LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb age, geochemistry and genesis of Neoproterozoic granitoids in the Biezhentao Mountain of Wenquan County, Xinjiang
-
摘要:
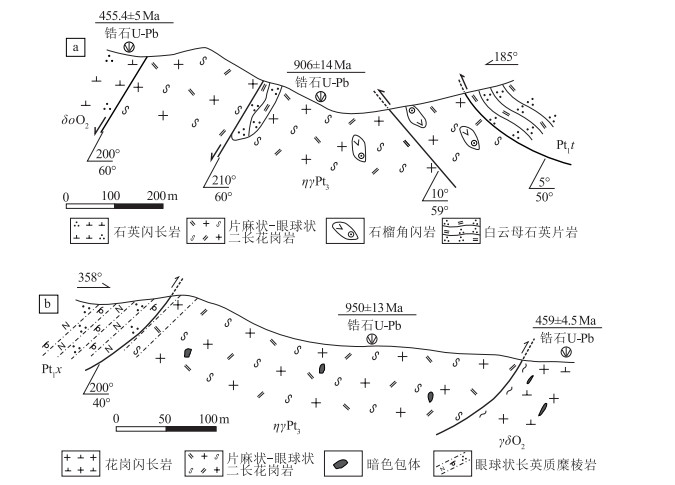
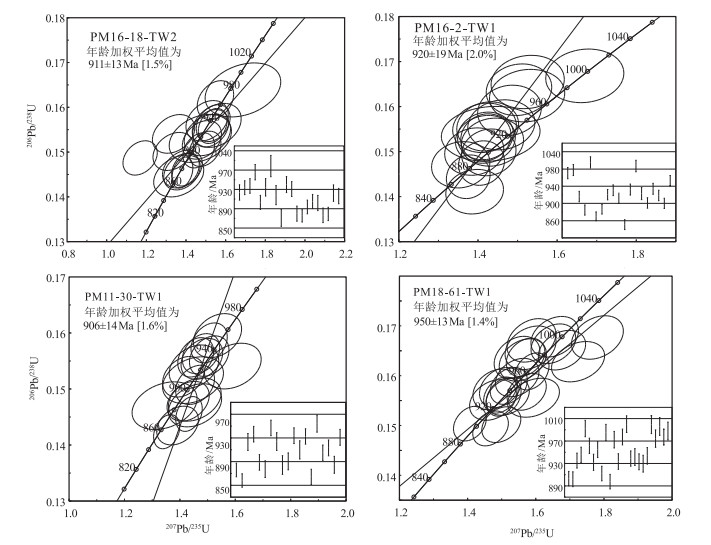
对新疆温泉县别珍套山新元古代花岗岩开展了相关研究。获得了3个片麻状-眼球状花岗岩4件锆石样品年龄,其中206Pb/238U年龄值一致,大多集中在910~950 Ma之间。极少量继承锆石的年龄大于1000 Ma。这些花岗岩以特有的粗粒、巨大的眼球状片麻结构为特征。岩体具有高硅(≥ 70%)、富碱(K2O+Na2O,6.5%~8.9%)且K2O>Na2O的特征,表现出从钙碱性到钾玄岩演化的变化趋势。稀土元素特征表明其与碱性花岗岩相似。样品的微量元素蛛网图几乎完全相同,均明显亏损Ba、Nb、Ta、Sr、P、Ti,富集Rb、Th、U、K等元素,显示活动大陆边缘岩石特征。全岩Sr-Nd同位素特征表明具典型壳源花岗岩(S型花岗岩)的特征。Lu-Hf同位素特征表明单阶段Hf模式年龄(tDM1)为883~1351 Ma,平均为1133 Ma;二阶段Hf模式年龄(tDM2)为891~1588 Ma,平均为1250 Ma,与锆石形成年龄较接近。新元古代早期(约9 Ga)片麻状花岗岩可能是与Rodinia超大陆会聚有关的格林维尔期造山作用、地壳增厚导致地壳物质部分熔融的产物。
Abstract:The Neoproterozoic granites of the Biezhentao Mountain in Wenquan County of Xinjang were studied in this paper.Four LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb ages of 910~950 Ma were obtained for granitic gneisses in the Biezhentao Mountain of Wenquan County of Xinjiang.These new zircon LA-ICP MS U-Pb ages, together with previously published data, indicate that the granites were emplaced during 910~950 Ma.A few inherited old zircons U-Pb ages of >1000 Ma were found in all dated samples; they may have derived from the source rocks. These granitoids are characterized by a very coarse grained and huge augen gneiss texture. Major element data indicate that they belong to peraluminous monzogranite, with SiO2 (≥ 70%), K2O+Na2O (6.5%~8.9%), and K2O > Na2O, thus defined as calc-alkaline to shoshonitic rocks. These rocks show nearly parallel REE patterns with different abundances and distinct negative Eu anomalies. All the granitoids display similar spider diagrams with obvious negative anomalies of Ba, Nb, Ta, Sr, P and Ti, and obvious enrichment of Rb, Th, U, K. Sr-Nd data suggest that the protoliths of Neoproterozoic granitoids belong to peraluminous S-type granites. Zircon εHf (t) values range from +1.7 to +5.7, with model ages (tDM1) of 883~1351 Ma and model ages (tDM2) of 891~1588 Ma. Furthermore, with the age information on the ancient terranes of Tarim basin, the authors hold that the Tianshan ancient block probably formed a part of Rodina supercontinent during Early Neoproterozoic period and these granitoid rocks were linked to lithospheric thickening.
-
Keywords:
- granite /
- zircon U-Pb age /
- geochemistry /
- Neoproterozoic /
- Wenquan County
-
北山地区花岗岩类岩石分布广泛,约占该区全部侵入岩的95%[1].虽然前人对本区的花岗岩类进行了大量的研究,积累了丰富的资料[2-19] ,但对北山同一时代花岗岩构造属性的认识却不相同,尤其是华力西期花岗岩,对其构造属性[20-21]和岩浆成因的认识存在分歧.对北山花岗岩地区构造属性、岩浆成因特点和与区域构造演化关系的认识影响了对区域动力学的进一步探讨.另外,花岗岩体的多集中在北山北带,而北山南带很少.目前仅有3 处石炭纪—二叠纪花岗岩的精确定年报道:桥湾北花岗岩303.7±2.4Ma[22]、音凹峡南花岗岩281.7±2.9Ma[23]、石板泉花岗岩280.5±5.5Ma[24].因此,对北山南带的花岗岩体形成时代、岩石成因的研究,对于研究其构造岩浆作用具有重要的意义.近年来,北山南带东段地区发现了一系列与花岗岩类侵入体密切相关的金属矿床,如白山堂铜矿[25]、玉山钨矿[26-28]等,对花岗岩类侵入体的认识在一定程度上制约了该地区的找矿勘探工作.基于此,本文针对北山南带东段梧桐沟马山花岗岩体,进行了详细的地球化学测试和锆石U-Pb 测年,对其形成时代和岩石成因进行约束,并结合区域资料,对其地球动力学意义进行探讨,以期为北山南带构造岩浆研究提供可靠的地质资料.
1. 区域地质背景
研究区梧桐沟—神螺山一带位于北山南带东段,内蒙古西南侧与甘肃省接壤位置.地质背景较复杂,左国朝等[3]、龚全胜等[29]、何世平等[30]认为其属于塔里木板块增生带北缘,并将其进一步划归为磁海-红柳园-白山堂晚古生代陆内裂谷带;刘雪亚等[31]、张新虎[32]、聂凤军等[1]认为其属于哈萨克斯坦板块的南缘.区内以晚古生代石炭纪—二叠纪火山-沉积地层为主,少量前震旦纪基底形成规模较小的推覆体,奥陶系浅变质碎屑岩发育;下石炭统红柳园组可分为上、下2 段,下段为正粒序的碎屑岩组合,底部为砾岩,向上变细,上段为火山熔岩及碎屑岩组合,熔岩包括安山岩和顶部的流纹岩,少量英安岩及流纹质熔结凝灰岩,局部为灰岩,上石炭统芨芨台子组为白云质灰岩;下二叠统双堡塘组为磨拉石组合,由砾岩、含砾砂岩、粗砂岩、杂砂岩组成正粒序层;双堡塘组与红柳园组为平行不整合接触或断层接触,与上覆中二叠统金塔组为整合接触,金塔组以大面积出露玄武岩、枕状玄武岩及少量安山岩、火山-沉积碎屑岩为主,上二叠统方山口组以凝灰质为主,夹少量沉凝灰岩,与金塔组无直接接触关系;差异性沉降地区为中新生界不整合覆盖.侵入岩以晚华力西期为主,主要岩石类型包括英云闪长岩、二长花岗岩、黑云母二长花岗岩、花岗闪长岩,多以岩株或小岩基产出,基性侵入岩十分发育,主要为辉长岩及辉绿岩,前者为小岩株,后者多为岩脉.
2. 岩体地质特征
马山小岩体位于北山南带东段梧桐沟一带(图 1-a),岩体外表似椭球状,长约2.7km, 宽约1km, 出露面积约2.67km2,中心坐标为北纬40°37′45″、东经98°35′30″.侵入下石炭统红柳园组砂岩中,后被下二叠统双堡塘组砾岩、含砾砂岩覆盖.前人粗略地将其归入到华力西中晚期岩浆侵入活动①.
① 甘肃省地质局第二区域地质测量队. 红柳大泉幅1∶200000 区域地质测量报告. 1971.
![]() 图 1 马山二长花岗岩体地质简图及大地构造位置图(b 据参考文献[30]修改)1—第四系;2—下二叠统双堡塘组;3—下石炭统红柳园组;4—二叠纪花岗岩;5—二叠纪辉长岩;6—不整合界线;7—锆石U-Pb 采样位置;8—国界;9—板块缝合带;10—早古生代缝合带;11—主干断裂;12—省界;13—隐伏断裂;14—构造单元.Ⅰ—西伯利亚板块;Ⅰ-1—大南湖-雀儿山-狐狸山早古生代活动带陆缘带;Ⅱ—塔里木板块;Ⅱ-1-1 —黄山-红石山-路井晚古生代陆内裂谷带;Ⅱ-1-2— 星星峡-明水-旱山地块;Ⅱ-1-3 —白玉山南-公婆泉-东七一山早古生代晚期活动带陆缘带;Ⅱ-2 —红柳河-洗肠井构造混杂岩带;Ⅱ-3-1 —方山口-营毛沱-鹰咀红山早古生代中期活动陆缘带;Ⅱ-3-2 —花牛山早古生代陆缘裂谷带(裂陷槽);Ⅱ-3-3— 磁海-红柳园-白山堂晚古生代陆内裂谷带;Ⅱ-3-4 —敦煌地块Figure 1. Simplified geological map and tectonic location map of Mashan granite
图 1 马山二长花岗岩体地质简图及大地构造位置图(b 据参考文献[30]修改)1—第四系;2—下二叠统双堡塘组;3—下石炭统红柳园组;4—二叠纪花岗岩;5—二叠纪辉长岩;6—不整合界线;7—锆石U-Pb 采样位置;8—国界;9—板块缝合带;10—早古生代缝合带;11—主干断裂;12—省界;13—隐伏断裂;14—构造单元.Ⅰ—西伯利亚板块;Ⅰ-1—大南湖-雀儿山-狐狸山早古生代活动带陆缘带;Ⅱ—塔里木板块;Ⅱ-1-1 —黄山-红石山-路井晚古生代陆内裂谷带;Ⅱ-1-2— 星星峡-明水-旱山地块;Ⅱ-1-3 —白玉山南-公婆泉-东七一山早古生代晚期活动带陆缘带;Ⅱ-2 —红柳河-洗肠井构造混杂岩带;Ⅱ-3-1 —方山口-营毛沱-鹰咀红山早古生代中期活动陆缘带;Ⅱ-3-2 —花牛山早古生代陆缘裂谷带(裂陷槽);Ⅱ-3-3— 磁海-红柳园-白山堂晚古生代陆内裂谷带;Ⅱ-3-4 —敦煌地块Figure 1. Simplified geological map and tectonic location map of Mashan granite该岩体由花岗闪长岩组成(图 2-a),其内部无明显结构分带和成分分带,为一次岩浆侵入活动的产物.岩石具有典型的花岗结构(图 2-b),矿物成分较简单,主要由斜长石、条纹长石和石英组成.长石0.4~3.8mm, 整体表面褐色粘土化显著,较石英脏,斜长石半自形-自形板状,双晶纹可见;石英呈他形粒状,表面干净透明,波状消光,粒径为0.3~2.7mm, 充填于其他矿物之间.
锆石U-Pb 年龄样品的采集位置为北纬40°37′46″、东经98°35′30″.
3. 分析方法
对采集的样品进行主量、稀土和微量元素及LA-ICP-MS 锆石U-Pb 年龄测定.在进行化学分析前,先在镜下观察薄片以确定样品的适应性.主量、微量元素由中国冶金地质总局西北地质勘查院测试中心测定,采用XRF 荧光光谱样分析方法,分析精度优于5%;微量和稀土元素采用ICP-MS 分析,利用国家一级标准物质进行质量监控(GB/T14506—1993),含量大于10×10-6的元素测试精度为5%,小于10×10-6的测试精度为10%.
用常规方法分选出锆石单矿物,然后在双目镜下根据锆石颜色、自形程度、形态、透明度等进行初步分类,挑选出具有代表性的锆石.将锆石样品用双面胶粘在载玻片上,放上PVC 杯,然后将环氧树脂和固化剂进行充分混合后注入PVC 杯中,待树脂充分固化后将其从载玻片上剥离,打磨和抛光至锆石中心部位暴露,然后拍摄透射光、反射光和阴极发光(CL)图像.最后用体积百分比为3%的HNO3清洗样品制成样品靶备用.
LA-ICP-MS 锆石U-Pb 同位素测定在西安地质矿产研究所实验测试中心完成.测定时根据可见光、CL 和BSE(背散射电子成像)图像选择合适的测点位置,如避免包裹体、裂隙位置等.详细的分析步骤和数据处理方法见参考文献[33-34],用Glit-ter(4.0 版)程序处理原始数据.普通铅扣除时,其组成由Stacey 等[35]的模式给出,年龄加权平均计算及U-Pb 谐和图的绘制采用Isoplot(3.0 版)[36]完成.
4. 锆石U-Pb 年龄
从样品中选取的锆石以浅黄色为主,个别颜色为浅玫瑰色和近于无色,玻璃-金刚光泽.按晶体形态可以分为2 类,一类呈自形双锥柱状,长60~160μm, 宽30~120μm, 长宽比多为2~3,透射光下可见锆石内部发育少量裂纹和包裹体,包裹体以长条形和椭圆形为主,多为小锆石包体,阴极发光图像显示,锆石具有典型的岩浆韵律环带和明暗相间的条带构造等,显示岩浆锆石的特征(图 3);另一类则有溶蚀现象,锆石长20~30μm, 宽100~120μm, 长宽比多为4~5.部分锆石具有残留的核部,为继承核或捕获核,部分锆石颗粒具有窄的浅色边,但核部仍显示出清晰的岩浆环带特征.测得的28 个颗粒的28 个数据中(表 1),21 个206Pb/238U 年龄(不包括1、4、10、12、14、20、28 点)介于270.7±6.0~294.0±8.0Ma 之间,给出的206Pb/238U 年龄加权平均值为281.8 ± 3.2Ma(MSWD=1.15,n=21,2σ)(图 4).U、Th 含量分别为155×10-6~1444×10-6和92×10-6~660×10-6.Th/U 值除2 个样品略低于0.4(0.39、0.31)外,其余的比值均介于0.42~0.99 之间,表现出典型岩浆锆石的特征.该年龄代表了岩体的结晶年龄.此外还获得了3 组年龄:①10、12、20 这3 个点的206Pb/238U 年龄分别为258.4±6.0Ma、258.2±7.6Ma、260.8±6.3Ma, 其年龄加权平均值为259.2±0.1Ma, 锆石具有较规则的外形,CL 图像较亮,具有弱分带特征,为热液变质锆石,可能代表一期热液蚀变活动;② 有2 个点获得了334.4Ma、369.9Ma 的年龄数据.这些锆石略磨圆,锆石环带特征不清楚,疑为继承性锆石;③1、28 这2 个点的年龄数据采用207Pb/206Pb 年龄,分别为2487±35.9Ma、1784.1±40.2Ma, 锆石外形不规则,具磨圆,环带特征不清楚,可能为老基底的捕获锆石.
表 1 马山花岗岩体LA-ICP-MS 锆石(TW01) U-Th-Pb 同位素数据Table 1. LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Th-Pb dating data of granite from Mashan(TW01)分析点 含量/10-6 232Th/238U 207Pb/235U 206Pb/238U 207Pb/235U 206Pb/238U 232Th 238U 比值 1σ 比值 1σ 年龄/Ma 1σ 年龄/Ma 1σ TW01-1 280.96 449.94 0.62 9.3972 0.2158 0.4182 0.0092 2377.6 21.07 2252.3 41.73 TW01-2 523.95 1099.59 0.48 0.3621 0.0089 0.0437 0.0010 313.8 6.64 275.4 5.97 TW01-3 375.06 699.75 0.54 0.3941 0.0100 0.0456 0.0010 337.4 7.29 287.1 6.31 TW01-4 594.83 576.85 1.03 0.8243 0.0212 0.0526 0.0012 610.4 11.79 330.4 7.55 TW01-5 349.29 359.94 0.97 0.3703 0.0110 0.0431 0.0010 319.9 8.13 272 6.38 TW01-6 92.39 154.58 0.60 0.4218 0.0152 0.0456 0.0012 357.3 10.86 287.3 7.47 TW01-7 401.97 1310.93 0.31 0.3223 0.0078 0.0438 0.0010 283.7 6.01 276.4 5.96 TW01-8 191.06 372.5 0.51 0.3463 0.0101 0.0438 0.0010 301.9 7.58 276.3 6.38 TW01-9 292.29 294.14 0.99 0.3421 0.0102 0.0444 0.0011 298.8 7.73 280 6.53 TW01-10 99.79 354.71 0.28 0.3287 0.0093 0.0409 0.0010 288.5 7.14 258.4 5.96 TW01-11 408.08 804.03 0.51 0.3764 0.0095 0.0436 0.0010 324.4 7.02 275 6.06 TW01-12 49.69 106.02 0.47 0.4079 0.0170 0.0409 0.0012 347.4 12.27 258.2 7.6 TW01-13 133.16 156.37 0.85 0.4344 0.0141 0.0433 0.0011 366.3 10 273 6.93 TW01-14 81.57 213.17 0.38 0.5080 0.0149 0.0603 0.0015 417.1 10.03 377.7 8.81 TW01-15 291.58 308.2 0.95 0.3552 0.0104 0.0437 0.0010 308.6 7.79 275.7 6.45 TW01-16 252.32 605.27 0.42 0.3590 0.0094 0.0429 0.0010 311.5 7 270.7 6.04 TW01-17 660.33 1444.13 0.46 0.4373 0.0104 0.0461 0.0010 368.4 7.36 290.5 6.29 TW01-18 216.72 353.49 0.61 0.4315 0.0124 0.0451 0.0011 364.2 8.77 284.6 6.69 TW01-19 477.93 938.69 0.51 0.3581 0.0090 0.0457 0.0010 310.8 6.72 287.9 6.32 TW01-20 212.5 325.28 0.65 0.3001 0.0098 0.0413 0.0010 266.4 7.68 260.8 6.33 TW01-21 108.44 260.92 0.42 0.3980 0.0129 0.0456 0.0012 340.2 9.38 287.2 7.13 TW01-22 158.92 169.8 0.94 0.4177 0.0160 0.0467 0.0013 354.4 11.43 294 8.04 TW01-23 372.22 946.18 0.39 0.3493 0.0087 0.0449 0.0010 304.2 6.53 283.2 6.21 TW01-24 315.24 351.81 0.90 0.4617 0.0139 0.0457 0.0011 385.5 9.65 288.2 7.02 TW01-25 261.36 418.89 0.62 0.3418 0.0098 0.0458 0.0011 298.6 7.41 288.6 6.66 TW01-26 157.57 259.58 0.61 0.3533 0.0108 0.0458 0.0011 307.2 8.13 288.7 6.87 TW01-27 157.3 231.78 0.68 0.3569 0.0112 0.0456 0.0011 309.9 8.4 287.7 6.93 TW01-28 77.52 182.09 0.43 4.3637 0.1037 0.2902 0.0066 1705.5 19.64 1642.3 32.72 5. 岩石地球化学特征
5.1 主量元素
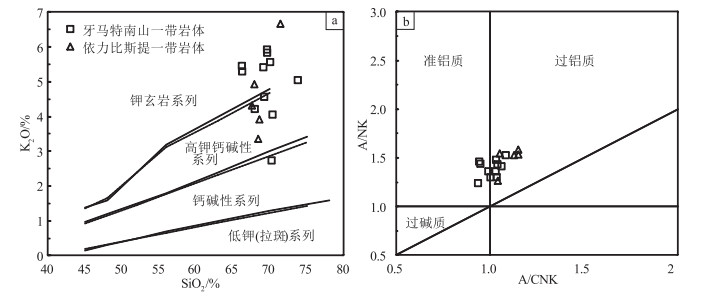
马山花岗岩类的岩石地球化学分析(表 2)表明,SiO2 含量为64.85%~69.75%,平均含量67.35%,属于酸性岩类,在SiO2-(Na2O+K2O)图解(图 5)上,大多数样品点投入花岗闪长岩区域;Na2O 含量为2.66%~4.72%,平均值3.68%,K2O含量为1.90%~2.71%, 平均值为2.23% ,Na2O + K2O 含量为5.13~6.62%,平均值为5.91%, Na2O/K2O 值为0.98~2.48,平均值为1.69;Al2O3含量为13.55%~15.49%,平均值为14.63% ;TiO2 含量为0.41% ~0.76% ,平均值为0.55% ;A/CNK 值为0.96~1.07,平均值为1.0,在A/CNK-A/NK 图解(图 6)中,样品点主要投入到偏铝质岩石范围内,2 个样品投入过铝质范围内;里特曼指数σ为1.15~1.84,为钙碱性系列岩石;在SiO2-K2O 图解(图 7)上,样品点全部投入中钾钙碱性系列;在K2O-Na2O 图解(图 8)上,样品点均投入I 型花岗岩区域.岩石的分异指数(DI)为65.74~76.80,表明原始岩浆的结晶分异程度一般.马山岩体主量元素特征显示,其具有钙碱性序列岩石的属性,属于中等分异程度的I 型花岗岩.
![]() 图 5 SiO2-(Na2O +K2O)图解(底图据参考文献[37])Figure 5. SiO2 versus Na2O +K2O diagram
图 5 SiO2-(Na2O +K2O)图解(底图据参考文献[37])Figure 5. SiO2 versus Na2O +K2O diagram![]() 图 6 A/CNK-A/NK 图解(底图据参考文献[38])Figure 6. A/CNK versus A/NK diagram
图 6 A/CNK-A/NK 图解(底图据参考文献[38])Figure 6. A/CNK versus A/NK diagram![]() 图 7 SiO2-K2O 图解(底图据参考文献[39])Figure 7. SiO2 versus K2O diagram
图 7 SiO2-K2O 图解(底图据参考文献[39])Figure 7. SiO2 versus K2O diagram![]() 图 8 K2O-Na2O 图解(底图据参考文献[40])Figure 8. K2O versus Na2O diagram
图 8 K2O-Na2O 图解(底图据参考文献[40])Figure 8. K2O versus Na2O diagram5.2 微量和稀土元素
(1) 稀土元素
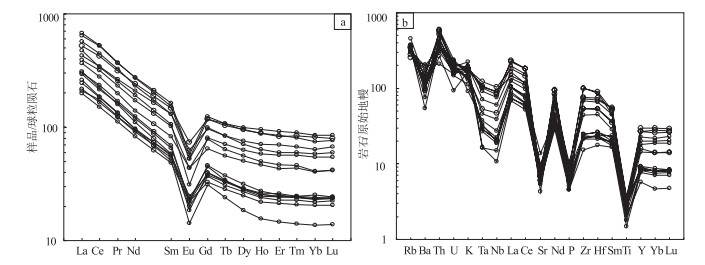
稀土元素分析结果如表 2 所示.样品的稀土元素总量为80.57 × 10-6~125.29 × 10-6,平均值为106.44×10-6,稀土元素总含量较低;在球粒陨石标准化配分模式图(图 9-a)上,具有相对平缓的富集轻稀土元素(LREE)的稀土元素配分模式,重稀土元素(HREE)分馏不明显且相对亏损,但都明显高于球粒陨石丰度10 倍.ΣLREE/ΣHREE 值为1.70~2.43, 平均值为1.99;轻稀土元素内部分异较明显,(La/Sm)N=2.37~3.37,平均值为2.80;La/Yb=5.81~7.23,平均值为6.23,(La/Yb)N=4.17~5.19,平均值为4.47;(Gd/Yb)N=0.85~1.25,δEu=0.65~0.91,平均值为0.80,具有弱负Eu 异常,可能与斜长石在源区残留有关.
表 2 马山花岗岩体主量、微量和稀土元素分析结果Table 2. Analytical data of major, trace, and rare earth elements of granite from Mashan样品号
岩石名称P1/GS1
花岗质碎裂岩P1/GS3
花岗质碎岩P13/GS3
中粗粒花岗闪长岩P13/GS5
中粗粒花岗闪长岩P16/GS1、XT1
黑云母花岗闪长岩P16/GS2、XT2
黑云母花岗闪长岩SiO2 65.48 68.06 69.75 69.21 64.85 66.77 Al2O3 15.00 13.55 14.09 14.33 15.30 15.49 Fe2O3 1.40 1.13 1.95 2.08 3.41 3.01 FeO 3.44 3.02 1.68 1.75 2.22 1.88 TiO2 0.76 0.62 0.41 0.43 0.56 0.53 MgO 2.55 2.05 1.36 1.20 1.78 1.62 CaO 3.92 2.93 3.15 3.57 3.48 3.25 P2O5 0.16 0.16 0.07 0.09 0.12 0.12 K2O 1.90 2.71 2.40 2.29 2.21 1.90 MnO 0.09 0.07 0.07 0.08 0.08 0.07 Na2O 3.23 2.66 3.74 3.67 4.05 4.72 烧失量 1.55 3.72 0.82 0.54 1.60 1.29 总量 99.46 100.69 99.49 99.23 99.66 100.65 A/CNK 1.04 1.07 0.97 0.96 0.99 0.99 NK/A 0.49 0.54 0.62 0.59 0.59 0.63 σ 1.17 1.15 1.41 1.35 1.79 1.84 Rb 88.84 114.35 75.02 170.00 47.34 48.32 Ba 430.78 435.03 370.10 481.29 109.25 283.55 Th 12.55 13.66 8.49 17.14 6.92 4.94 U 2.10 1.30 1.44 3.79 1.68 1.40 Nb 13.36 11.54 5.78 12.36 5.75 4.42 Ta 1.18 1.20 0.62 1.28 0.64 0.49 Sr 255.42 139.70 209.88 195.36 291.65 226.93 Zr 143.82 72.81 127.41 374.10 196.08 185.01 V 101.52 64.53 71.65 23.01 78.67 64.00 Cr 54.31 43.16 22.04 21.90 18.38 22.06 Co 13.38 6.74 6.29 1.34 10.11 7.72 Cu 15.99 16.80 7.21 3.16 22.49 17.54 Zn 76.13 53.91 33.03 41.80 47.13 39.88 Ga 18.83 16.43 15.27 16.56 14.36 13.37 La 18.00 18.59 15.70 12.85 14.47 13.48 Ce 24.17 31.86 31.06 19.91 37.94 34.31 Pr 5.07 4.90 3.65 3.23 4.69 3.94 Nd 19.47 18.51 14.39 12.23 18.34 15.69 Sm 4.14 4.16 3.01 2.83 3.94 3.60 Eu 1.08 0.85 0.86 0.74 0.91 0.90 Gd 3.76 3.84 2.77 2.56 3.31 3.16 Tb 0.74 0.81 0.55 0.48 0.60 0.59 Dy 4.40 4.95 3.57 3.00 3.52 3.57 Ho 0.88 1.00 0.81 0.66 0.75 0.76 Er 2.80 3.34 2.57 2.21 2.08 2.10 Tm 0.40 0.55 0.37 0.34 0.34 0.33 Yb 2.49 3.19 2.70 2.06 2.29 2.28 Lu 0.40 0.45 0.38 0.33 0.36 0.36 Y 23.71 28.29 20.30 17.14 19.75 20.25 REE 111.51 125.29 102.69 80.57 113.29 105.31 LREE 71.93 78.87 68.67 51.79 80.29 71.91 HREE 39.58 46.42 34.02 28.78 33.00 33.39 LREE/HREE 1.82 1.70 2.02 1.80 2.43 2.15 (La/Yb)N 5.19 4.18 4.17 4.47 4.54 4.25 (La/Sm)N 2.81 2.88 3.37 2.93 2.37 2.42 (Gd/Yb)N 1.25 1.00 0.85 1.03 1.20 1.15 δEu 0.84 0.65 0.91 0.84 0.77 0.82 注:元素由中国冶金地质总局西北地质勘查院测试中心测定;δEu=EuN/SQRT(SmN∗GdN);主量元素含量单位为%,微量和稀土元素为10-6 (2) 微量元素
在微量元素原始地幔标准化蛛网图(图 9-b)上,所有样品的稀土元素配分模式和原始地幔标准化图基本平行,显示同源演化的特征;显著亏损Ba、Nb、Ta、P、Ti, Zr、Rb、Th、U、K,富集Zr 和亏损Nb、Ta、Ti, 表明岩浆源区岩石以陆壳组分为主.
岩石具有高Rb、低Sr(均小于400×10-6)、高Yb(大于2 × 10-6)的特征,Sr/Y 值很低(Sr/Y=4.94~14.77, 平均值为10.57),马山花岗岩微量元素Sr、Yb特征与华南低Sr、高Yb 型花岗岩相似.低Sr 、高Yb 型花岗岩为浙闽型花岗岩,与其平衡的是斜长石和角闪石残留相[38],说明形成的压力较低(小于0.8GPa 或1.0GPa),可能是地壳伸展变形减薄达正常地壳厚度(30km 左右)或低于正常地壳厚度的造山后阶段形成的[43].在大洋中脊标准化图解(图 10)上,样品与典型的后碰撞花岗岩显示出类似的趋势,说明马山花岗岩为典型的后碰撞花岗岩.
![]() 图 10 马山花岗岩体大洋中脊标准化图解(标准化值据参考文献[42])Figure 10. Ocean ridge granite (ORG) normalized geochemicalpatterns for samples of Mashan granite
图 10 马山花岗岩体大洋中脊标准化图解(标准化值据参考文献[42])Figure 10. Ocean ridge granite (ORG) normalized geochemicalpatterns for samples of Mashan granite6. 马山花岗岩体形成的构造背景及其成因
北山地区西邻东天山,东接阿拉善,以阿尔金和星星峡两大走滑断裂为界,位于一个巨大的构造楔形区内,构造过程复杂.其大地构造的归属一直存在争议,一是将北山地区划分为北部的哈萨克斯坦板块和南部的塔里木板块,左国朝等[3]以明水-石板井-小黄山缝合带(早古生代末)为界;龚全胜等[29]、何世平等[30]则以红石山-黑鹰山-六陀山蛇绿混杂岩带(晚古生代)为界;部分学者[31-32]以柳园-大奇山(晚古生代末)和红石山-黑鹰山-六陀山2 条深大断裂为界,将北山从南向北依次划分为塔里木板块、哈萨克斯坦板块和西伯利亚板块;李锦轶等[44]则以星星峡—白玉山—牛圈子—小黄山作为北山地区西伯利亚与中朝2 个古板块之间二叠系的分界线,认为北山南部柳园一带可能代表了二叠纪弧后盆地环境,柳园与白玉山—小黄山之间的区域为早古生代岛弧带.
对区域地质演化,前人有不同的观点,分歧的关键点在于洋盆的最终闭合时间.左国朝等[3]认为,在志留纪末—早泥盆世,北山地区的塔里木-中朝与哈萨克斯坦两大古板块最终拼合,并导致洋盆消失和碰撞造山;刘雪亚等[31]认为,在早二叠世之前,随着北山南带及南天山古洋盆的封闭,敦煌地块北缘的安北-旧寺墩构造带与北山造山带前缘的柳园-大奇山地体碰撞,导致塔里木板块、哈萨克斯坦板块和西伯利亚板块最终拼接;龚全胜等[45]认为,北山地区自泥盆纪开始转化为古亚洲洋构造域演化体系,晚石炭世末实现塔里木板块、哈萨克斯坦板块的最终碰撞对接;何世平等[46]认为,石炭纪末,哈萨克斯坦板块和塔里木板块之间的洋盆最终闭合,形成新的统一大陆,认为在早二叠世研究区洋盆已经闭合,经历了碰撞造山.而朱江[24]则认为,北山南带洋壳俯冲作用可能持续到早二叠世,并在早—中二叠世洋盆最终闭合,认为北山南带石炭纪—二叠纪的岩浆作用形成于俯冲环境,与毛启贵[47]、肖文交[48-49]、郭谦谦[50]等观点一致.
很多学者[3, 51-52]认为,北山地区在二叠纪是一种伸展拉伸的构造背景.左国朝等[3]认为,早二叠世北山南带在拉张背景下形成了峡东-俞井子裂陷槽,但并没有形成真正的大洋;刘明强等[53]指出,音凹峡晚古生代陆内裂谷带为一多旋回裂谷,主要裂谷作用发生于奥陶纪、志留纪、石炭纪和二叠纪,反映了多期次、多旋回性、继承性“开”、“合”演化的特征;龚全胜等[45]认为,北山地区晚石炭世—二叠纪为大陆板块碰撞时期;何世平等[46]认为,早石炭世沿石板山—大奇山—神螺山一带在前震旦纪古老基底上形成北山南部陆内裂谷带,该裂谷带一直发展演化到二叠纪末,并在早二叠世发展到鼎盛时期.
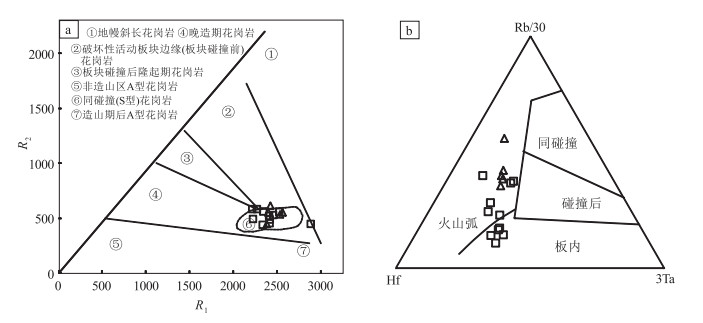
综上所述,结合野外地质特征,下石炭统红柳园组为火山-碎屑岩,火山岩组合为安山岩-英安岩-流纹岩组合;与红柳园组平行不整合接触的下二叠统双堡塘组为一套粗碎屑岩和细碎屑岩组合,中二叠统金塔组以出露海相枕状玄武岩为特征,并伴随大量的辉长岩、辉绿岩等幔源岩浆活动,其与双堡塘组为整合接触关系.多数学者[3, 46, 53]对区内北山南带存在晚古生代洋盆有异议,认为晚古生代为陆内裂谷环境,区内晚石炭世可能存在裂谷回返碰撞,导致石炭系与下二叠统之间的平行不整合接触,早二叠世裂谷进一步拉开,并在中二叠世达到鼎盛.结合地球化学特征,可进一步确定281.8±3.2Ma的马山花岗岩形成于后碰撞伸展环境.
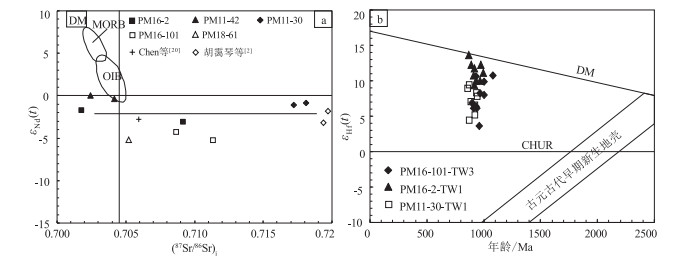
吴泰然[54]将这类花岗岩归为拉张型过渡壳花岗岩(ECG),认为其形成是由于地壳的拉伸减薄,上地幔热物质上涌,使地壳形成一种高温低压的环境,并使地壳发生部分重熔,同时上地幔上涌的热物质沿拉张的裂隙与地壳的热物质发生混染作用,对陆壳的物质进行改造,使之向过渡类型转化,形成拉张型过渡壳的花岗岩.冯继承[22]、张文等[23]研究认为,北山南带音凹峡花岗岩也是该类型的花岗岩体.区域上,前人对北山南带不同地段的石炭纪—二叠纪代表性的中酸性侵入岩体进行了Sr、Nd、Hf 同位素研究,桥湾北花岗岩体[22, 24]的εNd(t)值在-0.40~-0.06 之间,εHf(t)值在-1.2~5.8 之间,是典型的壳幔混合型花岗岩,代表了兴蒙造山带广泛出现的晚古生代—中生代大陆地壳生长现象;音凹峡南花岗岩体也位于北山南带,张文[23]报道的该岩体的εHf(t)值在+4.4~+7.8 之间;石板泉花岗岩体的εNd(t)值在-0.1~-1.6 之间[24].一般认为,具有正εNd(t)和εHf(t)值的花岗质岩石来自于亏损地幔,或由亏损地幔中新增生的年轻地壳物质的部分熔融形成.结合研究区二叠纪大量基性岩浆活动(枕状玄武岩和辉长、辉绿岩的发现),认为北山南带石炭纪—二叠纪(305~280Ma)的花岗岩具有普遍的壳幔混合成因特征.
7. 结论
(1) 马山花岗岩体的LA-ICP-MS 锆石U-Pb年龄为281.8±3.2Ma, 为后碰撞花岗岩.
(2) 马山花岗岩体具有典型的壳幔混合特征,其机制可能是幔源基性岩浆底侵后遭受地壳物质混合或混染.北山南带305~280Ma 之间的花岗岩普遍具有壳幔混合成因的特征.
(3) 马山花岗岩体及北山南带众多壳幔混合成因的花岗岩体说明,北山南带在早二叠世总体为后碰撞伸展环境.
-
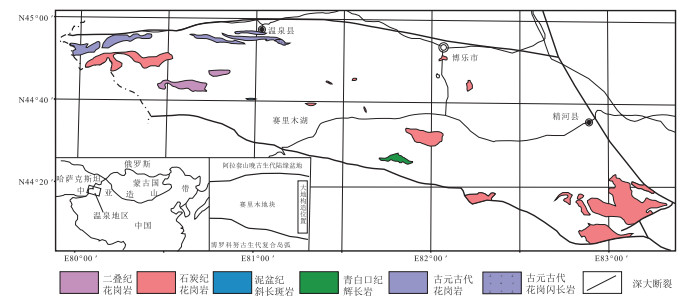
图 1 西天山温泉地区侵入岩分布简图(据参考文献②修改)
Figure 1. Simplified intrusive rock map of the Wenquan area in West Tianshan
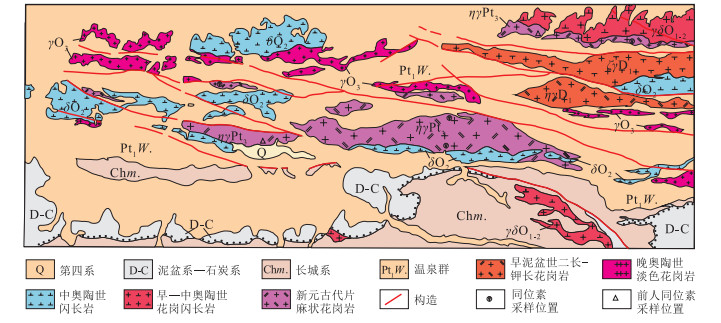
图 2 温泉县别珍套山地质简图(据参考文献②修改)
Figure 2. Simplified geological map for the Biezhentao Mountain of Wenquan County
表 1 新元古代片麻状花岗岩锆石U-Th-Pb年龄测试结果
Table 1 Zircon U-Th-Pb dating results of Neoproterozoic granitoids
测点 Pb
(总量)232Th 238U Th/U 同位素比值 同位素年龄/Ma 谐和
度/%/10-6 207Pb/206Pb 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ 207Pb/206Pb 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ PM16-2-TW1 1 122 78 688 0.11 0.0681 0.0017 1.524 0.039 0.1624 0.0024 870 50 940 16 970 13 96.9 2 172 253 948 0.27 0.0666 0.0014 1.504 0.034 0.1638 0.0023 826 44 932 14 978 13 95.3 3 178 159 1066 0.15 0.0674 0.0014 1.419 0.031 0.1527 0.0022 849 42 897 13 916 12 97.9 4 216 1387 1026 1.35 0.0669 0.0014 1.356 0.030 0.1471 0.0021 834 43 870 13 885 12 98.3 5 127 157 662 0.24 0.0726 0.0017 1.670 0.040 0.1668 0.0024 1003 46 997 15 995 13 100.2 6 507 619 3233 0.19 0.0691 0.0010 1.375 0.023 0.1444 0.0020 901 29 879 10 870 11 101.0 7 473 810 2945 0.28 0.0693 0.0010 1.409 0.024 0.1475 0.0020 908 30 893 10 887 11 100.7 8 233 180 1389 0.13 0.0671 0.0013 1.419 0.029 0.1535 0.0022 839 39 897 12 921 12 97.4 9 160 100 948 0.11 0.0662 0.0015 1.417 0.033 0.1553 0.0022 812 46 896 14 931 12 96.2 10 173 184 1040 0.18 0.0685 0.0015 1.437 0.032 0.1521 0.0022 884 43 904 13 913 12 99.0 12 204 617 1316 0.47 0.0716 0.0014 1.392 0.030 0.1411 0.0020 973 40 885 13 851 11 104.0 13 187 135 1109 0.12 0.0664 0.0014 1.425 0.032 0.1556 0.0022 820 44 899 13 932 12 96.5 14 139 193 749 0.26 0.0669 0.0016 1.526 0.038 0.1655 0.0024 834 49 941 15 987 13 95.3 15 62 120 351 0.34 0.0675 0.0024 1.432 0.051 0.1540 0.0025 853 72 903 21 923 14 97.8 16 182 135 1124 0.12 0.0673 0.0014 1.391 0.031 0.1500 0.0022 846 42 885 13 901 12 98.2 17 136 114 795 0.14 0.0679 0.0015 1.459 0.035 0.1560 0.0023 865 46 914 14 934 13 97.9 18 327 192 1985 0.10 0.0673 0.0011 1.420 0.026 0.1532 0.0021 846 34 897 11 919 12 97.6 19 234 1135 1436 0.79 0.0691 0.0013 1.427 0.028 0.1498 0.0021 902 37 900 12 900 12 100.0 20 149 109 872 0.13 0.0675 0.0014 1.480 0.033 0.1592 0.0023 852 43 922 13 952 13 96.8 PM18-61-TW1 1 222 346 1337 0.26 0.0679 0.0014 1.407 0.032 0.1504 0.0023 866 42 892 13 903 13 98.8 2 206 474 1171 0.40 0.0725 0.0017 1.499 0.038 0.1502 0.0024 999 47 930 15 902 13 103.1 3 320 344 1889 0.18 0.0696 0.0014 1.498 0.033 0.1561 0.0024 918 41 929 14 935 13 99.4 4 293 338 1694 0.20 0.0699 0.0015 1.521 0.036 0.1580 0.0024 925 44 939 14 945 14 99.4 5 276 369 1471 0.25 0.0721 0.0018 1.652 0.043 0.1664 0.0026 987 49 990 17 992 15 99.8 6 598 1050 3253 0.32 0.0717 0.0013 1.588 0.033 0.1609 0.0025 977 38 966 13 962 14 100.4 7 237 907 1313 0.69 0.0744 0.0023 1.593 0.050 0.1556 0.0026 1051 60 968 20 932 14 103.9 8 244 240 1408 0.17 0.0703 0.0018 1.546 0.042 0.1596 0.0025 937 52 949 17 955 14 99.4 9 836 2128 4386 0.49 0.0845 0.0016 1.770 0.037 0.1520 0.0023 1305 35 1035 13 912 13 113.5 10 396 511 2118 0.24 0.0737 0.0019 1.677 0.046 0.1651 0.0026 1034 51 1000 17 985 15 101.5 11 392 691 2348 0.29 0.0713 0.0015 1.467 0.035 0.1494 0.0023 966 43 917 14 898 13 102.1 12 195 344 1040 0.33 0.0769 0.0022 1.724 0.051 0.1628 0.0027 1118 56 1018 19 972 15 104.7 13 221 442 1231 0.36 0.0707 0.0019 1.518 0.042 0.1558 0.0025 949 53 938 17 934 14 100.4 14 296 413 1619 0.26 0.0696 0.0015 1.570 0.037 0.1637 0.0025 917 44 958 15 977 14 98.1 15 195 212 1065 0.20 0.0716 0.0019 1.656 0.046 0.1678 0.0027 975 53 992 18 1000 15 99.2 16 284 522 1594 0.33 0.0728 0.0016 1.573 0.038 0.1568 0.0024 1010 44 960 15 939 14 102.2 17 191 331 1064 0.31 0.0683 0.0019 1.481 0.043 0.1573 0.0027 877 55 923 18 942 15 98.0 18 416 544 2399 0.23 0.0701 0.0014 1.506 0.034 0.1557 0.0026 931 40 933 14 933 14 100.0 19 194 376 1091 0.34 0.0689 0.0020 1.474 0.045 0.1551 0.0027 896 59 920 19 930 15 98.9 20 296 460 1656 0.28 0.0688 0.0017 1.496 0.040 0.1576 0.0027 893 51 929 16 944 15 98.4 21 314 503 1621 0.31 0.0770 0.0020 1.781 0.050 0.1677 0.0029 1121 52 1039 18 999 16 104.0 22 244 368 1329 0.28 0.0694 0.0019 1.562 0.046 0.1632 0.0028 911 56 955 18 974 16 98.0 23 231 367 1217 0.30 0.0689 0.0019 1.587 0.047 0.1671 0.0029 895 57 965 19 996 16 96.9 24 269 485 1434 0.34 0.0684 0.0018 1.545 0.044 0.1637 0.0028 882 55 949 18 977 16 97.1 25 194 209 1063 0.20 0.0694 0.0021 1.585 0.049 0.1656 0.0029 910 60 964 19 988 16 97.6 PM11-30-TW1 1 209 380 1179 0.32 0.0714 0.0015 1.433 0.032 0.1455 0.0021 969 42 903 13 876 12 103.1 2 186 290 1081 0.27 0.0689 0.0015 1.352 0.031 0.1424 0.0020 896 45 869 13 858 11 101.3 4 57 97 302 0.32 0.0684 0.0028 1.451 0.059 0.1540 0.0026 879 82 910 24 923 14 98.6 5 120 258 609 0.42 0.0685 0.0020 1.476 0.045 0.1563 0.0024 884 60 921 18 936 13 98.4 6 89 195 471 0.41 0.0702 0.0025 1.430 0.050 0.1478 0.0023 933 70 902 21 889 13 101.5 8 62 143 321 0.44 0.0827 0.0034 1.662 0.067 0.1458 0.0025 1262 78 994 26 877 14 113.3 9 135 267 693 0.39 0.0690 0.0019 1.506 0.043 0.1582 0.0024 900 57 933 18 947 13 98.5 10 53 123 266 0.46 0.0749 0.0032 1.591 0.068 0.1541 0.0027 1066 84 967 26 924 15 104.7 11 35 120 181 0.67 0.0664 0.0039 1.345 0.077 0.1470 0.0028 818 117 865 34 884 16 97.9 12 52 139 274 0.51 0.0712 0.0031 1.454 0.063 0.1481 0.0026 963 86 911 26 890 14 102.4 13 97 187 500 0.37 0.0701 0.0022 1.506 0.047 0.1559 0.0024 931 62 933 19 934 13 99.9 14 38 114 191 0.60 0.0693 0.0035 1.447 0.073 0.1516 0.0028 907 101 909 30 910 15 99.9 15 108 223 551 0.40 0.0679 0.0020 1.457 0.043 0.1557 0.0023 866 59 913 18 933 13 97.9 16 66 169 354 0.48 0.0704 0.0025 1.392 0.050 0.1435 0.0023 939 71 885 21 864 13 102.4 17 56 111 281 0.39 0.0699 0.0026 1.536 0.057 0.1595 0.0026 924 75 945 23 954 14 99.1 18 81 202 414 0.49 0.0700 0.0022 1.455 0.046 0.1507 0.0023 929 63 912 19 905 13 100.8 19 66 161 340 0.47 0.0673 0.0024 1.412 0.050 0.1522 0.0024 848 71 894 21 913 13 97.9 21 41 113 211 0.54 0.0718 0.0032 1.455 0.063 0.1471 0.0025 979 87 912 26 885 14 103.1 22 80 190 399 0.48 0.0691 0.0023 1.479 0.050 0.1554 0.0024 901 67 922 20 931 13 99.0 PM16-11-TW3 1 72 186 395 0.47 0.063 0.0033 1.337 0.070 0.1541 0.0029 708 108 862 31 924 16 93.3 2 154 534 807 0.66 0.0715 0.0022 1.535 0.048 0.1558 0.0026 970 61 944 19 934 14 101.1 3 110 273 605 0.45 0.0713 0.0026 1.537 0.056 0.1565 0.0027 965 72 945 23 937 15 100.9 4 96 185 516 0.36 0.0695 0.0027 1.549 0.061 0.1616 0.0029 914 78 950 24 966 16 98.3 5 123 258 712 0.36 0.0706 0.0025 1.464 0.053 0.1504 0.0026 947 71 916 22 903 15 101.4 6 69 166 375 0.44 0.0723 0.0038 1.555 0.082 0.156 0.0032 995 104 952 32 934 18 101.9 7 35 73 175 0.42 0.0747 0.0057 1.687 0.126 0.1639 0.004 1060 146 1004 48 978 22 102.7 8 40 123 218 0.57 0.0698 0.005 1.472 0.104 0.1531 0.0035 922 140 919 43 918 20 100.1 9 56 154 319 0.48 0.0684 0.0042 1.363 0.083 0.1447 0.0031 880 123 873 36 871 17 100.2 10 78 207 418 0.49 0.0696 0.0033 1.506 0.070 0.157 0.003 917 93 933 29 940 17 99.3 11 97 163 543 0.3 0.0712 0.0028 1.524 0.060 0.1553 0.0028 963 78 940 24 931 15 101.0 12 47 134 272 0.49 0.0686 0.0033 1.382 0.066 0.1462 0.0028 885 96 881 28 880 16 100.1 13 207 544 1216 0.45 0.0689 0.0016 1.382 0.035 0.1454 0.0023 897 47 881 15 875 13 100.7 15 88 229 493 0.46 0.072 0.0025 1.496 0.053 0.1507 0.0026 985 70 929 22 905 15 102.7 16 59 154 332 0.46 0.0645 0.0033 1.335 0.067 0.1501 0.0028 758 103 861 29 902 16 95.5 17 61 102 379 0.27 0.0687 0.003 1.380 0.061 0.1456 0.0027 890 88 880 26 876 15 100.5 18 119 212 717 0.29 0.0694 0.0022 1.397 0.046 0.1461 0.0025 909 65 888 19 879 14 101.0 19 45 118 250 0.47 0.0711 0.0037 1.508 0.077 0.1538 0.0031 960 102 934 31 922 17 101.3 20 61 151 336 0.45 0.0703 0.0031 1.480 0.065 0.1527 0.0028 937 88 922 27 916 16 100.7 注:谐和度=100×(207Pb/235U年龄)/(206Pb/238U年龄) 表 2 新元古代早期片麻状-眼球状花岗岩主量元素分析结果
Table 2 Abundances of major elements of Neoproterozoic granitoids
% 样号 岩性 SiO2 Al2O3 Fe2O3 FeO CaO MgO K2O Na2O TiO2 P2O5 MnO 烧失量 H2O+ CO2 总量 Na2O+K2O A/CNK A/NK PM11-30-HQ1 片麻状-眼球
状花岗岩66.18 13.26 2.11 5.35 2.77 0.51 5.31 2 0.79 0.19 0.12 1.21 0.54 0.096 100.44 7.31 0.94 1.47 PM11-30-HQ2 69.04 12.96 2.03 3.75 1.98 0.44 5.43 2.19 0.61 0.14 0.1 1.17 0.68 0.032 100.55 7.62 0.99 1.37 PM11-30-HQ3 69.53 13.27 1.28 3.52 1.47 0.45 5.94 2.26 0.55 0.13 0.09 1.32 0.56 0.033 100.4 8.2 1.03 1.31 PM11-30-HQ4 69.96 12.85 1.7 3.42 1.64 0.55 5.58 2.31 0.6 0.13 0.08 0.99 0.58 0.082 100.47 7.89 1.00 1.31 PM11-42-HQ1 67.87 13.99 1.25 4.5 2.28 0.86 4.23 2.94 0.73 0.23 0.09 0.84 0.24 0.012 100.06 7.17 1.03 1.49 PM11-42-HQ2 69.16 13.88 1.45 3.48 2.04 0.62 4.58 2.85 0.54 0.18 0.08 0.95 0.44 < 0.01 100.25 7.43 1.04 1.44 PM16-2-HQ1 73.69 12.45 1.06 1.74 1.64 0.62 5.06 2.21 0.39 0.11 0.04 0.8 0.32 0.13 100.26 7.27 1.03 1.37 PM16-2-HQ4 69.55 13.32 1.66 2.5 1.95 0.49 5.85 2.65 0.55 0.13 0.06 1.12 0.34 0.362 100.53 8.5 0.94 1.25 PM16-11-HQ1 糜棱岩化眼
球状花岗岩70.28 14.21 1.01 2.08 1.86 1.04 4.07 3.41 0.48 0.1 0.04 1.25 0.55 0.33 100.71 7.48 1.06 1.42 PM16-11-HQ3 70.15 14.7 0.99 2.65 2.19 0.71 2.75 4.02 0.45 0.12 0.06 0.98 0.4 0.094 100.26 6.77 1.08 1.53 PM16-18-HQ2 片麻状-眼球
状花岗岩66.13 13.5 2.01 4.8 2.69 0.59 5.47 2.08 0.79 0.19 0.12 1.43 0.48 0.407 100.69 7.55 0.95 1.44 PM16-101-HQ2 68.35 13.91 1.47 3.42 1.84 1.58 3.37 3.1 0.69 0.17 0.07 1.83 <0.01 0.276 100.08 6.47 1.15 1.59 PM16-101-HQ3 67.83 14.37 1.67 2.92 1.85 1.39 4.94 2.45 0.63 0.15 0.07 1.52 0.96 0.078 100.83 7.39 1.13 1.53 PM18-61-YQ1 糜棱岩化眼
球状花岗岩71.35 13.74 0.8 1.42 1.31 0.76 6.68 2.18 0.32 0.1 0.04 1.1 0.72 0.081 100.6 8.86 1.04 1.27 PM18-61-YQ2 67.5 14.36 1.83 2.48 2.42 1.34 4.33 2.78 0.59 0.14 0.06 1.97 1.32 0.033 101.15 7.11 1.05 1.55 PM18-61-YQ3 68.51 13.92 1.76 2.72 1.68 1.54 3.93 2.91 0.62 0.14 0.06 2 1.48 0.117 101.39 6.84 1.15 1.54 表 3 新元古代早期片麻状-眼球状花岗岩稀土元素分析结果
Table 3 Abundances of rare earth elements of Neoproterozoic granitoids
10-6 样号 岩性 La Ce Pr Nd Sm Eu Gd Tb Dy Ho Er Tm Yb Lu Y ΣREE LREE HREE LREE/
HREELaN/
YbNδEu PM11-30-HQ1 片麻状-眼球
状花岗岩124 259 29.6 113 22.5 4.27 24.3 3.88 24.2 5 13.7 2.13 13.8 2.02 122 641.40 552.37 89.03 6.20 6.45 0.55 PM11-30-HQ2 152 319 34.9 128 24.8 3.31 25.4 4.01 25.3 5.38 15.2 2.28 14.5 2.16 136 756.24 662.01 94.23 7.03 7.52 0.40 PM11-30-HQ3 136 274 31 108 20.1 3.06 20.3 3.12 19.2 4 11.5 1.71 10.8 1.7 103 644.49 572.16 72.33 7.91 9.03 0.46 PM11-30-HQ4 160 321 35.2 127 23.5 3.09 24.3 4.01 23.8 4.99 14.1 2.06 12.7 1.95 123 757.70 669.79 87.91 7.62 9.04 0.39 PM11-42-HQ1 92.6 194 22 80.5 15.7 2.54 16.1 2.4 14.2 2.8 7.69 1.17 6.92 1.05 72.5 459.67 407.34 52.33 7.78 9.60 0.48 PM11-42-HQ2 86.4 171 18.9 65.2 12.7 2.53 13.3 2.1 12.8 2.63 7.17 1.11 6.91 1.06 65 403.81 356.73 47.08 7.58 8.97 0.59 PM16-2-HQ1 49.8 106 11.8 43.5 8.84 1.27 8.17 1.26 7.26 1.45 4.06 0.63 4.06 0.62 37.4 248.72 221.21 27.51 8.04 8.80 0.45 PM16-2-HQ4 112 206 24.2 89.2 16.2 1.81 16.5 2.66 15.9 3.3 9.36 1.45 9.31 1.38 82.8 509.27 449.41 59.86 7.51 8.63 0.34 PM16-11-HQ1 糜棱岩化眼
球状花岗岩73.2 136 15 51.2 8.89 1.07 8.12 1.25 7.28 1.48 4.28 0.63 4.28 0.62 42.2 313.30 285.36 27.94 10.21 12.27 0.38 PM16-11-HQ3 62.1 114 12.8 44.7 7.68 0.83 6.4 0.9 4.7 0.88 2.41 0.36 2.32 0.35 25.9 260.43 242.11 18.32 13.22 19.20 0.35 PM16-18-HQ2 片麻状-眼球
状花岗岩101 209 25.1 98 20 3.66 19.9 3.12 18 3.6 9.87 1.52 9.86 1.52 91.6 524.15 456.76 67.39 6.78 7.35 0.55 PM16-101-HQ2 69.1 131 15.5 55.7 9.95 1.33 9.22 1.27 7.16 1.4 4 0.62 3.96 0.61 39.9 310.82 282.58 28.24 10.01 12.52 0.42 PM16-101-HQ3 51.6 101 11.7 42.6 8.23 1.16 7.6 1.15 6.81 1.36 3.78 0.58 3.71 0.57 37 241.85 216.29 25.56 8.46 9.98 0.44 PM18-61-YQ1 糜棱岩化眼
球状花岗岩47 92.4 10.6 38.4 7.38 1.28 6.77 1.06 6.32 1.24 3.52 0.53 3.49 0.52 34.7 220.51 197.06 23.45 8.40 9.66 0.54 PM18-61-YQ2 57.8 112 12.5 45.3 8.52 1.42 7.77 1.23 7.17 1.45 4.02 0.61 3.92 0.6 39.6 264.31 237.54 26.77 8.87 10.58 0.52 PM18-61-YQ3 71.3 144 16.1 57.6 10.5 1.28 9.42 1.4 7.97 1.55 4.16 0.61 3.96 0.59 41.6 330.44 300.78 29.66 10.14 12.92 0.39 表 4 新元古代早期片麻状-眼球状花岗岩微量元素分析结果
Table 4 Abundances of trace elements of Neoproterozoic granitoids
10-6 样号 岩性 Pb Cr Ni Co Rb Cs Sr Ba V Nb Ta Zr Hf Ge U Th PM11-30-HQ1 片麻状-眼球
状花岗岩37 3.81 3.42 3.56 162 2.72 153 1410 15 73.2 5.02 1110 27.7 1.75 3.73 28.5 PM11-30-HQ2 41.2 2.73 2.07 2.7 180 1.56 126 1080 10.8 62.4 4.38 816 21.5 1.79 4.36 43.8 PM11-30-HQ3 43.5 3.45 2.25 2.95 204 2.02 156 1200 12 53.8 3.78 771 20.3 1.5 3.72 38.2 PM11-30-HQ4 39.6 3.4 3.3 3.13 217 2.82 142 1010 13.3 58.5 4.18 854 22.9 1.54 4.55 47.7 PM11-42-HQ1 26.5 20.1 8.17 5.39 226 9.97 142 647 38.3 33.7 2.2 596 16.3 1.82 3.7 50.9 PM11-42-HQ2 29.3 7.02 4.43 3.07 235 7.95 133 661 26.4 27.5 1.88 491 13.9 1.81 5 50.5 PM16-2-HQ1 42 11.4 5.63 4.06 204 4.7 185 729 28.3 10.7 0.67 275 8.06 1.45 1.94 22.6 PM16-2-HQ4 37.7 4.39 2.76 3.71 228 3.24 90.3 680 18.7 43.4 2.91 610 16.3 1.84 3.4 33.4 PM16-11-HQ1 糜棱岩化眼
球状花岗岩53 16 6.66 6.33 190 3.38 288 890 34.2 14 1.36 239 6.64 1.22 4.12 31.2 PM16-11-HQ3 31.2 7.54 3.82 4.7 211 5.75 206 383 27.1 19.6 1.52 264 6.97 1.47 4.92 31.1 PM16-18-HQ2 片麻状-眼球
状花岗岩38.8 4.61 3.02 4.44 199 3.13 180 1370 19.4 65.1 4.25 1140 26.4 1.66 3.26 18 PM16-101-HQ2 25.8 22.3 8.98 9.04 202 9.01 185 534 57.2 15.8 1.3 278 8.12 1.52 3.09 32 PM16-101-HQ3 48.3 19.5 7.94 8.43 241 8.01 152 769 52.8 14.8 1.16 248 7.36 1.43 3.42 25.9 PM18-61-YQ1 糜棱岩化眼
球状花岗岩54.6 11.2 5.49 4.1 289 2.89 130 936 22.6 7.68 0.68 171 5.42 1.66 4.05 32.4 PM18-61-YQ2 41.8 24.1 8.48 8.52 211 2.77 113 836 51.4 13.5 1.1 246 7.12 1.64 3.74 29.7 PM18-61-YQ3 36.9 22.4 8.6 9.42 209 3.31 126 732 51 14.5 1.2 251 7.36 1.42 3.96 37.8 表 5 新元古代片麻状花岗岩Sr-Nd同位素测试结果
Table 5 Abundances of Sr-Nd of Neoproterozoic granitoids
样号 PM11-30
-HQ1PM11-30
-HQ2PM16-2
-HQ1PM16-2
-HQ4PM11-42
-HQ1PM11-42
-HQ2PM16-101
-HQ2PM16-101
-HQ3PM18-61
-YQ387Rb/86Sr 2.923055 3.389836 2.773318 6.528700 4.065300 4.572700 2.796500 4.023900 4.511800 87Sr/86Sr 0.755071 0.761995 0.745629 0.787613 0.755898 0.764290 0.745911 0.764920 0.766481 2σ 0.000015 0.000015 0.000013 0.000017 0.000016 0.000015 0.000011 0.000021 0.000017 ISr 0.717223 0.718102 0.709161 0.701763 0.702440 0.704160 0.708695 0.711370 0.705204 147Sm/144Nd 0.122363 0.117179 0.122589 0.113100 0.121200 0.116300 0.112900 0.117400 0.113800 143Nd/144Nd 0.512140 0.512120 0.512034 0.512043 0.512183 0.512135 0.511907 0.511884 0.511856 2σ 0.000008 0.000008 0.000011 0.000010 0.000007 0.000010 0.000011 0.000010 0.000006 锆石年龄/
Ma906 906 920 920 920 920 931 931 950 εNd(0) -9.71 -10.10 -11.79 -11.61 -8.88 -9.81 -14.26 -14.71 -15.25 εNd(t) -1.10 -0.88 -3.07 -1.77 0.01 -0.35 -4.29 -5.27 -5.19 fSm/Nd -0.38 -0.40 -0.38 -0.43 -0.38 -0.41 -0.43 -0.40 -0.42 tDM1/Ma 1685 1626 1866 1677 1594 1588 1877 2001 1971 tDM2/Ma 1650 1632 1820 1715 1571 1600 1928 2007 2016 表 6 新元古代片麻状花岗岩锆石Lu-Hf同位素测试结果
Table 6 Abundances of Lu-Hf of zircons for the Neoproterozoic granitoids
测点 176Yb/177Hf 176Lu/177Hf 176Hf/177Hf 2σ U年龄/Ma εHf(0) εHf 1σ tDM1/Ma tDM2/Ma tcDM/Ma fLu/Hf PM16-101-TW3 1 0.078267 0.001728 0.282519 0.000022 934 -8.95 10.62 0.77989 1059 1129 1135 -0.95 2 0.029576 0.000610 0.282286 0.000022 960 -17.19 3.64 0.75455 1351 1588 1603 -0.98 3 0.053245 0.001114 0.282390 0.000021 1005 -13.50 7.99 0.74790 1222 1350 1360 -0.97 4 0.059385 0.001284 0.282426 0.000023 1080 -12.23 10.76 0.79838 1177 1233 1239 -0.96 5 0.061804 0.001398 0.282432 0.000023 895 -12.04 6.90 0.82005 1173 1333 1344 -0.96 6 0.049662 0.001164 0.282376 0.000019 942 -14.01 6.08 0.66361 1244 1421 1433 -0.96 7 0.057377 0.001272 0.282448 0.000024 1003 -11.47 9.88 0.82656 1146 1229 1236 -0.96 8 0.048773 0.001124 0.282397 0.000020 911 -13.27 6.17 0.68598 1214 1391 1403 -0.97 9 0.056592 0.001297 0.282425 0.000021 965 -12.29 8.21 0.72471 1180 1304 1314 -0.96 10 0.052120 0.001192 0.282393 0.000020 930 -13.39 6.43 0.69463 1220 1390 1401 -0.96 PM11-30-TW1 1 0.039581 0.000861 0.282503 0.000023 876 -9.51 9.35 0.78829 1056 1164 1172 -0.97 2 0.065358 0.001441 0.282509 0.000025 858 -9.29 8.84 0.87680 1064 1182 1191 -0.96 4 0.024860 0.000531 0.282389 0.000025 923 -13.54 6.54 0.88984 1205 1378 1389 -0.98 5 0.041721 0.000889 0.282437 0.000025 936 -11.85 8.30 0.86826 1150 1277 1286 -0.97 6 0.036587 0.000791 0.282428 0.000029 889 -12.18 6.99 1.02444 1160 1323 1333 -0.98 8 0.034472 0.000740 0.282361 0.000028 877 -14.53 4.42 0.97299 1251 1476 1489 -0.98 9 0.038083 0.000820 0.282413 0.000025 947 -12.68 7.73 0.88871 1181 1321 1331 -0.98 10 0.029821 0.000656 0.282351 0.000028 924 -14.90 5.11 0.99569 1263 1468 1481 -0.98 PM16-2-TW1 1 0.071121 0.001591 0.282475 0.000023 970 -10.49 9.95 0.81897 1117 1199 1207 -0.95 2 0.078792 0.001721 0.282539 0.000022 978 -8.24 12.27 0.77492 1030 1059 1063 -0.95 3 0.082549 0.001816 0.282496 0.000021 916 -9.75 9.40 0.72463 1093 1192 1200 -0.95 5 0.064821 0.001427 0.282490 0.000022 995 -9.96 11.10 0.75681 1091 1146 1151 -0.96 6 0.099852 0.001917 0.282644 0.000026 870 -4.53 13.59 0.89546 883 891 894 -0.94 7 0.104905 0.002159 0.282601 0.000024 887 -6.06 12.27 0.85205 952 988 992 -0.93 8 0.103184 0.002204 0.282568 0.000026 921 -7.22 11.78 0.92709 1001 1045 1050 -0.93 9 0.073635 0.001636 0.282503 0.000026 931 -9.52 10.05 0.89375 1079 1162 1169 -0.95 10 0.080479 0.001728 0.282535 0.000027 913 -8.39 10.74 0.94546 1036 1105 1111 -0.95 注:PM16-101-TW3锆石Lu-Hf同位素数据据参考文献② -
新疆维吾尔自治区地质矿产局.新疆维吾尔自治区区域地质志[M].北京:地质出版社, 1993. 胡霭琴, 张国新, 陈义兵.中国新疆地壳演化主要地质事件年代学和地球化学[M].北京:地质出版社, 2006, 119-161. Allen M B, Windley B F, Zhang C.Paleozoic Collisional Tectonics and Magmatism of the Chinese TianShan, Central Asia[J].Tectonophysics, 1993, 220:89-115. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=67dbb4e9b6c56d1efbb786efda224c5f
Gao J, Li M S, Xiao X C, et al. Paleozoic tectonic evolution of the Tianshan Orogen, northwestern China[J].Tectonophysics, 1993, 287:213-231. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S004019519880070X
胡霭琴, 张国新, 张前锋, 等.天山造山带基底时代和地壳增生的Nd同位素制约[J].中国科学(D辑), 1998, 29(2):104-112. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgkx-cd199902002 胡霭琴, 张国新, 陈义兵, 等.新疆大陆基底分区模式和主要地质事件的划分[J].新疆地质, 2001, 19(1):12-19. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/xjdz200101003 Hu A Q, Jahn B M, Zhang G X, et al, Zhang, Q.F.Crustal evolution and Phanerozoic crustal growth in northern Xinjiang:Nd isotopic evidence.Part Ⅰ:Isotopic characterization of basement rocks[J].Tectonophysics, 2000, 328:15-51. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0040195100001761
Wang B, Faure M, Cluzel D, et al.Late Palaeozoic tectonic evolution of the northern West Chinese Tianshan Belt[J].Geodinamica Acta, 2006, 19:237-247. doi: 10.3166/ga.19.237-247
Wang B, Chen Y, Zhan S, et al.Primary Carboniferous and Permian palaeomagnetic results from the Yili Block (NW China) and their implications on the geodynamic evolution of Chinese Tianshan Belt[J].Earthand Planetary Science Letters, 2007, 263:288-308. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0012821X07005560
胡霭琴, 王中刚, 涂光炽, 等.新疆北部地质演化及成岩成矿规律[M].北京:科学出版社, 1997:9-105. 胡霭琴, 韦刚健, 张积斌, 等.西天山温泉地区早古生代斜长角闪岩的锆石SHRIMP U-Pb年龄及其地质意义[J].岩石学报, 2008, 24(12):2731-2740. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200812007 胡霭琴, 韦刚健, 江博明, 等.天山0.9Ga新元古代花岗岩SHRIMP锆石U-Pb年龄及其构造意义[J].地球化学, 2010, 39(3):197-212. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqhx201003001 李孔森, 王博, 舒良树, 等.北天山温泉群的地质特征、时代和构造意义[J].高校地质学报, 2013, (3):491-503. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gxdzxb201303011 侯可军, 李延河, 邹天人, 等.LA-MC-ICP-MS锆石Hf同位素的分析方法及地质应用[J].岩石学报, 2007, 23(10):2595-2604. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200710025 Eby G N.Chemical subdivision of the A-type granitoids:Petrogenetic and tectonic implications[J].Geology, 1992, 20(7):641-644.
Xu B, Jian P, Zheng HF et al.U-Pb zircon geochronology and geochemistry of Neoproterozoic volcanic rocks in the Tarim Block of northwest China:implications for the breakup of Rodinia supercontinent and Neoproterozoic glaciations[J].Precambrian Research, 2005, 136:107-123. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science?_ob=ArticleURL&_udi=B6VBP-4F4H9TH-1&_user=3836898&_coverDate=01%2F26%2F2005&_rdoc=2&_fmt=high&_orig=browse&_origin=browse&_zone=rslt_list_item&_srch=doc-info(%23toc%235932%232005%23998639997%23552831%23FLA%23display%23
Xu B, Xiao S H, Zou H B, et al.SHRIMP zircon U-Pb age constraints on Neoproterozoic Quruqtagh diamictites in NW China[J].Precambrian Research, 2009, 168:247-258. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=1049f4eaa9953ac71602820c94238d72
丁海峰, 马东升, 姚春彦, 等.新疆果子沟埃迪科拉纪冰碛岩沉积环境[J].科学通报, 2009, 54(23):3726-3737. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kxtb200923022 王飞, 王博, 舒良树.塔里木西北缘阿克苏地区大陆拉斑玄武岩对新元古代裂解事件的制约[J].岩石学报, 2010, 26(2):547-558. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201002016 Chen B, Jahn B M.Genesis of post-collisional granitoids and basement nature of the Junggar Terrane, NW China:Nd-Sr isotope and trace element evidence[J].Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2004, 23:691-703. http://www.onacademic.com/detail/journal_1000035533767510_cea5.html
Huang B C, Xu B, Zhang C X, et al.Paleomagnetism of the Baiyisi volcanic rocks (ca.740 Ma) of Tarim, Northwest China:A continental fragment of Neoproterozoic Western Australia[J] Precambrian Research, 2005, 142:83-92. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S030192680500149X
Zhan S, Chen Y, Xu B, et al.Late Neoproterozoic paleomagnetic results from the Sugetbrak Formation of the Aksu area, Tarim basin (NW China) and their implications to paleogeographic reconstructions and the snowball Earth hypothesis[J].Precambrian Research, 2007, 154:143-158.
Windley B F, Alexeiev D, Xiao W J et al.Tectonic models for accretion of the Central Asian Orogenic Belt[J].Journal of the Geological Society, 2007, 164:31-47. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=407c8a0b623113b1dd6b69ee8fde6a21
Lu S N, Li H K, Zhang C L, et al.Geological and geochronological evidence for the Precambrian evolution of the Tarim Craton and surrounding continental fragments[J].Precambrian Research, 2008, 160:94-107. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=92cbf7cde9189410a5bd41a8161f2517
Wang B, Jahn B M, Lo C H, et al.Structural analysis and 40Ar/39Ar thermochronology of Proterozoic rocks in Sailimu area (NW China):Implication to polyphase tectonics of the North Chinese Tianshan[J].Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2011, 42:839-853. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1367912011003105
Wang B, Jahn B M, Shu L S, et al.Middle-Late Ordovician arc-type plutonism in the NW Chinese Tianshan:implication for the accretion of the Kazakhstan continent in Central Asia[J].Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2012, 49:40-53. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1367912011004457
Wang B, Liu H S, Shu L S, et al.Early Neoproterozoic crustal evolution in northern Yili Block:insights for migmatite, orthogneiss and leucogranite of the Wenquan metamorphic complex in the NW Chinese Tianshan[J].Precambrian Research, 2014, 242:58-81. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0301926813003756
Wang B, Shu L S, Liu H S, et al.First evidence for ca.780 Ma intra-plate magmatism and itsimplications for Neoproterozoic rifting of the North Yili Block andtectonic origin of the continental blocks in SW of Central Asia[J].Precambrian Research, 2014, 254:258-272. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0301926814003210
新疆维吾尔自治区地质矿产局.1: 200000地质图温泉幅(L-44-22).1992. 新疆维吾尔自治区地质矿产局.1: 50000区域地质调查报告(扎冷木特、柯克他乌、牧区医院、牙马特).2018.




 下载:
下载: