋中脊玄武岩、岛弧玄武岩及上地壳值,与全球平均俯冲沉积物接近,表明源区可能为早期俯冲交代作用形成的富集地幔。结合区域构造背景分析,推测桂北罗城地区云煌岩形成在中生代三叠纪(248±1 Ma)华南陆内岩石圈伸展减薄的背景下,软流圈上涌促使交代富集地幔发生部分熔融形成云煌岩岩浆,区域上NNE向的深大断裂为岩浆喷发提供通道。
-
关键词:
- 云煌岩 /
- 地球化学 /
- LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb测年 /
- 岩石成因 /
- 桂北罗城
Abstract:In this paper, the authors conducted detailed study of geochemistry and LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb geochronology of lamproites in Luocheng of northern Guangxi, and obtained a zircon age of 248±1 Ma, indicating that the lamprophyre magmatic activity in this area occurred during the Triassic.The potassium content of minette is significantly higher than average content of continental crust.The rock is characterized by rich potassium (K2O/Na2O=4.23~136.2) and alkali (K2O+Na2O=6.86%~8.03%) and enrichment of light rare-earth elements and large ion lithophile elements as well as depletion of high field strength elements with low La/Nb ratios, Nb/U ratio less than MORB, OIB and the value of the earth's crust, being close to average relevant values of global diving sediments.These results show that the source area might have been the enriched mantle formed by early subduction metasomatism.Combined with regional tectonic background analysis, the authors infer that the diagenetic process of minette from Luocheng in northern Guangxi was as follows:the intracontinental lithosphere of South China experienced stretching and thinning in Mesozoic Triassic (255.5±3.5 Ma), the upwelling of the asthenosphere caused the partial melting of the enriched mantle to form the minettes magma, and the NNE-trending deep fault in the region provided the channel for the magma eruption.
-
Keywords:
- minette /
- geochemistry /
- LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb dating /
- petrogenesis /
- Luocheng, northern Guangxi
-
花岗岩型铀矿床是中国重要的铀矿床类型,主要分布于华南地区,目前占中国已探明铀资源量的22.9%[1-6]。华南地区花岗岩型铀矿床主要产于花岗岩体内部或外接触带附近,受断裂构造控制[7-8]。鉴于其成因类型属于热液型铀矿床[9],因此成矿流体始终是探讨该地区铀成矿作用过程最重要和最直接的手段[10-13]。
桃山-诸广山铀成矿带位于南岭地区,是中国最大的花岗岩型铀成矿带[14],其预测资源量占整个花岗岩型铀矿床预测资源量的50%[6],长期以来一直是学者们关注的焦点[15-17]。长排矿区位于诸广山岩体南缘长江铀矿田中部,毗邻著名的棉花坑(302)铀矿床,被认为是桃山-诸广山铀成矿带最具找矿潜力的地区之一。前人对该矿区开展了大量的岩石学、年代学、找矿勘查等方面的研究工作[18-20],但关于成矿作用和成矿机制方面的研究则较少。众所周知,流体包裹体研究可以查明成矿流体性质和成矿物质沉积机制,是研究成矿作用和成矿机制的重要手段[21-24]。因此,本文选择长排矿区开展流体包裹体及同位素研究,通过查明成矿流体的性质并探讨其成矿机制,为总结区域成矿规律和找矿提供依据。
1. 区域及矿区地质特征
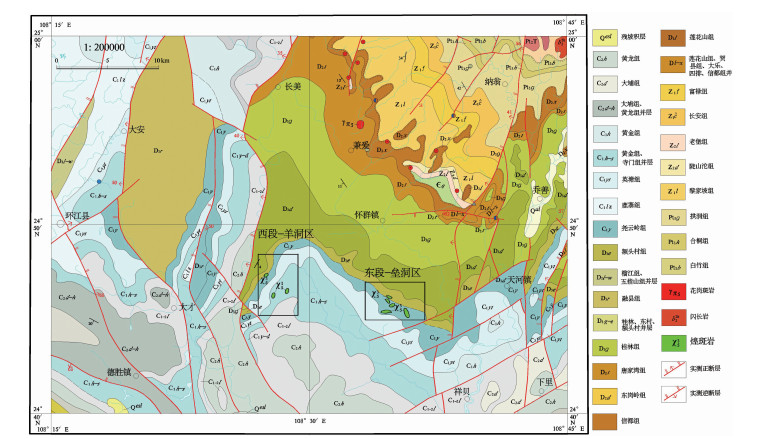
诸广山地区位于广东、湖南和江西三省交界处,以出露巨型诸广山花岗岩岩基为特点。诸广山花岗岩位于该区中部,产状受南岭东西向构造和诸广山南北向构造的联合控制[25]。诸广山花岗岩体主要为过铝质花岗岩,岩性有二云母花岗岩、黑云母花岗岩、二长花岗岩等。区内地层多分布于诸广山岩体边部,主要包括:震旦系、寒武系、奥陶系变质砂岩、泥岩;泥盆系、石炭系灰岩和砂岩;白垩系—新近系碎屑岩[26]。长江矿田位于诸广山地区中部,是中国重要的铀矿田之一。该矿田以出露白垩纪、侏罗纪和三叠纪花岗岩为主,几乎未见地层露头。区内构造由NE—SW向、NW—SE向、N—S向和E—W向断裂构造组成,由北向南还分布有NE— SW向的里周、棉花坑和黄溪水断裂及NW—SE向的油洞断裂4条区域性断裂(图 1)。
![]() 图 1 长江铀矿田及长排矿区地质图(据参考文献[26]修改)Figure 1. Geological map of the Changjiang Uranium ore district and Changpai area
图 1 长江铀矿田及长排矿区地质图(据参考文献[26]修改)Figure 1. Geological map of the Changjiang Uranium ore district and Changpai area长排矿区位于长江铀矿田中部,其北接棉花坑铀矿床,受油洞断裂控制(图 1)。区内出露的侵入岩体主要为油洞岩体和长江岩体,其次为中基性岩脉等。油洞岩体形成于印支期,岩性主要为中粒小斑状二云母花岗岩。长江岩体形成于燕山期,呈岩基状产出,岩性主要为中粒黑云母花岗岩,局部出露细粒不等粒黑云母花岗岩,与毗邻油洞岩体呈侵入接触。长排矿区铀矿化严格受断裂控制,矿体产于NW向油洞断裂及NNW向断裂中。矿区硅化、赤铁矿化、黄铁矿化、紫黑色萤石化等蚀变与矿化关系密切,且具有水平分带特征,即由构造带中心向外侧依次为硅化→赤铁矿化→绢云母化→粘土化。矿石矿物主要为沥青铀矿,多呈脉状、浸染状构造。根据矿物组合可将长排矿区矿化期次划分为成矿前期、成矿期和成矿后期。其中,成矿前期以形成白色石英脉为主要特点;成矿期主要形成灰色微晶石英沥青铀矿、红色微晶石英沥青铀矿、萤石、黄铁矿等;成矿后期主要为白色石英及少量萤石。
2. 样品采集及分析方法
2.1 样品特征
进行流体包裹体测温的10件样品分别采自长排矿区7号(ZK304- 3)、61号(ZK41- 1)和9号(ZK11-2,ZK223-1,ZK4-3)富矿带中,其中成矿期样品来自钻孔ZK11-2,ZK4-3,ZK41-1,是发育于蚀变花岗岩中的灰色-红色石英脉、紫黑色萤石脉;成矿后期样品来自钻孔ZK11- 2,ZK304- 3,ZK223-1,主要为淡绿(紫)色和白色方解石脉。硫同位素样品均采于长排矿区9号带南段的钻孔ZK11-2中。样品为产于不同深度含矿花岗岩中的成矿期黄铁矿,多为细粒结构、团块状构造。
2.2 流体包裹体显微测温和激光拉曼分析
流体包裹体显微测温工作在中国地质大学(北京)地球化学教研室流体包裹体实验室完成。测试仪器为LINK THMSGS 600型冷热台,显微测温采用标准物质(KNO3、K2CrO3、CCl4)及人工配制的NaCl标准溶液对仪器进行温度标定,测定温度范围为-196~600℃,测试环境始终保持在25℃左右。包裹体测定时选用的显微镜倍数为500倍,首先利用液氮对包裹体进行降温,并观察包裹体的变化,包裹体被冷冻后,缓慢升温,当接近相变点时,减慢升温速率至0.1℃/min,记录冰点温度;继续升温,观察相态变化,当接近相变点时,减慢升温速率至0.5℃/ min或1℃/min,记录笼形物消失温度、部分均一温度和完全均一温度。均一温度误差为1℃,冰点温度误差为0.1℃。NaCl-H2O体系盐度根据NaClH2O型流体包裹体在冰点与盐度关系表中查得[27],密度值根据经验公式计算求得[28]。
流体包裹体激光拉曼分析在核工业北京地质研究院分析测试所实验室进行,测试仪器为LABHR-VISLabRAM HR800型显微激光拉曼光谱仪,扫描范围为100~4200cm-1,波长为532nm,湿度为50%,测试环境为25℃。
2.3 硫同位素分析
硫同位素分析在核工业北京地质研究院分析测试中心完成。以Cu2O做氧化剂制备测试样品,仪器型号为Finnigan MAT-251型质谱仪,分析结果采用国际标准CDT表达,分析精度优于0.2‰。
3. 分析结果
3.1 流体包裹体岩相学特征
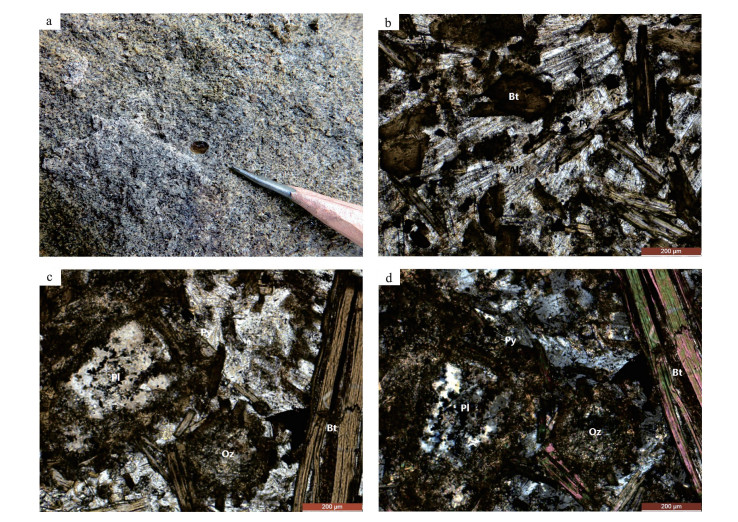
本次重点对成矿期和成矿后期的石英、萤石及方解石中的流体包裹体进行了岩相学观察和显微测温实验。根据室温下流体包裹体岩相学特征,可将原生包裹体分为2种类型:含CO2三相包裹体(Ⅰ型:VCO2 + LCO2 +LH2O)和气液两相包裹体(Ⅱ型:V+L)(图 2)。
Ⅰ型:含CO2三相包裹体(VCO2 + LCO2 +LH2O),室温下(25℃)可见到液相CO2围绕气泡呈环状分布,此类包裹体气相组分占15%~85%,主要形态为椭圆状、长条状,少数为不规则状,长轴为4~12μm,主要赋存在成矿期石英中,加热多数均一到气相。
Ⅱ型:气液两相包裹体(V+L),此类包裹体最发育,与其他类型包裹体共存。根据包裹体气液比,又可分为2个亚类型:Ⅱ-1型和Ⅱ-2型。Ⅱ-1型包裹体为富液相流体包裹体,气相组分占3%~30%,多为5%~15%,形态主要有椭圆形、长条形和不规则形,长轴为3~18μm,成群分布,均一化过程中多均一为液相。Ⅱ-2型包裹体为富气相流体包裹体,气相组分占50%~90%,形态多为椭圆形和多边形,长轴为3~10μm,呈孤立分布,均一化过程中多均一为气相。镜下观察显示,Ⅱ-1型包裹体比Ⅱ-2型包裹体更发育。
成矿后期包裹体主要以富液相流体包裹体(Ⅱ-1型)为主,气相组分占3%~30%,多为5%~10%,形态主要有椭圆形、近四边形和不规则形,长轴为4~19μm,个别可达40~50μm,属原生包裹体,在均一化过程中均一为液相。
3.2 流体包裹体显微测温和激光拉曼分析结果
在流体包裹体岩相学特征的基础上,对各类型流体包裹体进行显微测温工作。实验结果(表 1;图 3、图 4)显示,成矿期流体包裹体均一温度和盐度变化范围较大,分别为120~388℃和1.74% ~10.24% NaCleqv。其中,Ⅰ型流体包裹体初熔温度范围为-61.9~-58.9℃,其笼形物消失温度为5.5~8.2℃,部分均一温度为19.7~29.4℃,完全均一温度范围为291~388℃,盐度为3.52%~7.87% NaCleqv;Ⅱ-1型包裹体均一温度范围为113~356℃,主要集中在120~280℃范围,盐度为1.74% ~10.24% NaCleqv;Ⅱ-2型包裹体均一温度范围为222~378℃,盐度为3.23%~7.02% NaCleqv。成矿后期的原生Ⅱ-1型富液相流体包裹体均一温度范围为80~179℃,主要集中在120~170℃,盐度为0.35%~6.3% NaCleqv。
表 1 长排矿区流体包裹体显微测温结果Table 1. The temperature determination of fluid inclusions at Changpai成矿期次 包裹体类型 测试
数目CO2包裹体 均一温度/℃ 冰点/℃ 盐度/%NaCleqv 初溶温度/℃ 笼形物消失温度/℃ 部分均一温度/℃ 范围 平均 范围 平均 成矿期 I 17 -61.9~-58.9 5.5~8.2 19.7~29.4 291~388 338 - 3.52~7.87 5.40 Ⅱ-1 149 - - - 113~356 199 -6.8~-1 1.74~10.24 5.52 Ⅱ-2 12 - - - 222~378 314 -4.4~-1.9 3.23~7.02 4.63 成矿后期 Ⅱ-1 56 - - - 80~179 134 -3.9~-0.2 0.35~6.3 3.8 本文对成矿期流体包裹体的气相组分进行了激光拉曼分析。分析结果显示(图 5),成矿期Ⅱ-1型富液相两相水溶液包裹体气相组分主要为CO2、CH4和H2,Ⅱ-2型富气相两相水溶液包裹体气相组分主要为CO2。
3.3 硫同位素组成
本次共测定了成矿期4件黄铁矿的硫同位素组成(表 2),4件样品均采于长排矿区9号带南段的钻孔ZK11-2中。结果显示,黄铁矿的硫同位素组成变化范围不大,δ34S值在-10.2‰~-3.2‰之间。
表 2 长排矿区黄铁矿硫同位素组成Table 2. S isotopic compositions of the pyrite from the Changpai area序号 样号 矿物 δ34s/‰ 岩石名称 1 GZN201-3 黄铁矿 -9.1 产于灰色微晶石英脉屮 2 GZN201-1 黄铁矿 -3.2 产于灰色微晶石英脉屮 3 GZN201-11 黄铁矿 -9.7 产于猪肝色赤铁矿化蚀变花岗岩屮 4 ZK11-2-2 黄铁矿 -10.7 产于肉红色微晶硅质脉屮 4. 讨论
4.1 成矿流体性质
根据包裹体显微测温结果(表 1;图 3),可将长排矿区成矿期流体包裹体划分为2组。第1组为含CO2三相(Ⅰ型)和富气相包裹体(Ⅱ-2型),均一温度主要集中在300~400℃,盐度为3.2% ~7.9% NaCleqv。第2组主要为富液相包裹体(Ⅱ-1型),均一温度范围主要集中在140~260℃,盐度为1.74%~ 10.24% NaCleqv。由此可知,根据流体包裹体岩相学特征和显微测温结果,长排矿区的成矿期流体可分为2组,第1组具有中高温、中高盐度的特点,以含CO2三相和富气相包裹体为主,表现出岩浆水的特征,而第2组为中低温、中高盐度流体,以富液相流体包裹体为主,表现出大气水的特征。激光拉曼分析结果显示(图 5),长排矿区成矿流体含有CO2、CH4、H2等气相成分。其中,第1组包裹体中的Ⅱ-2型包裹体气相组分主要为CO2;第2组包裹体中的Ⅱ-1型包裹体气相组分主要为CO2、CH4和H2。此外,测温实验结果显示(表 1),第1组包裹体中的Ⅰ型流体包裹体初熔温度范围为-61.9~-58.9℃,低于其三相点温度-56.6℃,说明流体包裹体中应该存在CH4等气体。关于CO2气体的来源问题,华南花岗岩型铀矿床成矿流体中的CO2属地幔来源,是白垩纪—新近纪地壳拉张期间,由地幔去气作用或幔源基性岩浆侵入提供而不是来自于产铀花岗岩体[10]。综上所述,长排矿区的成矿流体可能主要为岩浆水和大气水,以含有CO2、CH4、H2等气相成分为特征。
本次研究对与成矿有关的石英和萤石进行了流体包裹体测温,所测温度代表了成矿期流体的温度范围。这一温度范围(120~400℃)与铀氧化物溶解的最大温度区间[29-31]基本一致。由上文可知,长排矿区成矿流体分为中高温(300~400℃)和中低温(140~260℃)2组。然而,中高温流体温度范围明显高于华南地区花岗岩型铀矿床的铀成矿温度范围(120~260℃)[32],但是与角砾状沥青铀矿成矿流体的温度范围基本一致(290~345℃)[31]。由此,考虑到长排矿区绝大部分成矿期流体包裹体均一温度范围(140~294℃;图 3)与华南地区花岗岩型铀矿床的铀成矿温度范围(120~260℃)[32]一致,以及华南地区铀矿床普遍发育角砾状沥青铀矿[31],笔者建议将长排矿区成矿流体划分为成矿期早阶段流体(300~ 400℃)和成矿期晚阶段流体(140~260℃)。其中,成矿期晚阶段流体最重要。这种成矿流体具有中高温和中低温2种情况的现象在华南地区其他矿床也有报道,如棉花坑矿床成矿流体划分为中高温(290~310℃)流体和中低温(140~270℃)流体,并指出这2种流体分别代表了早、晚2次成矿作用[31]。另外,根据粤北下庄铀矿田包裹体研究结果,指出该矿床成矿期存在2种不同来源流体[33],一种为高温(270~320℃)中等盐度岩浆流体;另一种为中低温(120~160℃)低盐度壳源流体。这一现象很可能说明长排矿区成矿期存在不同流体的混合。
4.2 成矿机制初探
根据成矿期黄铁矿的硫同位素分析结果(表 2)可知,δ34S值范围在-10.2‰~-3.2‰之间,含铀花岗岩的硫同位素范围[34],亦与华南地区其他铀矿床,如湖南340、380和广西376等铀矿床的硫同位素范围基本一致(δ34S=-9.36‰~-3.35‰)[35],反映了长排矿区硫化物的硫同位素组成受围岩制约的特点。强过铝质富铀花岗岩常被认为是华南地区重要的铀源岩[5, 12, 36-37],其形成与古元古代晚期—中元古代早期富铀基底部分熔融关系密切[5, 38-39]。最近研究显示,华南地区的富铀基底可能是在古元古代晚期之后(约2.2Ga)含铀矿物在浅海中沉积形成[12],而后期的构造-岩浆活动使这些古老沉积岩中的U在花岗岩中不断富集,进而导致花岗岩成为重要的铀源岩[34, 39-40]。长排矿区的铀矿化主要产于区内的长江岩体和油洞岩体中。元素地球化学特征和Sr-Nd同位素组成显示,长江岩体和油洞岩体的原岩分别为砂质岩和泥岩,是古元古代晚期基底(2.0~1.8Ga)部分熔融的产物[18-19],与南岭地区产铀花岗岩的特征[38, 41]基本一致。因此,结合成矿期黄铁矿硫同位素组成特征,本文认为长排矿区成矿流体中的U应主要来源于区内古老含铀地层部分熔融形成的花岗岩。
实验研究表明,U常与O结合成UO22+,进而和OH-、CO32-、SO42-、Cl-、F-等组成络合物在流体中运移[42]。长排矿区的铀矿化主要与硅化、赤铁矿化、黄铁矿化及紫黑色萤石化等蚀变密切相关,而且成矿流体具有中高盐度及富CO2、CH4、H2等气相成分的特点(图 4、图 5)。这说明,该区成矿流体中的U很可能与CO32-、F-、Cl-等结合成络合物进行运移和富集。在温度-盐度图解(图 4)中,第2组流体相对于第1组流体具有较低的均一温度及较大的盐度变化范围,说明成矿期晚期流体很可能发生了流体的混合作用。众所周知,降温、减压及流体的混合会导致U的CO32-、F-及Cl-络合物水解,进而使U发生沉淀[43]。因此,长排矿区U的沉淀很可能与流体温度的降低和流体的混合作用有关。此外,成矿后期流体包裹体均一温度和盐度明显低于成矿期流体(图 4),说明成矿物质卸载沉淀之后,流体温度继续降低,并形成淡(紫)绿色萤石、方解石等矿物。
大量证据表明,华南地区富铀花岗岩主要为印支期花岗岩,而且印支期花岗岩的成矿部位常见到燕山期岩浆作用的叠加[12, 37]。研究表明,华南地区燕山期大规模的铀矿化与华南和华北地块后碰撞及太平洋板块俯冲引起的岩石圈伸展有关[1]。岩石圈的伸展形成了大规模的断裂构造,不仅有利于花岗质岩浆的侵入和CO2等气体的上升[3],还为大气水的下渗提供了有利条件。长排矿区在印支期和燕山期发生了2期岩浆作用,分别形成了油洞岩体(232±4Ma)[18]和长江岩体(161.6±2.1Ma)[19],矿体即赋存于这些花岗岩岩体的断裂破碎带中。因此,结合区域地质背景可将长排矿区铀成矿作用机制初步概括为,①在印支期后碰撞和燕山期板块俯冲导致的伸展背景下,古元古代基底部分熔融形成岩浆,并沿深大断裂上侵,先后形成富铀的油洞岩体和长江岩体;②富含CO2、CH4、H2等的岩浆水与大气水可能沿油洞岩体和长江岩体内的断裂及裂隙淋滤出大量的U;③U以UO22+的形式与OH-、CO32-等组成络合物在成矿流体运移;④随着成矿流体温度的降低及流体混合作用的发生,U的络合物发生水解并沉淀,形成灰色微晶石英沥青铀矿、红色微晶石英沥青铀矿、萤石和黄铁矿等矿物。
5. 结论
(1)长排矿区成矿期流体包裹体可分为2组,气相成分主要为CO2、CH4和H2等。第1组均一温度主要在291~388℃之间,盐度为3.2%~7.9%NaCleqv,属Ⅰ型含CO2三相和Ⅱ-2型富气相包裹体。第2组均一温度为140~260℃,盐度为1.74% ~10.24% NaCleqv,属Ⅱ-1型富液相包裹体。
(2)长排矿区成矿流体中的U应主要来源于古老含铀地层部分熔融形成的富铀花岗岩。
(3)结合区域地质及地球化学特征可知,长排矿区铀成矿作用很可能形成于岩石圈伸展的背景下,温度的降低和流体的混合作用可能是导致U质沉淀的重要因素。
致谢: 在野外工作中得到项目组成员的大力支持,样品分析测试得到河北区域地质矿产研究所、中国地质科学院地质研究所及中国地质大学(武汉)地质过程与矿产资源国家重点实验室人员的帮助,在此表示衷心感谢。 -
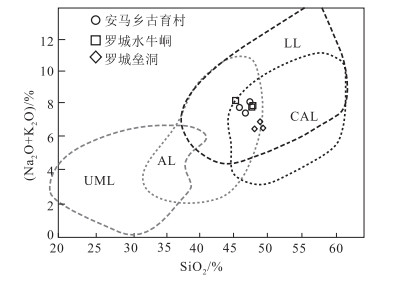
图 6 罗城地区SiO2-(Na2O+K2O)图解[16]
UML—超镁铁煌斑岩;LL—钾镁煌斑岩;CAL—钙碱性煌斑岩;AL—碱性煌斑岩
Figure 6. SiO2-(Na2O+K2O) diagram of Luocheng area
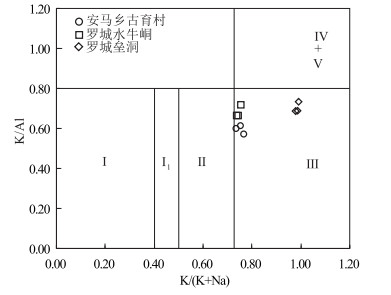
图 7 罗城地区K/(K+Na)-K/Al图解[17]
Ⅰ—钠质煌斑岩;Ⅰ1—弱钾质煌斑岩;Ⅱ—钾质煌斑岩;Ⅲ—超钾质煌斑岩;Ⅳ—过钾质煌斑岩;Ⅴ—钾镁煌斑岩
Figure 7. K/(K+Na)-K/Al diagram of Luocheng area
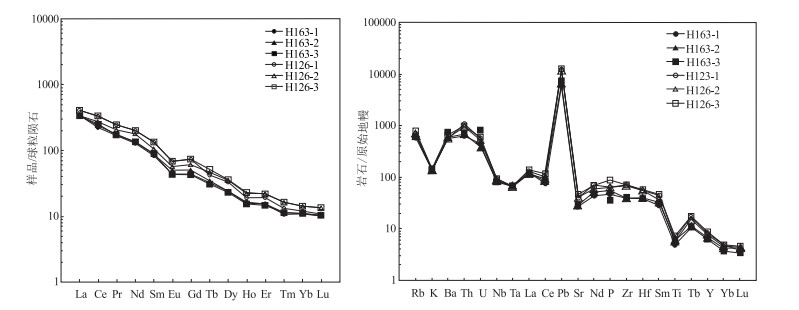
图 8 罗城地区云煌岩稀土元素球粒陨石标准化配分模式图(a)和不相容元素原始地幔标准化蛛网图
(球粒陨石标准化值和原始地幔标准化值据参考文献[18])
Figure 8. Chondrite-normalized REE patterns(a)and incompatible elements mantle-normalized trace element spider diagrams(b)of the minette from Luocheng, northern Guangxi
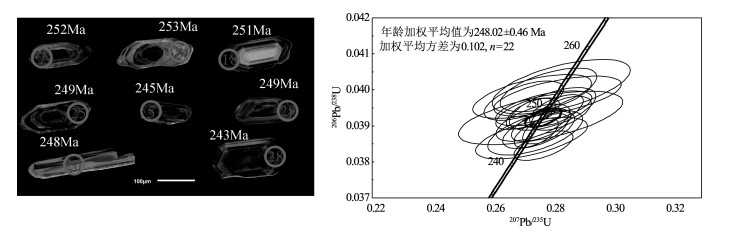
表 1 桂北罗城地区水牛峒云煌岩D127锆石U-Th-Pb分析结果
Table 1 U-Th-Pb data for zircons from minette D127 of Shuiniudong in Luocheng area, northern Guangxi
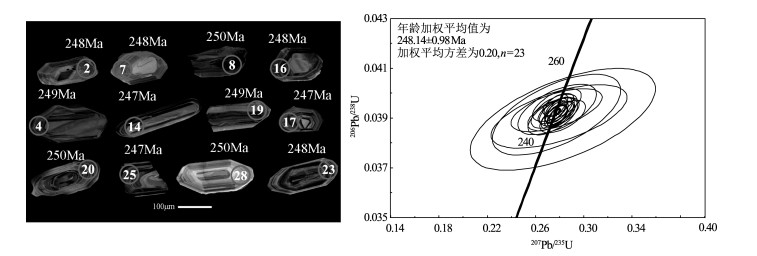
测试点 Th/10-6 U/10-6 Th/U 普通铅(207法)校对后同位素比值 普通铅(207法)校对后表生年龄/Ma 207Pb/206Pb 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ 207Pb/206Pb 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ D127-1 63 376 0.17 0.0552 0.0108 0.2958 0.0570 0.0388 0.0014 422 347 263 45 246 9 D127-2 118 208 0.57 0.0518 0.0020 0.3029 0.0115 0.0424 0.0004 278 91 269 9 268 2 D127-3 172 524 0.33 0.0514 0.0013 0.2764 0.0065 0.0390 0.0003 258 40 248 5 247 2 D127-4 80 444 0.18 0.0599 0.0035 0.4267 0.0239 0.0517 0.0008 600 95 361 17 325 5 D127-5 95 416 0.23 0.0513 0.0020 0.2745 0.0105 0.0388 0.0004 254 68 246 8 245 3 D127-6 148 188 0.79 0.0698 0.0011 1.4047 0.0194 0.1460 0.0010 923 17 891 8 878 6 D127-7 70 302 0.23 0.0514 0.0026 0.2819 0.0141 0.0398 0.0004 257 98 252 11 252 2 D127-8 72 198 0.37 0.0506 0.0020 0.2789 0.0107 0.0400 0.0004 222 70 250 8 253 2 D127-9 122 279 0.44 0.0509 0.0020 0.2773 0.0106 0.0395 0.0003 238 74 248 8 250 2 D127-10 161 456 0.35 0.0515 0.0018 0.2803 0.0096 0.0395 0.0004 264 60 251 8 250 2 D127-11 70 214 0.33 0.0497 0.0106 0.3113 0.0658 0.0455 0.0017 180 334 275 51 287 11 D127-12 78 336 0.23 0.0514 0.0016 0.2756 0.0079 0.0389 0.0003 259 50 247 6 246 2 D127-13 93 328 0.28 0.0518 0.0012 0.2815 0.0059 0.0394 0.0003 277 35 252 5 249 2 D127-14 72 344 0.21 0.0523 0.0027 0.3407 0.0174 0.0472 0.0006 300 95 298 13 297 3 D127-15 74 166 0.45 0.0506 0.0081 0.2853 0.0454 0.0409 0.0010 220 290 255 36 259 6 D127-16 80 254 0.32 0.0508 0.0016 0.2738 0.0082 0.0391 0.0003 232 53 246 7 247 2 D127-17 239 351 0.68 0.0501 0.0014 0.2719 0.0070 0.0393 0.0003 201 46 244 6 249 2 D127-18 84 239 0.35 0.0495 0.0017 0.2706 0.0088 0.0397 0.0004 169 59 243 7 251 2 D127-19 173 506 0.34 0.0518 0.0010 0.2778 0.0050 0.0389 0.0003 276 28 249 4 246 2 D127-20 85 203 0.42 0.0511 0.0034 0.2762 0.0181 0.0392 0.0005 245 127 248 14 248 3 D127-21 80.3 174 0.46 0.0512 0.0028 0.2831 0.0152 0.0401 0.0005 251 101 253 12 253 3 D127-22 69 891 0.08 0.0651 0.0007 1.1222 0.0096 0.1251 0.0008 776 23 764 5 760 4 D127-23 103 279 0.37 0.0498 0.0025 0.2735 0.0131 0.0398 0.0004 187 93 245 10 252 2 D127-24 397 390 1.02 0.0513 0.0024 0.2733 0.0123 0.0387 0.0004 253 86 245 10 245 2 D127-25 64 374 0.17 0.0503 0.0011 0.2730 0.0054 0.0393 0.0003 211 33 245 4 249 2 D127-26 63 823 0.08 0.0640 0.0023 0.6937 0.0240 0.0786 0.0009 741 78 535 14 488 5 D127-27 98 161 0.57 0.1625 0.0026 9.7355 0.1402 0.4346 0.0043 2482 12 2410 13 2326 20 D127-28 48 541 0.09 0.0523 0.0013 0.2772 0.0065 0.0385 0.0003 298 41 248 5 243 2 D127-29 89 342 0.26 0.0522 0.0013 0.2832 0.0066 0.0394 0.0003 294 39 253 5 249 2 D127-30 144 447 0.32 0.0514 0.0010 0.2748 0.0049 0.0388 0.0003 257 28 247 4 245 2 表 2 桂北罗城地区上呇云煌岩D130锆石U-Th-Pb分析结果
Table 2 U-Th-Pb data for zircons from minette D130 ofShuiqi in Luocheng area, northern Guangxi
测试点 Th
/10-6U
/10-6Th/U 普通铅(207法)校对后同位素比值 普通铅(207法)校对后表生年龄/Ma 207Pb/206Pb 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ 207Pb/206Pb 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ D130-01 92 347 0.26 0.0506 0.0015 0.2734 0.0074 0.0392 0.0003 221 49 245 6 248 2 D130-02 135 265 0.51 0.0509 0.0027 0.2749 0.0141 0.0392 0.0004 238 98 247 11 248 3 D130-03 92 481 0.19 0.0683 0.0009 1.2631 0.0118 0.1343 0.0008 876 10 829 5 812 5 D130-04 131 398 0.33 0.0519 0.0016 0.2800 0.0083 0.0392 0.0004 281 51 251 7 248 2 D130-05 79 335 0.24 0.0521 0.0013 0.2815 0.0065 0.0392 0.0003 291 39 252 5 248 2 D130-06 80 367 0.22 0.0580 0.0055 0.4343 0.0404 0.0543 0.0012 531 166 366 29 341 8 D130-07 74 267 0.28 0.0510 0.0025 0.2777 0.0133 0.0395 0.0004 240 91 249 11 250 3 D130-08 123 387 0.32 0.0513 0.0019 0.2777 0.0096 0.0393 0.0004 255 61 249 8 248 2 D130-09 84 294 0.29 0.0583 0.0024 0.3120 0.0123 0.0389 0.0003 539 74 276 10 246 2 D130-10 76 428 0.18 0.0503 0.0124 0.4311 0.1055 0.0621 0.0025 211 385 364 75 389 15 D130-11 66 265 0.25 0.0539 0.0059 0.4851 0.0528 0.0653 0.0011 367 216 402 36 408 7 D130-12 338 373 0.91 0.0530 0.0021 0.4414 0.0170 0.0605 0.0007 327 68 371 12 378 4 D130-13 74 447 0.17 0.0513 0.0014 0.2757 0.0073 0.0390 0.0003 252 46 247 6 247 2 D130-14 139 253 0.55 0.0512 0.0047 0.2774 0.0250 0.0393 0.0006 249 177 249 20 249 4 D130-15 314 312 1.01 0.0512 0.0041 0.2780 0.0216 0.0394 0.0007 252 145 249 17 249 4 D130-16 80 429 0.19 0.0516 0.0011 0.2781 0.0056 0.0391 0.0003 268 33 249 4 247 2 D130-17 95 394 0.24 0.0513 0.0011 0.2782 0.0054 0.0394 0.0003 253 31 249 4 249 2 D130-18 107 569 0.19 0.0514 0.0015 0.2788 0.0076 0.0393 0.0003 259 47 250 6 249 2 D130-19 54 473 0.11 0.0516 0.0011 0.2781 0.0053 0.0391 0.0003 270 30 249 4 247 2 D130-20 89 250 0.36 0.0508 0.0013 0.2769 0.0065 0.0395 0.0003 234 40 248 5 250 2 D130-21 55 435 0.13 0.0509 0.0026 0.2743 0.0135 0.0391 0.0005 238 91 246 11 247 3 D130-22 57 181 0.31 0.0526 0.0096 0.2825 0.0507 0.0390 0.0014 312 319 253 40 246 8 D130-23 75 410 0.18 0.0514 0.0012 0.2770 0.0061 0.0391 0.0003 258 36 248 5 247 2 D130-24 38 160 0.23 0.0519 0.0070 0.2795 0.0372 0.0391 0.0008 281 257 250 29 247 5 D130-25 60 506 0.12 0.0511 0.0016 0.2787 0.0085 0.0396 0.0003 247 57 250 7 250 2 D130-26 78 300 0.26 0.0513 0.0013 0.2774 0.0064 0.0392 0.0003 254 39 249 5 248 2 D130-27 53 250 0.21 0.0525 0.0024 0.2825 0.0125 0.0391 0.0004 306 81 253 10 247 3 D130-28 70 193 0.36 0.0509 0.0024 0.2755 0.0126 0.0393 0.0005 236 85 247 10 248 3 D130-29 111 568 0.19 0.0514 0.0066 0.2774 0.0351 0.0391 0.0011 260 235 249 28 248 7 D130-30 81 392 0.21 0.0527 0.0066 0.3331 0.0409 0.0459 0.0011 314 231 292 31 289 7 表 3 桂北罗城地区云煌斑岩主量元素含量测试结果
Table 3 Analyses of major elements of lamproite from Luocheng area, northern Guangxi
% 样号 SiO2 Al2O3 CaO Fe2O3 FeO K2O MgO MnO Na2O P2O5 TiO2 CO2 H2O+ 烧失量 总计 H163-1 46.44 11.47 13.65 1.64 1.98 6.1 4.06 0.06 1.24 1.06 1.17 8.68 2.22 11.12 110.89 H163-2 45.5 11.14 13.44 2 2.05 6.35 3.97 0.07 1.36 1.24 1.16 9.51 1.54 10.98 110.31 H163-3 47.2 11.57 12.83 1.53 1.9 6.48 4.07 0.07 1.53 0.78 1.18 8.81 2.26 10.53 110.74 H126-1 44.98 9.87 10.6 3.11 3.63 6.59 7.2 0.11 1.44 1.42 1.34 7.41 1.9 8.54 108.14 H126-2 47.63 10.25 9.19 3.1 3.02 6.33 7.79 0.1 1.46 1.44 1.29 5.81 2.24 7.37 107.02 H126-3 47.45 10.18 8.94 3.24 2.96 6.28 7.65 0.1 1.47 1.95 1.28 5.59 2.37 7.28 106.74 表 4 桂北罗城地区云煌岩微量元素含量测试结果
Table 4 Analyses of trace elements of minette from Luocheng area, northern Guangxi
10-6 样号 Li Be Cr Mn Co Ni Cu Zn Ga Rb Sr Mo Cd In Cs Sc Ba Tl Pb Bi Th U Nb Ta Zr Hf Sn Sb Ti W As V La Ce Pr Nd Sm Eu Gd Tb Dy Ho Er Tm Yb Lu Y H163-1 27.7 3.25 592 506 25.7 210 56.1 128 16.2 392 611 0.6 0.11 0.06 7.27 16.2 4368 2.46 33.4 1.41 59.2 9.64 59.1 2.68 444 12.5 6.68 0.99 6436 5.71 2.81 127 81.6 138 16 60.7 12.9 2.58 9.78 1.22 5.97 0.92 2.5 0.28 1.88 0.26 28.9 H163-2 26.2 3.62 707 591 51 267 66.3 223 17.8 400 613 0.59 0.08 < 0.05 7.24 18 3891 2.37 39.4 1.3 58.6 7.93 61.1 2.66 456 12.5 6.69 0.98 7387 5.48 2.44 147 80.6 144 16.5 65 14 3.03 10.2 1.26 6.49 0.94 2.59 0.29 1.9 0.26 31.3 H163-3 29.3 4.58 605 525 39 193 54.7 67.1 15.6 387 629 0.83 0.1 0.06 7.54 18.3 5259 2.57 60 1.31 61.7 17.4 59 2.62 459 11.9 6.65 0.9 7170 4.55 3.21 131 82.7 151 16.9 64.6 14.6 2.52 9 1.16 5.93 0.87 2.42 0.29 1.91 0.26 29 H126-1 33.7 9.89 742 914 41.7 274 61.2 80.6 14.4 412 837 1.03 0.06 0.06 23.2 19.8 4820 3.2 95.3 0.92 87.7 12.6 63.3 2.73 714 17.7 8.08 0.77 8596 3.14 1.94 144 100 203 23.3 90.8 19.4 3.72 13.2 1.63 8.07 1.11 3.07 0.33 2.05 0.28 33.5 H126-2 33.5 8.67 711 830 43.5 275 65.1 86.7 17.6 460 855 2.19 0.1 0.08 15.9 17.4 4127 3.93 94.8 1.01 82.4 11.7 64.5 2.76 749 17.8 7.73 0.85 7726 3.7 1.9 129 82.6 170 19.7 82 16.9 3.41 13.1 1.69 8.48 1.23 3.37 0.39 2.35 0.34 36.7 H126-3 40.3 11.6 843 1028 48.8 313 84.2 113 20.2 505 980 3.49 0.08 0.07 17.9 22 4646 3.97 99.7 1.12 84.2 12.5 66.9 2.75 812 18 8.78 1.08 9435 3.14 2.8 160 96.9 206 23.8 92.6 20.5 3.91 15.1 1.91 9.07 1.29 3.62 0.41 2.39 0.34 40 -
贾大成, 胡瑞忠, 卢焱, 等.湘东北蕉溪岭富钠煌斑岩地球化学特征[J].岩石学报, 2002, 18(4):459-46. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200204003 Mitchell R H.Aspects of petrology of kimberlites and lamproites: some definitions and disanctions, kimberlites and related rocks[J]. Geol.Soc., 1989, (1): 7-45.
叶德隆.云煌岩的鉴别标准和分类命名[J].地质科技情报, 1993, (01): 39-46. 张安棣.金刚石找矿指示矿物研究及数据库[M].北京:北京科学技术出版社, 1991. Taylor H P, Hart S R.Oxygen isotope geochemistry of the potassic igneous rocks from the Roccamonfina Volcano.Roman Comagmatic region, Italy[J]. Earth Planet.Sc.Lett., 1979, 46: 81-106. doi: 10.1016-0012-821X(79)90067-0/
Ferrara G, Preite-Martinaz M, Taylor H P, et al.Evidence for crustal contamination, mixing of magma, and a 87Sr-rich upper mantle-an oxygen and stontium isotope study of the M.Vulsini volcanic area, central Italy[J]. Contrib.Min, Petrol., 1986, 92: 269-280.
Beccaluva L, Di Girolamo P, Serri G.Petrogenesis and tectonic setting of the Roman Volcanic Province Italy[J]. Lithos, 1991, 26: 191-221. doi: 10.1016-0024-4937(91)90029-K/
王新宇, 彭松柏, 吴祥珂, 等.桂北地区云煌岩的发现及找矿意义[J].地质科技情报, 2013, (03): 93. 广西壮族自治区地质矿产勘查开发局.广西壮族自治区区域地质志[M].北京:地质出版社, 1985. Liu Y S, Hu Z C, Gao S, et al.In situ analysis of major and trace elements of anhydrous minerals by LA-ICP-MS without applying an internal standard[J]. Chemical Geology, 2008, 257: 34-43. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=babd721ac13e2675d9485b52683be64c
Liu Y S, Gao S, Hu Z C, et al.Continental and oceanic crust recycling-induced melt-peridotite interactions in the Trans-North China Orogen:U-Pb dating, Hf isotopes and trace elements in zircons of mantle xenliths[J]. Journal of Petrology, 2010, 51: 537-571.
Liu Y S, Gao S, Hu Z C, et al.Reappraisement and refinement of zircon U-Pb isotope and trace element analyses by LA-ICP-MS[J]. Chinese Sience Bulletin, 2010, 55:1535-1546. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kxtb-e201015011
Anderson T.Correction of common lead in U-Pb analyses that do not report204Pb[J]. Chemical Geology, 2002, 192:59-79.
Ludwig K.User's manual for isoplot/EX version 3.00: a geochronological toolkit for Microsoft Excel[J]. Berkeley Geochronology Center, Special Publication, 2003, 4: 1-70.
吴元保, 郑永飞.锆石成因矿物学研究及其对U-Pb年龄解释的制约[J].科学通报, 2004, (16): 1589-1604. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/kxtb200416002 Rock N M S.The nature and origin of lamprophyres: an overview[C]//Fitton J G, Upton B G J.Alkalinc Ingeoas Rocks.Geological Society Special Publication, 1987, (30): 191-226.
路凤香, 舒小辛, 赵崇贺.有关煌斑岩分类的建议[J].地质科技情报, 1991, (S1): 55-62. Sun S, Mcdonough W F.Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: implications for mantle composition and processes[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 1989, 42(1): 313-345. doi: 10.1144-GSL.SP.1989.042.01.19/
王磊, 金鑫镖, 王新宇, 等.桂北罗城垒洞煌斑岩形成过程:地球化学、年代学和Sr-Nd-Pb同位素约束[J].地质科技情报, 2015, 34(1):10-19. Ma C Q, Li Z C, Ehlers C, et al.A post-collisonal magnatic plumbing system: Mesozoic granotoid plutons from the Dabieshan high-pressure and ultrahigh-pressure metamorphic zone, east-central China[J]. Lithos, 1998, 45: 431-456.
Tamey J, Jones C E.Trace element geochemistry of orogenicigneous rocks and crustal growth models[J]. Journal of the Geological Society, 1994, 151: 855-868.
Menzies M A.Mantle ultramafic xenoliths in alkaline magmas: Evidence for mantle heterogeneity modified by magmatic activity[C]// Hawkesworth C J, Norry M J.Continental Basalts and Mantle Xenoliths.London: Shiva, 1983: 92-110.
孙景贵, 胡受奚, 凌洪飞, 等.胶西北两类金矿田的高钾-钾质脉岩元素地球化学与成岩作用研究[J].地球化学, 2002, 29(2):143-152. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqhx200002006 Taylor S R, Mclenann S M.The Comtomemtal Crust: Its Composition and Evolution[M]. Oxford: Blackwell, 1985.
Varne R.Ancient stubcontinental mantle:A source for K-rich orogeneic volcanic[J]. Geology, 1985, 13(6):405-408.
Rogers N W, Hawkesworth C J, Mattey D P, et al.Sediment subduction and the source of potassium in orogenic leucities[J]. Geology, 1987, 15(5):451-453.
柴凤梅, 帕拉提·阿布都卡迪尔, 张招崇, 等.塔里木板块西南缘钾质煌斑岩地球化学及源区特征[J].地质论评, 2007, (1): 11-21. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzlp200701003 Hofmann A W, Jochum K P, Seufert M, et al.Nb and Pb in oceanic basalts: New constraints on mantle evolution[J]. Earth and planetary Science Letters, 1986, 79(1/2): 33-45. doi: 10.1016-0012-821X(86)90038-5/
Plank T, Langmuir C H.The chemical composition of subducting sediment and its consequences for the crust and mantle[J]. Chemical Geology, 1998, 145(3/4): 325-394. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=c615b55cf7335665a5aef7d3270dbf1d
Rock N M S.Lamprophyres[M]. Glasgow: Blacki, 1990.
刘畅, 赵泽辉, 郭召杰.甘肃北山地区煌斑岩的年代学和地球化学及其壳幔作用过程讨论[J].岩石学报, 2006, (5): 1294-1306. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200605019 Mcdonough W F, Sun S.The composition of the Earth[J]. Chemical Geology, 1995, 120: 223-253. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/OAPaper/oai_doaj-articles_fb4dd133285d7a6db94ef688ee319429
Dupuy C, Liotard J M, Dostal J.Zr/Hf fractionation in intraplate basaltic rocks:Carbonate metasomatism in the mantle source[J]. Geochemistry et Cosmochimica Acta, 1992, 56(6):2417-2423.
Rudnick R L, McDonough W F, Chapell B W.Carbonatine metasomatism in the northern Tanzanian mantle:Petrographic and geochemical characteristics[J]. Earth and Planetary Sience Letter, 1993, 114(4):463-475.
Furman T, Graham D.Erosion of lithospheric mantle beneath the East African Rift system:Geochemical evidence from Kivn volcanic province[J]. Lithos, 1999, 48(1/4):237-262.
邱检生, 徐夕生, 蒋少涌.地壳深俯冲与富钾火山岩成因[J].地学前缘, 2003, (3): 191-200. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dxqy200303018 毛景文, 谢桂青, 郭春丽, 等.华南地区中生代主要金属矿床时空分布规律和成矿环境[J].高校地质学报, 2008, (4): 510-526. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gxdzxb200804005 Ding X, Chen P, Chen W, et al.Single zircon LA-ICPMS U-Pb dating of Weishan granite (Hunan, South China) and its petrogenetic significance[J]. Science in China Series D-Earth Sciences, 2006, 49(8): 816-827.
Li X, Li Z, Li W, et al.U-Pb zircon, geochemical and Sr-Nd-Hf isotopic constraints on age and origin of Jurassic I- and A-type granites from central Guangdong, SE China: A major igneous event in response to foundering of a subducted flat-slab?[J]. Lithos, 2007, 96(1/2): 186-204.
Li X H, Chen Z, Liu D Y, et al.Jurassic gabbro-granite-syenite suites from Southern Jiangxi province, SE China: Age, origin, and tectonic significance[J]. International Geology Review, 2003, 45(10): 898-921. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/NSTL_QKJJ029597509/
Zhou X M, Sun T, Shen W Z, et al.Petrogenesis of Mesozoic granitoids and volcanic rocks in South China: A response to tectonic evolution[J]. Episodes, 2006, 29(1): 26-33.
王强, 赵振华, 简平, 等.华南腹地白垩纪A型花岗岩类或碱性侵入岩年代学及其对华南晚中生代构造演化的制约[J].岩石学报, 2005, (3): 795-808. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200503019 谢桂青.中国东南部晚中生代以来的基性岩脉(体)的地质地球化学特征及其地球动力学意义初探: 以江西省为例[D].中国地球科学院地球化学研究所博士学位论文, 2003. 范蔚茗, 王岳军, 郭锋, 等.湘赣地区中生代镁铁质岩浆作用与岩石圈伸展[J].地学前缘, 2003, (3): 159-169. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dxqy200303015 蔡学林, 朱介寿, 曹家敏, 等.东亚西太平洋巨型裂谷体系岩石圈与软流圈结构及动力学[J].中国地质, 2002, 29(3):234-245. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgdizhi200203002




 下载:
下载: